heritability
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
mendel's laws
law of dominance
law of segregation
law of independent assortment
law of dominance
Some alleles are dominant and some are recessive
law of independent assortment
the law that states that genes separate independently of one another in meiosis
Law of Segregation
first law of heredity stating that pairs of alleles for a trait separate when gametes are formed
complete dominance
a relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over another
co dominance
both alleles are expressed
partial dominance
both alleles blend, can create intermediate phenotypes
a gene can have any
number of alleles
dominance hierarchy of alleles
In cases where genes have more than two alleles, 1 phenotype will be most dominant, 1 moderately dominant, and 1 will be the least dominant (the recessive).
dominance in human blood groups
A> O
B>O
A + B codominant
O is recessive
how is resistance to a disease that strongly affects the flea inherited?
epistasis
epistasis
interaction between genes/ loci for example one gene may supress another
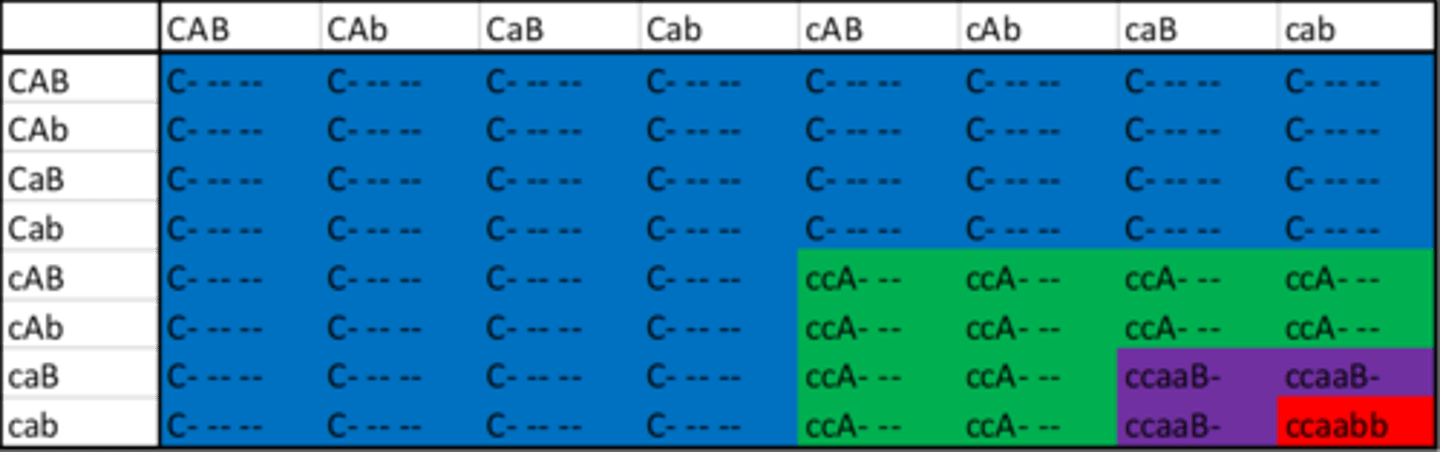
epistasis in water fleas
A masks B, animals with A susceptible regardless of B
A in water fleas
suppresses B, complete dominant resistance allele vs parasite
a in water fleas
recessive susceptible to allele C1
B in water fleas
complete dominant resistance allele vs parasite strain C19
b in water fleas
recessive susceptible allele C19
AaBb water fleas cannot exist in the lab
they do exist in the wild- evidence of another allele
C locus in water fleas
provides resistance to both parasites, A and B do not matter
epistasis of three genes in water fleas
C > A > B
epistasis in fur of mice
cannot express fur colour if pigment allele not present, pigment gene suppresses the effect of the fur colour gene
linkage
traits on the same chromosome, when inheritance occurs they are together
recombination
crossing over of chromosomes during meiosis
distance between loci determines
# of recombinants
close genes less likely to
recombine as genes on opposite ends of the chromosome
recombination rate is
species and condition dependent, eg cats vs opossum have different rates,
conditions like desication, starvation and infection effect it also
resistance in daphnia depends on
three linked loci that epistatic interact. each locus has 2 alleles with resistance completely dominant over susceptibility
T haplotype in mice
recombination can separate poison and antidote
inversions
reverse the direction of parts of chromosomes, suppress recombinants
inversions occur when
there was a failure to align chromosome regions
formed recombinants can have
unbalanced gametes
mouse T haplotype has ___ inversions
4
Quantitative genetics
many genes underly continuously varying phenotypes
many traits are coded for by
many loci, each is independently inherited which results in continuous distribution
examples of quantitative genetics
- Height
- Crop yield
- Weight gain in animals
- Fat content of meat
- IQ
- Learning Ability
- Blood Pressure
- etc.
Bdelloid rotifer
up to 10% of all genes from other species, during desiccation membrane becomes leaky and chromosomes break on drying out, upon rehydration genome is reassembled
Bdelloid rotifer genome
in a tetraploid state, four homolog sets of chromosomes
horizontal gene transfer
transformation, transduction, conjugation
Meloidogyne incognita
parasitic nematode that borrowed cell wall degrading enzymes from a bacteria
Tetranychus urticae
spider mite acquired carotenoid synthesis genes from a fungus
transformation
uptake of DNA from environment. needs cell to be competent, a state which is induced under stress but is costly
transduction
DNA introduced into host cell by virus, rare event where virus particle incapsulates part of bacterial chromosome, upon insertion into host can recombine with host chromosome
conjugation
bacterial sex
donor cell passes DNA and often plasmid through direct contact, requires bridge formation (pilus)
phenotypic plasticity
the ability of an organism to change its phenotype in response to changes in the environment.
phenotypic plasticity allows for
survival under changing conditions, allows for evolution when environmental variation is predictable
snails, sun fish and plasticity
predator fish= larger, stronger snail shells- selection for stronger shells
herbivore fish= large shells until snails realise they are safe= selection for smaller shells
arms race
natural selection, sun fish and snails
favours plasticity in areas where a predatory sunfish is frequent
will disadvantage snails that grow slower in presence of herbivorous sun fish where predators are absent
epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
C. elegens and epigenetics
modified with fluorescent gene which is only expressed at warm temps
worms warmed from 20-25 then cooled back to 25 so gene is expressed. offspring expressed for seven generations
C elegens warmed for 5 generations
offspring expressed gene for 14 generations
Zhang et al 2018
compared variation of lines that differed in DNA methylation patterns with near identical DNA sequences
some traits epigenetic variance was equal to natural pops
epigenetics can create
phenotypic variation
epigenetics may be important for
adaptation when genetic variation is limited, can move pops closer to a fitness peak
epigenetics will enable
survival in new environments, similar to plasticity, allows time for adaptative mutations to occur
Lamarck says…
inheritance of acquired characteristics- not entirely wrong with study of epigenetics
rate of spontaneous gains and losses of methylates sites (epimutation rate)…
is higher than DNA mutation rate
Epimutation rate is higher than
DNA mutation rate