Lecture 2: Membranes & Lipids
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
The Structure of Lipids
Head
changeable group
phosphate
glycerol
hydrophilic
Tails
made up of carbons and hydrogens
hydrophobic
Lipids & Membranes function & definition
Membranes are made of lipids & proteins, they act as a separation of the cell and the outside.
Definition of saturation and it’s implications
Saturation means that a carbon has the maximum number of hydrogens (3), making the bilayer more stiff
Definition of unsaturation and it’s implications
Unsaturation means that the carbon is NOT bonded to the highest number carbons possible (3), creating kinks in the bilayer and making it more fluid.
Amphipathic Definition
Lipids that have components that are hydrophilic (heads) and hydrophobic (tails)
How are lipids differentiated
the combinations of heads and tails and they way they individually differ, serving many diverse functions & lipids.
Sterols
a type of lipid where the head is an OH & it is amphipathic
Glycolipids
a kind of lipid where the head is a sugar and it is amphipathic
Cholesterol’s effect on the bilayer
cholesterol stiffens tha bilayer
Symmetrical & Asymmetrical Bilayers
whether or not the bilayer is the same on both sides,
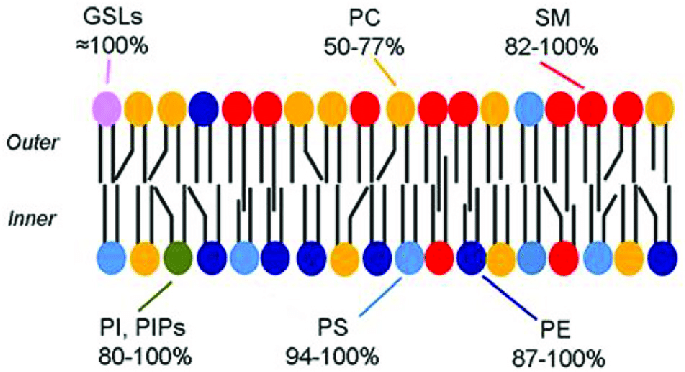
Things Asymmetrical Bilayers Assist With
Cell signaling
cell recognition
organelle recognition
membrane function
Two types of proteins in cell membranes
Integral Proteins
Peripheral Proteins
Intergal Proteins
Proteins that integrate and interconnect themselves with the bilayer in 3 ways
monolayer
transmembrane
lipid link: protein is covalently attached to the lipid
Also hydrophobic amino acids interact with he hydrophobic tails
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins that interact with the bilayer through electrostatic interactions in 2 ways
a protein integrated with the membrane
through interaction with the amphipathic parts of the membrane
FRAP: Fluorescence Recovery After PhotoBleaching
a technique used to test the fluidity of a membrane
FRAP Step by Step
Tag a membrane associated protein with GFP
Shoot the intense laser at a part of the membrane, bleaching it
The membrane will “recover” with non bleached lipids and proteins replacing the bleached
How quickly it recovers gives us insight on how stiff the membrane is, fast is fluid and slow is stiff.
Membrane Proteins
proteins that are associated with the membrane
Types of membrane proteins
Transporters & Channels
Anchors
Receptors
Enzymes
Importance & Function of Transporters & Channels
facilitate transport of molecules that wouldn’t be able to pass through between the membrane
speed up rate of diffusion
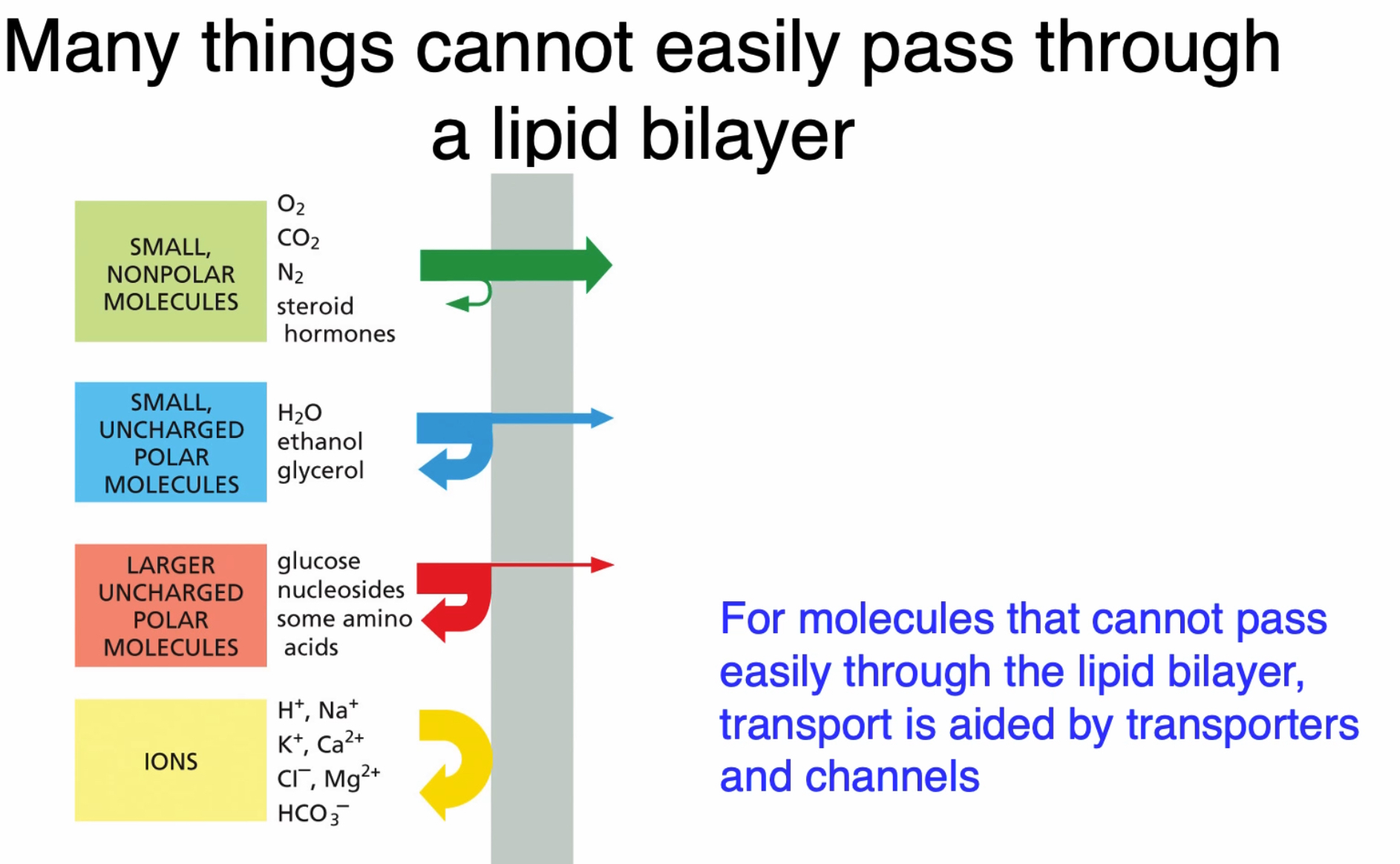
Remember
k
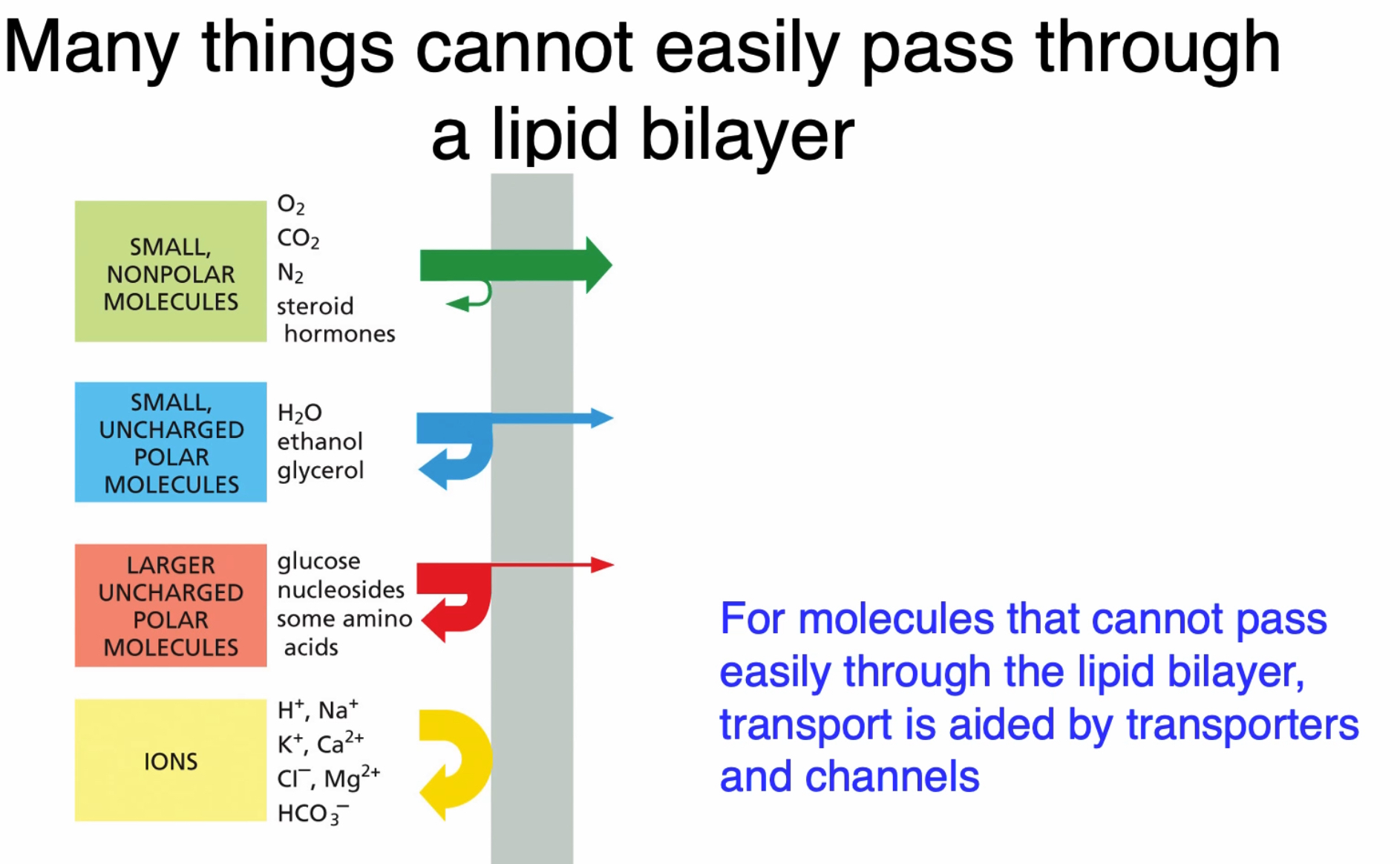
Channels definition & function
protein allow molecules with the correct charge & size pass through the membrane
can exist in open confirmation or closed confirmation
Passive transport through GDP
Transporters deifntion & funciton
protein that binds to molecules, changes, the releases molecules on the other side of the membrane
Concentration Gradient
The idea that molecules will move from areas fo high concentration to low concentration
Going with the grain
when molecules go from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, using passive transport.
energetically favorable
Passive transport
type of transport that occurs when molecules got with the grain
energetically favorable
can happen with channels & transporters
Going against the grain
when a molecule goes against the gradient & goes from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
energetically unfavorable so energy has to come from somewhere
only happens with transporters
Where the energy for Active Transport comes from
Light
ATP becoming ADP
Gradient Driven Pumps
Active Transport
transport that happens for energetically unfavorable movements (ATG)
can only happen with Transporters NOT Channels
has the 3 ways (name them)
Symports
during Active Transport when the molecule hitching a ride and the molecule driving are going in the same direction
Gradient Driven Transport
when the diffusion of one molecule through the membrane is coupled with another, the molecule hitches a ride
Antiports
during Active Transport when the molecule hitching a ride and the molecule driving are going in opposite directions