Unit 2 Mitosis and Meiosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
sexual reproduction
reproduction that results from combining genetic material from two individuals.

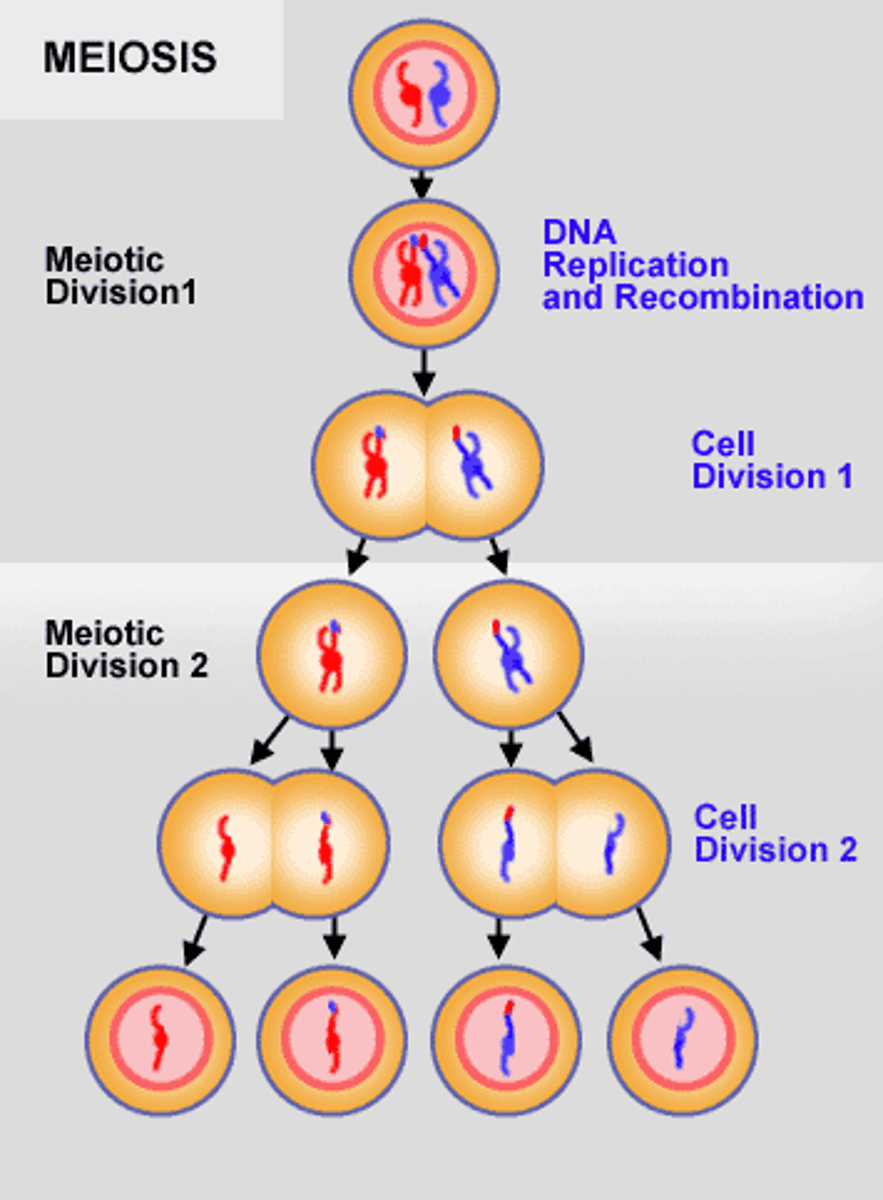
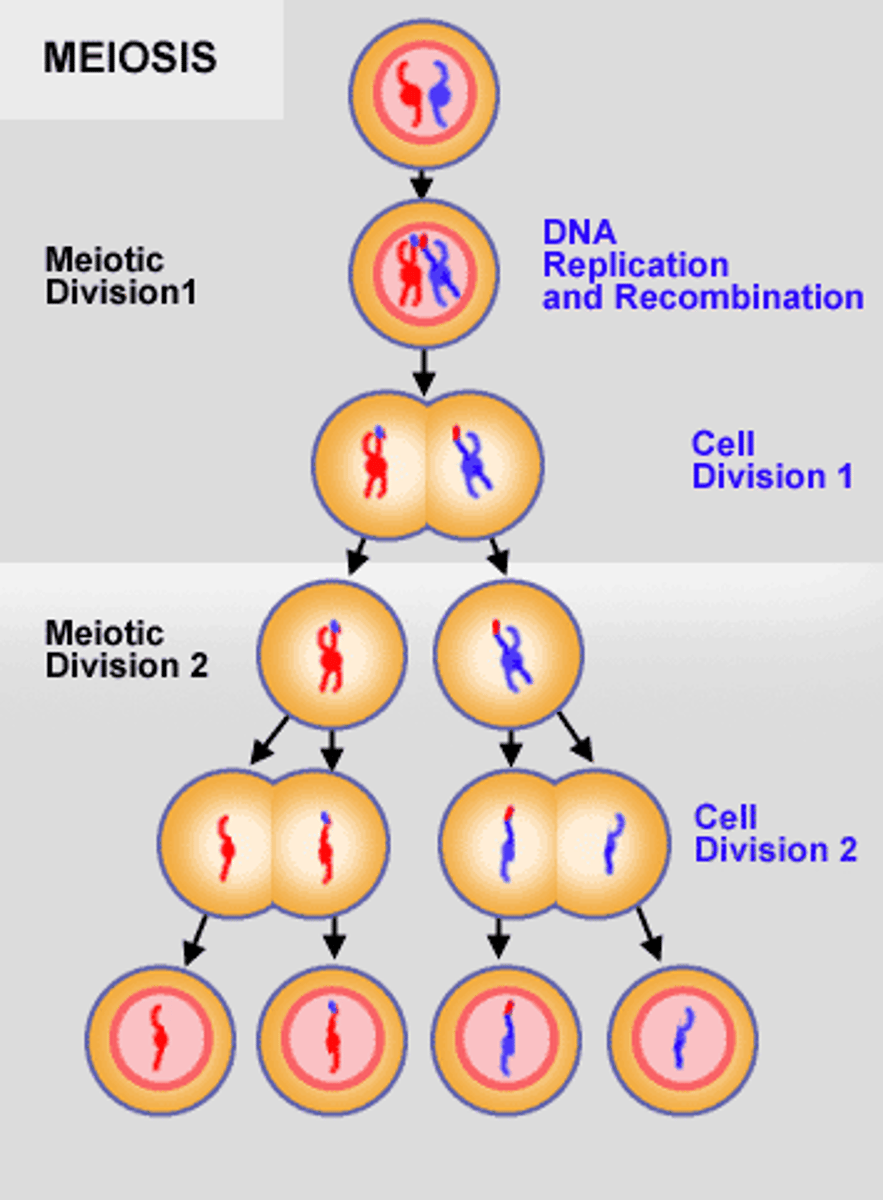
meiosis
type of cell division that results in 4 genetically unique haploid daughter cells that each have half the number of chromosomes as the diploid parent cell.
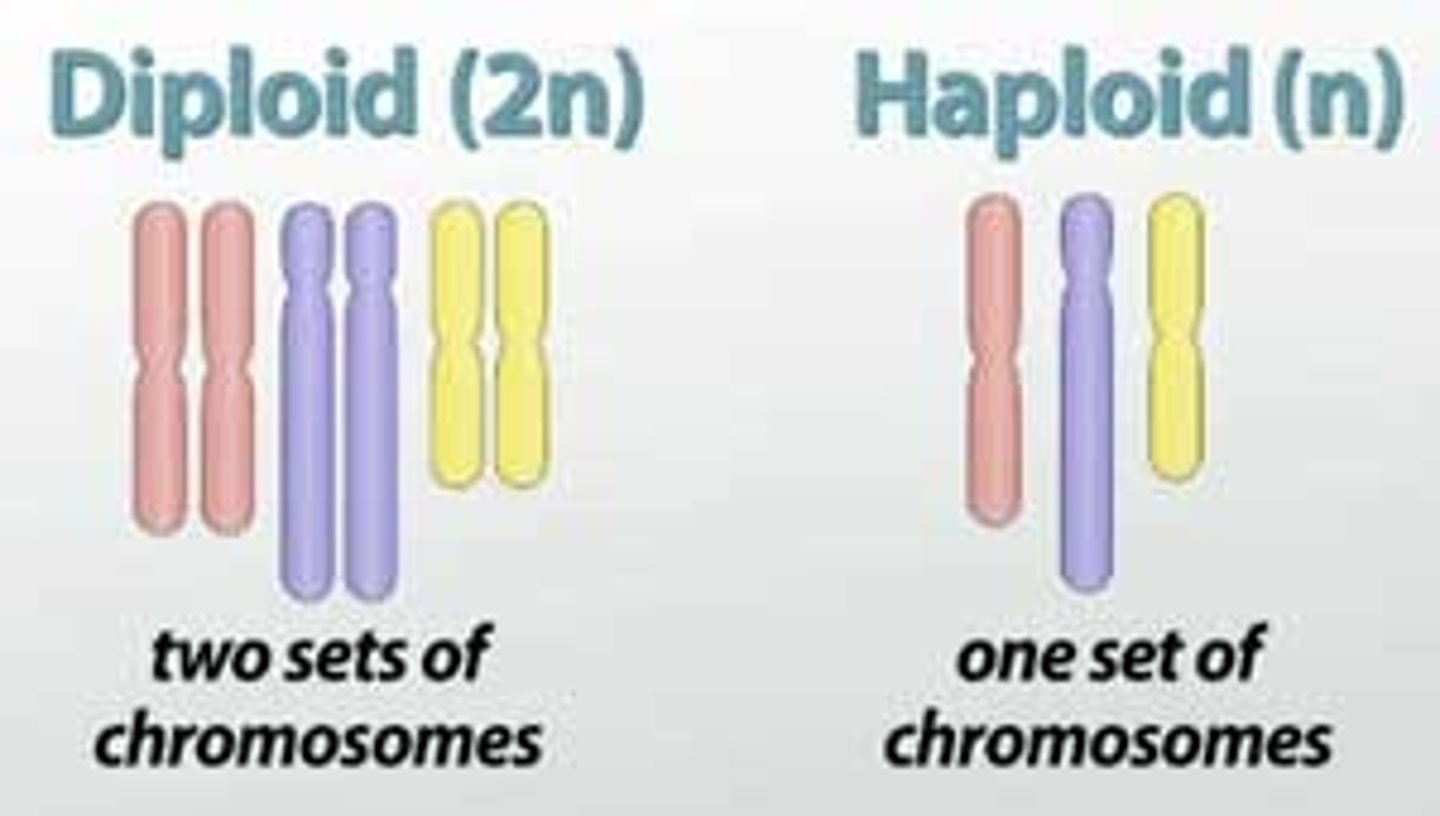
Diploid
A cell containing two full sets of chromosomes In humans: 2n=46.
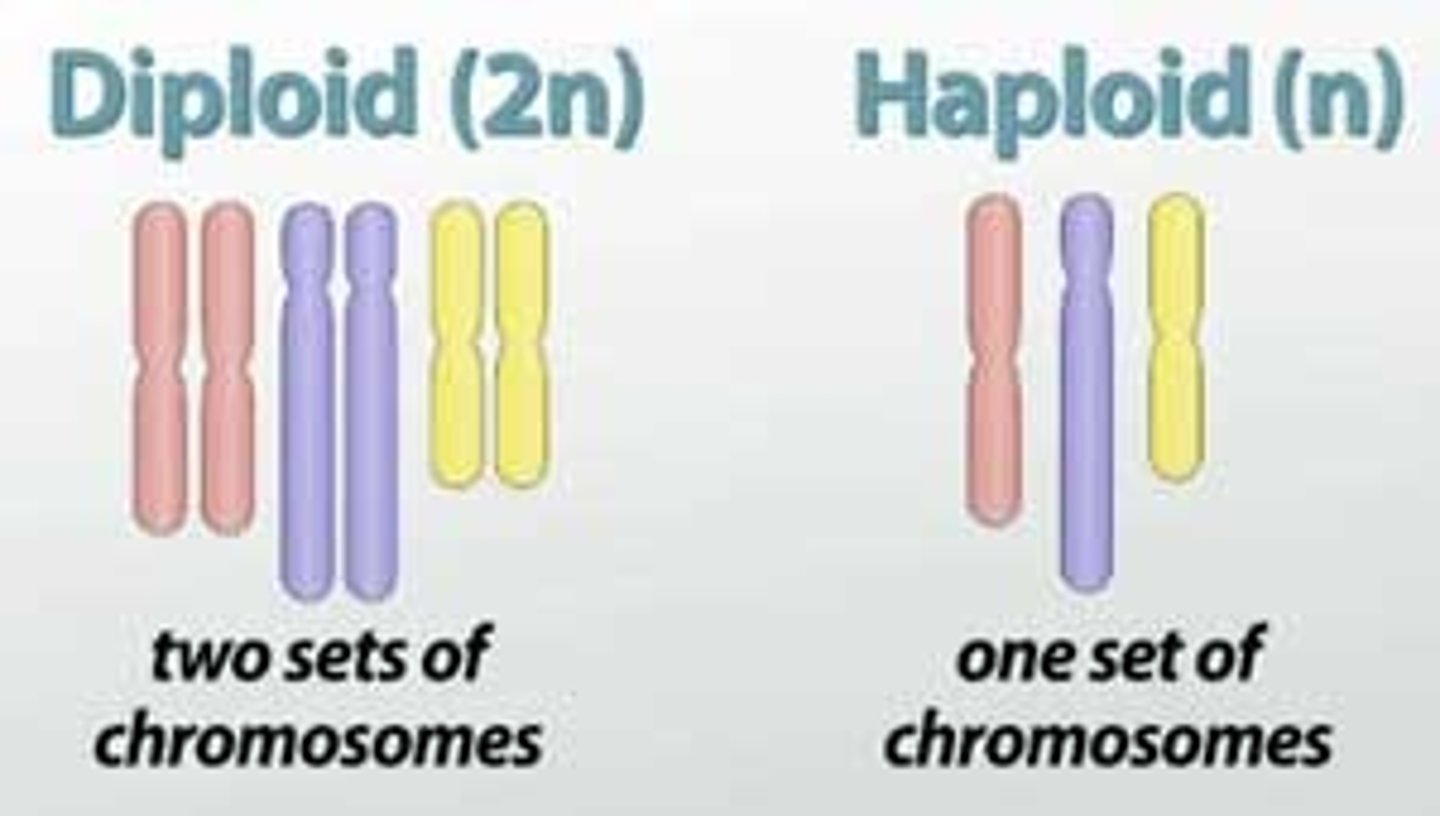
Haploid
A cell containing a single/ half set of chromosomes. In humans: n=23
Gametes
A haploid male or female germ cell (e.g. sperm and egg)
gene
a section of the DNA (chromosome) that codes for a specific trait (e.g. eye color or hair color) or functional protein
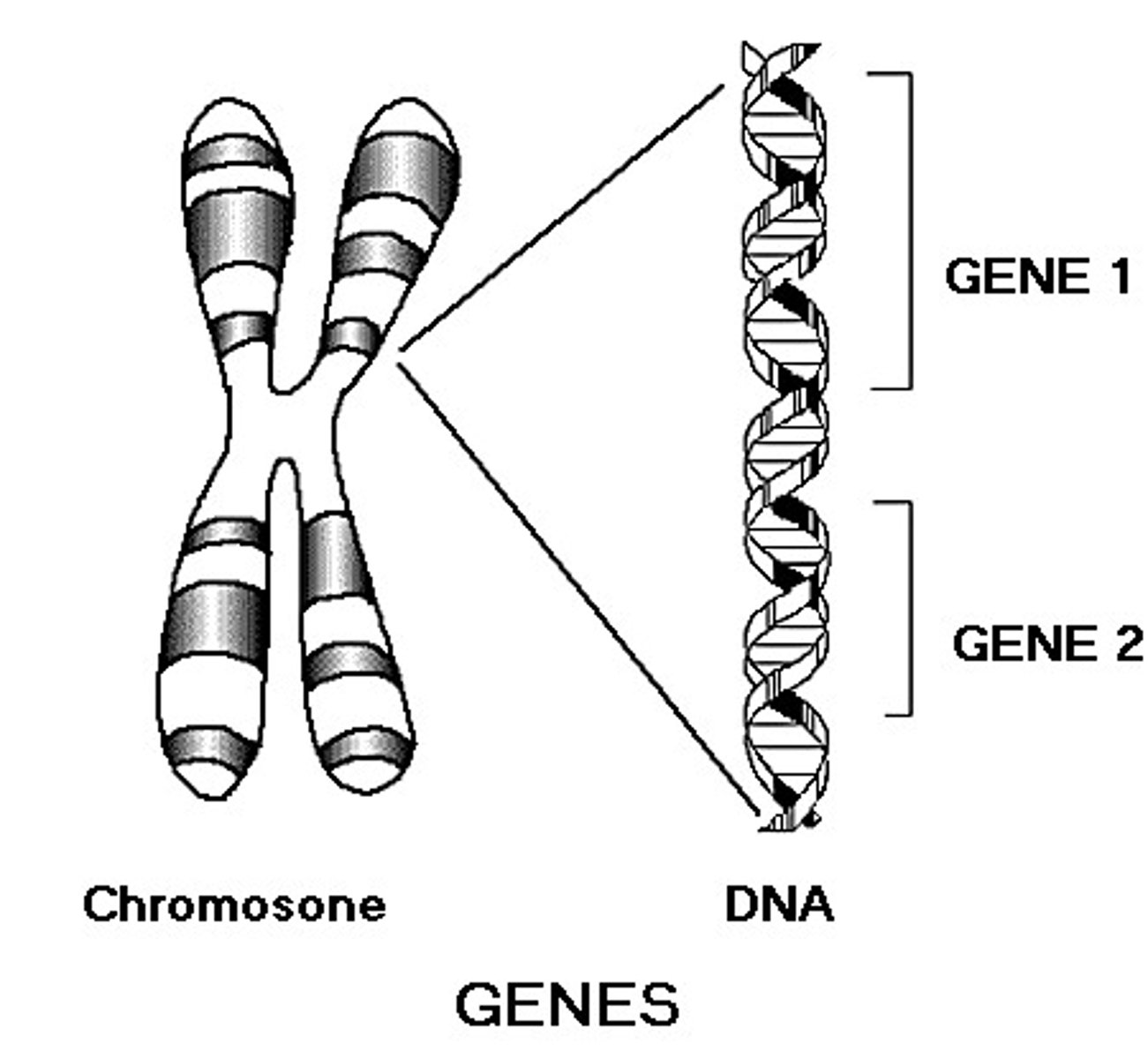
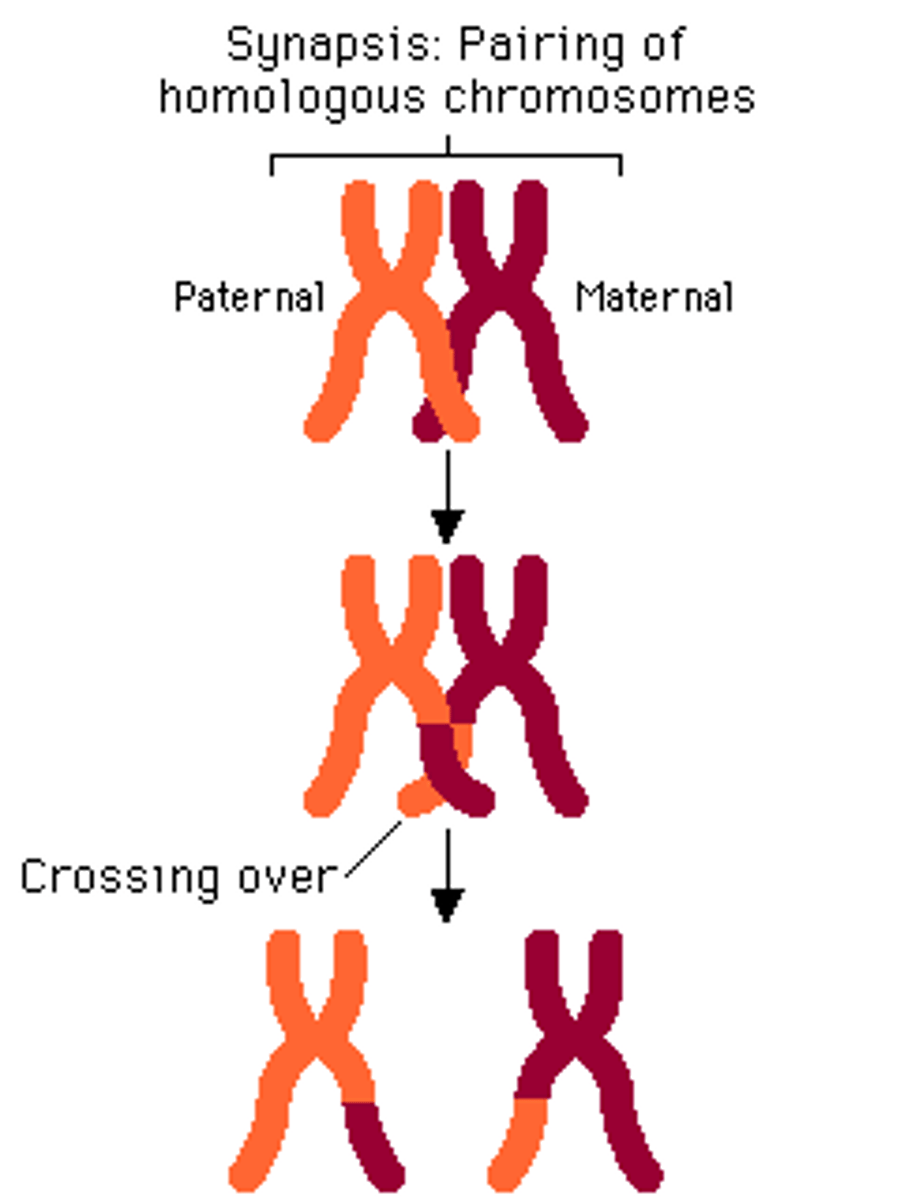
crossing over
when homologous chromosomes exchange segments of DNA during Prophase 1 creating new mixture of parent traits in their offspring
Meiosis I
The first cell division of meiosis when the homologous pairs are split up into two separate cells (two diploid daughter cells)
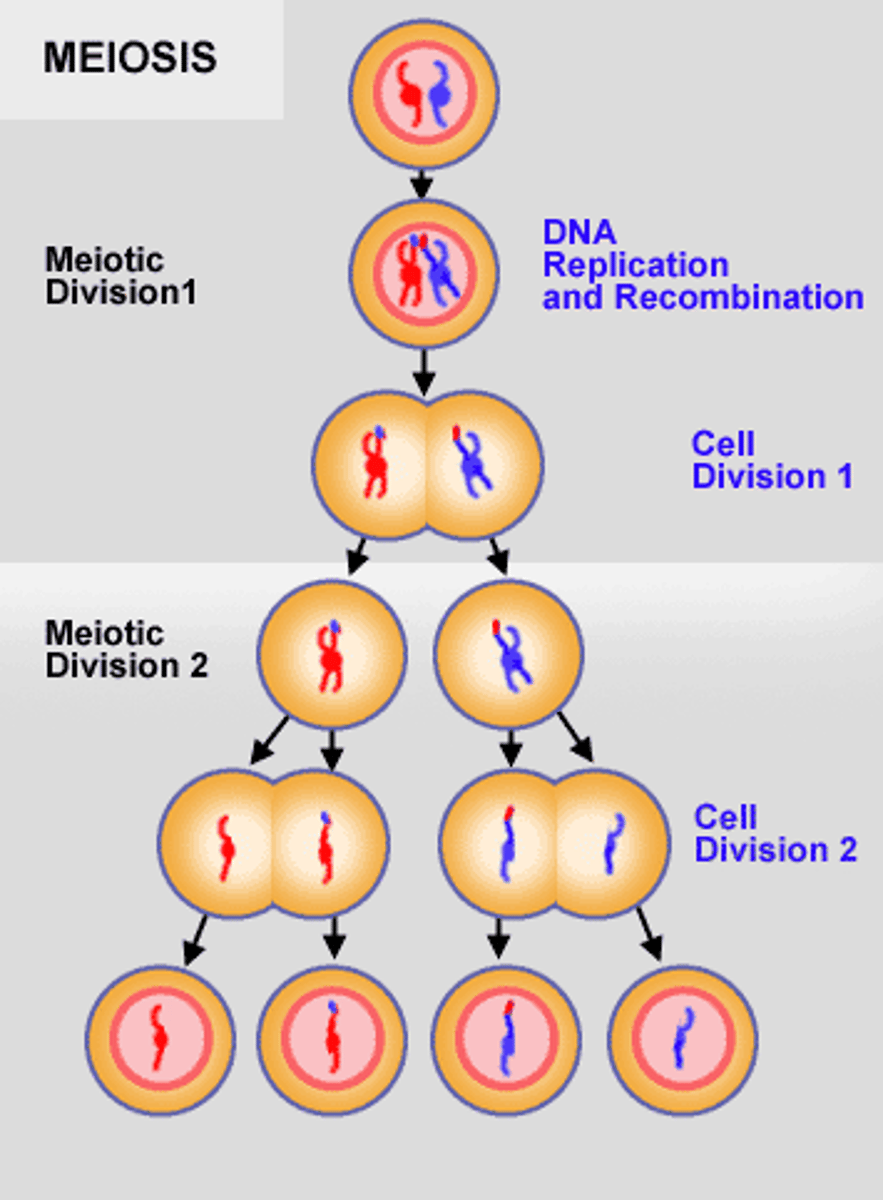
Meiosis II
The second cell division of meiosis. This is when the sister chromatids are split up into two separate cells (haploid daughter cells)
Mitosis
Produces cells almost genetically identical (only source of genetic variation is random mutation)
Asexual reproduction
Has the advantage of producing offspring in greater numbers, with no partner required
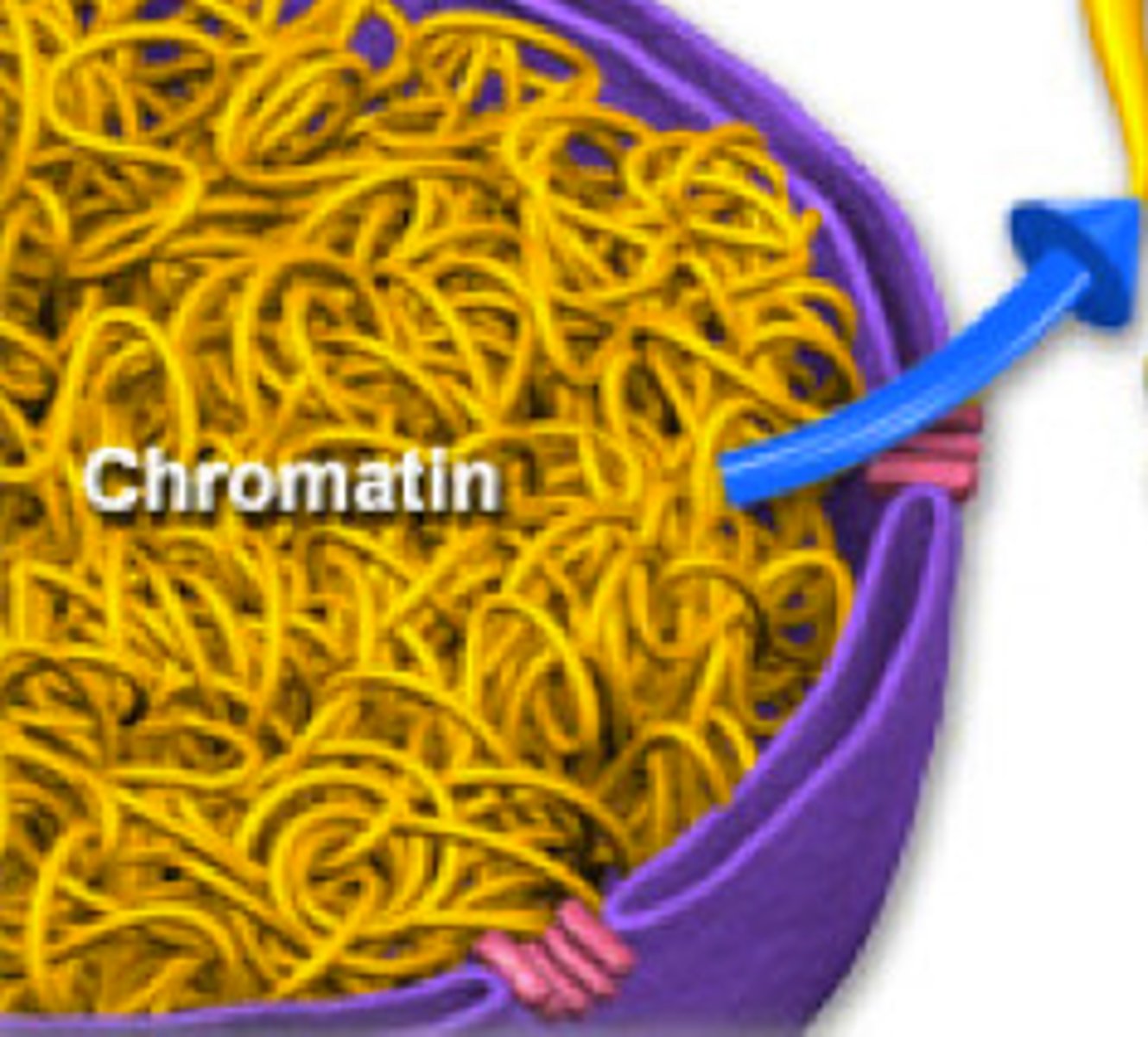
Chromatin
Uncoiled DNA. Present in interphase. Looks like bowl of spaghetti.
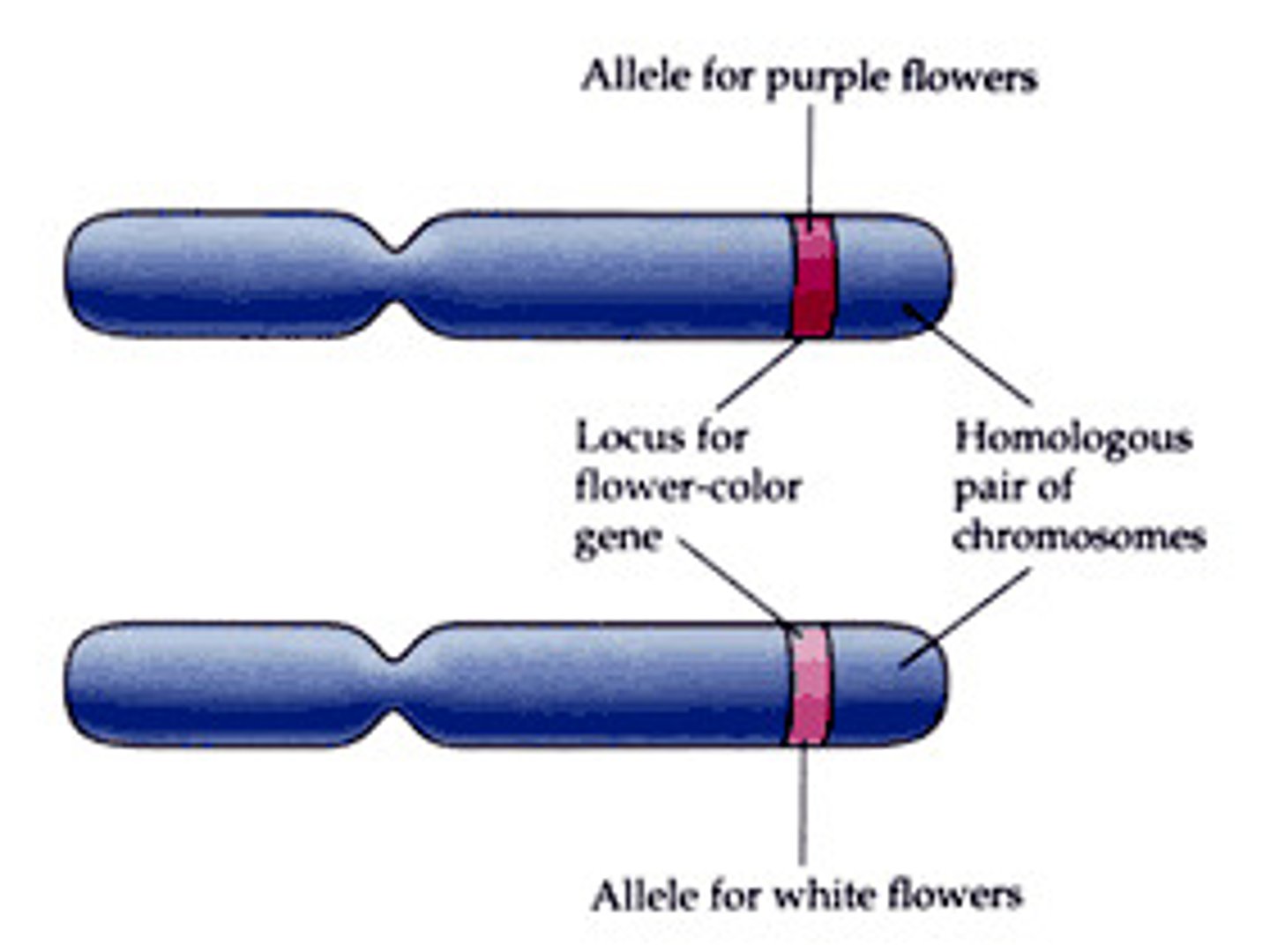
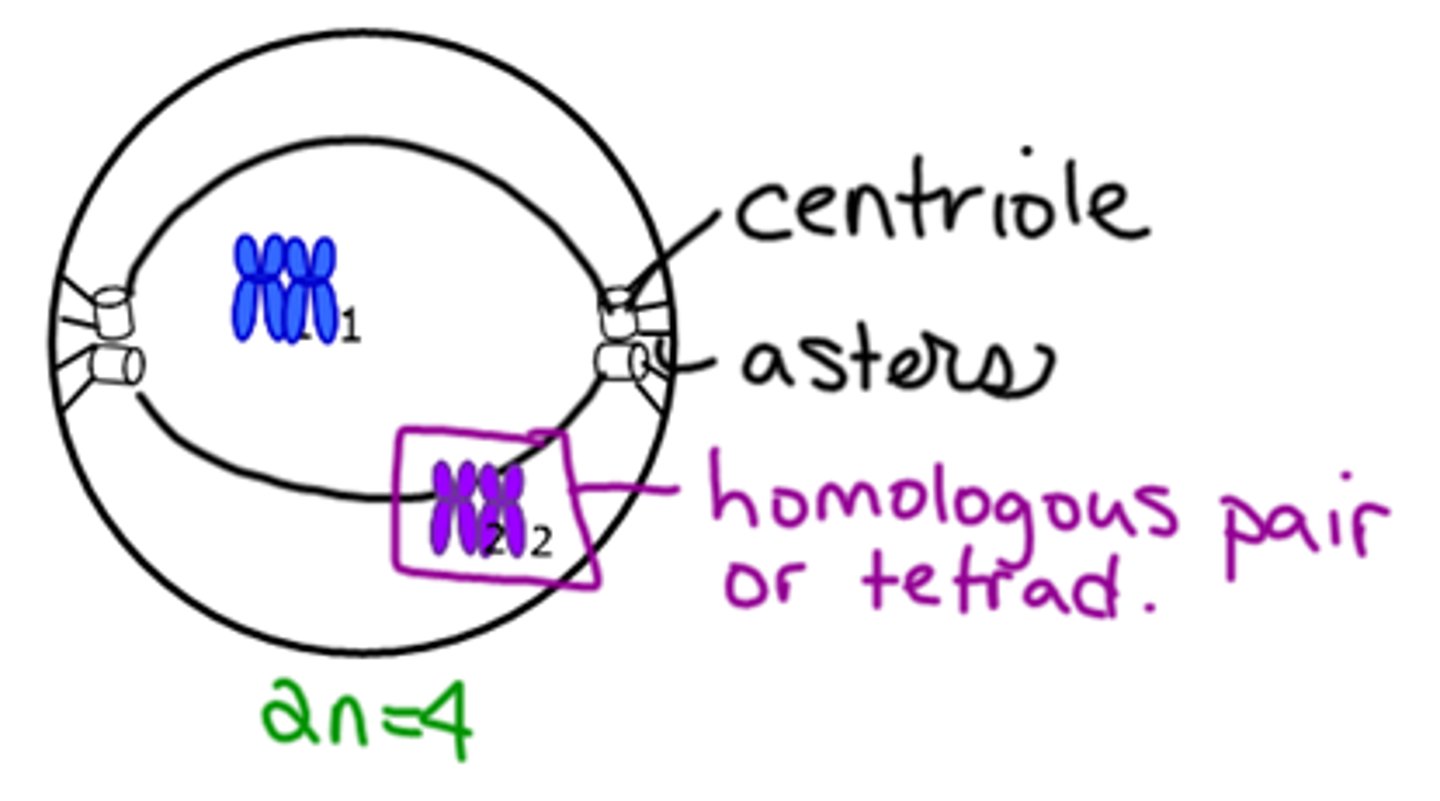
Homologous Chromosomes
Carry the same genes at the same locus (location). DNA sequence is not necessarily identical. One of maternal origin and one from paternal origin.
Ex. Chromosome 1 and Chromosome 1
Three phases of interphase
G1,S,G2
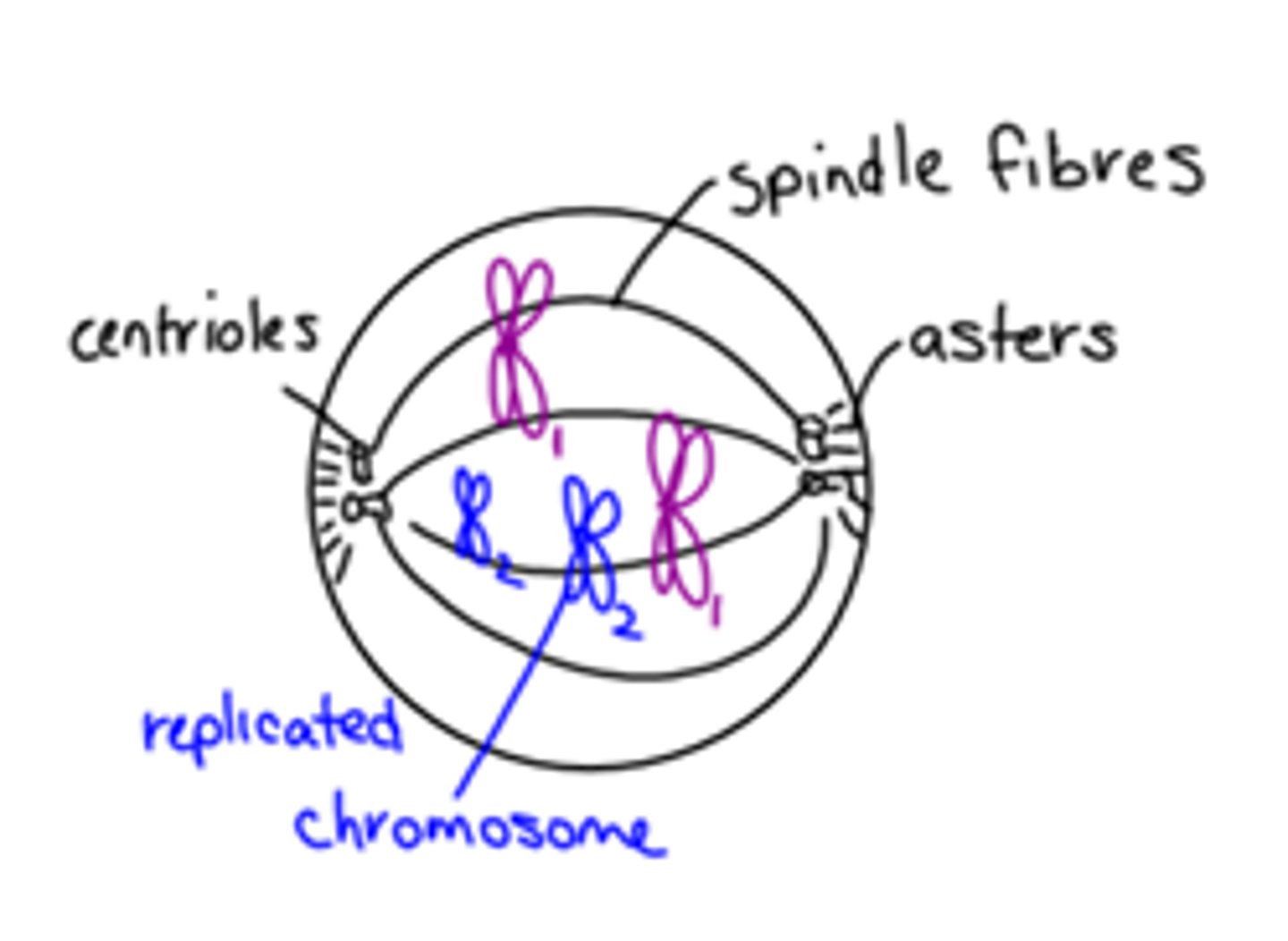
Prophase
Chromatin coils up into chromosomes.
Centrioles move to poles.
Spindle fibres and asters form. Nucleus and nucleolus
disappear.
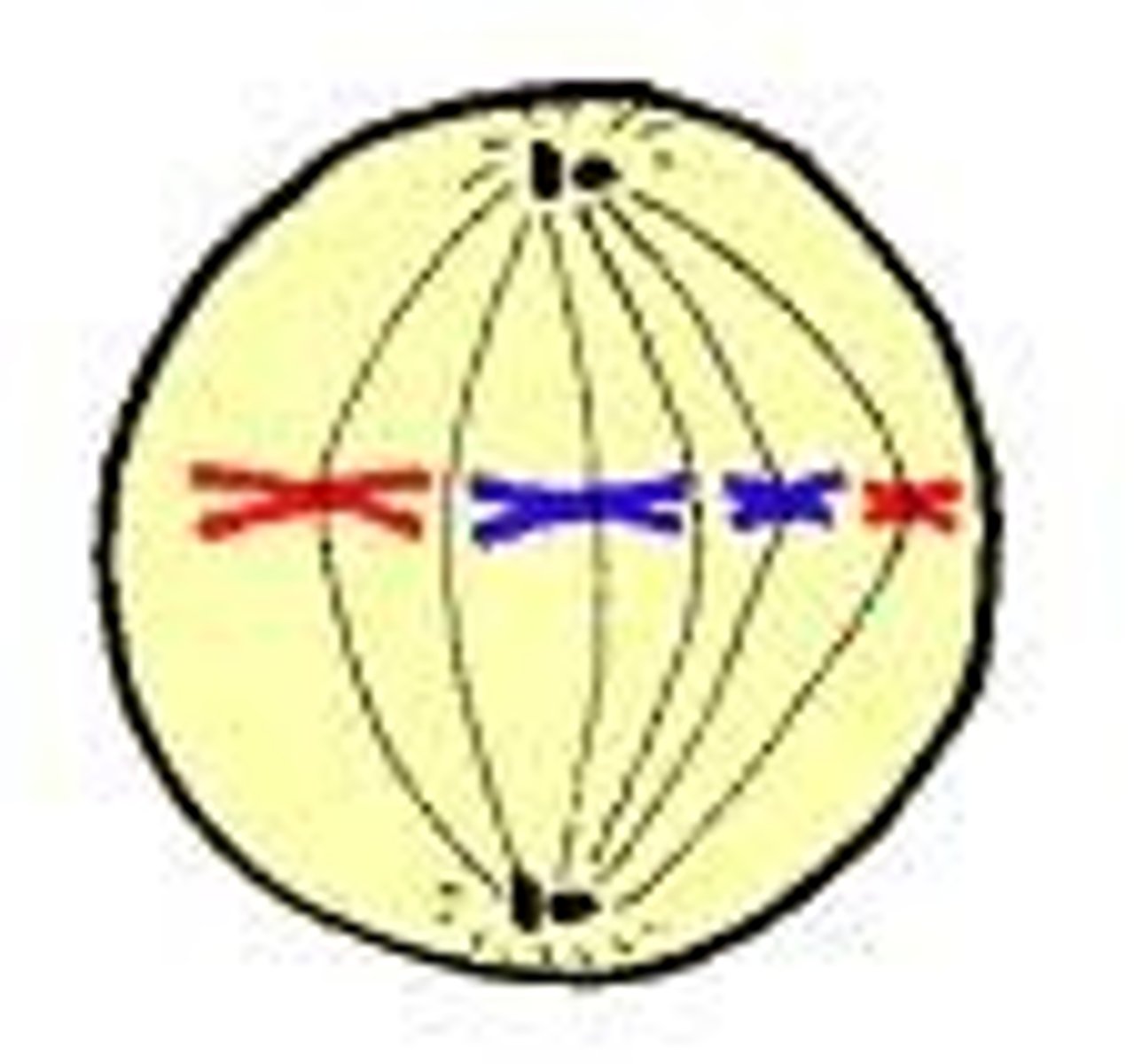
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
Anaphase
Centromeres divide. Sister chromatids move to opposite poles.
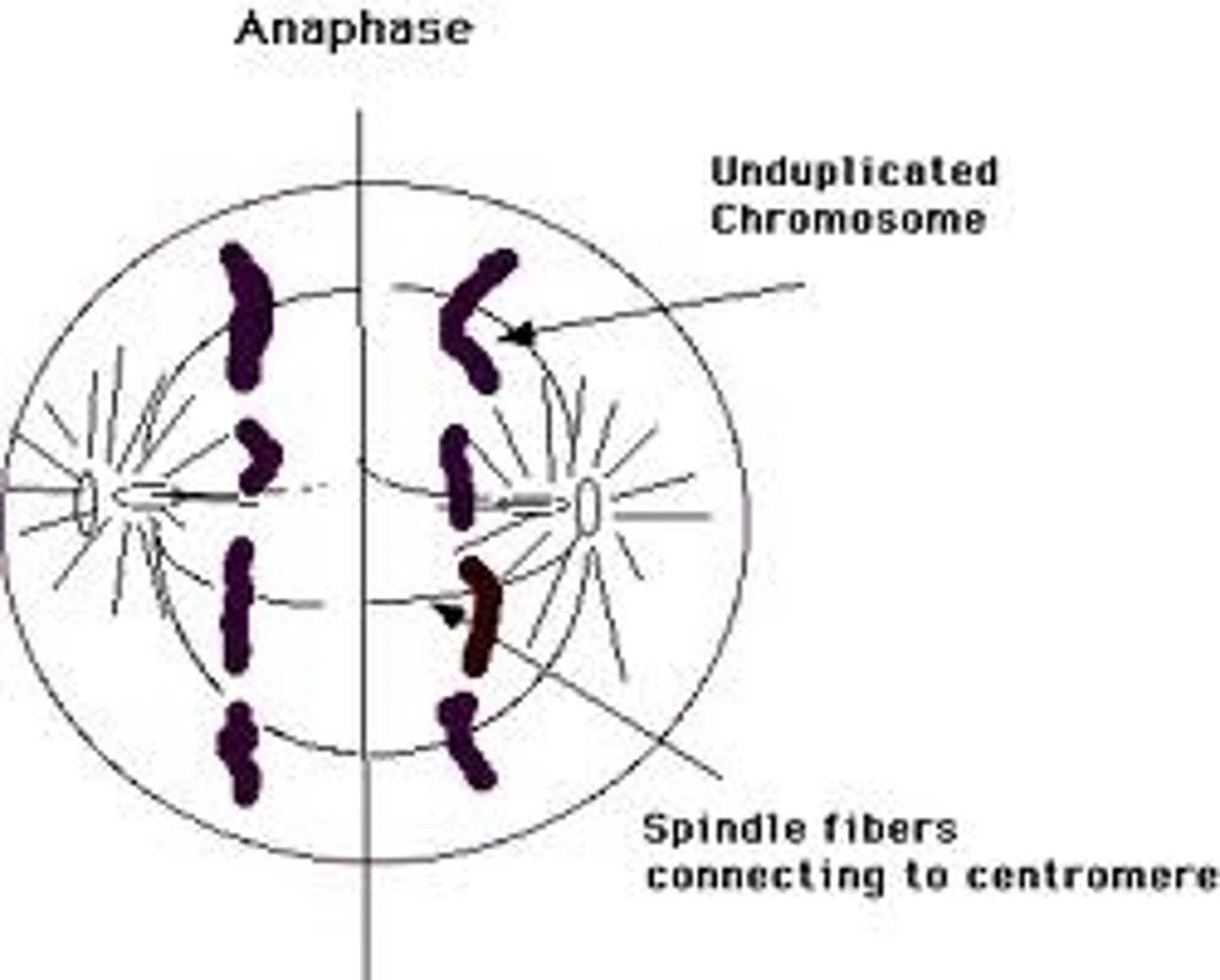
Telophase
Chromatids are totally apart. Cleavage furrow starts to form. Nuclear envelope starts to reform.
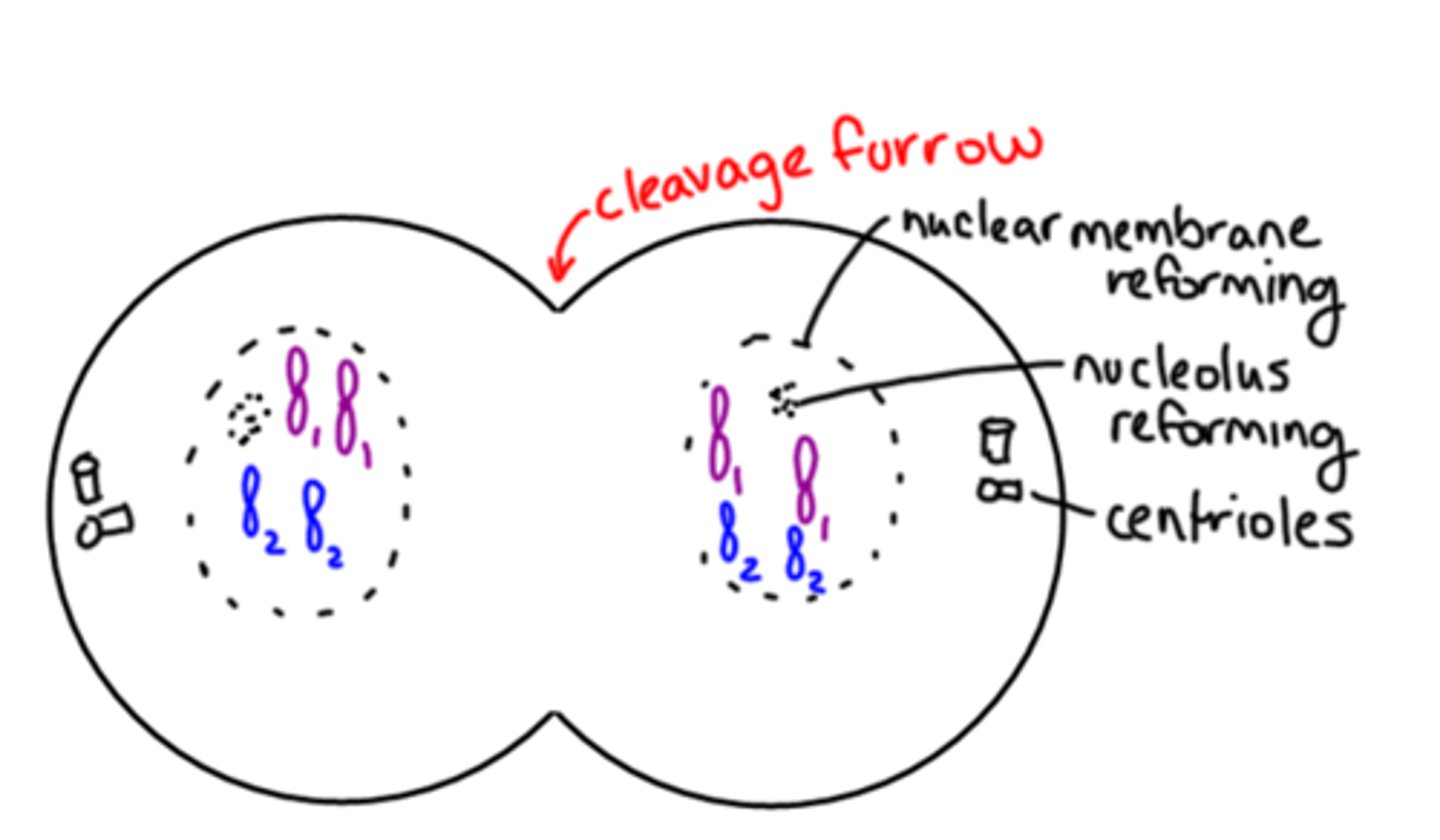
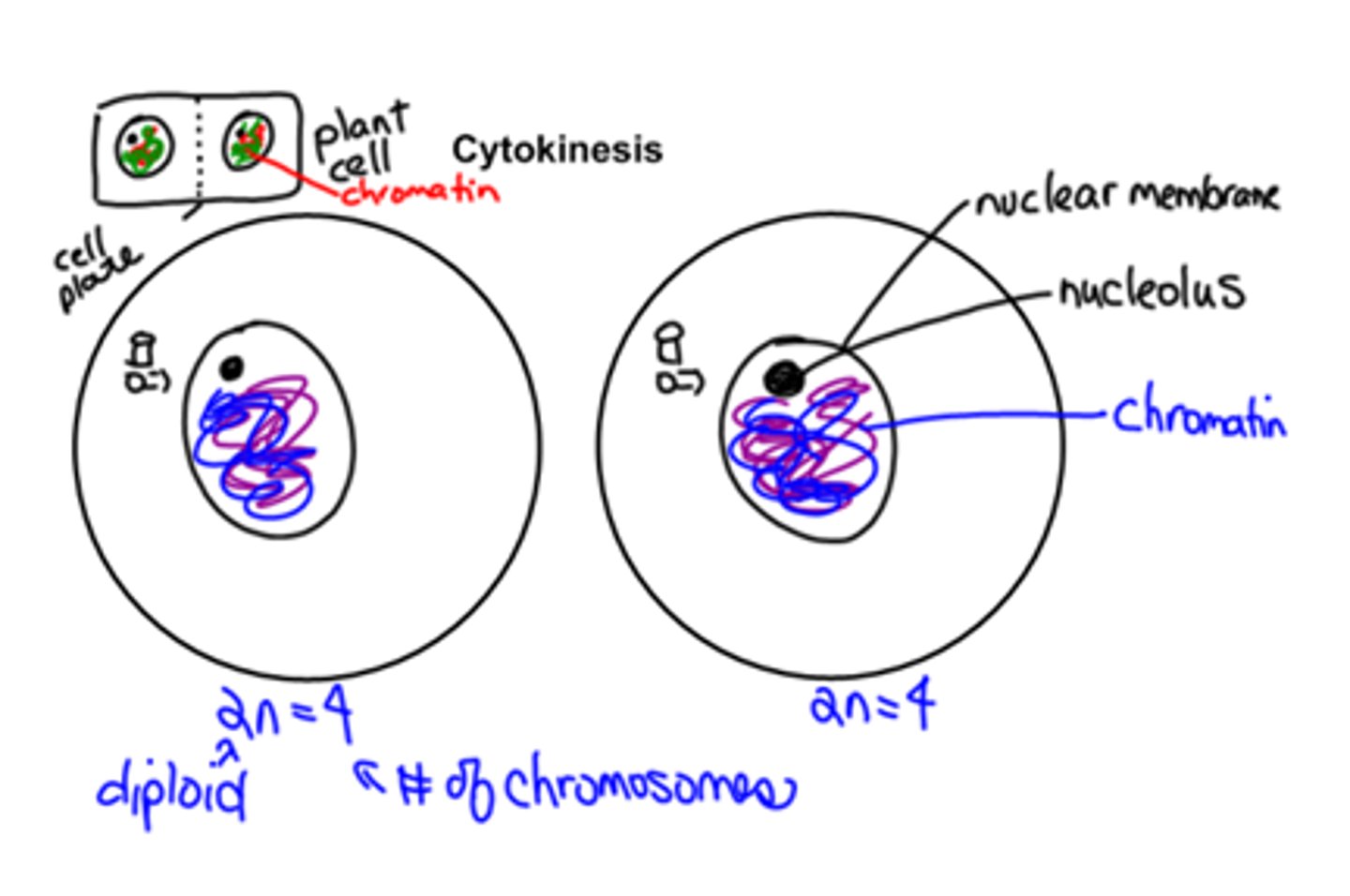
Cytokinesis
Cell divides into two. Cell plate forms in plant cells.
Sexual Reproduction
Requires male and female gametes. Much more genetic variation.
Asexual Reproduction
One parent only. (cloning)
Mitosis.
Crossing over
Non sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes may exchange genetic material during prophase I.
Occurs more often in genes that are further apart.
Prophase I
Synapsis - homologous chromosomes (tetrads) pair up.
Crossing over may occur - exchange of genetic material.
Metaphase I
Homologous pairs line up in the middle on the metaphase plate.
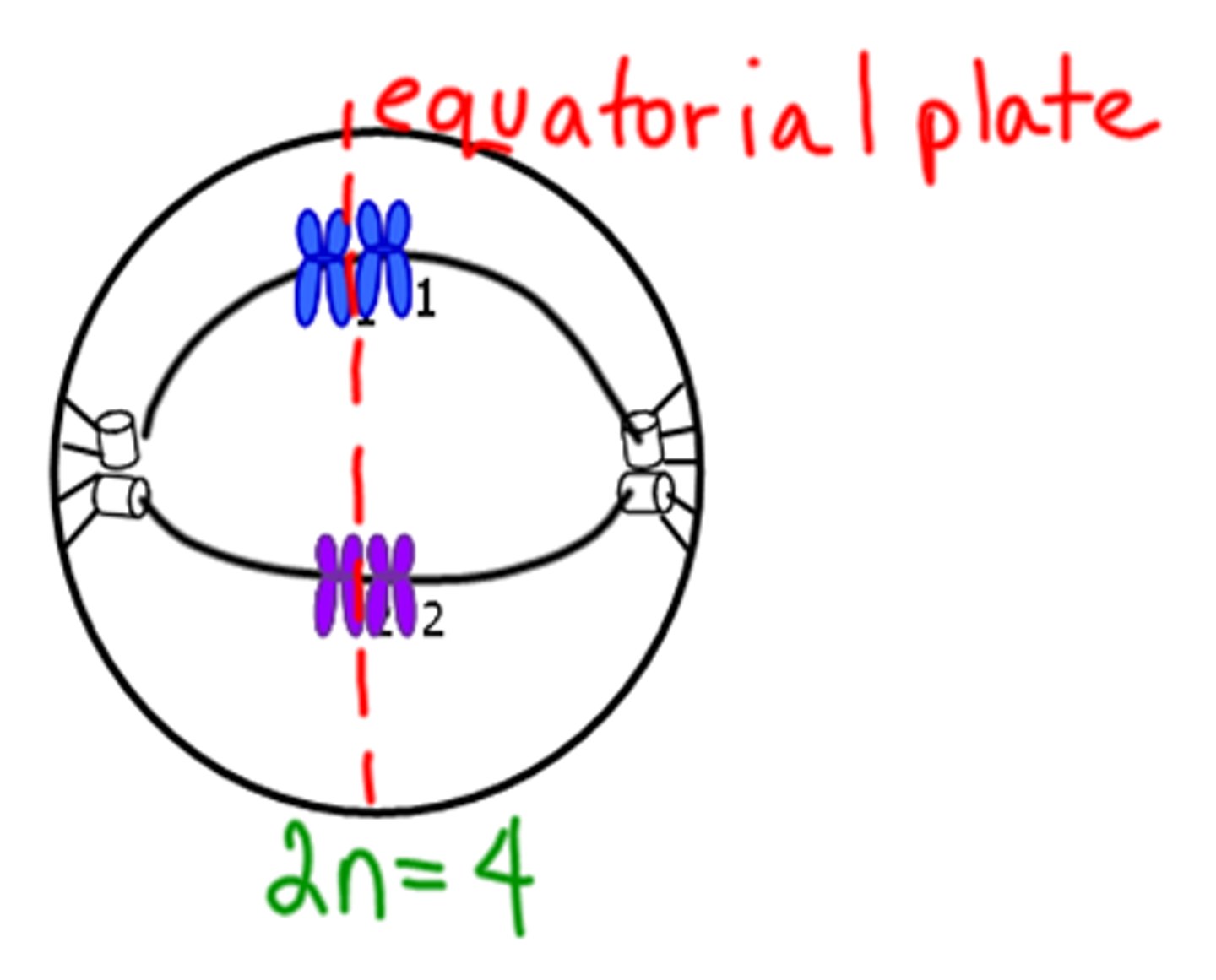
Anaphase I
Segregation - Homologous pairs separate to opposite poles.
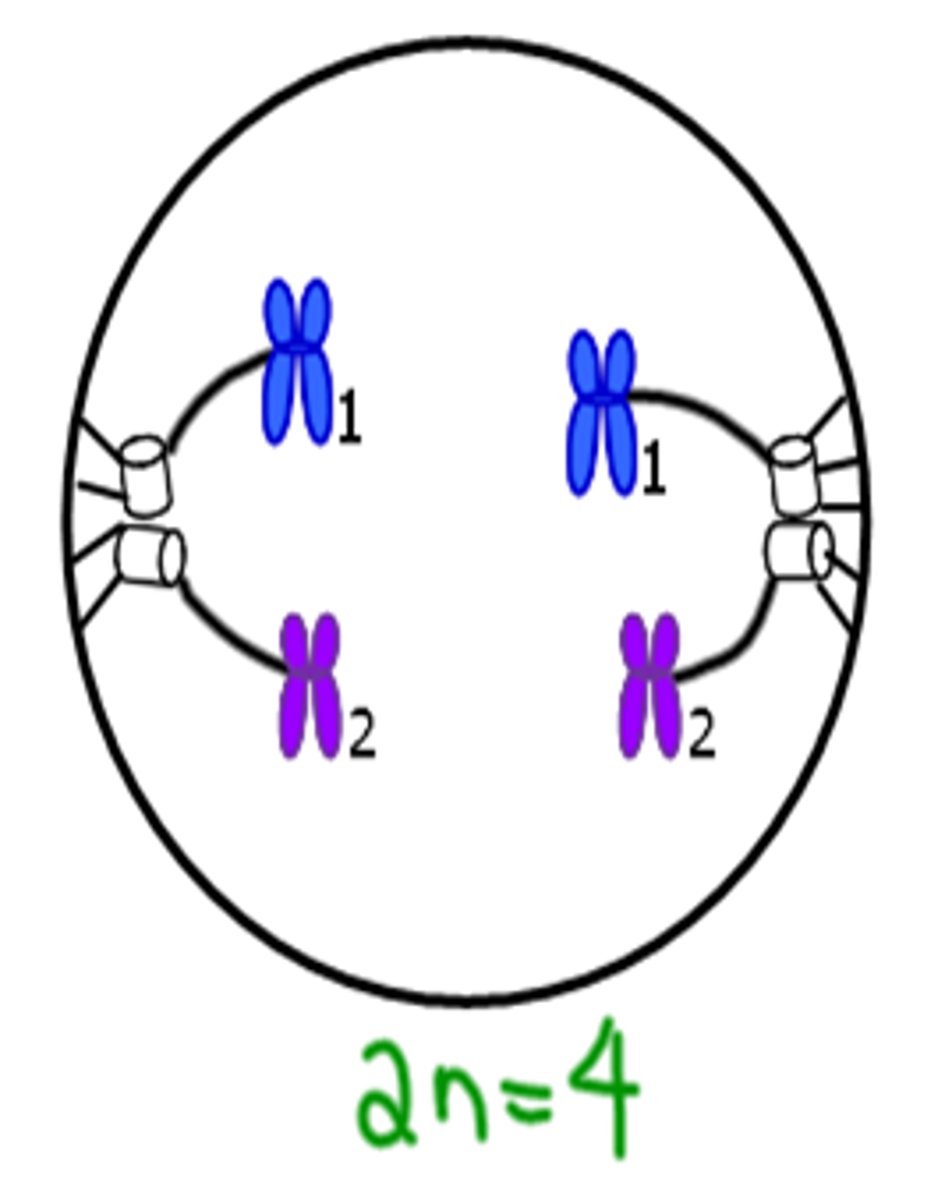
Telophase I
Chromosomes separate nuclei form.
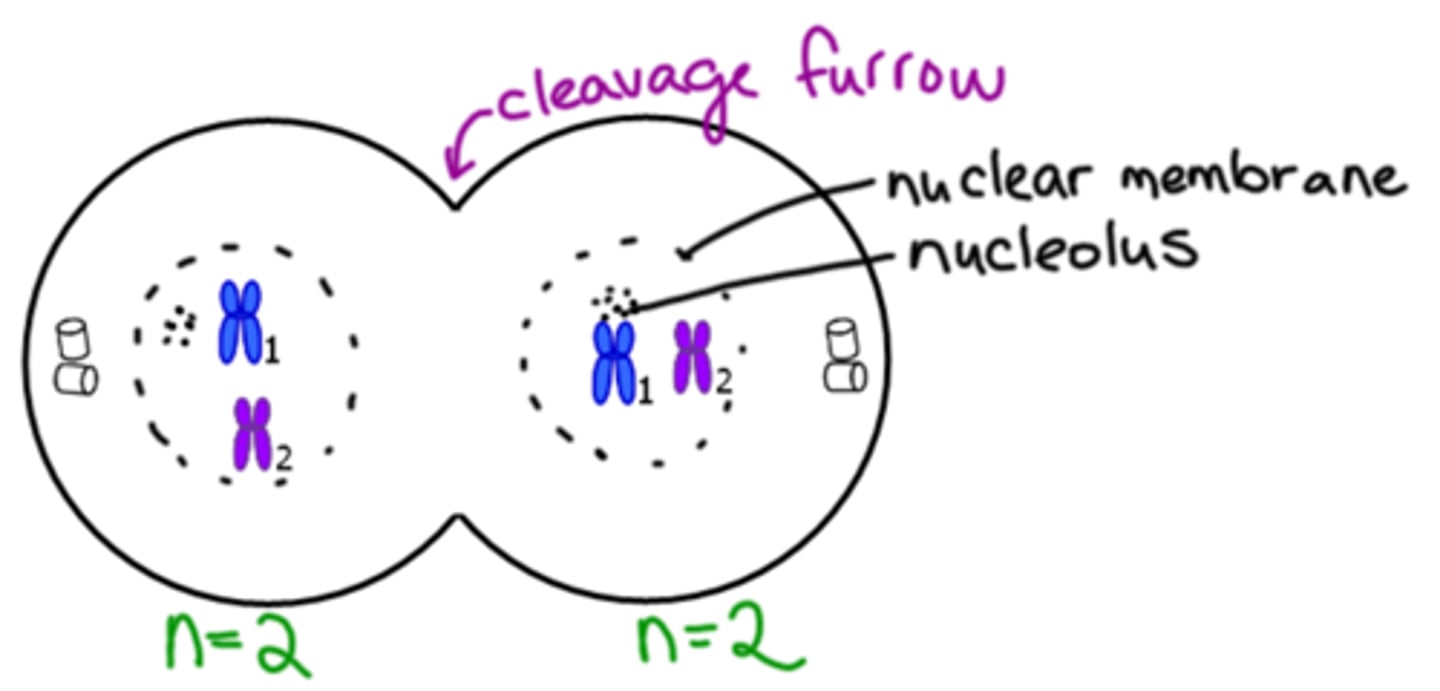
Prophase II
Two cells are present at the beginning.
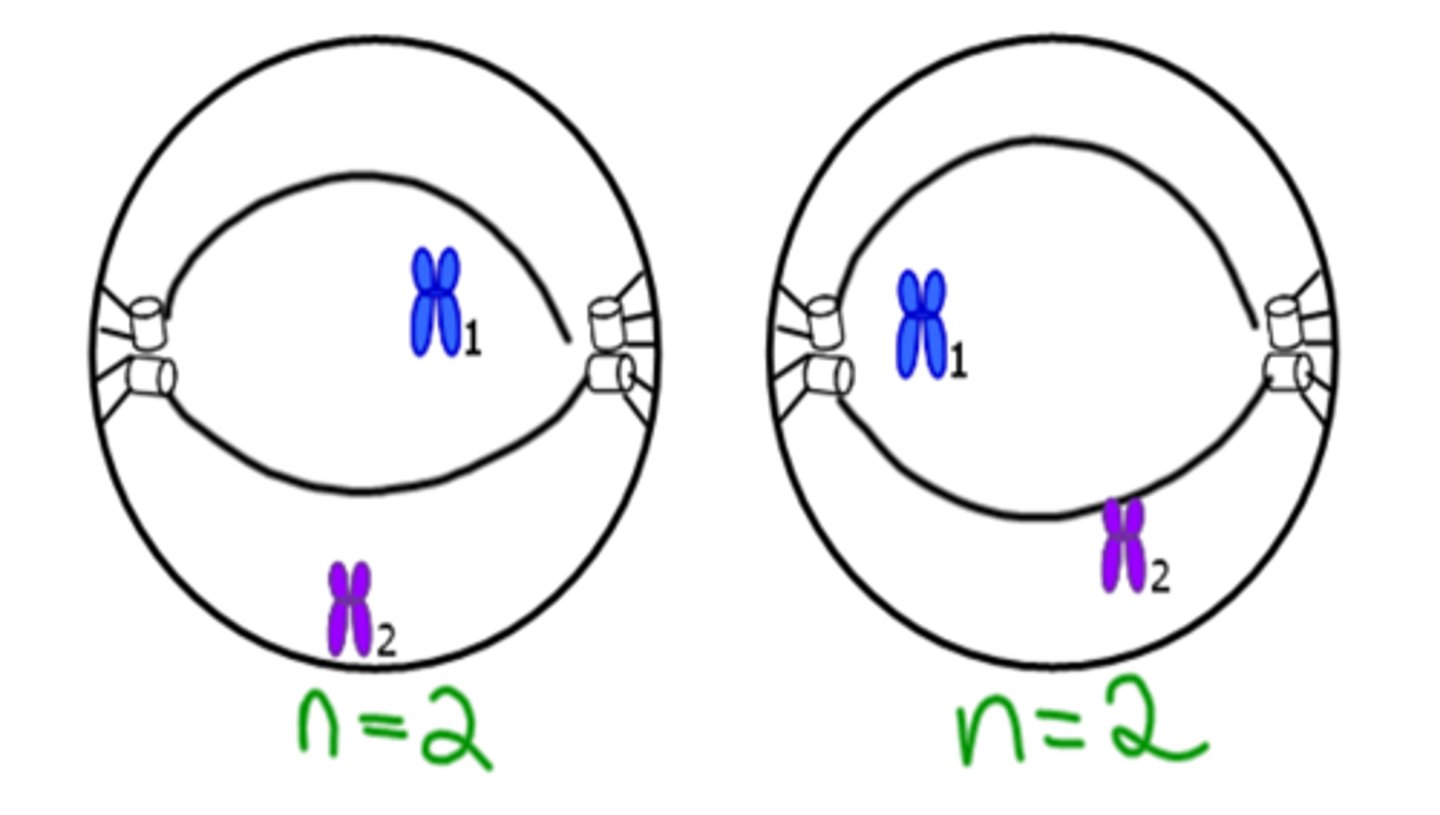
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up in the middle
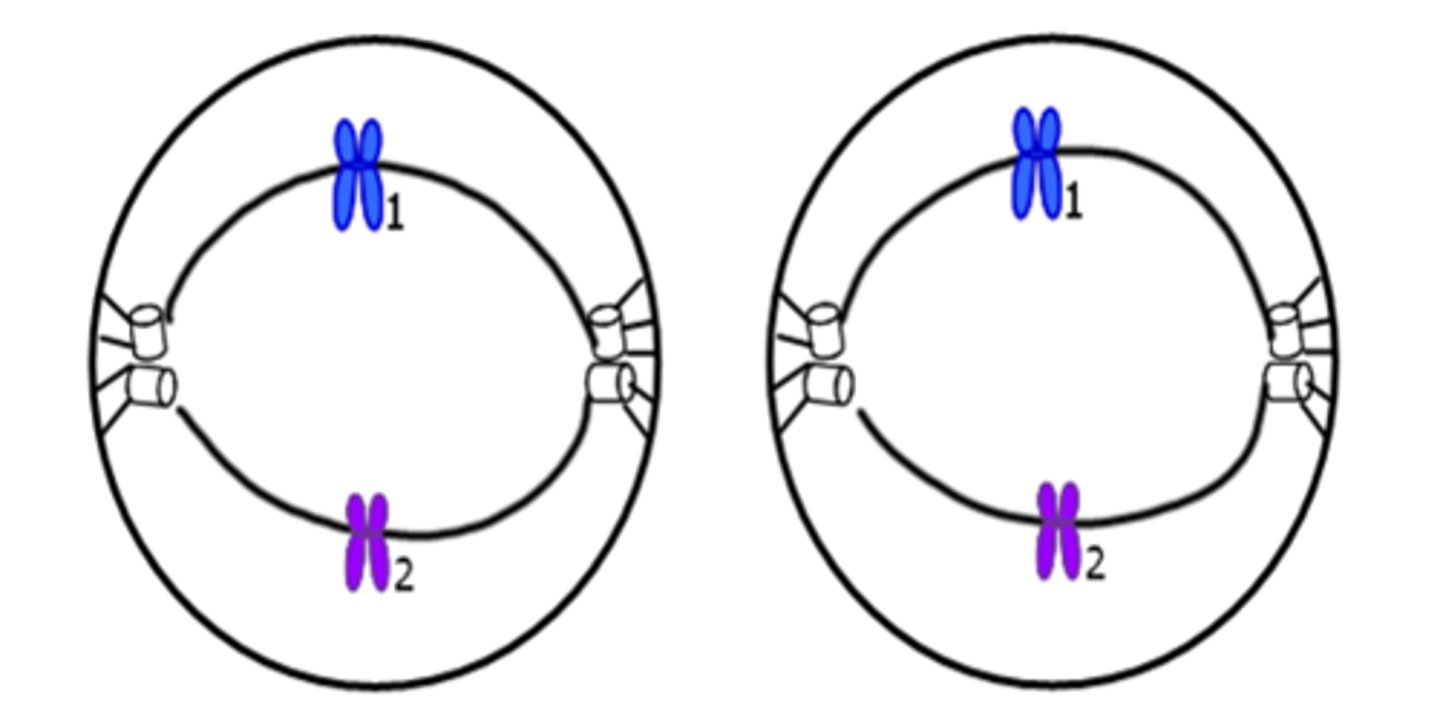
Anaphase II
Centromeres split. Single chromosomes move apart.
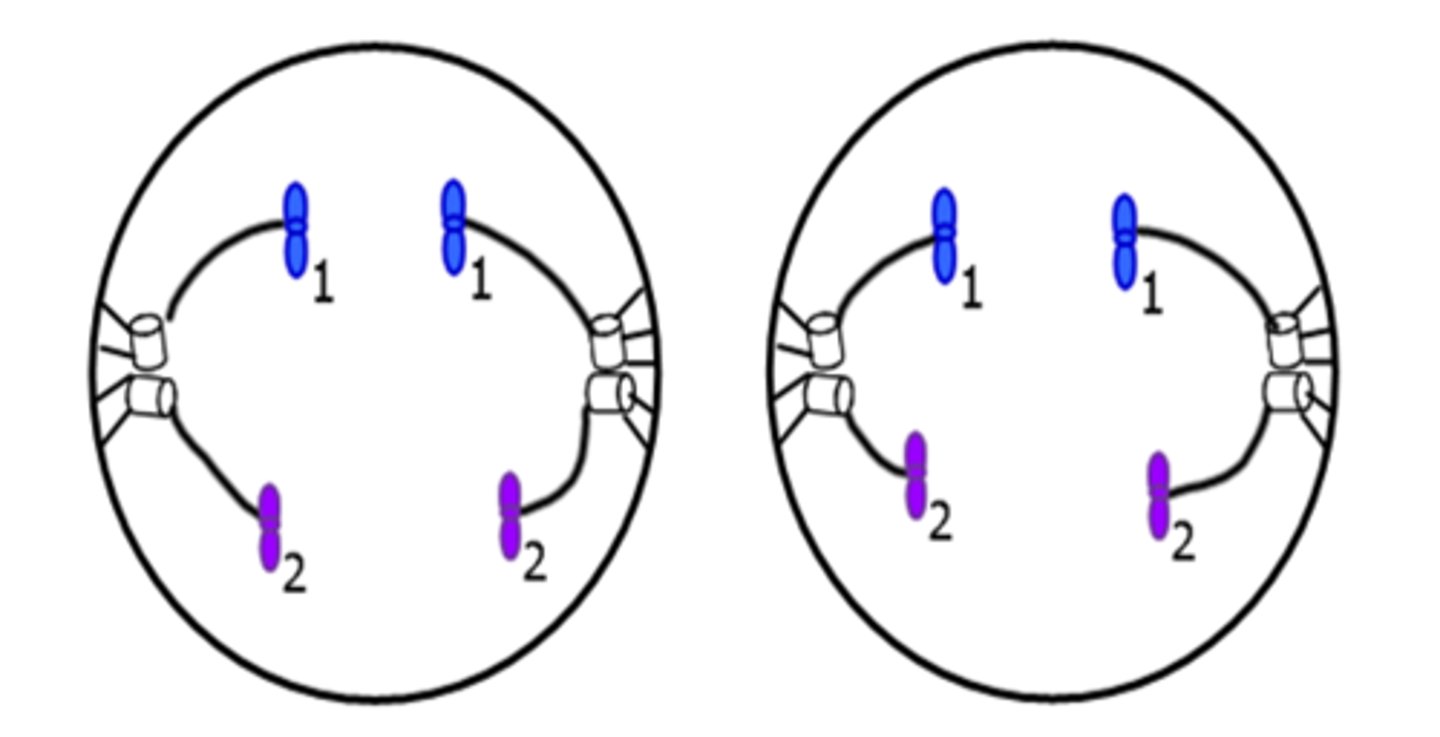
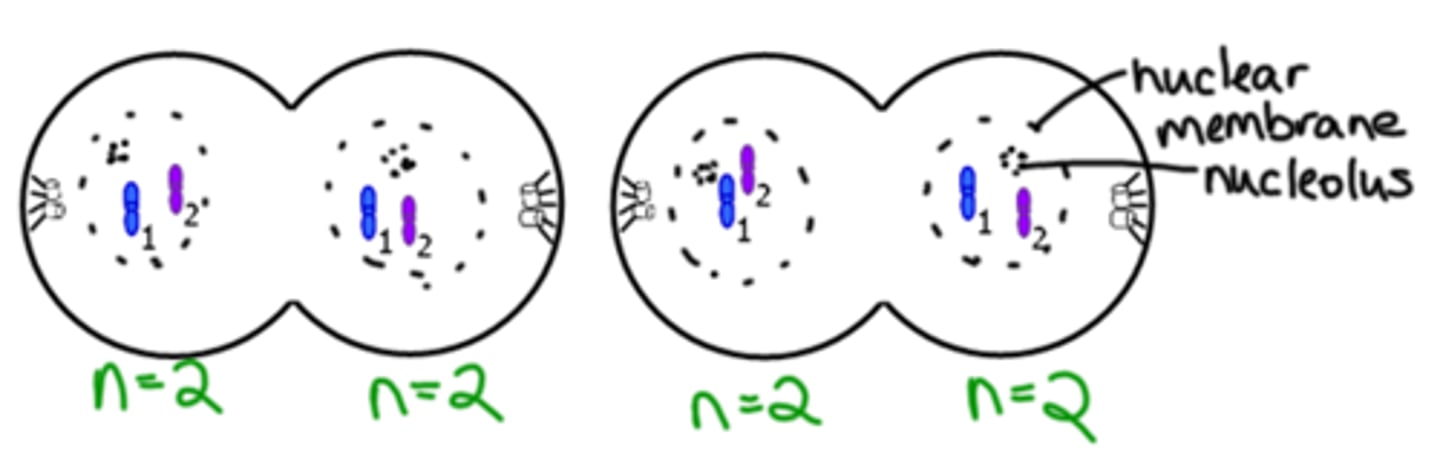
Telophase II
4 nuclei begin to form. Totally apart.
Zygote
sperm + egg
2n