Cell-Cell Interactions and Communication in Biology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Cell-Cell Interactions
Communication and cooperation among cells.
Extracellular Layer
Structure beyond the plasma membrane.
Cell Walls
Provide structure and protection for cells.
Extracellular Matrix
Fiber composite providing structural support.
Tight Junctions
Form watertight seals between epithelial cells.
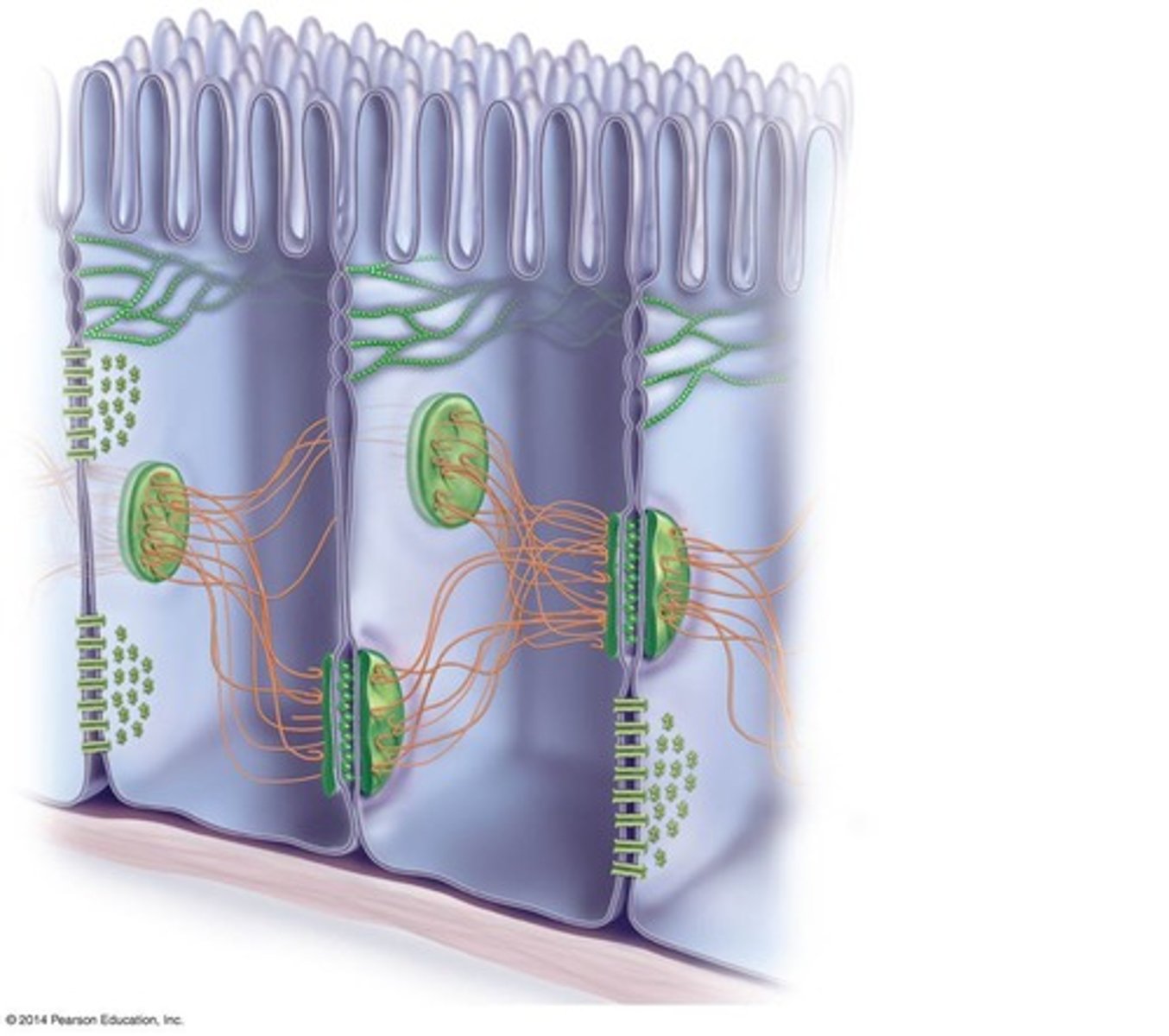
Desmosomes
Connect cytoskeletons of adjacent cells.
Gap Junctions
Channels allowing direct communication between cells.
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer controlling material flow.
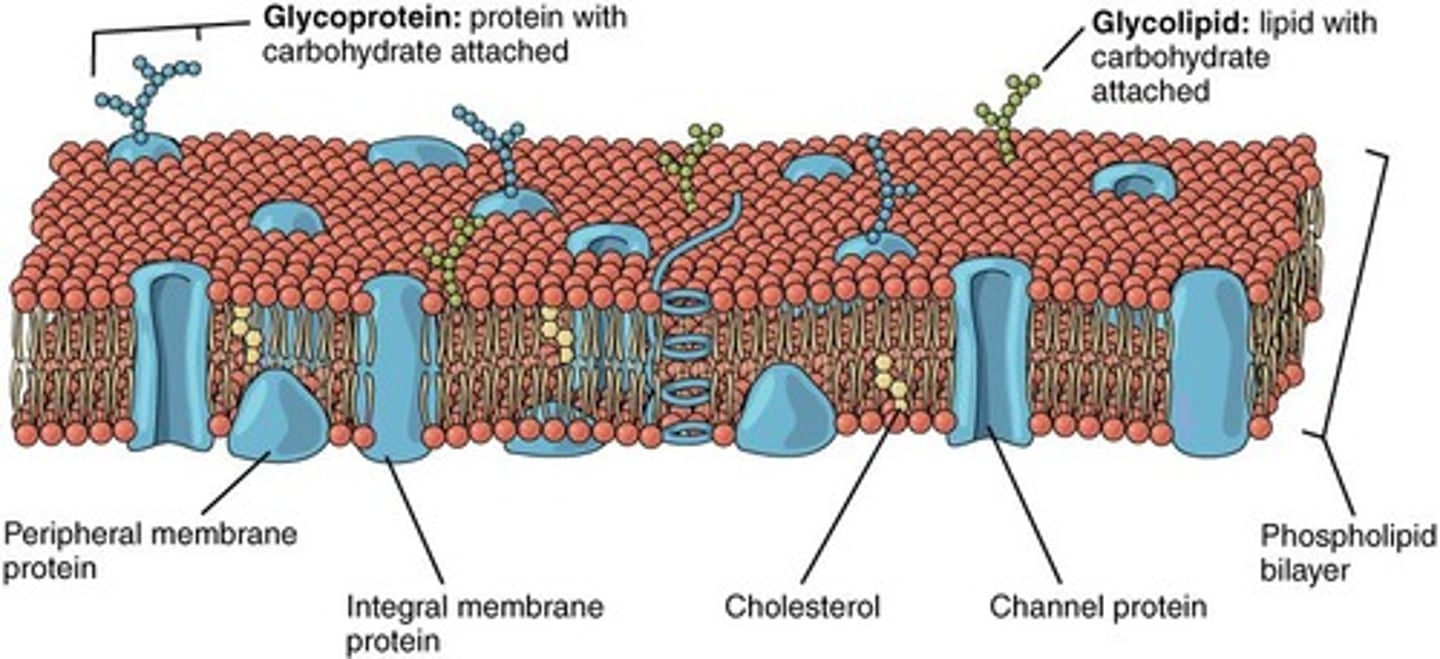
Integral Proteins
Proteins embedded within the plasma membrane.
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins attached to the membrane surface.
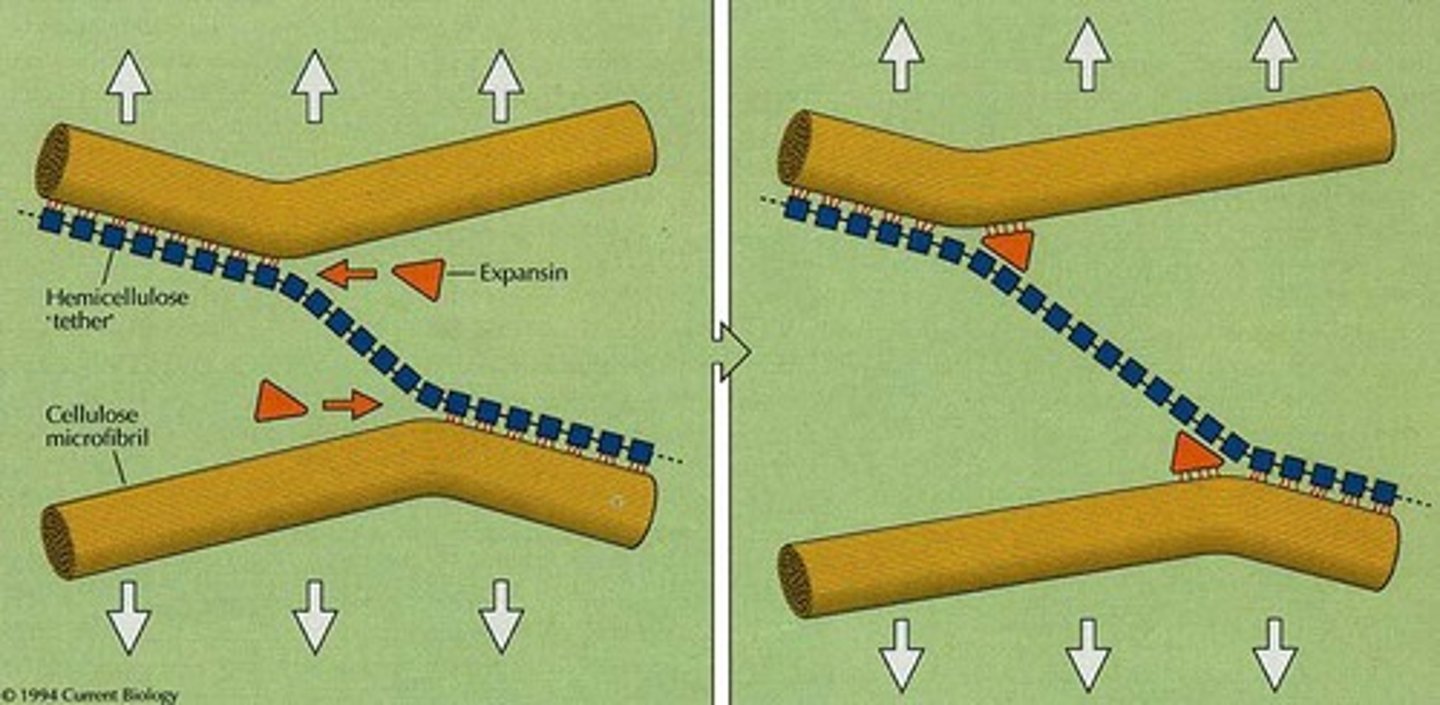
Turgor Pressure
Pressure from fluid in plant cells.
Expansins
Proteins that disrupt hydrogen bonds in cell walls.
Primary Cell Wall
First layer of plant cell structure.
Secondary Cell Wall
Layer secreted for additional support in specific cells.
Lignin
Rigid substance found in secondary cell walls.
Collagen
Main protein fiber in the extracellular matrix.
Proteoglycans
Gelatinous polysaccharides forming ECM ground substance.
Cytoskeleton
Network providing structural support within cells.
Integrins
Proteins linking cytoskeleton to extracellular matrix.
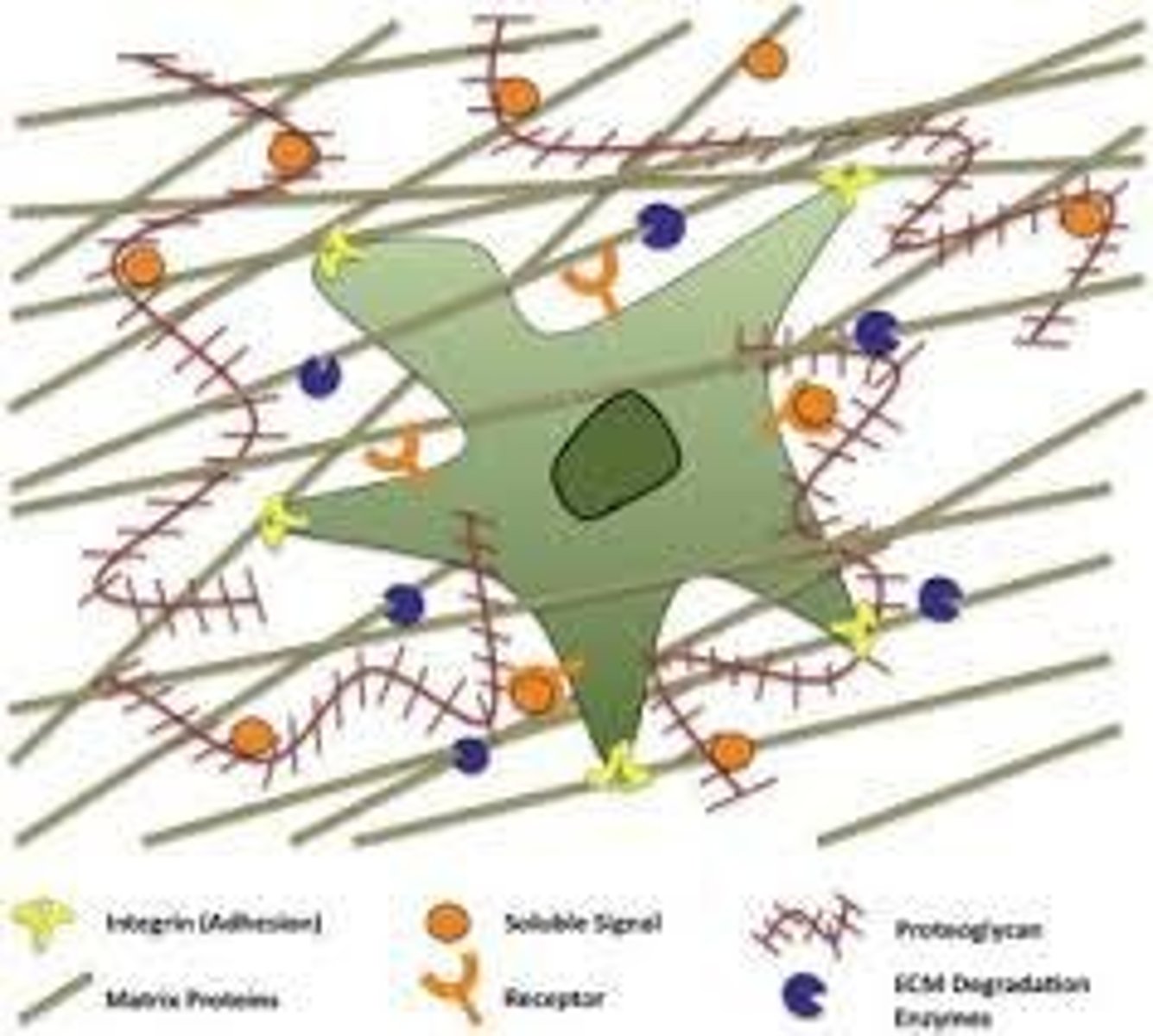
Middle Lamella
Layer gluing adjacent plant cells together.
Epithelial Tissue
Covers organs and lines body cavities.
Cell Communication
Essential for coordinated function in tissues.
Selective Adhesion
Specific attachment of cells via adhesion proteins.
Adhesion Proteins
Proteins that mediate cell-to-cell attachment.
Cadherins
Adhesion proteins involved in cell-cell adhesion.
Antibodies
Proteins that bind specifically to target molecules.
Signal Reception
Initial binding of hormones to signal receptors.
Signal Processing
Transduction of signals within the cell.
Signal Response
Cell's action following signal reception.
Signal Deactivation
Mechanisms to turn off cell signaling.
Hormones
Long-distance chemical messengers in the body.
Second Messengers
Small molecules amplifying hormone signals.
G Proteins
Membrane proteins activated by GTP.
Enzyme-Linked Receptors
Receptors that activate intracellular signaling pathways.
Phosphorylation Cascade
Series of phosphorylation events amplifying signals.
Crosstalk
Interaction between different signaling pathways.
Quorum Sensing
Bacterial communication based on population density.
Signal Amplification
Increasing signal strength through second messengers.
Phosphatases
Enzymes that remove phosphate groups from proteins.
Cell-Cell Signaling Steps
Four stages: reception, processing, response, deactivation.
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK)
A type of enzyme-linked receptor for signaling.
Intracellular Signaling Molecules
Molecules that relay signals within the cell.
Lipid-Insoluble Signaling
Signaling involving molecules that cannot cross membranes.
Target Genes
Genes affected by signaling pathways.
Cell Adhesion
Process by which cells attach to each other.
Signal Receptors
Proteins that bind signaling molecules.
Hormonal Effects
Diverse physiological responses triggered by hormones.
Microbial Biofilms
Communities of microbes adhering to surfaces.
Slug-like Body
Aggregated cells in slime molds for movement.