B8: Photosynthesis
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What do plants use as a source of energy?
Light
Reaction plants use to trap light energy
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Process by which plants make glucose from sunlight
What type of reaction is PS and why?
Endothermic
Energy taken in from the environment to the chloroplasts by light
Where does PS occur?
Leaves of the plant
What green chemical do leaves contain?
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
Absorbs light energy needed for PS
Stages of photosynthesis
Plant takens CO2 + H2O into the leaf
Light energy absorbed by chlorophyll
Light energy used to convert CO2 + H2O into glucose + O2
Word equation for photosynthesis
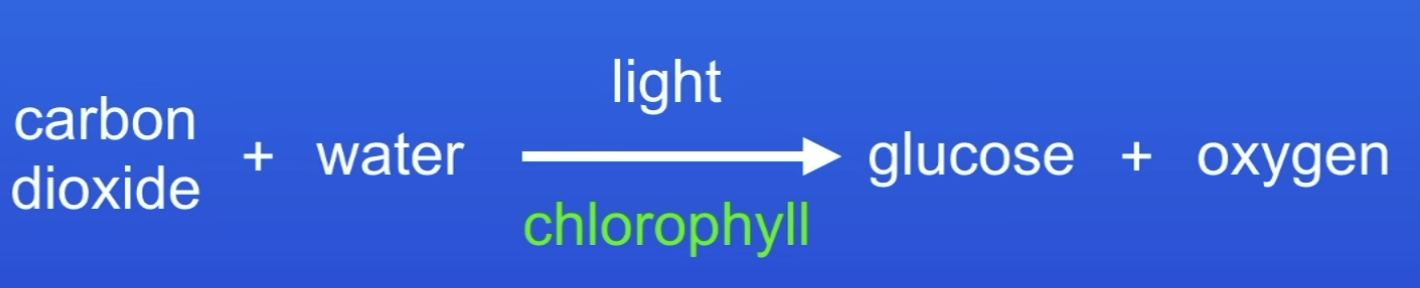
Symbol equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is needed for PS to take place?
CO2
Light
Factors affecting rate of PS
Temp
Light intensity
CO2 conc
Amount of chlorophyll
How to measure effect of light intensity on rate of PS?
Take plant, increase LI but keep everything else constant
Measure rate of PS at each level of LI
Rate of PS when LI is 0 and why
0
Plants need light to carry out PS
Describe this graph about the level of light intensity on rate of PS
As LI increases, rate of PS increases
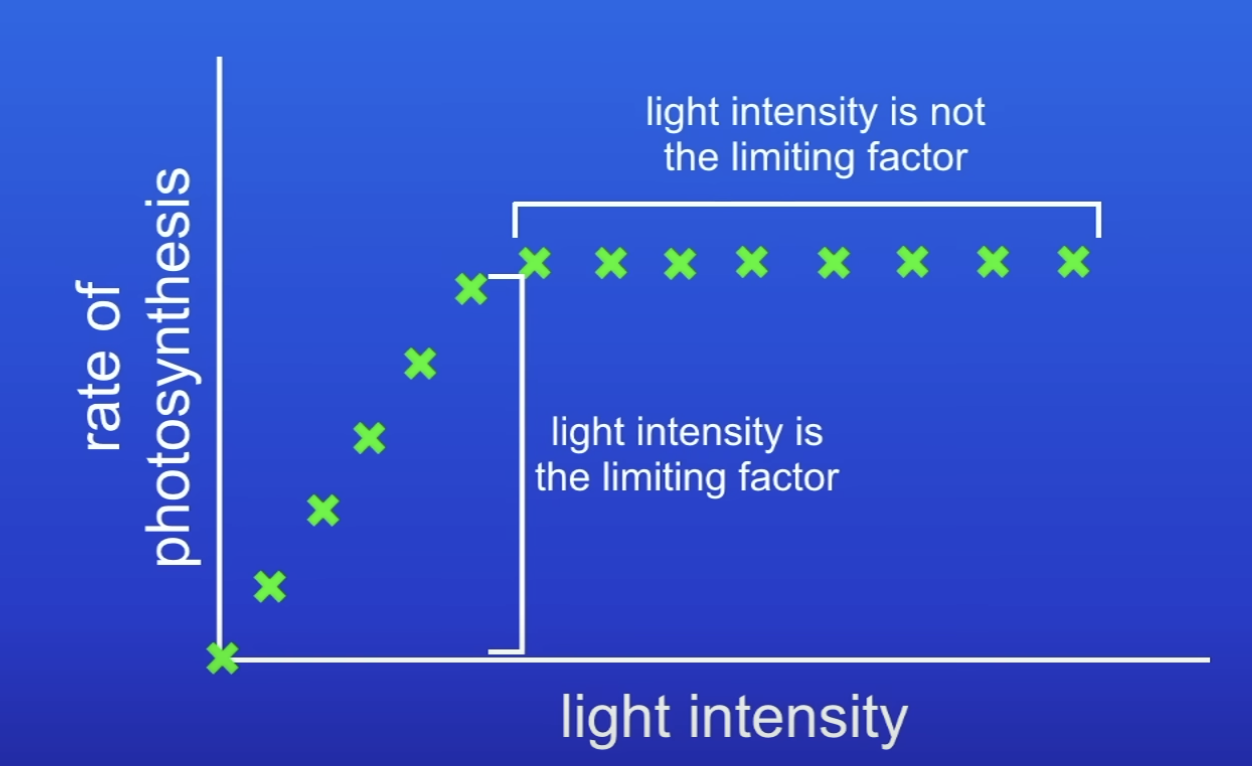
As LI increases, why does rate of PS increase?
Plant has more light energy to carry out PS → reaction gets faster
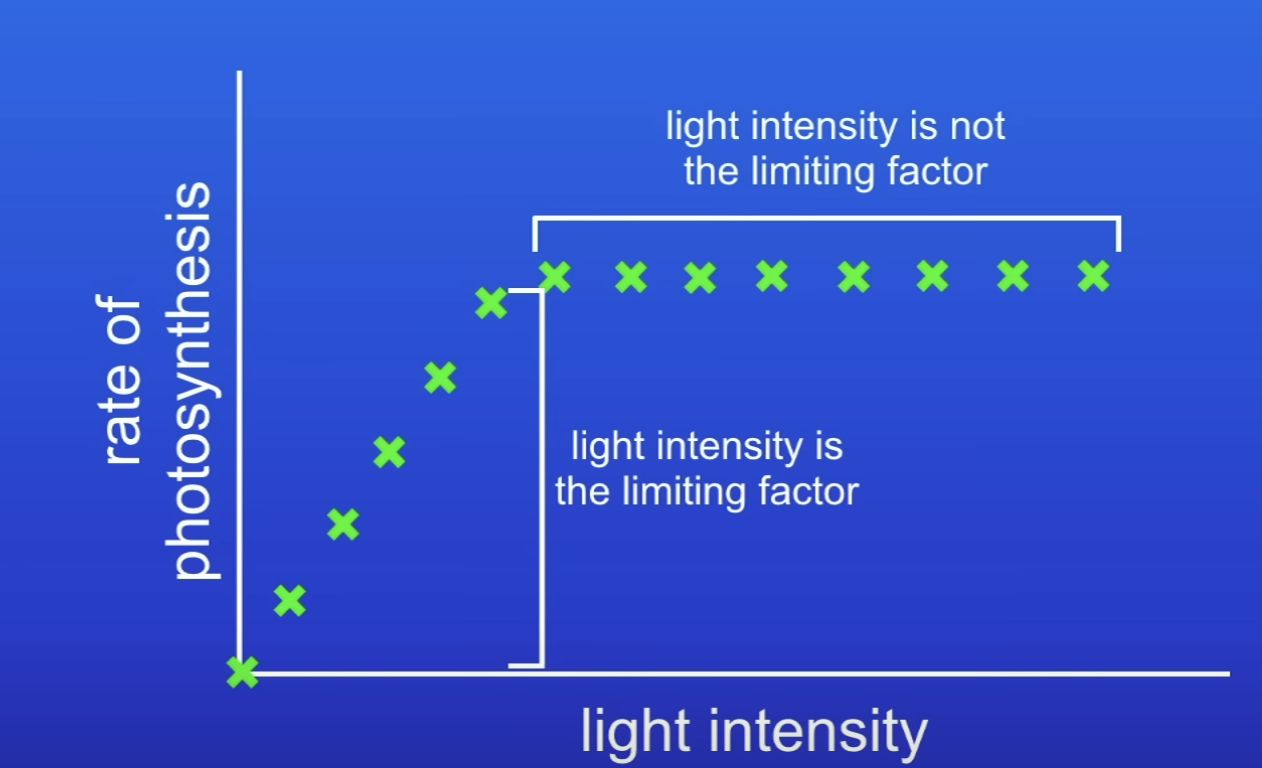
On this graph, how do you know light was initially a limiting factor?
If increase LI + PS rate increases → LI = limiting
What does it mean if light was a limiting factor of PS?
PS not as fast as it could have been
As there wasn’t enough light
Limiting factor
Factors that limit the rate of a reaction
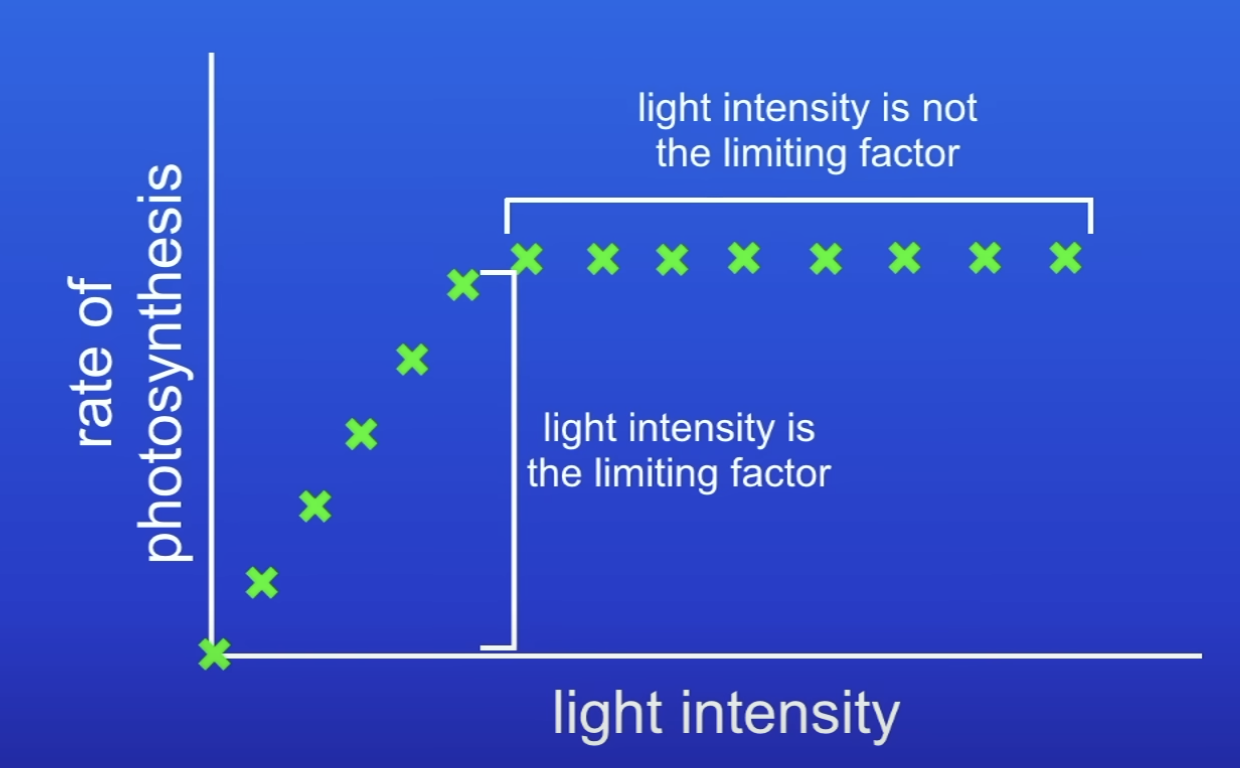
What is shown at the point where LI increases but the rate of PS doesn’t (it levels of)?
LI isn’t a limiting factor anymore- something else is

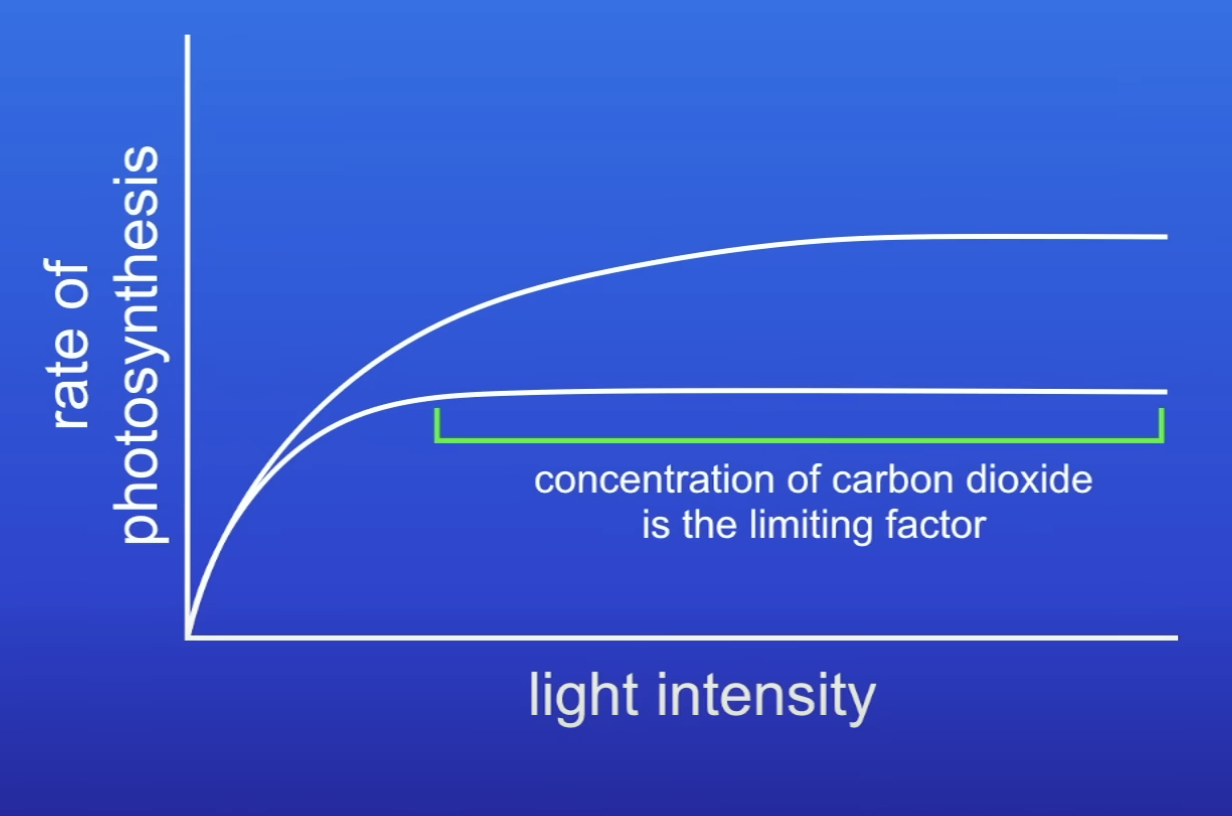
Describe this graph about effect of CO2 conc on rate of PS
Initially, increase CO2 conc → PS rate increases
At a certain point, graph levels off → CO2 isn’t a LF anymore
How can low levels of chlorophyll in the leaf affect the rate of PS?
Low chlorophyll levels → leaves trap less light energy → lower PS rate
What is PS controlled by?
Enzymes
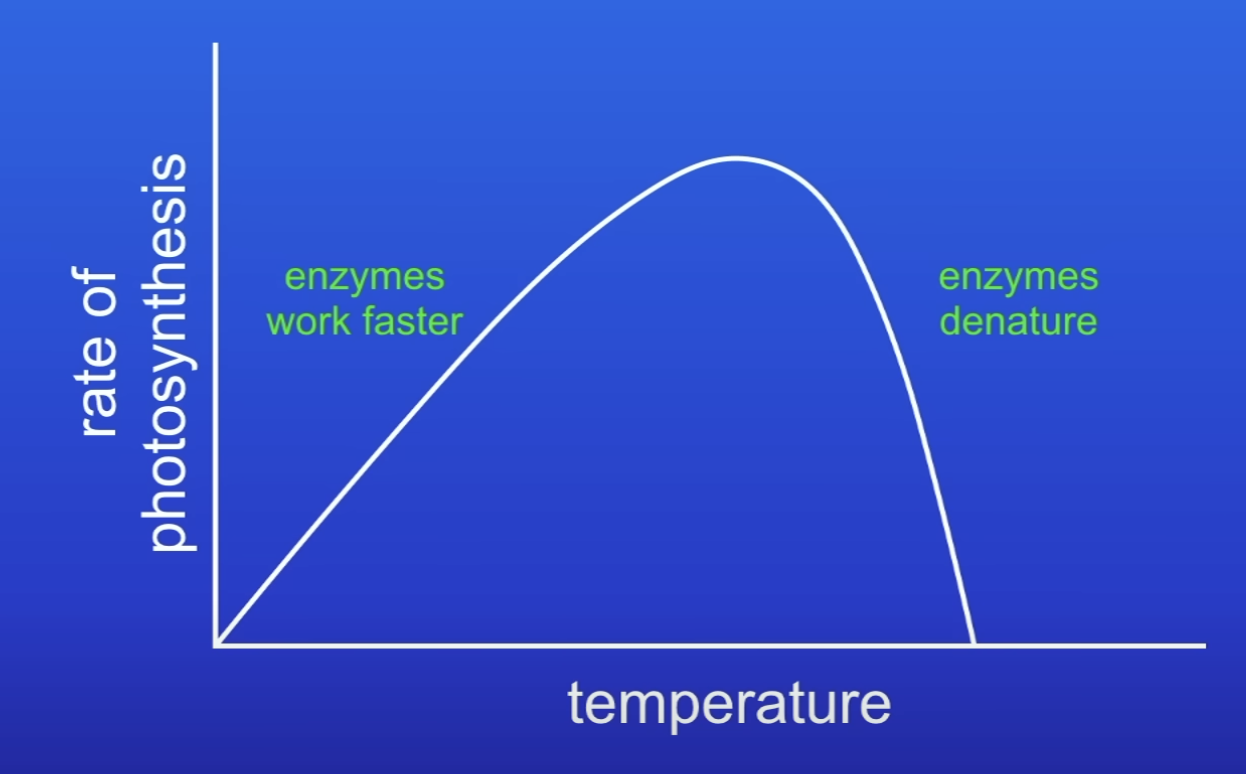
Explain this graph about the effect of temperature on rate of PS
Increase temp (before optimum), enzymes in PS work faster → rate increases
Increase temp (beyond optimum), enzymes denature → PS rate falls
Uses of glucose produced in PS
5
For respiration
Converted into insoluble starch for storage
To produce fat or oil for storage of energy
To produce cellulose, which strengthens the cell wall
To produce amino acids for protein synthesis
Why is glucose used for respiration?
To release energy from respiration
Where does respiration occur?
In mitochondria
When does photosynthesis produce glucose?
Only in the day (when there is light)
When do plant cells respire?
All the time
What does the plant do with stored starch?
Converts it back to glucose when needed (eg at night)
What can fats and oils store in plants?
Energy
What does a plant cell wall contain and why?
Cellulose → gives it strength
What do plants need to do to make amino acids from glucose?
Absorb nitrate ions from soil
Is glucose and starch soluble in water?
Glucose- yes
Starch- no
Why is glucose not stored in plant cells?
Soluble in water
So affects way water moves into + out of cells by osmosis
Why is glucose stored as starch in plant cells?
Starch insoluble in water
Doesn’t affect water balance of plants
So large amounts of starch can be stored
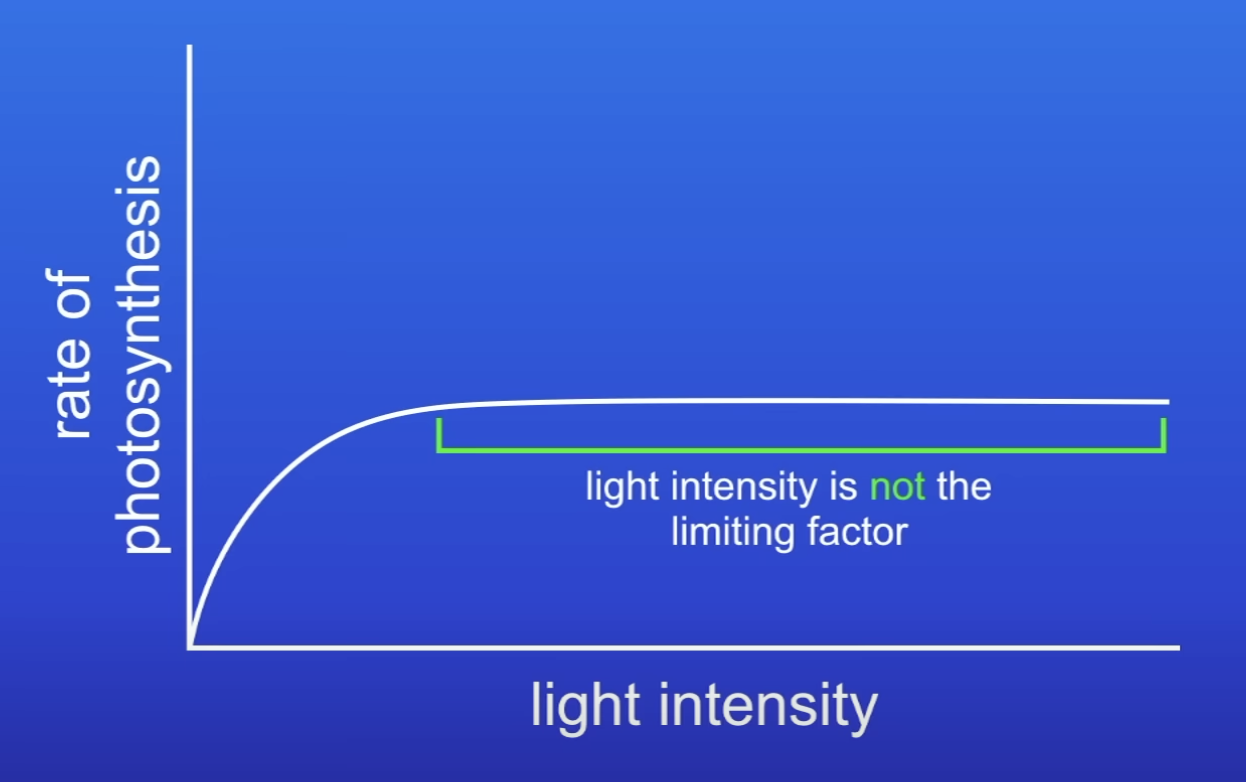
What does this graph show about LI as a limiting factor?
Initially, LI was an LF
Then LI isn’t an LF- something else is
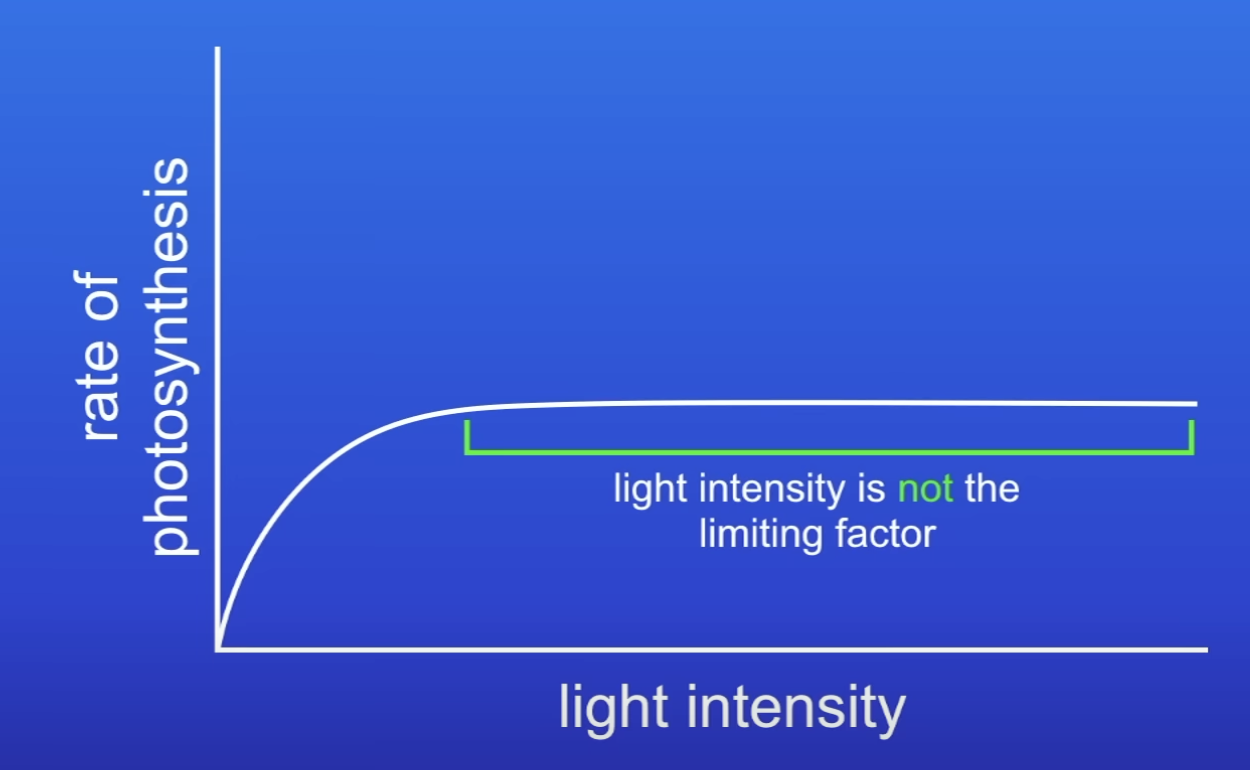
When LI stops being a limiting factor, what else could be a LF as this point?
CO2 conc
Temp
Amount of chlorophyll in leaves
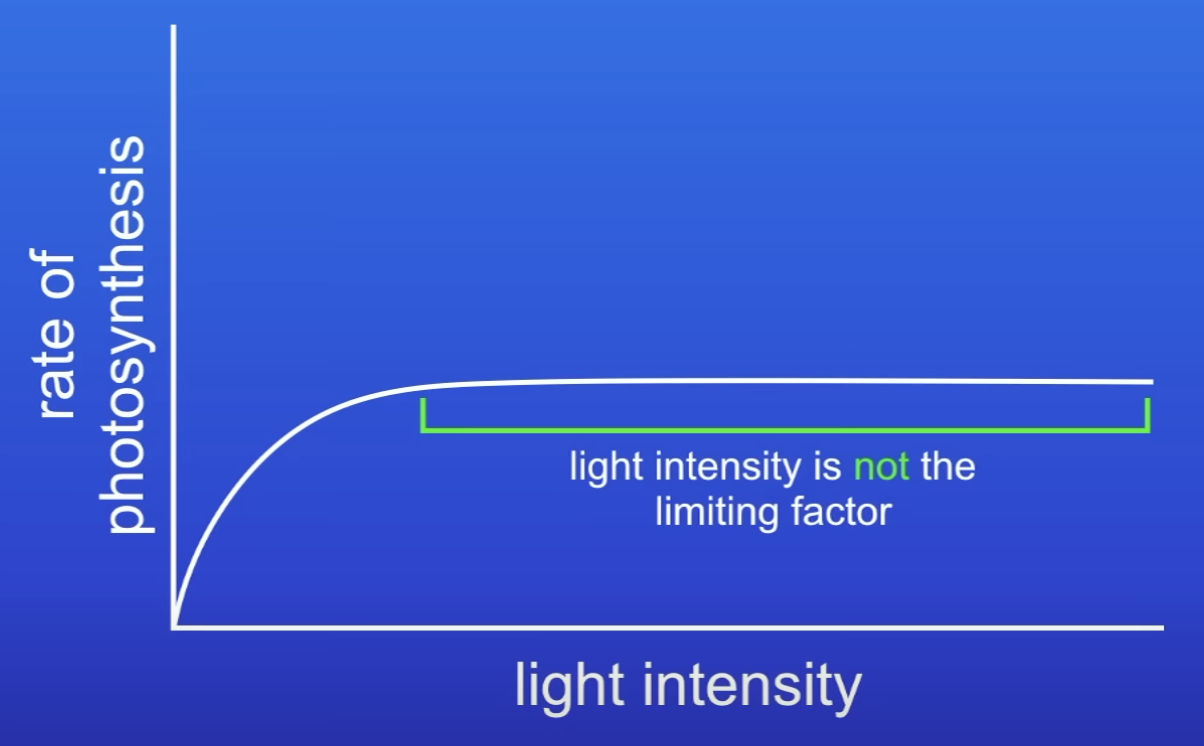
How to find out which factor is the limiting factor when LI stops being one?
Repeat experiment
Change CO2 conc / temp
Plot graph
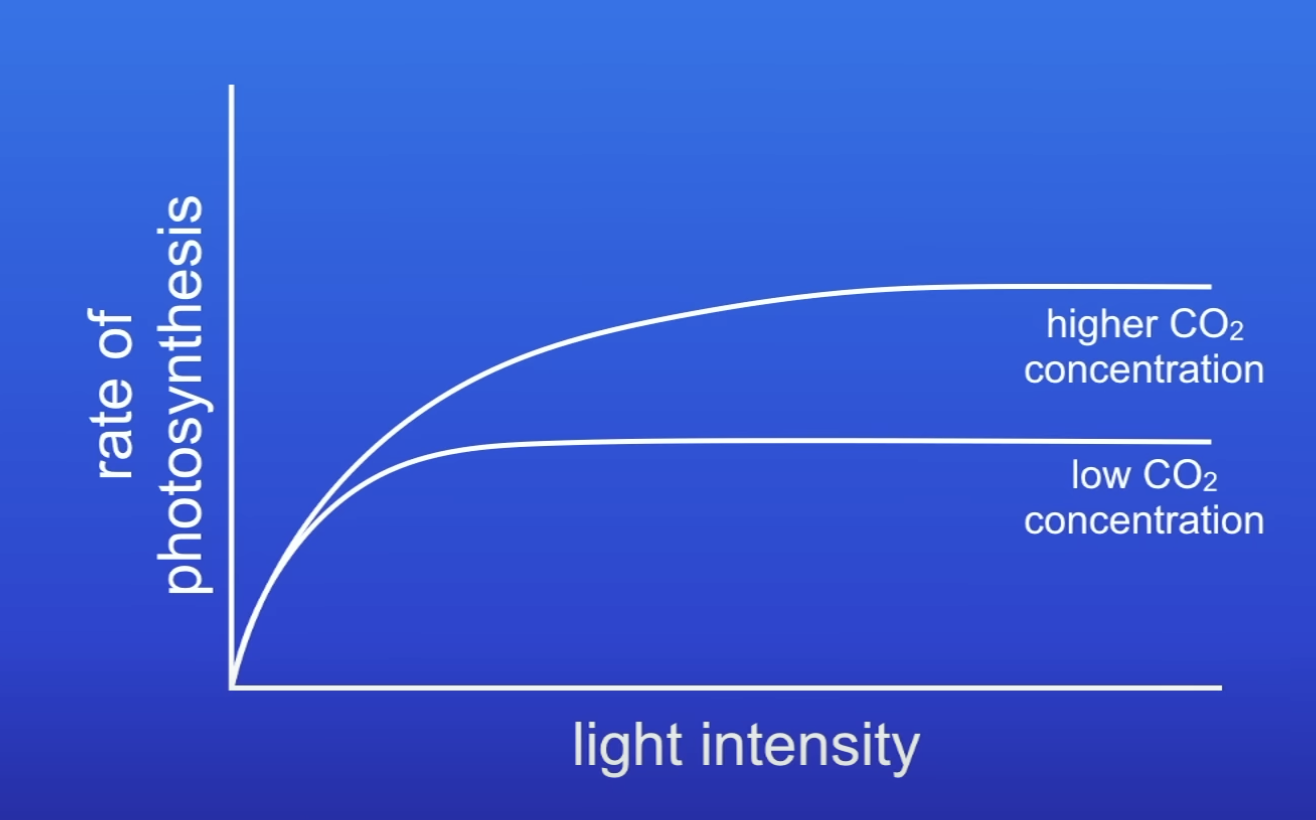
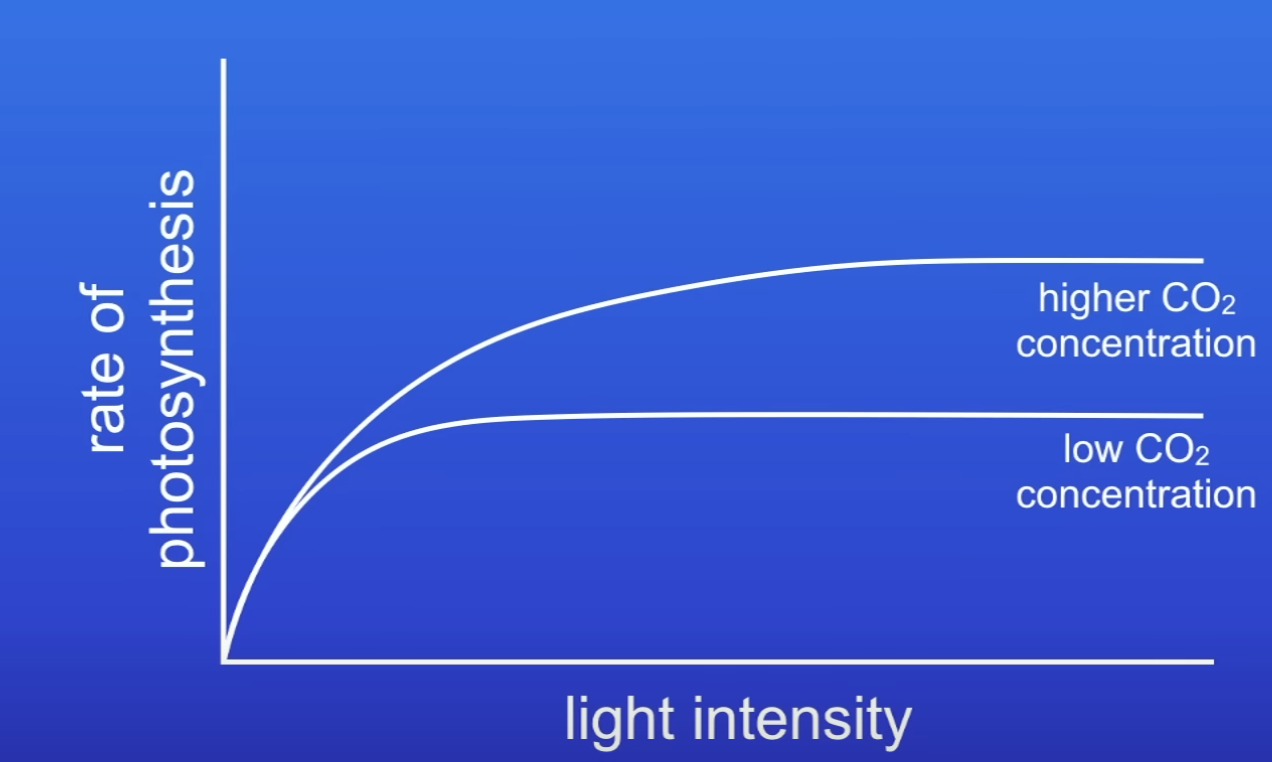
What does this graph show?
When CO2 conc increases, PS rate increases
CO2 conc was a LF
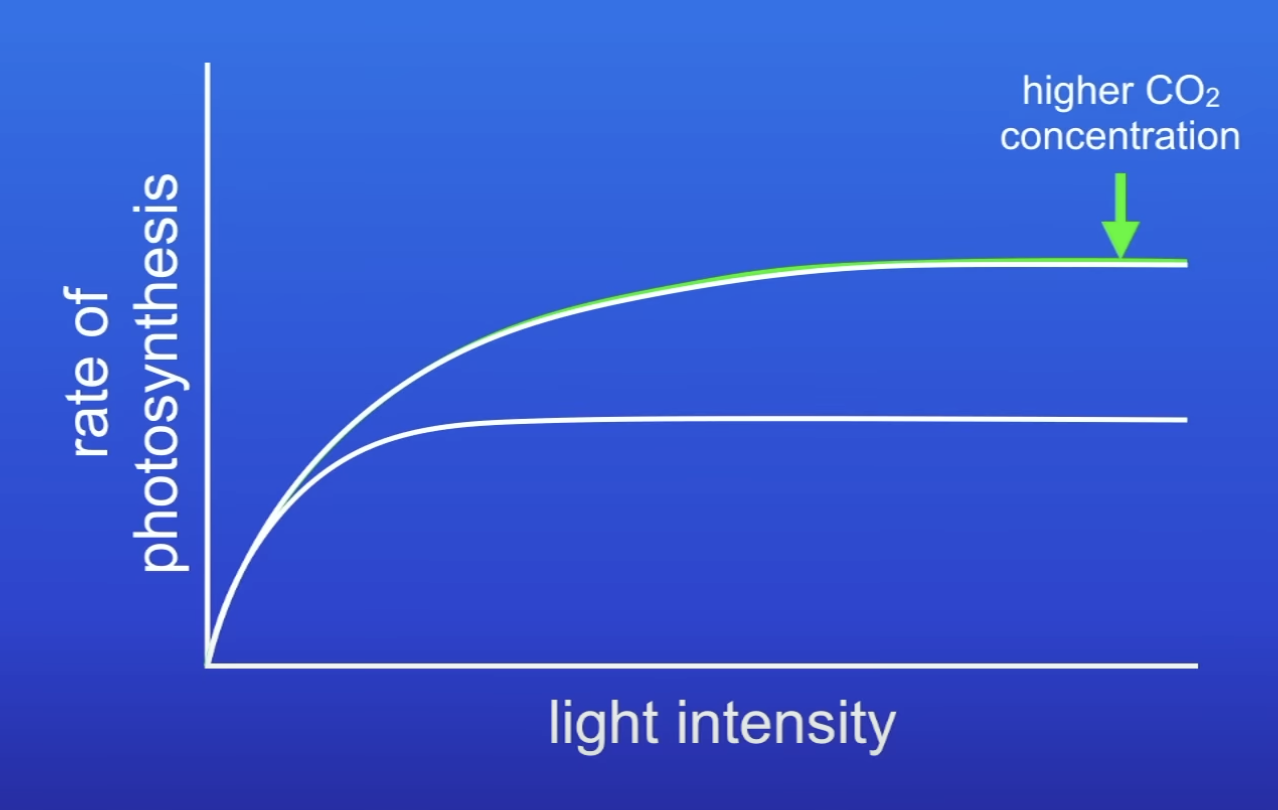
At a higher conc of CO2, why isn’t CO2 conc a LF anymore?
Plenty of CO2 available at higher concs
Why are limiting factors important in farming?
To increase rate of PS using a greenhouse
Why do farmers want to increase PS rates?
Increases yield of crops they produce
Why is a greenhouse used?
To grow plants in the most suitable conditions
How do farmers increase the rate of PS?
They light + heat greenhouses
+ Add extra CO2
Cons of increasing rate of PS using a greenhouse
Expensive
Extra cost of increasing rate of PS must be?
Justified by the increase in yield
Why do gardeners use oil burners?
Release heat + CO2 at the same time
Why are LF important in the economics of enhancing the conditions in greenhouses?
To gain max rate of PS while still maintaining profit
How does a greenhouse ensure temp isn’t a LF for PS?
Traps suns radiation as heat inside the greenhouse
How does a greenhouse ensure LI isn’t a LF for PS?
Artificial lighting provides constant light energy
What do the enclosed conditions of a greenhouse prevent?
Pests
How can you show a plant is photosynthesising?
Use aquatic plant
Place in beaker with water + collect bubbles of gas given off when photosynthesising
Gas will relight a glowing splint
Issue with showing a plant is photosynthesising using a land plant?
O2 = colourless gas
Evidence a plant is photosynthesing
O2 produced
Presence of starch in leaves