Biotechnology and Evolution
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 4 Bio 1011
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
DNA Sequencing
Based on DNA replication, basis of sequencing is Dideoxy sequencing, RNA sequencing in cancer
SNP
single nucleotide polymorphism
Types of SNPs
Could be in coding region or in promoter (noncoding region)
GWAS
Genome Wide Association Studies (look for genes that have small effects)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Make many replicates, primer has to sit so 3’ end is next to sequence we want to amplify so it copies it. Number of copies you can get is 2n , cycle n product
PCR Steps
Denaturing (heat), opens DNA
Anneal, primers bind
Add DNA polymerase (use polymerase from a bacteria found in a hot spring in Yellowstone)
Need bacterial DNA polymerase
Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes are isolated from bacteria, they cut specific DNA sequences. Often create sticky ends
Sticky ends
crooked cut, not straight
Non sticky ends
Straight cut
Plasmids/Vectors
Isolate gene of interest
Put gene into a plasmid/vector
Use restriction enzymes to specifically cut DNA\
Use the plasmid/vector to insert gene somewhere
Often another cell or organism
GMO (Genetically modified organisms)
Added a gene to rice to make it make more vitamin A, used to produce drugs
Bacteriophage
Virus that infects bacteria
CRISPR - Cas (Clustered Regularly Interspersed Short Palindromic Repeat)
Gene editing, genome editing
CRISPR RNA
matches virus target, will bring system to viral DNA to match
Cas 9
Protein/enzyme that cuts DNA that is complementary to crRNA, they work as endonucleases
Cells try to fix cut ends and use two repair mechanisms:
Merge unstable ends, just put them back together: results in deletions/insertions frameshift mutations, loss of function
Use a template for homology directed repair: Add a template that has the required sequence, recombination with good DNA and cut DNA, create new sequences you want, repair
Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
frequent insertion or deletion mutations
Homology directed repair (HDR)
Recombination with DNA carrying engineered gene. Precise insertion at target locus.
Evolution
Source of genetic diversity. Change in allele/genotype frequencies in a population from one generation to the next.
Population Genetics
Study the origin, amount, and effects on genetic variation in natural populations. How it changes over time and through generations
Population Genetics is the effects of:
Mutation in creating variation, recombination in shuffling variation, mating patterns, genetic drift, migration and gene flow, natural selection.
Species
Individuals that can exchange genetic material through interbreeding
Population
Interbreeding groups of organisms of the same species living in the same area
Fixed Alleles
Population has only 1 allele at a particular gene
Gene Pool
All the alleles present in all the individuals in a population
p
frequency (%) of dominant allele in population
q
frequency (%) of recessive allele in population
If Hary-Weinberg Equations do not work from one generation to the next then…..
Evolution is occurring
Nonrandom Mating
For Hardy-Weinberg equations to hold, gametes must be picked from the gener pool at random and paired to create offspring
Mating is not always random
Some plants can self-fertilize
INdividuals living closer together may be more likely to combine gametes
INbreeding
Assortive mating - choosing a mate based on their characteristics
Interbreeding Depression
Occurs when closely related individuals mate together so rare, deleterious alleles can increase in frequency. This results in less fit populations
Sexual Selection
Intersexual selection: mate choice
Intrasexual selection: where individuals of the same sex compete with one another to obtain mates
Genetic Drift
change in allele frequencies due to chance (sampling error). It causes allele frequencies to drift up and down randomly over time)
Mutation
Although most evolutionary mechanisms reduce genetic diversity, mutation restores genetic diversity and creates new alleles. Because errors are inevitable, mutation is always adding new alleles into populations at all gene loci.
Adaptation
a heritable trait that increases an individual’s fitness in a particular environment relative to individuals lacking that trait.
Fitness
ability to produce offspring relative to ability of other individuals in the population
Evolution General Definition
the generally based change in a population’s traits over time
Natural Selection (Darwin’s Definition)
Variation exists among individual organisms that make up a population
Some of the trait differences are heritable
Some individuals survive and reproduce better than other individuals
The subset of individuals that survive best and produce the most offspring is not a random sample of the population. Differential survival and reproduction (darwin fitness) is influenced by the heritable traits of individuals.
Natural Selection
occurs when individuals with certain heritable phenotypes survive and reproduce better than others. The alleles responsible for the increased reproduction then increase in frequency.
Sticky Ends Definition
The unpaired nucleotides produced by the action of restriction enzymes are referred to as______ because they will “stick” to a complementary single-stranded sequence
In order to insert a human gene into a plasmid, both must_________
be cut by the same restriction enzyme, doing so will result in the formation of complementary sticky ends
What enzyme forms covalent bonds between restriction fragments?
DNA ligase
Gel Electrophoresis of DNA
The shorter the DNA molecule, the farther it moves. An electrical current is generated across the gel
IN gel electrophoresis DNA molecules migrate from _____ to ____ ends of the gel
negative to positive
Information the can be obtained from the sequence of a gene:
Effects of mutation on gene function
Amino Acid sequence of the protein
Relationship between two species
What is the polymerase chain reaction?
A method to amplify a fragment of DNA. Makes many copies of a single DNA fragment.
True or false? Comparison of the sequences of the same gene across species can give some insight into the existence of a common ancestor with that gene.
True
True or false? The Taq enzyme is a type of DNA polymerase that allows researchers to separate the DNA strands during the annealing step of the PCR cycle without destroying the polymerase.
False, Taq polymerase is used for the denaturing step of PCR as it was derived from a species of bacteria living in hot springs
How many DNA molecules would there be after four rounds of PCR if the initial reaction mixture contained two molecules?
Thirty-two DNA molecules are produced if two molecules are doubled four times.. (24+24=32)
During which step in the PCR cycle are nucleotides used?
Nucleotides are used to synthesize the complementary strand to the DNA template during the extension step.
During which step in the PCR cycle do primers form bonds with a single-stranded template?
Primers form hydrogen bonds with the single-stranded DNA template during the annealing step
What accounts for the precision of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing?
The base-pairing between an extensive region of the sgRNA and the target DNA sequence. This extensive overlap allows CRISPR-Cas9 to be very selective in the region that it is able to excise and then replace.
In large-scale, genome-wide association studies in humans we look for ________.
SNPs where one allele is found more often in persons with a particular disorder than in healthy controls
Suppose that Gene B occurs in a sea turtle gene pool where the frequency of the B1 allele is 0.5 and the frequency of the B2 allele is 0.4.
What is the frequency of the B3 allele, assuming that there are only three alleles in the population?
The frequency of B3=0.1 because 0.5+0.4+?=1.
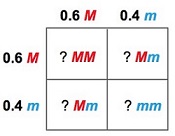
Examine this Punnett square. What does the number 0.6 refer to?
The numbers outside the Punnett square represent gametes and the allele frequencies are represented by p+q=1.
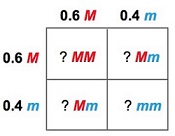
Use this Punnett square to calculate the predicted genotype frequencies of the offspring.
MM:p2=0.36 |
Mm:2pq=0.24+0.24=0.48 |
mm:q2=0.16 |