Tietze Chapter 5 Diagnostics (Hema, Immuno, Neuro, Nutrition, Renal)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
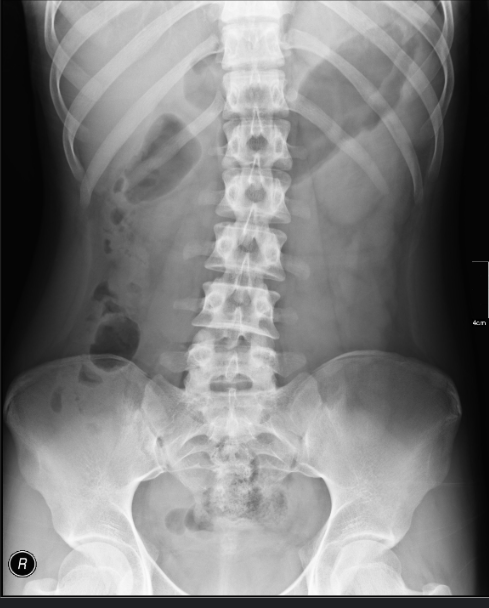
Abdominal Radiography
including the kidneys, ureter, and bladder (KUB), is obtained with the patient lying supine and is used to identify intestinal obstruction and other organ-specific structural abnormalities.
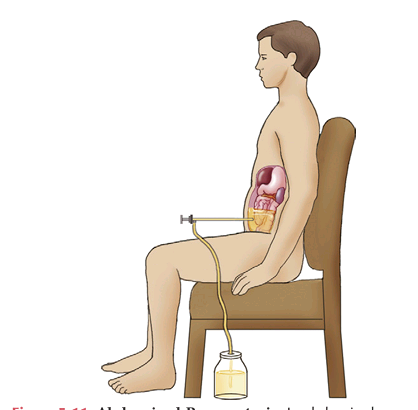
Abdominal Paracentesis
is used to obtain ascitic fluid for analysis. The fluid is assessed for each of the following characteristics
Ascitic fluid
It may be yellow in cirrhosis, cloudy in infection, brown in hyperbilirubinemia, or bloody in malignancy or after a traumatic tap.

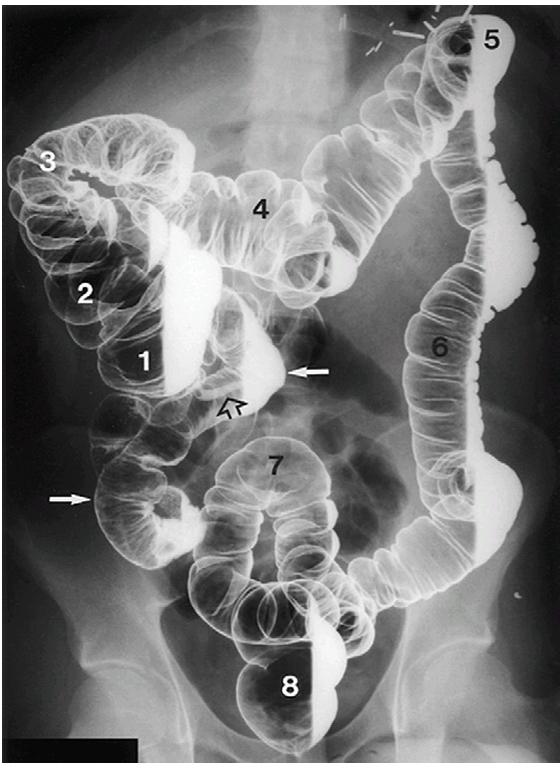
Barium enema
— are used to visualize the large intestine. The double-contrast technique uses a combination of barium and air to visualize the large intestine and is considered a more precise procedure
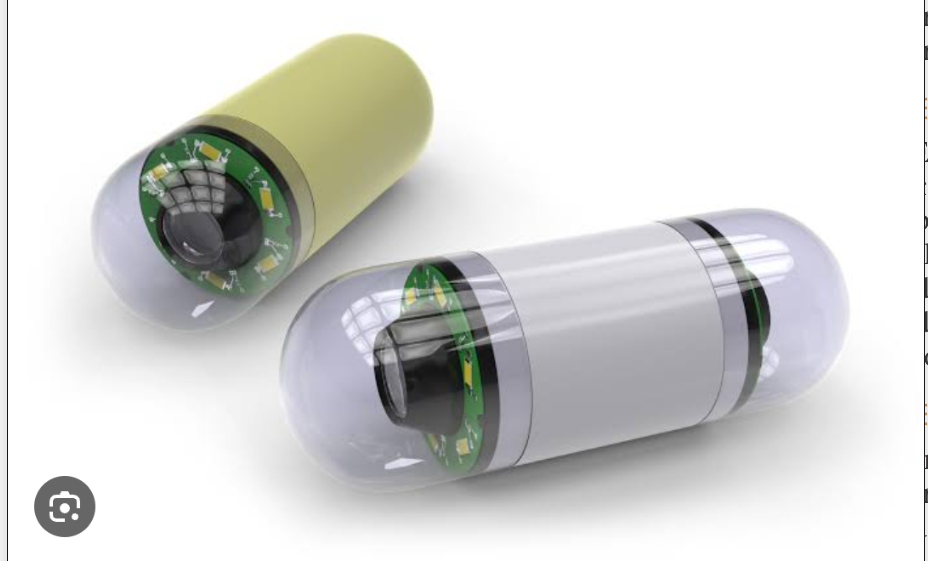
Capsule endoscopy
The patient swallows a disposable capsule about the size of a large vitamin tablet that contains a miniature video camera, a light source, a miniature transmitter, antenna, and battery. Images are transmitted to an external receiver in a belt worn around the patient’s waist. Peristalsis moves the capsule through the gastrointestinal tract; the capsule is excreted rectally
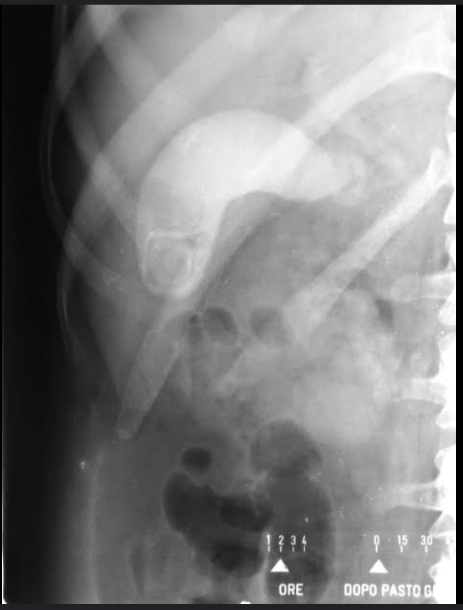
Cholecystography
— is used to evaluate gallbladder function and anatomy. Orally administered iopanoic acid concentrates in the gallbladder, opacifying it for visualization.
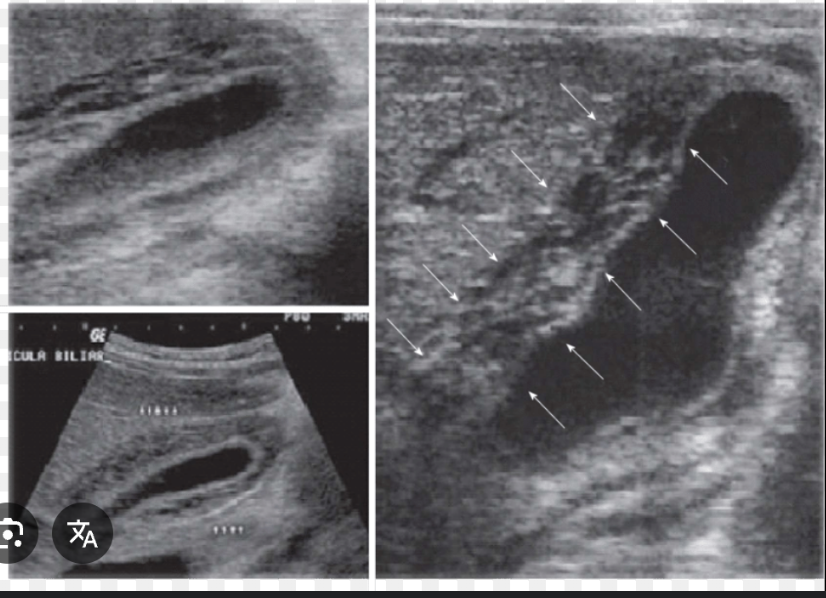
Cholecystosonogrphy
Sonography is used to detect gallstones and evaluate the gallbladder, biliary system, and adjacent organs. Sonography has nearly replaced cholecystography.
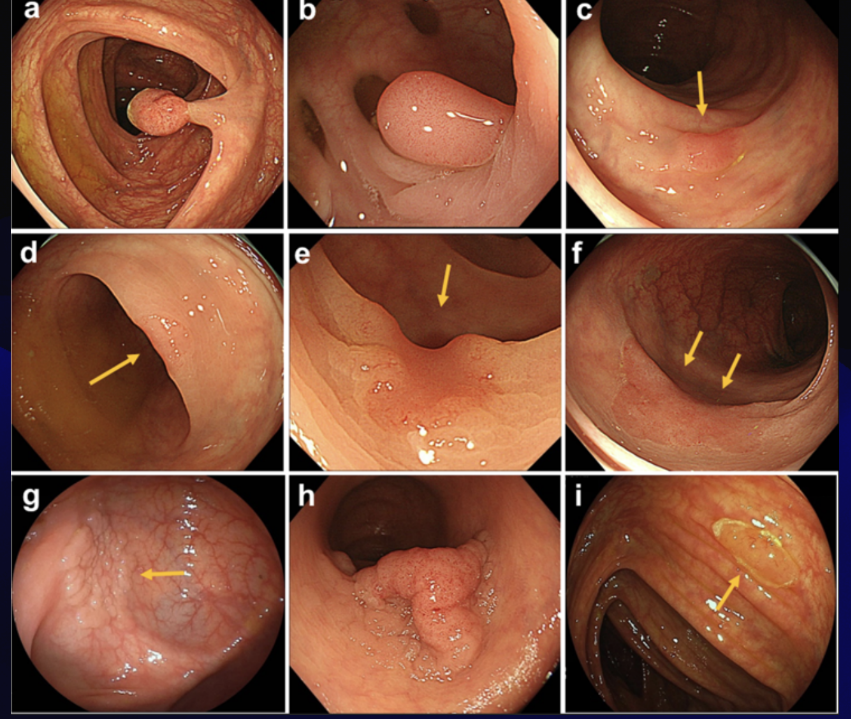
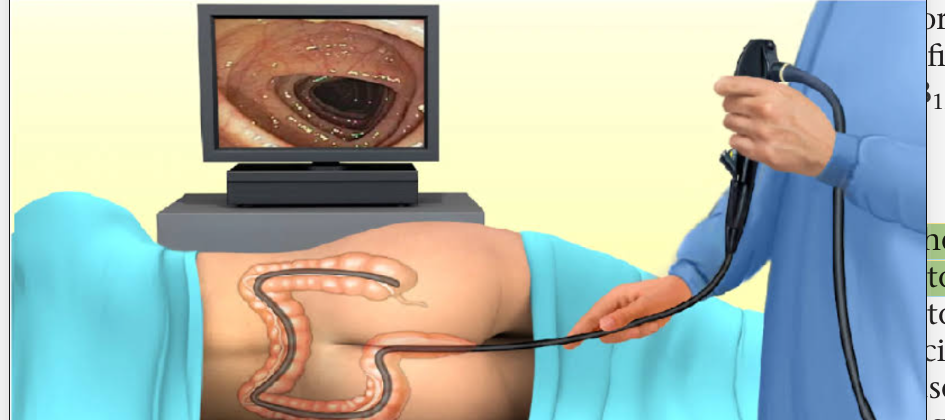
Colonoscopy
a flexible fiberoptic tube is inserted rectally to visualize the lining of the large intestine from the rectum through the colon to the lower end of the small intestine.
D-xylose test
test is used to screen for carbohydrate malabsorption. For this test a dose of 25 g of d-xylose is administered with water, and the urine is collected for a 5-hour period. Normally, more than 3 g of d-xylose is excreted in the urine during this period; lower amounts indicate impaired carbohydrate absorption.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
combines endoscopy and radiography to visualize the biliary system and pancreas. An endoscope is inserted in the esophagus and advanced to the point where the bile duct and pancreatic duct open in the duodenum; contrast dye is injected into the ducts. Radiography is performed to visualize the ducts.
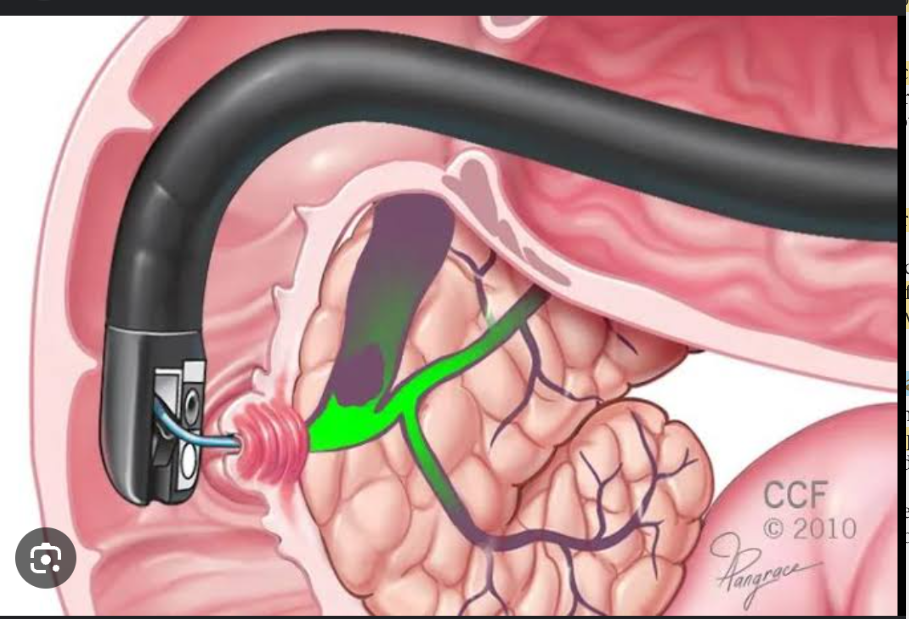
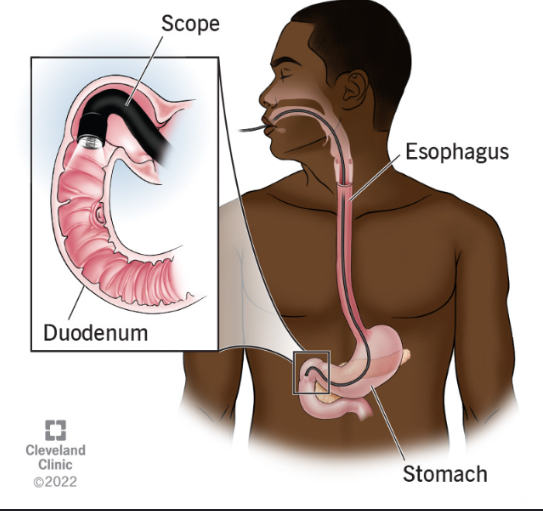
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
an endoscope is inserted into the esophagus to visualize the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. Biopsy specimens and fluid for culture and cytologic analysis may be obtained. Interventions such as polypectomy and vessel obliteration may be performed
Intragastric pH
The pH of gastric secretions is sometimes measured to monitor the effectiveness of acid-suppressive drug therapy or to document the presence and severity of acid reflux.
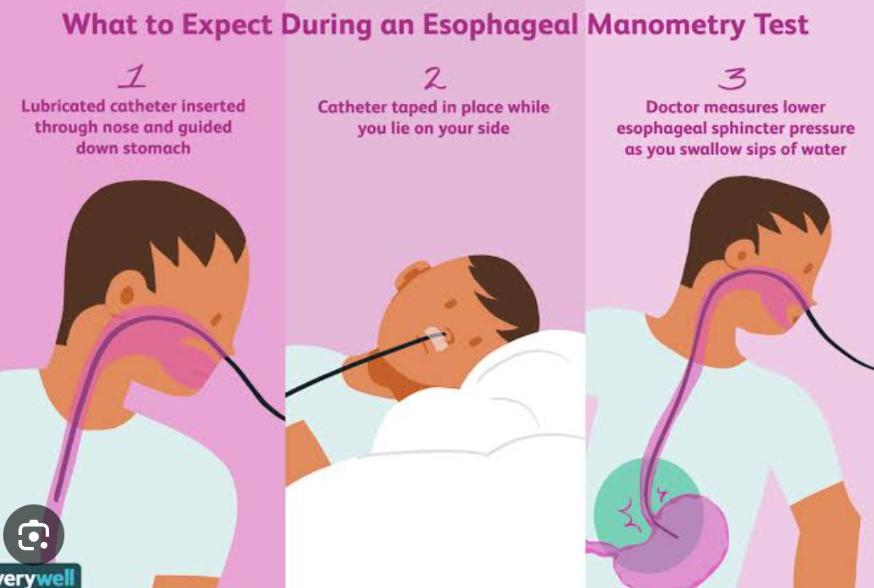
Manometry
It is used to evaluate esophageal contractions and esophageal sphincter pressures. Pressures are measured by pressure transducers on a tube inserted orally.
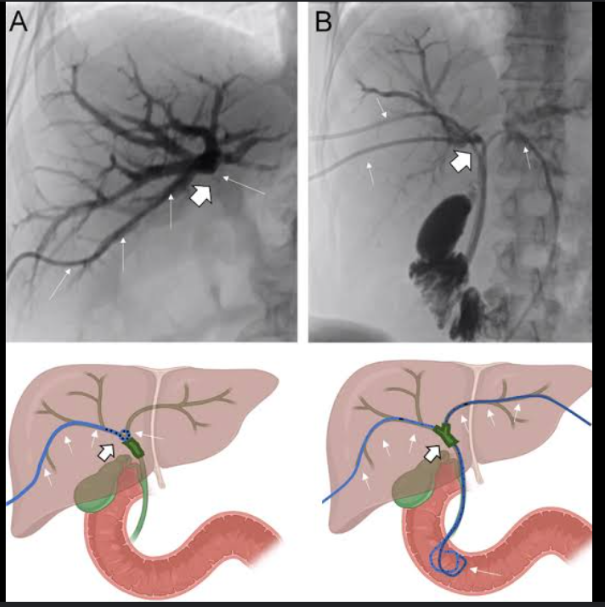
percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
a contrast medium is injected directly into the biliary radicle within the liver, and fluoroscopy is used to visualize the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts.
pH stimulation tests
used to determine the response of gastric acid secretion to a chemical stimulus; they are sometimes used to diagnose hyposecretory and hypersecretory gastric acid disorders. Gastric secretions are collected from the stomach by aspiration through a nasogastric tube. Secretions are collected at baseline and after stimulation with betazole or pentagastrin
Schilling test
It is used to evaluate the absorption of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin).
Sigmoidoscopy
an endoscope is used to evaluate the gastrointestinal tract from the anus to about 60 cm into the terminal colon.
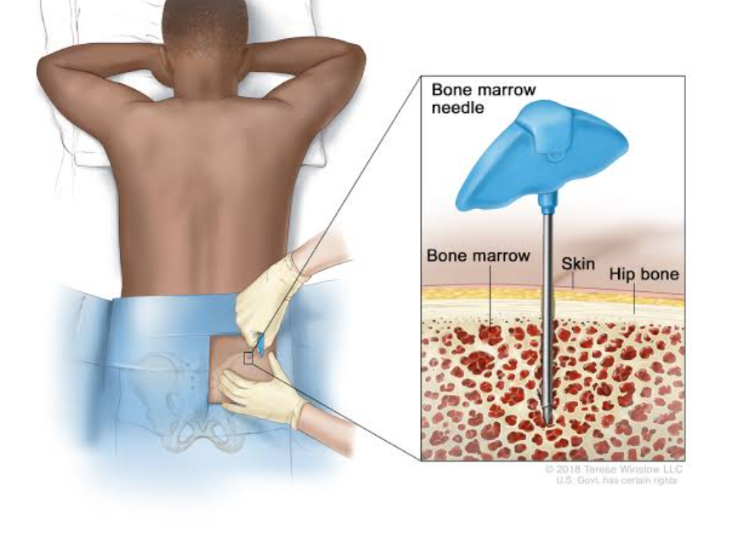
Bone marrow aspiration
It is obtained by penetrating the iliac crest or sternum with a large-bore needle and withdrawing a sample of the bone marrow. The sample is smeared on a slide and evaluated microscopically for cell-line precursors and iron stores. Bone marrow aspirates are used to diagnose anemia and leukemia
Anergy Panel
is used to test the patient’s reactivity to a variety of antigens (purified protein derivative antigen, mumps antigen, Streptococcus antigen, Candida antigen, Trichophyton antigen, histoplasmin). The antigens are injected intradermally, and the skin is evaluated for redness and swelling at the injection site. Reaction to one or more of the antigens indicates a responsive immune system. Reaction to a specific antigen indicates that the patient has antibodies to that antigen
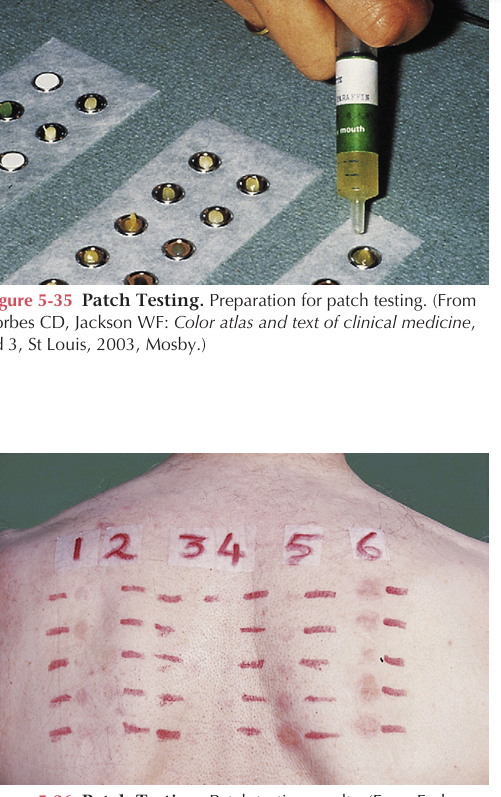
Patch testing
It is used to detect delayed hypersensitivity reactions to a variety of allergens. Potential allergens are applied directly to the skin (Figure 5-35). The sites are evaluated in 72 hours for characteristic erythema and blistering indicating positive reactions
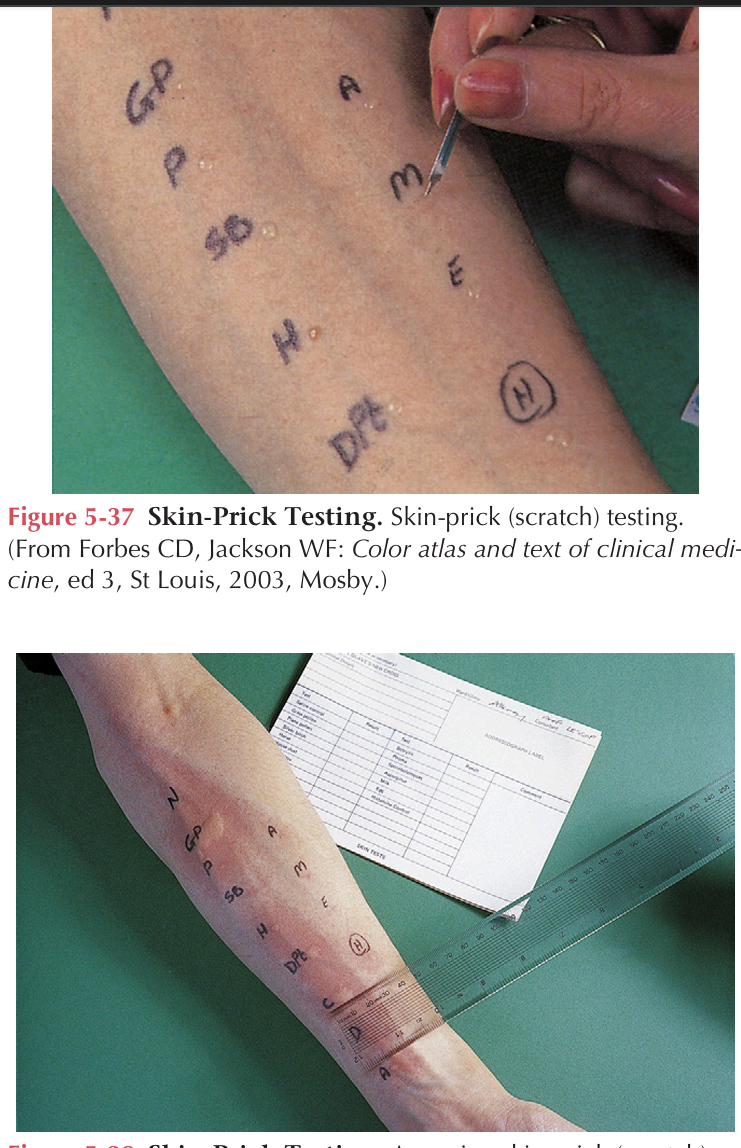
Skin prick testing
IT is used to detect immediate hypersensitivity reactions. Drops of allergen in solution are placed on the skin. The skin is pricked to a depth of about 1 mm by passing a lance or needle through the solution and into the skin. The sites are evaluated in about 30 minutes for characteristic wheal formation indicating positive reactions
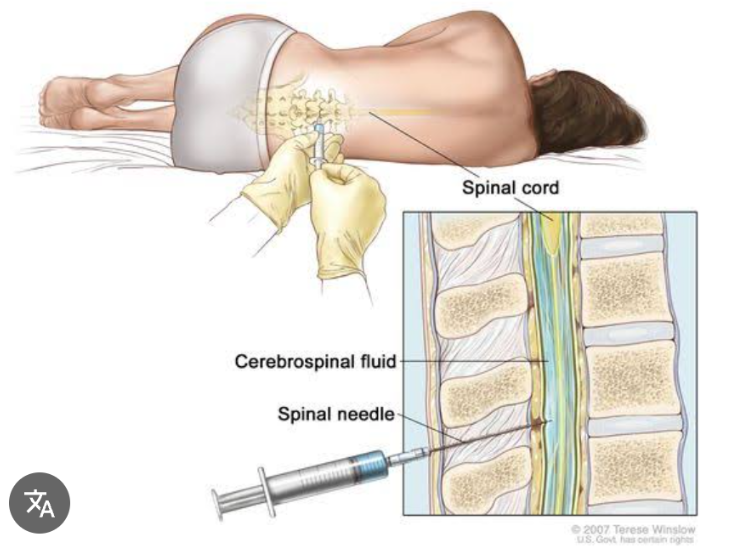
Spinal Tap/Lumbar Puncture
It is used to obtain cerebrospinal fluid for analysis. The fluid is assessed for each of the following characteristics.
WBCs
RBCs
There are normally no cells in the CSF.
The —- count may be increased in infections or inflammatory conditions.
The presence of — may indicate a traumatic tap or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Xanthochromia
The CSF normally has no color.
Discoloration due to the presence of RBCs ranges from frankly bloody to pink to yellow (—) as the RBCs degrade
0.6
The normal CSF/serum glucose ratio is —.
A variety of infections, including bacterial meningitis, mycobacterial infection, and fungal infections, are associated with a lower than normal CSF glucose level. Other causes of low CSF glucose include subarachnoid hemorrhage and some malignancies.
60 to 200 mm Hg
The normal opening pressure is —. Infections, bleeding, and tumors may increase the CSF pressure.
23 to 38 mg/dL
The CSF normally contains very low concentrations of protein (—). The CSF protein level may be elevated with a traumatic tap, subarachnoid hemorrhage, diabetes mellitus, or meningitis
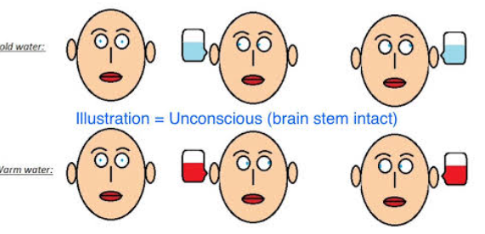
Cold Caloric Test
It assesses brainstem function in comatose patients. The intact external auditory canal is filled with ice-cold water. Both eyes will move toward the cold ear and then snap back to the center if brainstem function is normal.
Edrophonium (Tensilon) Test
is used to diagnose myasthenia gravis and to determine whether the maintenance dosage of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor is appropriate. It is administered parenterally, and the muscle strength of the patient is evaluated subjectively.
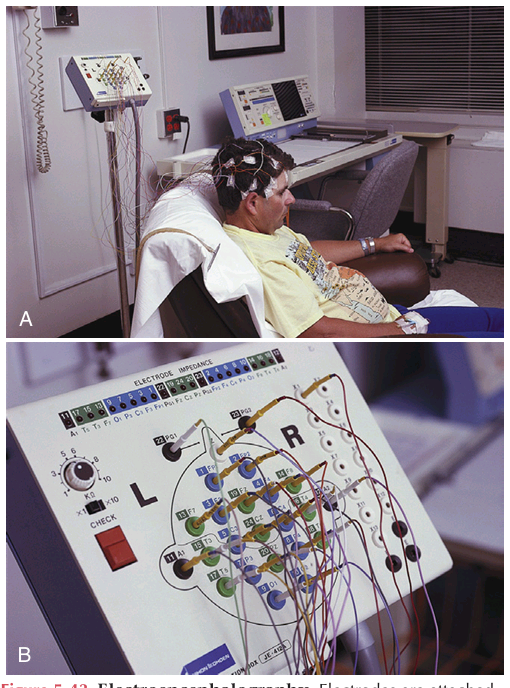
Electroencephalography EEG
It records the electrical activity of the brain from electrodes attached to the scalp. It is used to diagnose seizures, assess patient response to drug therapy, and assess stages of sleep
Electromyography
It evaluates muscle action potentials. EMG is used to diagnose muscle disease and to evaluate patient response to therapy
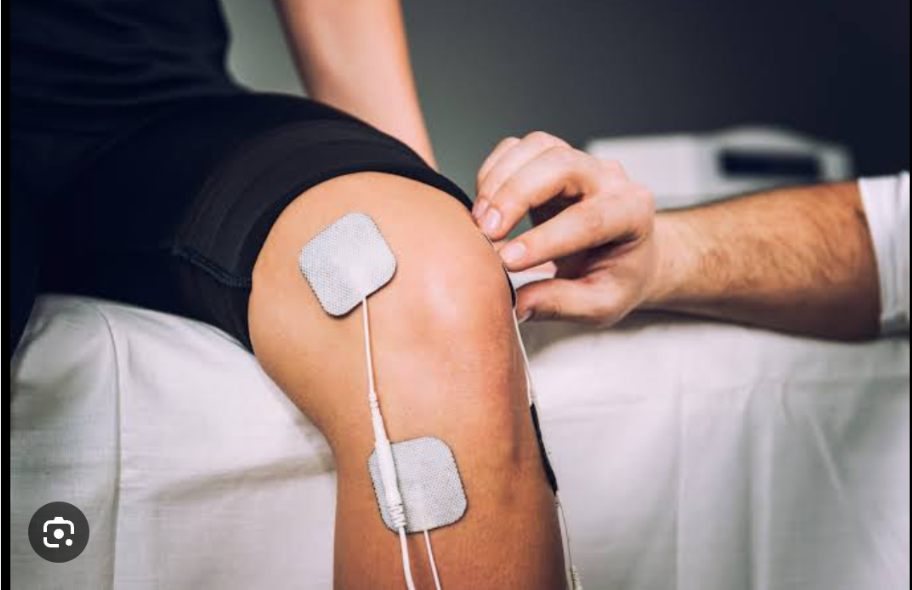
Peripheral nerve stimulation
It assesses depth of neuromuscular blockade. Four supramaximal (“train-of-four,” or TOF) electrical impulses are applied to a peripheral nerve (ulnar, posterior tibial, facial, or peroneal); the number of resultant twitches is counted. No twitches, one twitch, two twitches, three twitches, and four twitches indicate 100%, 90%, 75%, and 50% blockade, respectively.
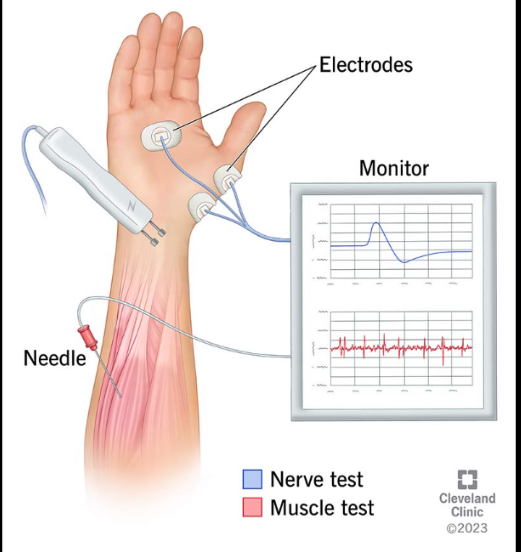
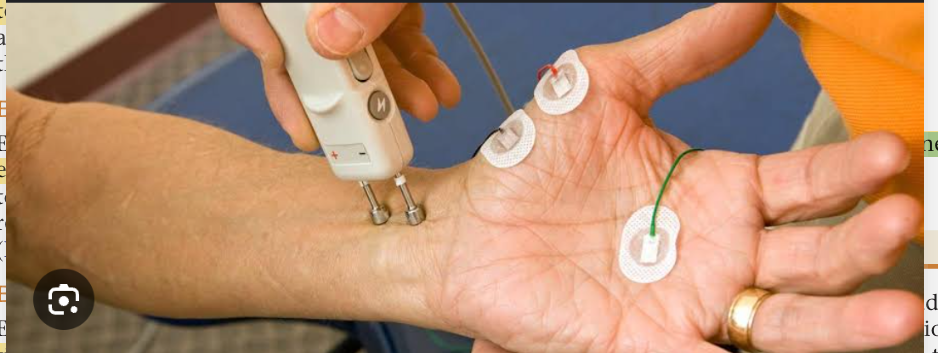
Nerve conduction studies
The rate of nerve conduction is evaluated by stimulating the nerve and recording the velocity of conduction to electrodes placed over the muscle. Nerve conduction studies are used to diagnose nerve injuries and neuromuscular disease.
Anthropometrics
Comparative body measurements assess nutritional status. Parameters such as skinfold thickness of the upper portion of the nondominant arm, middle upper arm circumference (MUAC), and arm muscle circumference (AMC) are assessed. In general, a 20% to 40% decrease compared with normal values is associated with moderate malnutrition. A greater than 40% decrease is associated with severe malnutrition.
Intravenous Pyelography
is a procedure used to visualize the entire urinary tract. A parenteral contrast medium cleared by glomerular filtration is used to detect ureteral obstruction, masses, tumors, and cysts.
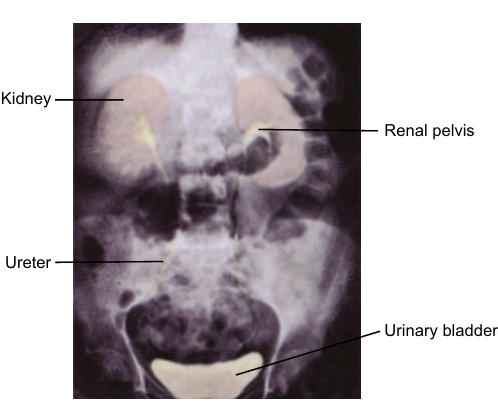
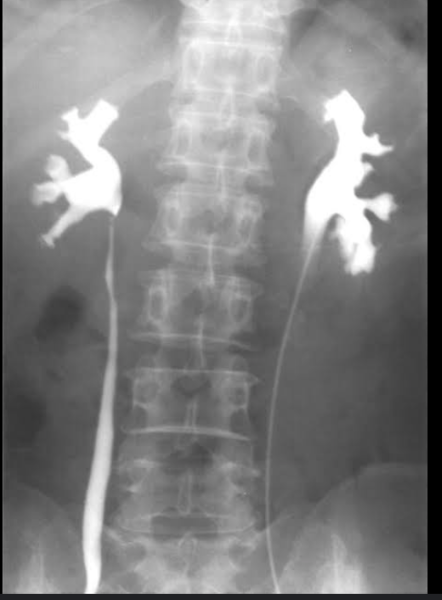
Retrograde pyelography
IT is used to visualize the urine-collecting systems independent of renal function. Contrast media are instilled through a catheter placed in the bladder.