Part 4: Brain & Forebrain
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 3 dips of the dura mater?
falx cerebri
tentorium cerebelli
falx cerebelli
term. falx cerebri
def. the dip of the dura mater into the longitudinal fissure
term. tentorium cerebelli
def. the dip in the dura mater in to the transverse fissue
term. falx cerebelli
def. dip of the dura mater between the two hemispheres of the cerebellum
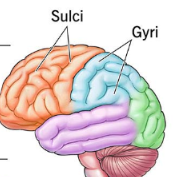
term. sulci
shallow grooves
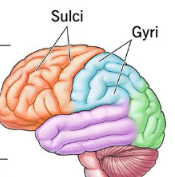
term. gyri
aka
def
aka. convolutions
def. folds between the grooves
Name all the fissures:
longitudinal
transverse
central
lateral (or Sylvian fissue)
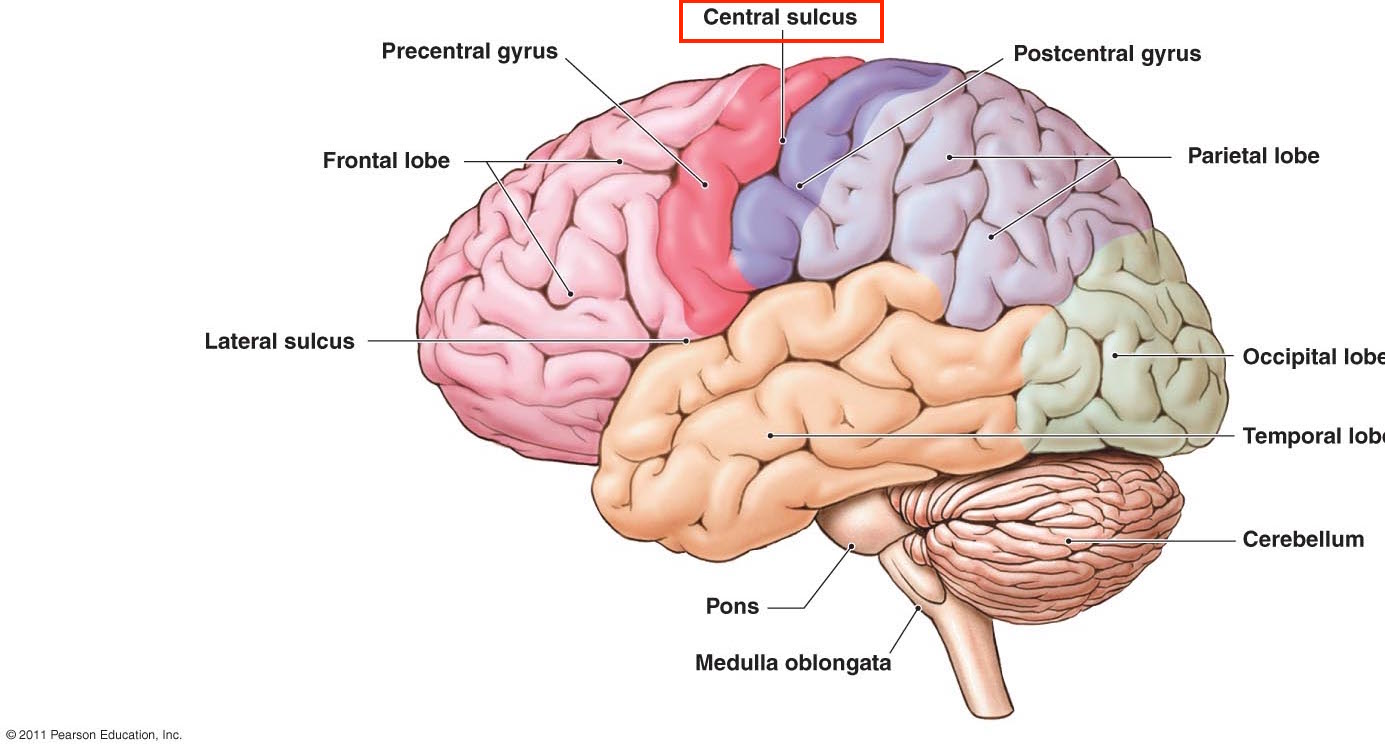
What do each of the following divide/ separate:
longitudinal
transverse
central
lateral (or Sylvian fissure)
longitudinal: R. Hemisphere | L. Hemisphere of cerebrum
transverse: Occipital lobe (cerebrum) | cerebellum
central: frontal lobe | parietal lobe
lateral (or Sylvian): Frontal & Parietal lobes | temporal lobe
Corpus callosum function
communication between the 2 hemispheres
Corpus callosum parts
Genu: anterior portion
Body/ trunk: main part
Splenium: posterior portion
Number of lobes in each cerebral hemisphere?
each hemisphere has the same 5 lobes:
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Occipital
Central (insula)
What is the largest part of the brain? IDK
Cerebrum
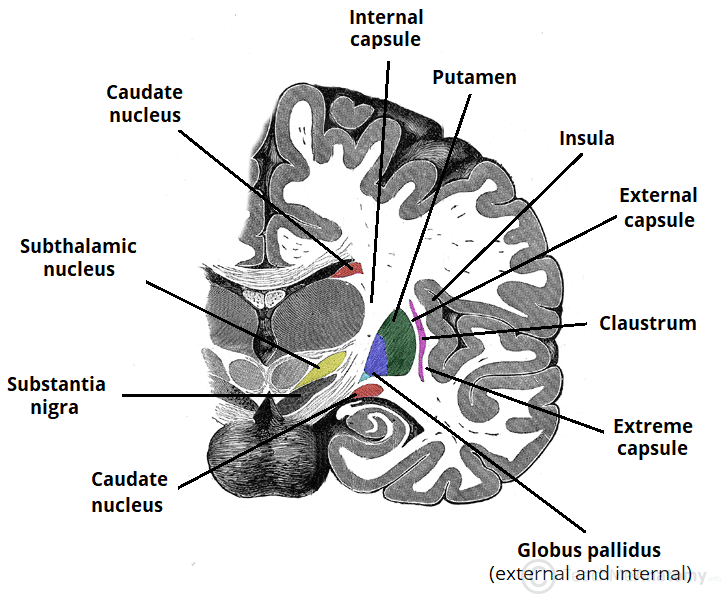
Which basal ganglion is C-shaped?
Caudate nucleus
What do each of the capsules in the basal ganglia separate?
Internal capsule: globus pallidus | thalamus. Composed of white matter.
External capsule: putamen |claustrum. Composed of white matter.
The pituitary gland is also know as:
“master gland”
the optic nerves cross over at the ___, forming the optic tracts which terminate at the ___
optic chiasma
thalamus
Function of the intermediate mass
a bridge of gray matter that connects parts of the thalamus
Name Basal Ganglia
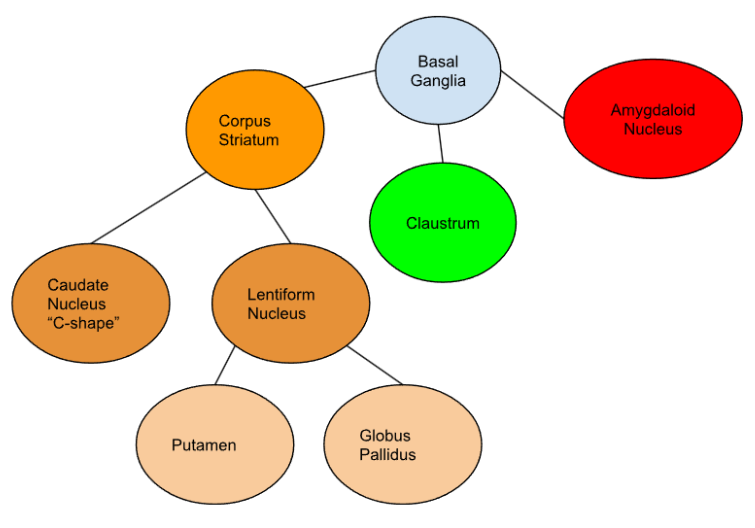
Location of each:
globus pallidus:
Putamen:
Claustrum:
globus pallidus: medially
Putamen: lateral to globus pallidus
Claustrum: lateral to putamen