AP World Unit 4
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Omani-European Rivalry
A trade rivalry between the Omani of the Middle East and the European traders.
Astronomical Chart
Map of the night sky (stars) that can be used to aide maritime navigation. (Improvements helped transoceanic travels.)
Lateen Sail
triangular sail that made it possible to sail against/into the wind
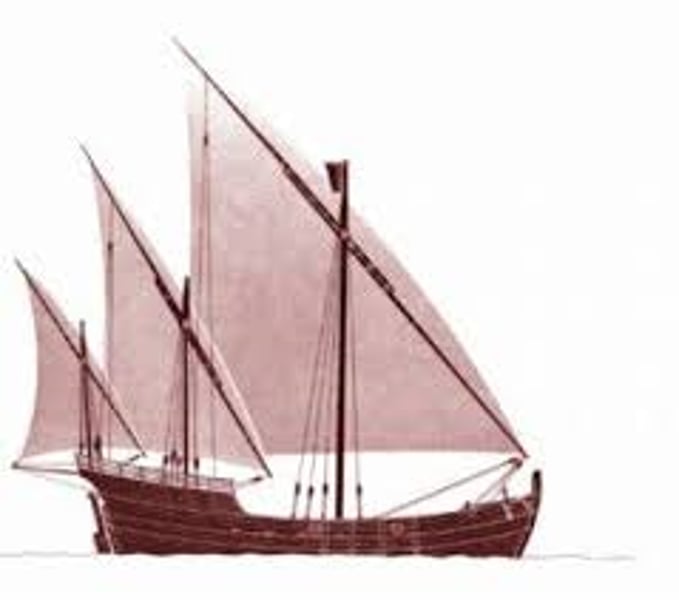

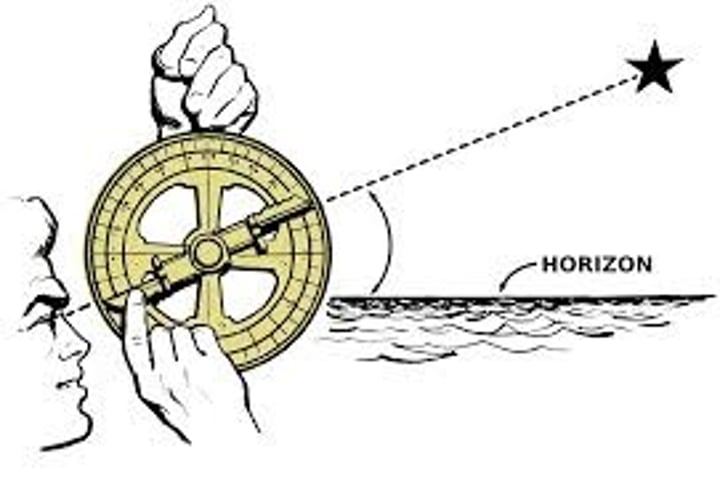
Astrolabe
An instrument used by sailors to determine their latitude location by observing the position of the stars and planets
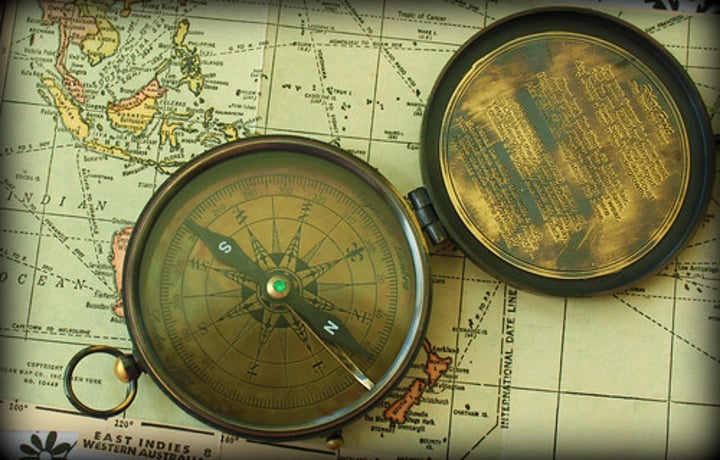
Compass
an instrument that shows the direction of magnetic north (invented in China)

Rudder
the hinged plate at the back and bottom of a boat, used for steering
Carrack
Large Portuguese ship used for ocean travel
Caravel
A small, easily steerable ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in their explorations
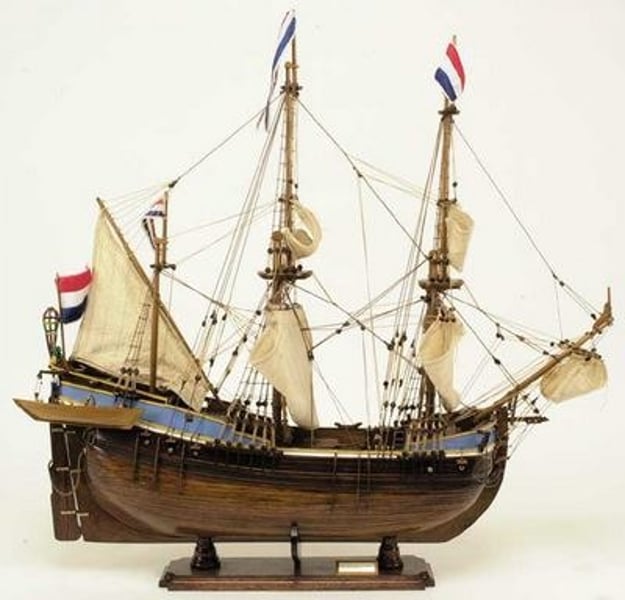
Fluyt
A shallow-draft ship of large capacity, which enabled Dutch transport of enormous quantities of cereals, timber, and iron:

Maritime Empires
empires based on sea travel and trading posts
Cartography
science of making maps and charts

Christopher Columbus
Claimed areas in Caribbean after "discovering" the Americas in 1492 while searching for a faster route to India.
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by exporting more goods than they imported.
Prince Henry the Navigator
Portuguese Prince who established a school that brought together sailors, cartographers etc. Searched for bottom of Africa.
Bartholomew Dias
Dias was an early Portuguese explorer who traveled down the coast of Africa in search of a water route to Asia. He rounded the southern tip of Africa in 1488, now the Cape of Good Hope.

Vasco da Gama
Portuguese explorer who each India by sea sailing around the tip of Africa. (1498) Huge profits on goods brought back to Europe.

Trading Post Empire
16th Century. Built initially by the Portuguese. Used to control trade routes by forcing merchant vessels to dock at fortified trading sites and pay duties there.
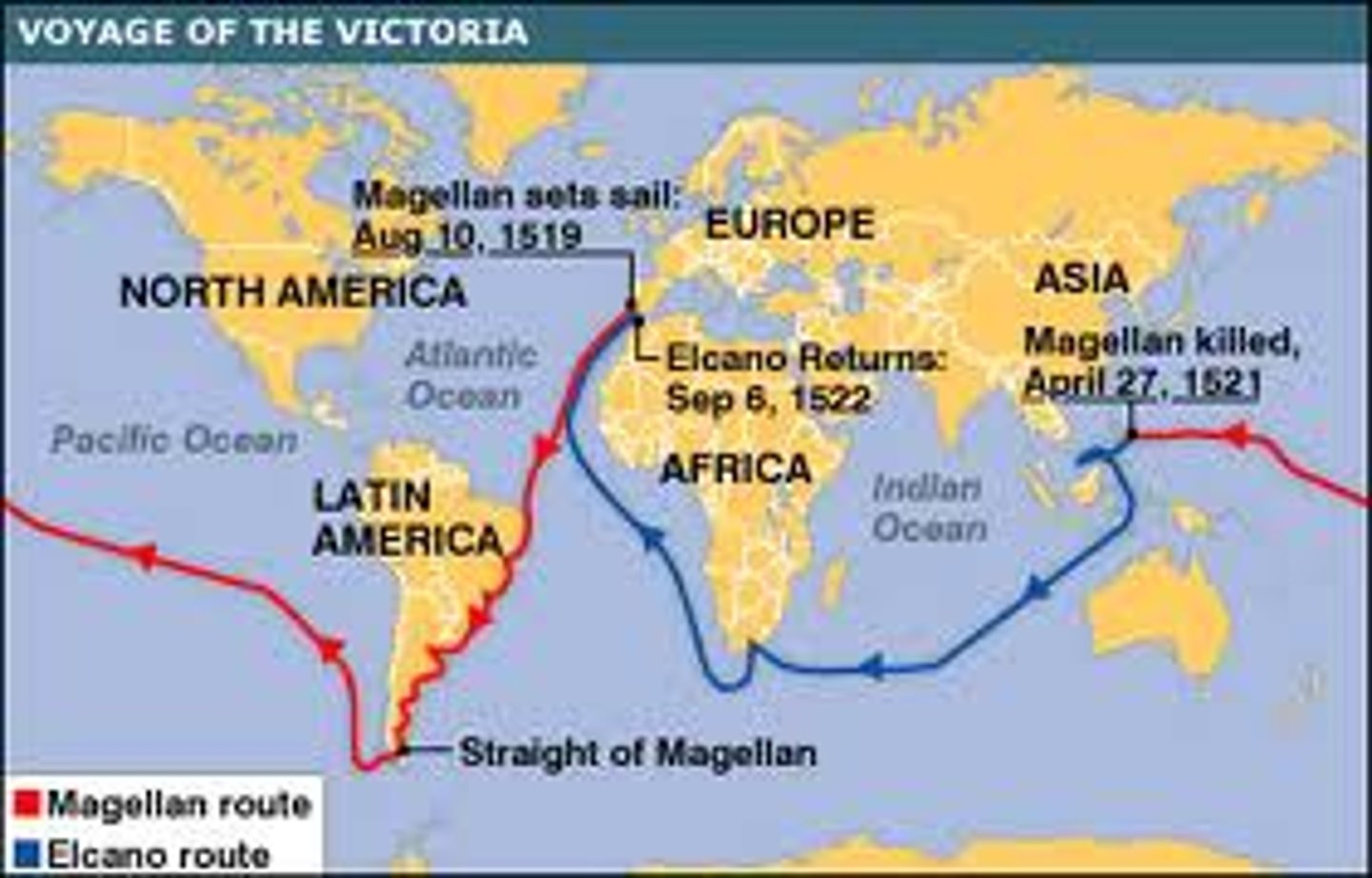
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese navigator who led the Spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to circumnavigate the earth
Galleon
a large sailing ship used especially by the Spanish in the 1500s and 1600s

Monopoly
the exclusive possession or control of the supply or trade in a commodity or service.
Jacques Cartier
The first French explorer to explore mainland Canada in the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
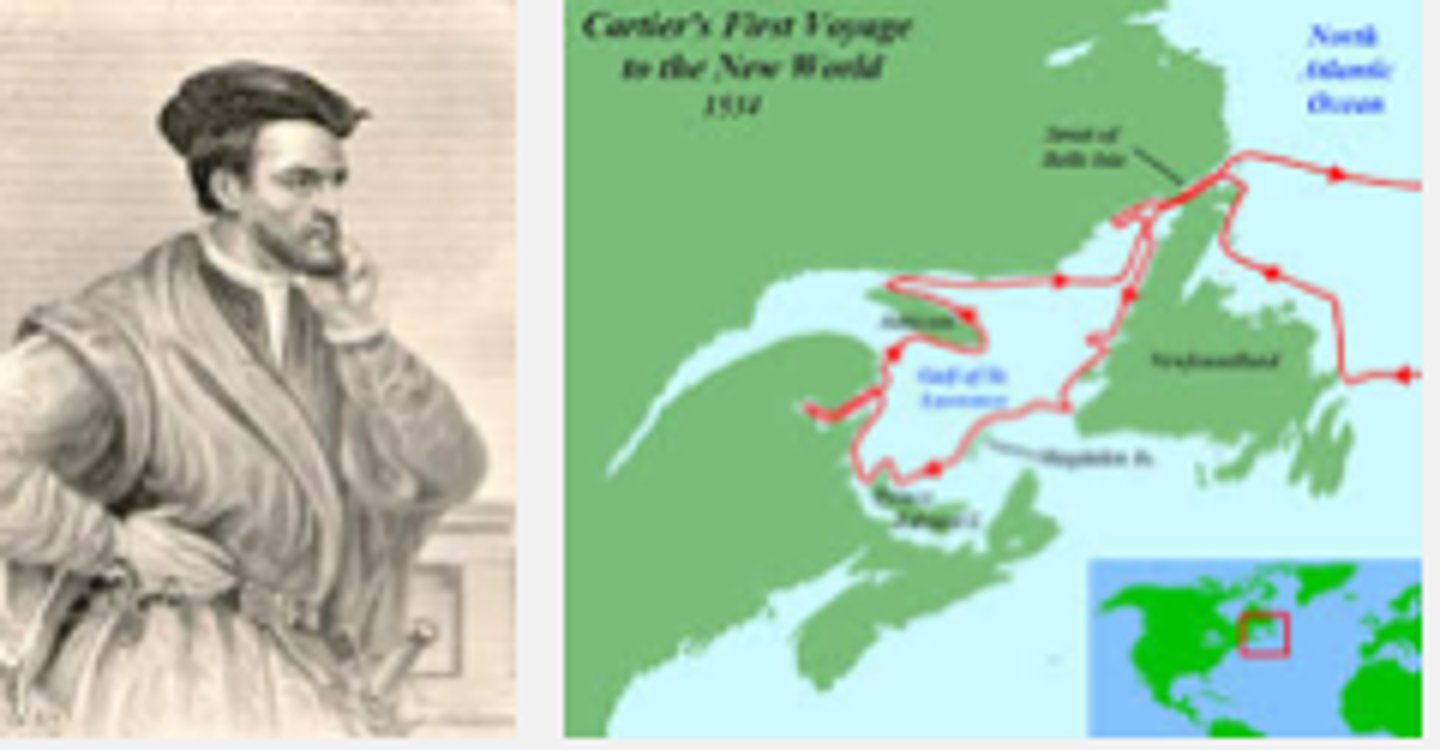
New France
French colony in North America, with a capital in Quebec, founded 1608. New France fell to the British in 1763.
Jamestown, Virginia
First permanent English settlement, founded in 1607 by the Virginia Company for economic reasons
Henry Hudson
An English explorer who explored for the Dutch. He claimed the Hudson River around present day New York
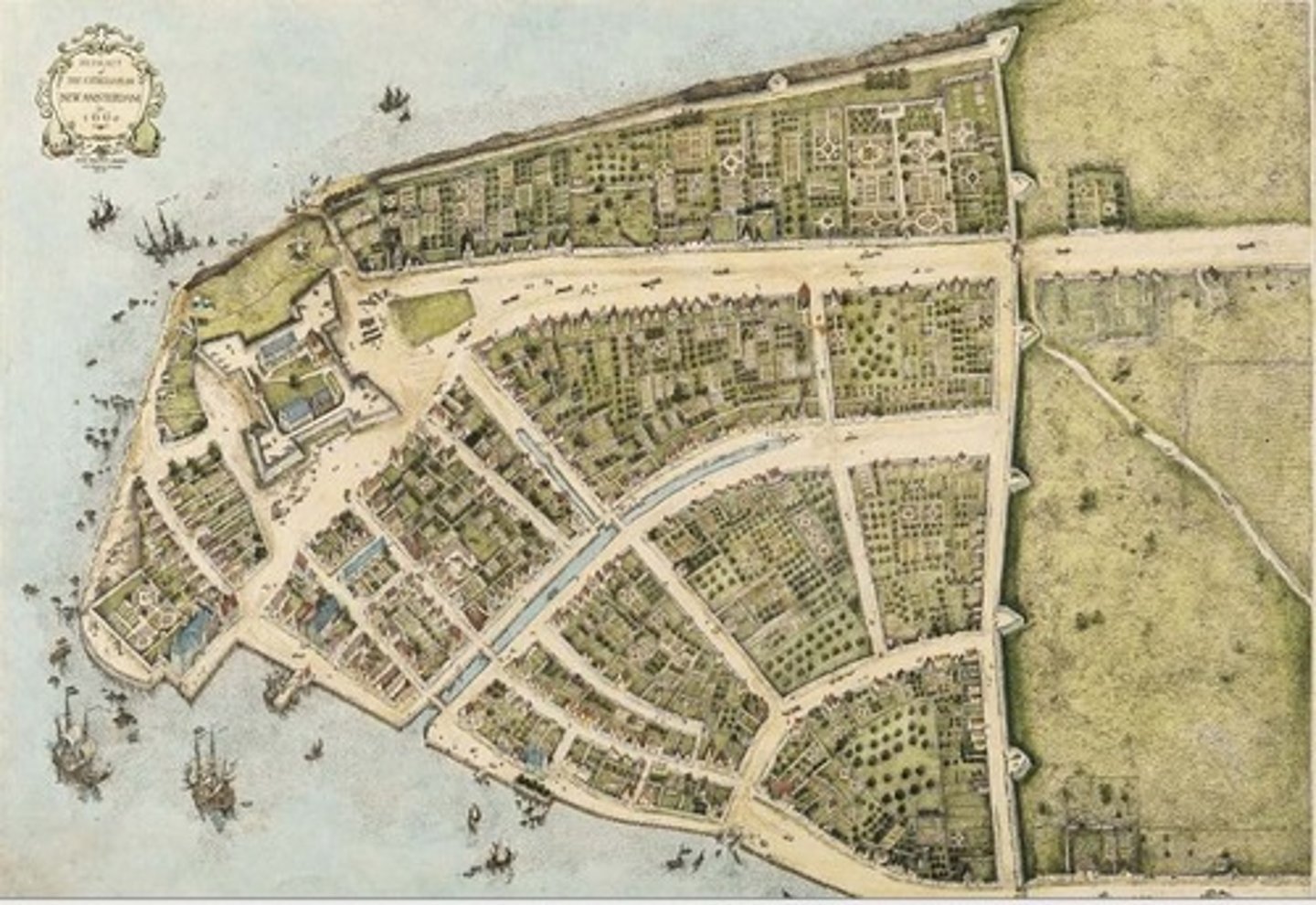
New Amsterdam
Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. This later became "New York City"
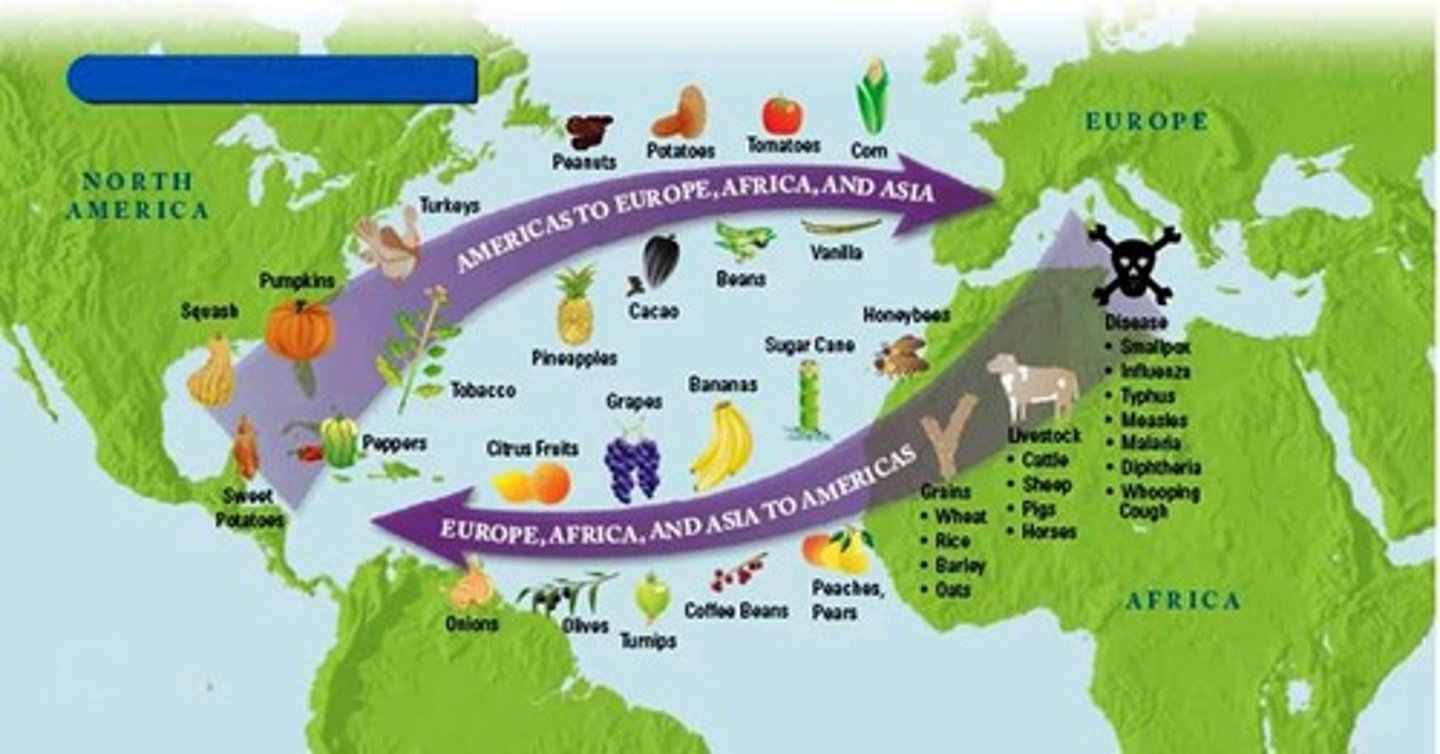
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
Conquistador
A Spanish conqueror of the Americas
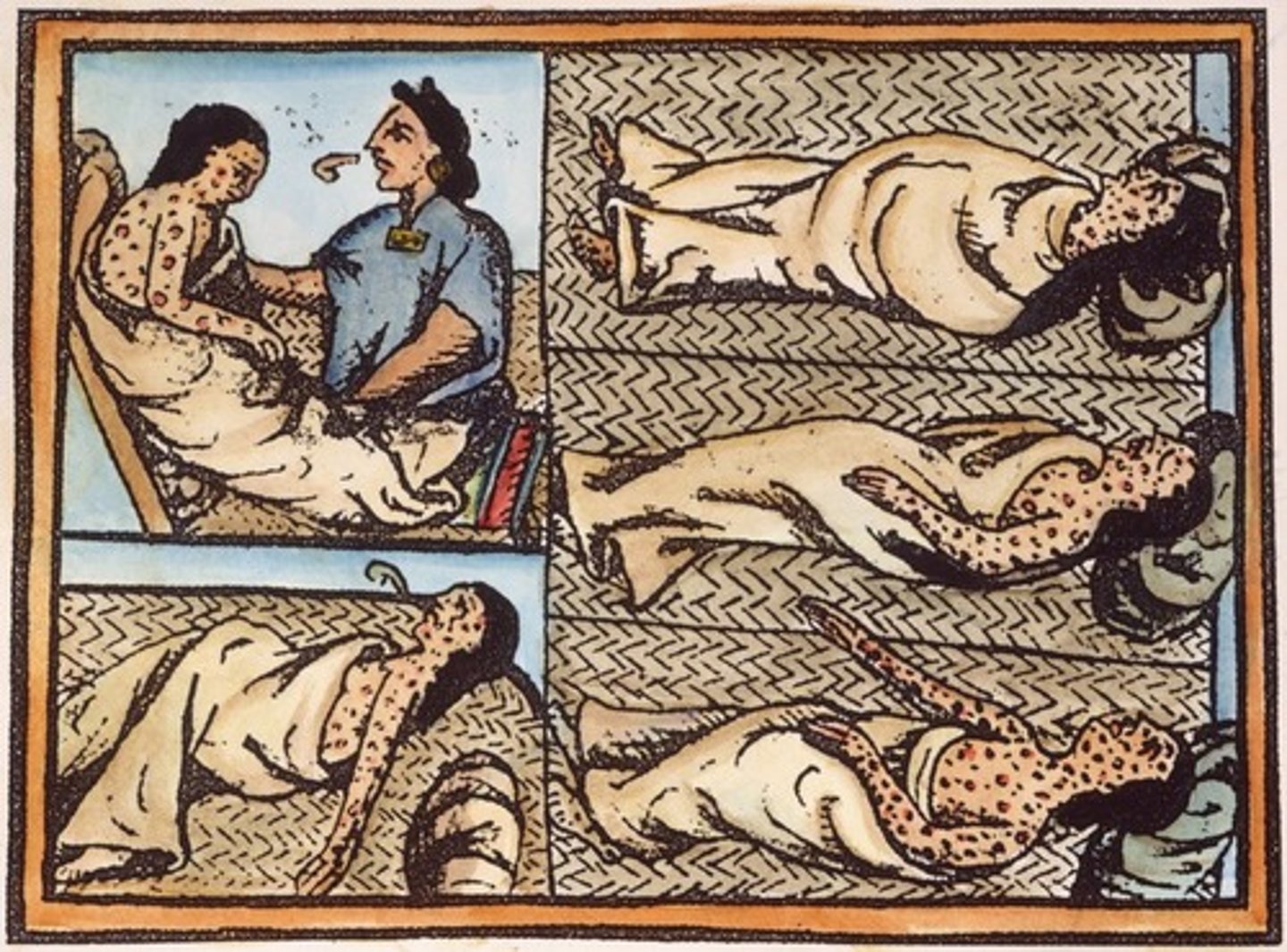
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, weakness, and skin eruption with pustules that form scabs; responsible for killing millions of Native Americans.
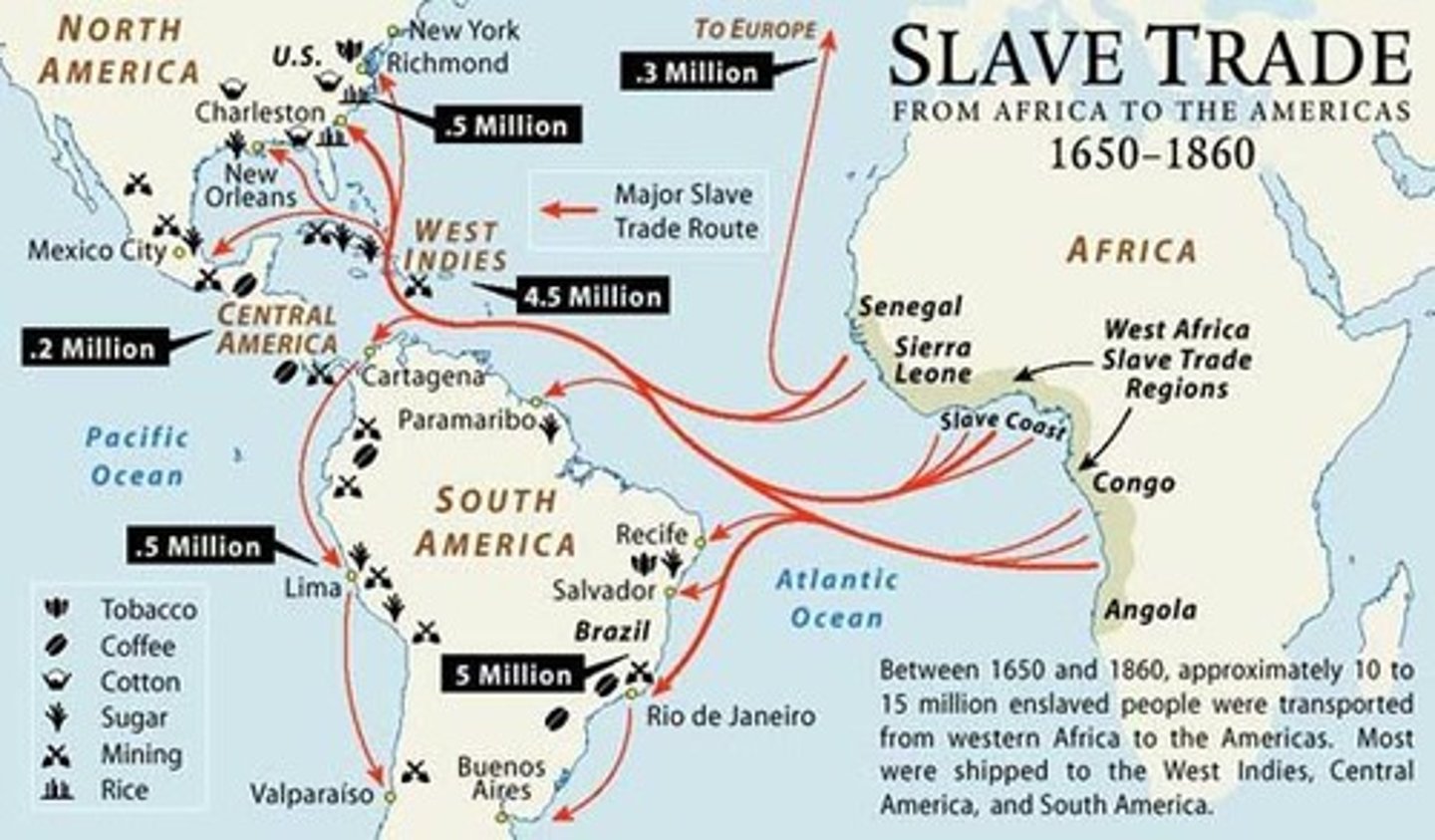
Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
Trading of African people to the colonies of the New World in and around the Atlantic ocean
cash crop
farm crop raised to be sold for money (not just subsistence)
African Diaspora
The separation of Africans from their homeland through centuries of forced removal to serve as slaves in the Americas and elsewhere. (living away from the homeland)
Indentured Servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination.
Chattel Slavery
A system of bondage in which a slave has the legal status of property and so can be bought and sold like property.
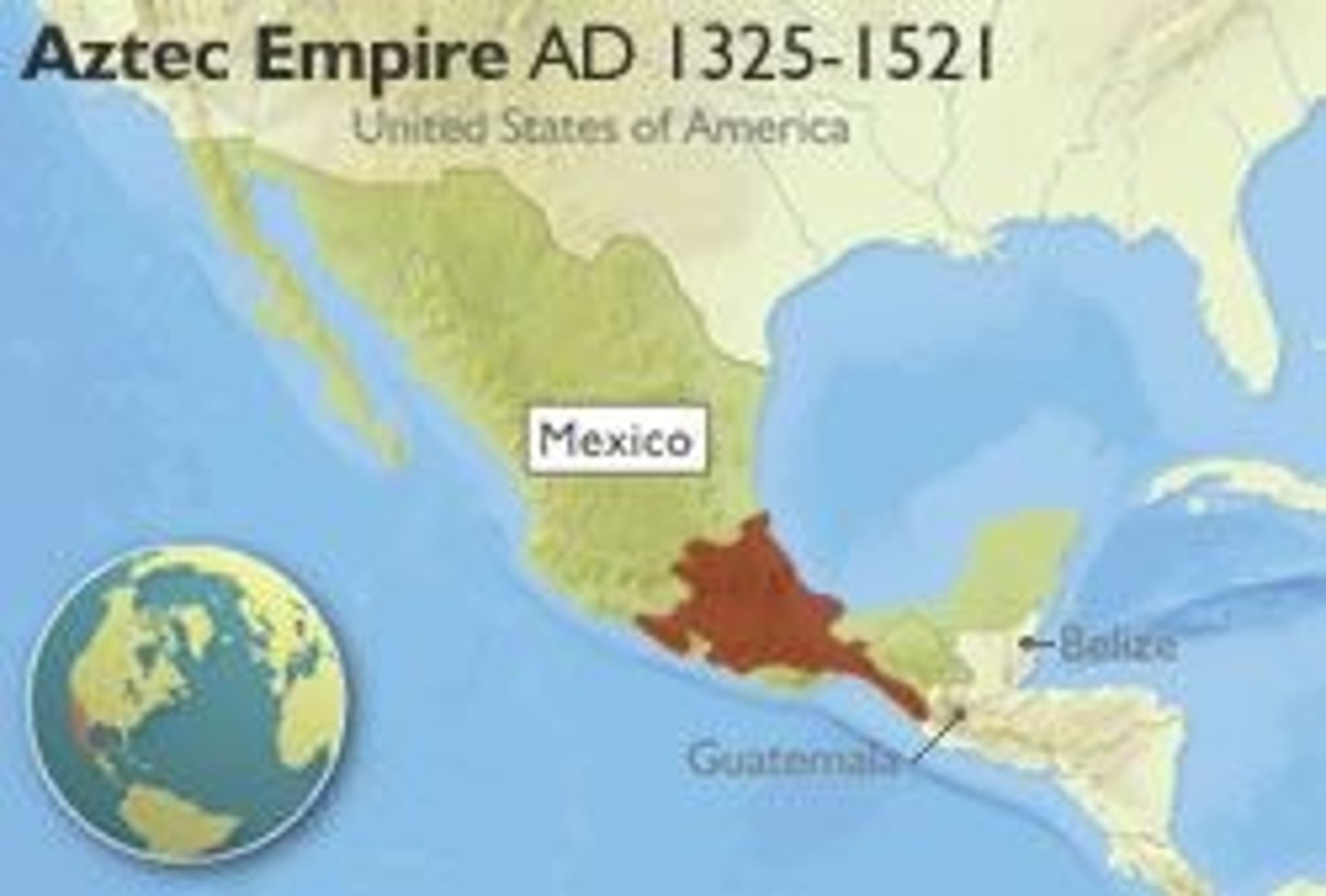
Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century.
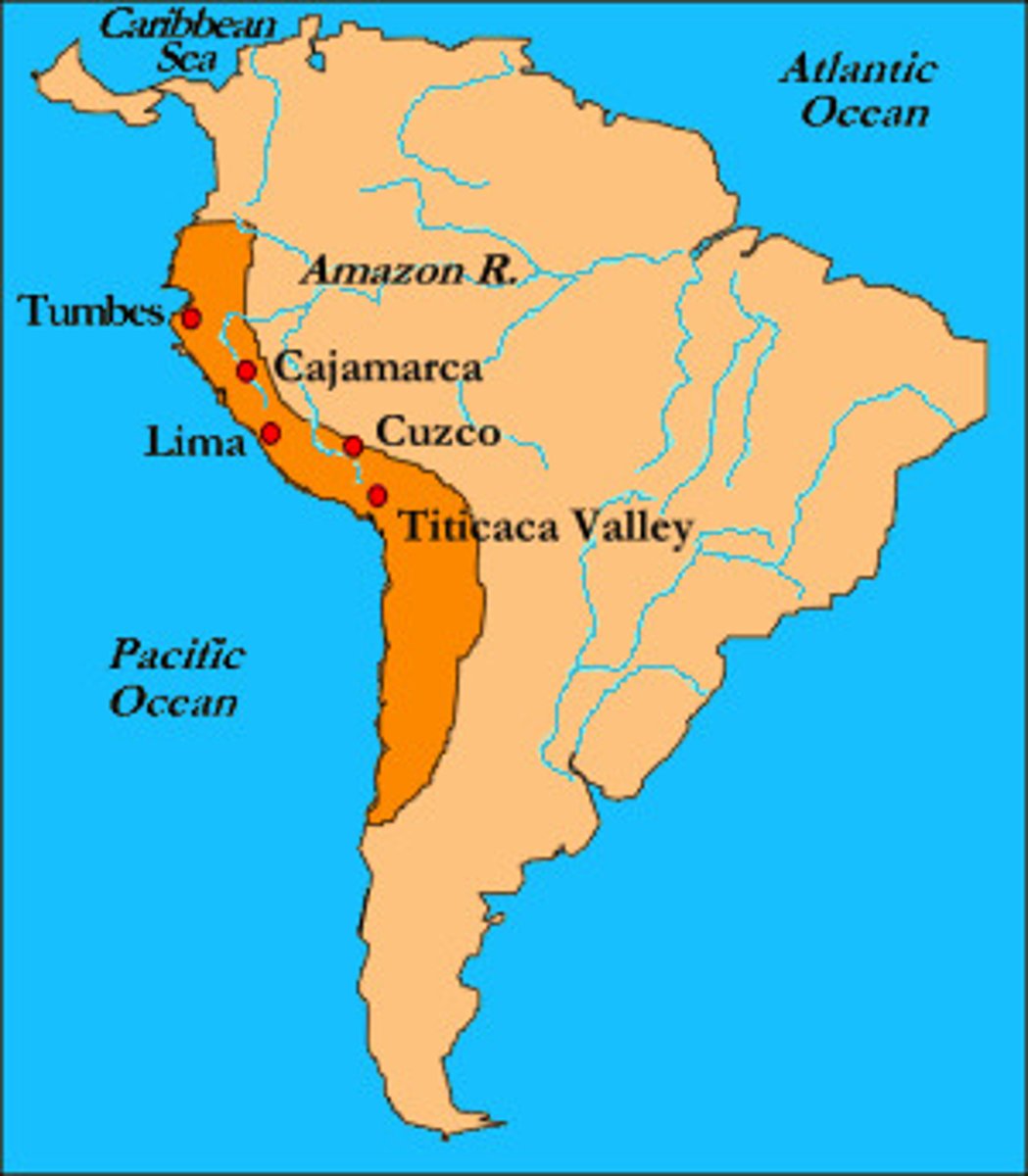
Inca Empire
Advanced Empire stretching along the western side of South America.
Francisco Pizarro
Spanish explorer who conquered the Incas in what is now Peru and founded the city of Lima (1475-1541).
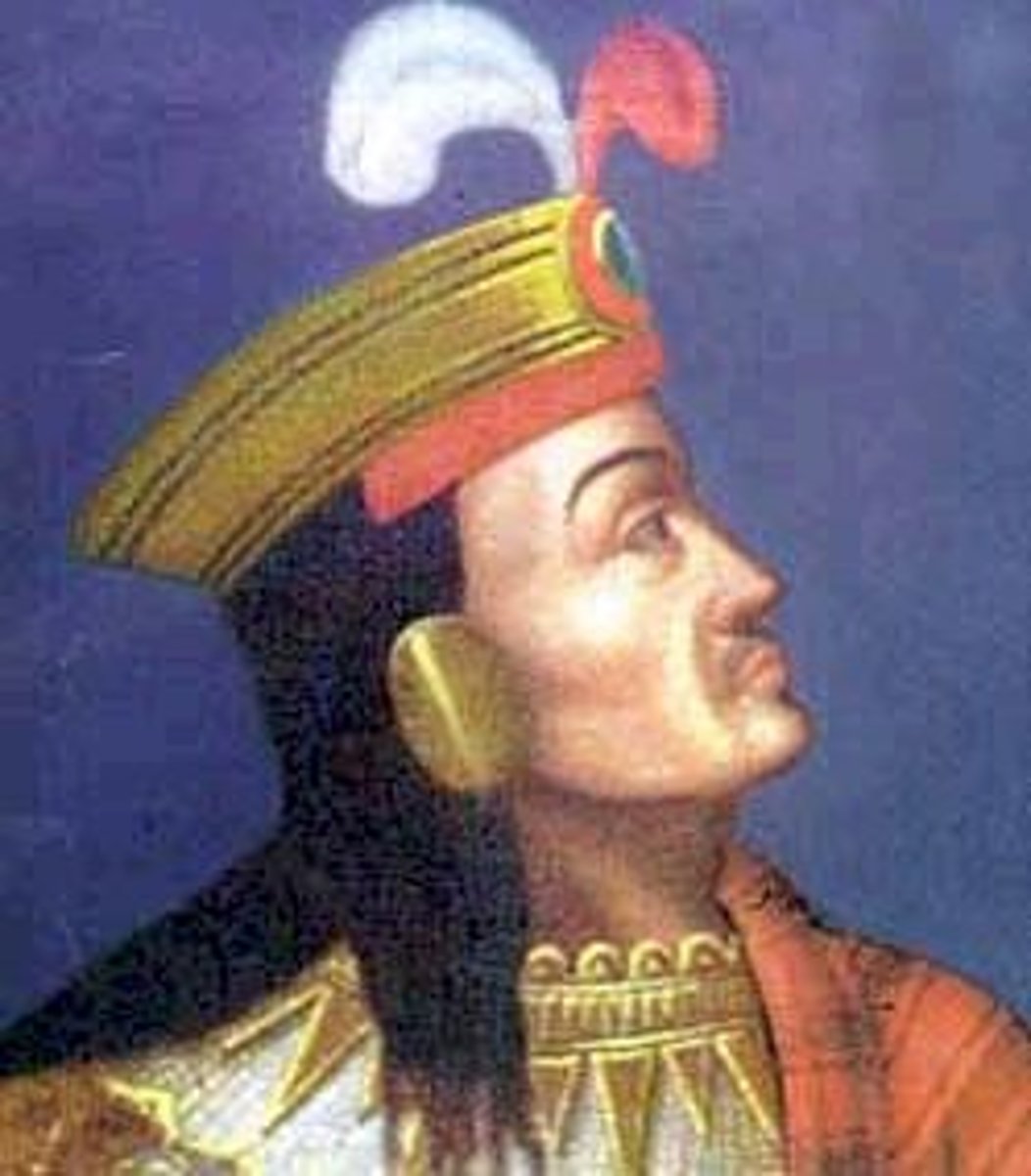
Atahualpa
Last ruling Inca emperor of Peru. He was executed by the Spanish.

Hernan Cortes
Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico (1485-1547)
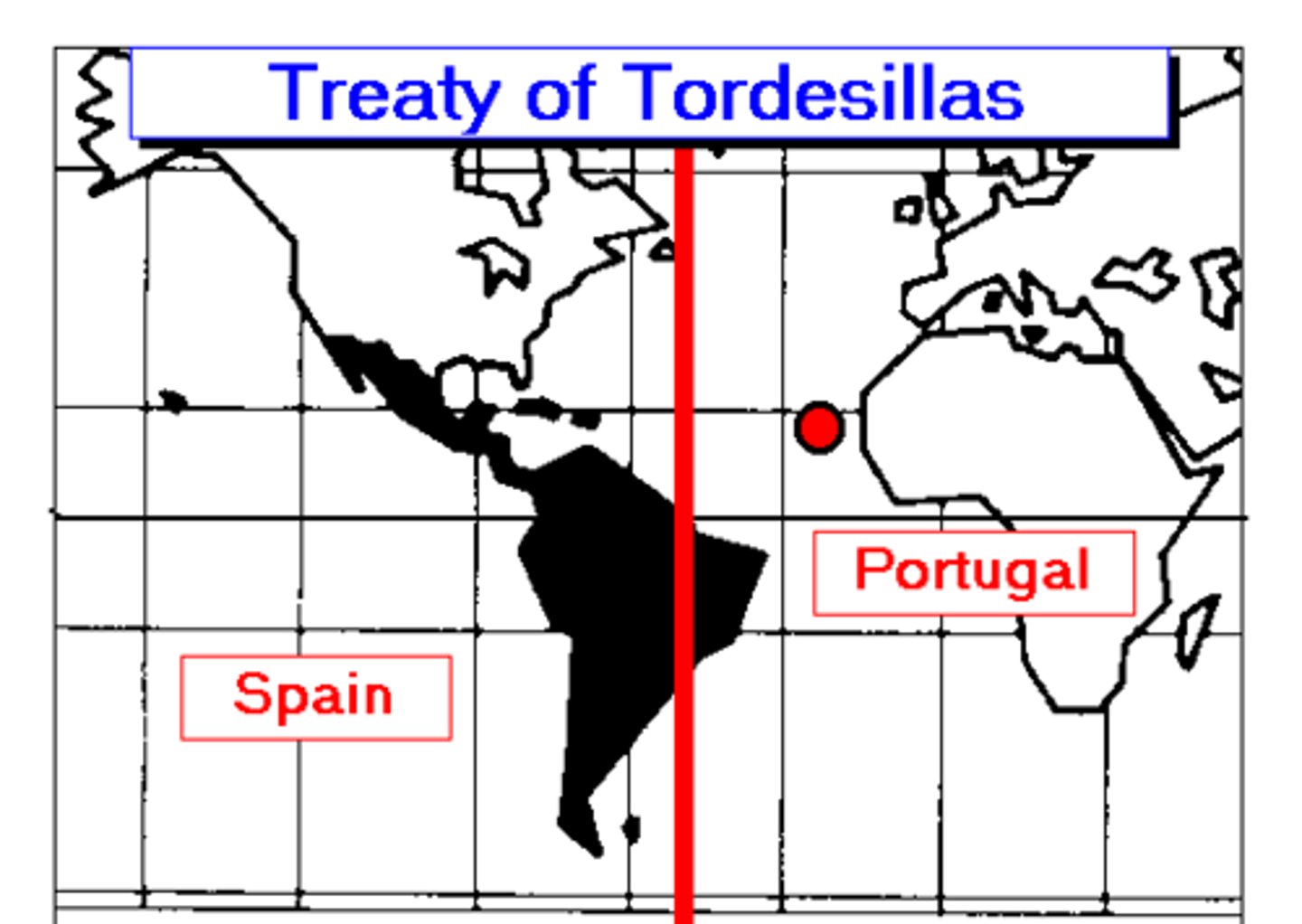
Treaty of Tordesillas
Set the Line of Demarcation which was a boundary established in 1493 to define Spanish and Portuguese possessions in the Americas.
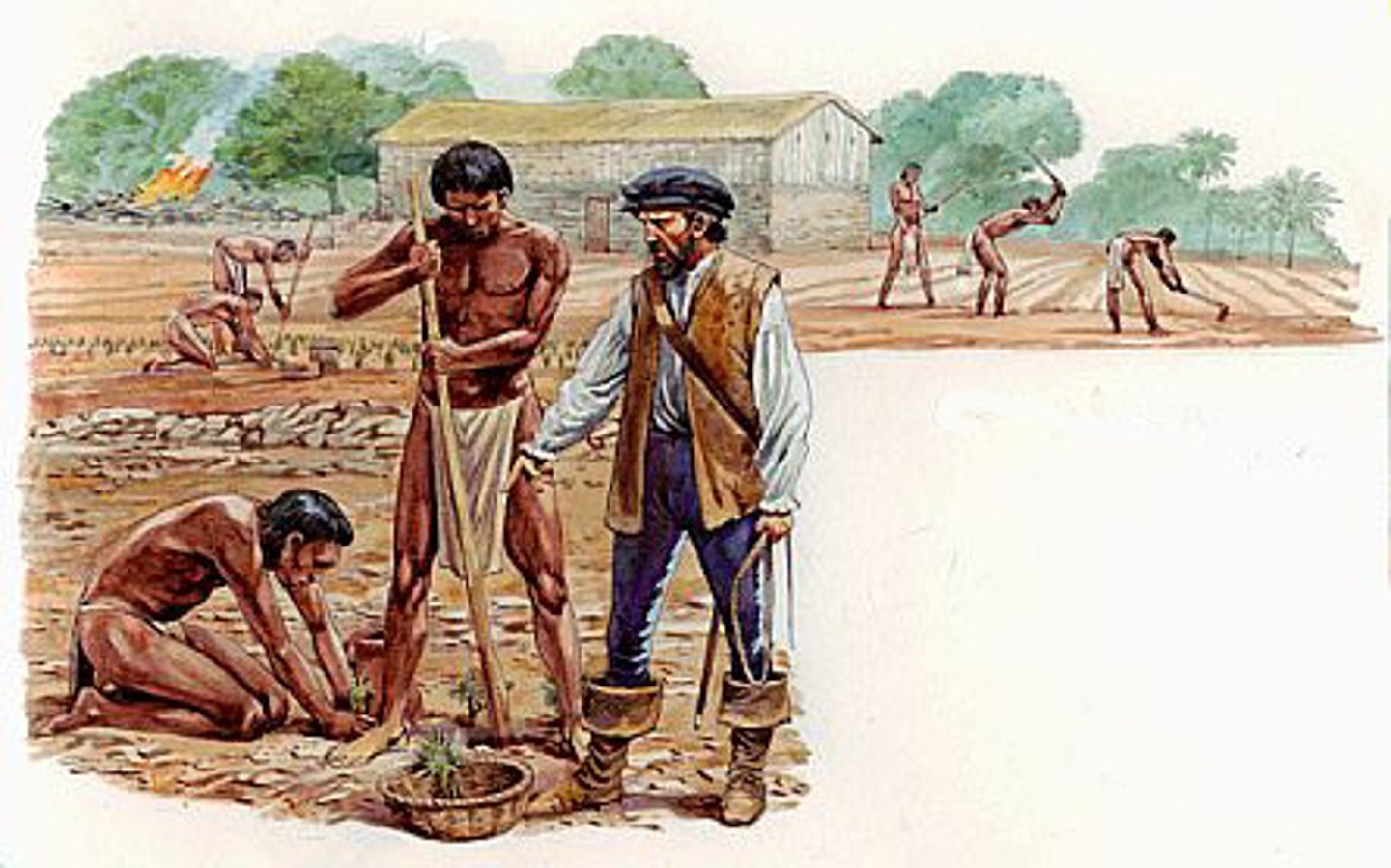
Ecomienda System
System by which the natives were essentially enslaved and forced to provide labor to conquistadors.

Hacienda system
Rural estates in Spanish colonies in New World; produced agricultural products for consumers in America; basis of wealth and power for local aristocracy.
Coercive Labor Systems
Included slavery, indentured servitude, serfdom, and other coercive labor systems in the Americas.
Potosi
Mine located in upper Peru (modern Bolivia); largest of New World silver mines; produced 80 percent of all Peruvian silver.
Mita System
economic system in Incan society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced
Plantation
A large farming operation that specializes in the production of one or more cash crops for sale. Large scale production for profit.
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
Capital
Money used for investment in business ventures

Commericial Revolution
the expansion of trade and business that transformed European economies during the 16th and 17th centuries
joint-stock company
A company made up of a group of shareholders. Each shareholder contributes some money to the company and receives some share of the company's profits and debts.

East India Company
An English company formed in 1600 to develop trade with the new British colonies in India and southeastern Asia.

Dutch East India Company
Government-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the East Indies.

Triangular Trade
A system in which manufactured goods were traded in Africa for slaves that were then transported to the Americas/Caribbean and traded for raw goods that were then sent back to Europe to be sold at a high profit.
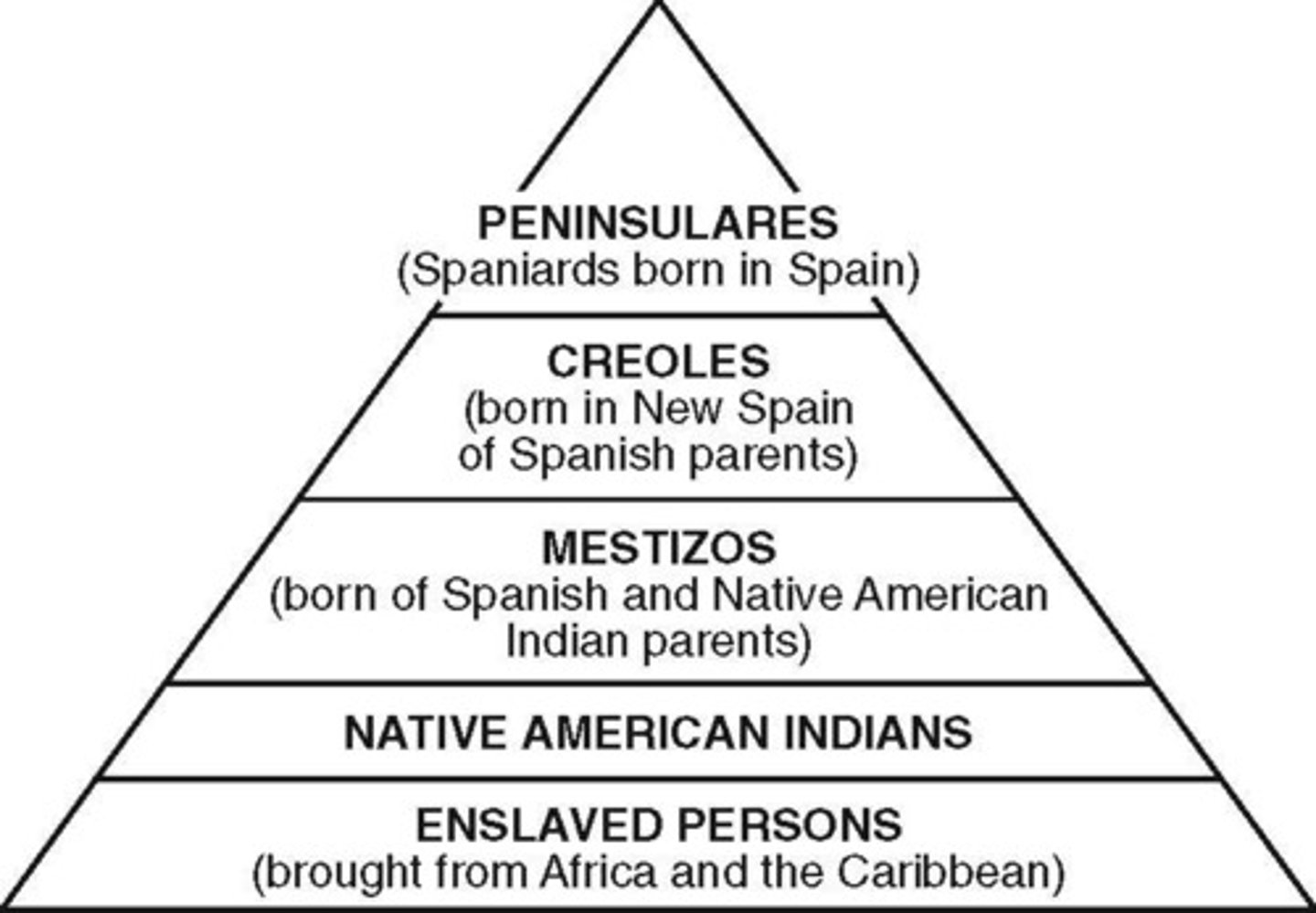
Creoles
Spaniards born in Latin America
Peninsulares
Spanish-born, came to Latin America; ruled, highest social class.
Syncretism
a blending of beliefs and practices from different religions into one faith
Vodun
or voodoo is a New World syncretic faith that combines the animist faiths of West Africa with Christianity
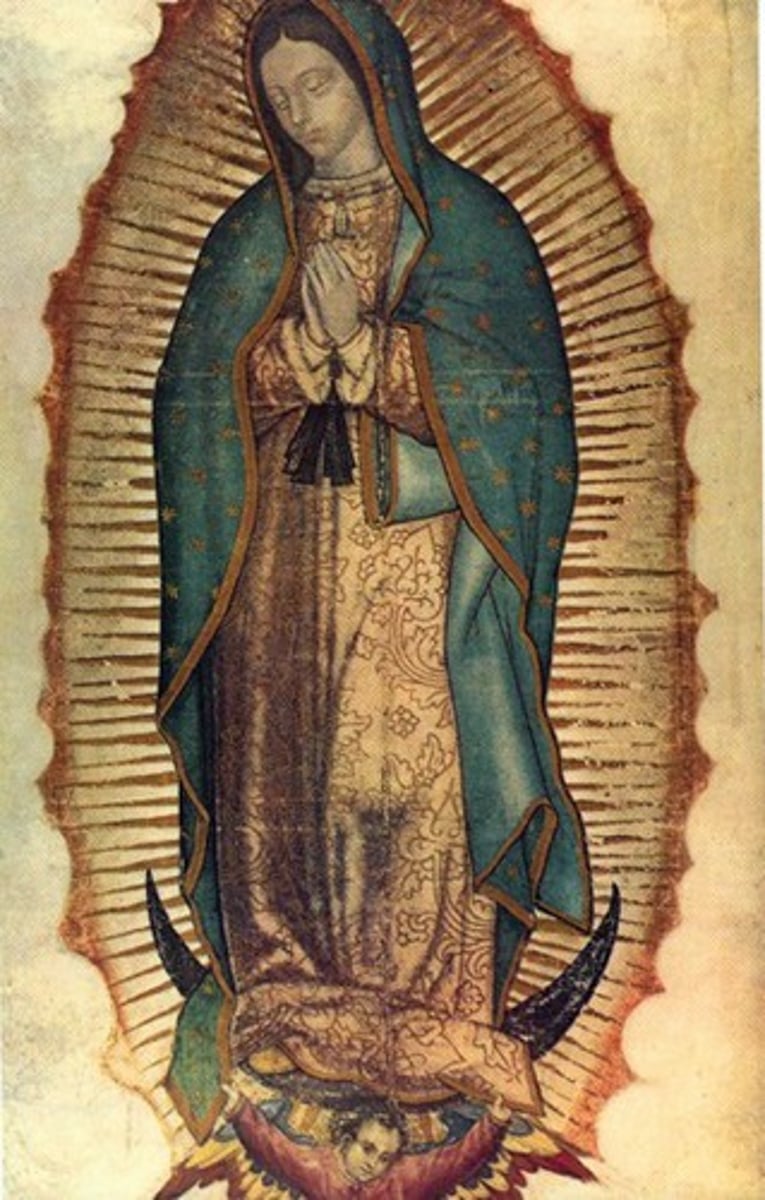
Virgin of Guadalupe
An apparition of the Virgin Mary said to have appeared to a Mexican farmer (Juan Diego) in 1531. She exerted a powerful attraction to Mesoamerica's surviving Amerindians and became an icon of Mexican identity and Catholicism.

Metacom's War
First large-scale conflict between colonists and Native Americans, waged in Plymouth, Massachusetts Bay, Rhode Island, and Connecticut (1675-1676)

Ana Nzinga
17th century Angolan queen who eventually fought off the Portuguese colonizers. She developed a powerful trade system with the Dutch.

Cossacks
Peoples of the Russian Empire who lived outside the farming villages, often as herders, mercenaries, or outlaws. Cossacks led the conquest of Siberia in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
Pugachev Rebellion
unsuccessful peasant rising led by Cossack Pugachev during the 1770s; typical of peasant unrest during the 18th century and thereafter.

Pueblo Revolt
Native American revolt (New Mexico area) against the Spanish in late 17th century; expelled the Spanish for over 10 years
Maroon Wars
Conflicts between the Jamaica Maroon settlements and the British after the British gained control of the island from the Spanish.
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange. (English Bill of Rights issued in 1689)

Mestizo
a person of European and Native American descent
Mullatoes
People of African and European descent
Casta system
A system in colonial Spain of determining a person's social importance according to different racial categories.