Quality Assurance
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is quality assurance?
All the procedures needed to ensure proper and consistent operation of the imaging systems.
Quality assurance is what kind of process?
A proactive process.
Why is QA performed?
It promotes:
Proper equipment management
Detection of gradual degradation of performance
Minimal ‘down-time’
Few repeat scans
Sonographer and patient safety
QA is required for what?
All accredited ultrasound departments.
What does AIUM stand for?
American Institute of Ultrasound Medicine.
Who is responsible for QA? (3)
Physician
Sonographer
Service personnel
What are the physician’s responsibilities with QA?
Assess image quality
Director of quality assurance program
What are the sonographer’s responsibilities with QA?
Assess image quality
Routine preventative maintenence
+/- performance testing and record keeping
What are the service personnel’s responsibility with QA?
Acceptance testing
Preventative maintenance (PM)
Routine performance testing
Repair
Service is typically performed by who under a service contract?
The manufacturer.
What are the components of a QA system?
Acceptance testing
Routine preventative maintenance
Manufacturer’s preventative maintenance (PM)
Performance testing
What is acceptance testing?
Testing done when system is first placed in operation.
Who is acceptance testing performed by?
The service personnel who ensures the equipment meets standards and measures the imaging performance and power output.
What is preventative maintenance?
The regular and routine maintenance in order to prevent down-time from unexpected equipment failure.
Who is preventative maintenance performed by?
The sonographer or a qualified service personnel.
What does the sonographer do for preventative maintenance?
Clean surfaces of the machine
Cleans the trackball
Clans the fan filters
Assess cables and transducer integrity
What is strain relief?
Used to provide a transition point from flexible cable to a rigid connector or connection point.
Can the strain relief be damaged?
Yes it can.
What is the definition of cleaning?
It is the removal of soil, and the reduction in numbers of microorganisms from a surface. Cleaning can be achieved by washing with soap and water or wiping with 70% alcohol. Essential first step prior to either dist=infection or sterilization. Cleaning is appropriate for transducers used in normal transabdonimal scanning.
What is the definition of disinfection?
It is the inactivation of vegetative bacteria, viruses, and fungi, but not necessarily of bacterial spores. It is required for medium risk or semi-critical medical instruments including those used in contact with intact mucous membranes, eg. vaginal transducer. Before disinfection, instruments should be cleaning and dried.
What is the definition of sterilization?
It is the complete destruction of mircoorganisms, including bacterial spores. Sterilization is generally achieved by autoclaving. However, this process must NEVER be used with an ultrasound transducer. Ethylene oxide (gas) is an alternative. Covering with a sterile sheath is common practice. Sterilization is required for high-risk or critical medical procedures involving penetration of the skin, membranes or other tissues, eg. oocyte harvesting or chrorionic villus sampling.
What are probe covers?
A cover that is used to cover the transducer to maintain sterility. This is the most common approach when ultrasound is used in the operating room.
Who is preventative maintenance performed by?
Service personnel who are performing +/- electronic testing, which is usually covered under service contract.
What is performance testing?
A measurement of imaging performance. (Axial resolution, lateral resolution, sensitivity, accuracy, etc.)
Performance testing uses what?
A tissue equivalent phantom (TE).
Performance testing assesses changes in performance…?
Over time.
Performance testing is done on a…
Regular schedule.
Performance testing requires what?
Consistent imaging controls (must be set the same they were for each test) and must have good record keeping.
What are some performance testing devices?
TE phantom (plexiglass enclosure containing gels mixed with graphite)
Test objects (old - plexiglass enclosure containing water)
Sophisticated measuring devices (force balance, calorimeter, hydrophone, spectrum analyzer)
What is a TE phantom?
Plastic case
Gel mixed with graphite powder
Pin/wire groups + solid and cystic ‘lesions’
Good approximation of clinical performances
Grayscale
Attenuation
Speed of sound
What are some Doppler devices for performance testing?
TE Doppler phantom (closely matches clinical experience, but expensive)
“String” phantoms (old)
Moving string in water bath
Not a close match clinically
Less expensive
Doppler QC tests include?
Doppler signal sensitivity
Doppler angle accuracy
Colour display
Grayscale image congruency
Range-gate accuracy
Flow read out accuracy
When is acceptance testing performed?
Once, upon arrival.
When is preventative maintenance by the sonographer performed?
Daily/weekly.
When is manufacturer’s Preventative Maintenance (PM) performed?
Semi-annually.
When is performance testing by the sonographer done (if done)?
Semi-annually.
What are the types of performance tests that are performed with a phantom to measure system performance? (11)
Sensitivity
Uniformity
Dead zone
Axial resolution
Lateral resolution
Slice thickness
Range accuracy
Horizontal accuracy
Lesion detection
Contrast resolution
Beam profile
What is sensitivity is also known as?
Depth of penetration or maximum depth of visualization.
What is sensitivity?
The systems ability to detect weak echoes.
What is a common technique used to test sensitivity?
Maximum depth of visualization.
What type of phantom is involved with measuring sensitivity?
TE phantom.
How is sensitivity measured?
By using a TE phantom, ensuring the power, gain, and focus optimized for penetration. Measure the max depth of visualization at which the echoes are no longer available. Record these results.
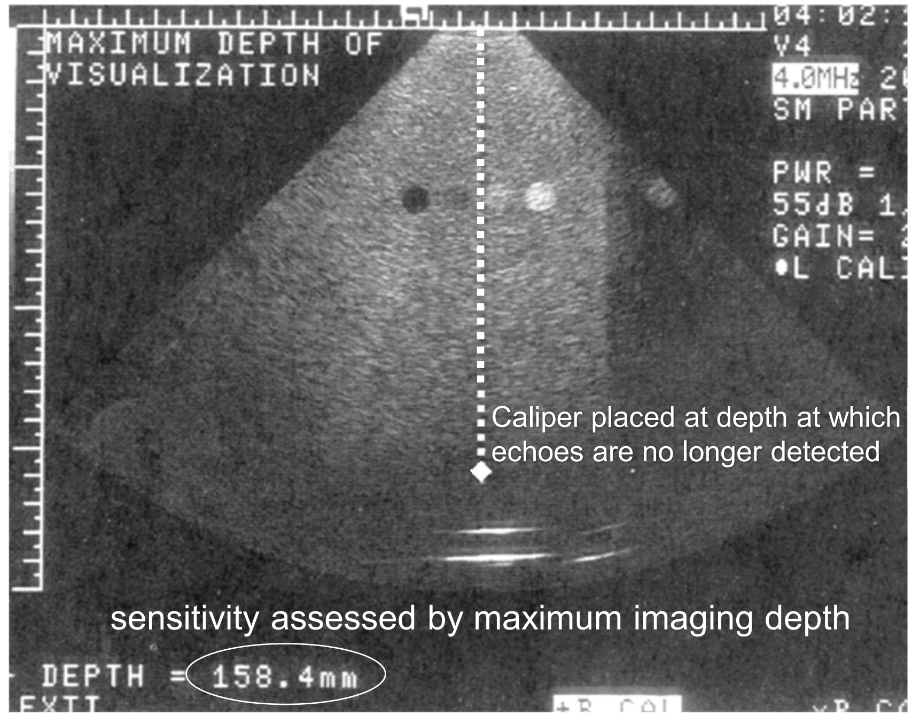
True or False: A less than 1 cm difference overtime in sensitivity is acceptable?
True.
What is uniformity?
Tests a linear array’s consistency along the array.
What technique and how is uniformity tested?
Using a TE phantom, image a homogeneous region and look for any areas of non-uniformity.
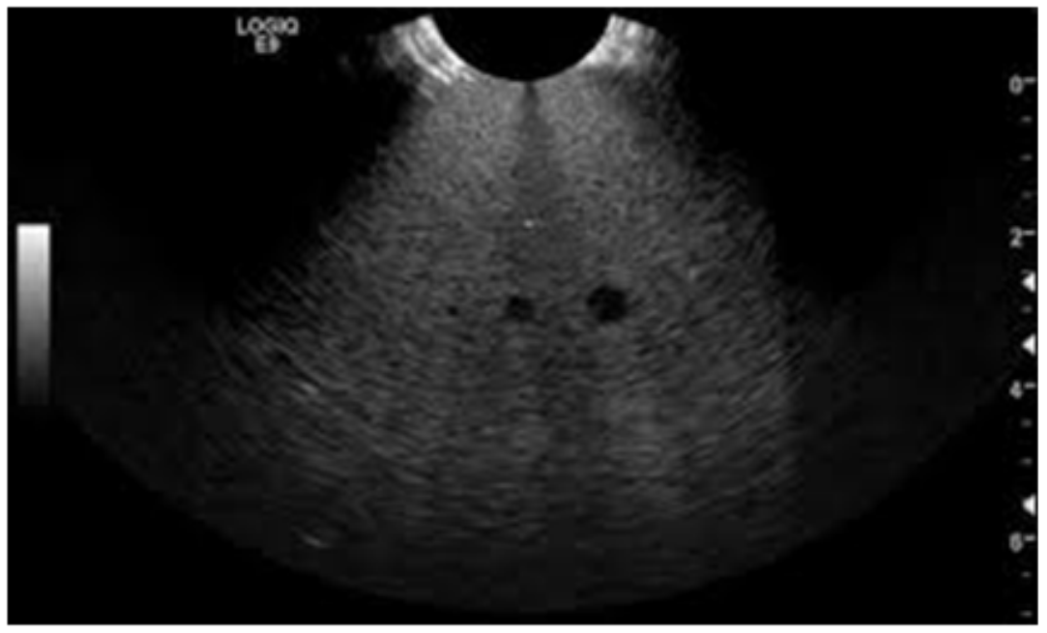
The quality of an ultrasound image is strongly dependent on what?
The quality of the transducer.
Defective transducers can lead to what?
A wrong or missed diagnosis.
Regular assessment of transducer operation and quality control are critical for what?
Optimal patient care.
Users should regularly check the performance of their transducer by monitoring?
For element dropout to help ensure that high-quality images are being obtained.
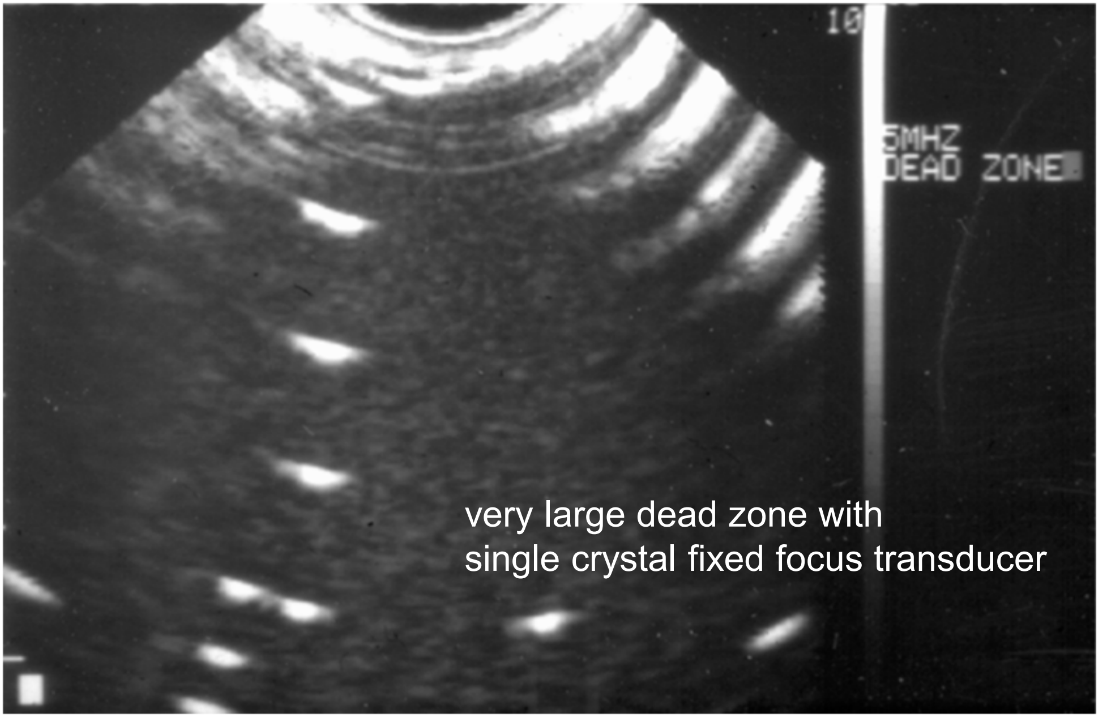
What is the dead zone?
The area in the near field close to the transducer having poor imaging due to artifact.
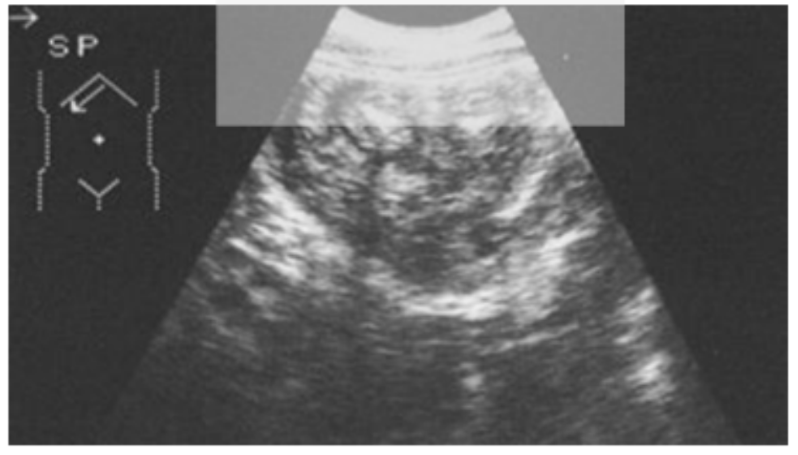
The dead zone is worse with old mechanical transducers or new array transducers?
Old mechanical transducers.
What technique is used to assess for the dead zone?
The TE phantom using the dead zone pins. < 15 mm is acceptable. Watch overtime for change.
Axial resolution tests the system’s ability to do what?
Separate interfaces along the beam.
How is axial resolution measured?
Using a TE phantom and using the axial resolution pins. The typical value is 0.5-3.0 mm.
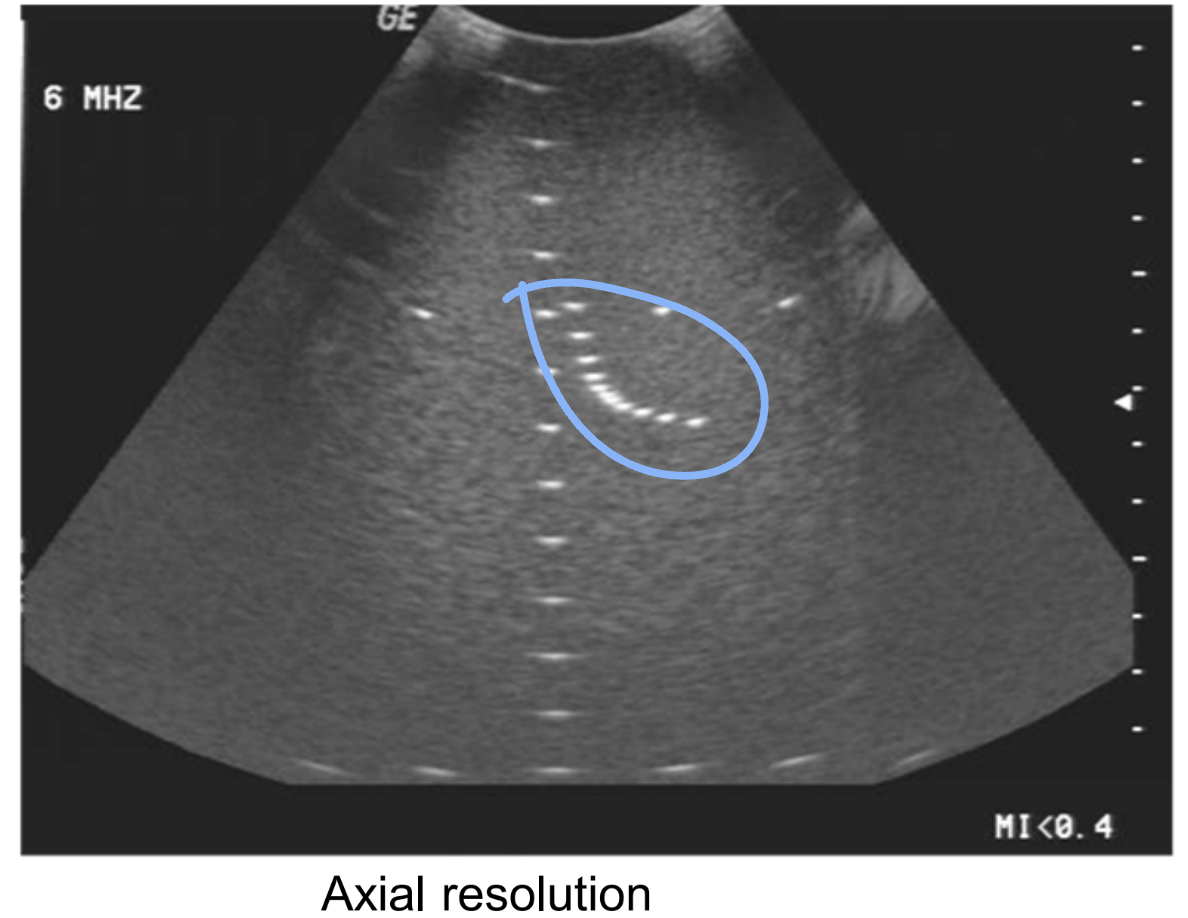
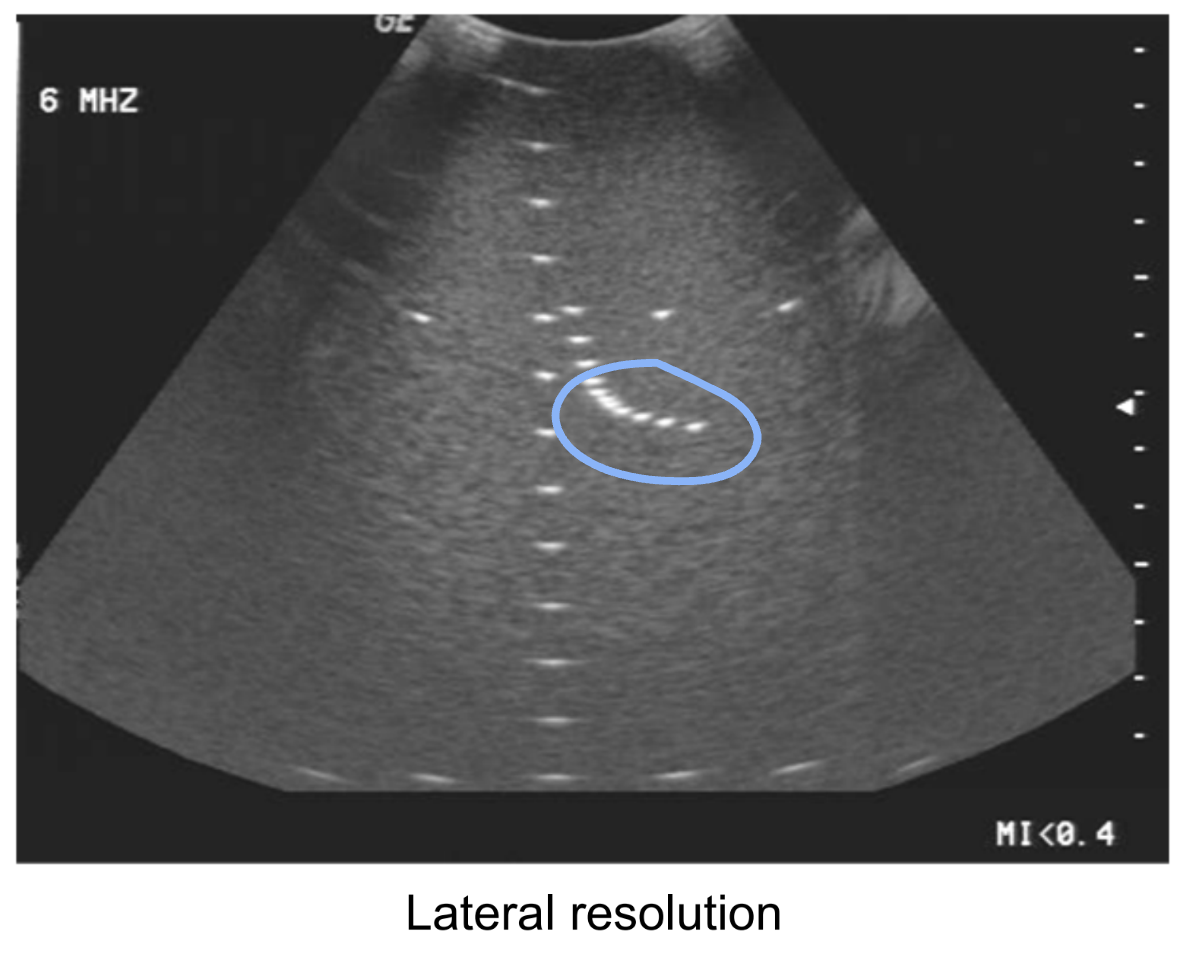
Lateral resolution tests the system’s ability to do what?
Separate interfaces across the beam.
How is lateral resolution measured?
Using a TE phantom and using the lateral resolution pins. This is depth dependent and focus dependent. The typical value is 1-10 mm.
What is slice thickness also known as?
Z axis and elevation axis.
What does slice thickness test?
The system’s slice thickness at a variety of depths.
What technique is used to measure slice thickness resolution?
A slice thickness spherical void phantom or a slice thickness, beam profile phantom.
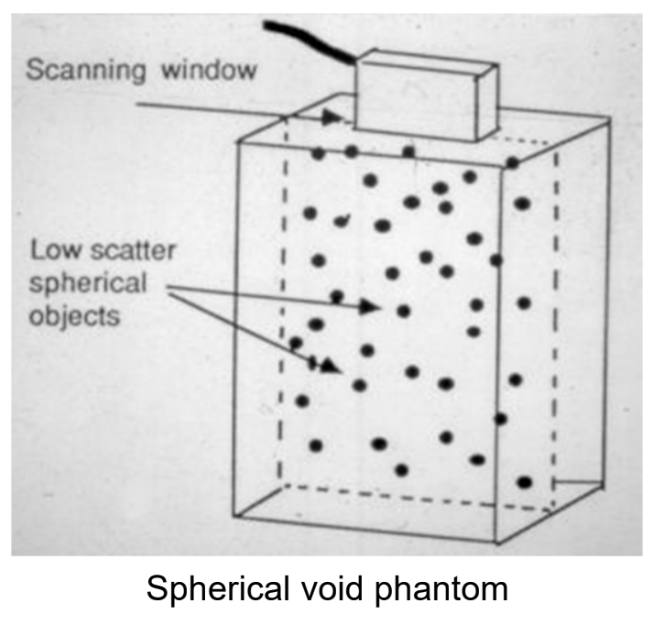
The scan plane thickness has a sound scattering plane at what degree to the beam?
45° to the beam.
The vertical thickness of the line when looking at scan plane thickness indicated what?
The slice thickness at the image depth of the line.
What is range accuracy also known as?
Vertical distance accuracy.
What does range accuracy test for?
The system’s ability to accurately measure distances along the beam.
The range accuracy is looking for what question?
It looks for, “is the range equation working properly?”
What technique is used to measure range accuracy?
Using a TE phantom and the equally spaced vertical dots, use the electronic calipers to measure 2 pins, 10 cm away from each other. Compare the measurement to the actual separation and calculate the percent error, if there is any.
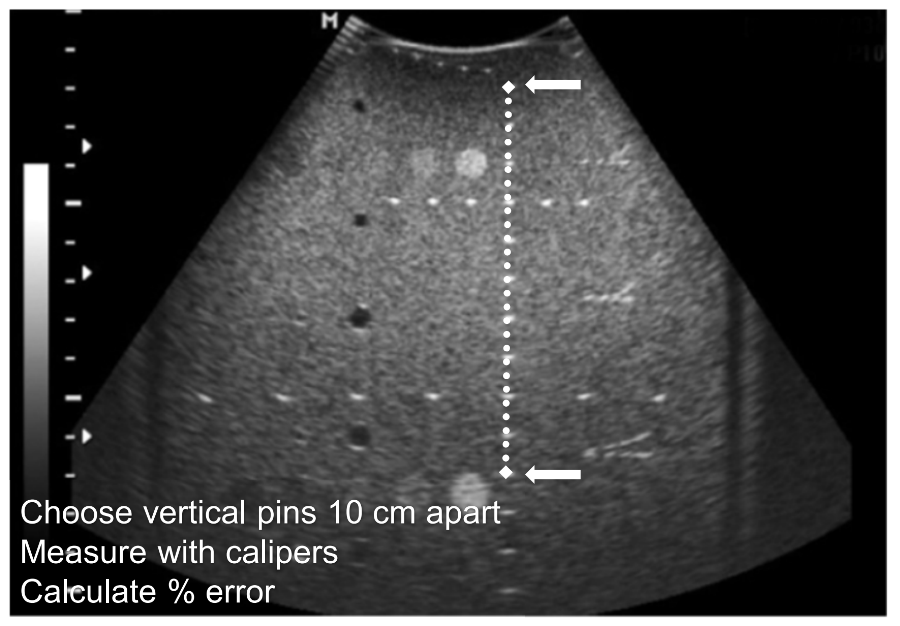
What is the percent error formula?
((Actual measurement - measurement on display)/actual measurement) x 100
What is horizontal accuracy also known as?
Horizontal distance accuracy.
What does horizontal accuracy tests for?
The system’s ability to accurately measure horizontal distances.
What technique is used for measure horizontal accuracy?
A TE phantom using the equally spaced horizontal dots. Using electronic calipers, measure 2 pins that are 10 cm apart and compare it to the actual separation, and calculate the percent error if there is one.
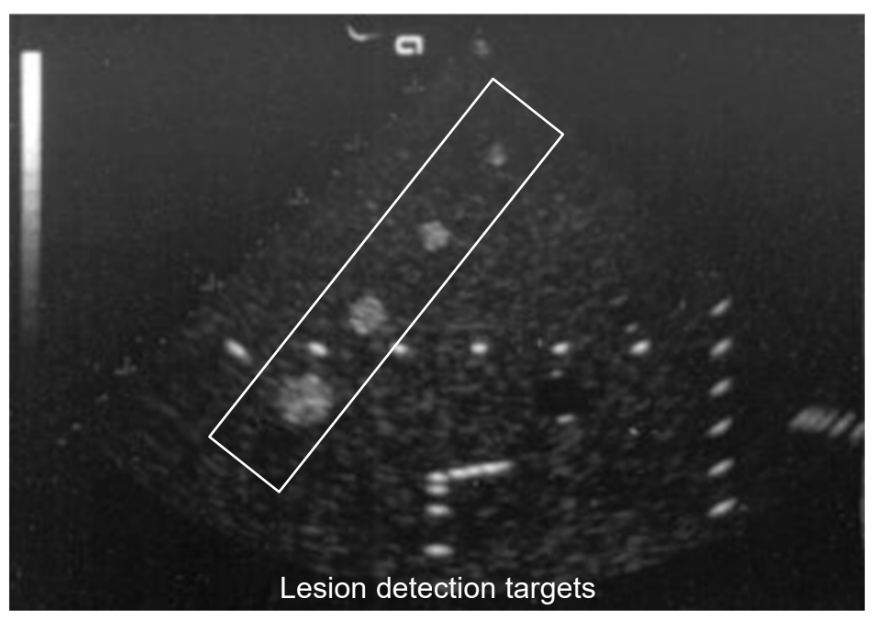
What is lesion detection?
It tests the system’s ability to detect small lesions with a variety of apearances.
What technique does lesion detection use?
TE phantom with a variety of lesions (solid, cystic, echogenic, hypoechoic, etc.). Image this and compare to previous results. This is done using the variably sized dots.

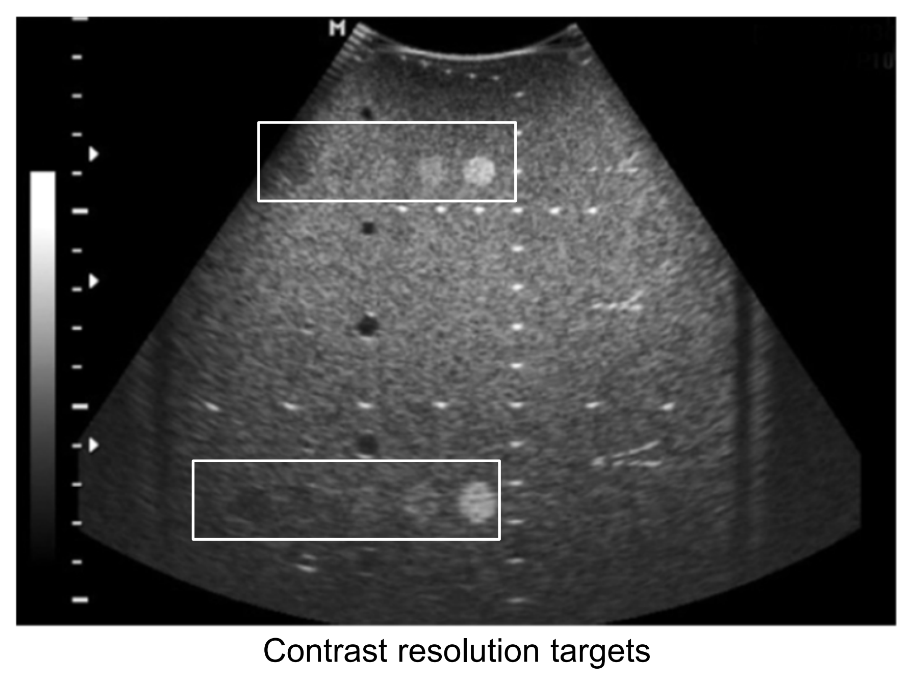
How is contrast resolution assessed?
By evaluating targets of different echogenicity. This assesses grayscale contrast and targets different echogenicity on the TE phantom.
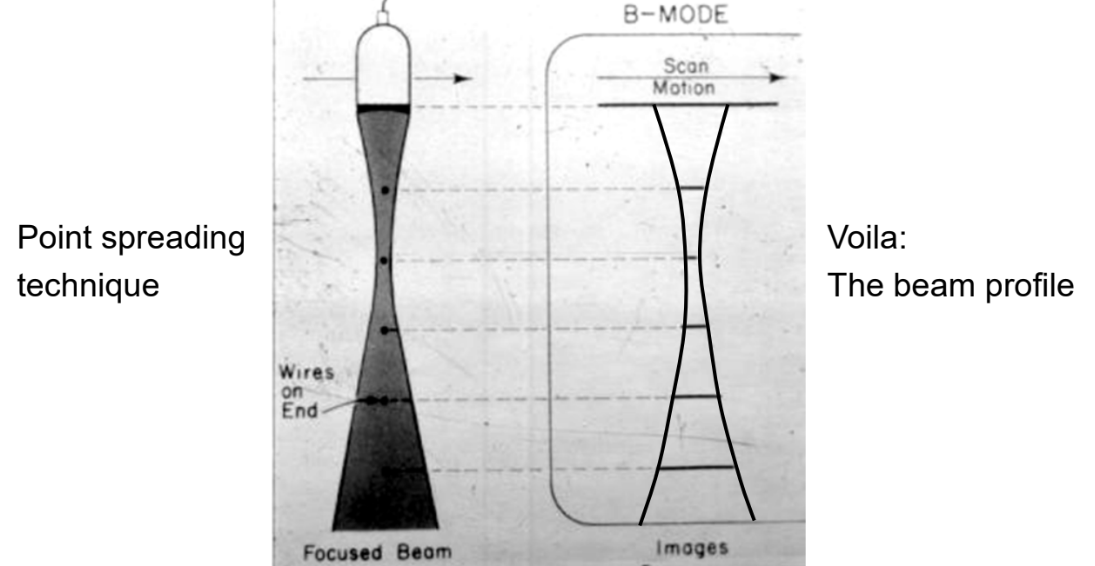
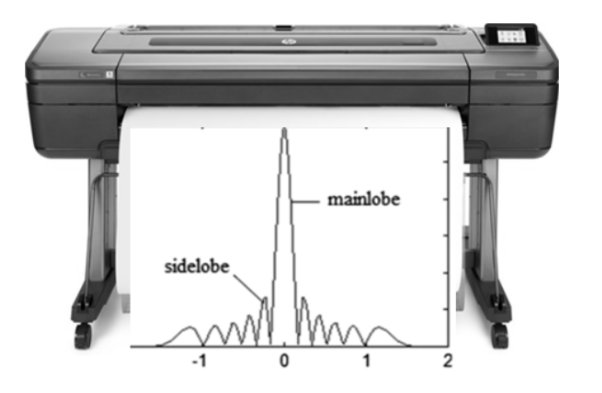
What information does the beam profile test provide?
Information on the shape of the main beam ± side lobes.
What technique is used to assess the beam profile?
A TE phantom using vertical pins and point spreading, and a beam profile phantom.
What are some sophisticated testing devices used by service personnel?
Hydrophone
Spectrum analyzer
Force balance
Calorimeter
What is a hydrophone?
A small (1mm) transducer that is placed in a water bath and assesses the ultrasound transducer.
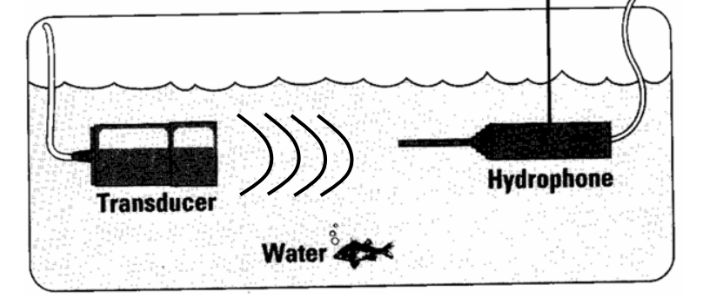
The hydrophone produces a voltage proportional to?
The amplitude of the pulse.
The signal from the hydrophone can output to various devices like…?
Plotter
Oscilloscope
Spectrum analyzer
What is a plotter?
Can be used to obtain a detailed beam profile.
What is an oscilloscope?
It displays sound characteristic, like the pulse amplitude, SPL, PD, PRP, PRF, and DF.
What does a spectrum analyzer display?
Resonant frequency
Bandwidth
Quality factor
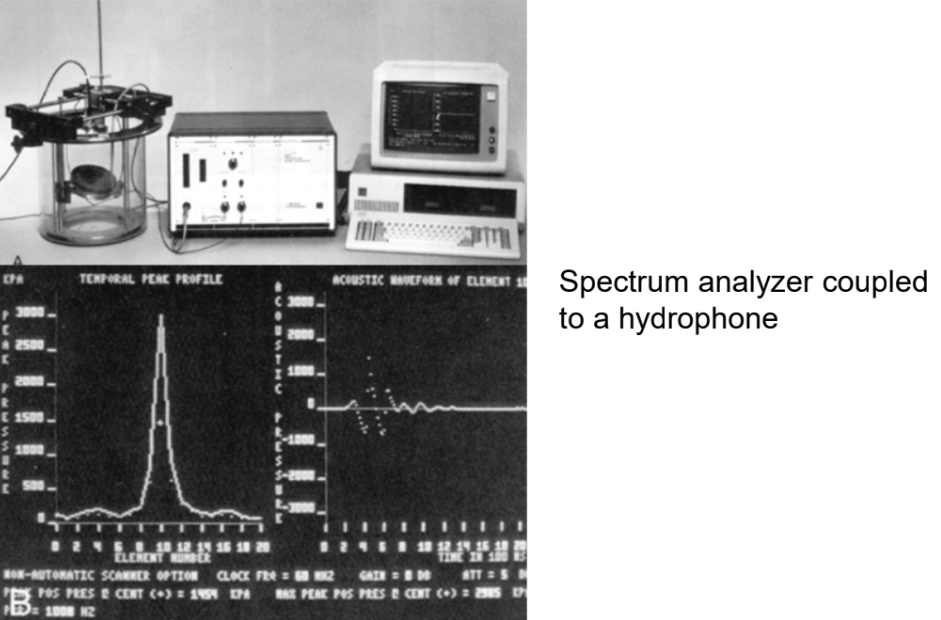
What is force balance?
Used to measure acoustic power. It is sophisticated and sensitive micro balance - placed in the sound field.

What does a force balance measure?
Measures acoustic pressure
Calibrated to determine acoustic power and intensity
What is a calorimeter?
A “heat meter”. It is used to measure acoustic power.
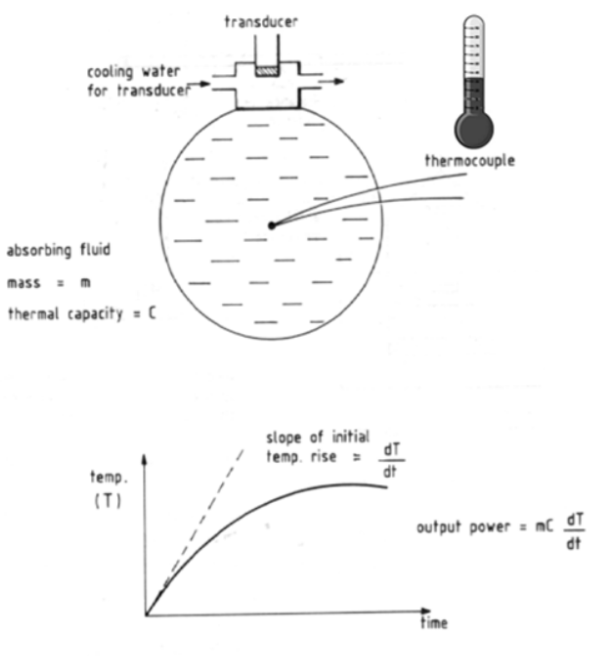
What is a calorimeter made out of?
An enclosed fluid container with a very sensitive thermocouple (thermometer).
The calorimeter is calibrated to extract what?
Acoustic power from the temperature increase.
What is a display monitor test?
A test that is used to ensure the display on the ultrasound machine is working correctly. This can be found by clicking your “F1” button on the keyboard.
What does gold standard mean?
The definitive test against which the diagnostic test is compared (ie. surgery, biopsy, CT, etc.)
What is the gold standard for kidney stones?
Unenhanced CT.
What is a true positive (TP)?
When the test is positive and the gold standard is positive.
What is a false positive (FP)?
When the test is positive but the gold standard is negative.
What is a true negative?
When the test is negative and the gold standard is negative.
What is a false negative?
When the test is negative but the gold standard is positive.
False positive is also known as what?
Overcall.
False negative is also known as what?
Miss.
What is sensitivity?
The ability of a test to find a disease when the patient has it (few “misses”, few false positives).
What is specificity?
The ability of a test to rule out a disease when the patient does not have it (few “overcalls”, few false positives).
What is a positive predictive value (PPV)?
Percentage of test-positives that truly have the disease.
What is another way of understanding PPV?
What is the chance of having the disease based on a positive test?
What is a negative predictive value (NPV)?
Percentage of test-negatives that do not have the disease.