Respiration biology a level aqa
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Describe the process of Glycolysis
1) Glucose is phosphorylated to make it more reactive, with the addition of 2 phosphate molecules which come from the hydrolysis of ATP. Lowers activation energy.
2) Splitting of phosphorylated glucose into two 3 carbon molecules of triose phosphate
3)Oxidation of triose phosphate, hydrogen is removed and transferred to NAD forming reduced NAD
4) Production of ATP, enzyme controlled reactions convert each triose phosphate molecules into 3-carbon pyruvate molecules, two molecules of atp produced.
Describe the process of the Link reaction
-Pyruvate is oxidised to form acetate, looses a carbon dioxide molecule and two hydrogens which are accepted by NAD to form reduced NAD
-2C acetate combines with coenzyme A to produce acetylcoenzyme A
Write the formula for the link reaction
Pyruvate + NAD + Coenzyme A→ Acetyl Coenzyme A + reduced NAD + CO2
What are the products of glycolysis?
2 ATP molecules, 2 pyruvate molecules, 2 reduced NAD molecules
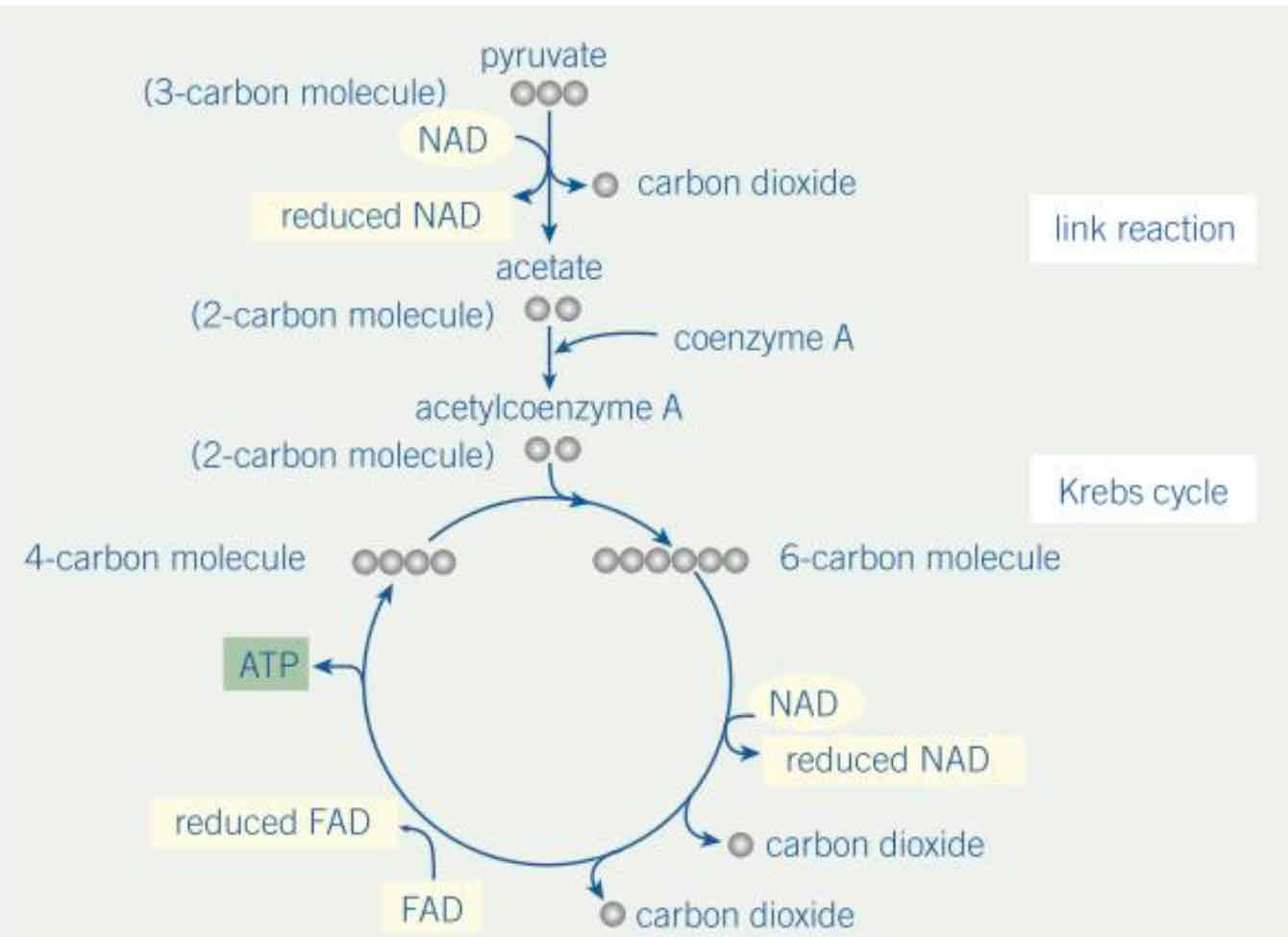
Describe the process of the Krebs Cycle
2 carbon acetylcoenzyme A combines with 4 carbon molecule to produce 6 carbon molecule
This molecule looses CO2 and hydrogen (accepted by NAD and FAD) to give a 4 carbon molecule and a single molecule of ATP due to substrate level phosphorylation
The 4 carbon molecule is combined with new molecule of acetylcoenzyme A
What are the products of the Krebs Cycle?
Reduced coenzymes NAD and FAD
One ATP molecule
3 CO2 molecules
What is the site of oxidative respiration?
Mitochondria
Describe the steps of oxidative phosphorylation (step 4 of aerobic respiration)
H atoms produced during glycolysis and Krebs combine with coenzymes FAD and NAD
Reduced NAD and FAD donate electrons of the H atoms they are carrying to first molecule in electron transfer chain
Electrons pass along chain of electron transfer carriers in a series of oxidation reduction reactions. The energy released from this is used to actively transport protons into the inter membranal space of mitochondria.
protons accumulate and concentration gradient formed, they then diffuse back into mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase channels
Electrons then combine with these protons and oxygen to form water. Oxygen is therefore the final acceptor of the transport chain.
What are two alternative respiratory substrates?
Lipids and proteins
How are lipids used for respiration?
hydrolysed to glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol phosphorylated and converted to triose phosphate
The fatty acid component is broken down into 2 carbon fragments which are converted to acetyl coenzyme A. Enters Krebs cycle
Oxidation of lipids produces 2 carbon fragments of carbohydrates and H atoms
Hydrogen atoms used to produce ATP in oxidative phosphorylation. Produced more than double mass of carbohydrate
Describe the respiration of proteins
First hydrolysed into amino acids
their amino groups are removed (deamination) before entering the respiratory pathway at different points
3-carbon compounds converted to pyruvate
4 and 5 carbon molecules converted to intermediates in the Krebs cycle
Why can’t the Krebs cycle or the electron transfer chain continue in the absence of oxygen?
Because FAD and NAD are reduced and can’t take up the H+ produced during the Krebs cycle.
How are the products of pyruvate and hydrogen removed in anaerobic respiration?
Hydrogen is released from the reduced NAD in order to regenerate NAD, each hydrogen molecule is taken up by pyruvate to produce lactate. Pyruvate+ reduced NAD———→ lactate + oxidized NAD