(Complete) ANA LE2 (6) The Immune System and Lymphoid Organs
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Based on 2029 Trans
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Which type of immune response involves physical barriers like skin, mucous membranes, cells like:
Granulocytes
Leukocytes
Tissue resident cells:
Macrophages
Follicular dendritic cells (in lymphoid organs)
Natural Killer Cells (NK cells)
Innate Immune
Which type of immune response is immediate, NON-specific, and has the same magnitude of response every time?
Innate Immune
Which type of immune response is delayed, SPECIFIC, magnitude increases with repeated exposure.
Adaptive Immune
Which Type of immune response involves B and T lymphocytes and the formation of Memory cells and Antigen-presenting cells (APCs)?
Adaptive
There are 2 types of Adaptive Immune Responses:
Humoral
Cell-mediated
Which is involved in the production of plasma cells that eventually produce antibodies such as IgA, IgE, IgM etc. ?
Humoral response
Which lymphocytes produce Plasma cells?
B lymphocytes
There are 2 types of Adaptive Immune Responses:
Humoral
Cell-mediated
Which is an MHC-restricted-response and involves T lymphocytes that eliminate the antigen?
Cell-mediated
Which cells ingest the pathogen and display the antigen fragments on their cell surface?
Macrophages (when displaying the antigen they become Antigen-presenting cells APCs)
What cells recognizes the Antigen being presented on the APCs?
T-helper cells!
When Macrophage APCs interact with the T-helper cells, what happens?
Macrophage releases Interleukin-1 (IL-1)
IL-1 tickles T-helper cells to produce IL-2
What does IL-2 do?
Triggers the proliferation of Cytotoxic T cells and B cells.
What do Cytotoxic T cells do?
Recognize the antigen being displayed on the surface of infected cells
Release chemicals to kill the infected cells
What are the 3 types of APCs found in different organs?
Macrophage
Dendritic Cells
Epithelial Reticular cells
What kind of APCs can be found in these organs?
Connective Tissue →
Lymphoid Organs →
Thymus →
Connective Tissue → macrophage
Lymphoid Organs → Dendritic cells
Thymus → Epithelial Reticular Cells
All APCs express which type of MHC class?
MHC Class 2
Lymphocytes are found in which type of immunity? (Innate or Adaptive)?
Adaptive Immune!
Where do lymphocytes originate from?
Bone Marrow.
Which lymphocytes Differentiate AND Mature in the bone marrow
B-cells
NK Cells (these are part of the Innate Immune sys. though)
Which lymphocytes originate from the bone marrow BUT MATURE in the thymus?
T LymphoBlasts
T or F. The T, B and NK cells are morphologically INDISTINGUISHABLE. They can only be differentiated through immunohistochemical methods.
True
AIDS virus infects which cells? and thus crippling the patient’s immune system.
Helper T cells
What are the 2 Primary Lymphoid Organs?
Bone Marrow
Thymus
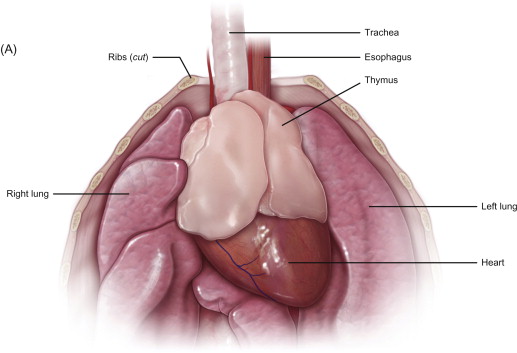
Where does Lymphocyte activation and proliferation occur?
Secondary Lymphoid Organs
Give the 3 Secondary lymphoid organs
Lymph Nodes
Spleen
Mucosa-associated lymph node tissues (MALT)
What is the primary lymphoid organ where precursor lymphoblasts orginate from?
Bone Marrow
What is the primary lymphoid organ where T cells mature and differentiate?
Thymus
How many lobes does the thymus have?
2 Lobes (Bi-lobed)
T or F? The THYMUS undergoes INVOLUTION at puberty and eventually becomes surrounded by FAT cells.
True
T or F? The THYMUS has a dual embryonic origin.
True!
T or F? The Thymus is ENcapsulated!
True
T or F? The Thymus’s Thymic Epithelium is Mesoderm derived while its Lymphocytes of Endoderm derived.
FALSE!
Thymic Epithelium → Endoderm derivative
Lymphocytes → Mesoderm derivative
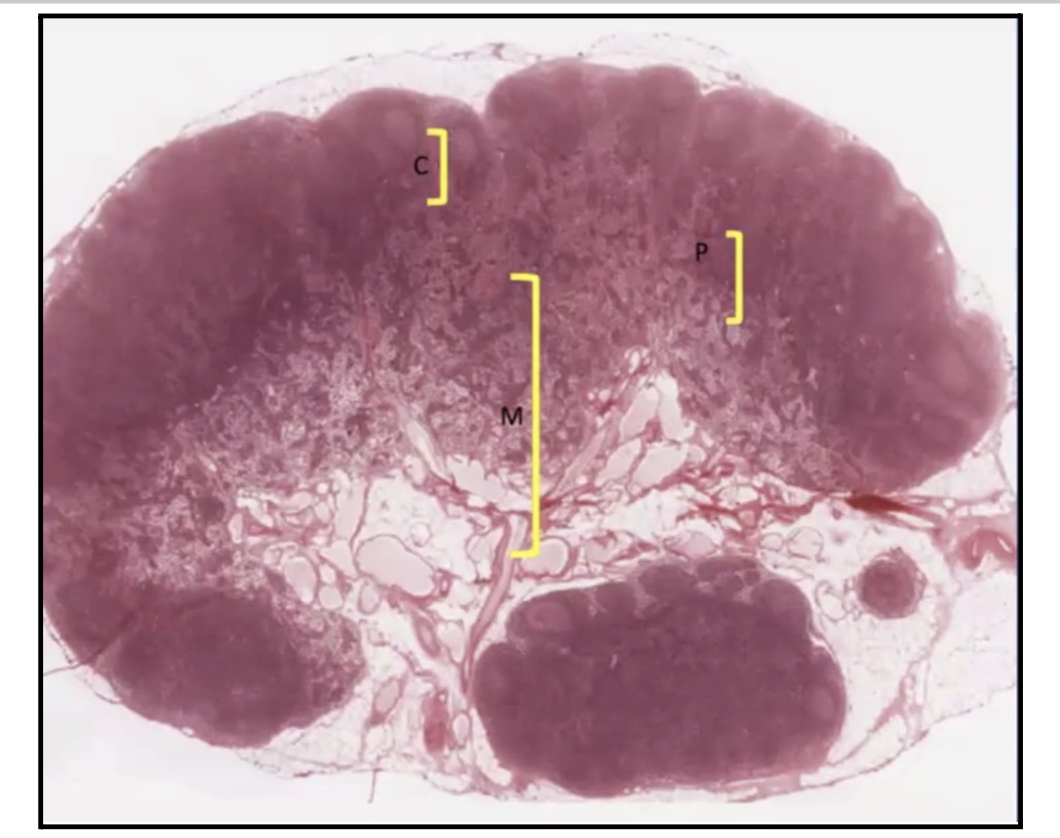
What are the 2 regions found in the Thymus?
Cortex and Medulla
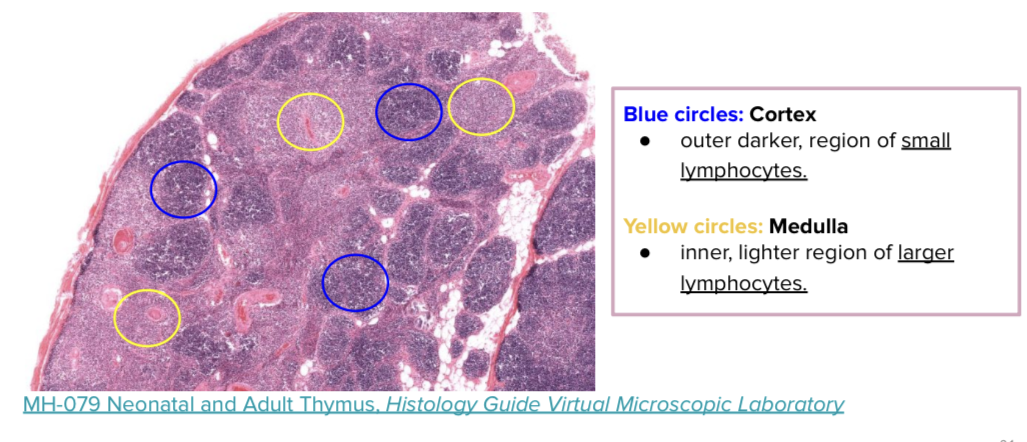
T or F? Lahat ng Primary Lymphoid organs walang Cortex and Medulla.
FALSE! May Cortex and Medulla yung Thymus
In the Thymus, where can you find T lymphoblasts and Mature T Lymphocytes?
Cortex → T LymphoBLASTS (immature) (darker region)
Medulla → Mature T lymphocytes (lighter region)
In which region of the Thymus can you find the Blood-thymus barrier?
Cortex!
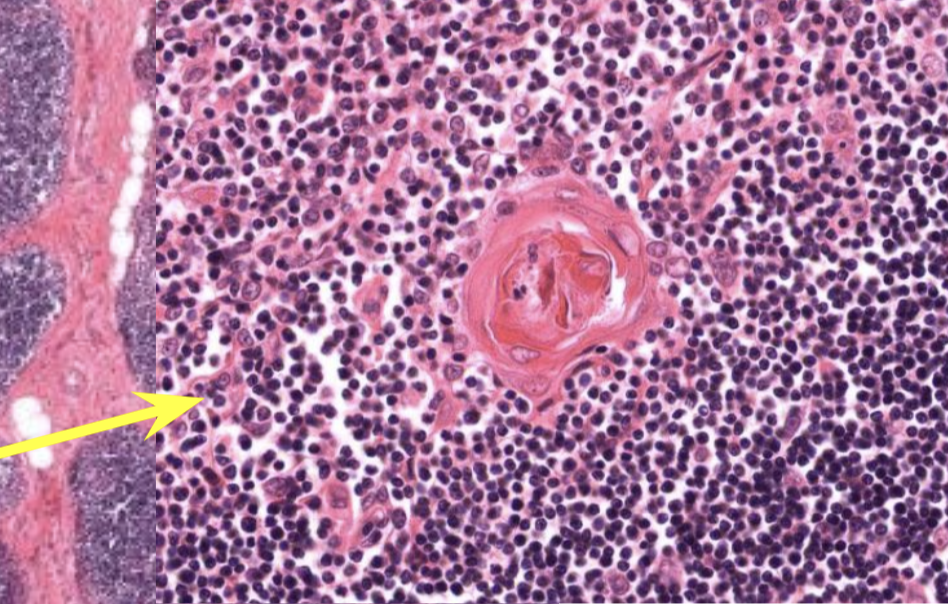
Which organ and where can you find Hassall Corpuscles?
Thymus! In the Medulla
Thymic Epithelium originates from the (Endoderm or Mesoderm?) of the embryo’s (?) pharyngeal pouch.
Thymic Epithelium
ENDODERM derivative
Embryo’s 3rd pharyngeal pouch
Embryonic Origin of Bone Marrow?
MESODERM = BONE MARROW
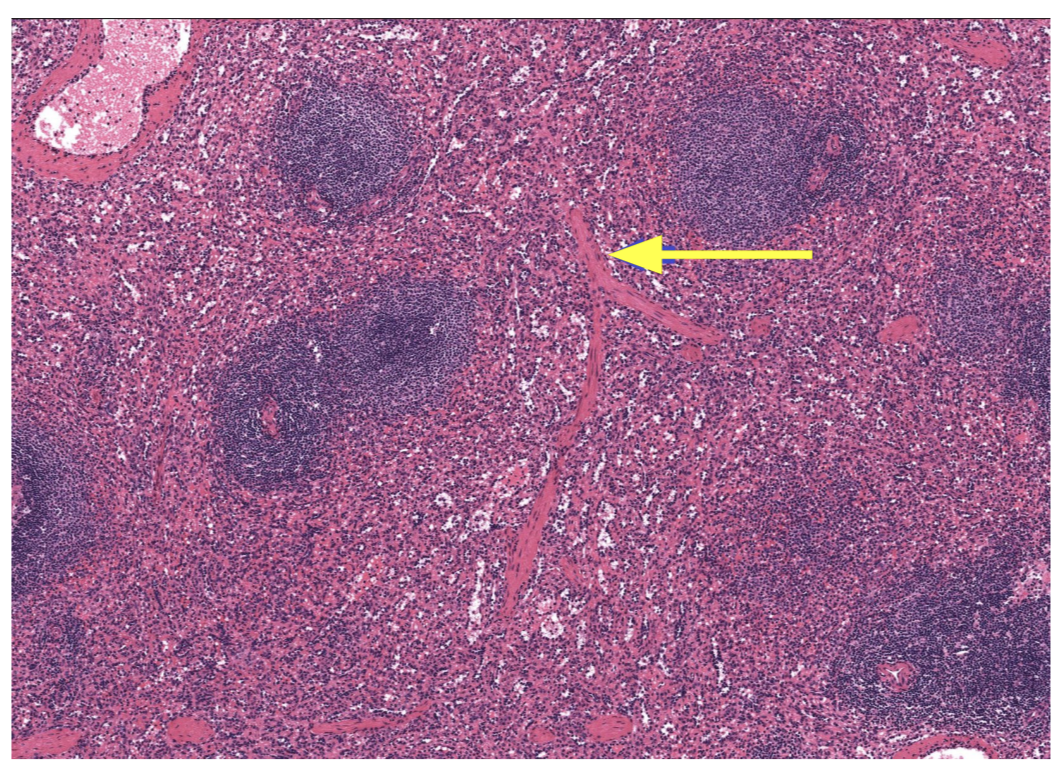
Which lymphoid organ is encapsulated with trabeculae dividing the organ into incompletely separated lobules.
The Thymus
Note: image shows Trabeculae
Role of Cortical Epithelial Cells of the Thymus?
Provide mechanical supporting framework for development of T Lymphoblasts
Promotes T cell differentiation and proliferation.
Forms sheets around the blood vessels to form the blood-thymus barrier
Role of the Blood-Thymus Barrier?
Prevent unregulated exposure of immature and developing T lymphoBLASTS from ANTIGENS in the blood.
The dark staining portion of the Thymus is the?
Cortex
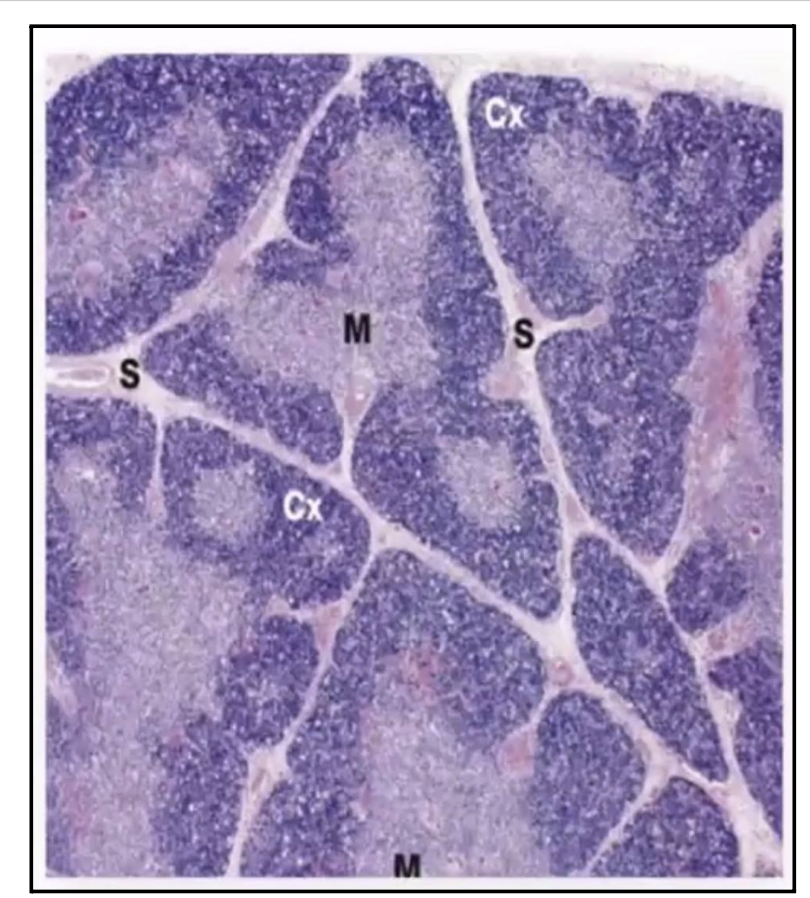
T or F, Hassall Corpuscles can be found in the Cortex of the Thymus
False. In the Medulla.
T or F? The Positive Selection or the First Stage of the selection process of T lymphoblasts occurs in the CORTEX checks to see if if can recognize and bind to MHC molecules.
True
The Negative Selection or the second stage of the selection process occurs in the ___ and checks if T lymphoblasts can recognizes SELF antigens.
If they do recognize self, they undergo apoptosis. (T or F)
Medulla
True
In the 2nd stage, the T lymphoblast does NOT recognize self and survives to complete maturation. What do they differentiate into?
T4 (T-helper cell) - Retains only CD 4 protein
T8 (Cytotoxic T Cell) - Retains only CD 8 protein
Lymphoid Nodules found in Secondary Lymphoid organs are made up of what cells?
B Lymphocytes
What is the main feature of Secondary Lymphoid organs?
Lymphoid Nodules
There are two types of Lymphoid Nodules.
Primary Lymphoid Nodules
Secondary Lymphoid Nodules
Which has a GERMINAL CENTER?
Secondary Lymphoid Nodule
There are two types of Lymphoid Nodules.
Primary Lymphoid Nodules
Secondary Lymphoid Nodules
Which one is at a resting state?
Primary Lymphoid Nodule
The Germinal Center of Secondary Lymphoid Nodules represent?
The active site of Lymphocyte proliferation.
Where ANTIGENS ARE BEING PRESENTED
T or F? The Mantle Zone contains small Naive Lymphocytes because the proliferation of activated B lymphocytes which PUSH the small lymphocytes aside to form an outer ring around the germinal center.
TRUE
T or F? The Mantle zone of the Germinal Center contains MATURE lymphocytes.
FALSE!!! Immature!!!
T or F. Lymphatic Vessels allow BIDIRECTIONAL FLOW
False. Unidirectional lang.
The (AFFERENT/EFFERENT) lymphatic vessels bring lymph towards the lymph nodes for filtering by penetrating the convex side of the lymph node.
Afferent!
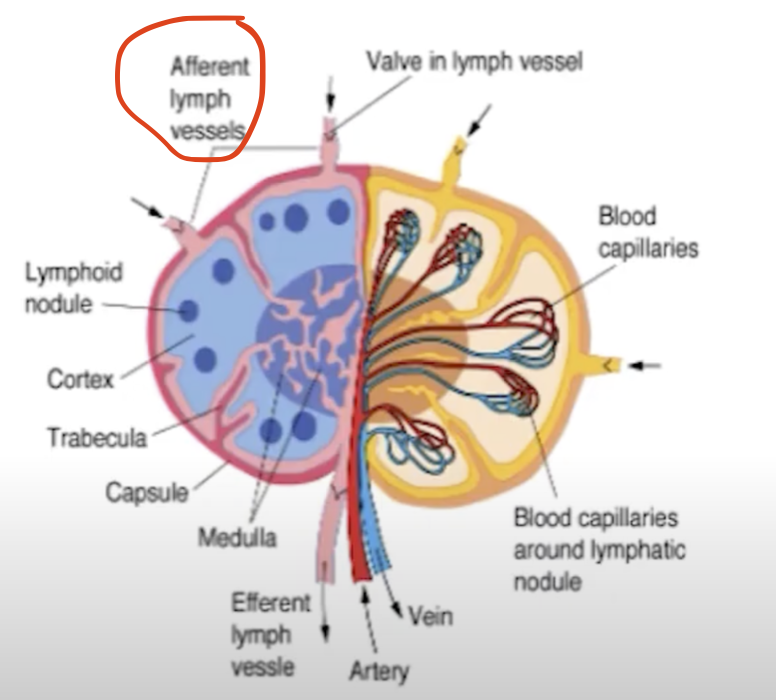
*****Pathway of Lymphatic Circulation?
Afferent LV
Subcapsular sinus
Trabecular/Cortical sinus
Medullary sinus
Efferent LV
*trace mo ung image!
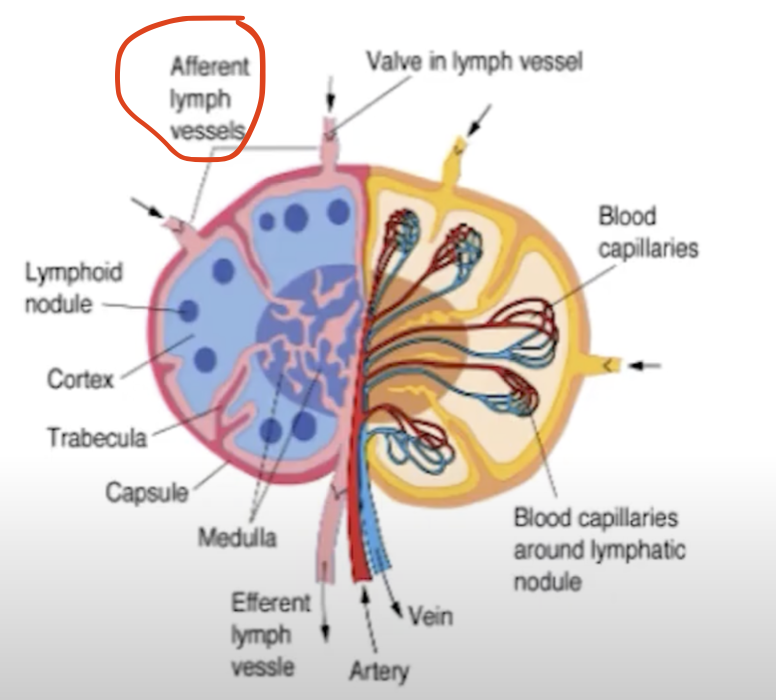
T or F? Lymphoid Nodules ALWAYS have germinal centers.
False. Only Secondary Lymphoid Nodules
Which organs are where Antigens presented to Immune Cells that trigger the development of Plasma Cells?
Lymph Nodes
What can cells can be abundantly found in the tissue of the Lymph Nodes?
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Plasma Cells
Dendritic Cells
Are lymph nodes Encapsulated?
Yes.
Do lymph nodes have Trabeculae?
Yea. I think basta encapsulated meron Trabeculae.
Therefore meron rin ganito:
Afferent LV
Subcapsular sinus
Trabecular/Cortical sinus
Medullary sinus
Efferent LV
Lymph nodes have how many regions and what are they?
Cortex
Paracortex
Medulla
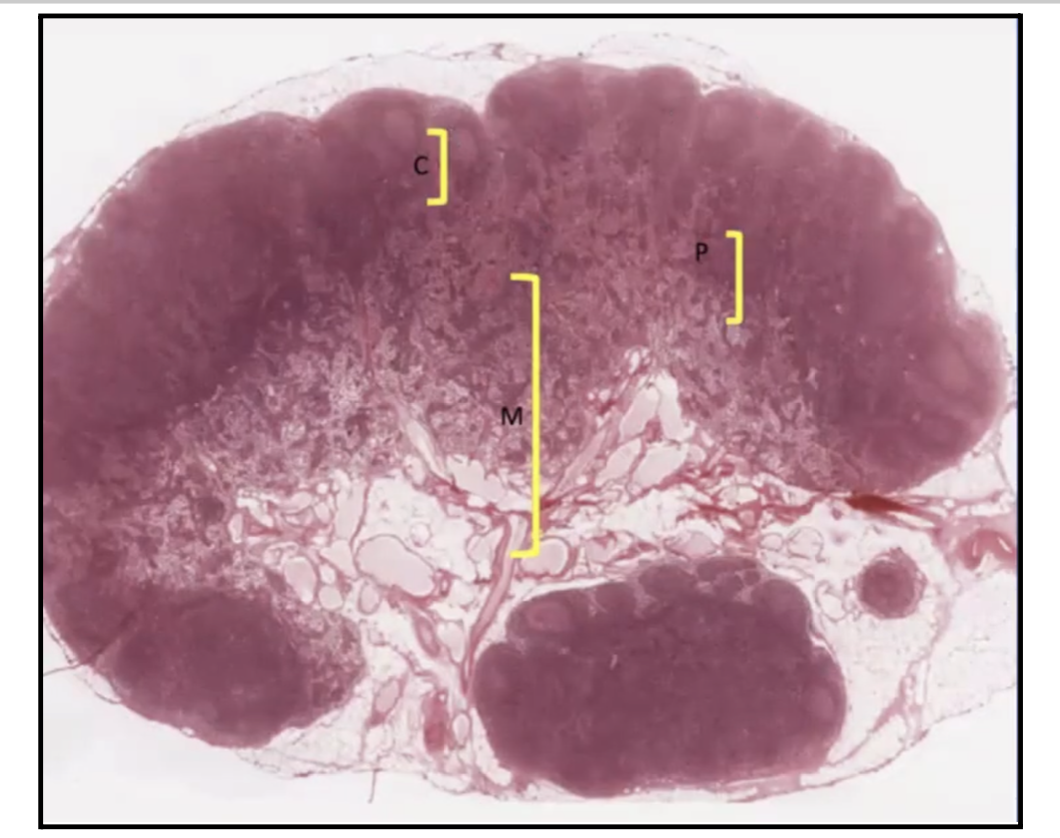
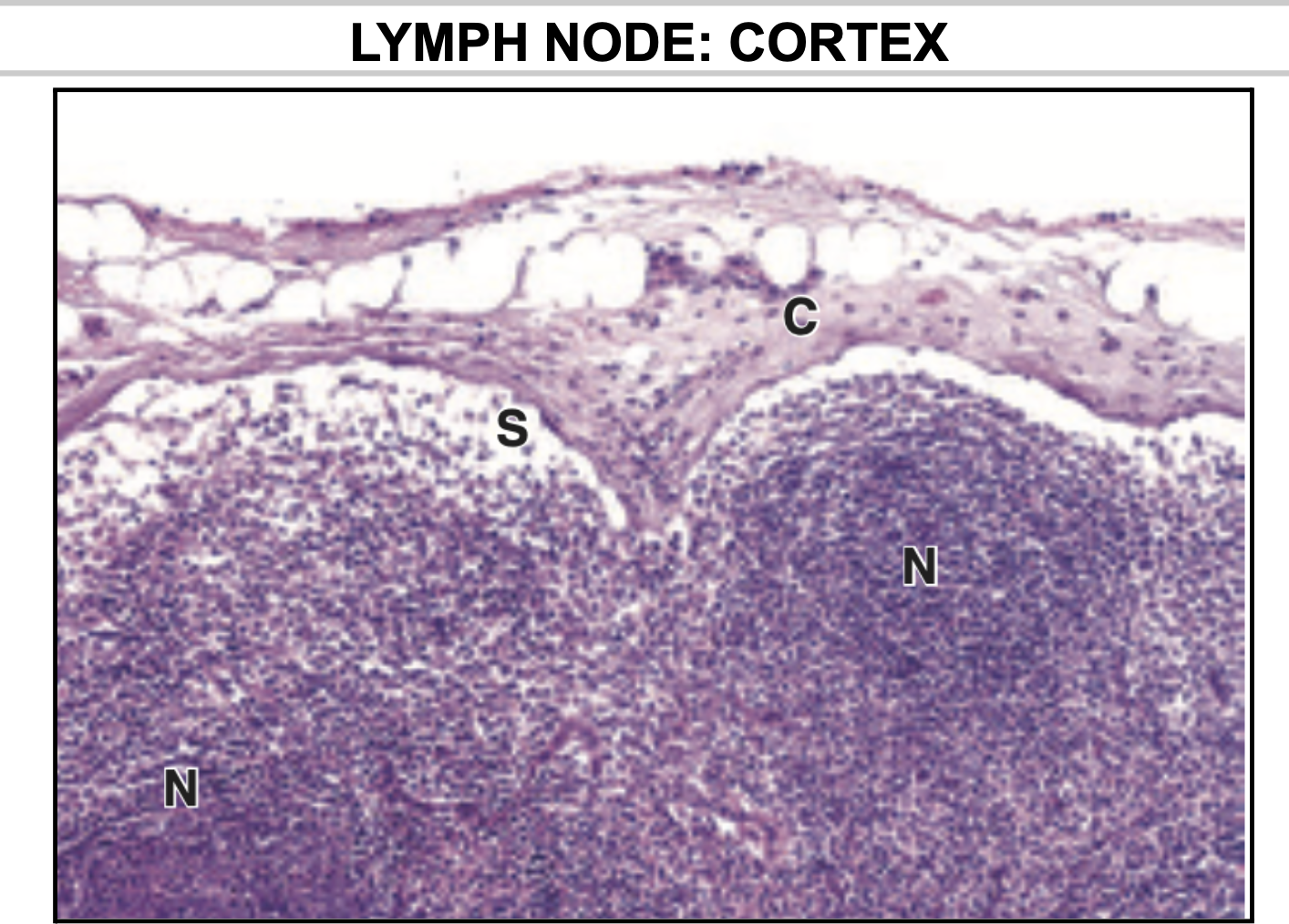
In the Lymph node, where can you find the lymphoid nodules?
Cortex
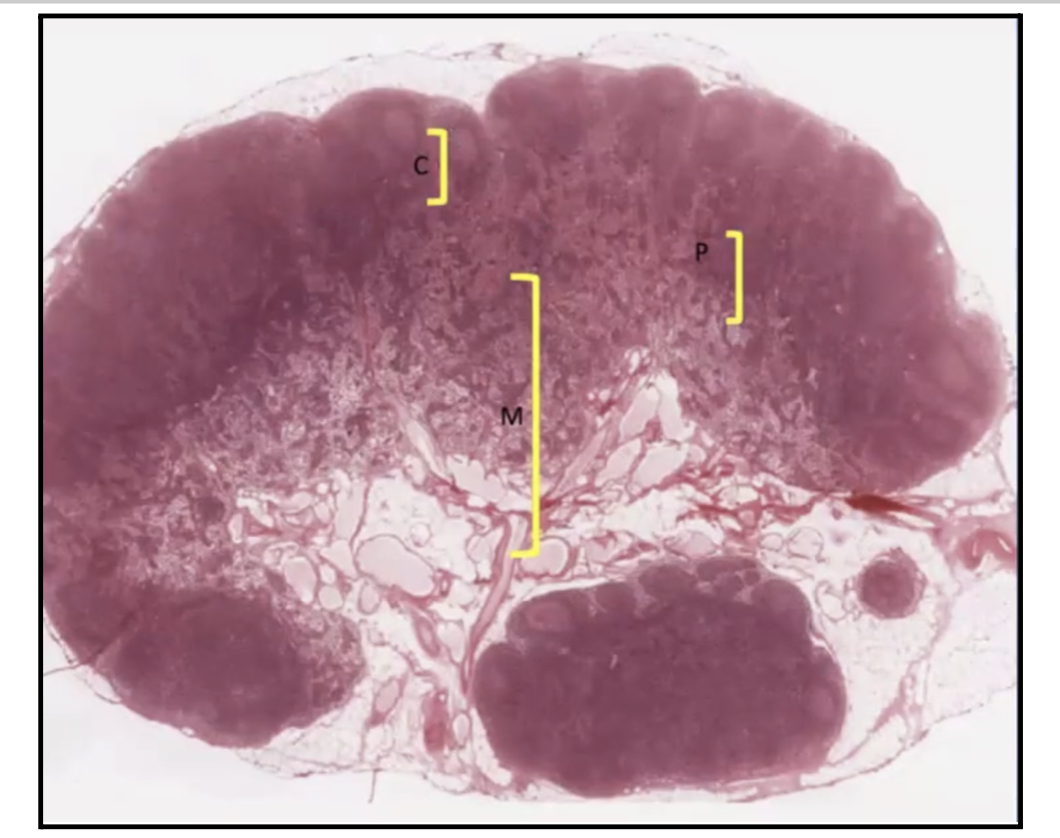
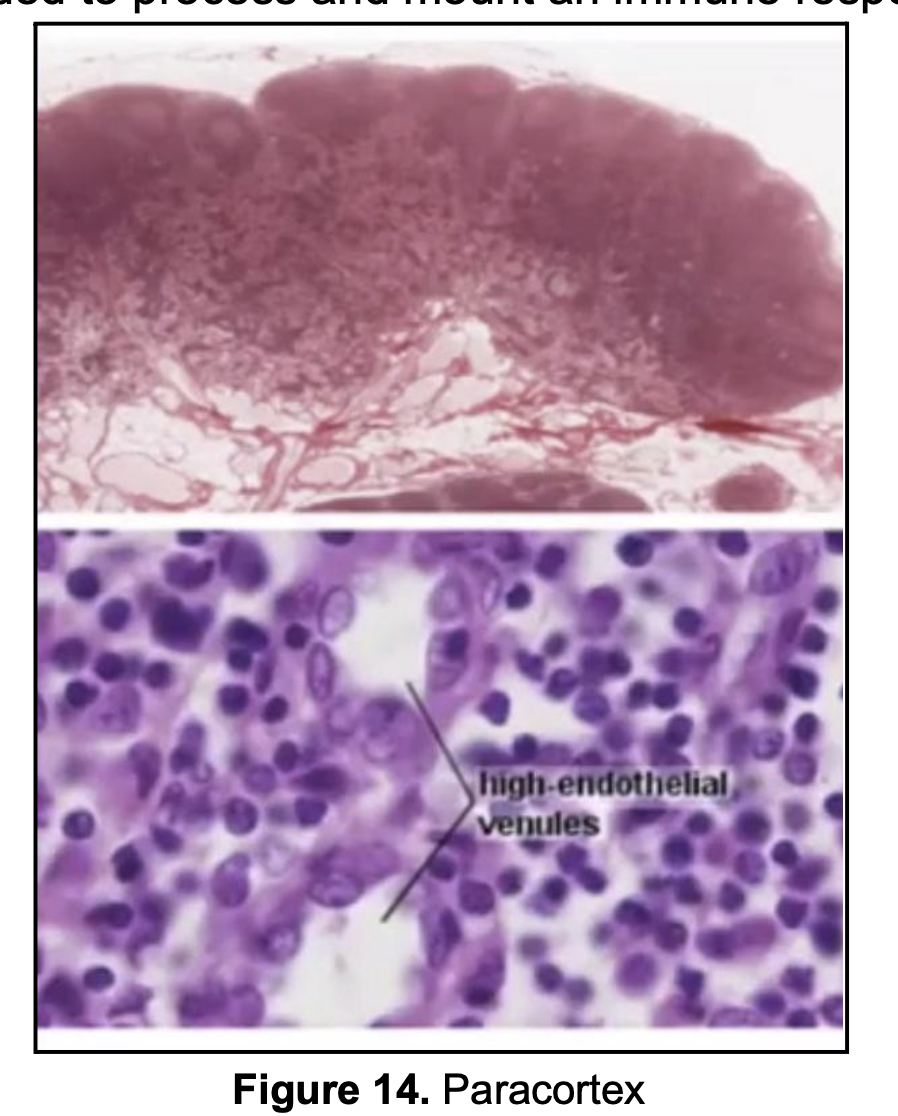
In the Lymph node, where can you find the High Endothelial Venules and T lymphocytes?
Paracortex
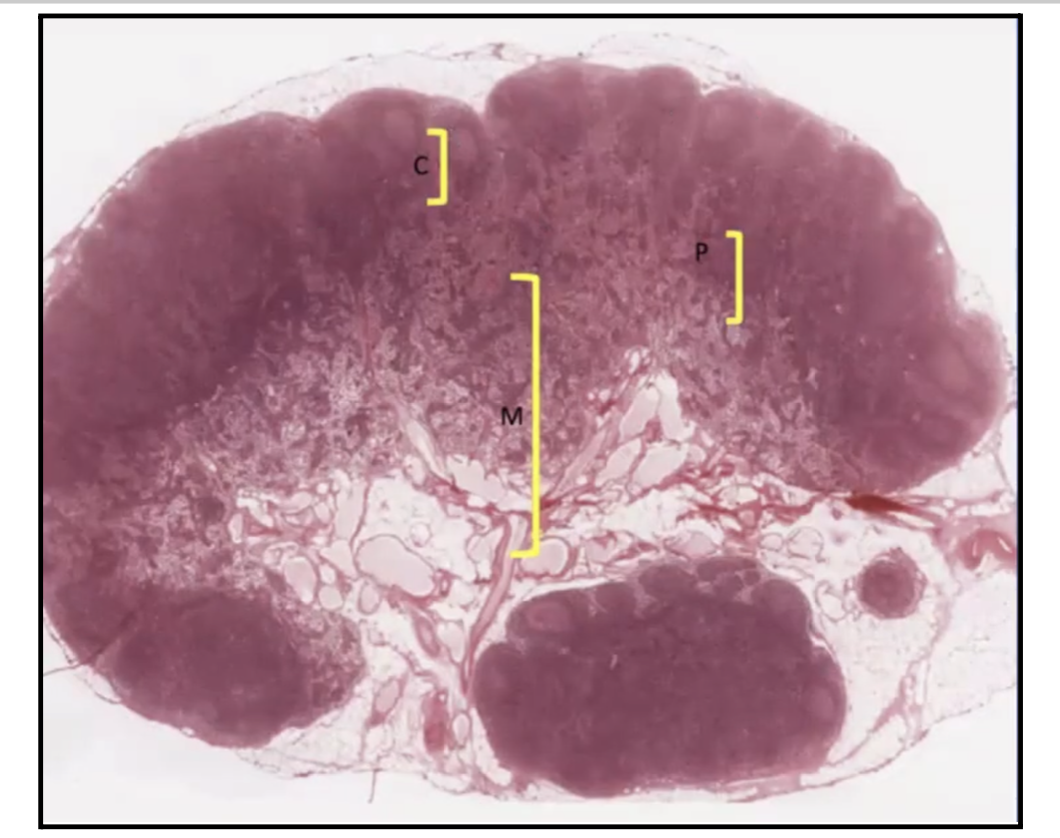
What separates the Cortex of the Lymph nodes from the Capsule?
Subcapsular Sinus!
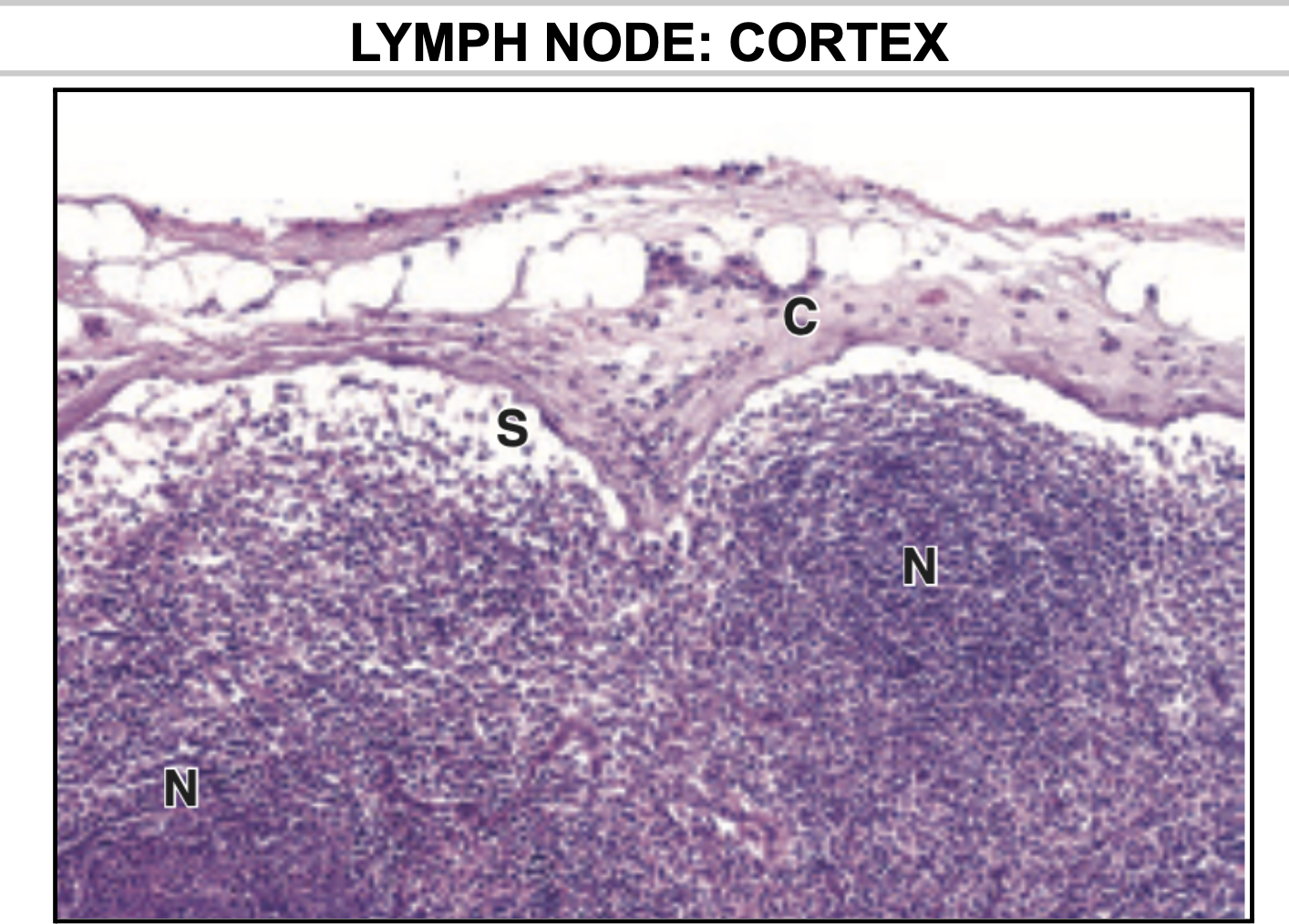
What does the Subcapsular sinus of Lymph nodes contain?
B Lymphocytes
APCs or Macrophages
Which lymphoid organs can you find High Endothelial Venules?
this is the entry way for lymphocytes
lined by cuboidal cells and INTEGRIN for rapid translocation
Paracortex of Lymph Nodes
MALT (but not as prominent)
T or F? The Medullary Sinuses of the Lymph nodes are continuous with the Cortical Sinuses.
true! They are continuous.
Lymph from the RIGHT UPPER SIDE OF THE BODY will drain into?
RIGHT UPPER SIDE of Body → RIGHT Lymphatic Duct → RIGHT Subclavian Vein
Lymph from the the rest OF THE BODY other than the right upper side of the body will drain into?
Thoracic duct → Left Subclavian vein
What is the Largest ORGAN in the Immune System?
Spleen.
What is the lymphoid organ that is the ONLY ONE INVOLVED IN THE FILTRATION OF BLOOD?
SPLEEN
Where is the Main site of destrcution of Old Eythrocytes?
SPLEEN
Location of Spleen?
LEFT SIDE
Upper Quadrant of Abdomen
Behind the Stomach
T or F? The spleen decreases in Size after puberty.
True
Is the Spleen Encapsulated?
Yes!
The Splenic Pulp has 2 components:
White Pulp
Red Pulp
Which one has Blood filled sinusoids? Which one has Lymphoid nodules?
White Pulp - Lymphoid Nodules
Red Pulp - Blood filled Sinusoids
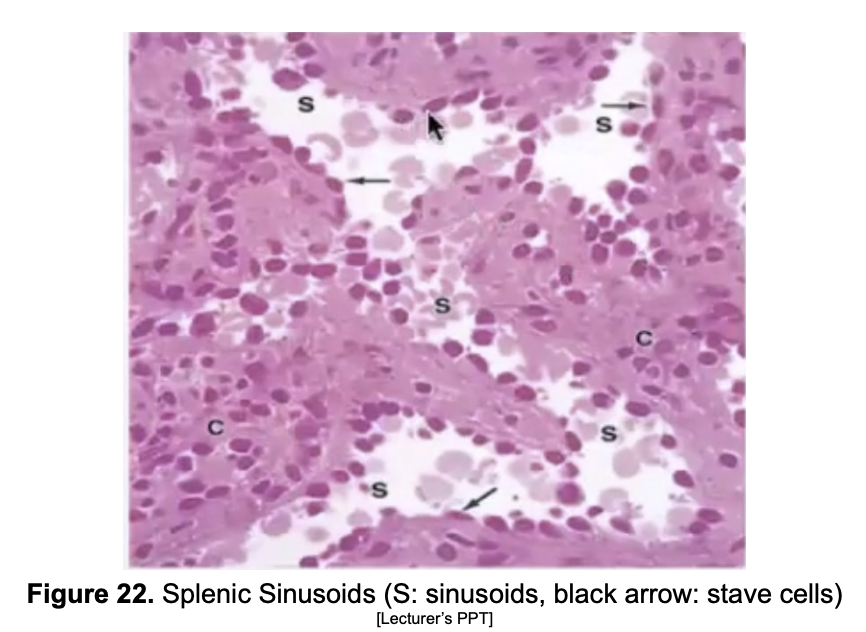
Where can you find STAVE CELLS?
Spleen
RED pulp
The Splenic Pulp has 2 components:
White Pulp
Red Pulp
Where can you find the Central Arteriorle of the Trabecular Artery?
WHITE PULP
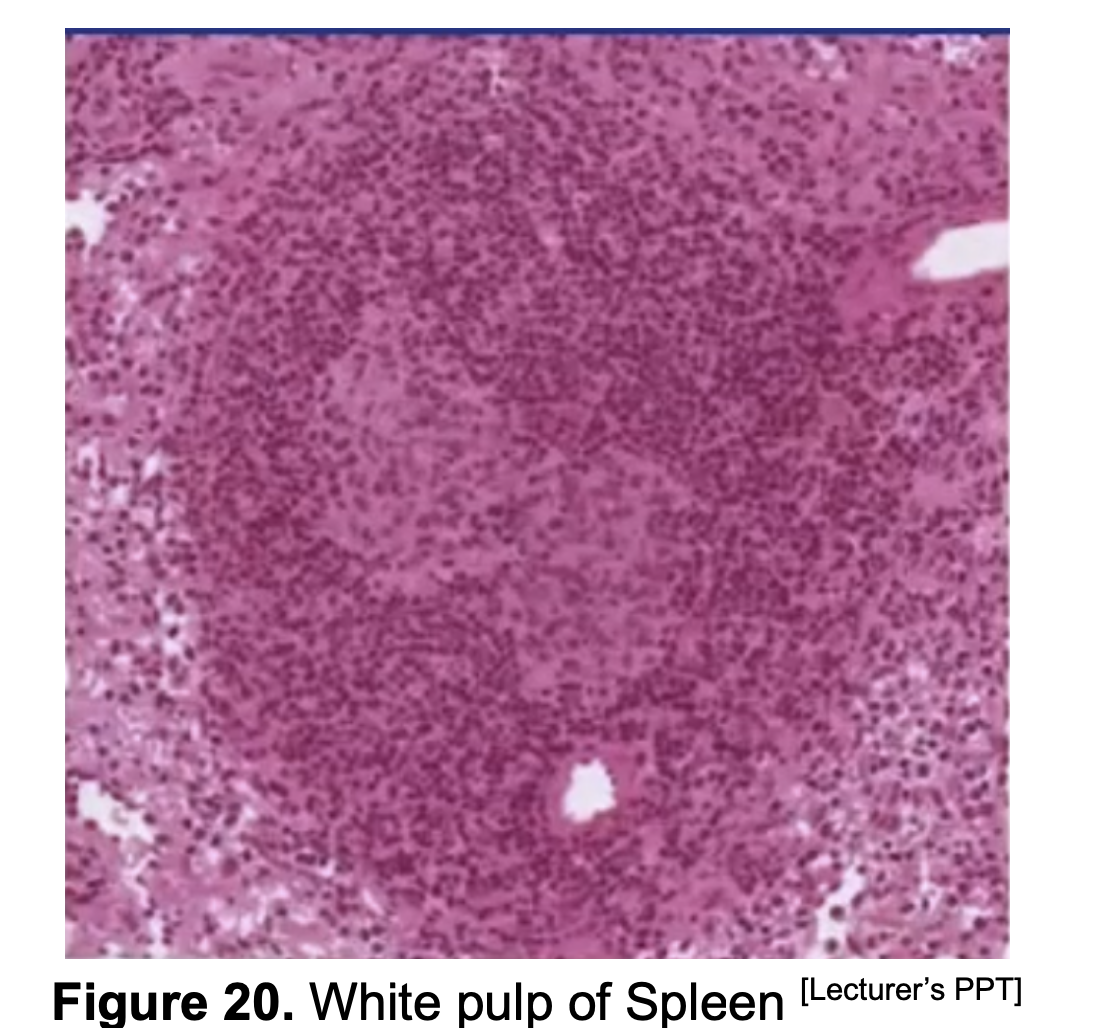
Central Arteriorle of the Trabecular Artery really found in the center ._. ?
No. Nasa periphery sya ng Lymphoid nodule
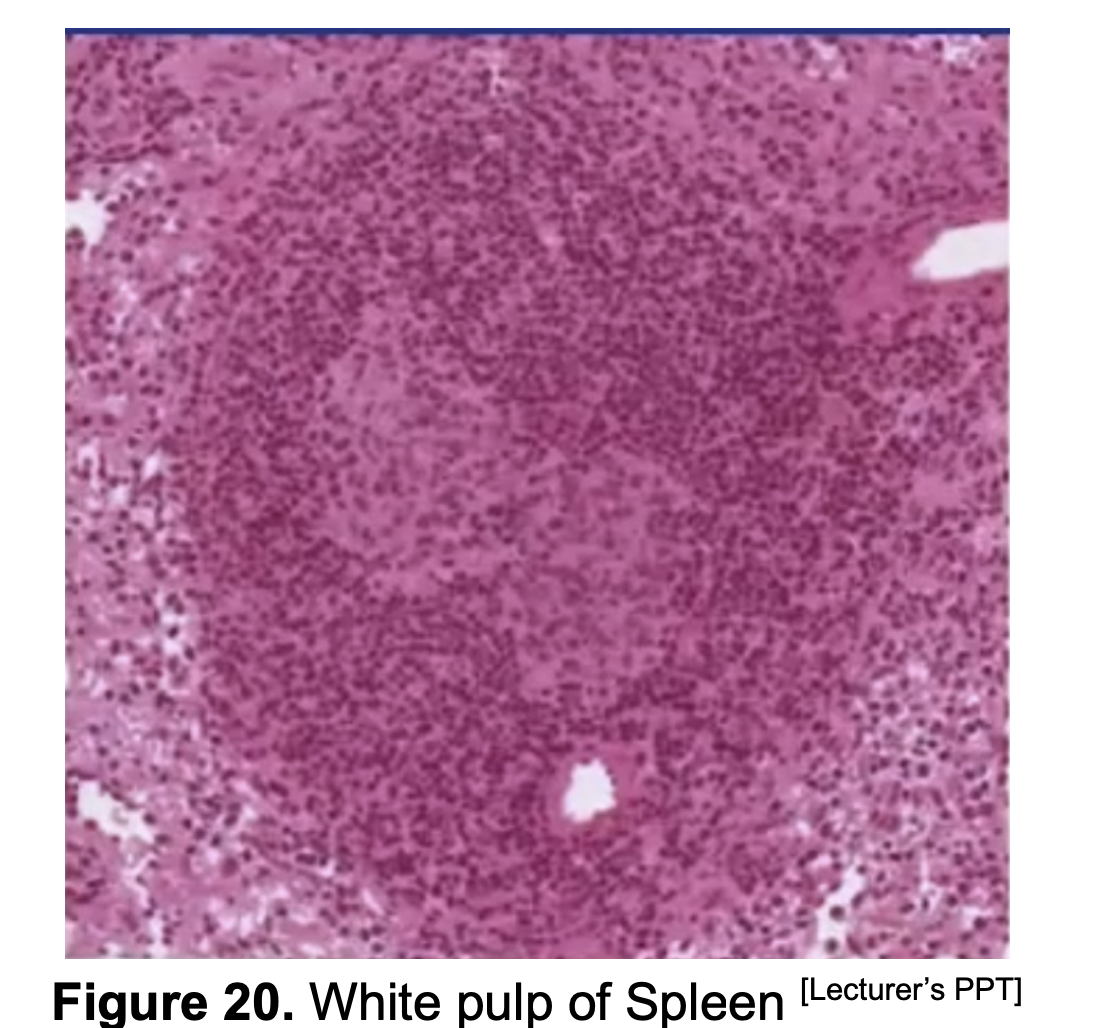
What surrounds the Central Arteriole of the Trabecular Artery?
Periarteriolar Lymphatic Sheath (PALS)
Pathway of blood circulation in the SPLEEN
Splenic artery
Trabecular artery
Central arteriole
Pinicillar Artery
CAPILLARIES
Red Pulp Veins
Trabecular Veins
Splenic Vein
Hepatic Portal Vein
Inferior Vena Cava
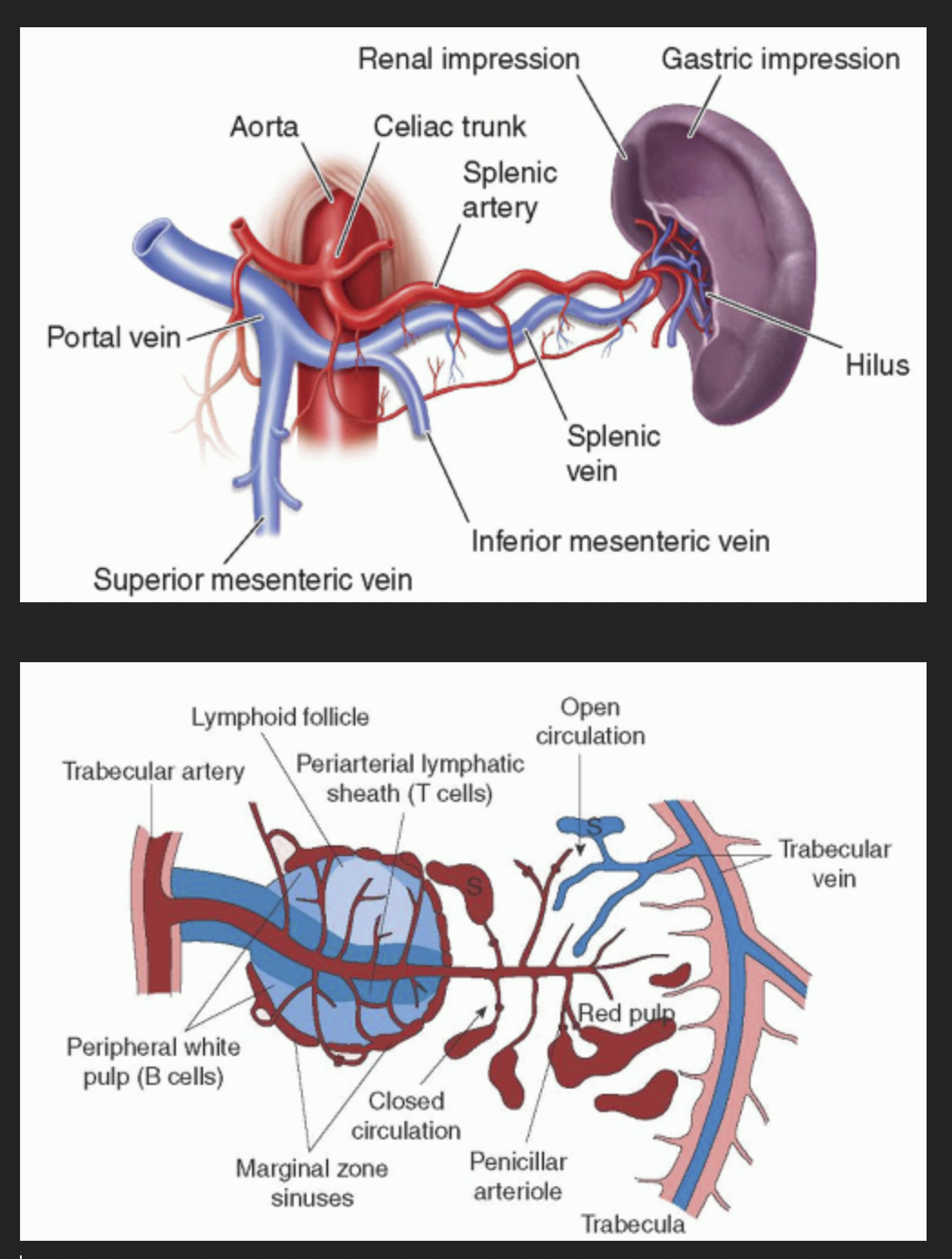
***The Central Arteriole of the Spleen branches off from which Artery?
Splenic Artery
Trabecular Artery
Trabecular!
The Central arteriole of the spleen is found in which pulp?
White Pulp!!!!!!!
The central arteriole branches into?
Several Penicillar arterioles
T or F? Macrophages surround the capillaries of the Spleen
True
What is the difference between Closed and Open circulation?
Closed flow directly into sinusoids
What do Stave cells in the RED PULP do?
Stave cells are specialized endothelial cells in the spleen's red pulp that form tiny slits to mechanically filter blood and select old or damaged red blood cells for destruction.
What are Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissues (MALT)?
They are Peripheral Lymphoid tissues that respond to antigens that enter the body through the Mucosa.
Where can MALT be found?
Mucosal CT of the
gastrointestinal tract
Respiratory tract
Genitourinary tract
Solitary Lymphoid Nodules can be found in which organs?
Esophagus
Colon
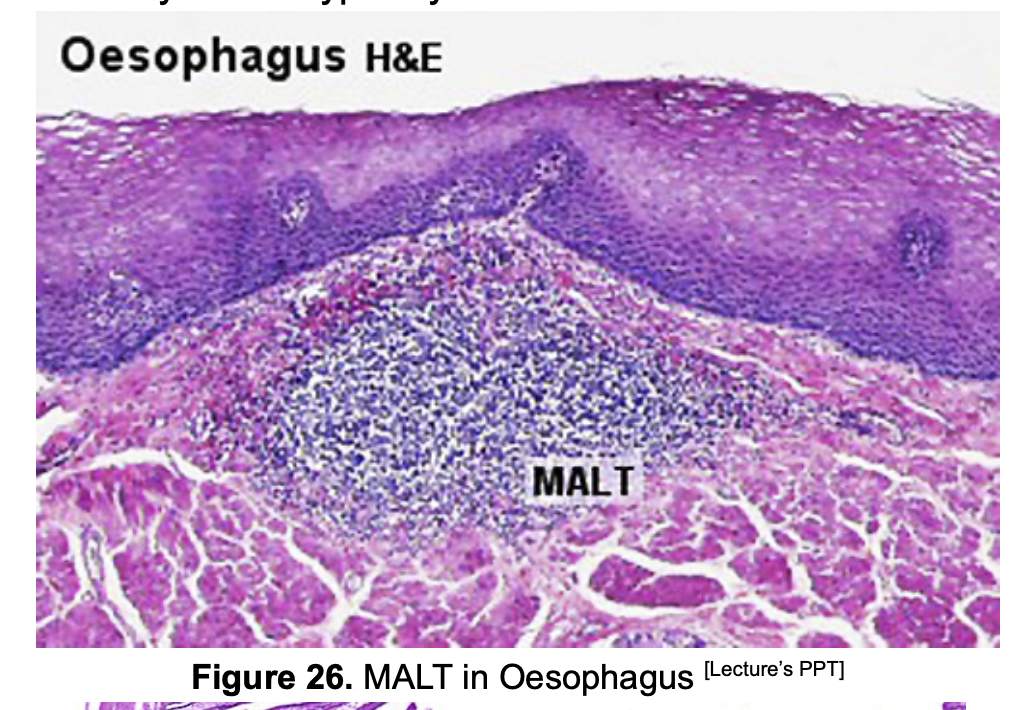
Aggregated Lymphoid nodules can be found in which organ?
Ileum only
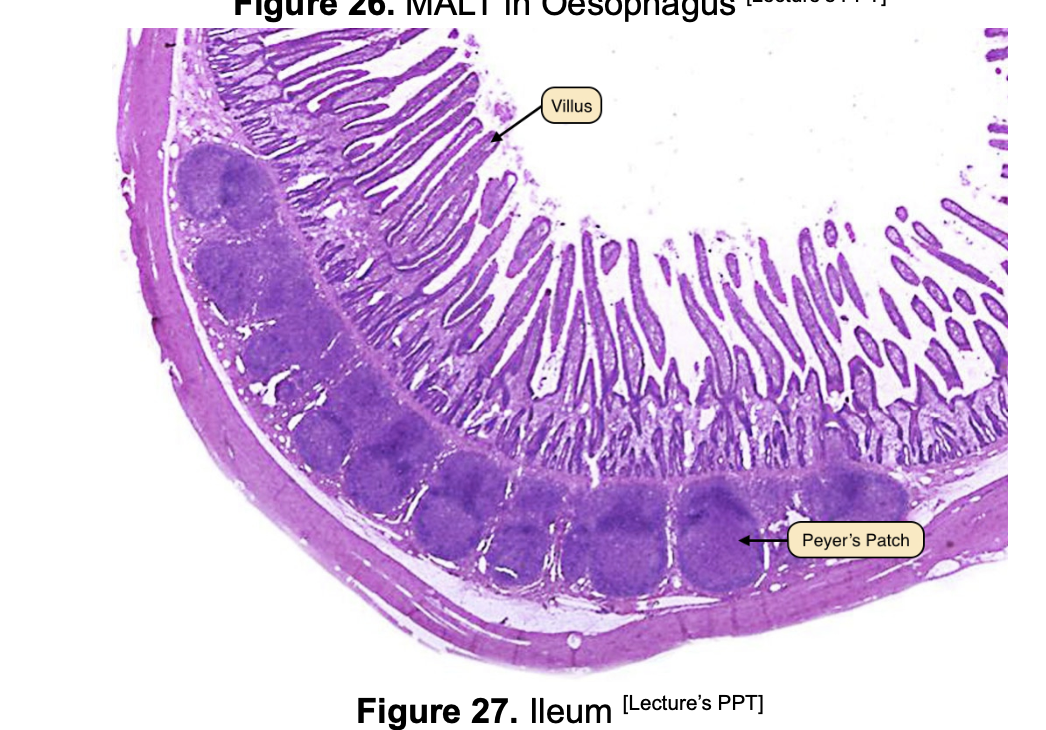
T or F? Peyer’s patches in the ilieum are examples of Aggregated lymphoid nodules.
True!
T or F? Solitary lymphoid nodules are usually found in transitory structures like the esophagus and Colon
True!
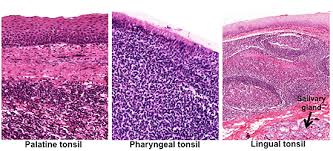
What are the 3 MALT found in the mucosa of the Posterior Oral Cavity and Nasopharynx?
Pharyngeal tonsil
Palatine tonsil
Lingual tonsil
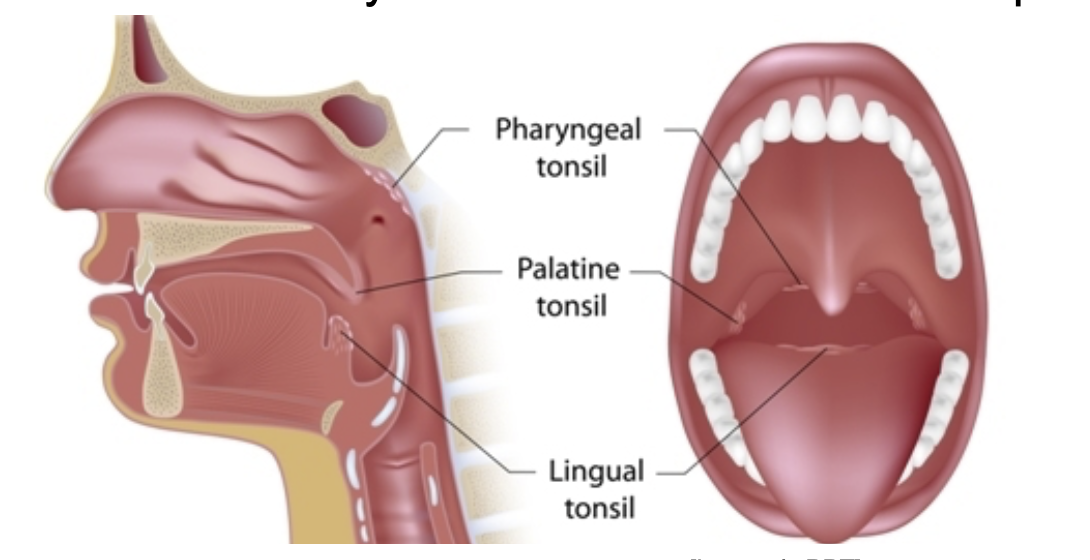
Which tonsil is located at the base of the tongue?
Lingual Tonsil
T or F? The Palatine Tonsil is found more anteriorly than the lingual tonsils.
False. Mas anterior si Lingual Tonsil.
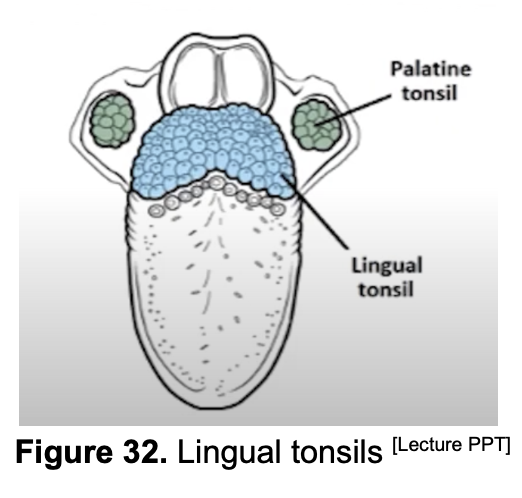
Which tonsils can you find 10 to 20 TONSILAR CRYPTS?
Palatine Tonsils
Which tonsils are lined by Stratified Squamous Epithelium?
Palatine and Lingual Tonsils
Which tonsils is lined by pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium?
PHARYNGEAL
just remember, both lingual and palatine are found in the mouth while the Pharyngeal is found separately in the nasal cavity kaya medjo naiba sya