ALL OF EDEXCEL BIOLOGY PAPER 2
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
-Carbon Dioxide + Water -> Glucose + Oxygen
What is photosynthesis?
-Photosynthesis = an endothermic reaction that uses light energy from sun to convert carbon dioxide + water into glucose + oxygen.
-Takes place in the chloroplasts of plants, which contain chlorophyll (which absorbs light)
How are photosynthetic organisms the main producers of food?
-The glucose made in photosynthesis is used to make larger, complex molecules that plant use for growth. --These make up the organism's biomass, which is passed along the food chain as animals eat them.
What are the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis?
- Light intensity
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Temperature
How can you investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis?
1) Place a number of algal balls in a conical flask w/ some sodium hydrogencarbonate to provide the algal balls with enough carbon dioxide.
2) Use a ruler to measure + place the connical flask a set distance away from a light source.
3) Use a heat filter in front of the light source as temperature may also affect the rate of reaction and is not what is being measured.
4) Attach a gas syringe to the top of the conical flask + leave for a set amount of time. You can assume that the rate of oxygen production corresponds to the rate of reaction, so measure the rate of oxygen production.
5) Repeat w/ the algal balls at different distances from the light source.
How does the light intensity affect photosynthesis?
-Light transfers the energy needed for photosynthesis, so if the light intensity level is raised then the rate of photosynthesis will also increase steadily.
-They are said to be directly proportionate.
-But, after a point, increasing the light intensity will have no effect as either carbon dioxide concentration or temperature will be the limiting factor.
What is the relationship between the distance from the lamp and the light intensity?
-They are inversely proportional to each other
-as the distance increases, the light intensity decreases.
What is the inverse square law?
-Light intensity∝ 1/ (distance)^2
What does the inverse square law mean?
-The inverse square law means that if you double the distance, the light intensity will be four times smaller -The light intensity decreases in proportion to the square of the distance
How does the carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
-CO2 is one of the raw materials that is needed for photosynthesis.
-So, increasing the carbon dioxide concentration increases the rate of photosynthesis. ---However, this is only true up to a point and after this, the graph flattens out as CO2 is no longer the limiting factor.
How does the temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
-Usually, if temperature is limiting factor then it is because it is too low > the enzymes used in photosynthesis work slower in low temperatures.
-But, if the plant gets too hot then the enzymes needed for photosynthesis will be denatured as their active site changes shape.
What temperature do the enzymes involved in photosynthesis usually denature?
-45 degrees
What is the role of root hair cells?
-To take in minerals and water
What are the adaptations of root hair cells?
-Root hair cells have "hairs" that stick out into the soil -This increases the surface area which increases the area that is available for absorbing water + mineral ions + increases the SA:V.
-Root hair cells also contain lots of mitochondria - this is crucial bc concentration of mineral ions = usually higher in the cell than in the soil so active transport is required to take the minerals in
-The energy from this is gained from respiration that takes place in the mitochondria.
What is the role of the phloem tubes?
-The phloem tubes transport food substances (mainly sucrose) to areas in the plant for immediate use e.g in growing regions but also for storage.
-This process known as translocation + requires energy from respiration.
What are phloem tubes like?
-Phloem tubes = made of columns of elongated living cells which contain pores in the end walls to allow food to flow through.
-Companion cells around the phloem also contain lots of mitochondria to provide the energy needed.
What is the role of xylem tubes?
-xylem tubes transport water + mineral ions from the roots + to the leaves as part of the transpiration stream.
What are xylem tubes like?
-Xylem tubes = made of dead cells joined end to end w/ no end walls so that the water + mineral ions can travel.
-also strengthened with a substance called lignin.
What is transpiration?
-Transpiration stream is caused by the diffusion + evaporation of water from the leaves.
-This loss of water creates a slight shortage of water in the leaves, so more water is drawn up from the rest of the plant through the xylem vessels.
-This means that there is more water drawn up from the roots.
What is the role of the stomata in transpiration?
-stomata are tiny pores on the surface of the plant and they allow CO2 and O2 to diffuse in and out from photosynthesis.
-They also allow water vapour to escape during transpiration therefore meaning that transpiration is a side-effect of the way that leaves are adapted for photosynthesis.
-They have to have stomata so that gases can be exchanged but bc there's more water inside the leaf than outside the leaf, it diffuses out.
What are guard cells and what is their role?
-Guard cells surround stomata + change shape to control the size of the pore
-When the guard cells = turgid (swollen with water) the stomata = open
-When the guard cells = flaccid (low on water) the stomata = closed.
What are the factors that affect the rate of transpiration?
- Light intensity
- Temperature
- Air flow
How does light intensity affect the rate of transpiration?
-Brighter the light = greater the transpiration rate.
-Stomata begin to close at night bc there is no light for photosynthesis > they don't need to be open to let CO2 in.
How does temperature affect the rate of transpiration?
-The warmer it is = faster transpiration happens.
-bc when it's warm, the water particles have more energy to evaporate + diffuse out of the stomata more quickly.
How does air flow affect the rate of transpiration?
-better the air flow = faster the rate of transpiration.
=If the air flow = poor > the water vapour just surrounds the leaf + doesn't move, meaning there's a high concentration of water inside the leaf as well as outside the leaf > diffusion cannot happen as fast.
What do you use to estimate the transpiration rate?
-You can use a potometer > measures water uptake by a plant but it is assumed that the water uptake by a plant is directly related to the water loss from the leaves.
-Start a stopwatch + measure the distance that the bubble moves.
-Then calculate the speed of the air bubble.
What are hormones?
-Hormones are chemicals that are secreted into the blood by glands (known as endocrine glands) and that affect a target organs.
What are the different endocrine glands?
-The Pituitary Gland - secretes hormones that regulate body conditions, the hormones act on other hormones.
-The Thyroid Gland - secretes thyroxine > controls metabolic rate
-The Adrenal Gland - secretes adrenaline > controls the 'fight or flight' response
-The Pancreas - Secretes insulin > control blood glucose levels
-The Ovaries - Secretes oestrogen > interacts with other hormones in ovulation.
-The Testes - secretes testosterone > controls male puberty + sperm production
What is adrenaline?
-Adrenaline = a hormone that is secreted by the adrenal glands > prepares your body for a 'fight or flight' response by increasing the supply of oxygen + glucose.
How does adrenaline work?
-Adrenaline = binds to specific receptors in heart causing the heart to beat faster + w/ more force so that blood pressure also increases.
-This then increases blood flow to the muscles so that these cells receive more glucose + oxygen for respiration.
-Adrenaline also binds to receptors on the liver > causes liver to break down it's glycogen stores into glucose > increase the blood glucose levels.
What is negative feedback?
-When body detects that level of a substance has gone above or below normal level > it triggers a response > to bring the level back to normal.
-E.g. of this is through thyroxine regulating the metabolic rate.
What is the metabolic rate?
-The speed at which chemical reactions in the body occur.
How does thyroxine regulate the metabolic rate?
-When the thyroxine level in the blood is too low, the hypothalamus will secrete TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone).
-This stimulates the pituitary gland to release TSH, which then stimulates the thyroid gland to release Thyroxine.
-When the thyroxine level in the blood is too high the release of TRH is inhibited which then inhibits the release of TSH + in turn thyroxine so the thyroxine levels fall.
What are the hormones that are involved in the menstrual cycle?
-Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
-Oestrogen
-Luteinising Hormone (LH)
-Progesterone
What does FSH do?
-FSH is released by the pituitary glands > causes a follicle to mature in one of the ovaries.
-Then stimulates the production of oestrogen.
What does oestrogen do?
-Oestrogen is released by the ovaries > causes the lining of the uterus to thicken + grown as well as stopping the production of FSH.
-This then stimulates an LH surge as well.
What does LH do?
-LH = released by the pituitary glands + causes ovulation at day 14.
-This is where the follicle ruptures + the egg is released.
-The remains of the follicle form a structure called a corpus luteum.
What does progesterone do?
-Progesterone is released by the corpus luteum + it maintains the lining of the uterus + inhibits the production of FSH and LH.
-When the egg is not fertilised, the levels of progesterone falls + the uterus lining breaks down FSH can increase + the cycle can begin again.
What is clomifene therapy and how can hormones be used in it?
-Clomifene is a drug that infertile women can take if they do not ovulate or do not ovulate regularly.
-This drug works by causing more FSH + LH to be released by the body which stimulates egg maturation + ovulation.
-By knowing when the woman will be ovulating, the couple can have intercourse during this time period to improve changes of fertalisation.
What is IVF and how can hormones be used in it?
-IVF involves collecting eggs from the woman's ovaries + fertilising them in a lab using the man's sperm.
-These are then grown into embryos + are inserted back into the woman's uterus to improve chances of pregnancy.
-FSH and LH are given before egg collection to stimulate the egg production.
What forms of hormonal contraceptives are there?
-Progesterone can be used to prevent fertalisation by stopping the eggs from maturing or being produced as well as by producing a thick cervical mucus which prevents any sperm from getting through.
-Oestrogen can also be taken as if it is taken regularly then it can inhibit the production of FSH and therefore the production of a follicle.
-The contraceptive pill inhibits FSH production.
What are the benefits of using hormonal contraceptives?
-They are generally more effective than barrier methods
-You don't have to remember to use a condom before sex
What are the negatives of using hormonal contraceptives?
-They may have side effects
-They don't protect against sexually transmitted infections
What are the positives of using barrier methods such as condoms?
-They protect against sexually transmitted infections
- No side effects
What are the negatives of using barrier methods?
-You have to remember to use them before intercourse
What is homeostasis?
-Homeostasis is maintaining a constant internal environment
Why is homeostasis important?
-Homeostasis = important bc your cells need to have the right conditions in order to function correctly (e.g. the right conditions for enzyme action).
-Our cells must function correctly > for us to live a healthy life + it can be dangerous for health reasons is our body conditions vary too much.
How is glucose stored in our bodies?
-Eating foods containing carbohydrate puts glucose into the blood from the small intestine.
-The normal metabolism + vigorous exercise removes glucose from the blood.
-Excess glucose can be stored in the liver as glycogen.
-When these stores are full then the excess glucose is stored as lipid.
What happens when our blood glucose concentration is too low?
-Glucagon is secreted by pancreas > makes the liver turn glycogen into glucose.
-This is then released into the blood by the liver > so blood glucose level can return to normal levels.
What happens when our blood glucose concentration is too high?
-Insulin is secreted by the pancreas.
-Glucose then moves from the blood into the liver + insulin makes the liver turn this glucose into glycogen to be stored.
-The blood glucose level is then reduced.
What is type 1 diabetes?
-Type 1 diabetes = the pancreas produces little to no insulin, meaning that a person's blood glucose level can rise to a level that can kill them.
-Person w/ type 1 diabetes will need to be treated w/ insulin therapy.
-This insulin = usually injected into the subcutaneous tissue.
-Amount of insulin needed depends on how active they are and their diet. They also need to think about limiting the intake of foods rich in simple carbohydrates + taking regular exercise
What is type 2 diabetes?
-Type 2 diabetes = the person becomes resistant to insulin causing blood glucose levels to rise.
-Can be controlled by eating a healthy diet + getting regular exercise to remove the excess glucose
How do you calculate BMI?
-weight / height^2
How do you calculate waist-tp-hip ratio?
-waist / hip
What is the correlation between obesity and type 2 diabetes?
-Many people who get type 2 diabetes = obese bc their glucose cannot be stored in the liver so is instead stored as lipid.
What substances to organisms share with their environment?
-Cells need oxygen for aerobic respiration which produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. These 2 gases move between cells + the environment by diffusion
-Water is taken up by cells by osmosis as well as mineral ions that diffuse along with it.
-Urea as a waste product that diffuses from cells to the blood plasma for removal.
-How easy it is for an organism to exchange substances depends on the SA:V.
How do single-celled organisms exchange substances?
-Gases + substances can diffuse directly into or our of the cell across the cell membrane bc they have a large surface area compared to their volume > enough substances can be exchanged to supply the volume of the cell
-There's a larger diffusion area compared to the actual volume.
How do multicellular organisms exchange substances?
-Multicellular organisms = smaller surface area to volume ratio.
-Makes it difficult to exchange substances to supply their entire volume > they need an exchange surface for efficient diffusion + a mass transport system to move the substances b/w the exchange surface + the body.
What is the job of the alveoli?
-The job of the lungs is to transfer oxygen to blood so that it can be taken to cells for respiration + to remove waste carbon dioxide.
=To do this, the lungs contain millions of air sacs known as alveoli where the gas exchange takes place.
How is the alveoli adapted for it's function?
-Blood arriving at the alveoli contains lots of CO2 + little oxygen + the alveoli contains lots of O2 from breathing and little CO2 > maximises concentration gradient in both directions as substances diffuse faster if there is a large difference in concentration.
-The alveoli have moist lining for dissolving gases
>they have a good blood supply to maintain the concentration gradient.
-The alveoli have very thin walls to minimise the distance that the gases have to move > they have a large surface area to increase the area of diffusion.
What is the role of red blood cells?
-Red blood cells (also called erythrocytes) carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
How are the red blood cells adapted to their function?
-They have a biconcave disc shape to give a large surface area for efficient diffusion of oxygen
-They don't have a nucleus which gives them more space for storing oxygen in them
-They contain a red pigment called haemoglobin, which contains iron. The haemoglobin binds to the oxygen to become oxyhaemoglobin in the lungs + this then splits up in the body cells.
-The more red blood cells you've got = more oxygen that can reach your cells.
What are the two different types of white blood cells?
-Phagocytes and lymphocytes
What do phagocytes do?
-Phagocytes are white blood cells that can change shape to engulf unwelcome microorganisms
What do lymphocytes do?
-Lymphocytes are white blood cells that produce antibodies against microorganisms.
-Some also produce antitoxins to neutralise any toxins that the micro-organisms produce.
What do platelets do?
-Platelets = small fragments of cells that have no nucleus.
-They help the blood to clot at a wound to stop all of your blood from pouring out + to prevent microorganisms from getting in.
What is plasma?
Plasma is a pale liquid that carries everything in the blood including:
-Red and white blood cells
-Nutrients such as glucose
-Carbon dioxide
-Urea
What are the three different types of blood vessel?
-Veins carry blood towards the heart
-Arteries carry blood away from the heart
-Capillaries are involved in the exchange of materials
How are arteries adapted to their function?
-The heart pumps blood out at a high pressure so the artery wall is strong, thick and elastic.
-The walls are thick compared to the size of the lumen.
-They contain thick layers of muscle to make them strong and elastic fibres to allow them to stretch.
How are capillaries adapted to their function?
-Arteries branch into capillaries.
-They are very narrow so that they can squeeze into the gap b/w cells + can carry blood to every cell in the body to exchange substances with them.
-They have permeable walls so that substances can diffuse in and out
-Their walls are usually only one cell thick to increase the rate of diffusion by decreasing the distance.
How are veins adapted to their function?
-The blood flows at a lower pressure in the vein so the walls are not as thick as they are in the artery.
-They have a bigger lumen than arteries to help the blood flow + they have valves to help them flow in the right direction.
What does it mean that mammals have a double circulatory system?
-This means that the heart pumps blood around the body in two circuits.
-In the first circuit, the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to take in oxygen + then in the second circuit the heart pumps oxygenated blood around all the other organs of the body.
-Fish have a singular circulatory system.
Describe the structure of the heart and the blood vessels that are involved with the heart.
-The heart is split into four chambers - the right atrium, the right ventricle (our left), the left atrium and the left ventricle (our right).
-The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava which moves through the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs from the pulmonary artery.
-From the lungs, oxygenated blood is pumped back to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein + then goes through the left ventricle to be pumped around the rest of the body through the aorta.
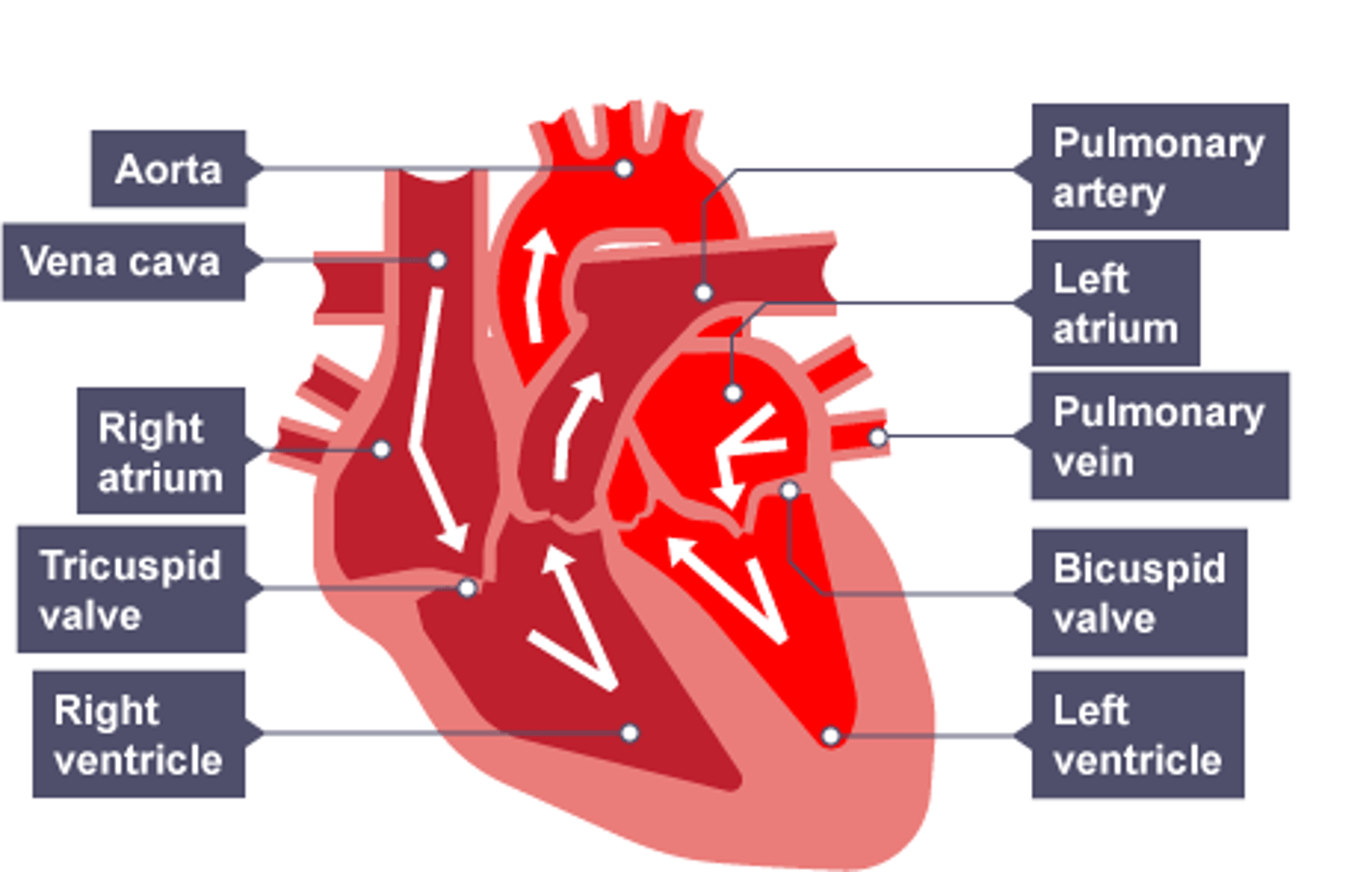
What are the two valves of the heart and what do they do?
-The tricuspid valve is on the right side of the heart (our left) + the bicuspid valve is on the left side of the heart (our right).
-They prevent the backflow of blood in the heart.
Which ventricle wall is thicker than the other and why?
-The left ventricle wall is much thicker than the right ventricle wall.
-It needs more muscle because it has to pump blood around the whole body at a high pressure whereas the right ventricle only has to pump it to the lungs.
What is the heart rate?
-The heart rate is the number of beats per minute
What is the stroke volume?
-The stroke volume is the volume of blood pumped by one ventricle each time it contracts
What is cardiac output?
-Cardiac output is the total volume of blood pumped by a ventricle every minute.
What is the equation that involves cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate?
-Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
What is cellular respiration?
-Respiration = exothermic reaction > takes place in the mitochondria of all living organisms + is where energy is released from the breakdown of glucose + oxygen.
What is the energy released in respiration used for?
-Metabolic processes
-Contracting muscles
=Maintaining a constant internal environment
What is the chemical equation for respiration?
-Glucose + Oxygen -> Carbon dioxide + water
Why does anaerobic respiration take place?
-When your body does really vigorous exercise your body cannot supply enough oxygen to all your muscle cells for aerobic respiration, so your muscles have to start respiring anaerobically.
What is anaerobic respiration?
-Anaerobic respiration is when your cells begin to respire w/o oxygen.
-It transfers much less energy than aerobic respiration so it's much less efficient.
-Lactic acid is also produced, which leads to cramp.
-Anaerobic respiration usually has to occur more quickly to produce the same amount of energy needed.
What is the equation for anaerobic respiration?
-Glucose -> Lactic acid
How can you measure the rate of respiration?
-In aerobic respiration, organisms use up oxygen.
-By measuring the amount of oxygen consumed by organisms in a given time, you can calculate the rate of respiration
What is the experiment you can use to measure the rate of respiration?
1) Add some soda lime granules to two test tubes - this absorbs the CO2 that is produced in the experiment so that only the oxygen is measured
2) A ball of cotton wool is placed above the soda lime in each tube so that the woodlice don't come in contact with the soda lime. Glass beads with the same mass as the woodlice are used as the control (to make sure there are no other influential factors)
3) A syringe is then used to set the fluid in a manometer to a known level
4) The apparatus is then left in a water bath for a set amount of time
5) During this time, there will be a decrease in the volume of air which will reduce the pressure in the tube, causing the coloured liquid to move towards the test tube
6) The distance moved in a given time can then be measured to calculate the rate of respiration
7) Repeat with different temperatures
What ethical issues are there with this experiment?
-Any live animals must be treated ethically + you must be careful not to leave the woodlice in the respirometer for too long or they may die.
-You cannot let them get too cold or too hot either.
What is the definition of a population?
-A population is all the organisms of one species in a habitat
What is the definition of a community?
-A community is all the organisms of different species living in a habitat
What is the definition of an ecosystem?
-An ecosystem is a community of organisms along with all the abiotic conditions.
What does it mean if species are interdependant?
-Means that species depend on each other for food and resources to survive and reproduce.
-If there is change in a species then this may have knock on effects in it's prey and predators.
-This is demonstrated by the food chain, if one of the consumers dies out in an area then the animals that depend on them may also die + the animals that the consumers consume will grow in numbers.
What is the predator-prey cycle?
-When the predator numbers are low, the number of prey increase
-An increase in the number of prey means that there is more food for the predators
-The population of predators increase
-The number of prey then decrease which means that there is little food for predators so their number decreases
What is a mutualistic relationship?
-A mutualistic relationship = relationship b/w two organisms where both organisms benefit. e.g. flowers + bees.
-Bees get pollen from the flower + the flower gets help reproducing from the bee.
What is a parasitic relationship?
-A parasitic relationship is one between organisms where the parasite benefits but the host does not. e.g. fleas and dogs.
-The fleas live in the dog where they get both food from the dog's blood and shelter, but the dog doesn't get anything.
What is a biotic factor?
-A biotic factor is a living factor
What is an abiotic factor?
-An abiotic factor is a non-living factor
How are communities affected by abiotic factors?
-Temperature
-Light intensity
-Water
-Levels of pollutants
How does the abiotic factor of temperature affect a community?
-An increase in tempt. may cause the presence of a species that did not usually inhabit the area or the fall in a species which can have knock on effects to the food chain , a decrease in temperature can have the reverse effects
How does the abiotic factor of light intensity affect a community?
-Areas w/ more shade = have less trees + grassy areas but will instead have more fungi + mosses that can cope w/ it better