General Optometry Terms
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
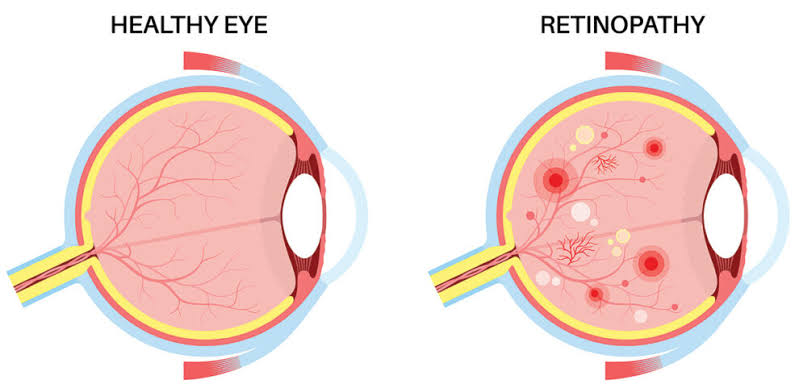
Diabetic Retinothopy
Damage to the delicate blood vessels in the retina caused by diabetes type 1 on 2.
Macular edema
Swelling of the macula due to diabetes.
Amplyopia
Commonly called "lazy eye." It is the loss or lack of central vision in one eye or the inability of the eye to focus.
Astigmatism
An additional curvature on the surface of the cornea, or lens of the eye, that makes it difficult to focus. Can result in headaches and, in more severe cases, blurred vision.
Cataracts
Opacity or cloudiness that usually develops gradually as the lens in the eye loses transparency and the lens material yellows. Cataracts are the leading cause of visual disability in people older than 65.
Conjunctivitis
An inflammation of the conjuctiva, the thin, transparent layer that lines the inner eyelid and covers the white part of the eye.
Diplopia
Also known as double vision.
Dry Eye
Occurs when tear glands produce too few tears, causing itching, burning or even reduced vision.
Hyperopia
Also called far sightedness. A vision condition in which distant objects are usually seen clearly, but close ones do not come into proper focus.
Automated Visual Field
Determine peripheral and central vision disorders.
Autorefractor
Determines nearsightedness, farsightedness and astigmatism.
Biomicroscope
Also called a slit lamp Examines the eye in layer-by-layer detail.
Floaters
Tiny spots or specks that float across the field of vision. Generally harmless, they can be a warning of certain eye problems, especially if there is a sudden change.
Glaucoma
A condition in which the pressure in the eye increases, causing eye damage and potential blindness. A leading cause of blindness in the United States, glaucoma can be prevented if the disease is detected and treated in time.
Intraocular Pressure
Pressure of the fluid inside the eye; normal IOP varies among individuals.
Keratometer
An instrument used to check the front curvature of the cornea's surface. This test is important for anyone interested in contact lenses.
Lensometer
Measures the power of your current prescription lenses.
Macular degeneration
The progressive deterioration of the part of the retina responsible for central vision and a leading cause of blindness in America.
Myopia
Also called near sightedness. A vision condition in which near objects are seen clearly, but distant objects do not come into proper focus.
Ocular Hypertension
An increase in the pressure in your eyes with no detectable changes in vision or damage to the eyes. The term is used to distinguish people with elevated pressure from those with glaucoma. It is also more common in people who are very nearsighted or who have diabetes.
Ophthalmologist
A physician (doctor of medicine or doctor of osteopathy) who specializes in the comprehensive care of the eyes and visual system and the prevention of eye disease and injury. The ophthalmologist is a physician who is qualified by lengthy medical education, training and experience to diagnose, treat and manage all eye and visual system problems, and is licensed by a state regulatory board to practice medicine and surgery.
Ophthalmoscope
A noninvasive, handheld instrument that allows the doctor to examine the internal portion of the eye for a wide range of problems.
Optician
Professionals in the field of designing, finishing, fitting and dispensing of eyeglasses and contact lenses, based on an eye doctor's prescription. The optician also might dispense colored and specialty lenses for particular needs, as well as low-vision aids and artificial eyes.
Optometric assistant
Primarily involved in front-office procedures, optical dispensing and contact lens patient education. A registered optometric assistant is designated by Opt. A., R
Optometric technician
Through academic and clinical experience, these technicians are prepared for diverse job duties. Technicians work directly with optometrists in the areas of patient examination and treatment, including contact lenses, low vision, vision therapy, optical dispensing and office management. A registered optometric technician is designated by Opt. T., R.
Optometrist
Independent healthcare providers who examine, diagnose, treat and manage diseases and disorders of the visual system, the eye and associated structures. They are also trained to diagnose related systemic conditions. Optometrists are state-licensed healthcare professionals. They prescribe glasses, contact lenses, low-vision rehabilitation, vision therapy and medications; They hold a doctor of optometry (O.D.) degree.
Paraoptometric
Working under the direct supervision of a licensed doctor of optometry, they collect patient data, administer routine yet technical tests of the patient's visual capabilities and assist in office management. The paraoptometric also might assist the optometrist in providing primary patient care examination and treatment.
Phoropter
A mask-like instrument positioned so that each eye sees through a separate lens.
Presbyopia
Gradual decline in the ability to focus on close objects or to see small print. Regardless of your prior vision correction needs, presbyopia is considered a normal and almost inevitable part of the aging process.
Retinal Dettachement
The separation of the light-sensitive membrane in the back of the eye (the retina) from its supporting layers.
Sclera
The tough, white outer layer of the eyeball; with the cornea, it protects the entire eyeball
Strabismus
Also known as "cross eyes." One or both eyes turn in, out, up or down, independent of the other eye.
Tonometer
Tests eyes for increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma).