Chemistry- Exam 3 Review
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Solutions
transparent, do not separate, contain small particles, ions, or molecules that cannot be filtered, cannot pass through semipermeable membranes.
Colloids
medium sized particles, cannot be filtered, can be separated by semipermeable membranes.
Suspensions
heterogenous, nonuniform mixtures, have very large particles that settle out of solution, can be filtered, must be stirred to stay suspended
ex: blood platelets
hypotonic
a solution with a lower solute concentration than that in another solution, lower osmotic pressure
a hypotonic red blood cell gains water, swells up, and bursts
hypertonic
a solution with a comparatively greater solute concentration than that in another solution, greater osmotic pressure than the other.
hypertonic red blood cell loses water and shrinks.
isotonic
water comes in and out at an equal rate
isotonic red blood cell retains normal volume
Adding Reactants
rate of the forward reaction increases to from more product until the system is again at equilibrium.
Equilibrium shifts towards the products
Removing Reactants
The rate of the reverse reaction will increase to form more reactant until equilibrium is reached.
Equilibrium shifts toward reactants.
Removing Products
There is a decrease in collisions of product molecules
Rate of forward reaction therefore increases to form more product
Shifts toward products.
Adding Products
There is now more product, so the reaction will shift toward reactants to reduce the added product.
Shift toward reactants.
Adding a Catalyst
speeds up reaction by lowering activation energy, does not change equilbirum
Decreasing Volume
only in gases, decreasing volume increases the concentration of the gases, so the system shifts in direction of the smaller number of moles to compensate
Increasing Volume
only in gases, increasing volume decreases concentration, so the system shifts in the direction of the larger number of moles to compensate
Decreasing Temperature Endothermic
Decreasing temperature of endothermic reaction causes the system to shift the reaction toward more heat.
Shifts reaction toward reactants, increasing heat in system.
Decreasing Temperature- Exothermic
Decreasing temp of exothermic reaction causes the system to respond by shifting the reaction toward more heat
Shifts reaction toward the products, increasing heat in system.
Increasing Temperature Endothermic
Increasing temperature of an endo reaction causes the system to respond by shifting the reaction to remove heat.
Shifts the reaction toward the products, using up heat.
Increasing Temperature Exothermic
Increasing temp of an exothermic reaction causes the system to responds by shifting the reaction toward removing heat.
Shifts reaction toward the reactants, decreasing heat in system.
Arrhenius Acids
Produce hydrogen ions (protons) when they dissolve in water.
Electrolytes, because they produce H+ in water
Sour taste, turn blue litmus red, corrode some metals
Naming acids with a hydrogen ion and nonmetal ion
named with prefix hydro and end with -ic acid
HCl- hydrochloric acid
Naming acids with a hydrogen ion and a polyatomic ion
change the end of the name of the polyatomic ion from
-ate to -ic acid or -ite to -ous acid
HClO3- chloric acid
HClO2- chlorous acid
Arrhenius Bases
Produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in water
Also electrolytes
Taste bitter or chalky, soapy and slippery, turn litmus paper blue and phenolphthalein pink
Bronsted-Lowry Acids
acids donate a proton (H+) in aqueous solutions
Bronsted-Lowry Bases
Bases accept a proton (H+) in aqueous solutions
Conjugate Acid
base that gains a proton
gain a H+ and have a 1+ charge when compared to the base
H2O (base) → H3O+ (con acid)
Conjugate Base
acid that loses a proton
lose a H+ and have a -1 charge when compared to the acid
HCl (acid) → Cl- (con base)
Strong Acids
HNO₃ - nitric acid
H₂SO₄- sulfuric acid
HClO₄- perchloric acid
HCl- hydrochloric acid
HBr- hydrobromic acid
HI- hydroiodic acid
Strong Bases
Formed from metals of Group 1 and 2
NaOH- sodium hydroxide
LiOH- lithium hydroxide
KOH- potassium hydroxide
Rb and CsOH- rubidium and cesium hydroxide
Ba(OH)₂- barium hydroxide
Ca(OH)₂- calcium hydroxide
Sr(OH)₂- strontium hydroxide
Weak Bases
include NH₃
Solvent
substance present in larger amount
ex: water
Solute
substance present in a smaller amount
Electrolyte
substances that produce an electrically conducting solution when dissolved
Strong Electrolyte
dissociate (split into cation and anion) 100% in water, conduct a strong electric current.
Weak Electrolyte
dissociate slightly in water, forms a solution with a few ions and most undissociated molecules, weak electric current
Nonelectrolytes
substance that does not ionize in solution, dissolve as molecules in water, do not produce ions, no electric current
Unsaturated Solution
contain less than maximum amount of solute, can dissolve more solute
Saturated Solution
contain the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve, have undissolved solute at the bottom of the container.
Supersaturated Solution
contain more than the maximum amount of solute, due to how the solution was created- excess heat or pressure.
Henry’s Law
solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly related to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
at higher pressures, more gas dissolves
when pressure of a gas above a solution decreases, the solubility decreases
Dilution Equation
C1 x V1 = C2 x V2
Osmosis
water (solvent) flows from a lower to a higher solute concentration.
Chemical Equilibrium
the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
Equilibrium Expression, Dissociation of Acid or Base
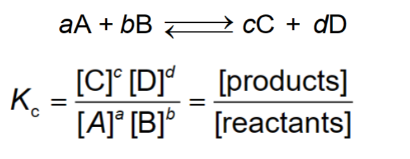
Large Kc (equilibrium constant)
at equilibrium, the reaction mixture contains mostly product and few reactants
Small Kc (equilibrium constant)
at equilibrium, the reaction mixture contains mostly reactants and few products
Kc near 1 (equilibrium constant)
at equilibrium they have about equal concentrations of reactants and products
Acid Dissociation Constant
If it is less than one, the equilibrium lies to the left, favoring the reactants.
Greater than one, the equilibrium lies to the right, favoring the products.
Weak acids have small Ka values, while strong acids have very large Ka value.
Base Dissociation Constant
If it is less than one, the equilibrium lies to the left, favoring the reactants.
Greater than one, the equilibrium lies to the right, favoring the products.
The stronger the base is, the large the Kb value
Water Dissociation Expression
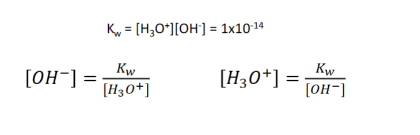
Acidic Solution
H30+ is larger than OH-
Basic Solution
OH- is larger than H3O+
pH
pH = -log[H3O+]
pH = -log[H+]
pH = -log[OH] - 14
[H3O+] =
10^pH
(1×10^-14) / [OH-]
[OH-] =
1x10^14 / [H3O]
Molarity
moles of solute / liters of solution
pH of a Buffer
Ka (acid dissociation constant) x weak acid / conjugate base to get [H3O]
Then put into: pH is the –log(H3O+)
![<p>Ka (acid dissociation constant) x weak acid / conjugate base to get [H3O]</p><p><span>Then put into: pH is the –log(H3O+)</span><span style="color: windowtext"> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ea1b7f8c-9909-41c9-9c55-a6c6d11010c9.jpeg)
Hemolysis
in a hypotonic solution, water rushes into the cell causing it to burst.
Crenation
in a hypertonic solution, water rushes out of the cell causing it to shrink
Buffers Consist Of
a weak acid and its conjugate base
Function of Weak Acid in Buffer
If a small amount of base is added to this same buffer solution, it is neutralized by the acetic acid, which shifts the equilibrium in the direction of the product’s acetate ion and water.
Function of Conjugate Base in Buffer
If a small amount of acid is added to this same buffer solution, it is neutralized by the acetate ion, which shifts the equilibrium in the direction of the reactants acetic acid.