5_Threats to Biodiversity & Extinction
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Incomplete set
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
How many extinction episodes have occurred so far on earth?
5, currently going through the 6th
What is the number of species present on an island determined by?
A balance between immigration and extinction
Generally, as the number of species present increases, the immigration rate decreases and the extinction rate increases
What are two important, general relationships in the Equilibrium Hypothesis of Island Biogeography?
Immigration higher on near islands than distant islands (in relation to mainland), so the equilibrium number of species present will be greater on near islands
Extinction higher on small islands than on larger islands, so the equilibrium number of species present will be greater on large islands
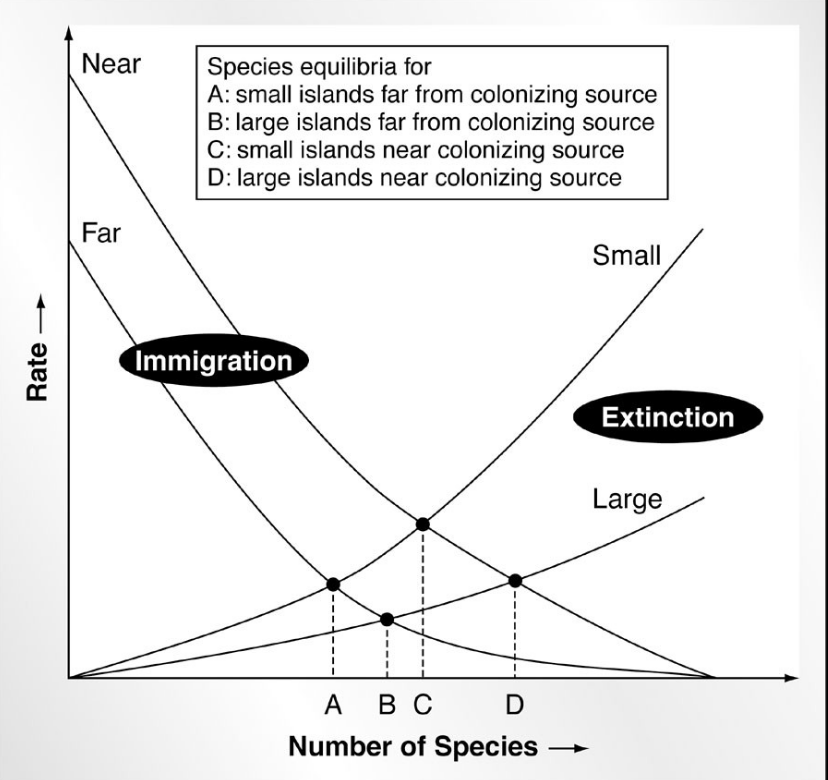
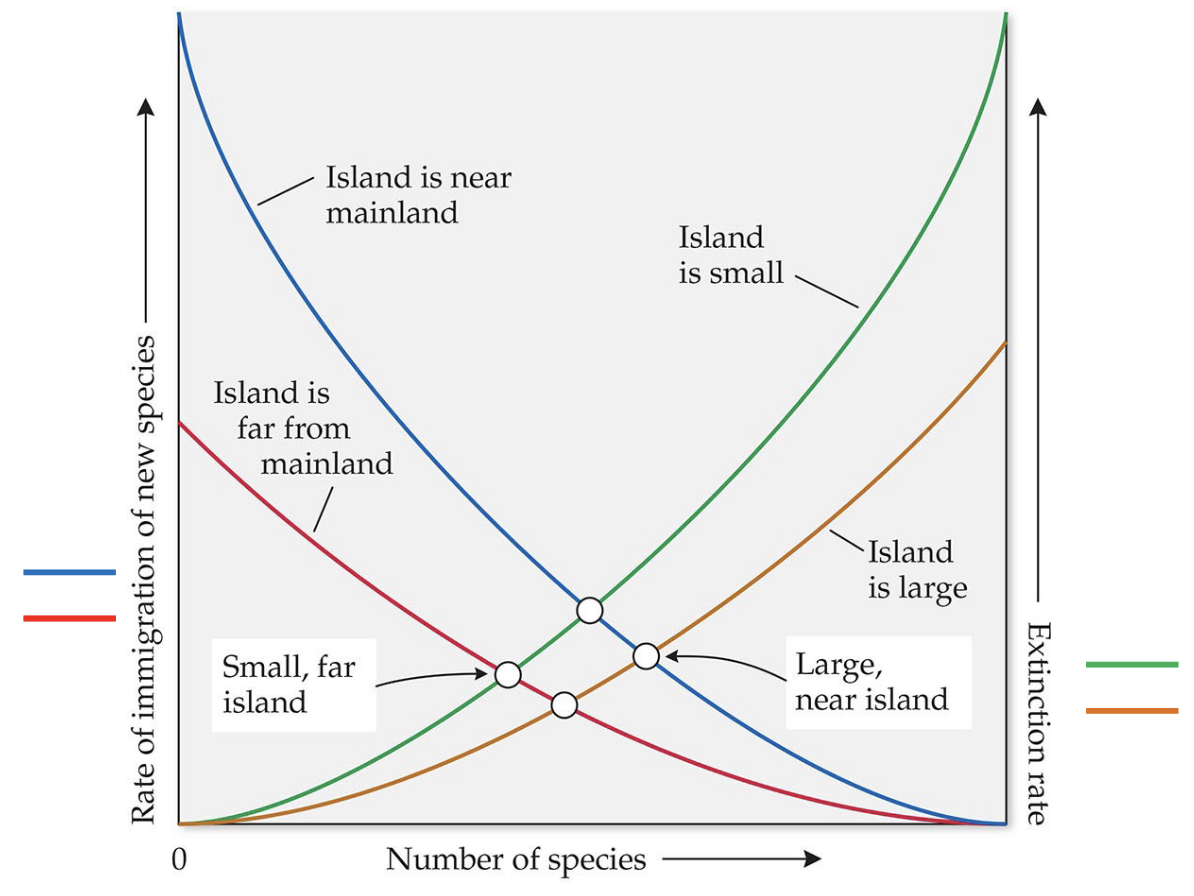
Determine the Graph:
Small, far islands with a low species number have a low immigration rate as well as low extinction rates. If they were to increase in species, extinction rate would increase.
Large, near islands with a large number of species have low extinction rates. As immigration increases, extinction rate will increase.
What is The Island Biogeography Model? What does it do?
explains the species-area relationship: as area increases, the number of species present (diversity) also increases
S = CA^z
S = number of species
A = area
Island Biogeography Model (S=CA^z):
What factors influence z?
climate (e.g., latitudinal gradient factors)
habitat complexity
isolation (e.g., distance from the mainland)
types of species represented (e.g., mammals vs birds)
What are the major threats to biodiversity?
Habitat loss / degradation
Overexploitation
Invasive species and disease
Pollution
Climate change
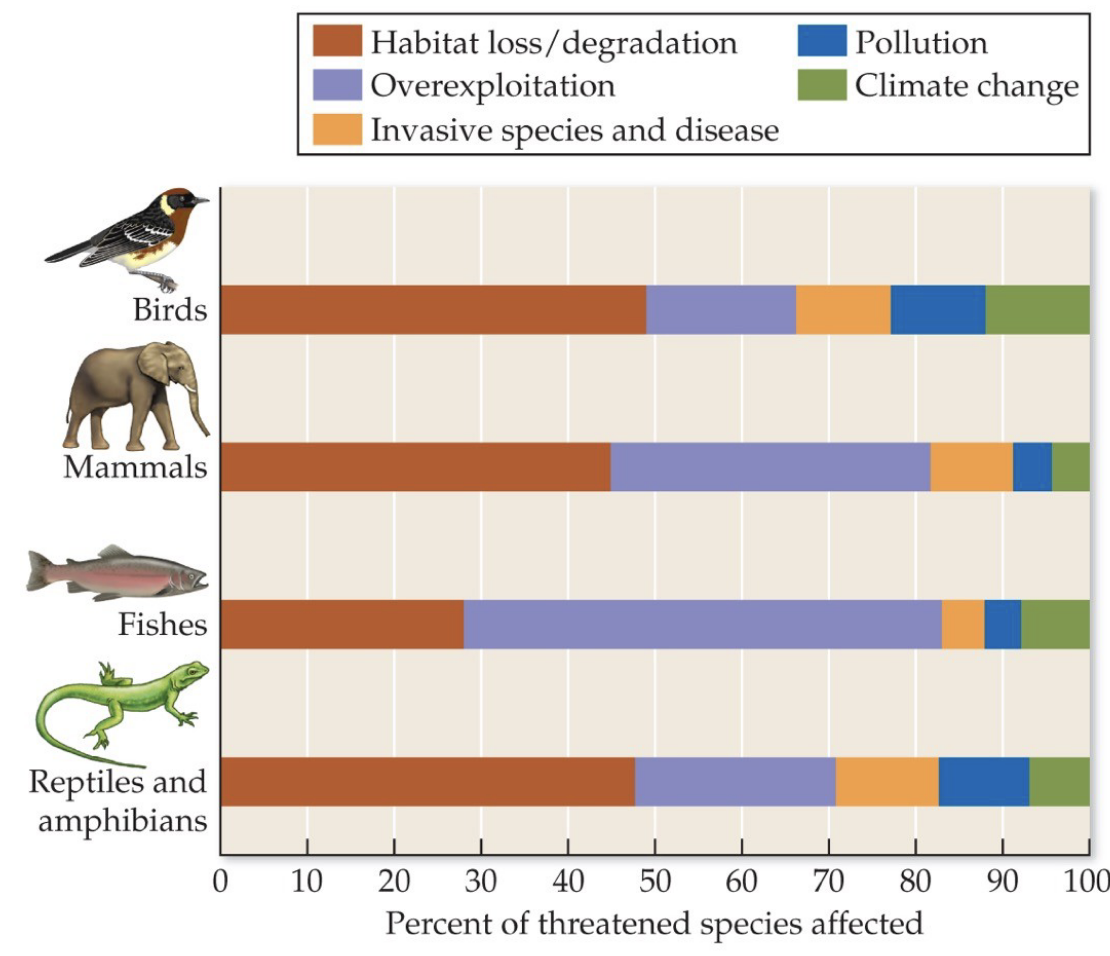
What are some examples of species and habitats affected by these threats?
What are the major threats to biodiveristy? The top three?
Habitat loss / degradation
Overexploitation
Invasive species and disease
Give an example of this threats impact on biodiversity:
Overexploitation
Give an example of this threats impact on biodiversity:
Pollution
Give an example of this threats impact on biodiversity:
Invasive Species
Give an example of this threats impact on biodiversity:
Diseases
Give an example of this threats impact on biodiversity:
Climate Change
What are the negative consequences to biodiversity of habitat fragmentation?
What are edge effects? How are species and habitats affected by edge effects?
Edge Effects — altered environmental and biological conditions at the edges of a fragmented habitat
Microclimate changes
Increased incidence of fire
Interspecies interaction (exotic & pest species; domestic species)
Potential for disease
Population Effects
Limits to dispersal and colonization
Restricted access to food and mates
Creation of smaller populations
How do habitat fragments differ from the original habitat?
Fragments have a greater amount of edge per area of habitat
The center of each habitat fragment is closer to an edge
Large populations are divided into smaller populations
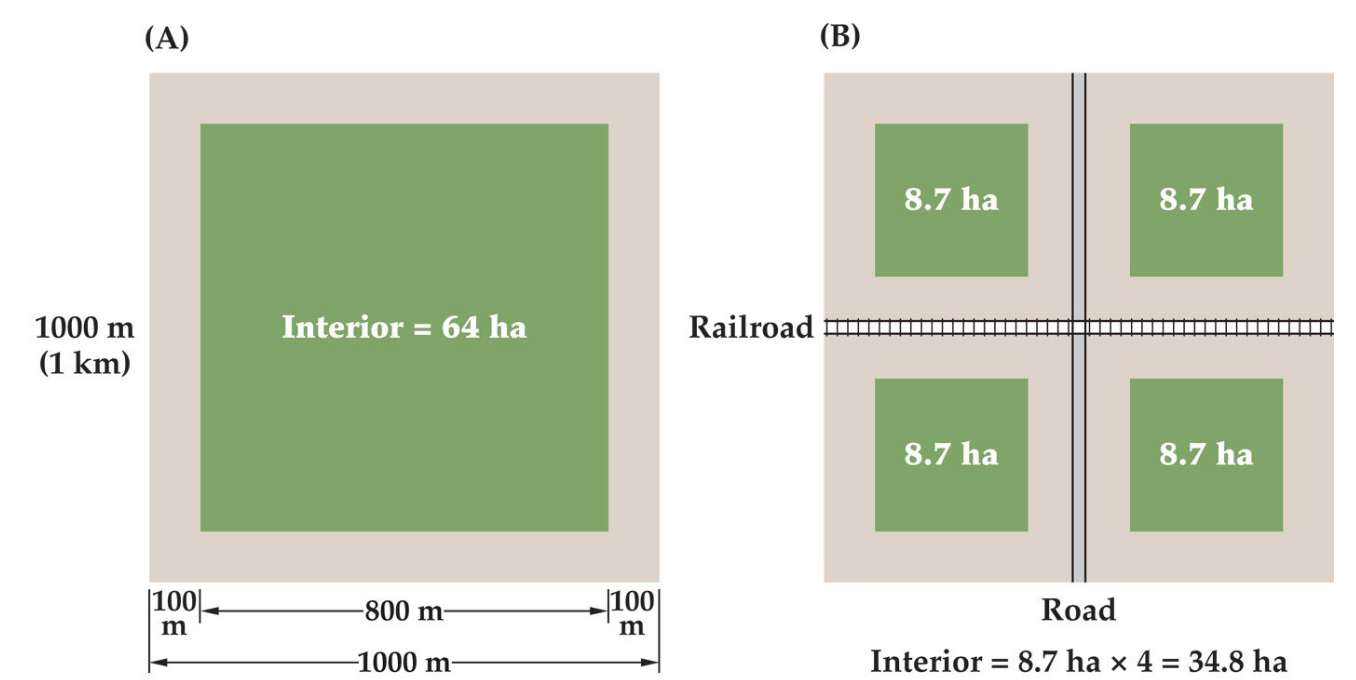
What are three pollution problems that threaten biodiversity?
Pesticide pollution
Biomagnification
Water pollution
Pesticides, herbicides, etc.
Eutrophication (nitrates and phosphates)
Microplastics
Air pollution
Acid rain, ozone production and nitrogen deposition, toxic metals
Define: Endemic Species
species found in one place and no where else
Define: Exotic Species
species transported or established outside its native range by the activities of humans, whether done so intentionally or not
Define: Invasive Species
species that become established and proliferate in new (i.e.. nonhistorical) ranges where they cause environmental harm