gcse dt
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ocr gcse dt (might have missed a bit)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Give 2 examples of products with planned obsolescence
Washing machines
Mobile phones
what is cradle to cradle
Cradle to Cradle: all material inputs and outputs are seen either as technical or biological nutrients.
what are technical nutrients
can be recycled or reused with no loss of quality
what are biological nutrients
nutrients that can be composed or consumed
give an example of a cradle to cradle product
Adidas and Parley - Ocean Trainers (Made using plastics from the ocean)
name 2 types of paper
copier paper
sugar paper
what are the thickness of boards measured in
microns- a micron is one thousandth of a millimeter
between what gsm is thin card
180-300gsm
what is the gsm of cardboard
300gsm<
what are the 3 main categories of timber
Hardwood
Softwood
Manufactured Boards
2 examples of hardwood
Ash
Birch
2 examples of softwood
Pine
Spruce
2 examples of manufactured boards
Plywood
Chipboard
what is a veneer
A thin slice of wood less than 3mm thick
what are MF Laminates usually used for
Decorative covering for chipboard for kitchen worktops
what is seasoning wood
removing the excess moisture by 80-90%
what are the 2 main forms of seasoning
Air Seasoning
Kiln Seasoning
name 2 points about kiln seasoning
More expensive (than air seasoning)
Controlled method which is very quick (up to a few weeks)
name 2 advantages of seasoning planks
Greater immunity from decay
Increased resistance to rot
ferrous
contains iron
will corrode quickly and easily
2 examples of ferrous metals
Stainless steel
Cast iron
2 points about non-ferrous
Much more resistant to corrosion
Generally more expensive than ferrous metals
2 examples of non-ferrous metals
Aluminum
Tin
what is an alloy (DT SPEC)
A metal made by combining 2 or more metals to give different characteristics
2 examples of alloys
Brass
Bronze
what are thermo-polymers
polymers that soften when heated and can be moulded into shape
2 examples of thermo-polymers
PVC
Acrylic
What is a thermosetting polymer
A non recyclable polymer that undergoes a chemical change to become hard. Once set they cannot be re-moulded
Give 2 examples of thermosetting polymers
Epoxy resin
Silicone
What are fibres
They are tiny hair-like structure that are spun together to make yarns, which are woven together to make fabrics
What are the 2 types of fibres
natural and synthetic
natural fibers:
creation
source
made into yarns by?
Examples
Nature
animals/insects/plants
spinning
wool/cotton
synthetic fibres :
creation
source
made into yarns by?
Examples
man made
Coal/Oil
extrusion
polyester/nylon
name the 3 ways that yarns can be processed into fabrics.
woven
knitted
bonded
Explains weaving from yarns to fabrics
-Produced manually or automatically
-Made up of warp(horizontal) or weft yarns(vertical)
-different weaves create different fabrics
Explain knitting from yarns to fabrics
There are two types of knit: warp and weft
warp cannot be done by hand
weft can be done by hand
Explain non woven forms of transforming yarns to fabrics ( a disadvantage, when they are used, the 2 categories and how they work)
-Lack strength
-Normally used of decorative purposes
-Bonded fabrics are made by applying heat and pressure of adhesives to bond together (one use)
- Felted fabrics are produced by applying heat, moisture and friction to matt the fibres together. Most commonly with wool or acrylic
What are technical textiles
textiles specifically developed for their function and are often made from microfibres
What does Coolmax do and what is it used for
Wicks water away from the body and improves breathability
Used for bedding, sportswear and underwear
What does Nomex do and what is it used for
I is heat and fire resistant and protects from fire and heat
Used for protective clothing for racing drivers and oven gloves
What does Kevlar do and what is it used for
Resistant to damage from sharp or pointed objects
Used for stab and bullet proof vests ,and is used in linings in motorcycle clothing
What does fastskin do and what is it used for
Mimics the skin of a shark to improve performance
Used in competitive sportswear
What are modern materials
Materials that are continually being developed through processes.
What is Teflon used for?
As a non stick coating on cookware
What is Plexiply
A form of plywood that is extremely flexible and can be bent into shapes
What are conductive polymers
Plastic products that can conduct electricity
What are smart materials
Materials that respond to differences in the environment
Give three examples of smart materials
Shape memory alloy
Photochromic materials
Thermochromic pigments
What doe shape memory alloy do
Remembers its original shape and returns to it when heated
What do photochromic materials do
React to light. Some glasses have these and darken in bright sunlight
What do Thermochromic pigments do
They change colour with temperature, and can be added to polymers to create plastics which react to heat.
What are geotextiles
Permeable fabrics which, when used with soil, can separate, filter, or reinforce, protect or drain
What to geotextiles do
Make poor soil manageable.
What is Rhovyl
An innovative fibre containing an antibacterial substance, preventing the development of bacteria
What is carbon fibre made out of
Thin, strong crystalline filaments of carbon
Give 5 properties of carbon fibre
-High in stiffness
-High in tensile strength
-Low weight to strength ratio
-High in chemical resistance
-Temp. tolerant to excessive heat
Give 3 advantages of Glass reinforced plastic (GRP)
- Resistant to corrosion
- High tensile strength
- Non-conductive
what are the 5 steps of Identifying primary user and wider stakeholder requirements
1. Find a target market
2. Assess who the stakeholders should be
3. Develop a brief (in relation to your market and stakeholders)
4. Research the market
5. Create a target market
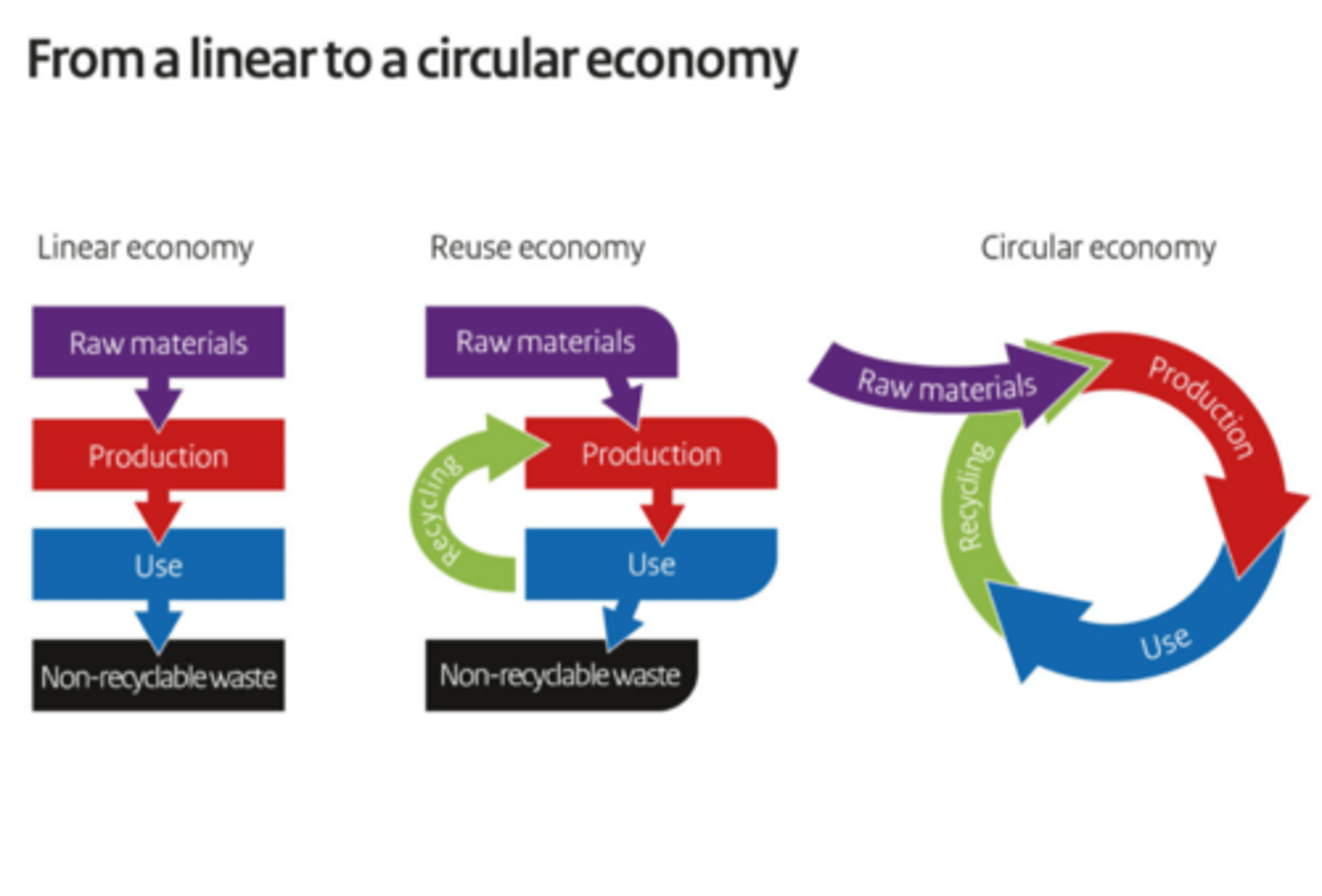
linear economy vs reuse economy vs circular economy
Linear Economy- take,make,dispose
Circular economy- make,use,recycle
what are the 6 Rs
Reduce
Reuse
Recycle
Rethink
Refuse
Repair
what is planned obsolescence
The business practice of deliberately outdating an item before the end of its useful life
what is context
The situation or context which a design solution is intended has an affect on many decisions that will be made
what is important to consider when creating a context
Place it will be used
Users
Purpose
Price
what is ergonomics
understanding interactions between people and things
what is anthropometrics
people measurements 5-95%
what is inclusive design
designing for the widest possible audience
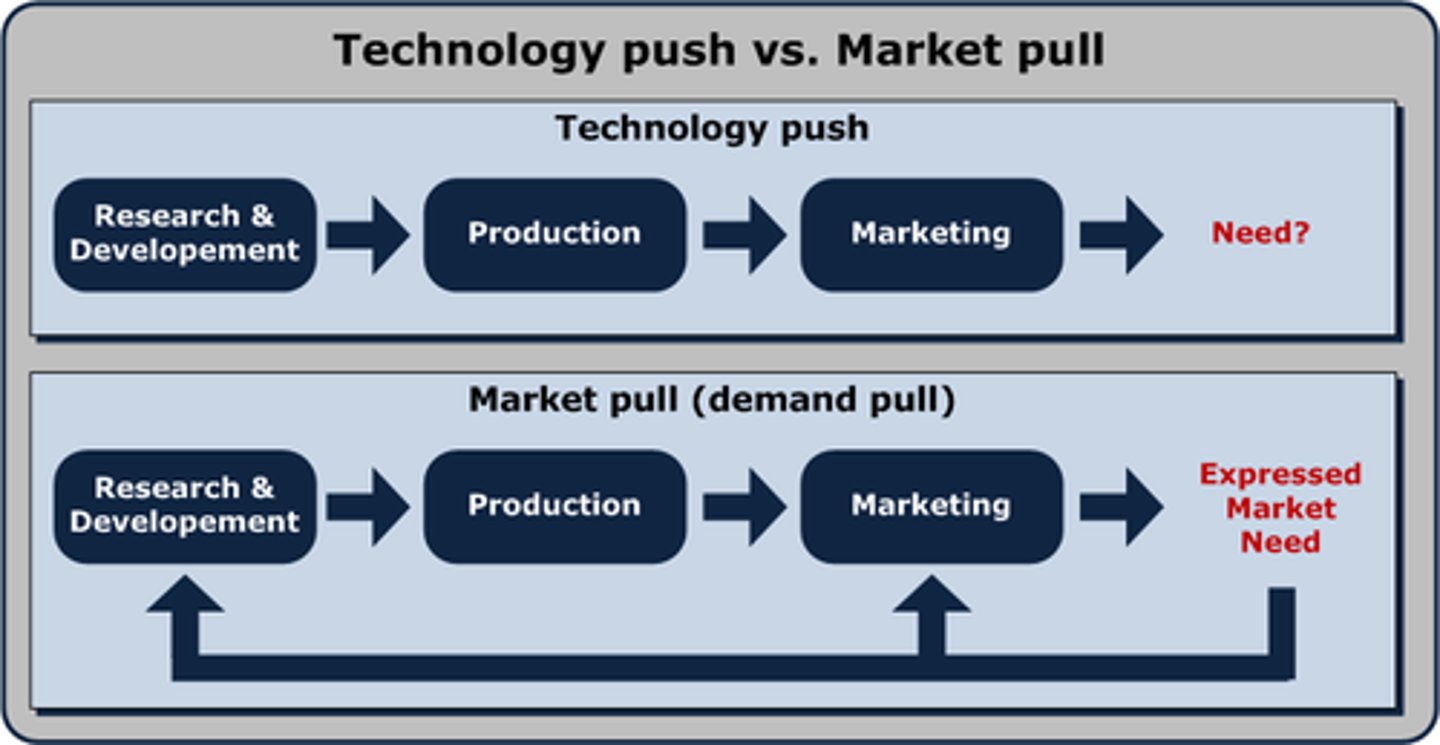
technology push vs market pull
technology push is a new innovative product whereas market pull is something needed from the market