Menstrual Disorders, Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, Pelvic Floor Relaxation/Dysfunction (PFD), Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
amenorrhea
lack of menstrual cycle
primary amenorrhea
occurs is the girl passes the age by which menses is normally started (15y/o), w/ normal growth & secondary sexual characteristics or w/i 3 years of breast development
secondary amenorrhea
when established menses (>3 mos) ceases
most commonly caused by pregnancy
causes of amenorrhea
hypothalamic dysfunction
systemic stress related to marked weight loss (anorexia, bulimia, fad dieting) or excessive exercise (elite athletes, dancers, low body fat)
functional hypothalamic amenorrhea
pituitary dysfunction
some anxiety & psych meds
chronic anovulation or ovarian failure
anatomic abnormalities
intermenstrual bleeding
bleeding or spotting btwn regular periods
heavy menstrual bleeding
excessive menstrual bleeding that occurs at regular intervals
prolonged duration (>7 days) or excessive amount; women’s perception of heavy bleeding
polymenorrhea
frequent regular menses (cycles <21 days)
oligomenorrhea
bleeding occurs < every 35 days; infrequent
dysmenorrhea
painful menses
primary dysmenorrhea
caused by prostaglandins (HA, nausea, cramps, diarrhea)
cramps felt at onset of menses in low back & pelvis
2-3 days
typically disappears after 1st pregnancy
primary dysmenorrhea tx
heat, NSAIDs, hormonal contraception
secondary dysmenorrhea
pathology of reproductive tract
onset usually after age 25 or after years of painless cycles
endometriosis, PID, cervical stenosis, fibroids, ovarian cysts, tumors of pelvis or abdomen, IUDs
premenstrual syndrome
second half of menstrual cycle anywhere from days to 2 wks prior to the next cycle
dysmenorrhea & PMS tx
NSAIDs (ibuprofen, aspirin, naproxen) to act as prostaglandin inhibitors
COCs to inhibit ovulation (less prostaglandins)
self-care
regular exercise, good nutrition, avoid alcohol, rest
heat
supplements: vit B6, E, calcium, mag
herbal: black cohosh, ginger, red raspberry leaf, evening primrose oil
avoid salt
increase natural diuretic: asparagus, cranberry juice, peaches, parsley, watermelon
heat/warm packs
stress reduction/adequate sleep
vit B6
relieve premenstrual bloating, irritability
vit E
ease cramping & breast tenderness
calcium 1200mg
alleviate physical & psychological sx
magnesium 400mg
bloating
premenstrual dysphoric disorder
more severe form of PMS
emotional/behavioral sx
DSM-5 as depressive disorder
sx relieved by menses
PMDD tx
same for PMS
SSRIs: prozac, zoloft, paxil
mittelschmerz
mid-cycle ovulatory pain, typically unilateral
cause r/t follicular rupture & peritoneal irritation from follicular fluid or blood
mittelschmerz sx
sharp cramp-like pain lasting from few hours to 1-2 days
light vaginal spotting
mittelschmerz tx
analgesics, reassurance that it’s benign, hormonal contraceptives
endometriosis
endometrial-like tissue outside of uterus
ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic peritoneum
theory caused by retrograde menstruation, immune dysfunction, genetics
pathophys: adhesions, hormone-responsive, proliferative during cycle —> inflammation, adhesions, scarring
retrograde menstruation
when blood from your period flows backward into your abdomen instead of out your vagina
endometriosis sx
cyclic pelvic pain (progressive & severe)
dysmenorrhea
sx depends on affected area
dyspareunia
infertility
GI sx: diarrhea, constipation, bloating
rectal pain
endometriosis medical tx
NSAIDs
hormonal suppression
COCs to suppress endometrial lining proliferation
progestins
GnRH agonists — hypoestrogenic, pseudomenopausal state
endometriosis surgical tx
laparoscopic excision or ablation of lesions & adhesions
hysterectomy & BSO
endometriosis complementary tx
acupuncture, yoga, pelvic PT, massage, chinese herbal meds
pelvic floor relaxation/dysfunction (PFD)
occurs when muscles, ligaments, & connective tissue (fascia) that support pelvic organs (bladder, uterus, rectum) become weakened, overstretched, or damaged
d/t childbirth, aging, hormonal changes, chronic straining, surgery
can lead to
pelvic organ prolapse (POP)
other PFD types: urinary/fecal incontinence, pelvic pain, sexual dysfunction, obstructed defecation
pelvic organ prolapse (POP)
organs descend into or outside vaginal canal
cystocele, rectocele, uterine prolapse, enterocele
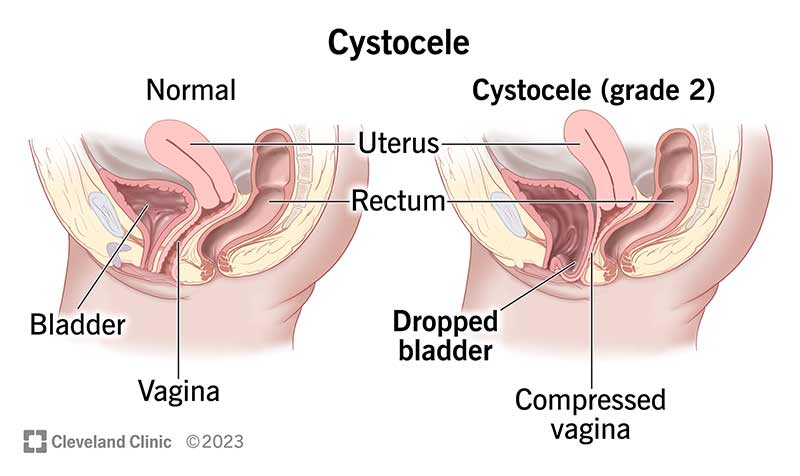
cystocele
weakened upper anterior wall of vagina is no longer able to support weight of urine in bladder
bladder protrudes downward into vagina
incomplete emptying of bladder
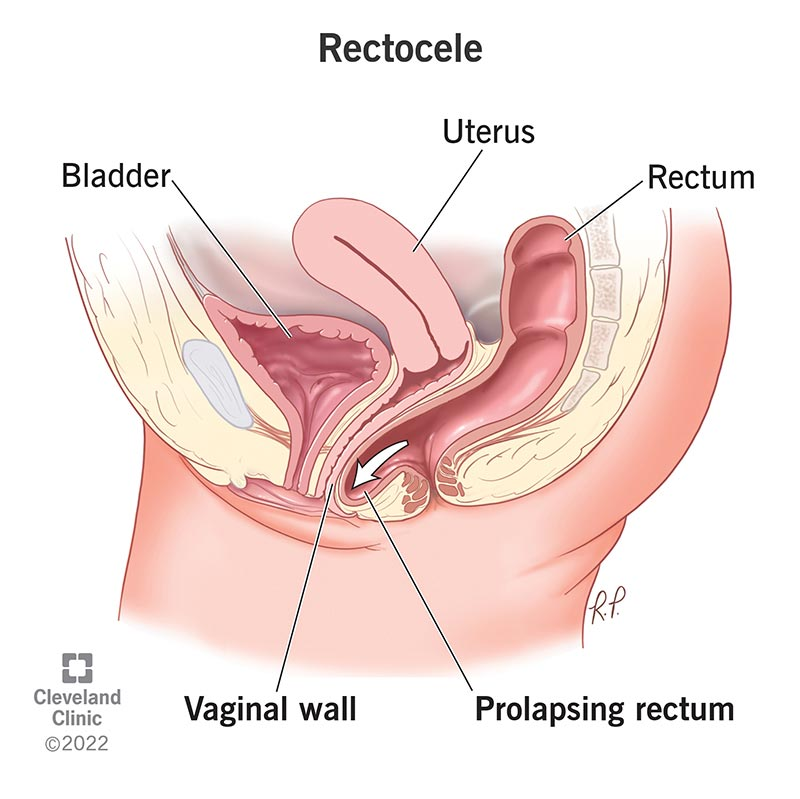
rectocele
posterior wall of vagina becomes weakened & thin
straining at defecation
digital pressure on posterior vaginal wall to facilitate BM
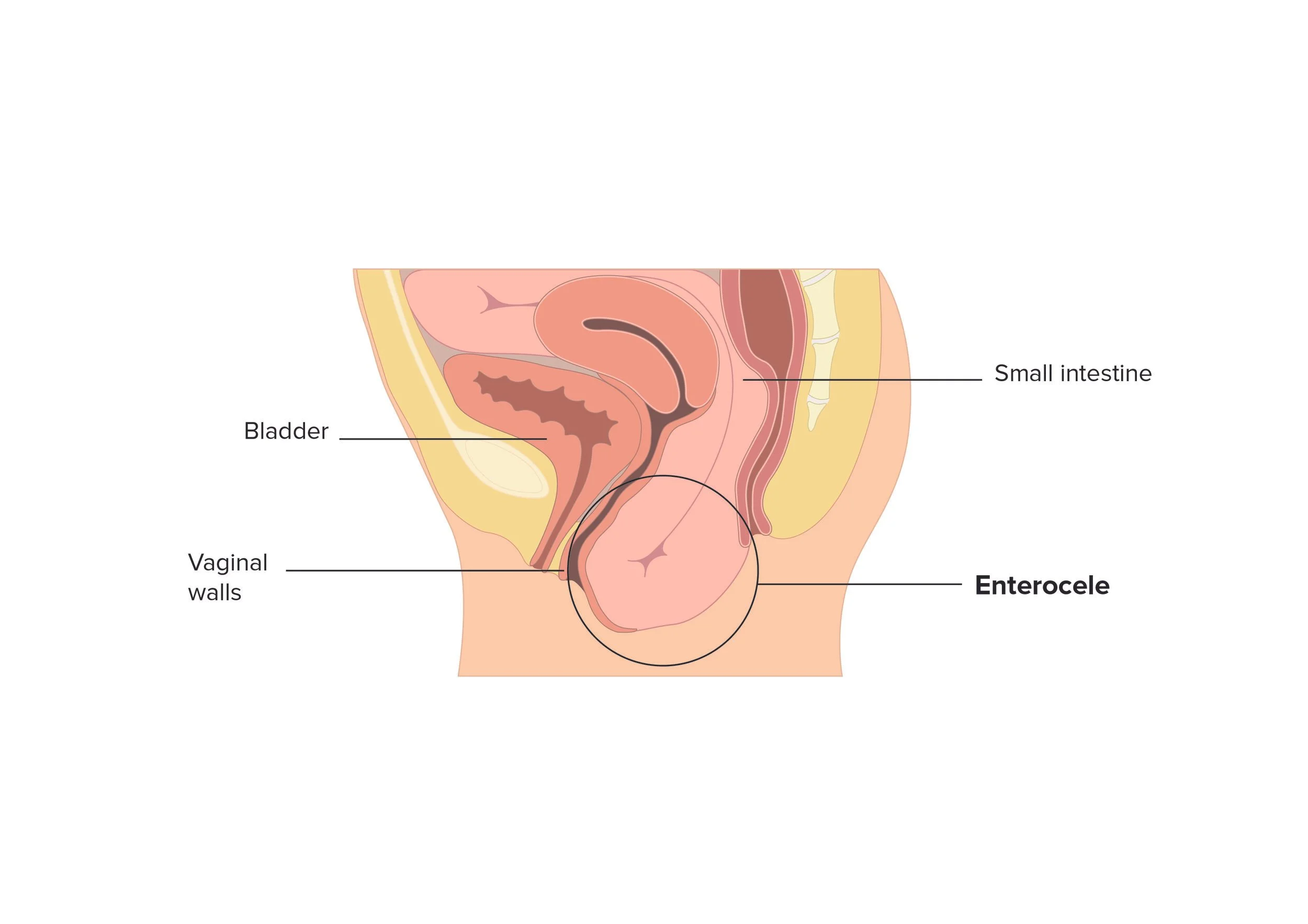
enterocele
prolapse of upper posterior vaginal wall btwn vagina & rectum
often contains loop of bowel
uterine prolapse
occurs when cardinal ligaments which support uterus & vagina are stretched during pregnancy & do not return to normal
1st degree: uterus remains in vagina
3rd degree: cervix extends outside body
uterine prolapse sx
pelvic fullness
dragging sensation
fatigue
urinary frequency & urgency
constipation & flatulence
cervical ulceration & bleeding
uterine prolapse tx
kegel exercises
for urinary stress incontinence, meds
vaginal pessarie or ring (not surgical)
surgical intervention
fistula
hole or opening btwn 2 organs
rectovaginal, vesicovaginal
urinary incontinence
stress: leakage with coughing, sneezing, exercise
urge (overactive bladder): sudden urge followed by leakage
mixed
first-line interventions: pelvic floor PT, biofeedback, bladder training, behavioral strategies
fecal incontinence
involuntary loss of stool or gas
often linked to obstetric injury, aging, chronic constipation, nerve damage
pelvic pain syndrome
chronic pelvic pain d/t muscle hypertonicity, nerve entrapment, scar tissue
includes elevator ani syndrome, pudendal neuralgia
obstructed defecation
difficulty evacuating stool caused by paradoxical contraction or poor coordination of pelvic floor muscles
anemia
hemoglobin < 11g/dL
associated w/ preterm birth & LBW
nutrition deficiency anemia
iron & folic acid deficiency
hemolysis anemia
sickle cell disease & thalassemia
iron deficiency anemia
dietary iron required to synthesize hemoglobin, affecting O2 transport
difficult to meet pregnancy needs
most common
begin pregnancy anemic
baby needs O2 → need more hemoglobin = more iron
greatest need in second half of pregnancy
iron deficiency anemia maternal s/sx
pallor, fatigue, lethargy, HA, pica
iron deficiency anemia maternal risks
asymptomatic, prone to infection, increased risk of pre-e & PPH, delayed wound healing
iron deficiency anemia fetal/neonate effects
take from mom → mom at risk for anemia
reduced fetal red cell volume, hemoglobin, iron stores
LBW, preemie, stillbirth (severe anemia Hgb < 6g/dL)
iron deficiency anemia management
prevention
pregnant women start on 30mg/day (PNV) & eat iron rich diet
if diagnosed
increased 60-120mg PO daily routine supplemental iron therapy
reevaluate 1mo PP
iron supplementation teaching
can cause constipation, black stool
stool softener? nighttime
vit C aids in absorption
calcium or caffeine can inhibit absorption
take on empty stomach
iron rich foods
meat, fish, chicken, green leafy vegetables
folic acid
cell duplication, fetal & placental growth, RBC formation
needs double during pregnancy
folic acid deficiency
megaloblastic
increased risk for neural tube defects
folic acid deficiency anemia prevention
0.4mg/day folate supplement
folic acid deficiency anemia tx
1mg folic acid & iron supplement
folic acid sources
fresh leafy green vegetables, OJ, red meat, fish, chicken, legumes
sickle cell disease
autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes anemia d/t abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in distortion & destruction of RBC
worsened by pregnancy changes
sickle cell disease anemia maternal risks
crisis: sudden attacks of pain (general, localized in bones, joints, lungs, abdominal organs, spine) d/t ischemia from occluded capillaries
complications: require blood transfusion, infections, emergency c/s, CHF, renal failure
sickle cell disease anemia fetal risks
fetal death following an attack
prematurity, IUGR
hepatitis B
A-G, can be transmitted perinatally
hepatitis B modes of transmission
blood, saliva, vaginal secretions, s3men, breast milk that readily cross placental barrier
hepatitis B maternal symptoms
vomit, abdominal pain, jaundice, fever, rash, painful joints
most adults recover w/i 6mos, then have immunity
hepatitis B fetal & neonatal effects
increased incidence of prematurity, LBW, neonatal death
risk of developing acute hep B infection at birth
if acquired prior age 5, more likely to become chronic carriers of the disease (reservoirs)
hepatitis B management
safe sex, universal precautions
vax
all pregnant women screened for HbsAg
if neg, offer vax
if pos during delivery, infant should be given w/i 12hrs of birth
hep B immune globulin (HBIG)
hep B vax (dose 2 at 2-3mos, dose 3 at 6mos)