Biology- "Chapter 16: Gross and Microscopic Anatomy of the Respiratory System"
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
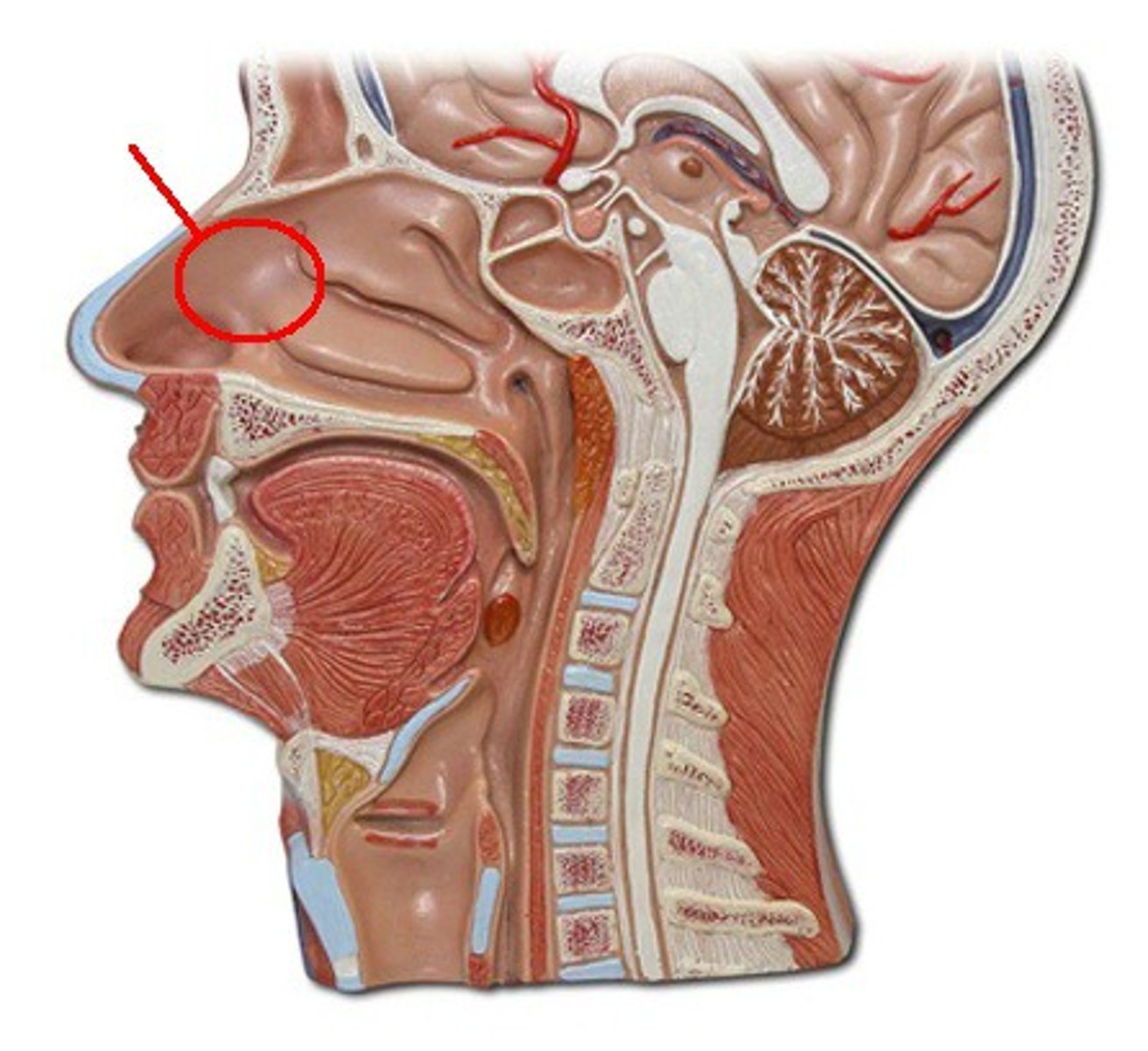
nasal cavity
is divided into a left and right portion by the nasal septum
nares
external openings of the nose that allow air to enter the nasal cavity; also known as nostrils.
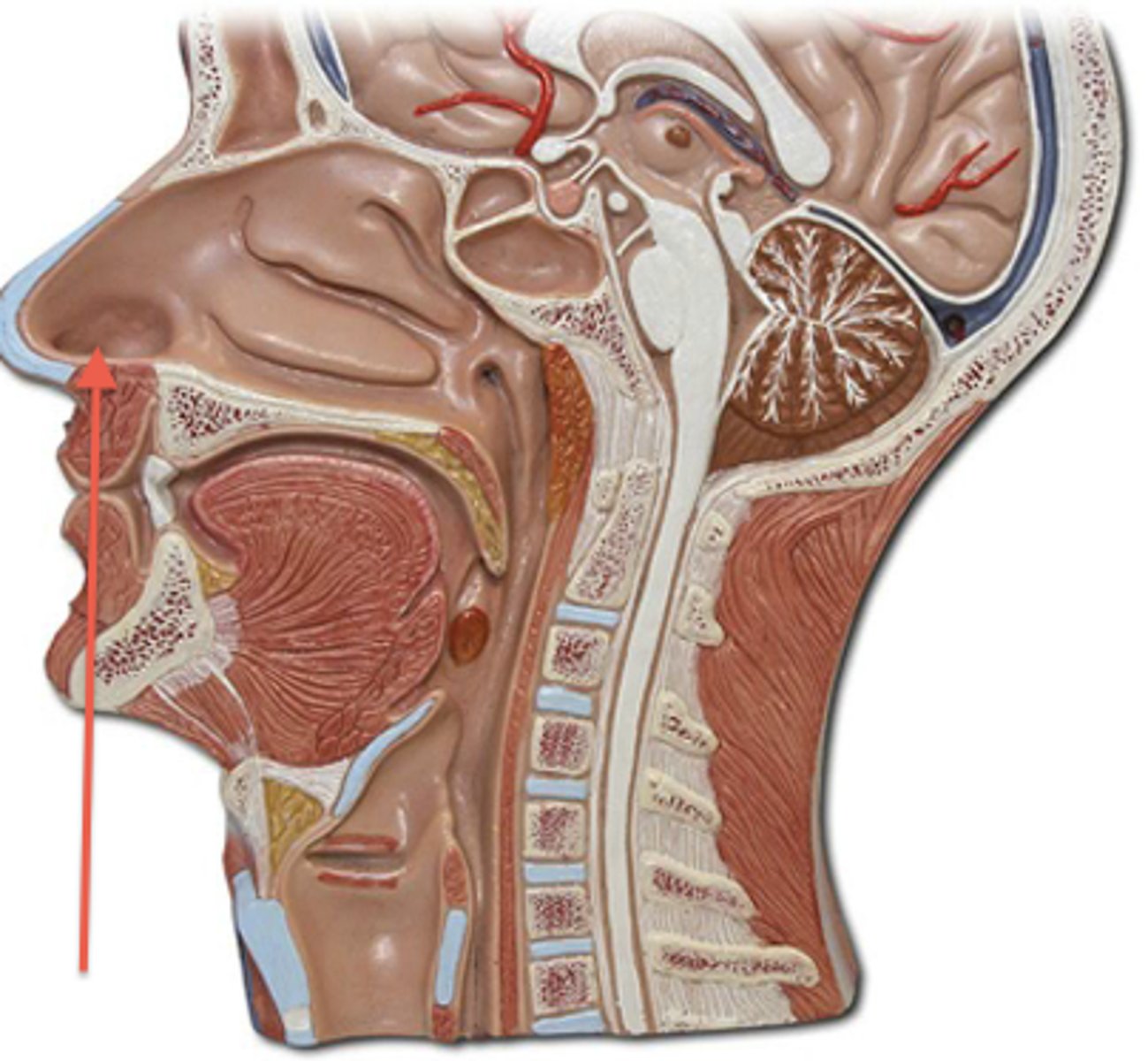
nasal septum
The vertical wall that divides the nasal cavity into left and right halves. It supports the structure of the nose while directing airflow.
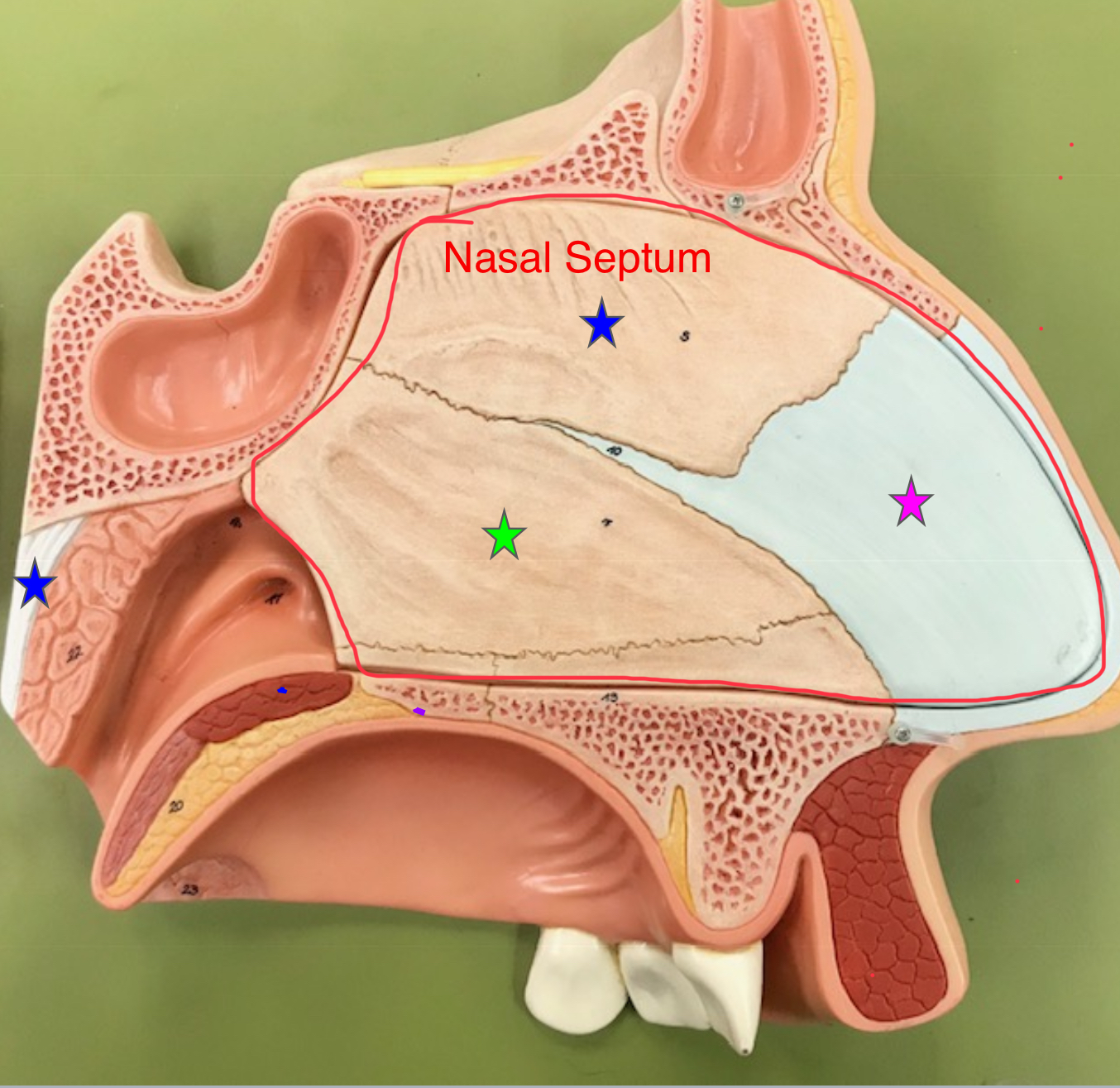
septal cartilage
flat cartilage structure that forms the anterior portion of the nasal septum
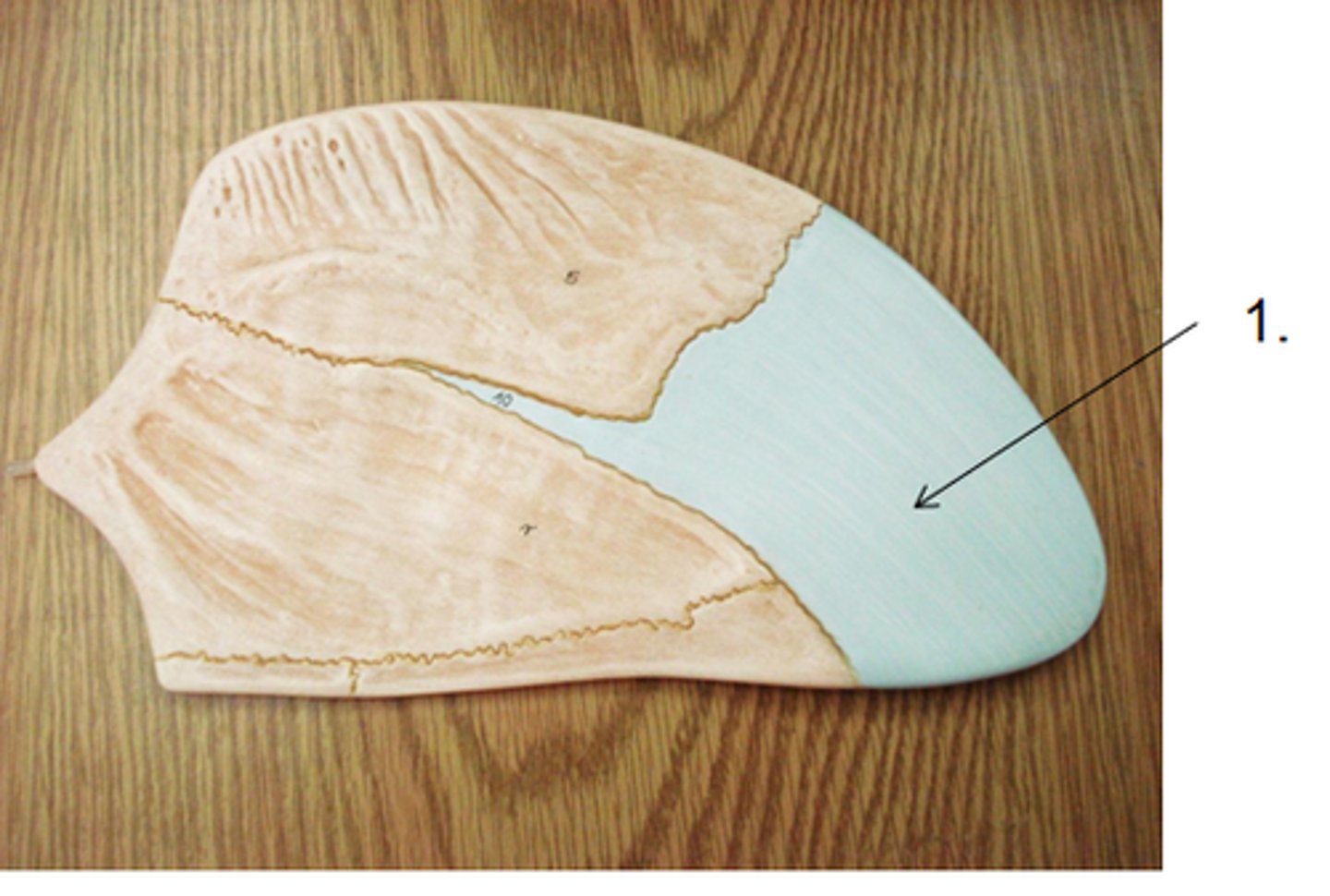

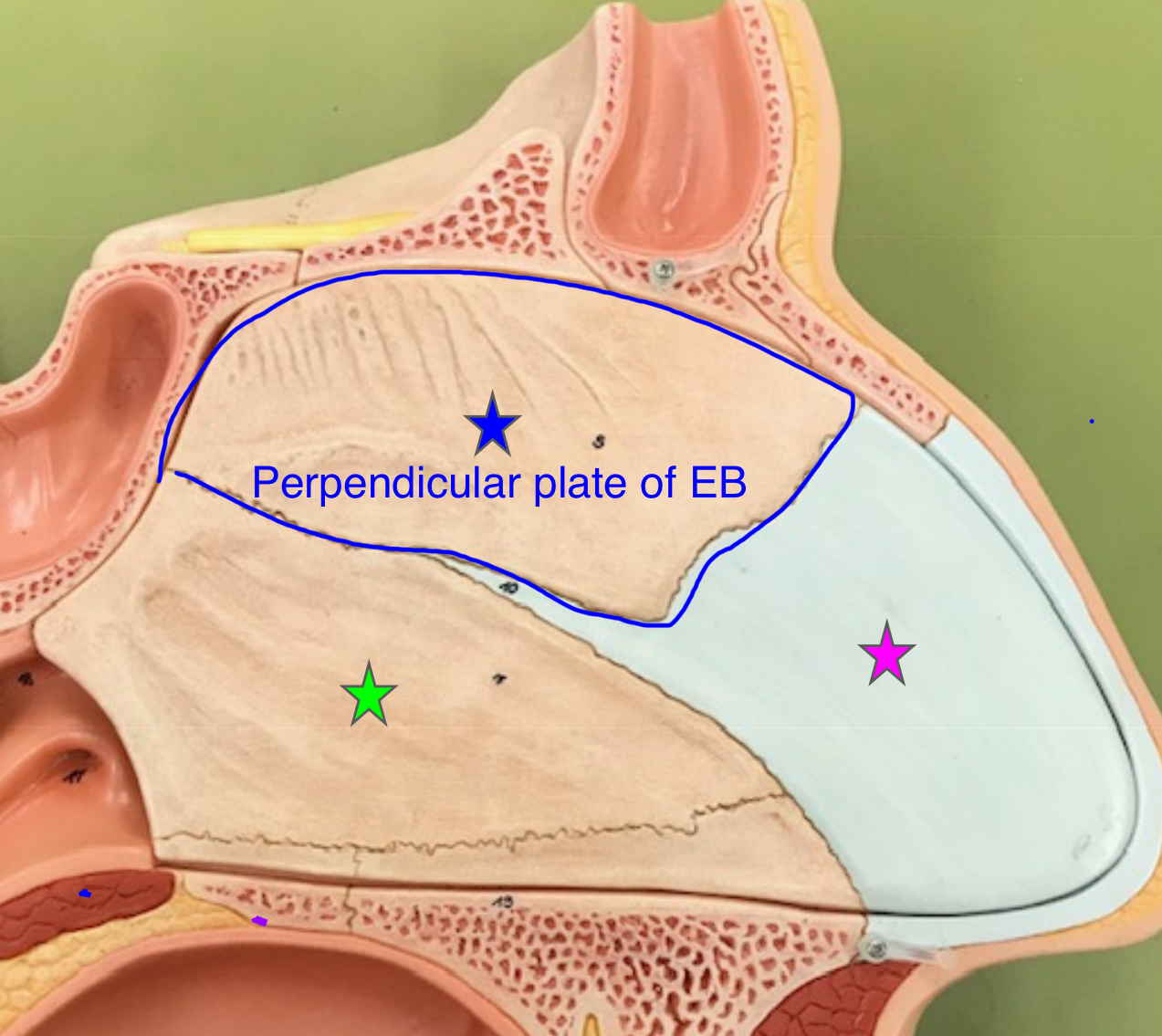
perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
superior portion of the bony nasal septum
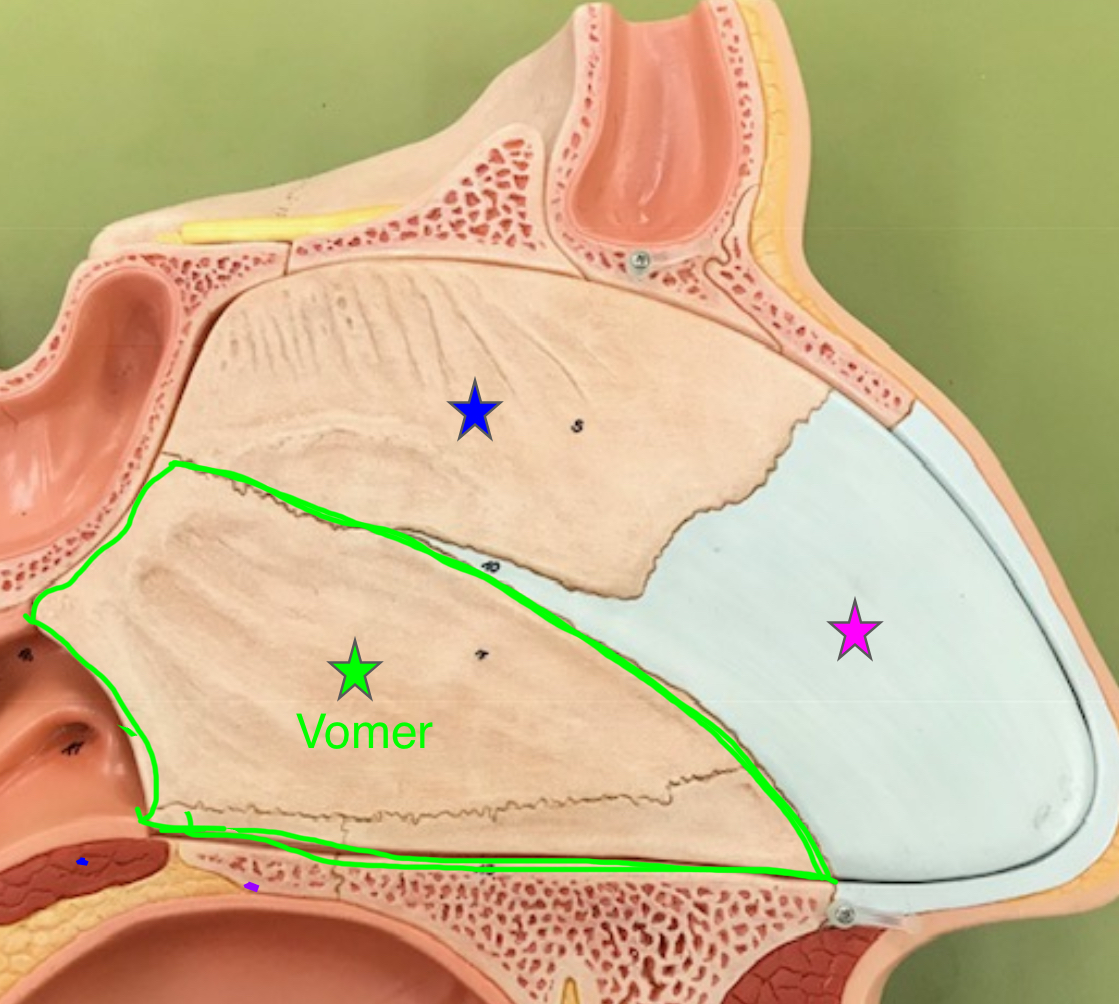
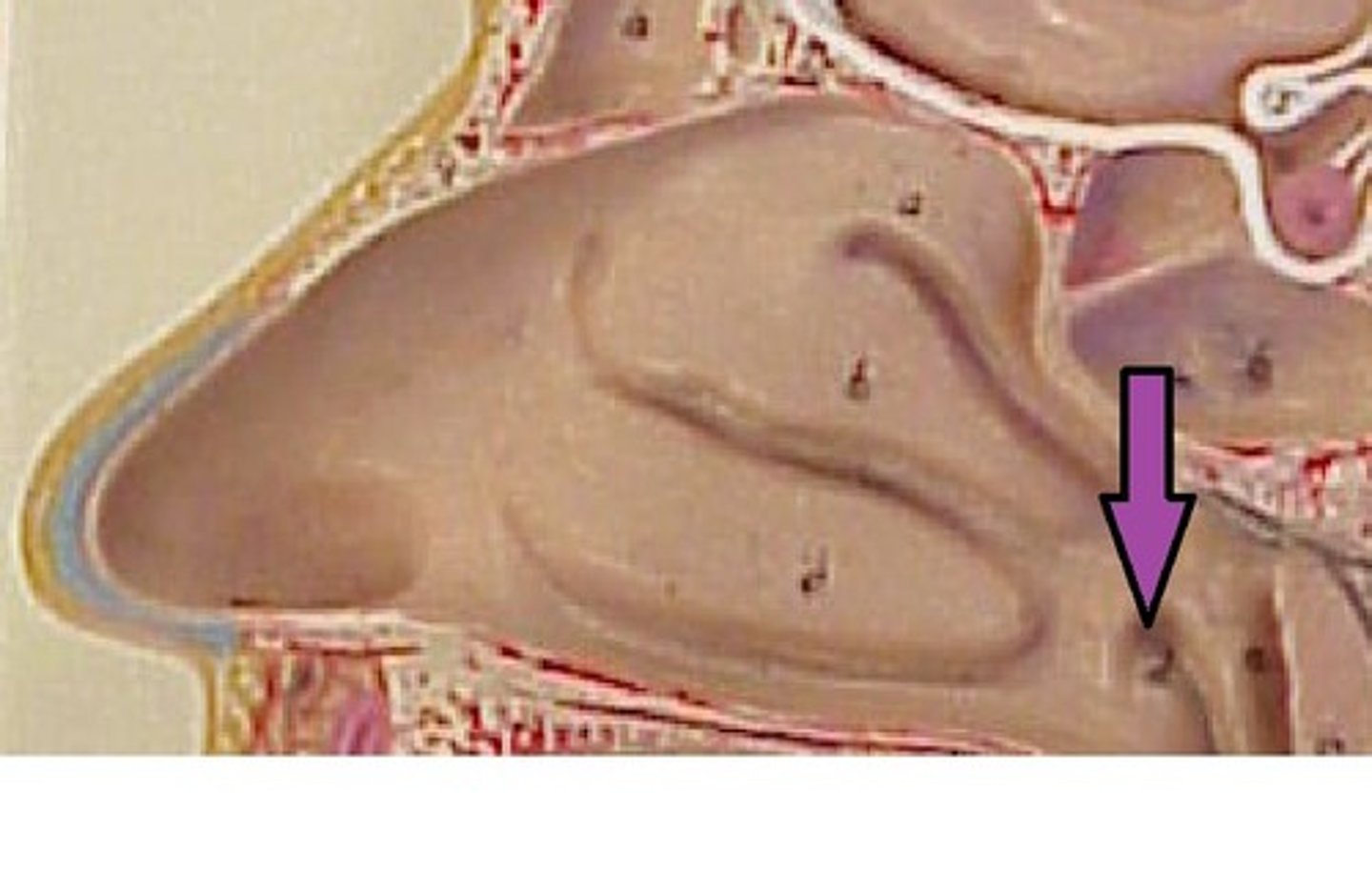
vomer
forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum
ethmoid bone (nasal cavity)
anterior to the sphenoid and takes up most of the area between the nasal cavity and the orbits. Forms some boundaries of the nasal cavity, also separates nasal cavity from the brain.
sphenoid bone (nasal cavity)
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit. Contributes to the structure of the nasal cavity by supporting surrounding bones and forming part of the nasal septum.
hard palate
roof of the oral cavity
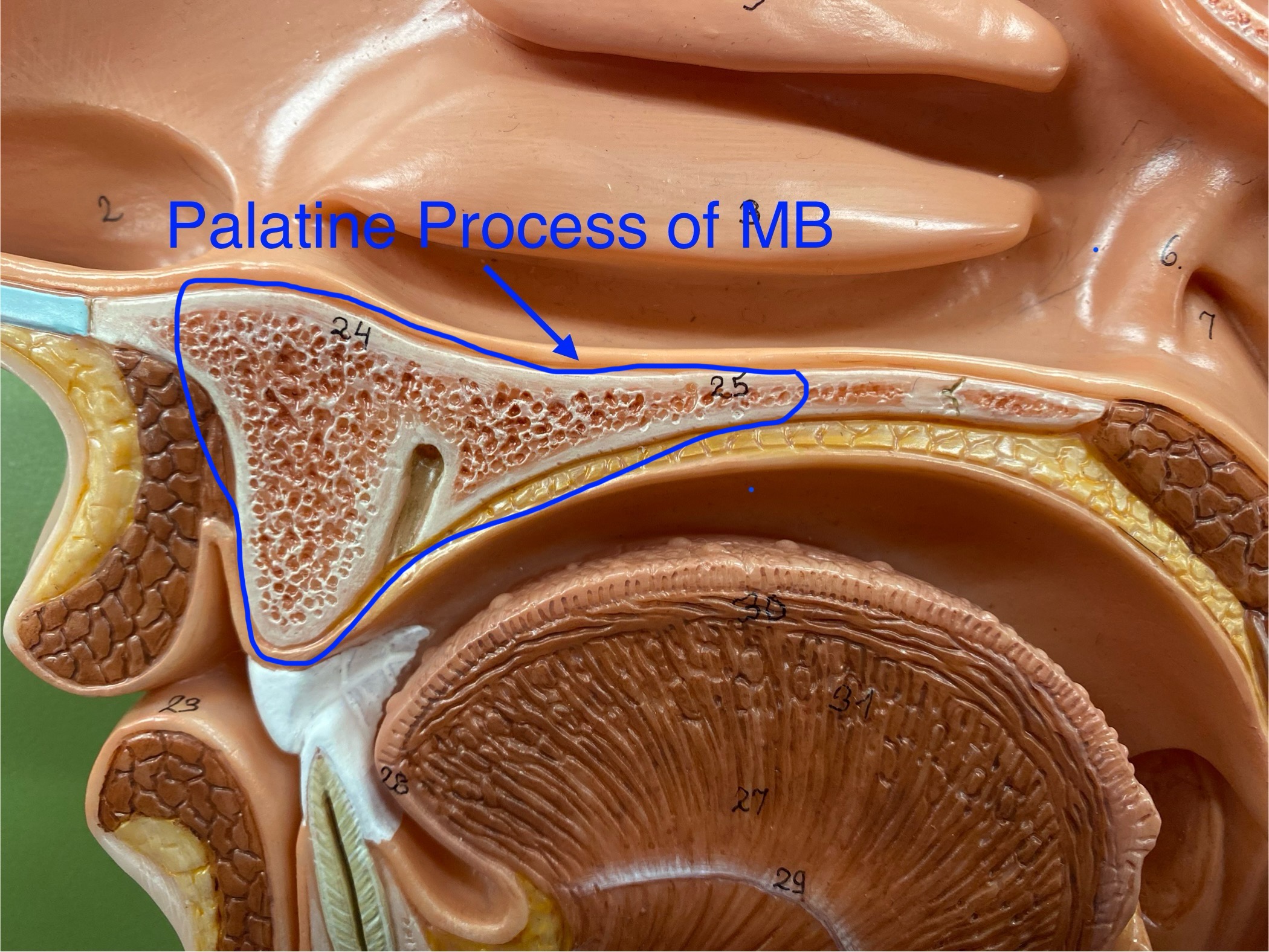
palatine process of the maxillary bones
a bony plate that extends from each maxilla and forms the anterior of the hard palate (roof of the mouth).
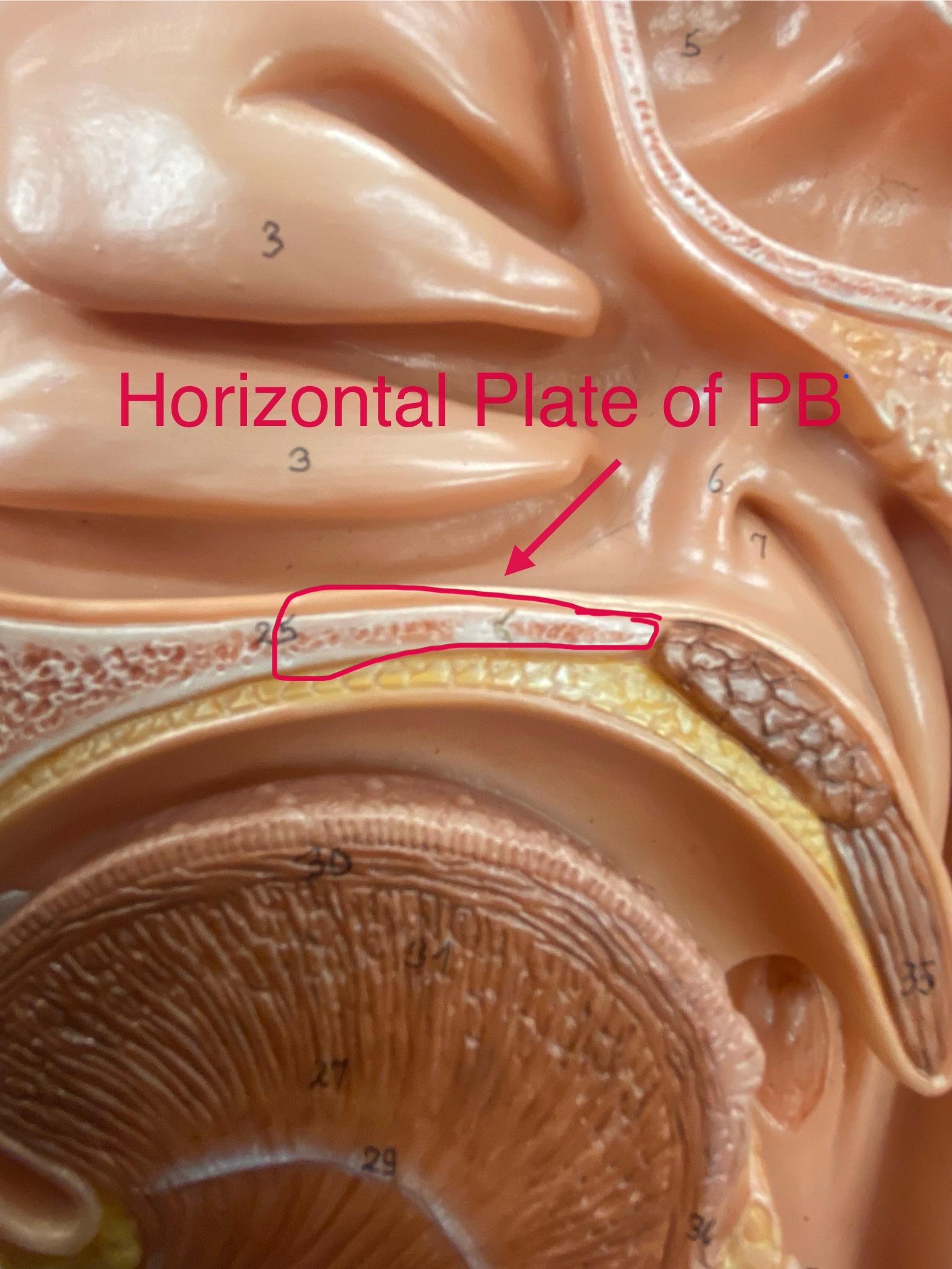
horizontal plate of the palatine bones
form the posterior portion of the hard palate
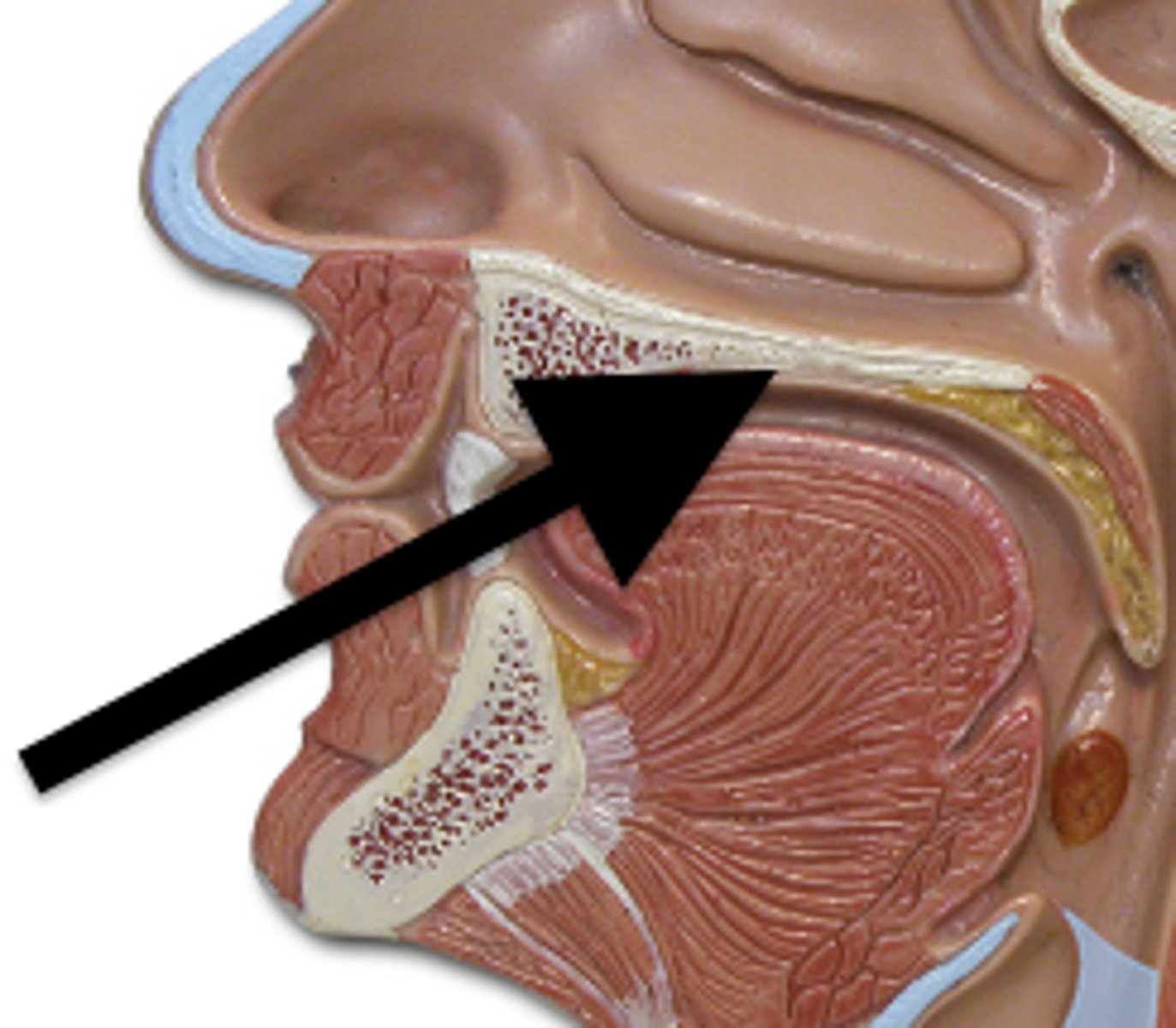
nasal conchae
two bones that help to complete the nasal cavity by forming the side and lower wall.
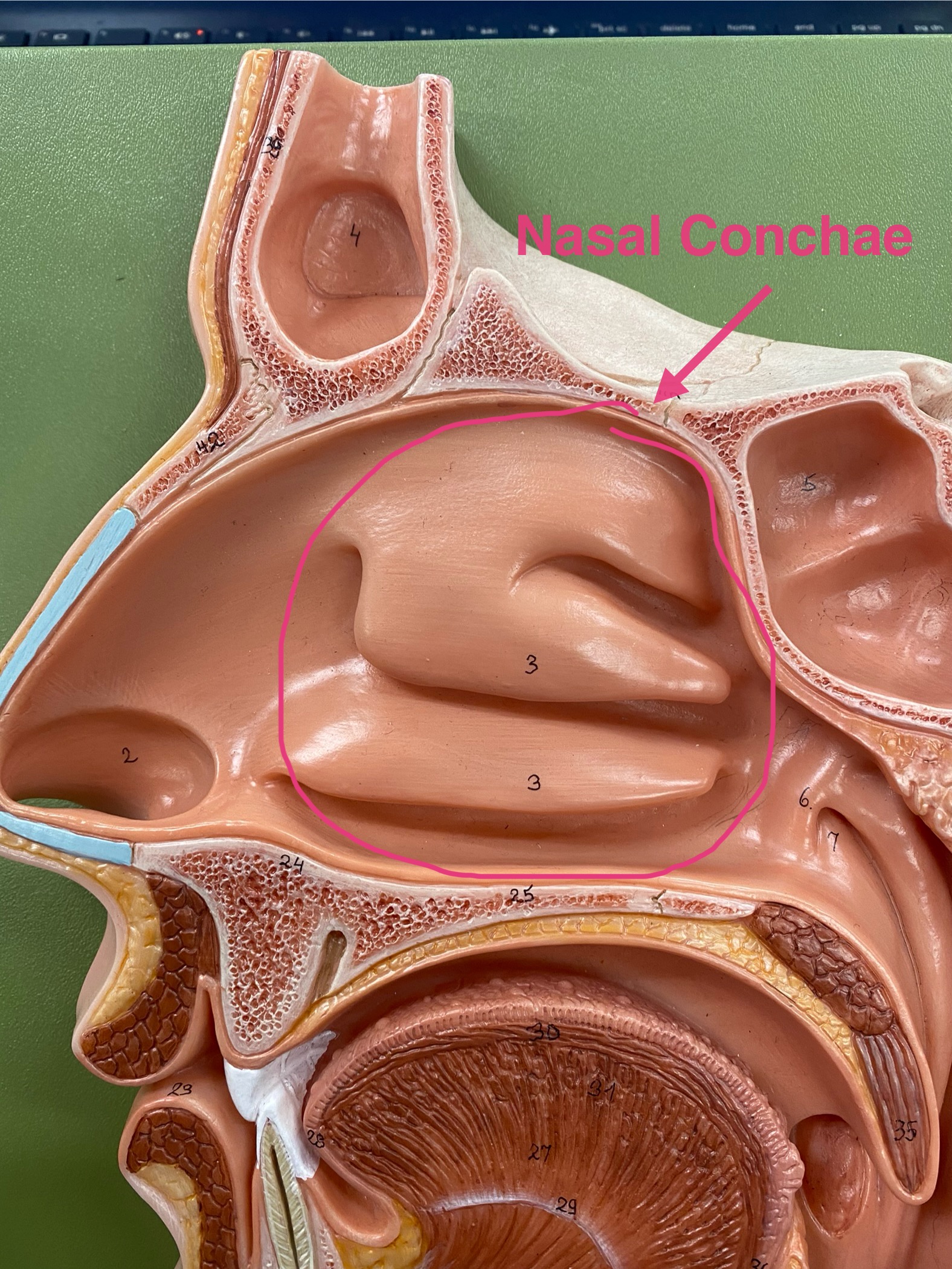
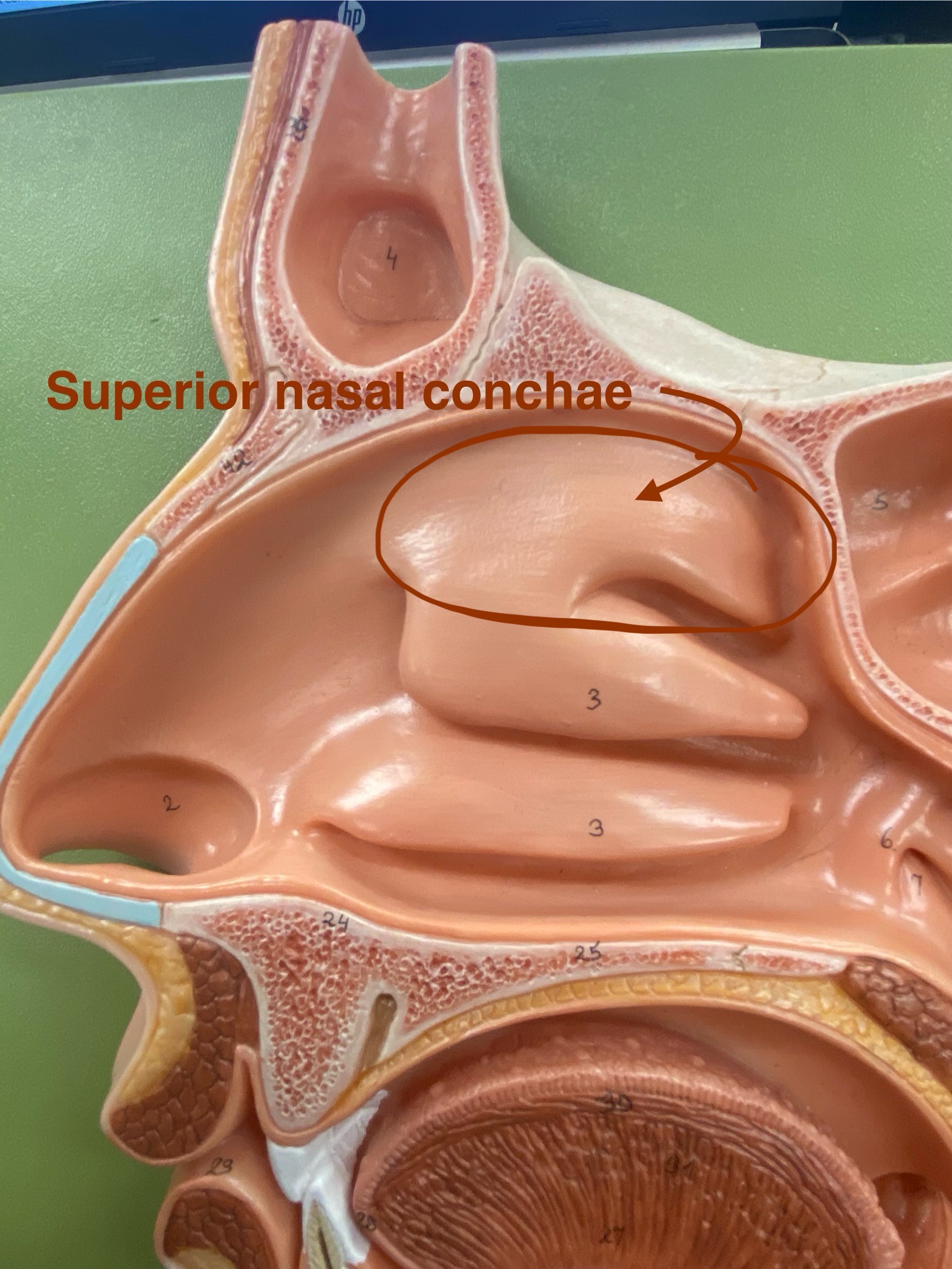
superior nasal conchae
Makes the airflow turbulent and thee surfaces are mucus which traps particles to stop them from going down the trachea
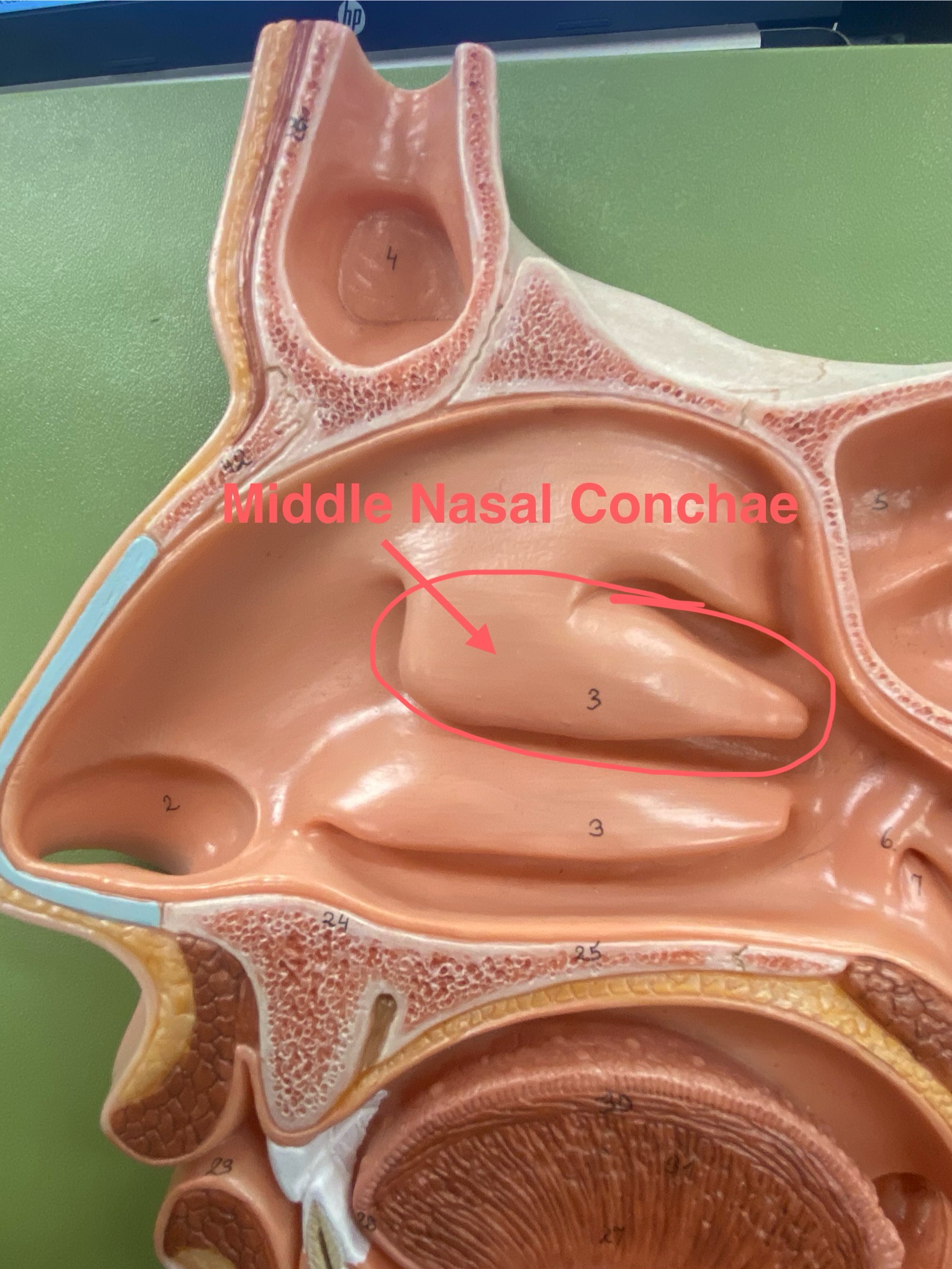
middle nasal conchae
Makes the airflow turbulent and thee surfaces are mucus which traps particles to stop them from going down the trachea
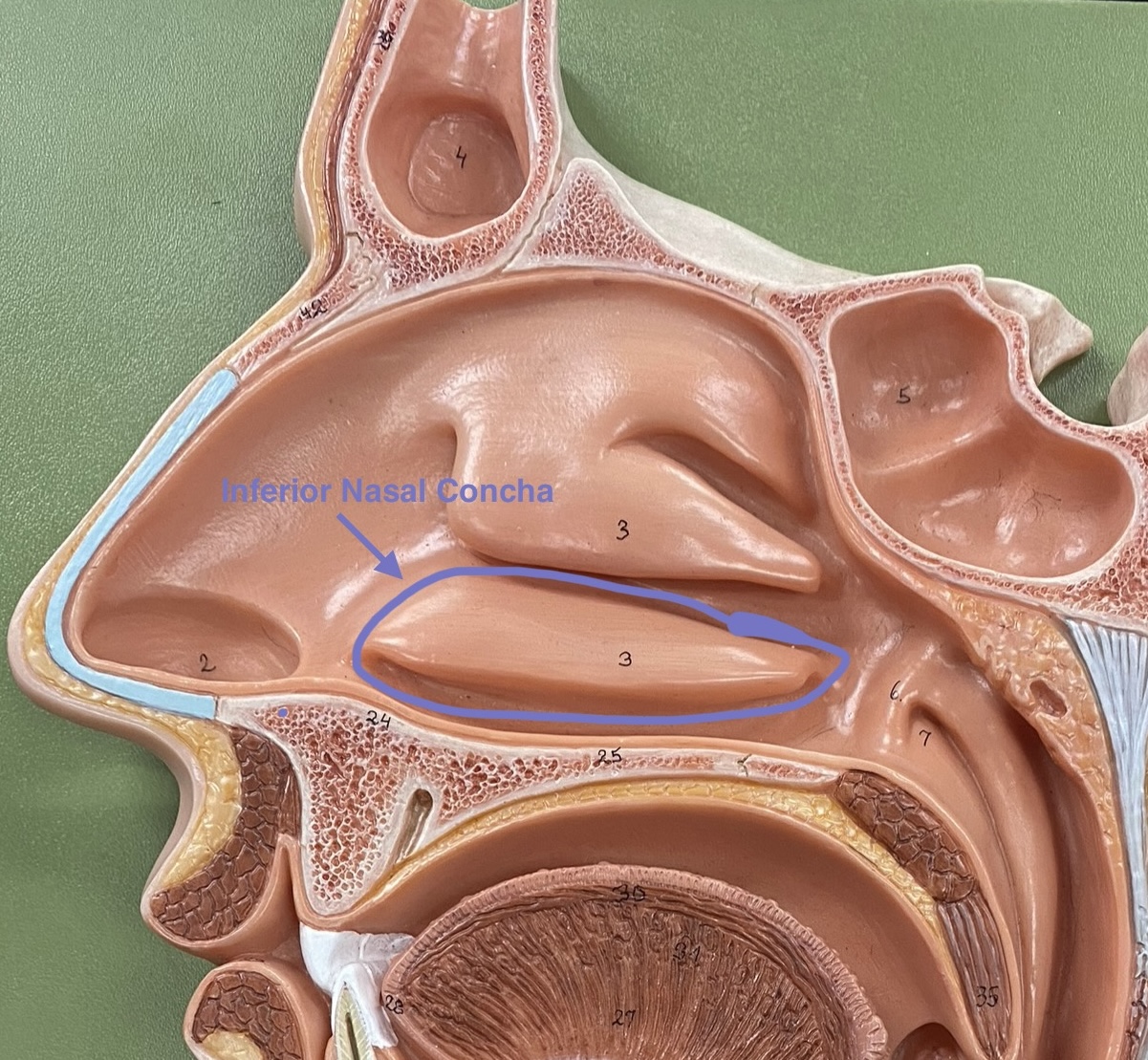
inferior nasal conchae
Makes the airflow turbulent and thee surfaces are mucus which traps particles to stop them from going down the trachea
paranasal sinus
an air-filled cavity within a bone connected to the nasal cavity
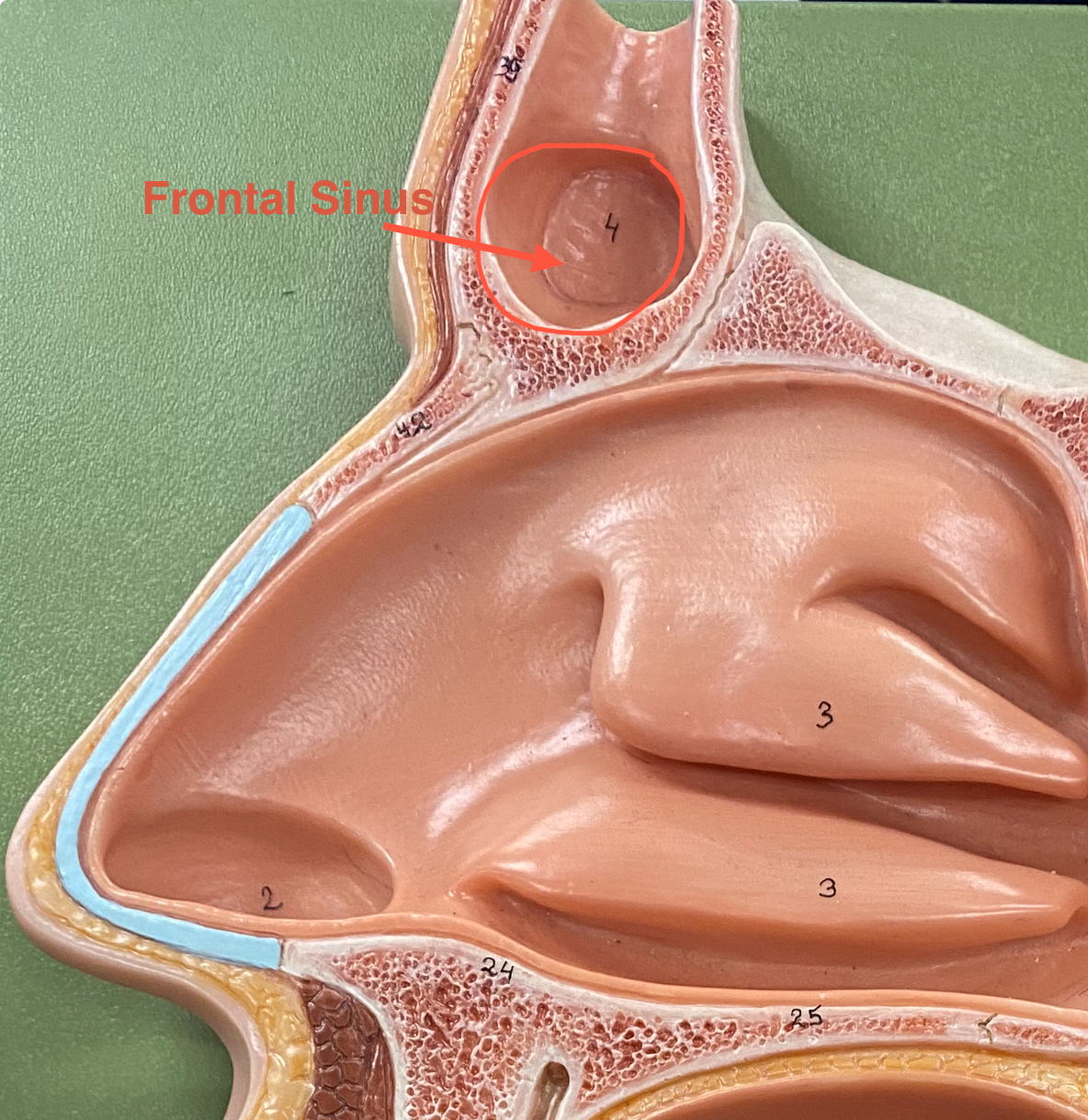
frontal sinus
It appears as a hollow, air-filled cavity that opens into the nasal cavity and helps lighten the skull, produce mucus, and enhance voice resonance.
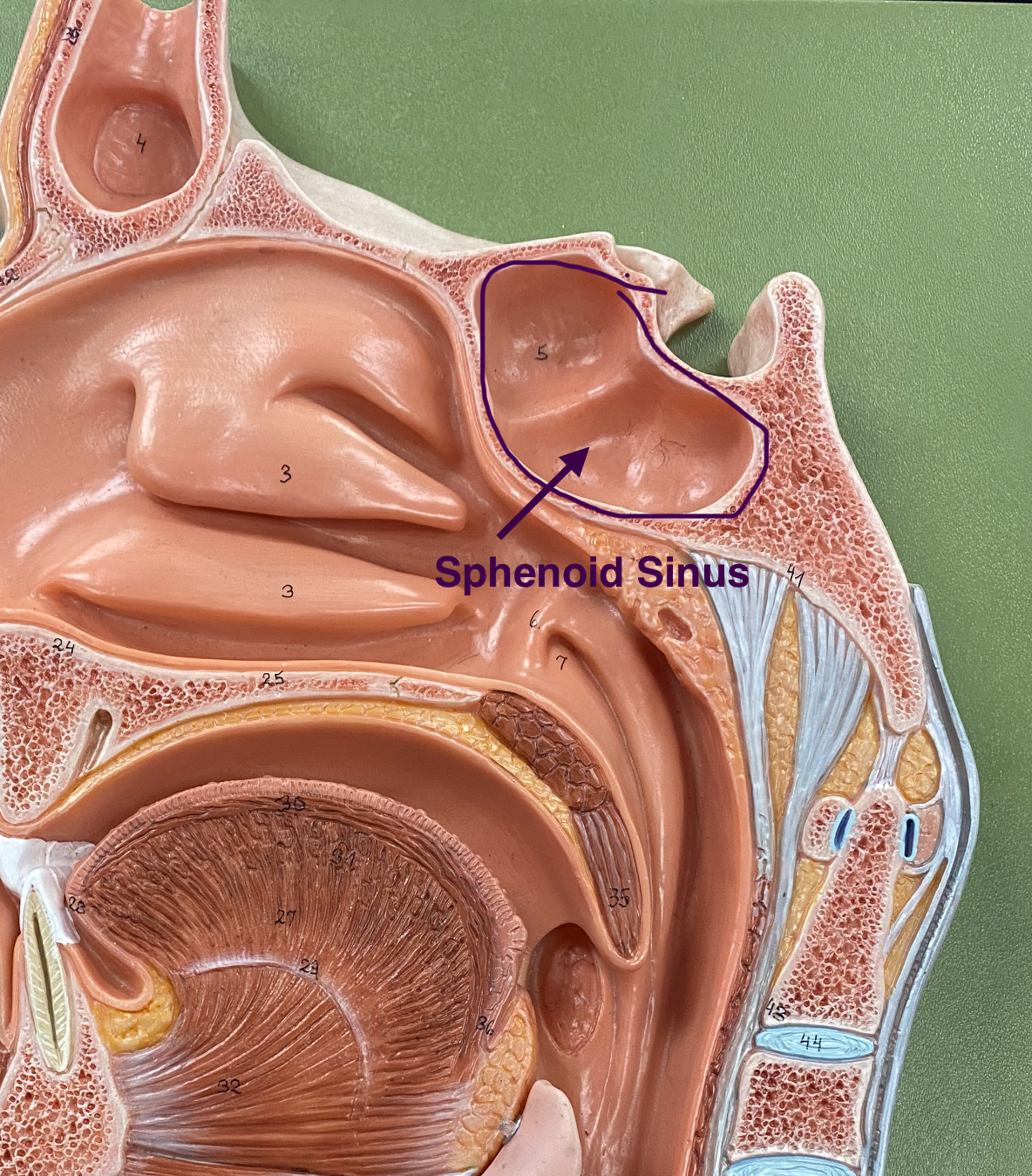
sphenoid sinus
located within the sphenoid bone, deep behind the nasal cavity. Air-filled cavity that drains into the nasal cavity and helps lighten the skull. Aid in filtering inhaled air.
ethmoid sinuses
located within the ethmoid bone, behind the bridge of the nose. Function to produce mucus, lighten the skull, and aid in filtering inhaled air.
maxillary sinuses
located within the maxillary bones. Air-filled cavity that drains into the nasal cavity and helps lighten the skull, produce mucus, and enhance voice resonance.
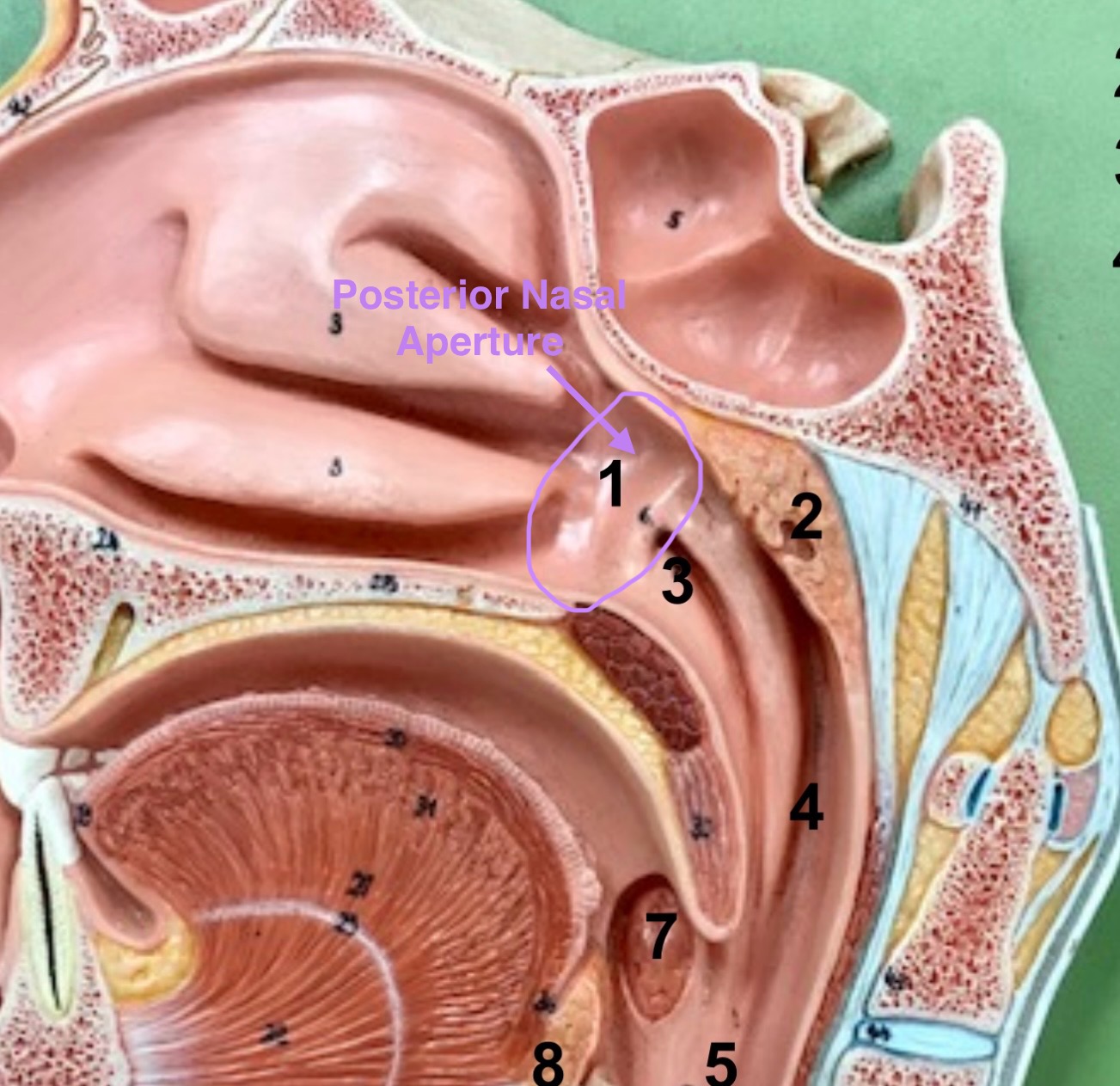
posterior nasal aperture
open passageway at the end of the nasal cavity leading into the pharynx
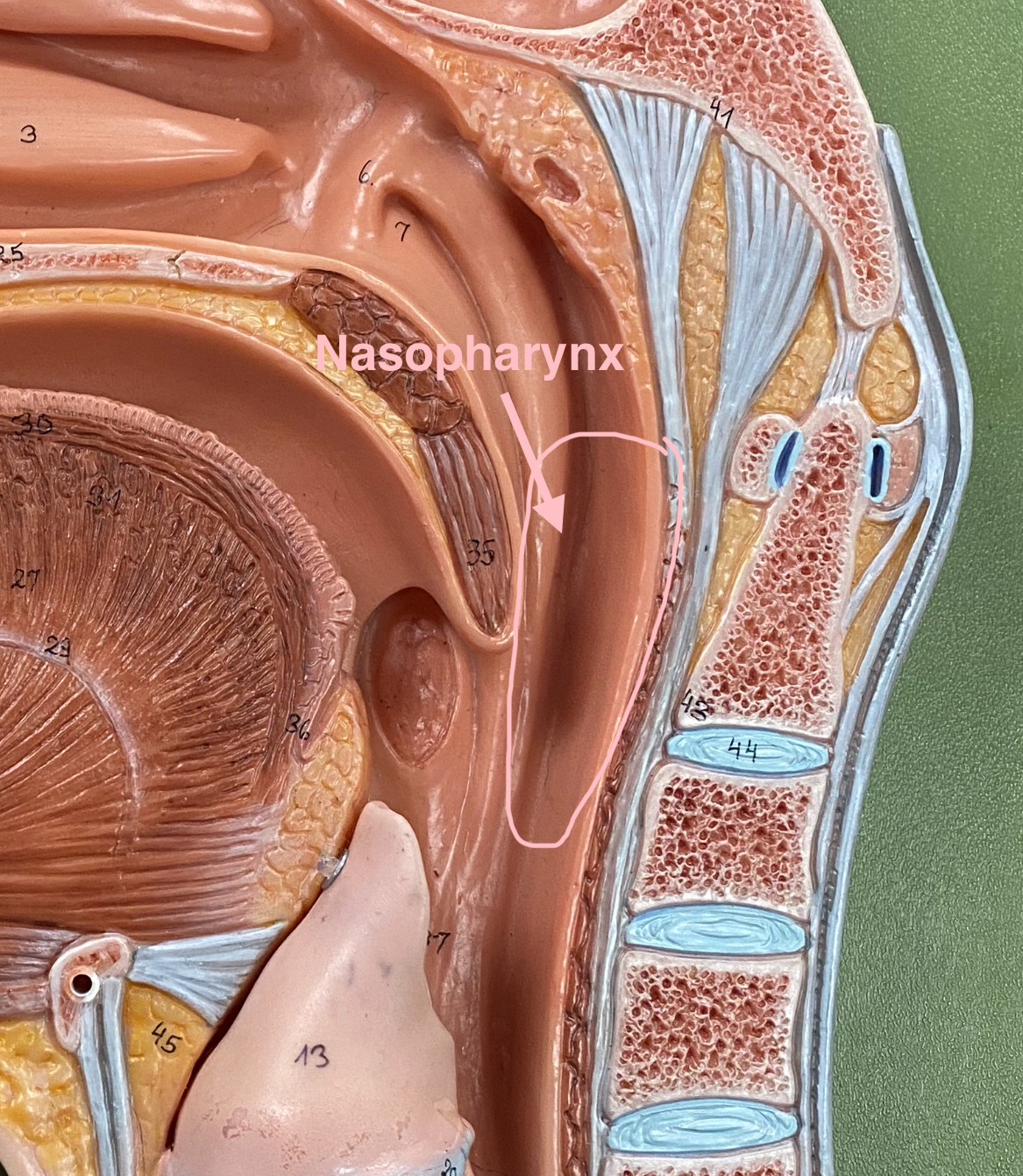
nasopharynx
It appears as a region where air passes from the nasal cavity into the oropharynx, and it contains the pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids)
oropharynx
The middle part of the throat behind the mouth, where air and food pass through.
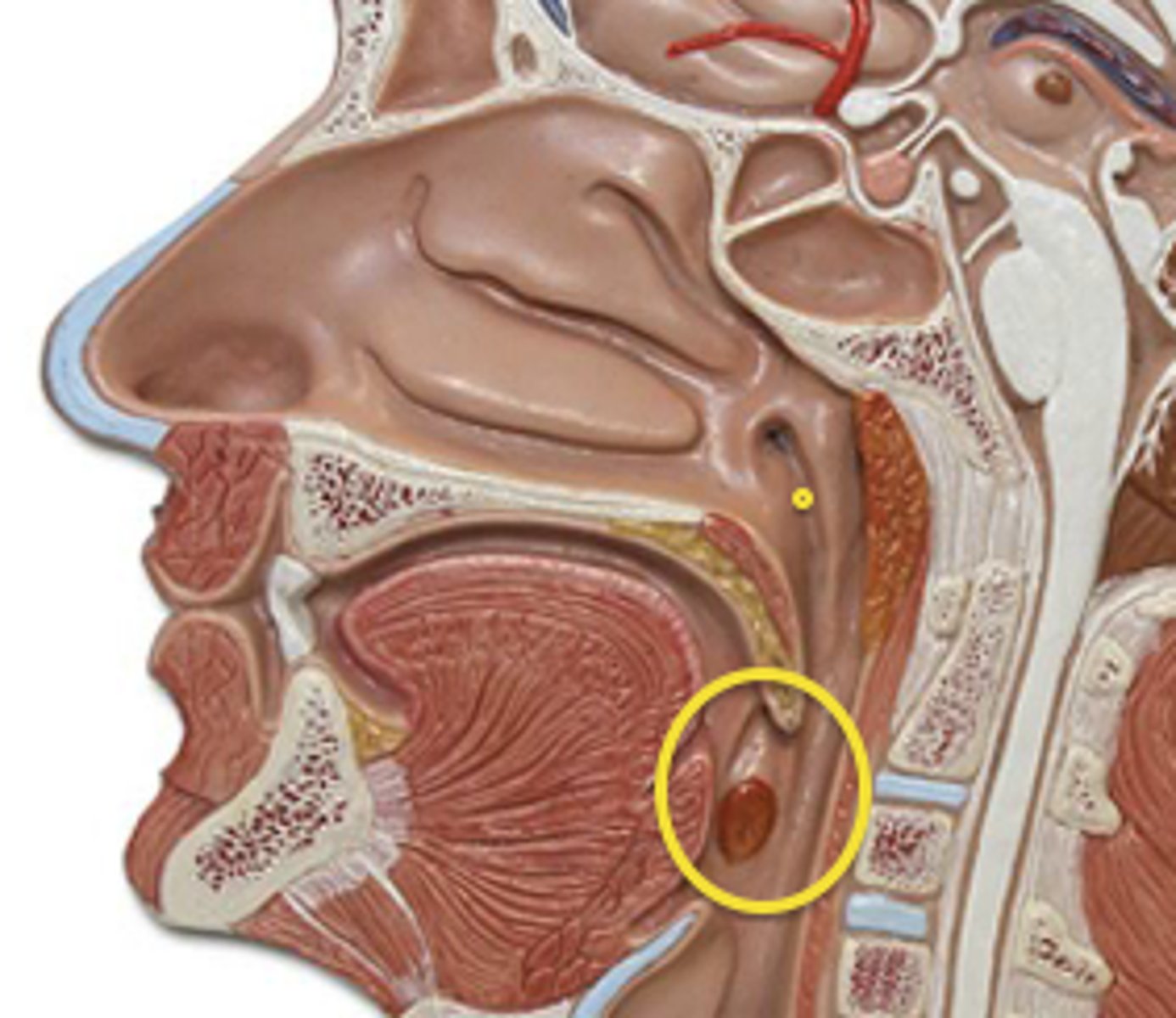
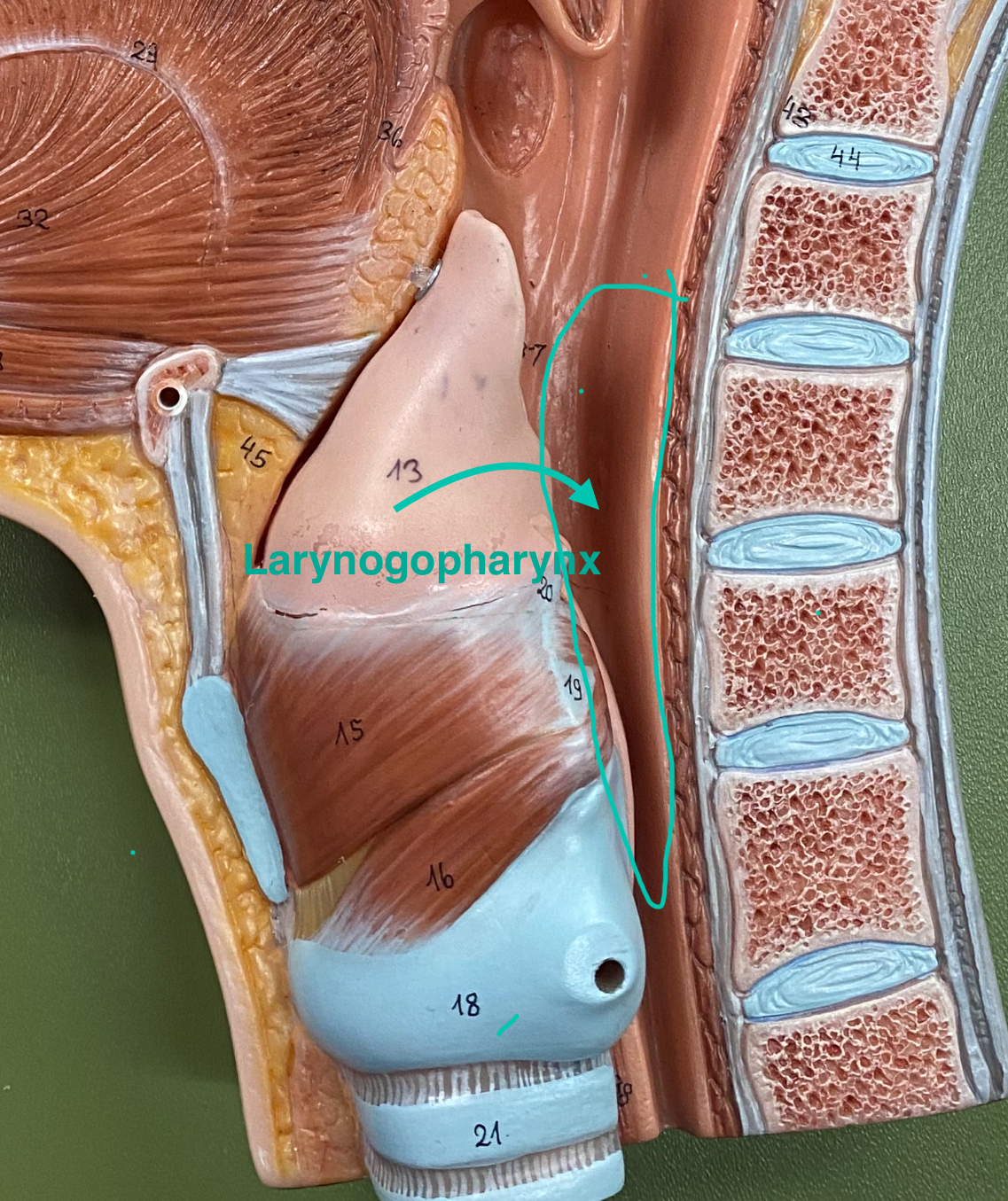
laryngopharynx
The lower part of the throat, located behind the larynx, where air passes to the larynx and food to the esophagus.
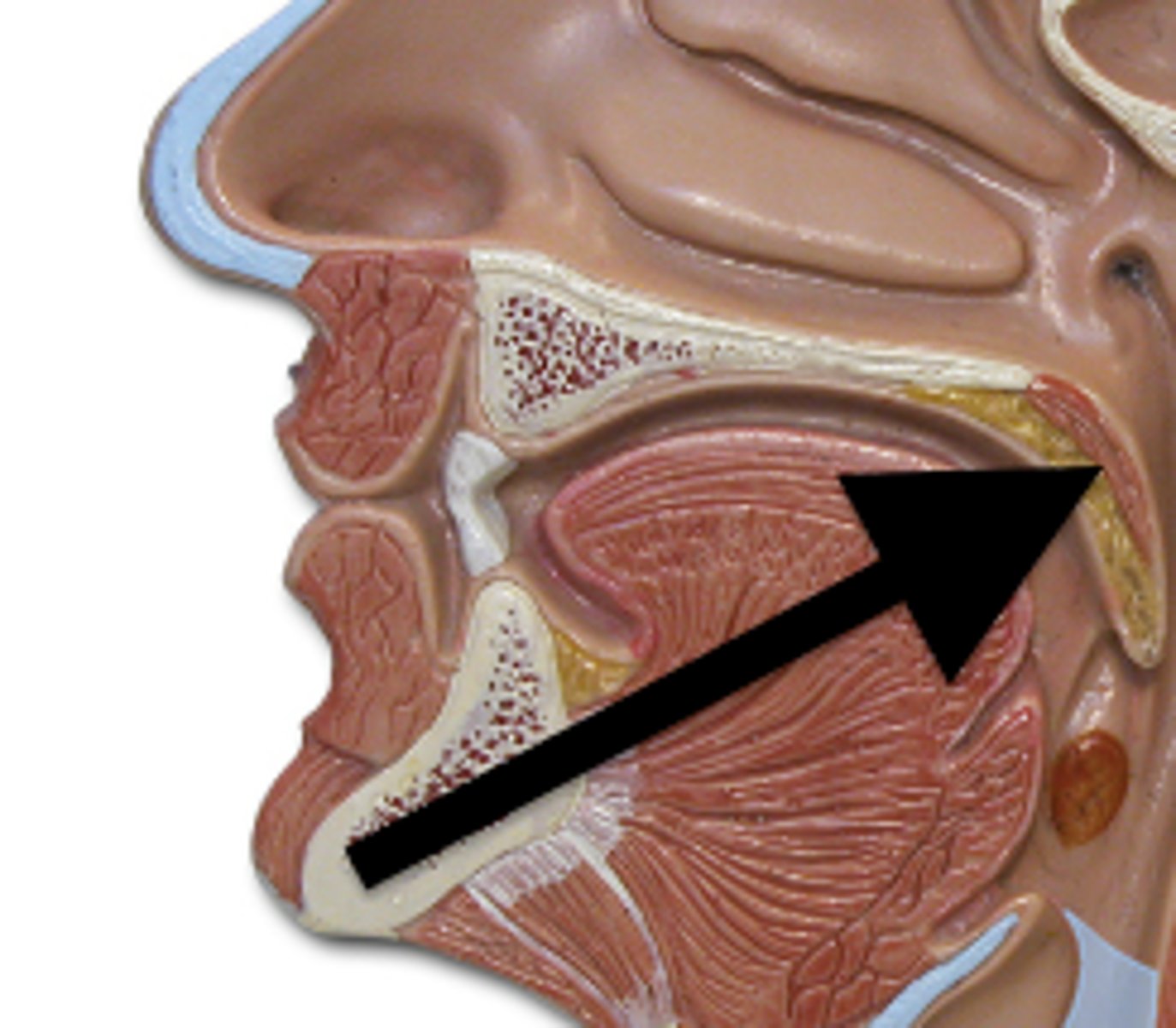
soft palate
composed primarily of skeletal muscle and connective tissue. It separates the nasopharynx from the oropharynx.
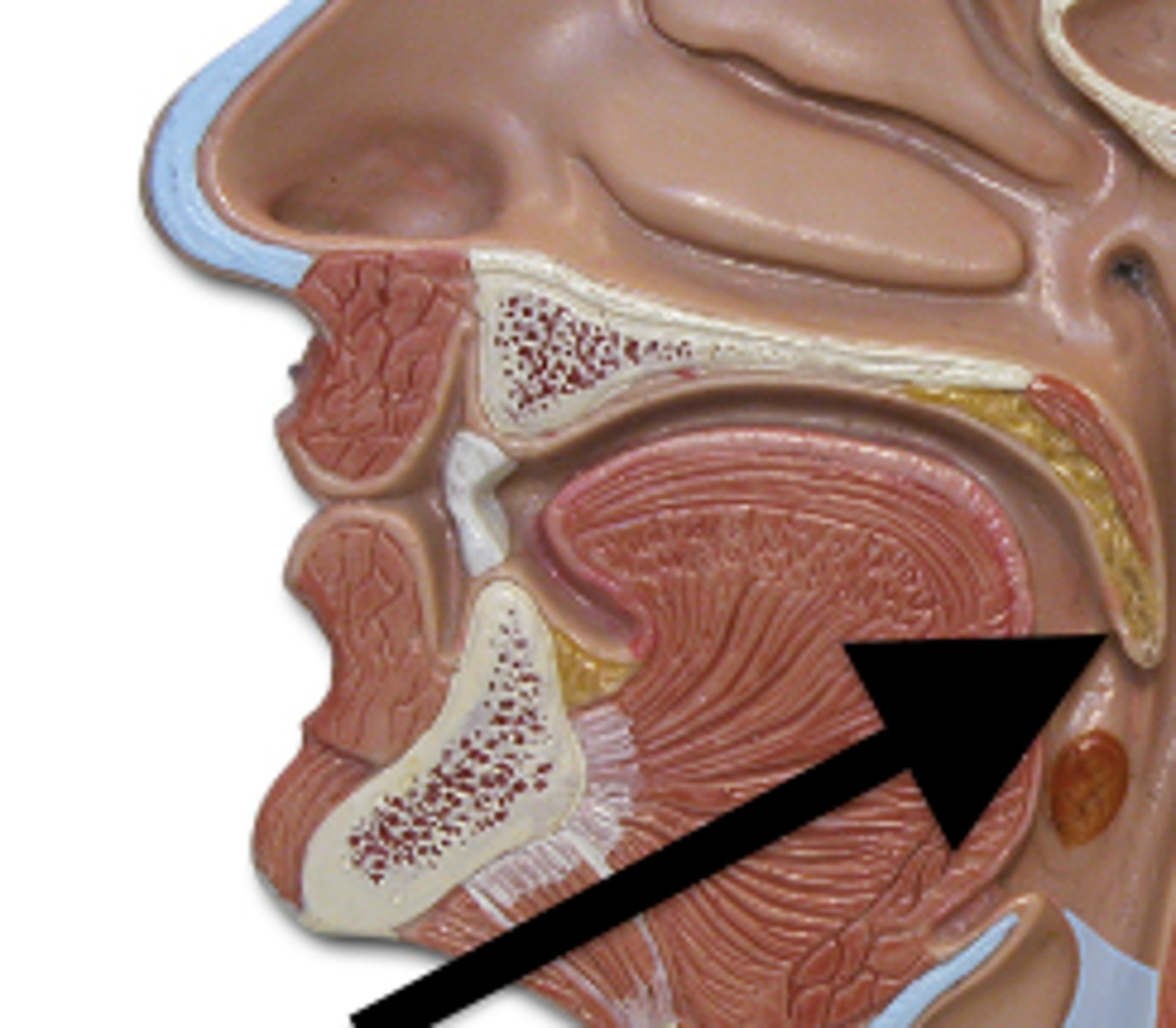
uvula
free projection hanging down from the middle of the soft palate
pharyngeal tonsil
also called adenoids; located in posterior wall of nasopharynx
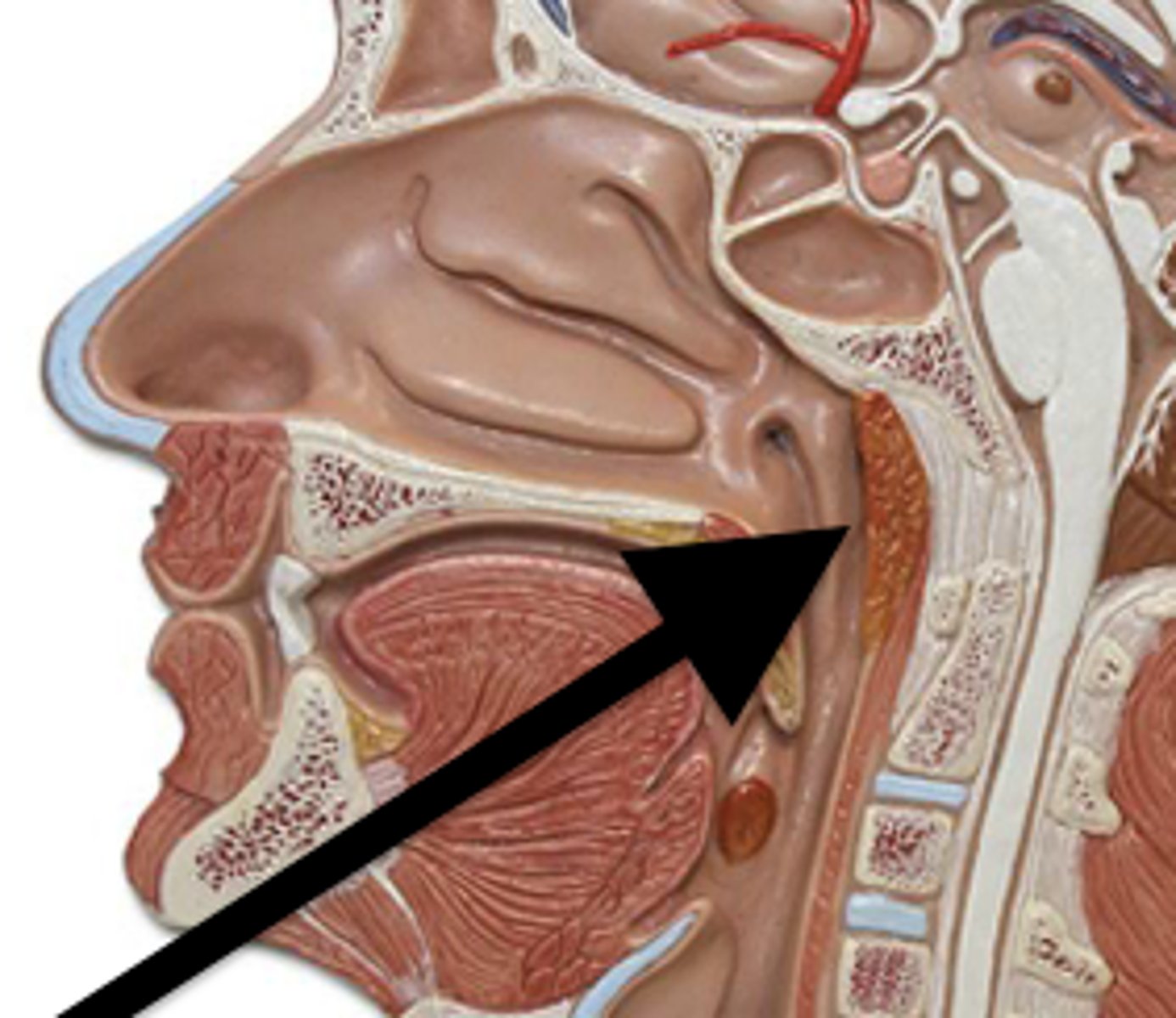
auditory tube
channel between the middle ear cavity and the nasopharynx

epiglottis
A flap of cartilage at the base of the tongue that covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food and liquid from entering the airway.
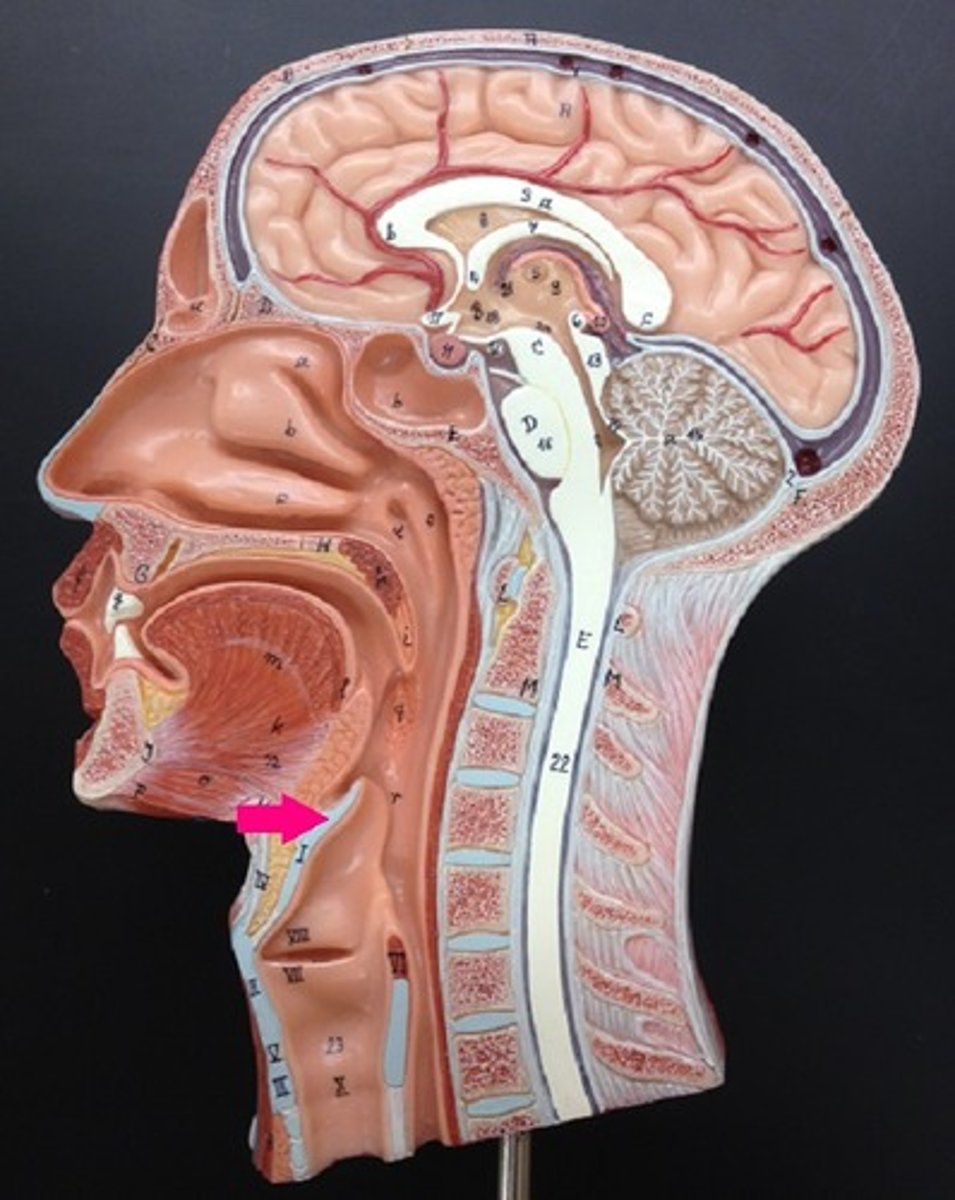
larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
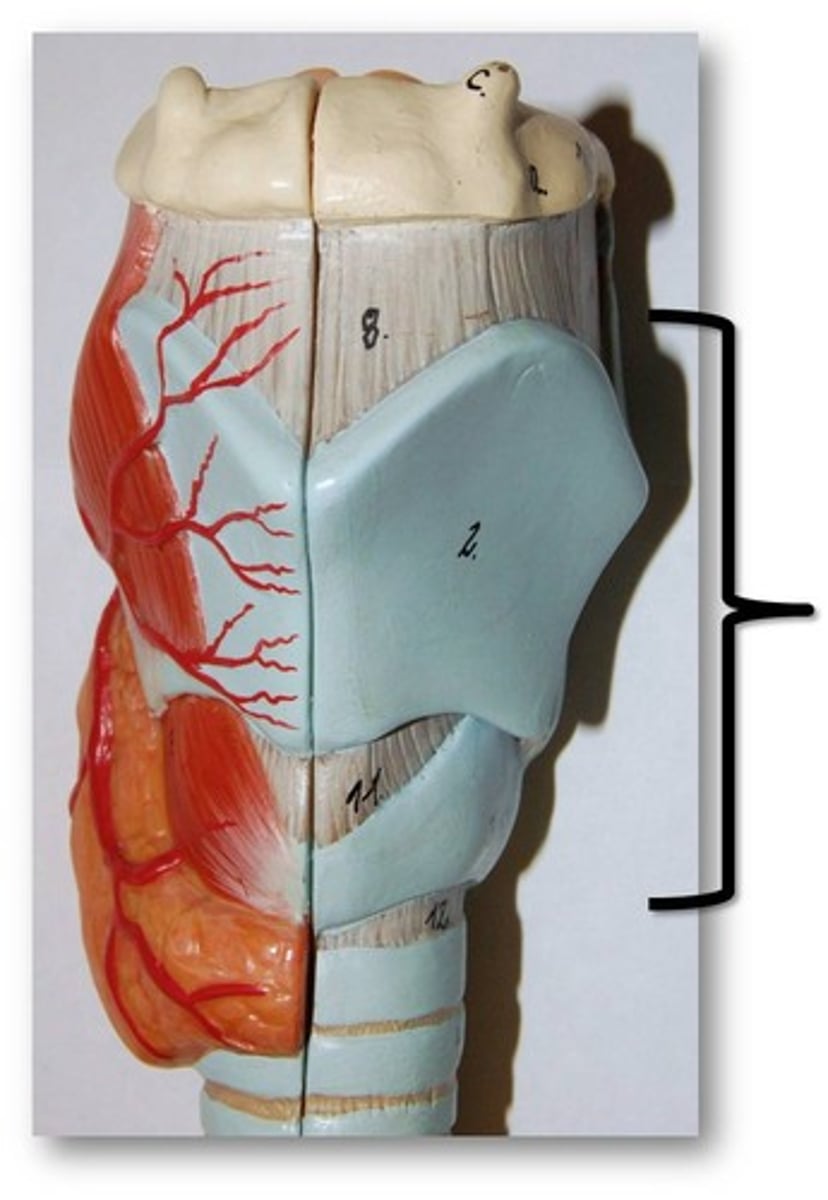
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles.
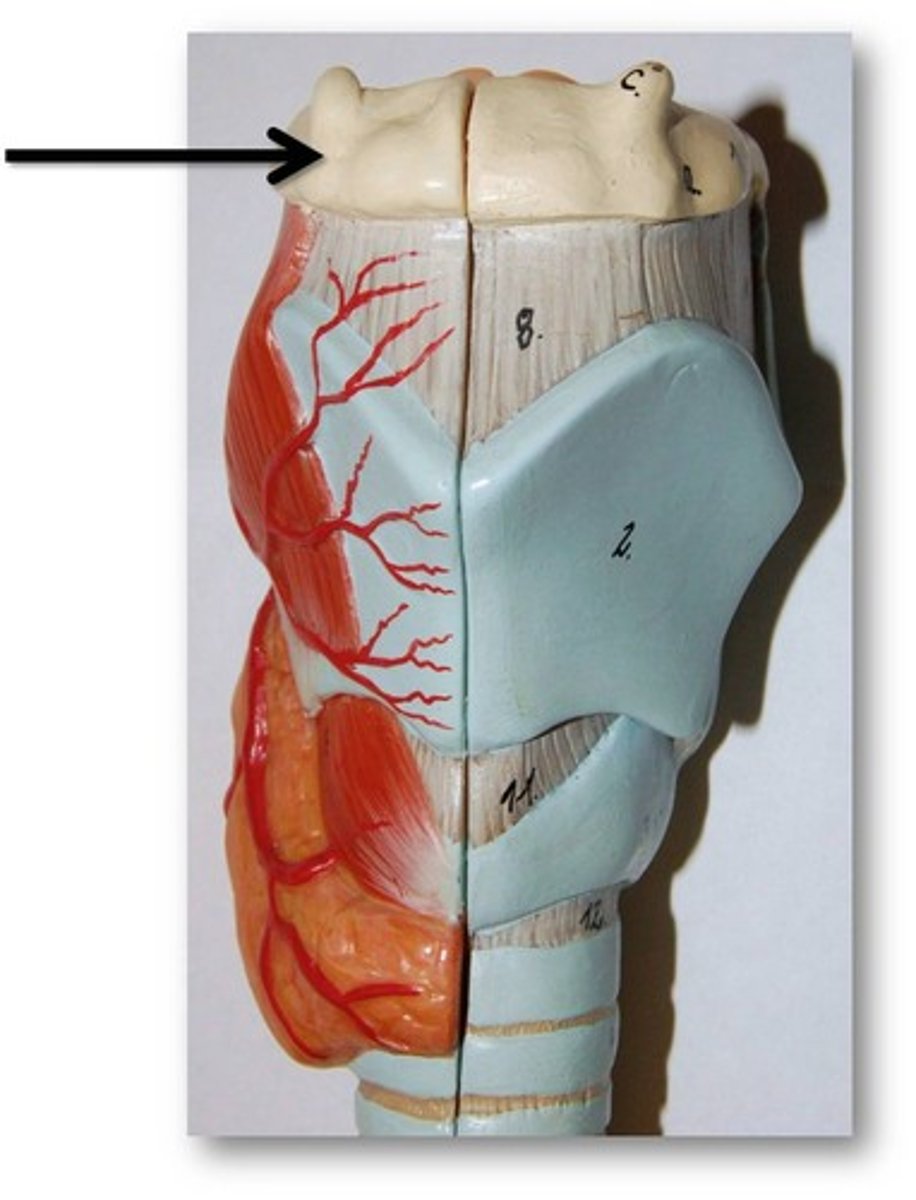
thyroid cartilage
The largest cartilage in the larynx, forming the front and sides of the voice box. It appears as a shield-like structure
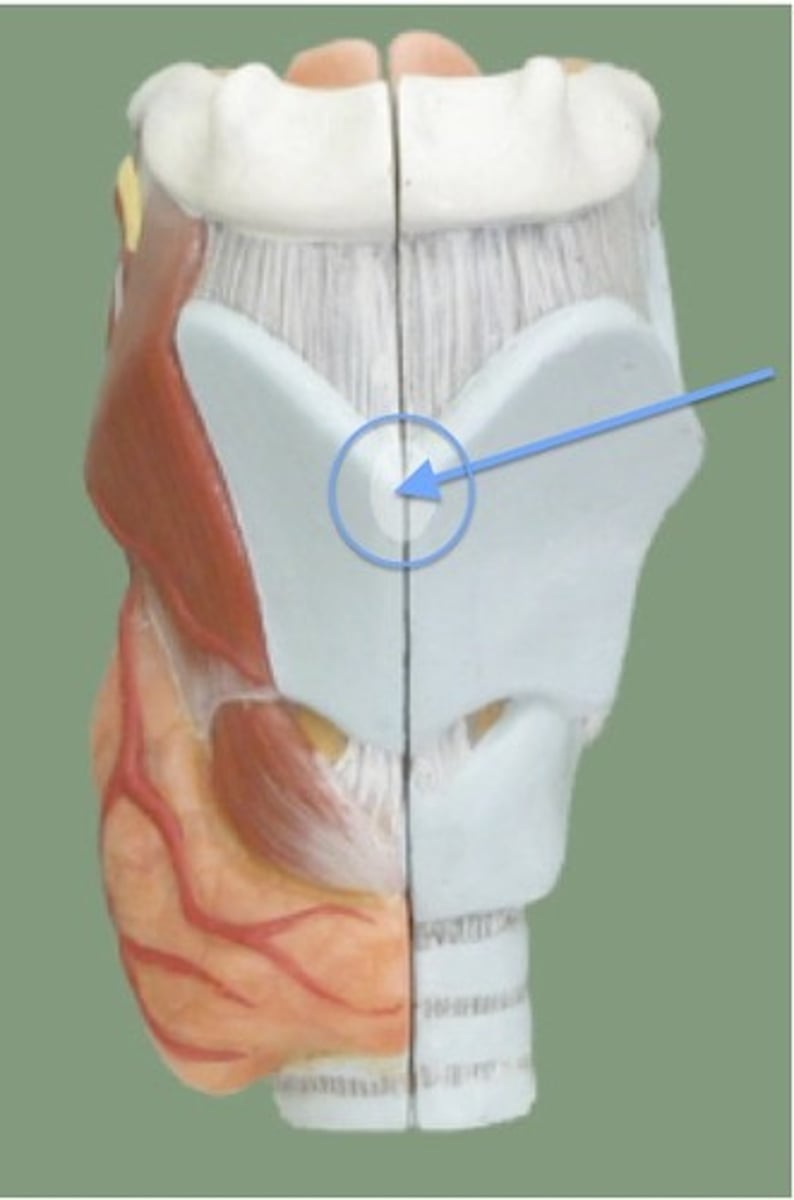
laryngeal prominence
the visible bump or protrusion at the front of the neck, which is a part of the thyroid cartilage. It is more prominent in males and is commonly known as the Adam's apple.
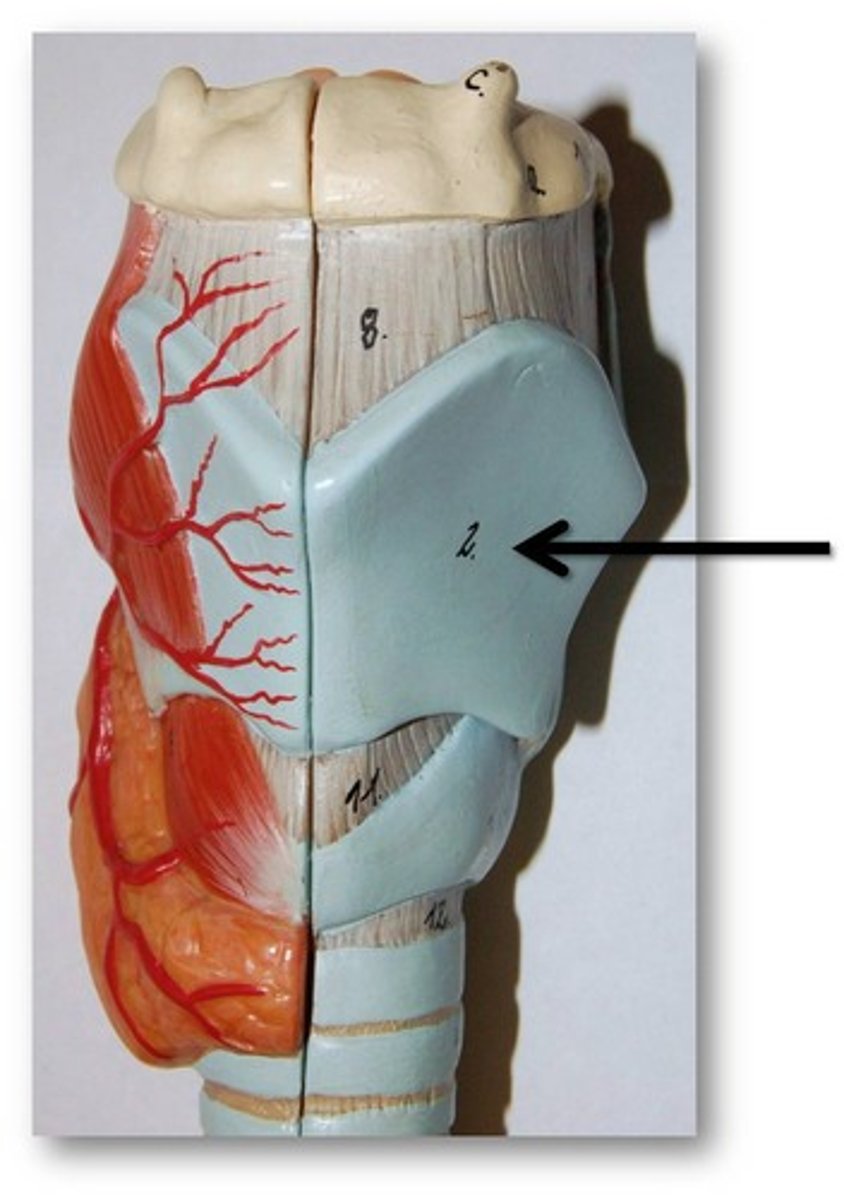
thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
cricoid cartilage
the ring-shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx
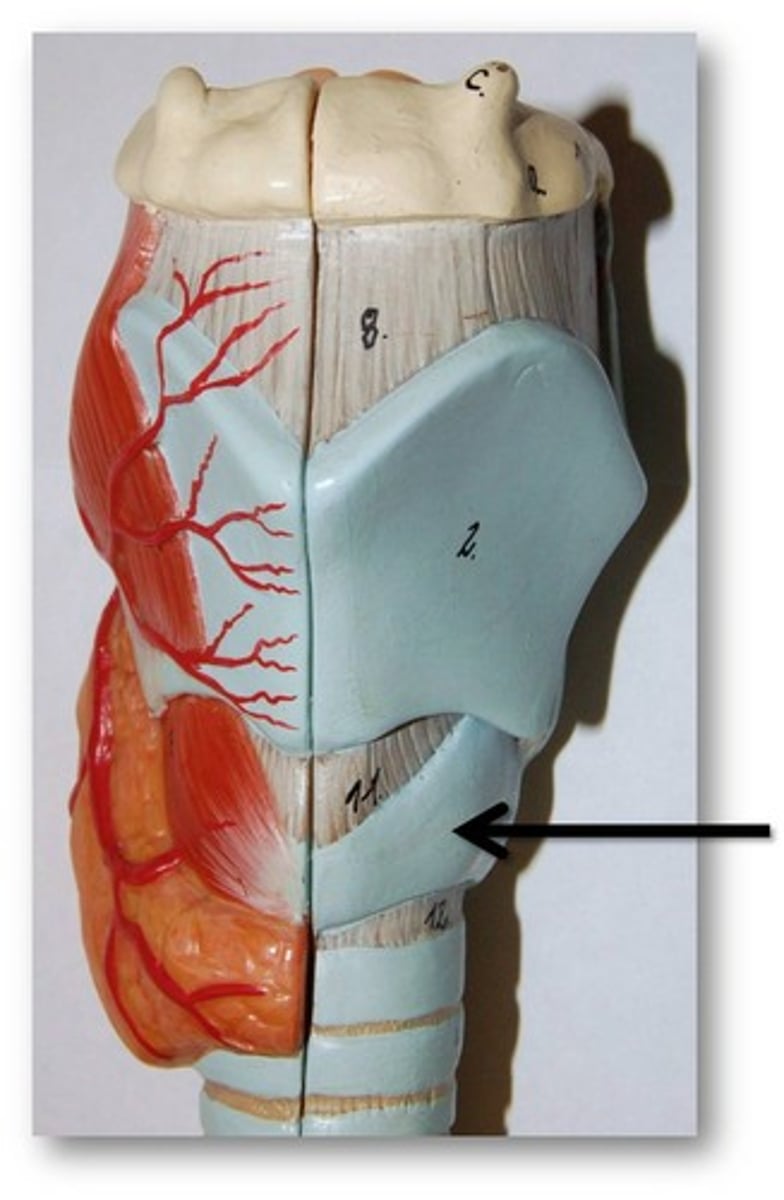
vestibular folds (false vocal cords)
pair of horizontal mucosal folds superior to vocal folds; play no part in sound production
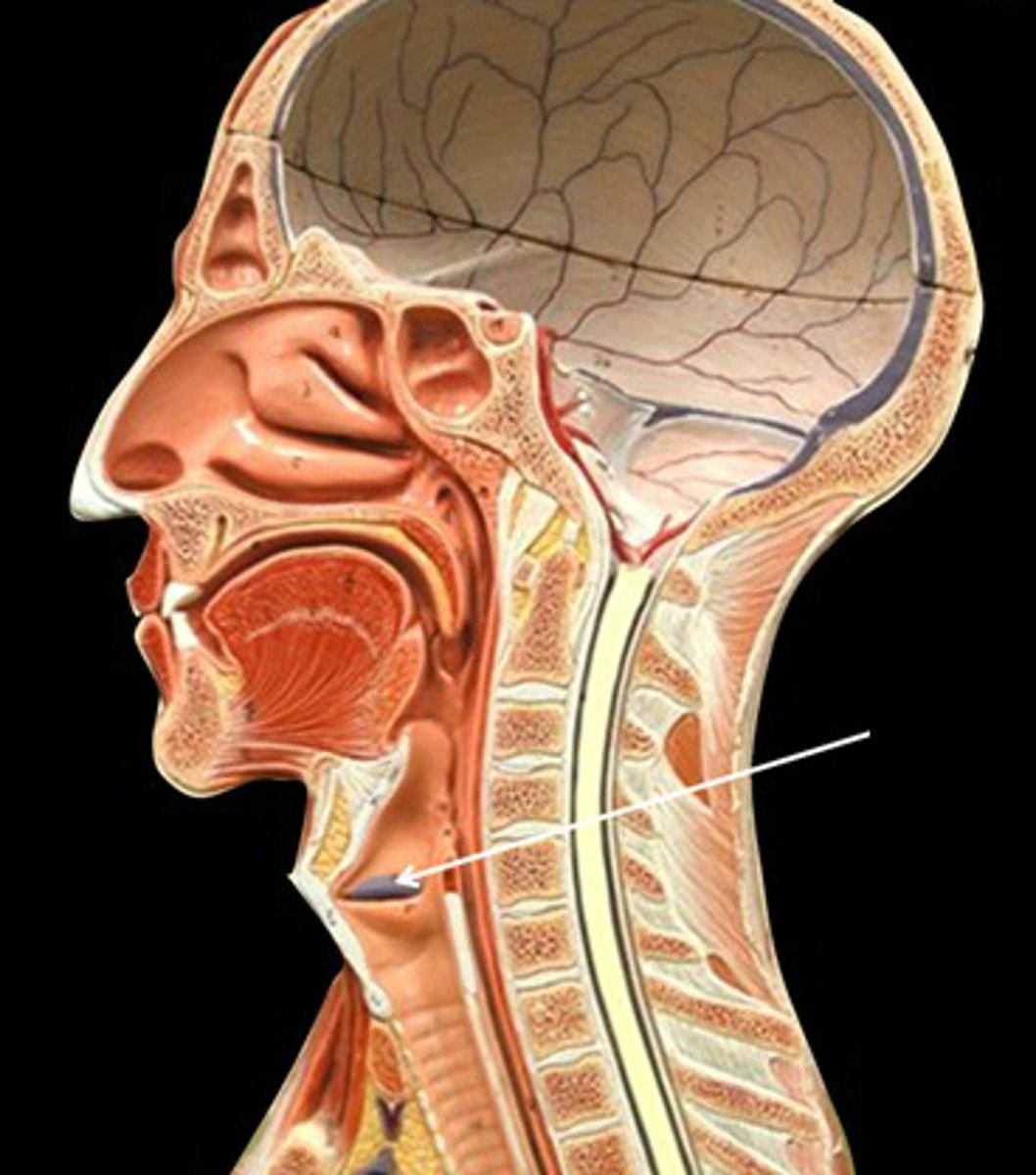
vocal folds (true vocal cords)
contain bands of elastic tissue called vocal ligaments and are involved in voice production.
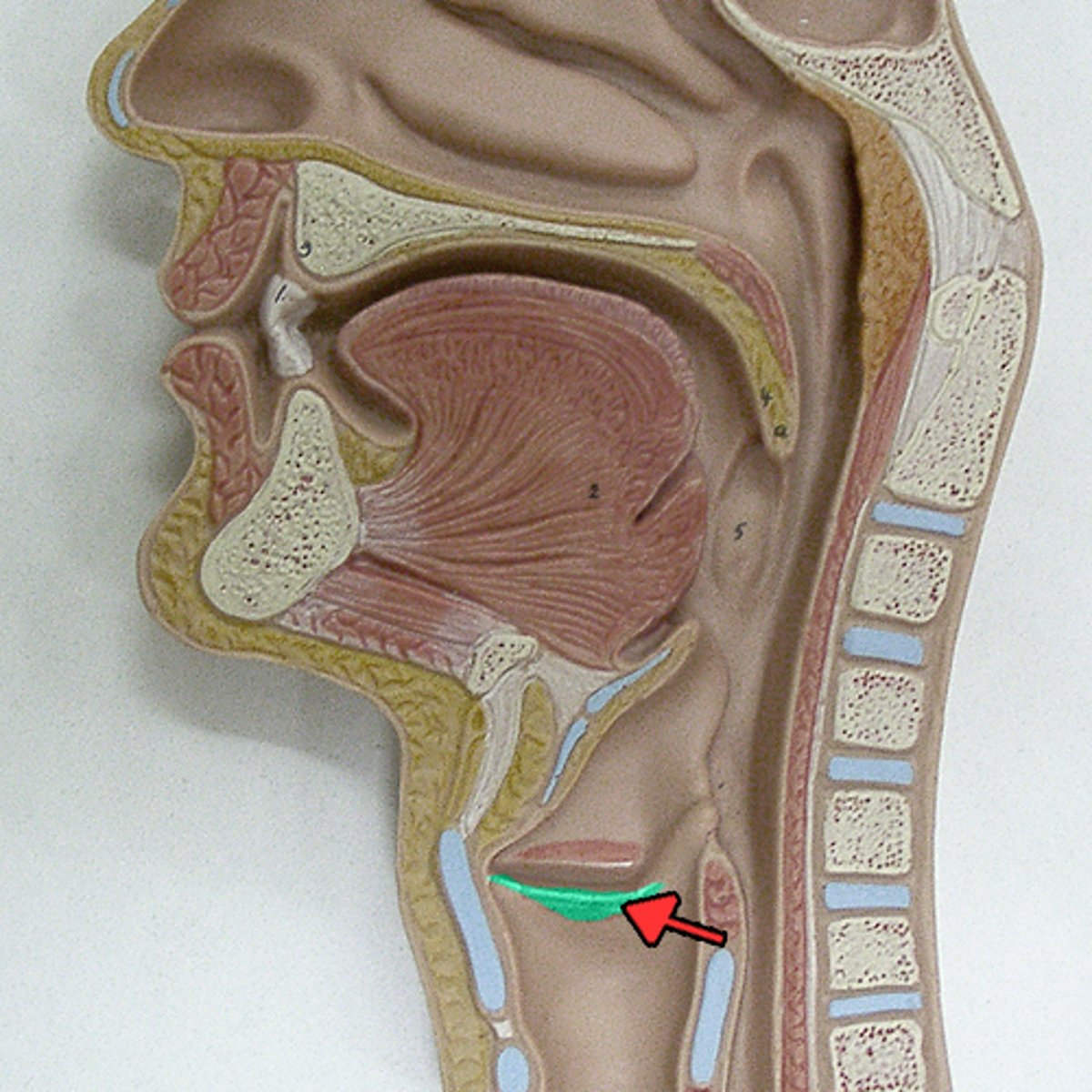
glottis
space between the vocal folds and can be regarded as the entrance to the larynx
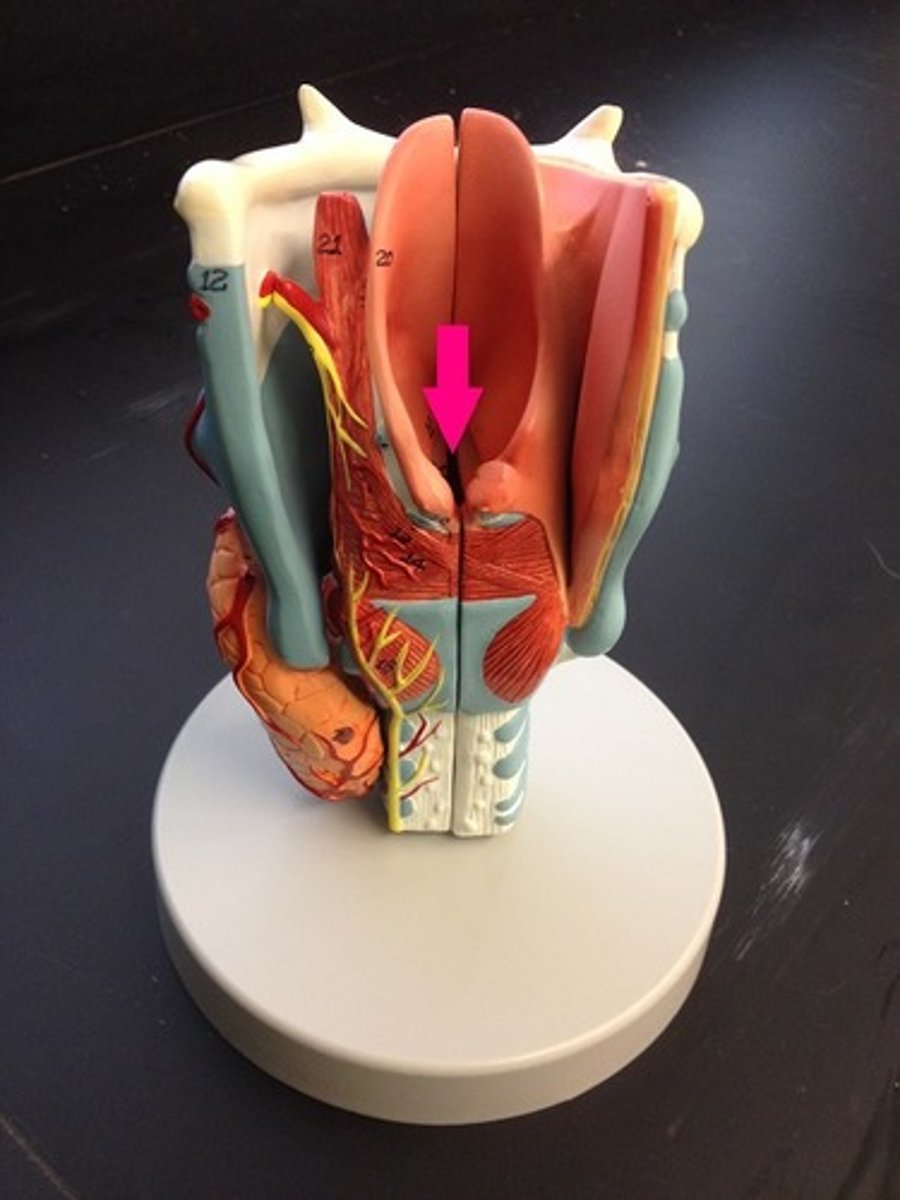
Trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
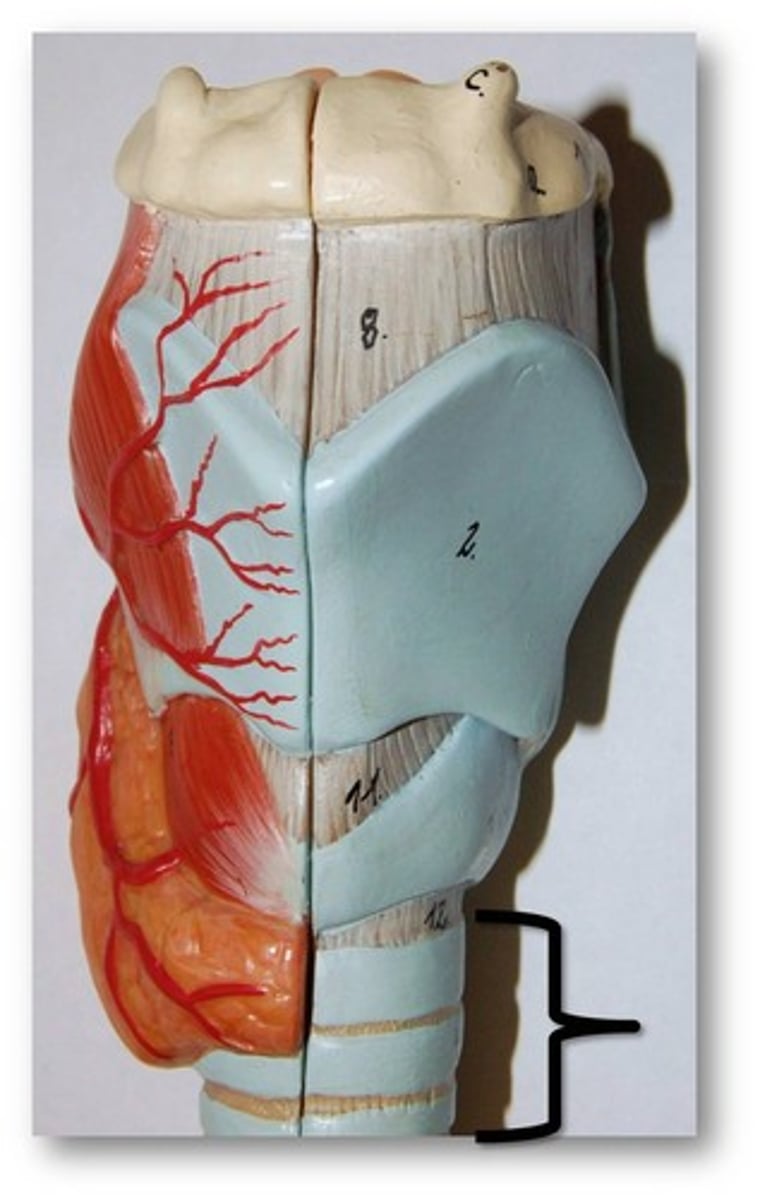
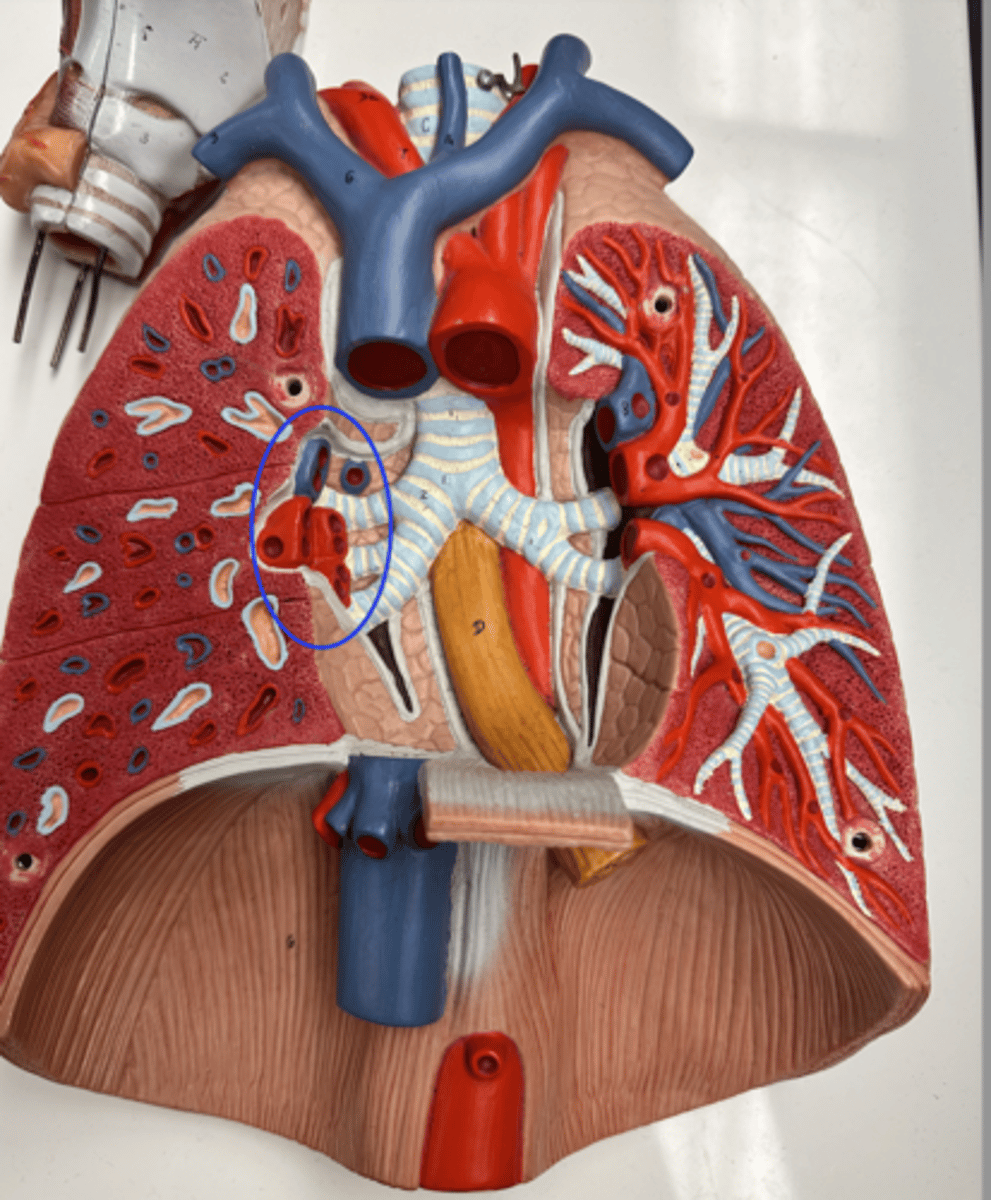
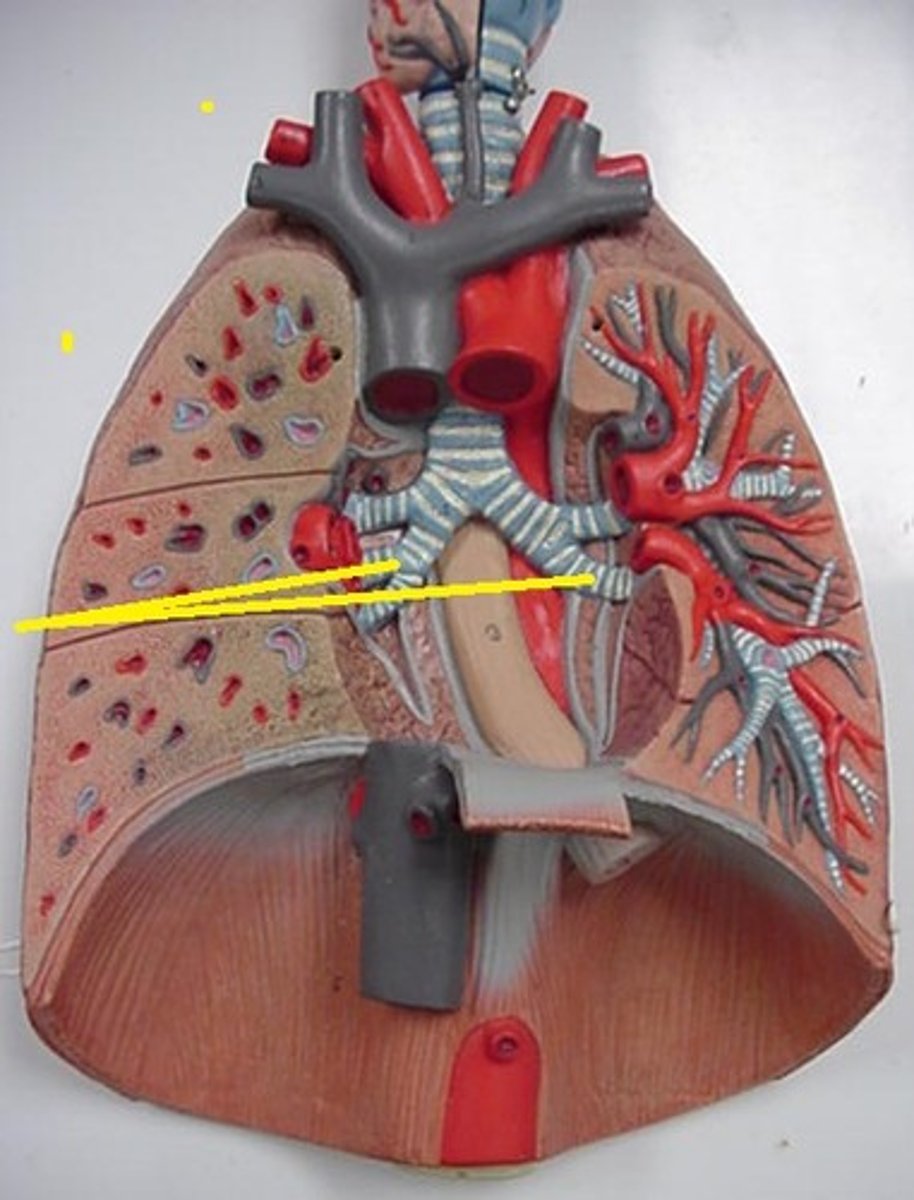
main bronchi (primary bronchi)
division of trachea which divide into each lung
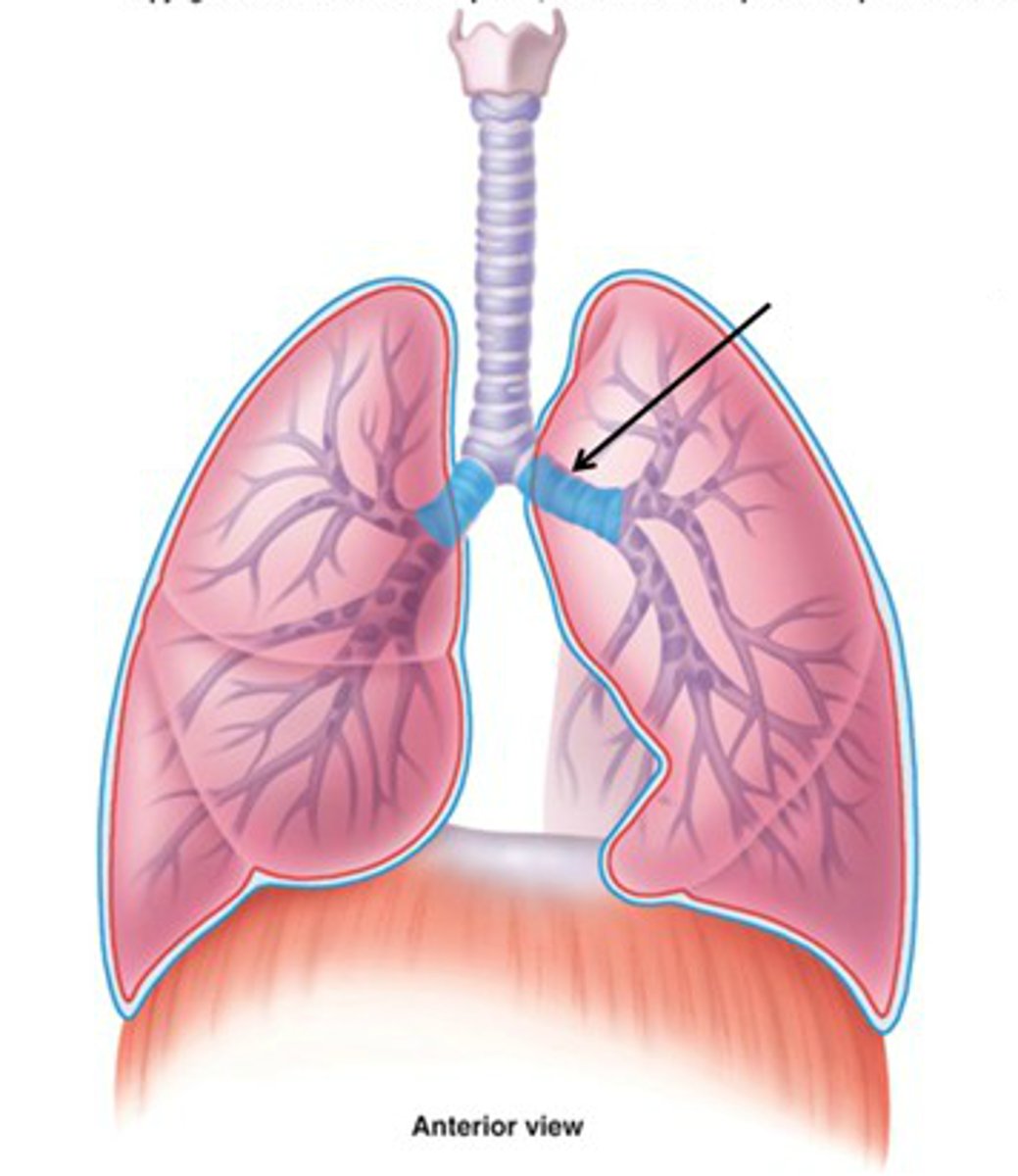
Lungs
main organs of the respiratory system, where gas exchange takes place
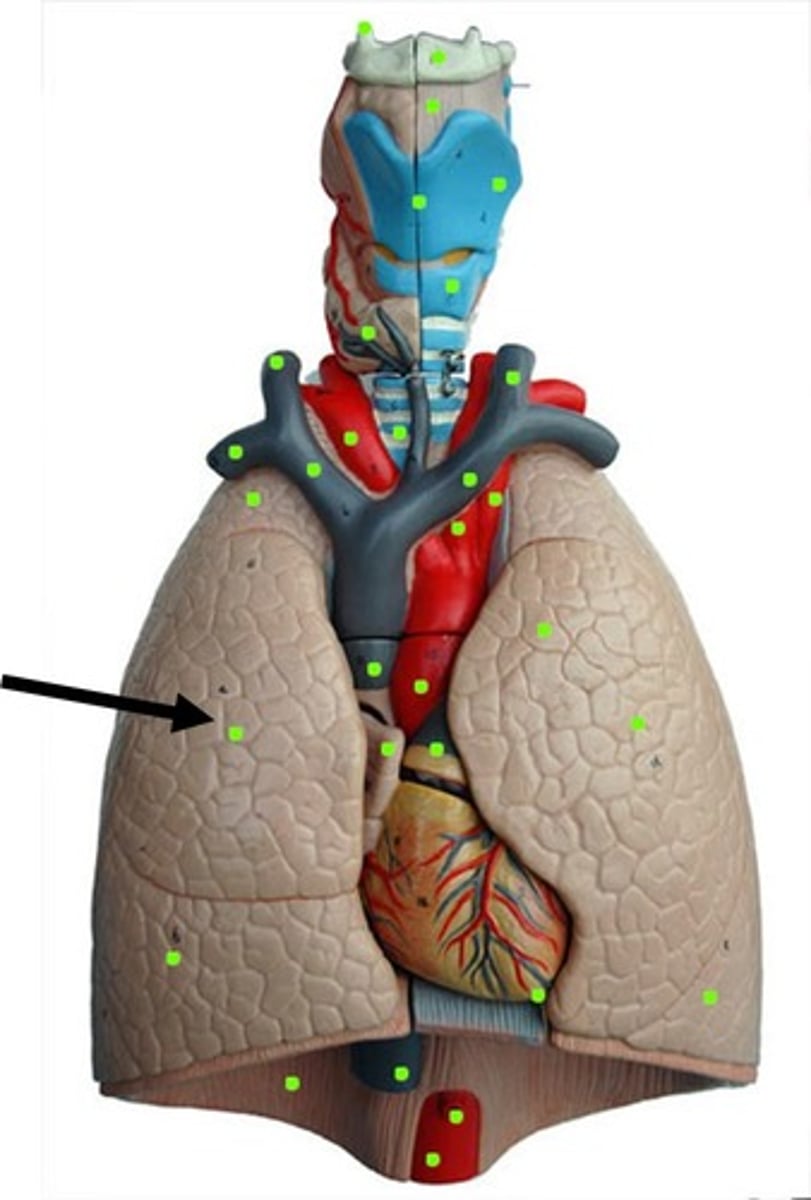
hilium of the lung
provides an entry point for the bronchi as well as an entry and exit point for blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves.
apex of the lung
tip or uppermost portion of the lung
base of the lung
lower portion of the lung
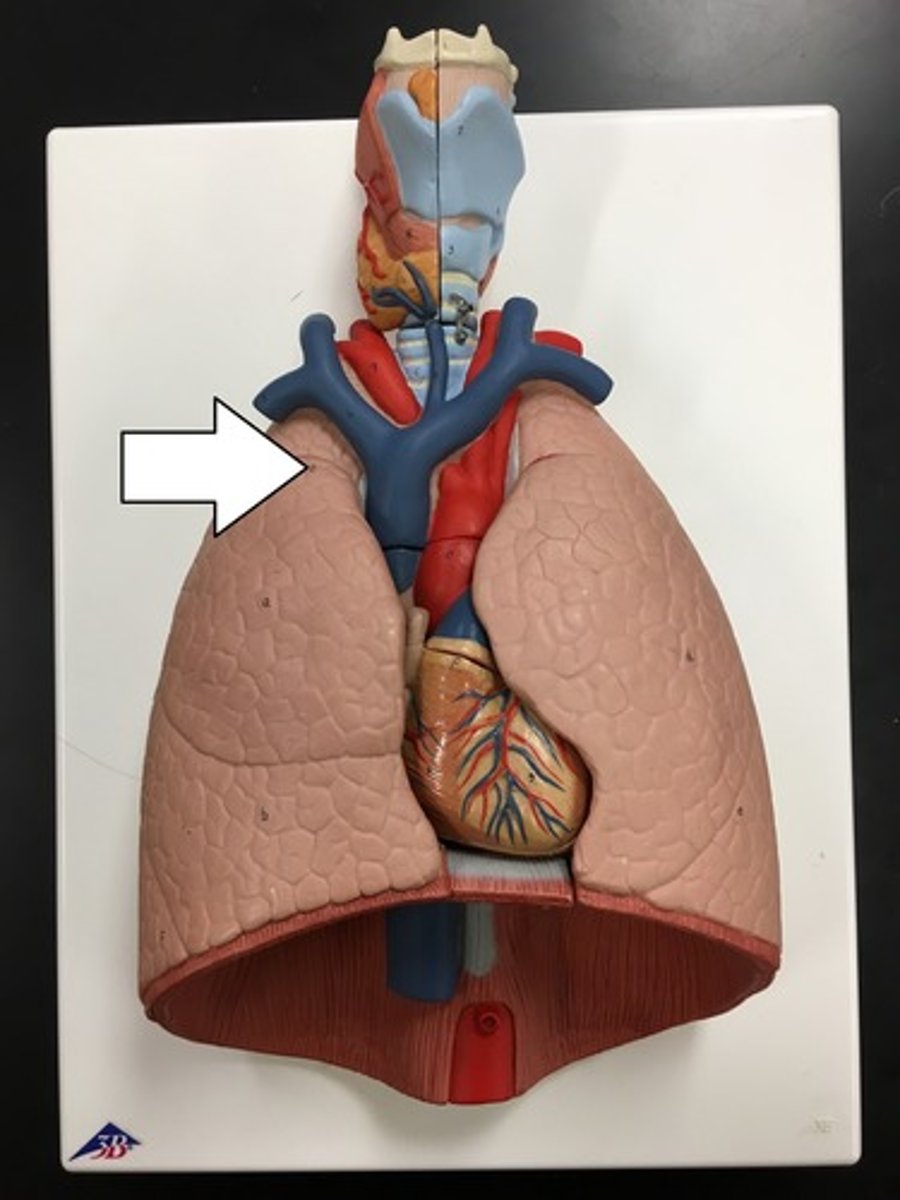
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing

Three lobes of the right lung
superior: The topmost lobe, located near the clavicle.
middle: Located beneath the upper lobe and above the lower lobe.
inferior: The bottom lobe, located near the diaphragm.
Two lobes of the left lung
Upper lobe - The top lobe, located near the clavicle.
Lower lobe - The bottom lobe, located near the diaphragm.
Why is there asymmetry between right and left lungs?
The asymmetry is due to the fact that the heart and most of the great vessels project into the left half of the thoracic cavity.
cardiac notch
a concave space on the left lung in which the heart lies.
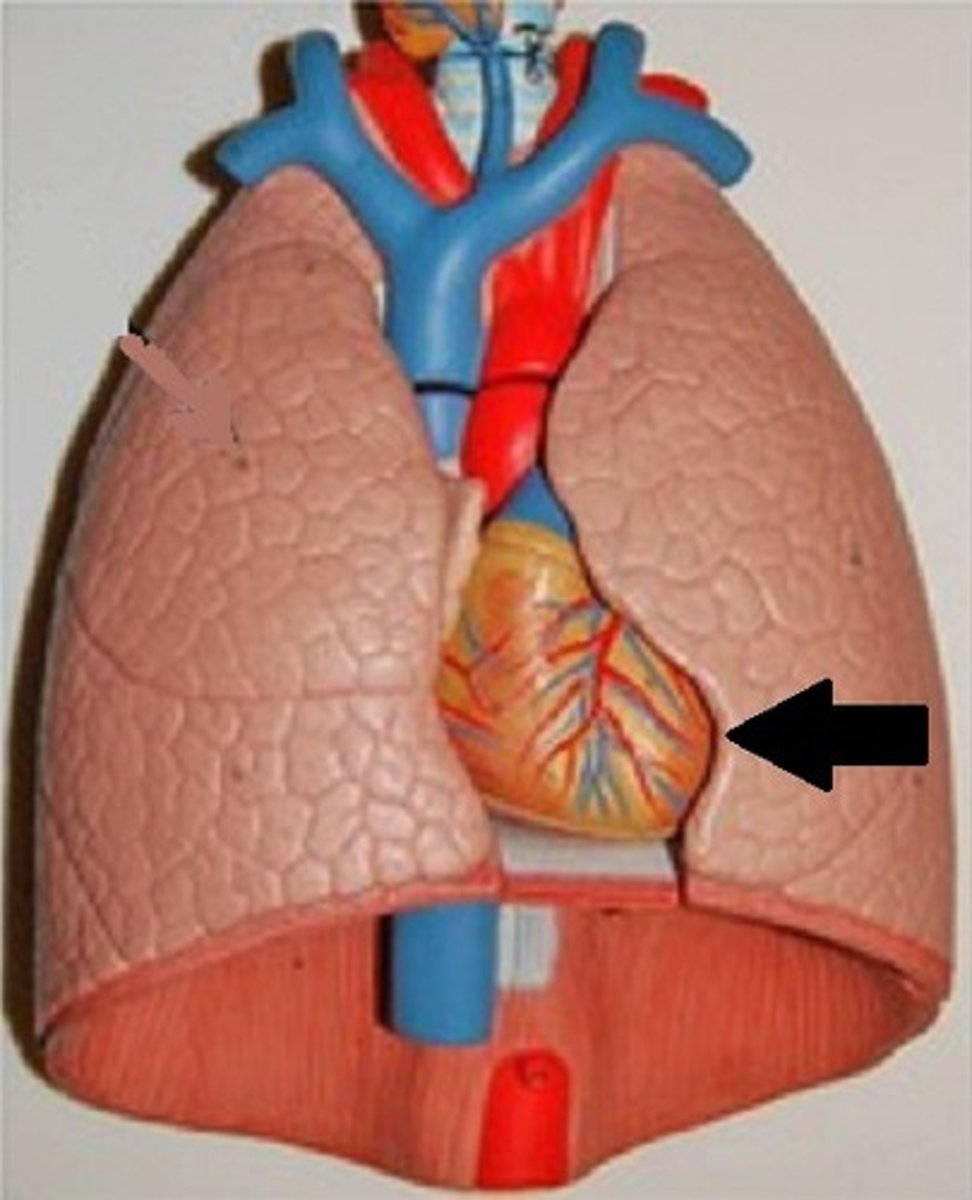
visceral pleura
the inner layer of pleura that surrounds each lung.
parietal pleura
lines the inside of the thoracic cavity
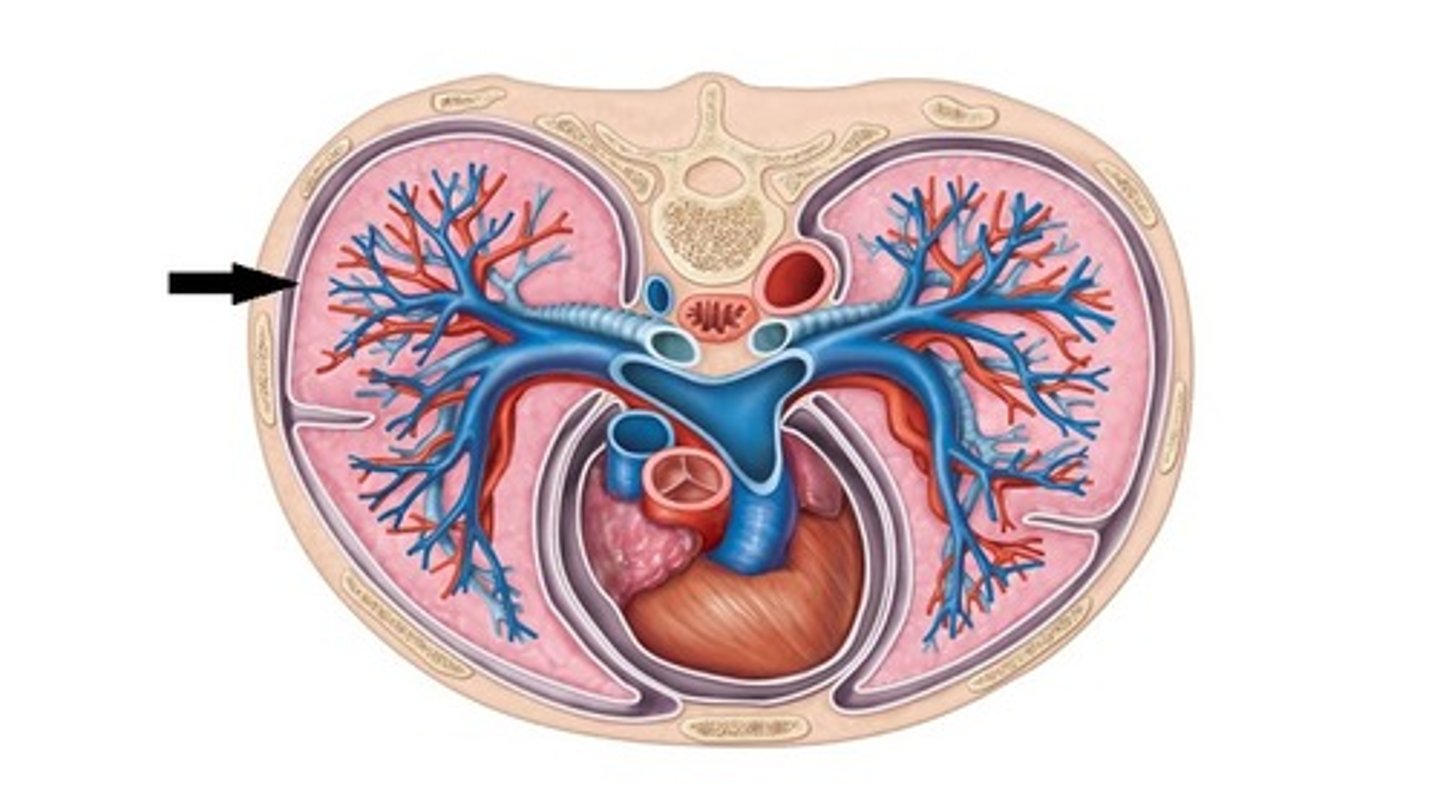
lobar bronchi
The right lung has three lobar bronchi (one for each lobe), while the left lung has two lobar bronchi (one for each lobe). They are responsible for directing air into the individual lobes of the lungs.
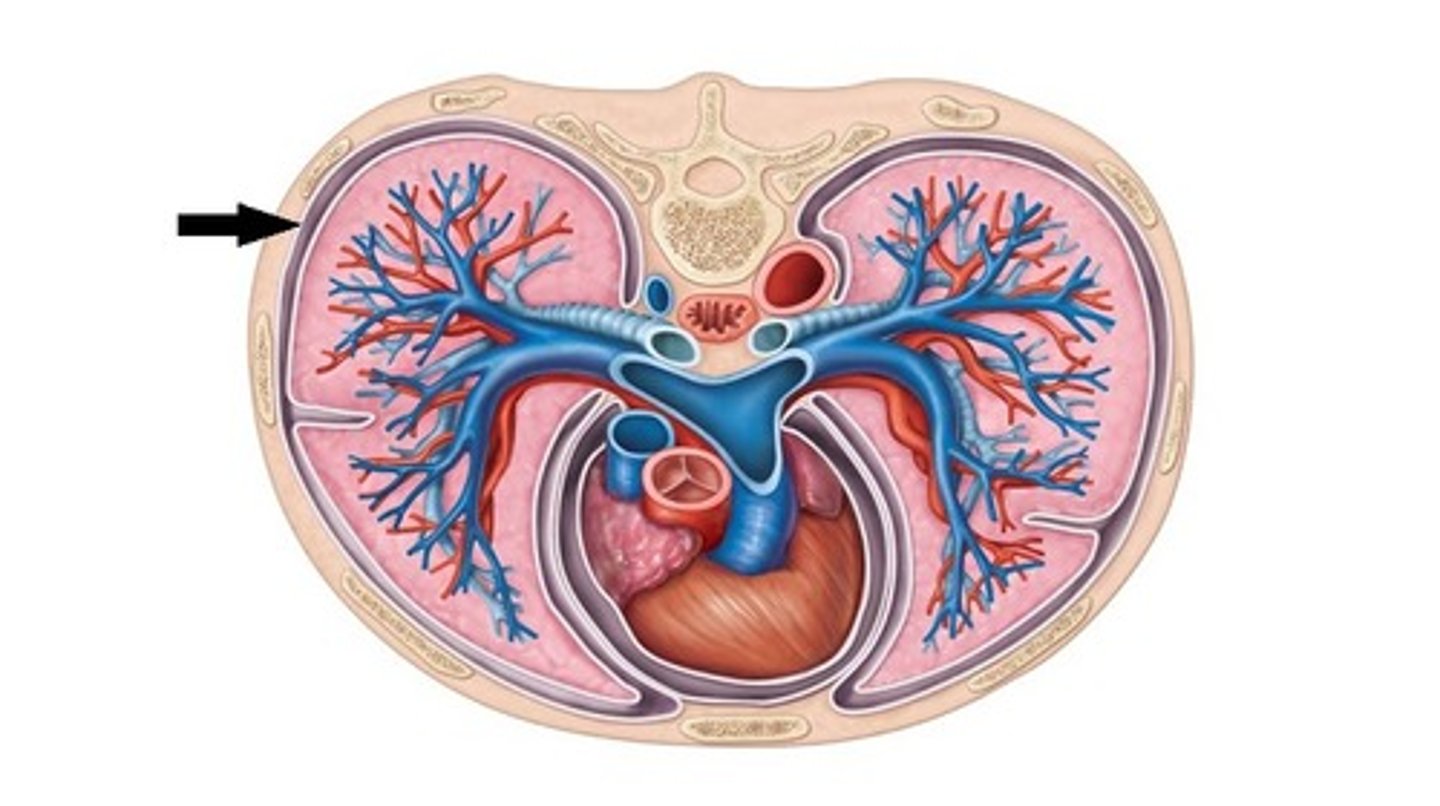
segmental bronchi
The smaller branches of the lobar bronchi that further divide to supply air to distinct lung segments.
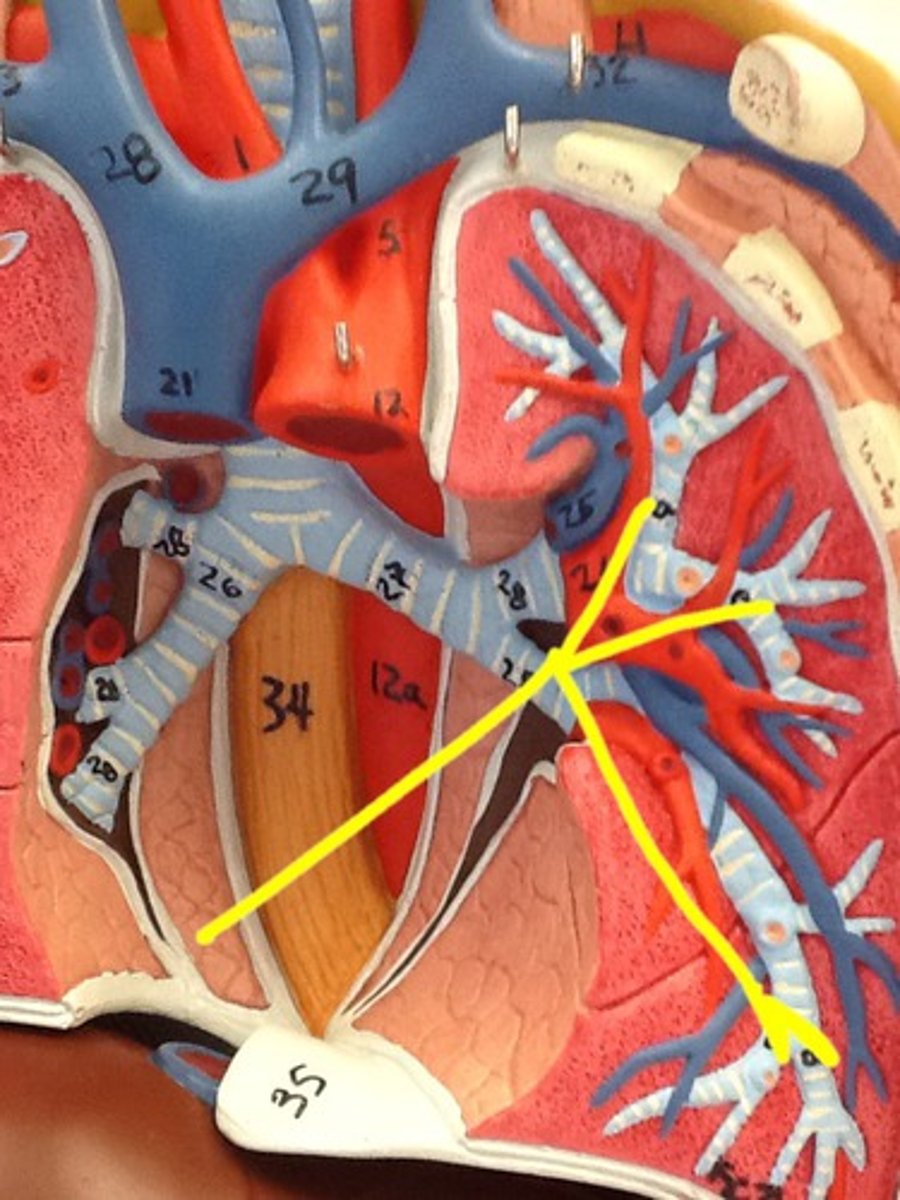
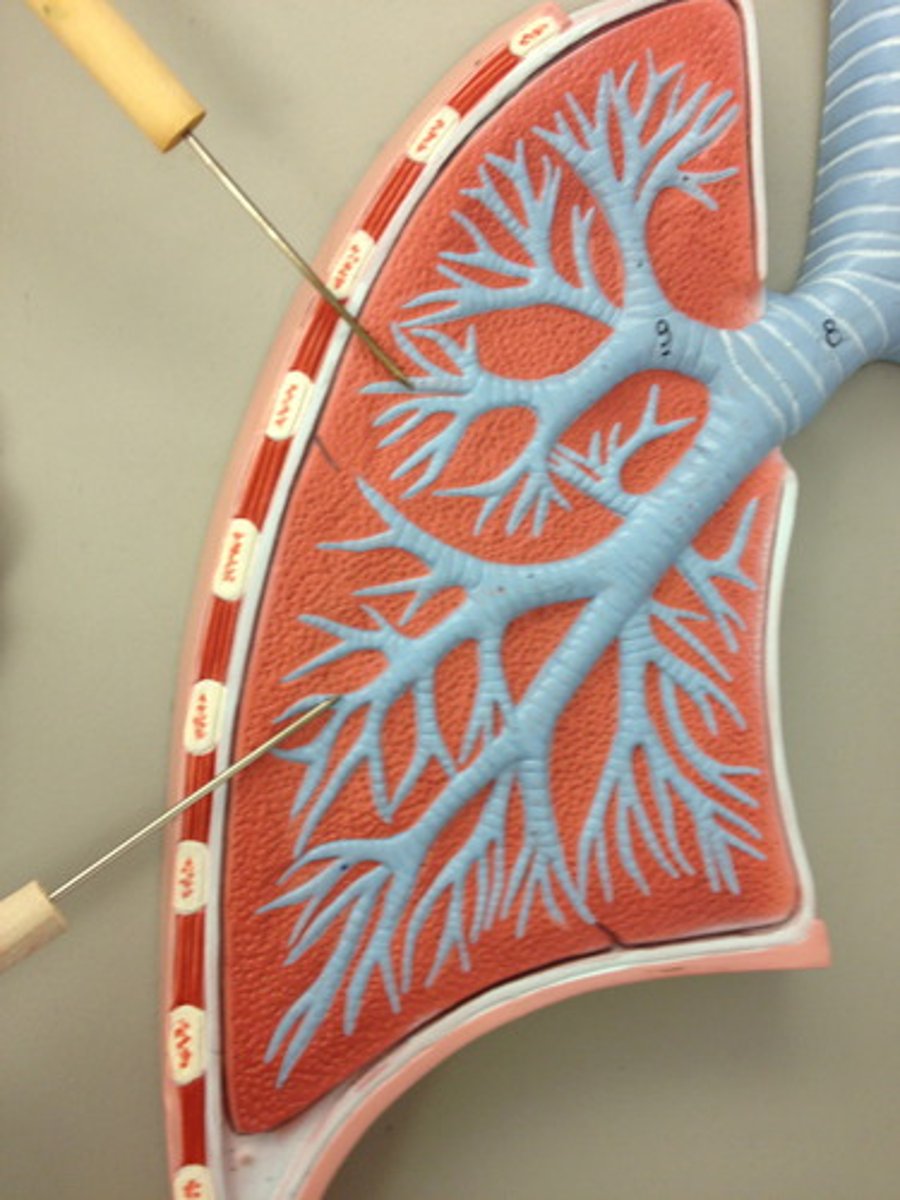
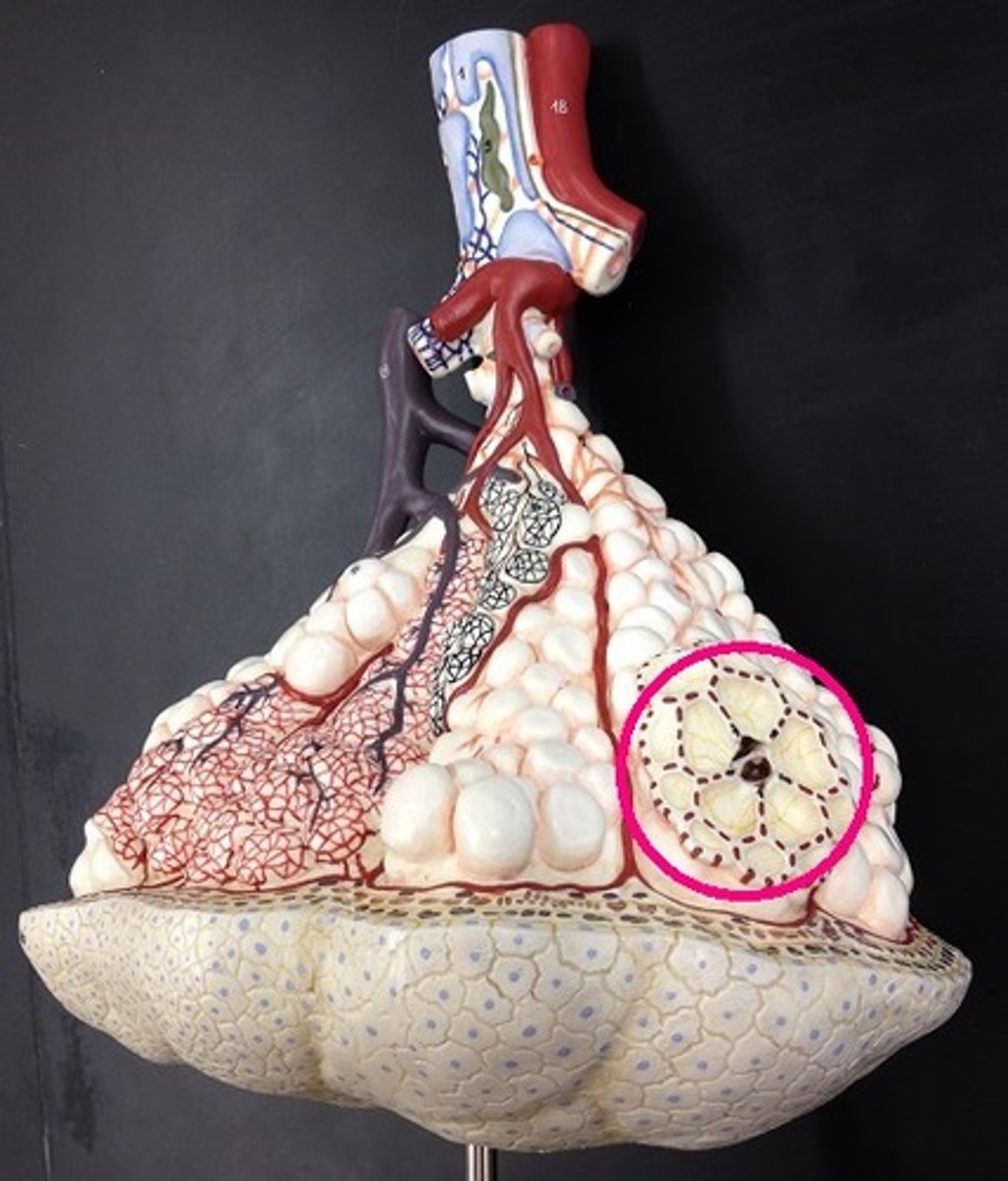
Bronchioles
Smallest branches of the bronchi. tubes that completely lack cartilage and less than 1mm in diameter.
respiratory mucosa
mucus-covered membrane that lines the tubes of the respiratory tract.
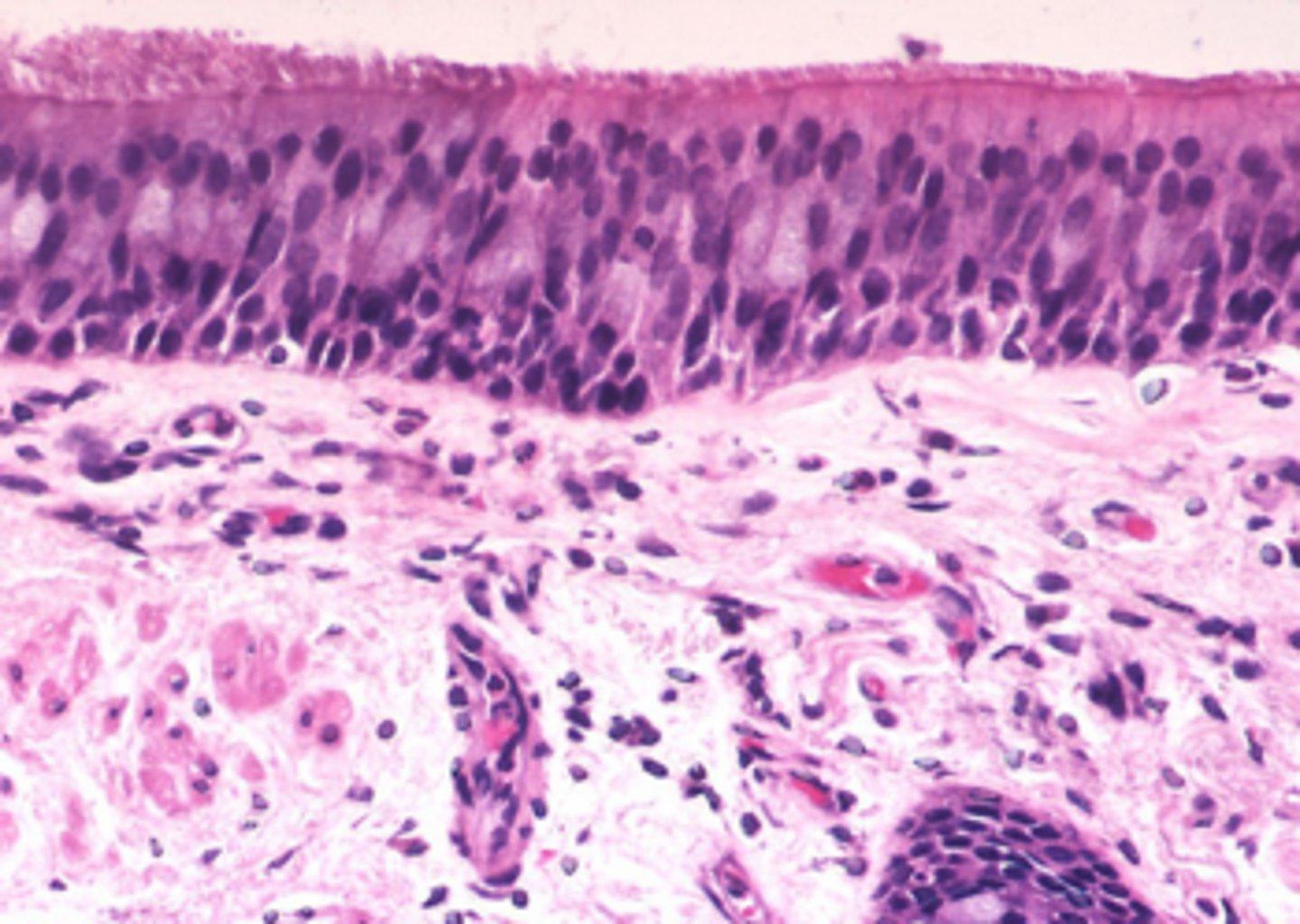
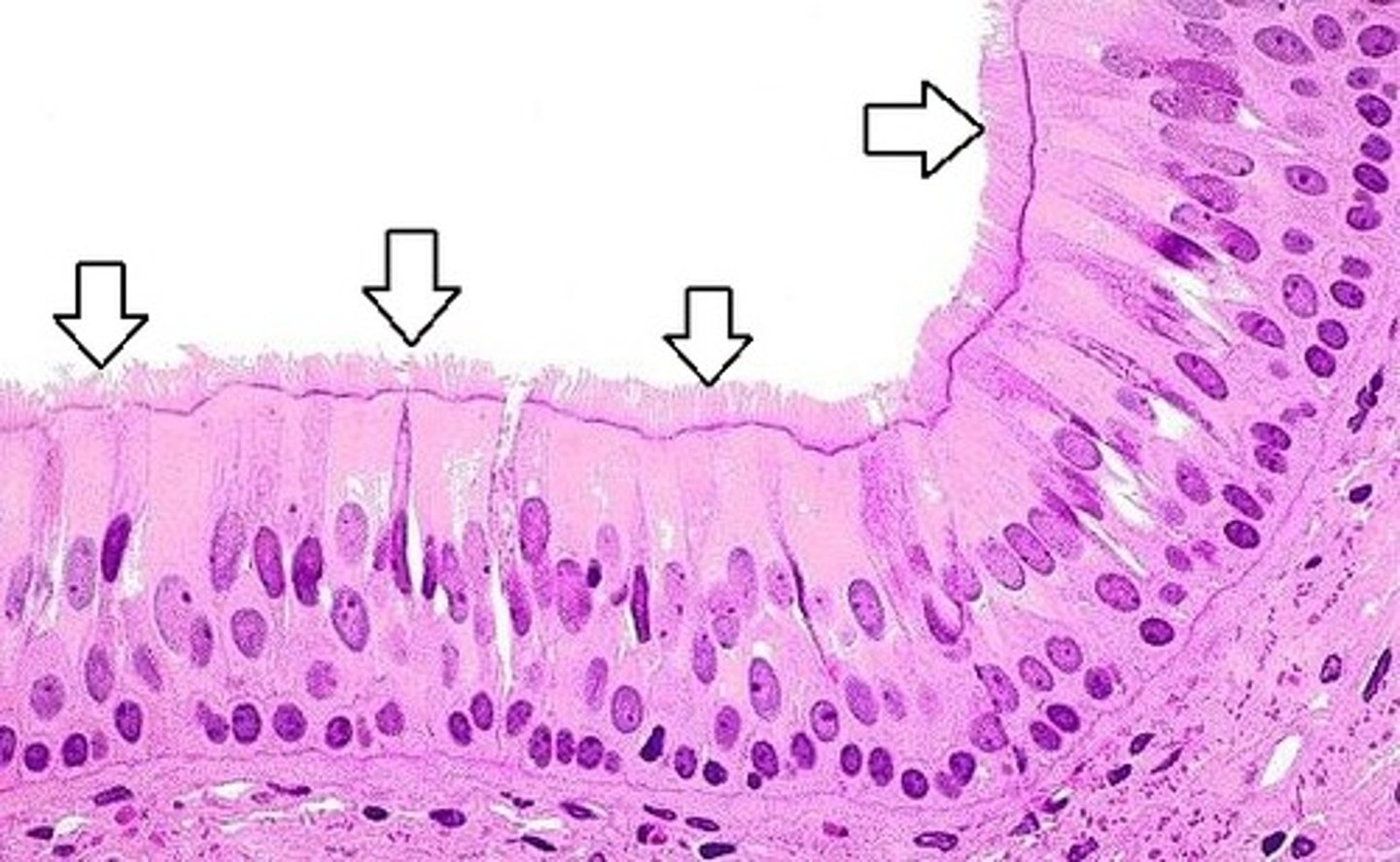
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
lines the respiratory tract, such as the trachea and bronchi.; secretes or absorbs substances (goblet cells)
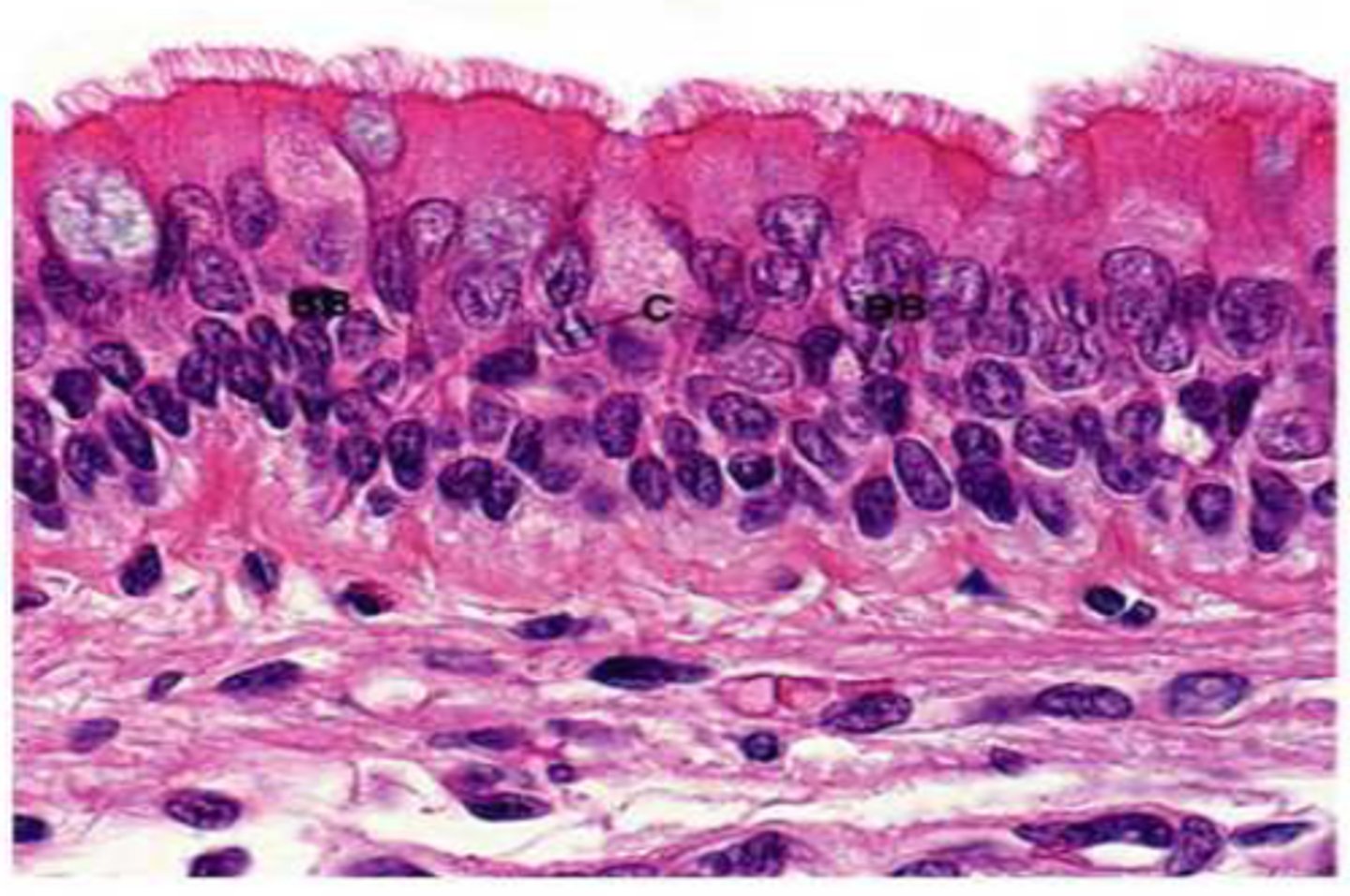
Cilia
Hairlike particles that help move mucus and trapped particles out of the airways, aiding in cleaning and protecting the respiratory system.
alveoli
Terminal air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs.
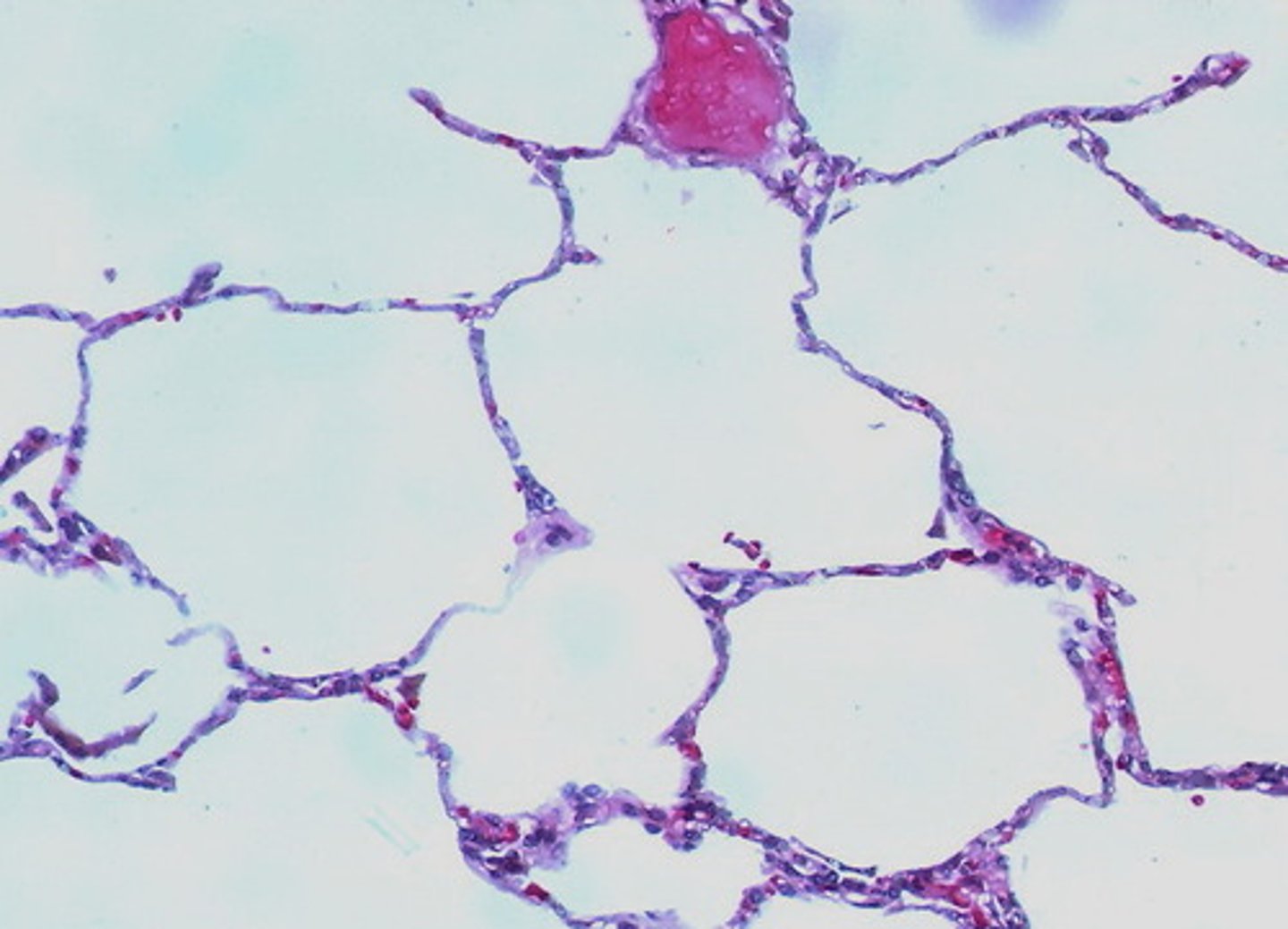
alveolar sacs
Clusters of tiny air-filled pouches at the end of the respiratory bronchioles, made up of multiple alveoli.
what are the functions of the paranasal sinuses?
the sinuses secrete mucus, lighten the skull, and provide resonance for one's voice.
Smoking can cause an increase in mucus production and a decrease in cilia function. Explain why this combination can be so detrimental to one's health
Without the cilia, becomes difficult to move the excess mucus superiorly to the pharynx where it can be swallowed. Pathogens can accumulate in the mucus and chronic infections may result.
Why is the epithelium lining the nasopharynx different from the epithelium that lines the oropharynx and laryngopharynx?
Because the nasopharynx is not a passageway for food/drink and thus lacks the need for the protection provided by stratified squamous epithelium.
What makes epiglottis (inflammation of the epiglottis) an extremely dangerous condition?
It can cover the airway and can be fatal.
If an individual were born with O-shaped tracheal cartilages, what activity would be quite difficult?
Swallowing because the esophagus could not expand anteriorly when trying to accommodate a large bolus of food.
What two structures are involved in routing food and liquid away from the respiratory passage?
soft palate/ uvula and the epiglottis.
Lois has an obstruction of her right main bronchus. How would this affect the carbon dioxide levels in her right pulmonary veins?
It would increase.
What occupies the dorsal groove between the two lungs?
Vertebral column, esophagus, descending thoracic aorta, azygos vein, intercostal a/v sympathetic trunk, thoracic duct, hemiazygos vein.