Organic chemistry
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
polymer
long chain molecule
monomer
small molecules used to form a polymer
viscous
thick sticky liquid
volatile
liquid that readily turns into a gas
flammable
substance that readily ignites
hydrocarbons
compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen
fractions contain
mixtures of hydrocarbons with a similar number of carbons in their chains and therefore a similar boiling point
organic chemistry
study of compounds containing carbon
carbon facts
strong covalent bonds
4 electrons in the outer shell
up to 4 single covalent bonds
can have double or triple bonds
fossil fuels
crude oil, natural gas and coal
remains of organisms form millions of years ago
finite, non-renewable resources
obtained by drilling
formation of fossil fuels
dead plants/animals buried under sediment
high pressures and temps produced
anaerobic decay converts the organic matter to crude oil and natural gas
crude oil
complex mixture of hydrocarbons
crude oil cannot be used directly as a fuel
mixture of molecules of many diff chain lengths
diff physical and chemical properties which need to be separated
too viscous and does not burn
burning can cause pollution (sulphur impurities -> acid rain)
fractional distillation of crude oil method
1. Crude oil is first heated
2. Compounds evaporate and the vaporised crude oil enters the lower part of the fractionating tower
3. Fractionating tower is hot at the base and cooler at the top
4. Vapours rise until it condenses where its bp is lower than the temp of the column
5. Smaller the molecules, the lower the bp, the higher they rise
6. Fractions collect at diff heights
fractional distillation
process by which a mixture of miscible liquids is separated (heating) due to diff boiling points
evaporation + condensation
fractional distillation of crude oil
produces more long chain hydrocarbons which are commercially useless
petroleum or refinery gases
fuel for domestic heating and cooking
gasoline (petrol)
fuel for cars
kerosene (paraffin)
fuel for aircraft and domestic heating
diesel oil (gas oil)
fuel for larger vehicles e.g. lorries
fuel oil
fuel for ships
bitumen
pitch for roads and roofs
as molecules get larger, the fractions get
more viscous
less flammable
less volatile
darker in colour
burn with smokier flames
bp increases
problems with burning fossil fuels
Fossil fuels contain sulphides as impurities
Sulphides burn in air to form sulphur dioxide which leads to acid rain
Upsets the natural balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, lead to global warming
acid rain
Caused by sulphur dioxide from coal-fired power station or nitrogen oxide from exhaust fumes of cars
pH of uncontaminated rain
6.5
pH of acid rain
2.5-5.5
acid rain harms
Marble statues and stone buildings dissolve away
Enhanced corrosion of metals
Water in lakes and rivers become acidic, pH too low for fish and they die
Acid rain damages trees and plants
preventions of acid rain
Calcium oxide sprayed into acid lakes
Low sulphur fuels used
Exhaust gases from factory chimneys are scrubbed with ammonia
Quantities of nitrogen monoxide from car exhausts can be reduced by using catalytic converters
molecular formula
tells you the actual number of atoms of each element e.g. C4H10
Empirical formula
simplest whole number ratio of the atoms of each element e.g. C2H5
General formula
chemical formula used to represent any member of a homologous series e.g. CnH2n+2
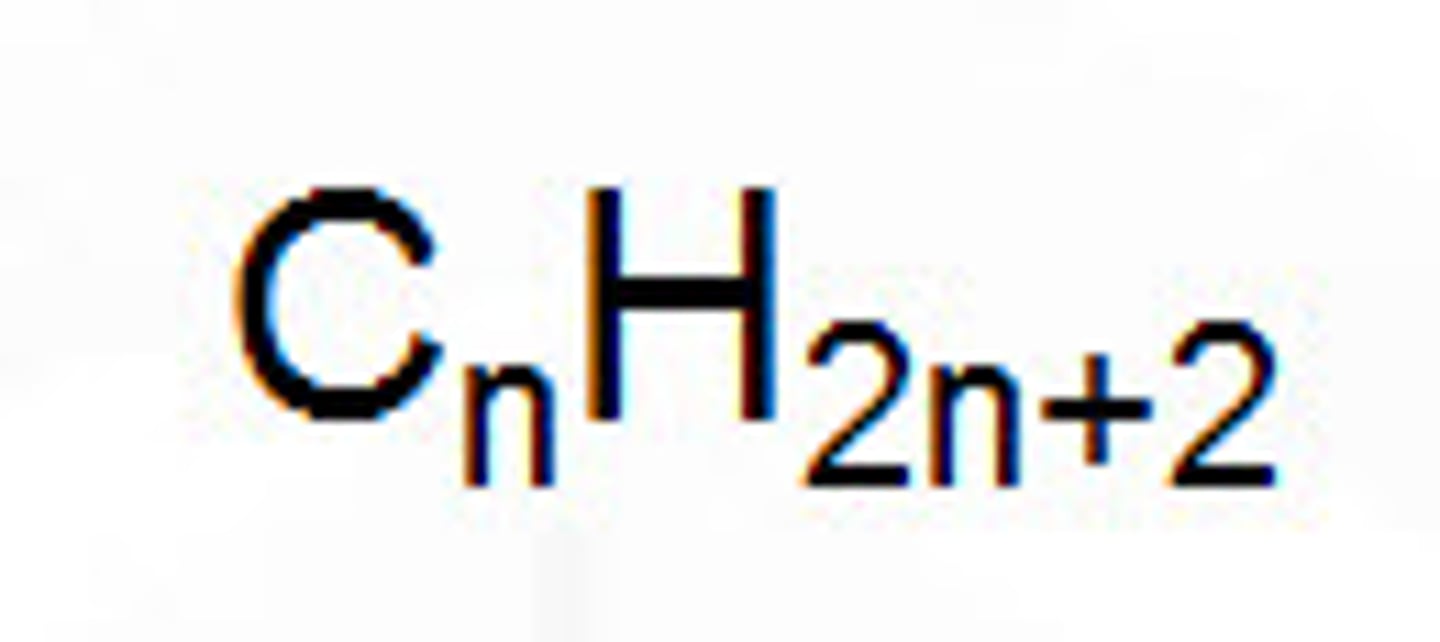
structural formula
tell you how atoms are joined together in a molecule e.g. CH3CH2CH2CH3
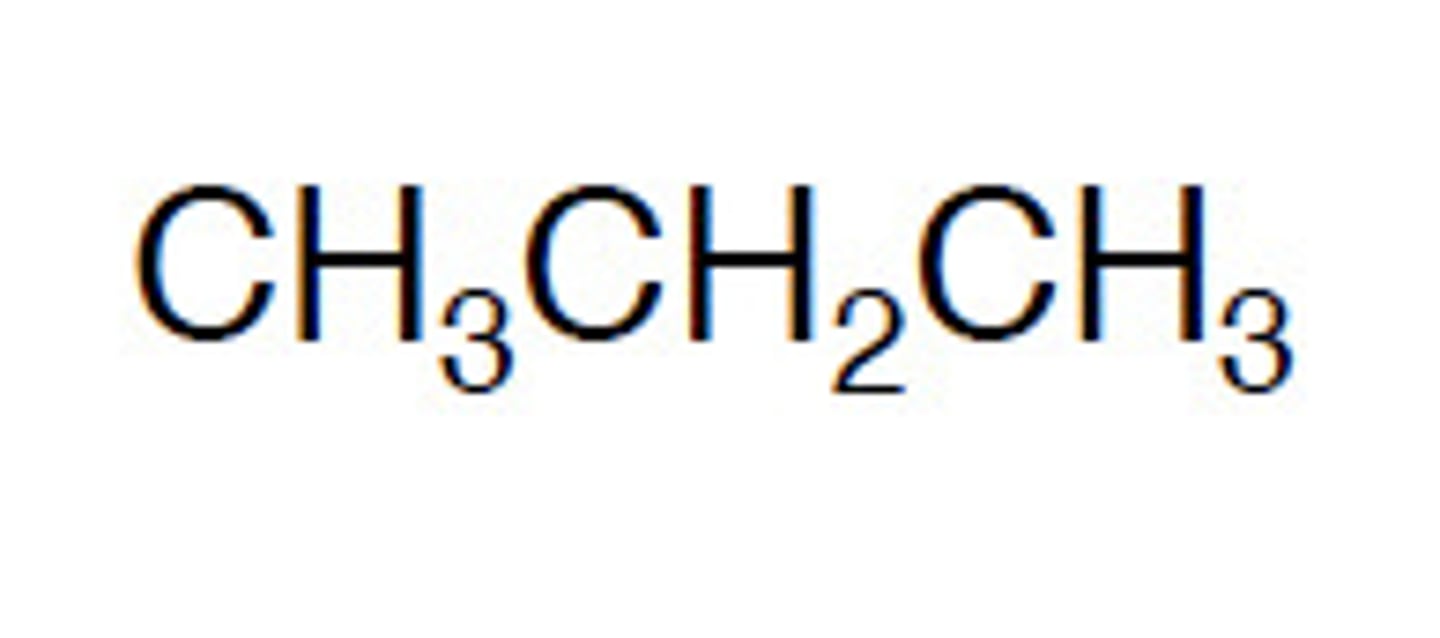
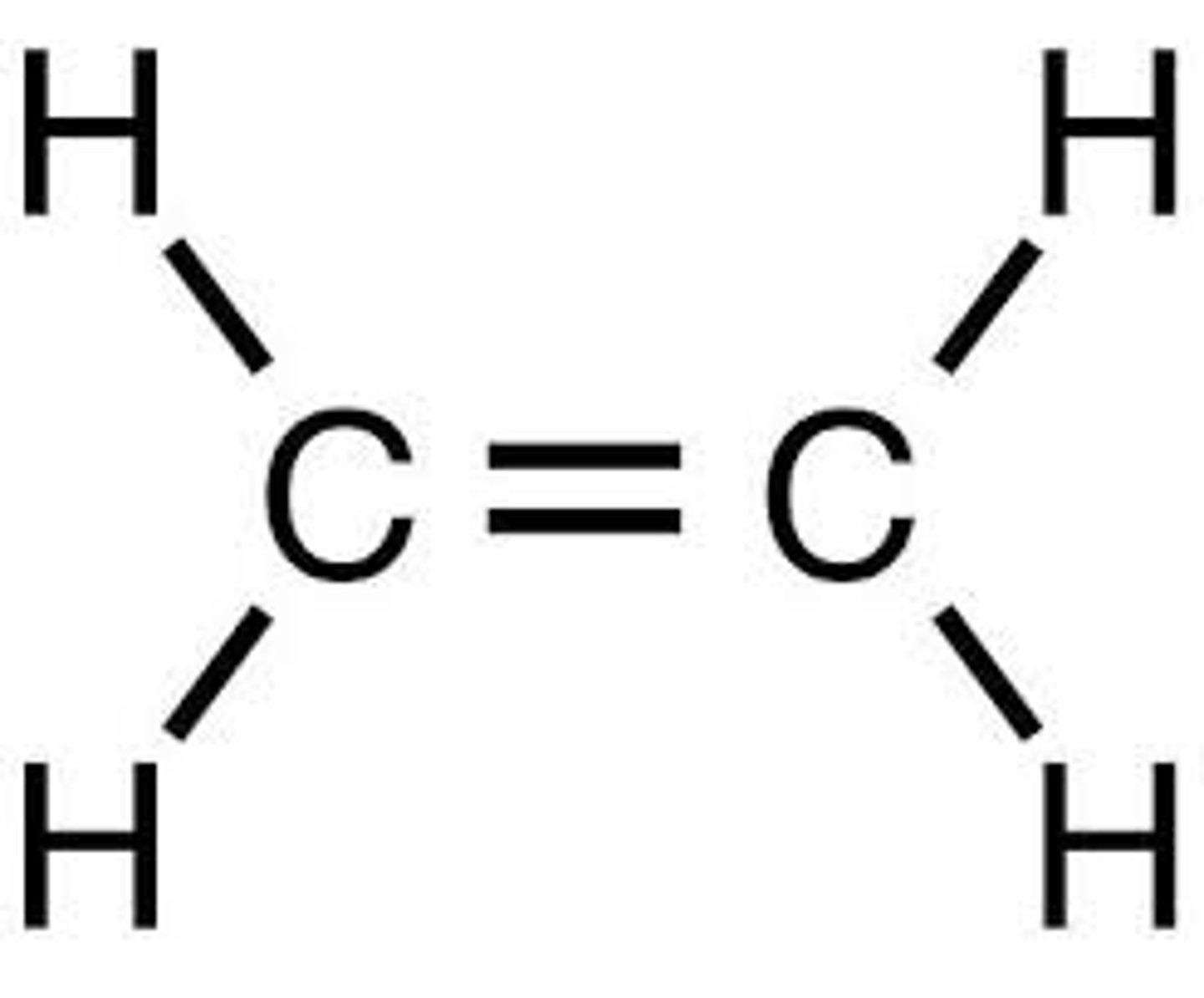
displayed formula
structural formula to show all the bonds present in a molecule
substitution
an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms
e.g. ethane + bromine -> bromoethane + hydrogen bromide
(presence of UV light)
addition
one molecules combines with another to form one product
e.g. ethene + bromine -> 1,2-dibromoethane
combustion
molecule reacts with plentiful oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water (complete combustion)
incomplete combustion
inadequate oxygen to form carbon monoxide/carbon and water (incomplete combustion)
CO
colourless, odourless, toxic gas
combines with haemoglobin in the red blood cells, reducing the ability of the blood to carry oxygen around the body, fatal
homologous series
Family of compounds which have common features
Successive members differ by a CH2 group
Same general formula but diff length carbon chains
Same functional group
Similar chemical properties
Similar bonding
Gradually changing physical properties e.g. mps, bps, viscosity
Alkanes
General formula - CnH2n+2
Hydrocarbons
Homologous series
saturated compounds
molecules held together by weak intermolecular forces
Monkeys Eat Peanut Butter
Greater number of carbon atoms (alkanes)
Greater chain length
Greater surface of contact between molecules
Greater attractions between molecules
More energy required to separate the molecules
Bp increases
Viscosity increases
Less volatile
Less flammable
substitution reaction (halogenation)
alkanes react with halogens in the presence of UV light
substitution reaction of halogenation to alkanes example
e.g. methane + bromine -> bromomethane + hydrogenbromide
orange bromine water turns colourless with alkanes in the presence of UV light
structural isomers
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural or displayed formula
branched - methyl, dimethyl
physical differences of structural isomers
Branched chain molecules have weaker intermolecular attractions
Less surface of contact between molecules
Less energy is required to separate molecules
Bp decreases
Alkenes
General formula - C2H2n
double bonds have an angle of 120 degrees
double bonds can change places
saturated compounds
contain only single c-c and c-h covalent bond, contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms for a given number of carbons
unsaturated compounds
contain one c-c double bond, if this breaks then more atoms can be added on
Addition reactions of alkenes
2 molecules react to form one molecule
One of the c-c double bond breaks and a small molecule is added
Become saturated
Hydrogenation of alkenes example
e.g. ethane + hydrogen, nickel catalyst at 150 degrees
used to make margarine
Addition of Halogens to Alkenes example
e.g. bromine + ethene at room temp
addition with steam to form alcohols (alkenes) example
e.g. ethene + steam, 300 degrees, 60-70 atmospheric pressure, phosphoric acid (catalyst)
chemical test for c-c double bond
add orange bromine water, turns form orange to colourless
cracking
Breaking down of long chain molecules (useless) into small chain molecules (useful)
Produces mixtures of shorter chain alkenes and alkanes
anything less than or equal to 11 carbons is counted as a short chain
cracking example
thermal decomposition, 600-700 degrees, finely divided mixture of SiO2 (silica) / Al2O3 (alumina) catalyst
cracking used to
Provide commercially useful short-chain alkanes for use in petrol
Provide reactive alkenes, used to make polymers
polymers
Long chain molecule made up by joining many small molecules or monomers
natural polymers
silk, wool and cotton
synthetic polymers
polyethene, nylon
addition polymers
Made by addition polymerisation, formed by joining many small molecules (monomers)
Usually requires heat, pressure and an initiator
Polyethene
Used to make plastic bags, cling film, buckets, toys
poly propene
Used to make ropes, plastic, fishing nets
polychloroethene
Used to make window frames, drainpipes
polytetrafluoroethene
o Used to make non-stick coating on frying pans, burette taps
pros of plastics
Corrosion resistant
Good electrical and thermal insulators
Low density
Non toxic
Strong/durable
Cons of plastics
Inert and non-biodegradable, persist in environment
Some produce toxic gases when burnt
Starting materials come from a finite resource
Preventions of environmental problems
Recycling plastic
Reusing plastic
Biodegradable plastics
20-80 (fractional distillation of synthetic crude oil)
pale yellow
runny
burns very easily
clean flame
81-120 (fractional distillation of synthetic crude oil)
yellow
fairly runny
burns easily
yellow flame and smoke
121-170 (fractional distillation of synthetic crude oil)
dark yellow
fairly viscous
burns quite easily
quite smoky flame
171-240 (fractional distillation of synthetic crude oil)
brown
viscous
difficult to burn
smoky flame