History of Architecture - Greek Architecture
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
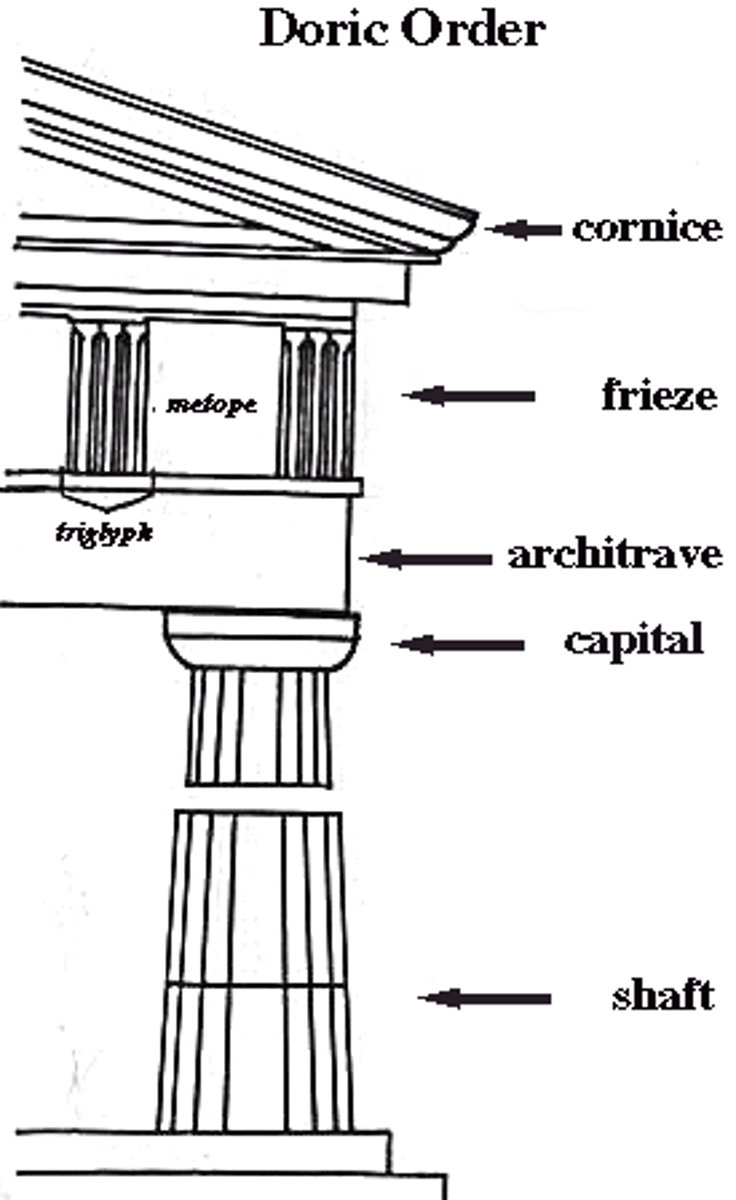
Doric
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek or classical architecture, most easily recognised by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns.
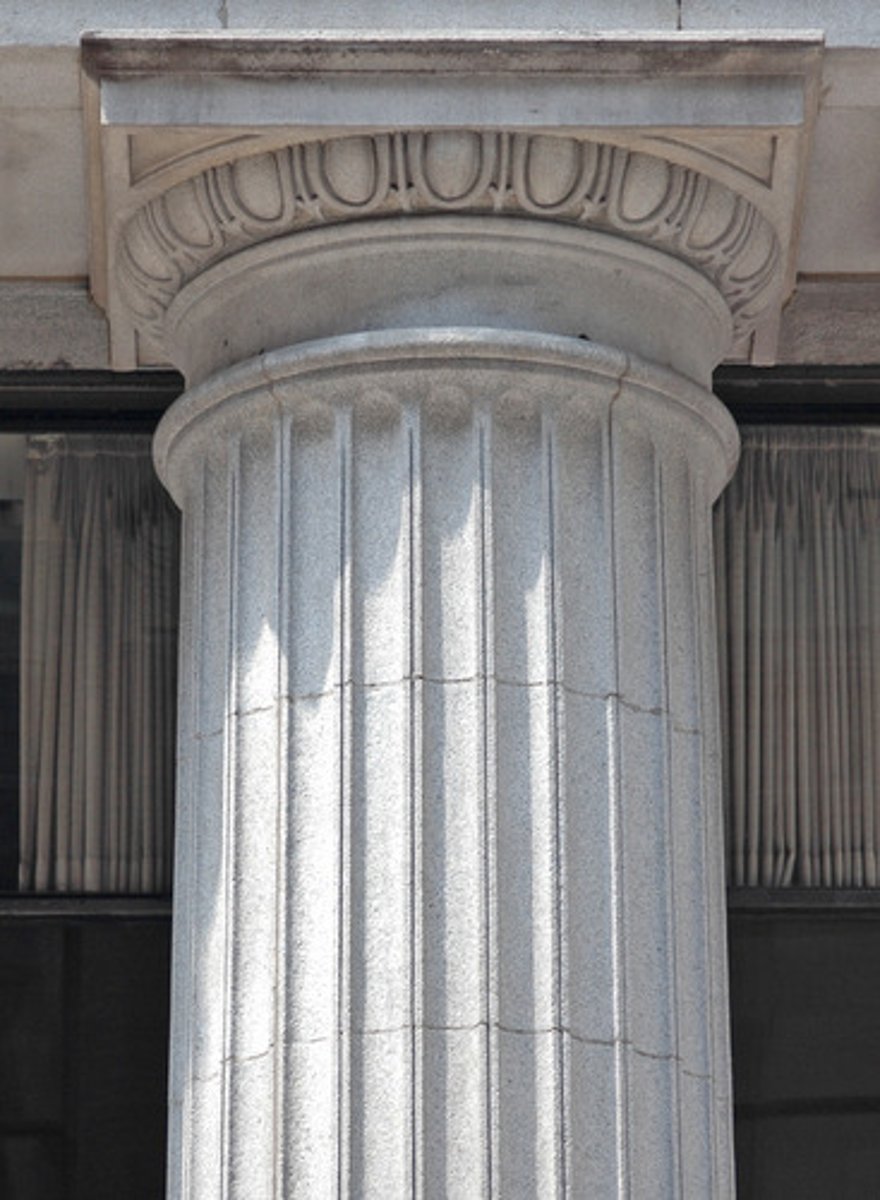

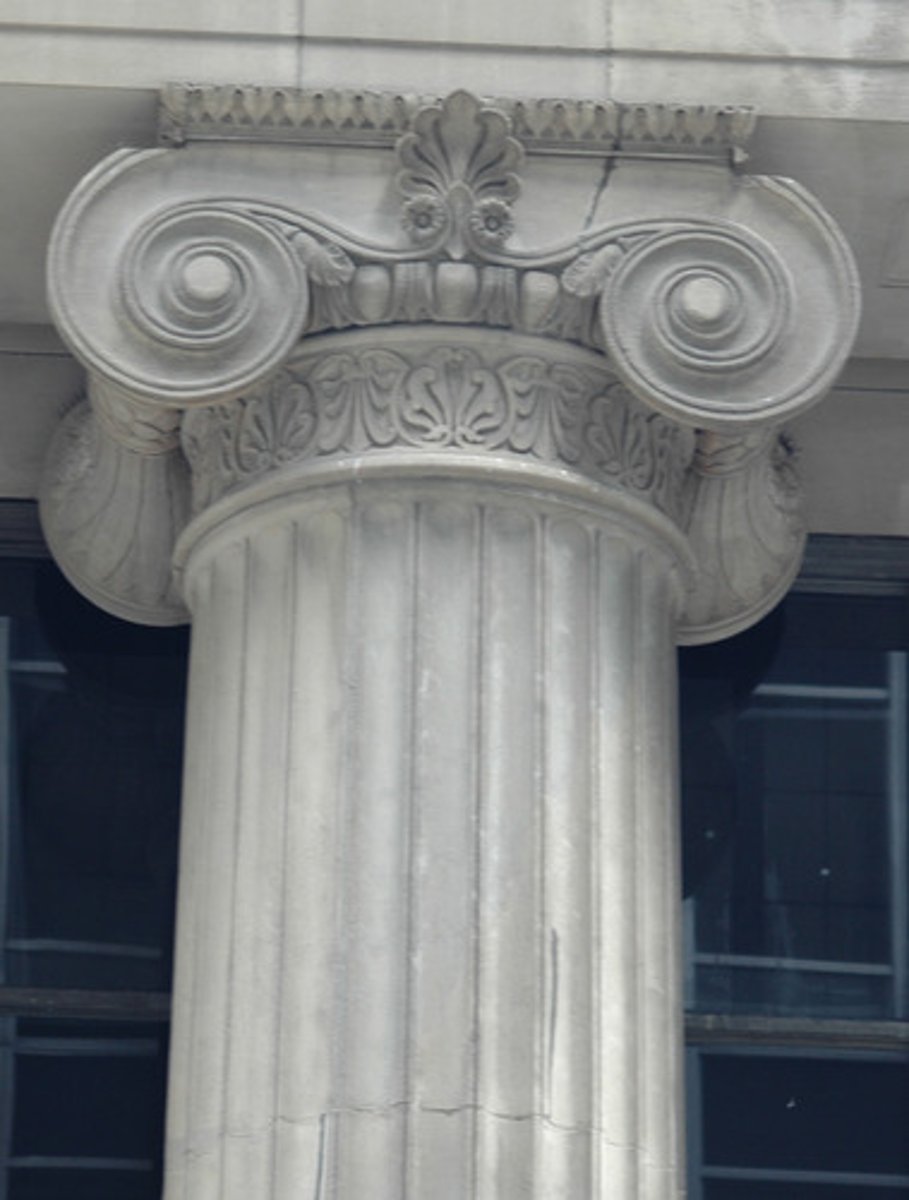
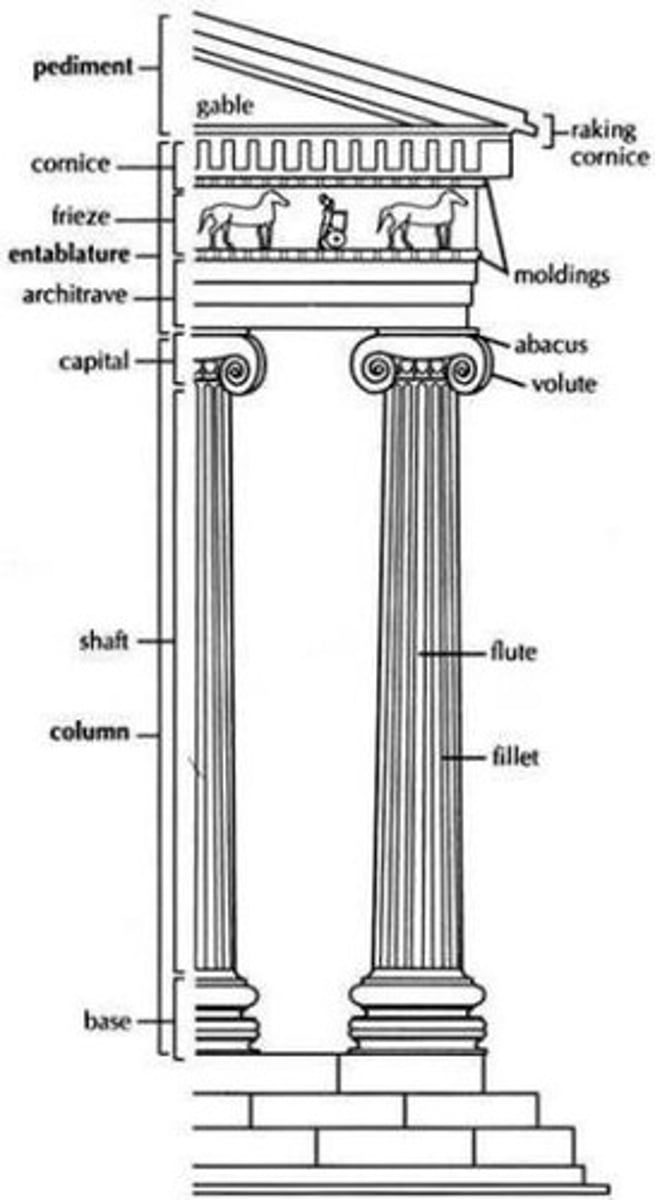
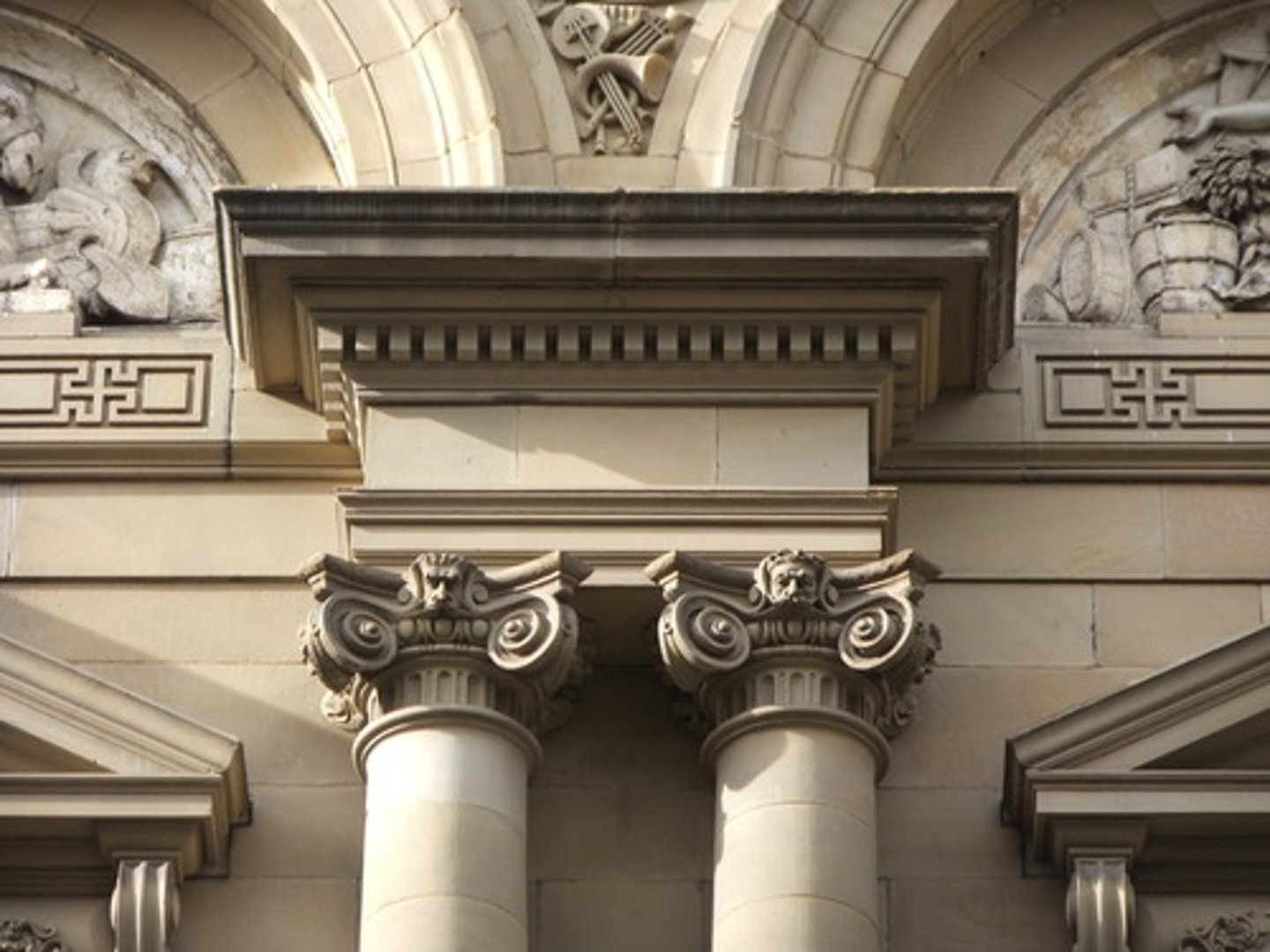
Ionic
One of the three orders of classical architecture. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes.

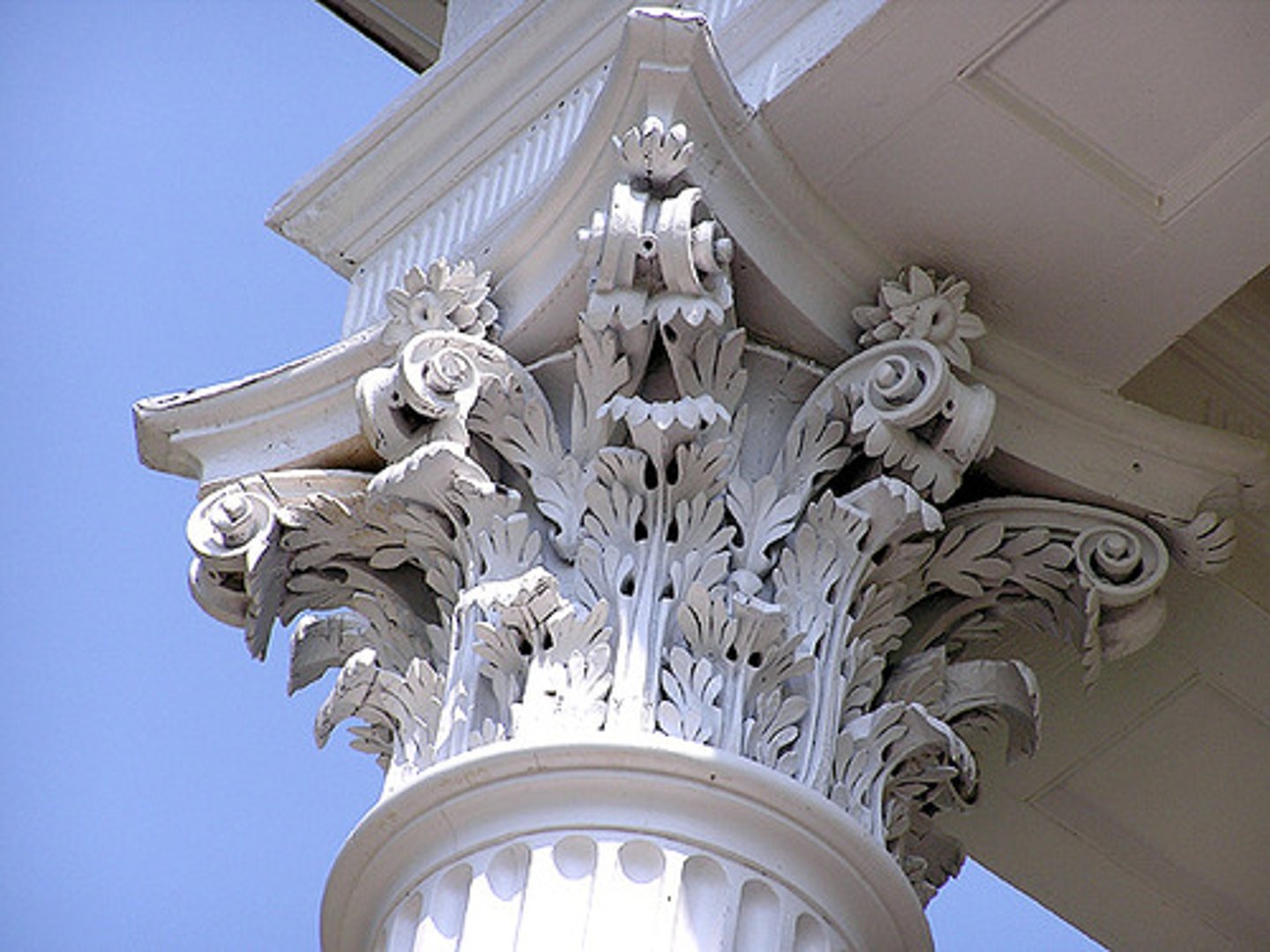
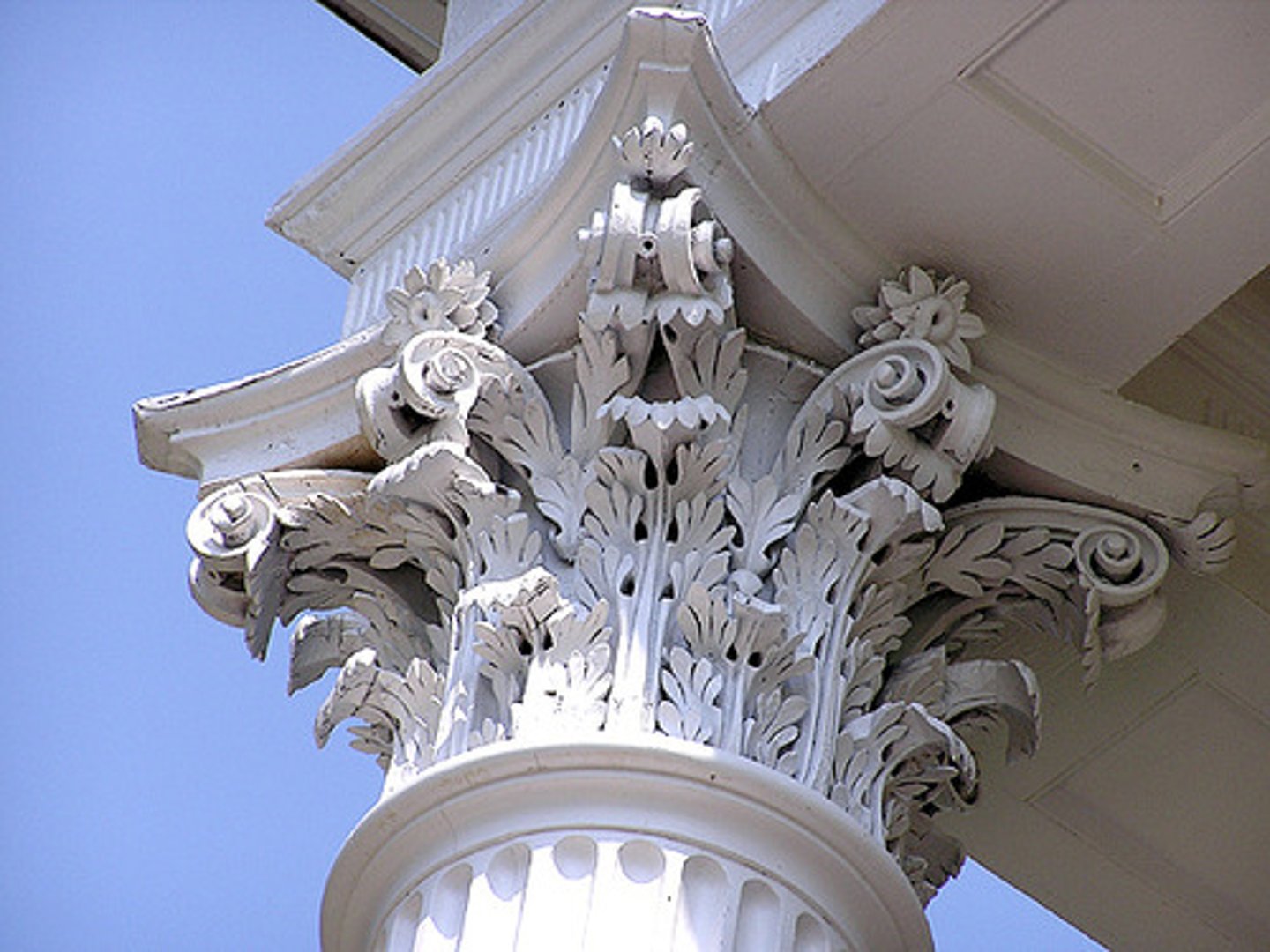
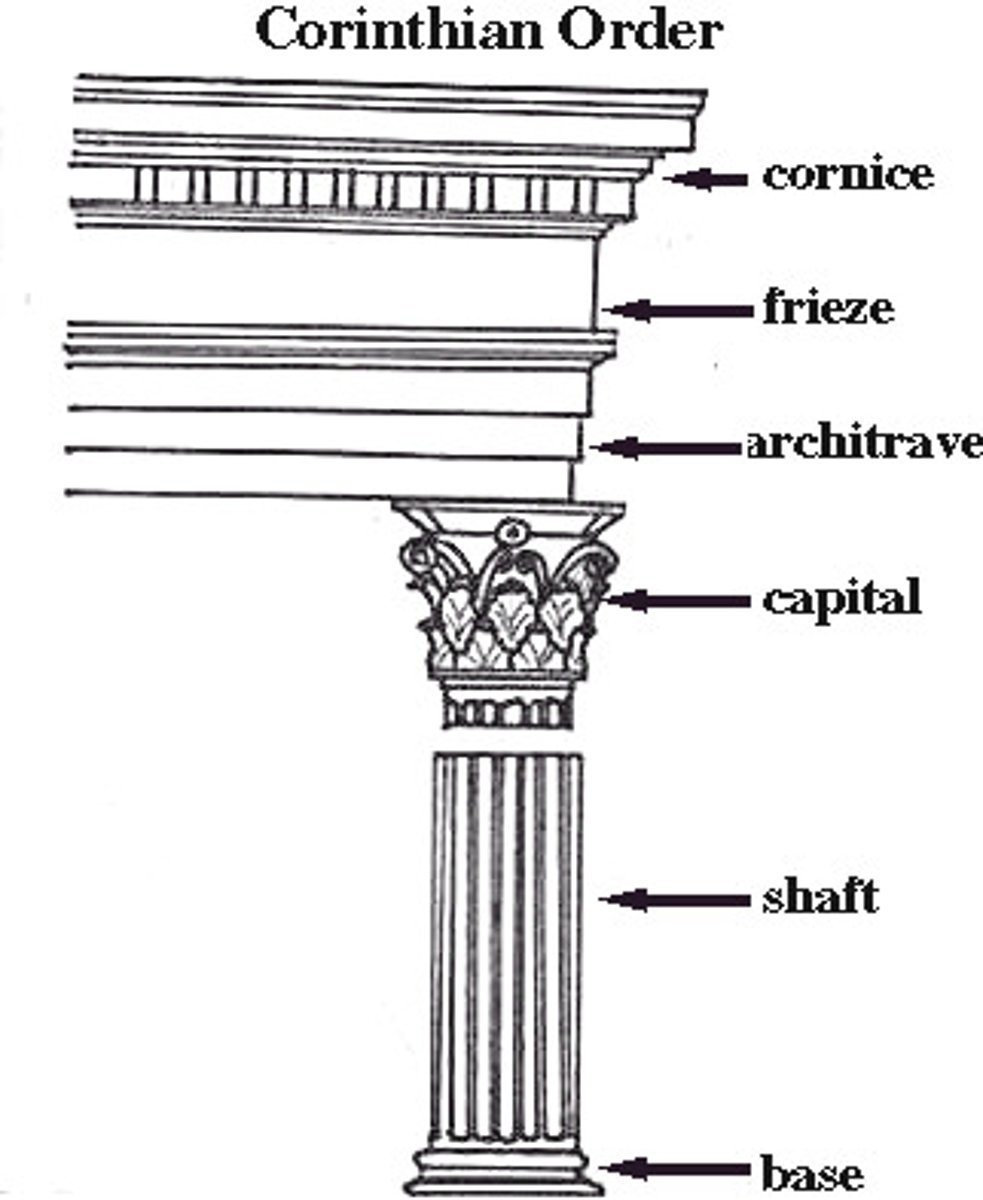
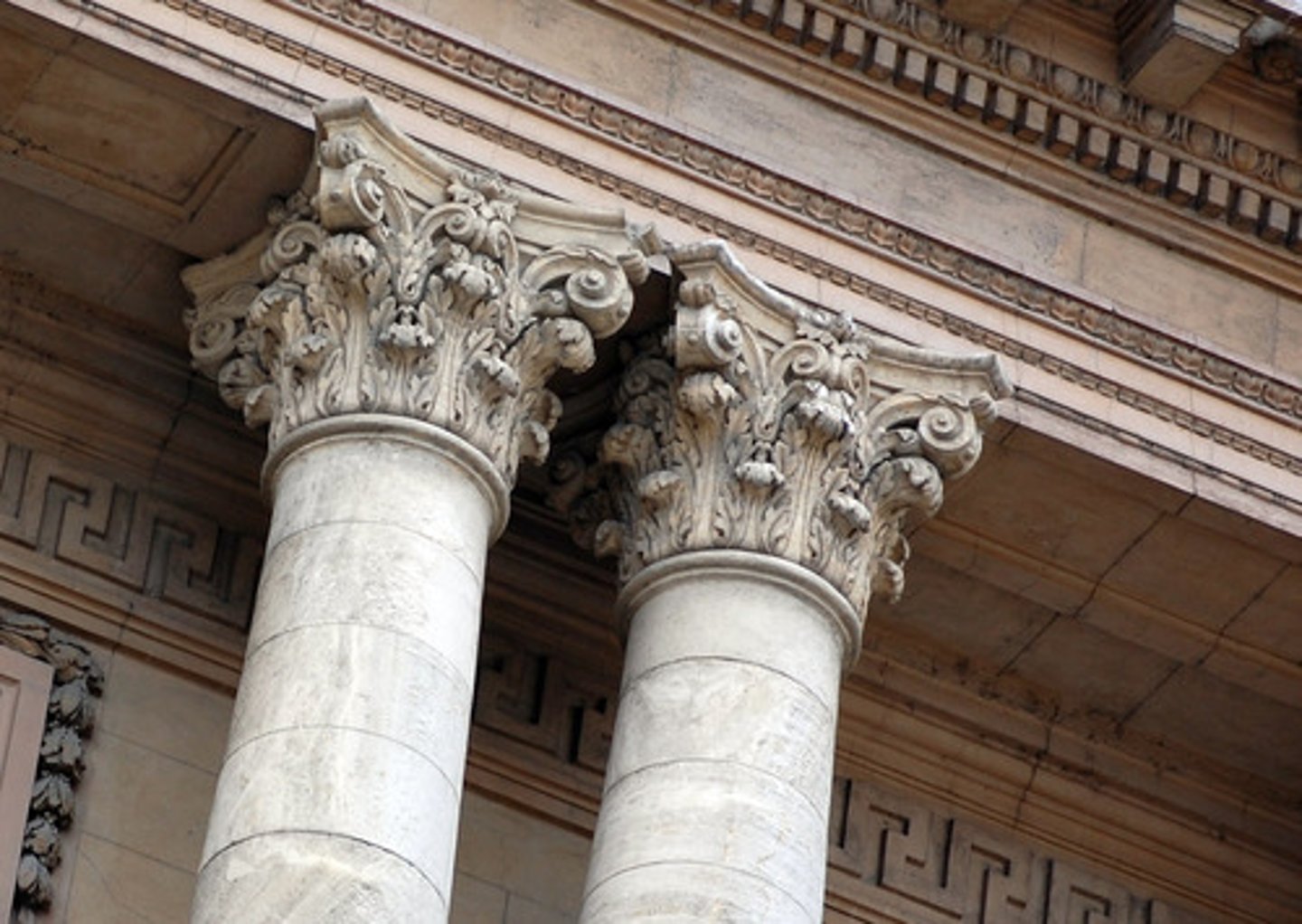
Corinthian
The last developed of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture. A capital (the distinguishing feature, consisting of two rows of acanthus-leaves over the astragal, with caules rising from the acanthus-leaves and sprouting helices or volutes from each calyx with bud).

Capital
Forms the topmost member of a column
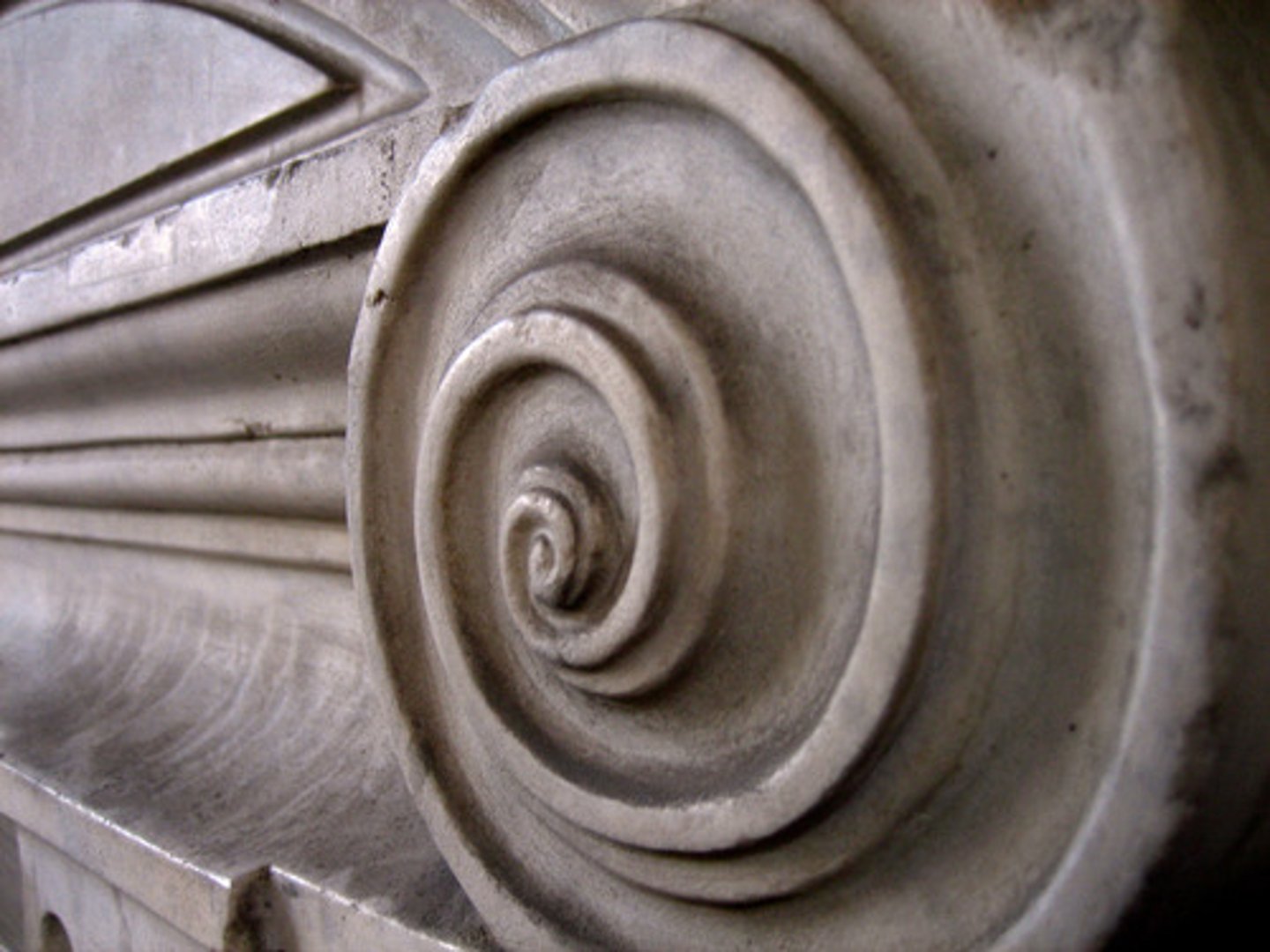
Volutes
A spiral scroll characteristic of Ionic capitals

Triglyphs
An architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture
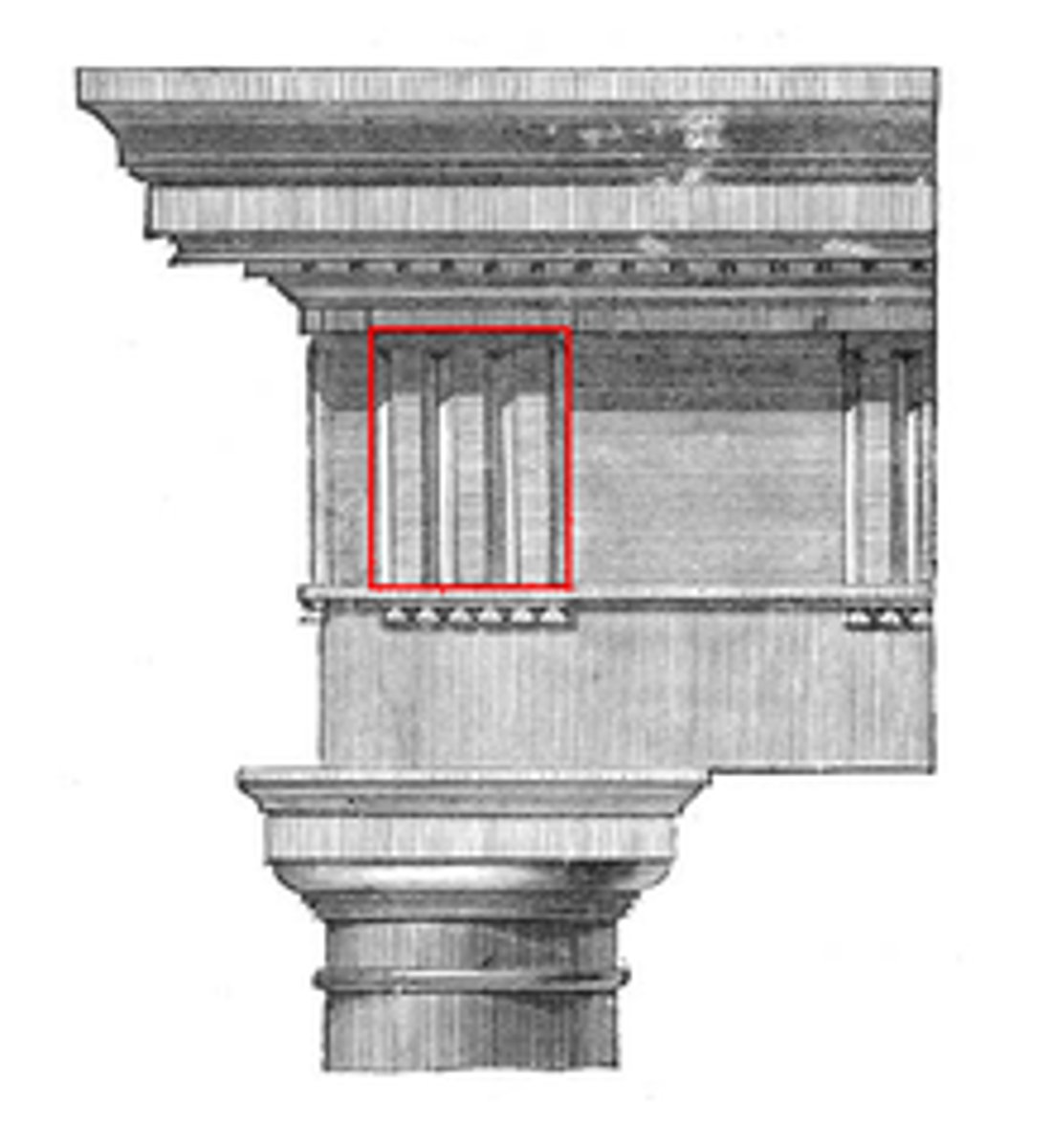
Metope
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze
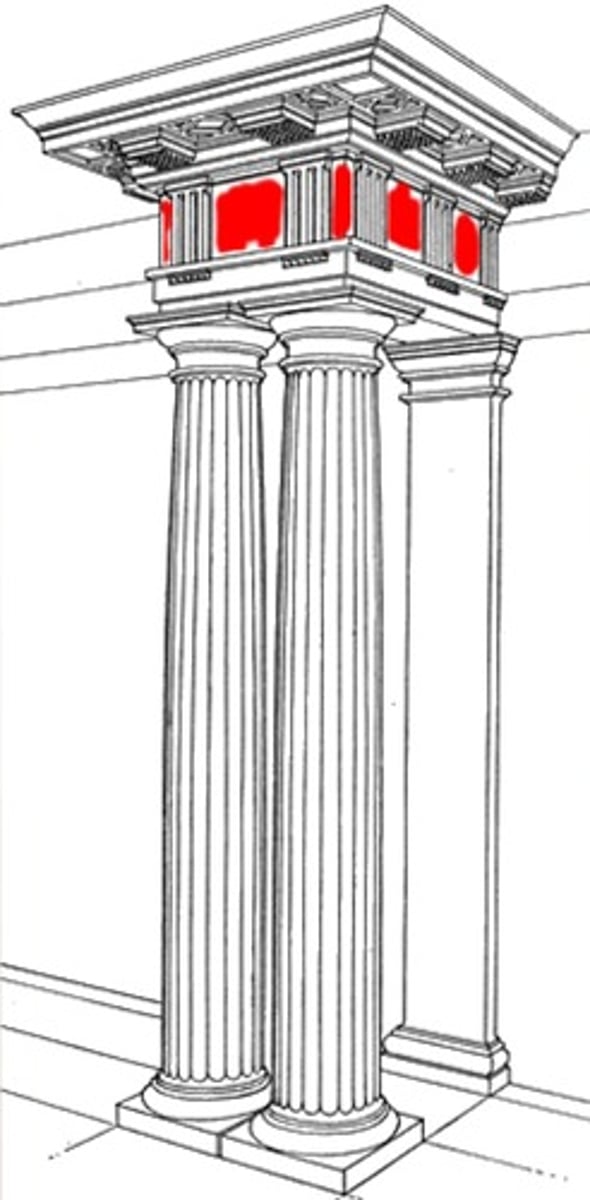
Frieze
A long narrow band of sculpture that runs along the architrave of a Greek temple or another building

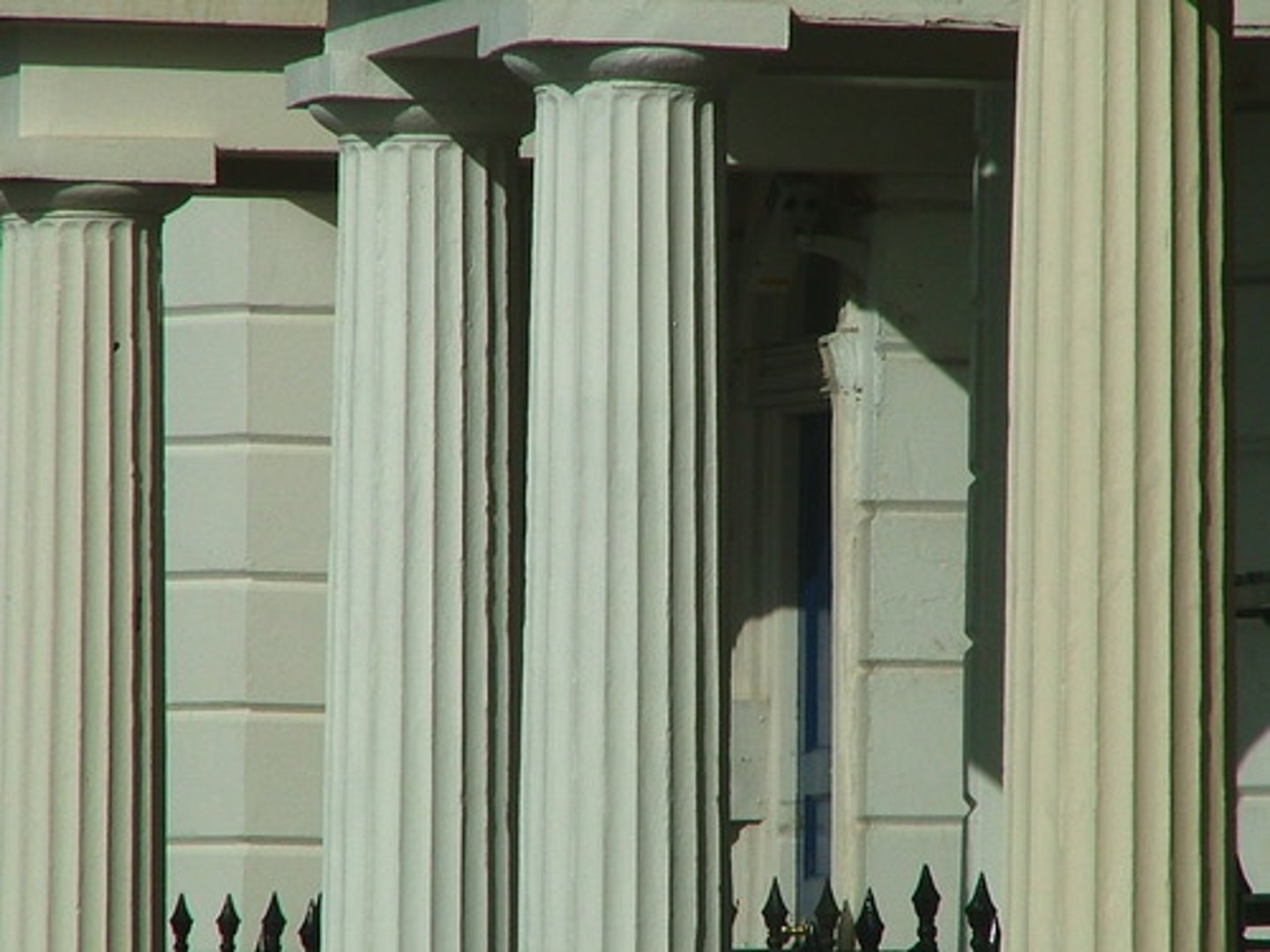
Fluting
Narrow channels running up and down them columns

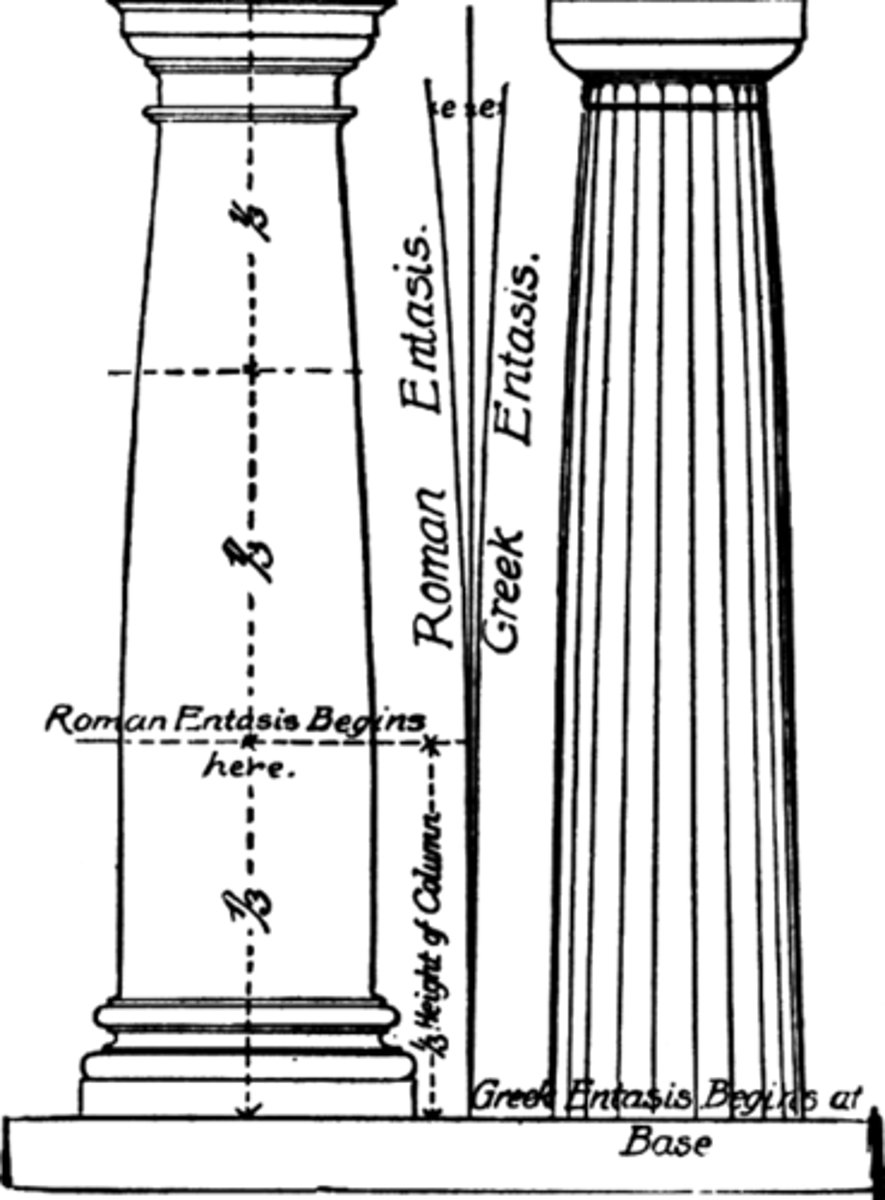
Entasis
A slight convex curve in the shaft of a column, introduced to correct the visual illusion of concavity produced by a straight shaft
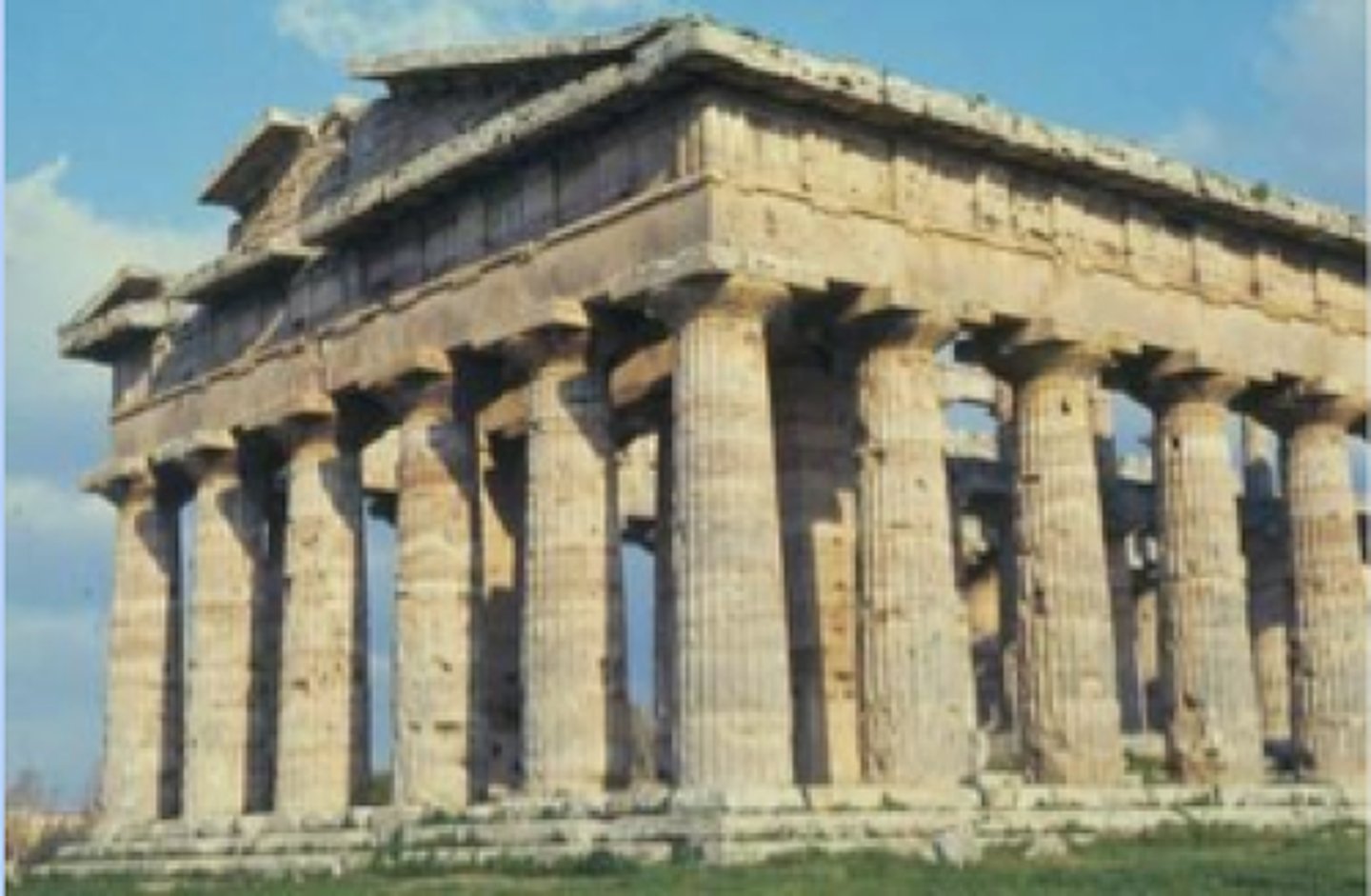
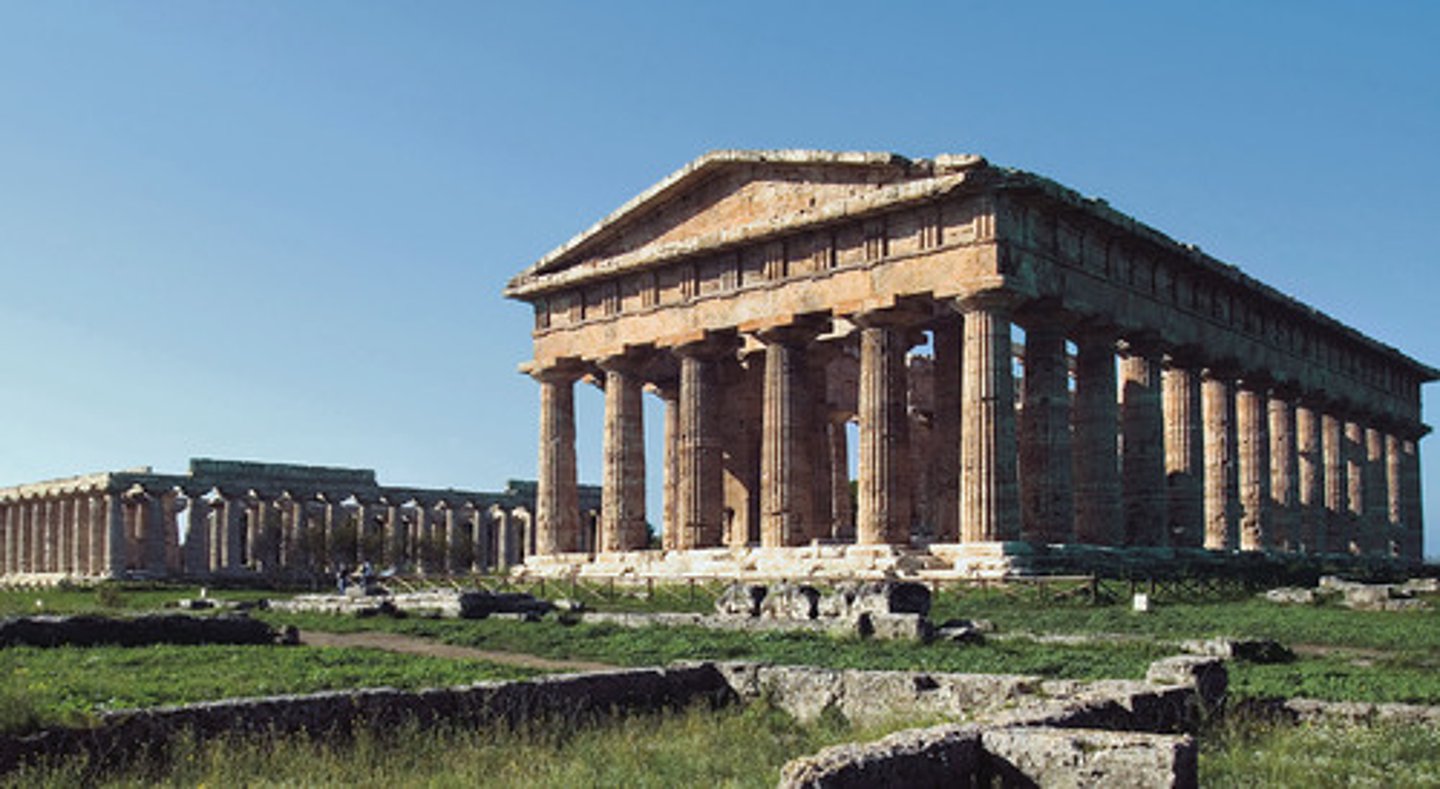
ca. 460 B.C. - Temple of Hera II, Paestum
Sometimes called the Temple of Neptune or the Temple of Poseidon is an archaic Doric temple in the ancient city of Paestum. It is one of the best preserved Greek temples in the world.

ca. 427-424 B.C. - Temple of Athena Nike, Acropolis, Athens, Greece
A temple on the Acropolis of Athens. It was named after the Greek goddess, Athena Nike. Built around 420BC, the temple is the earliest fully Ionic temple on the Acropolis.
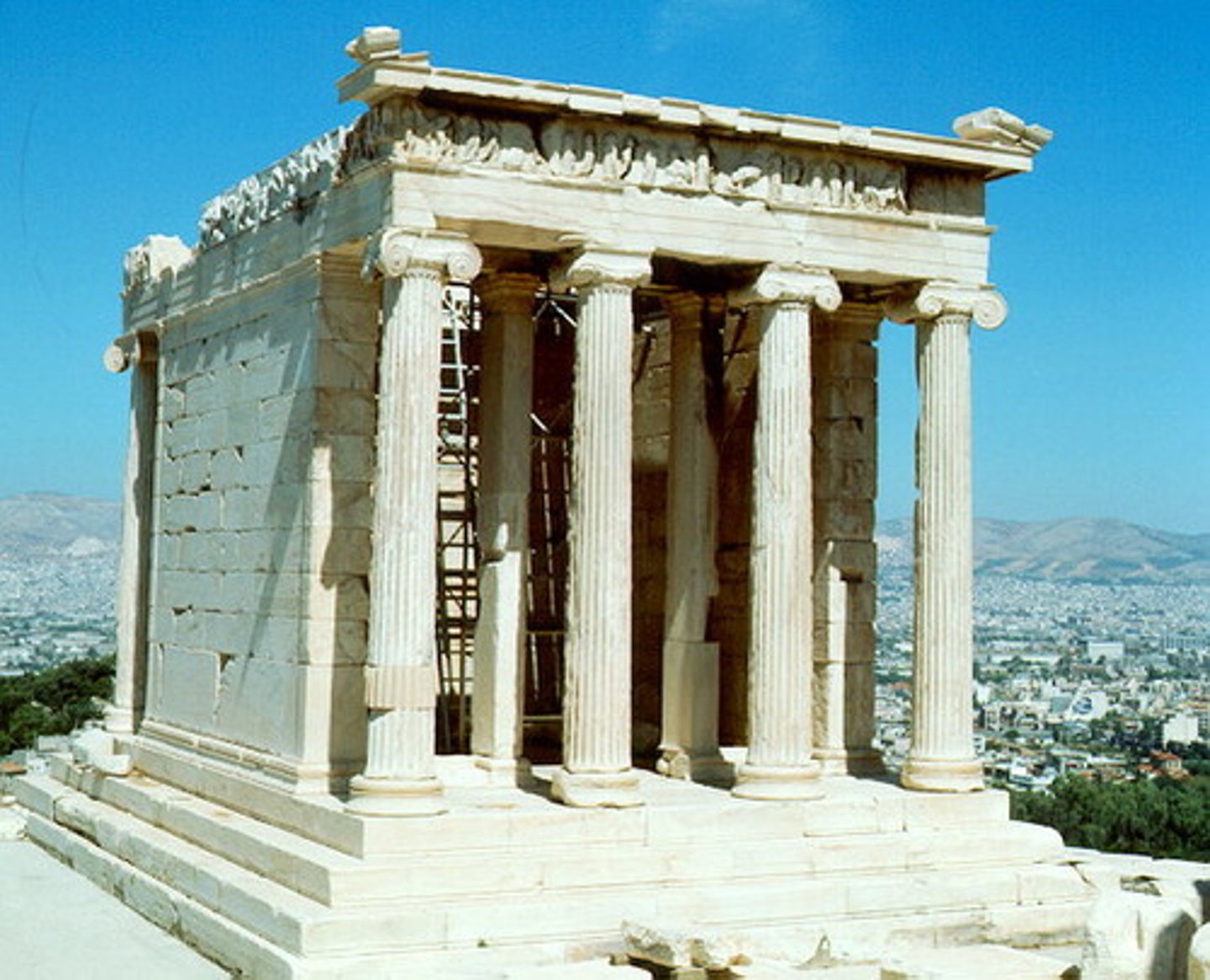

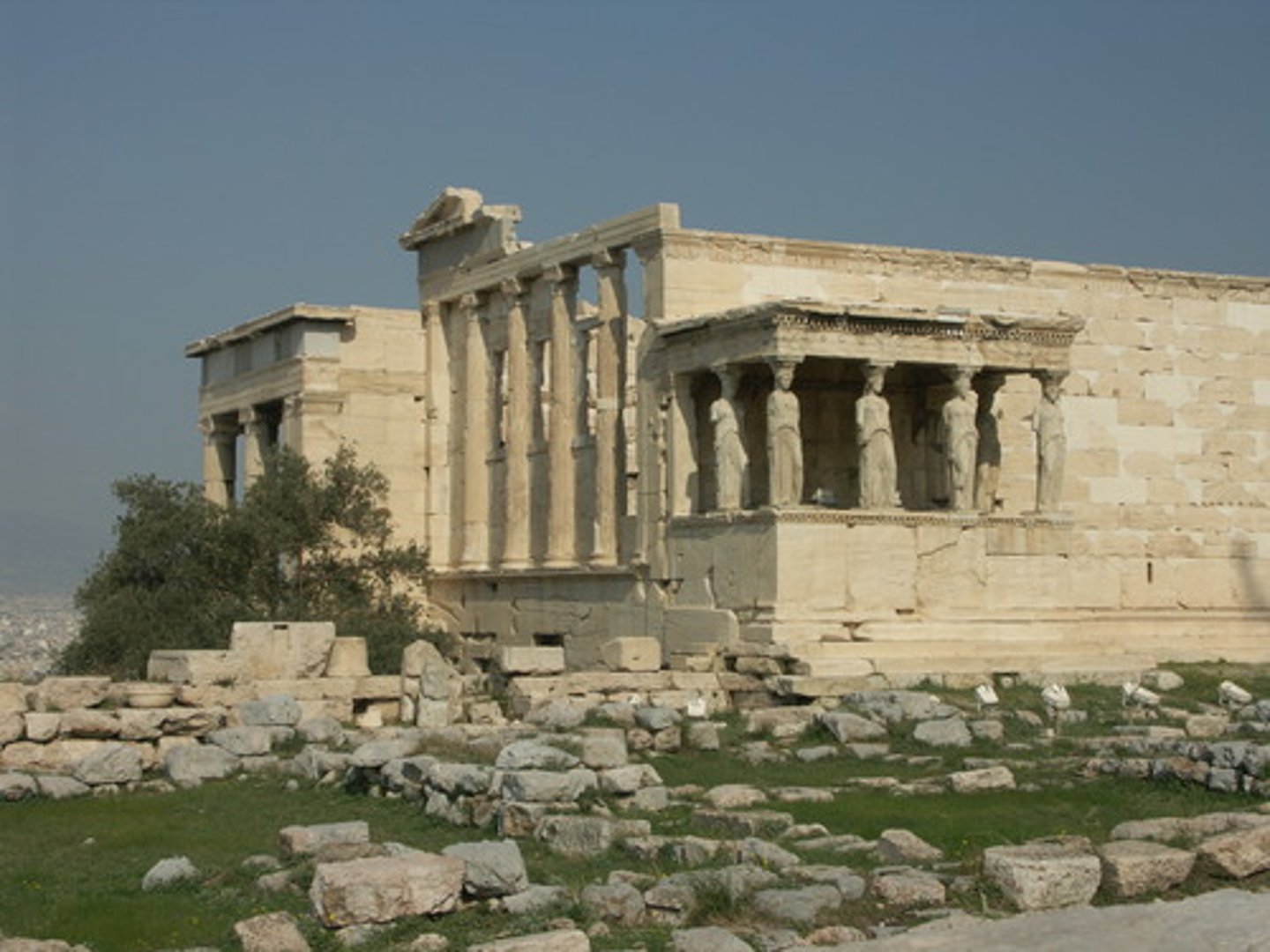
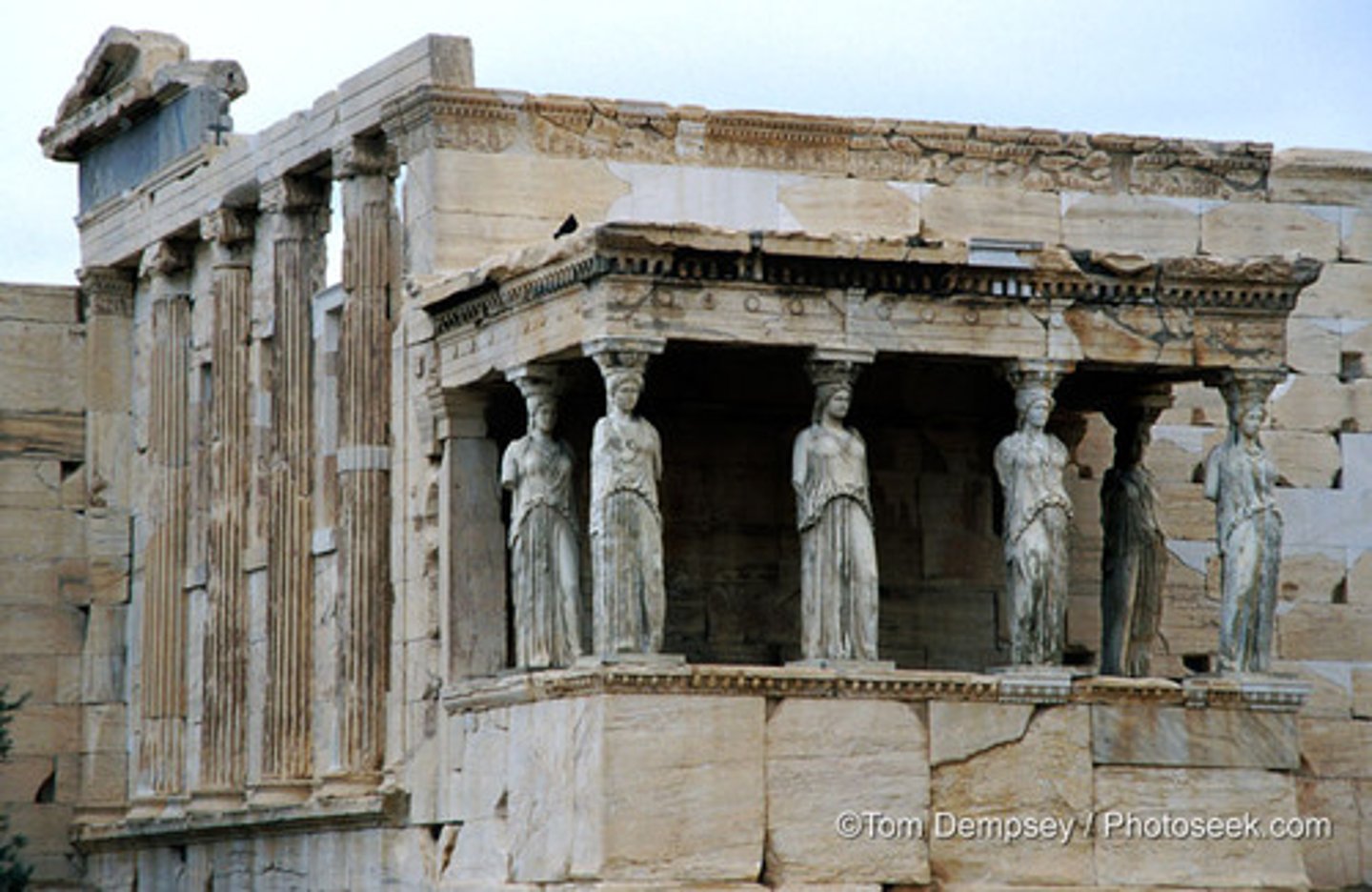
ca. 421-405 B.C. - Erechtheion (view from the southeast),
Acropolis, Athens, Greece
An ancient Greek temple on the north side of the Acropolis of Athens in Greece which was dedicated to both Athena and Poseidon.

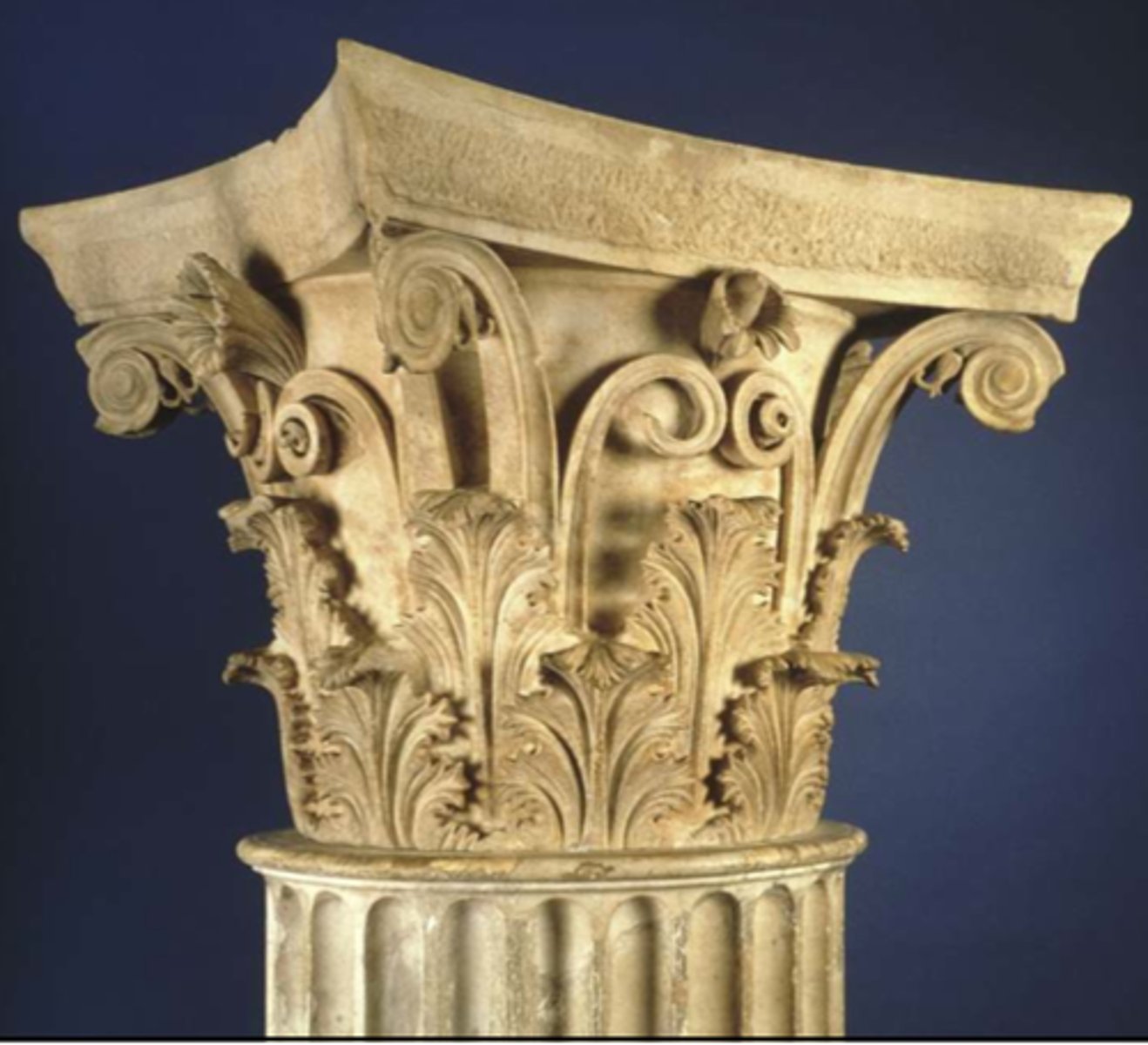
ca. 350 B.C. Corinthian capital, from the Tholos, Epidauros, Greece

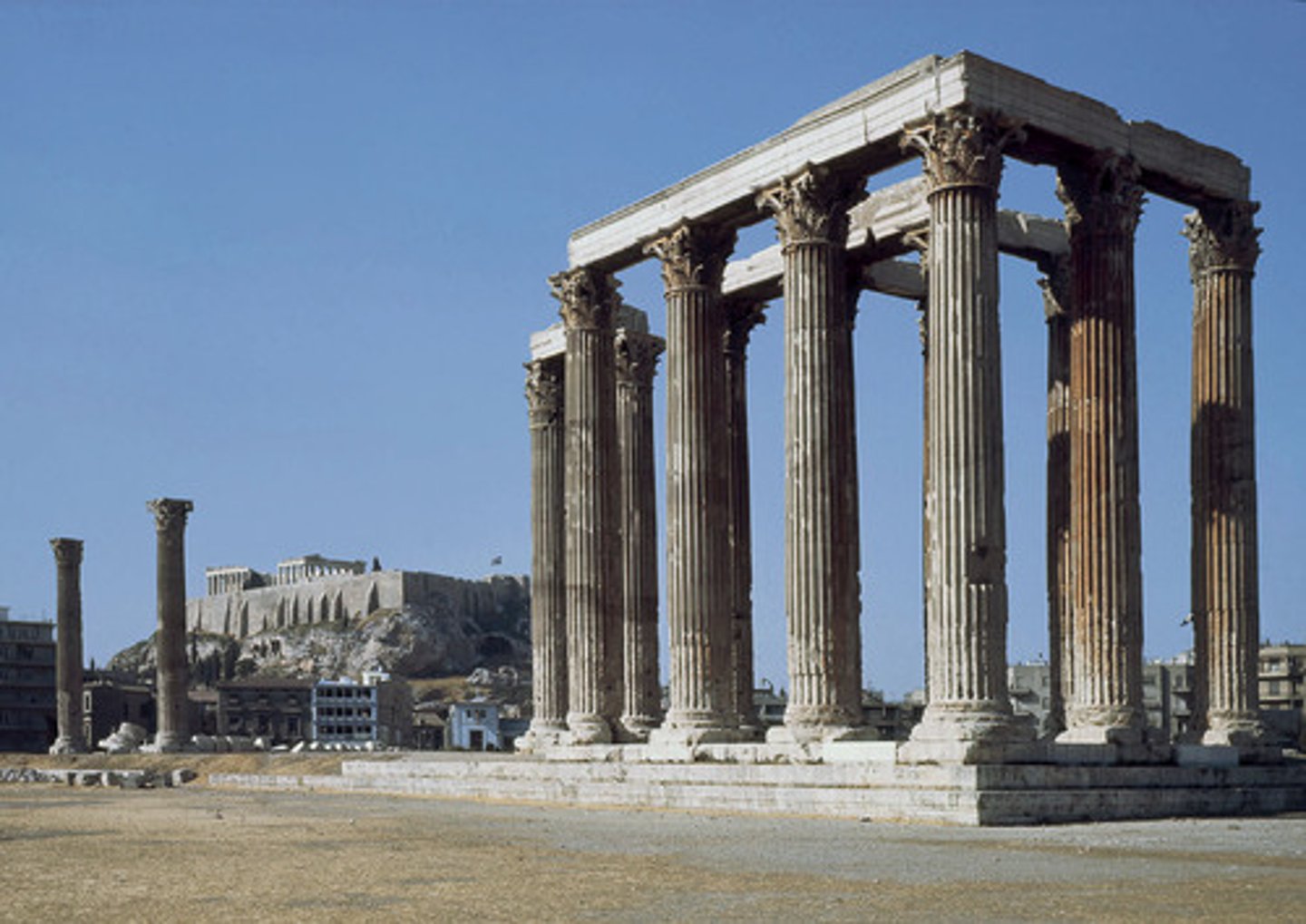
ca. 131 A.D. - Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens
A colossal ruined temple in the center of the Greek capital Athens that was dedicated to Zeus, king of the Olympian gods.

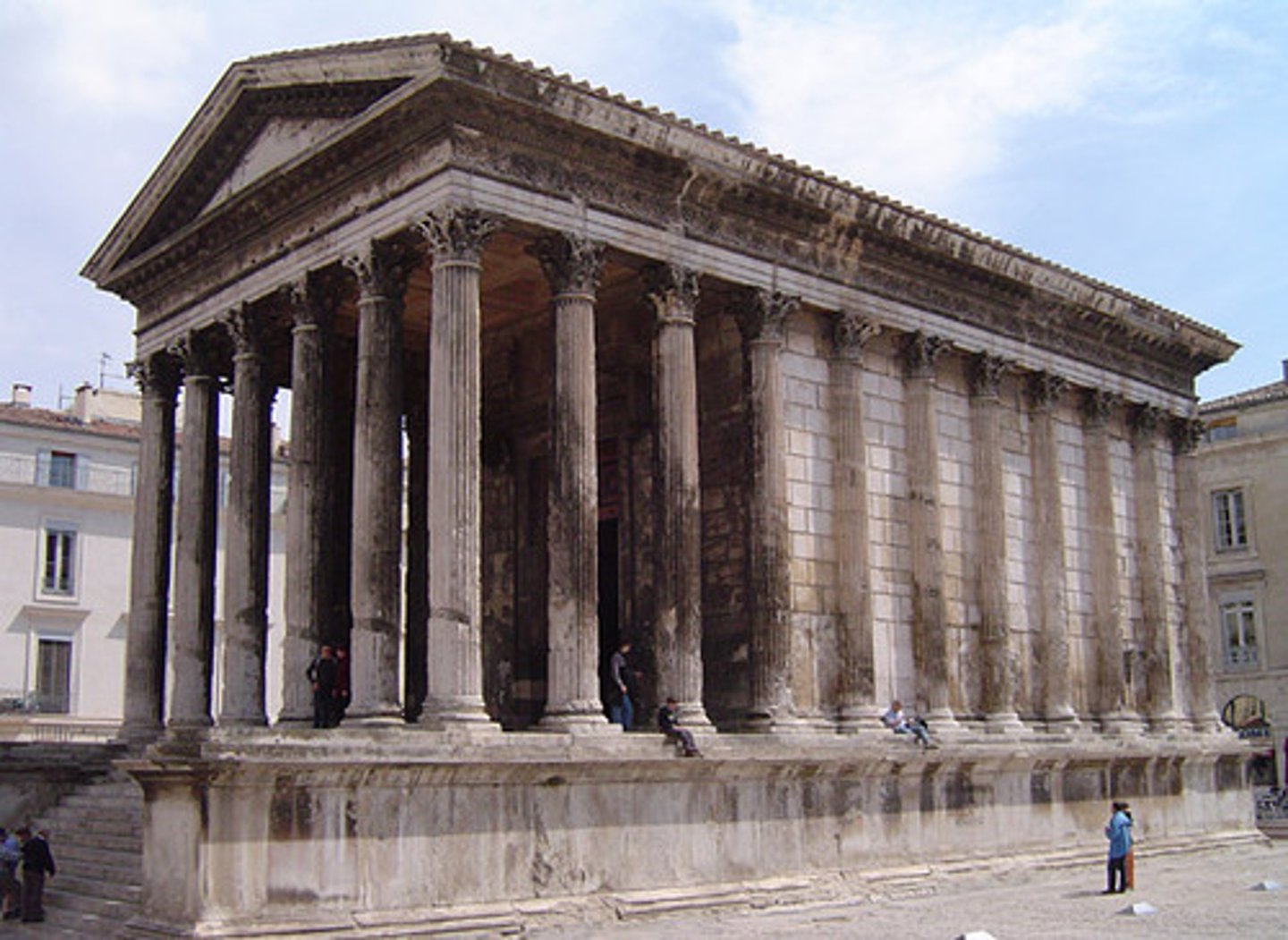
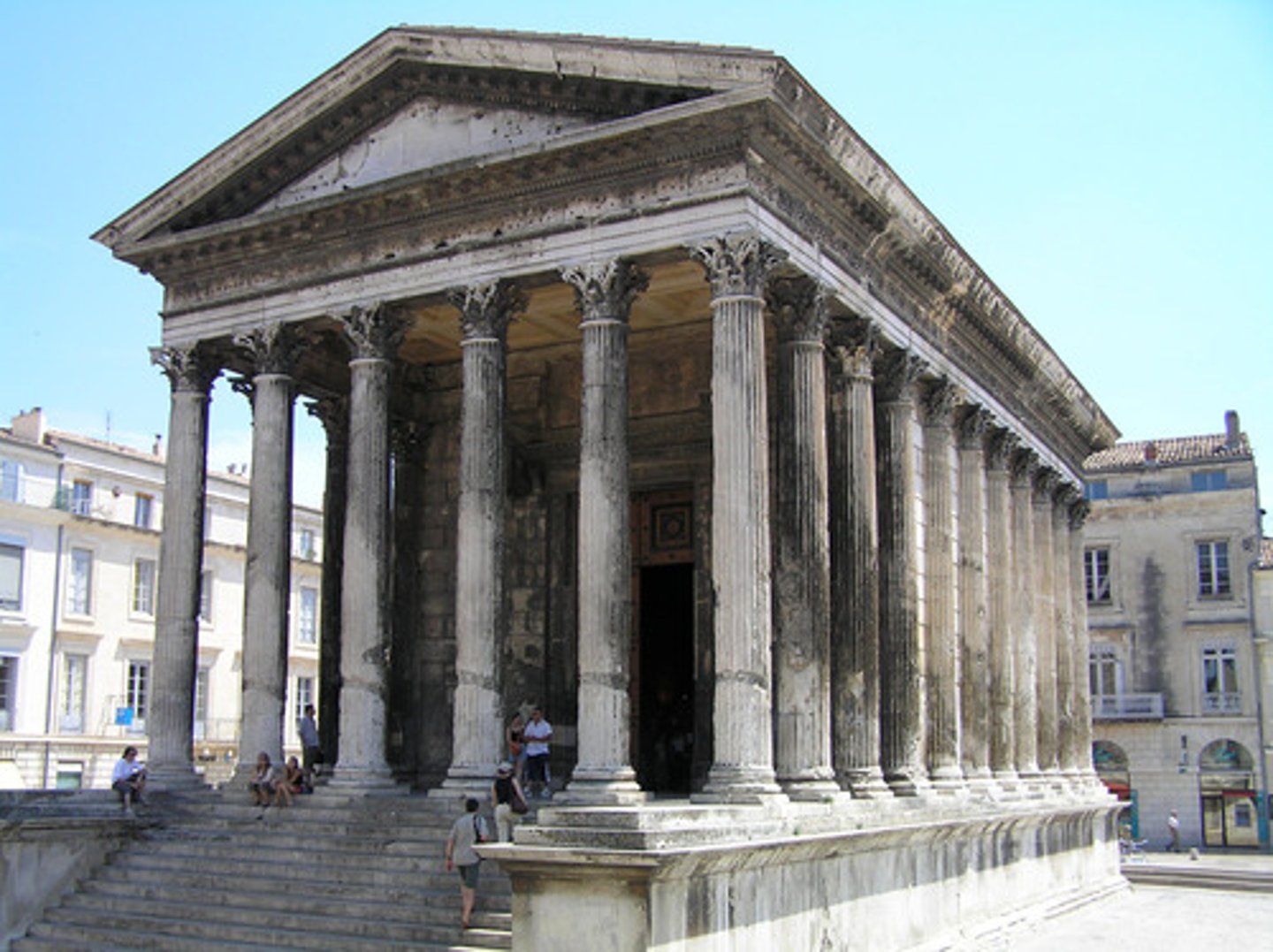
ca. 1-10 A.D. - Maison Carrée, Nîmes, France
An ancient building in Nîmes, southern France; it is one of the best preserved Roman temple façades to be found in the territory of the former Roman Empire.

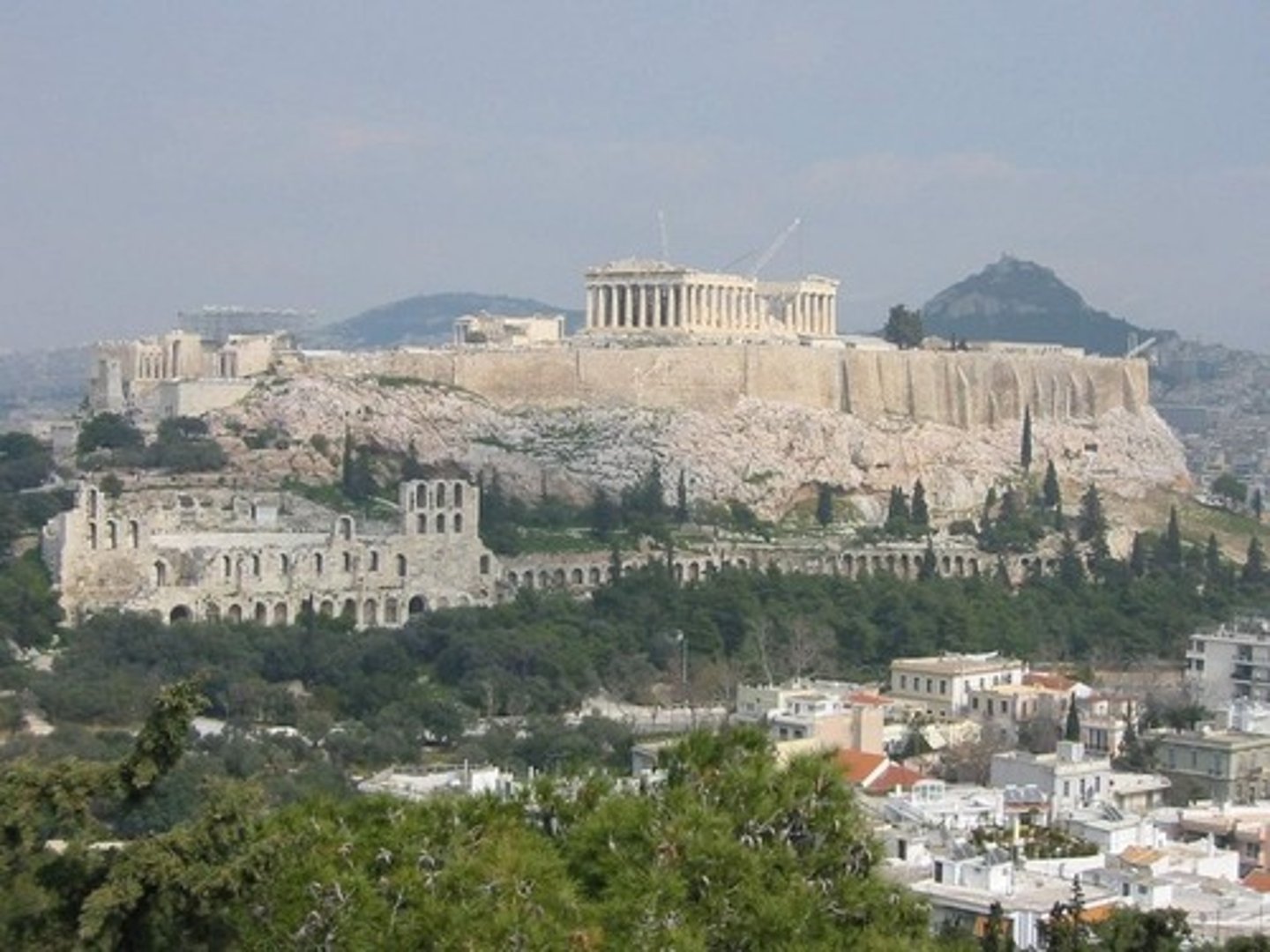
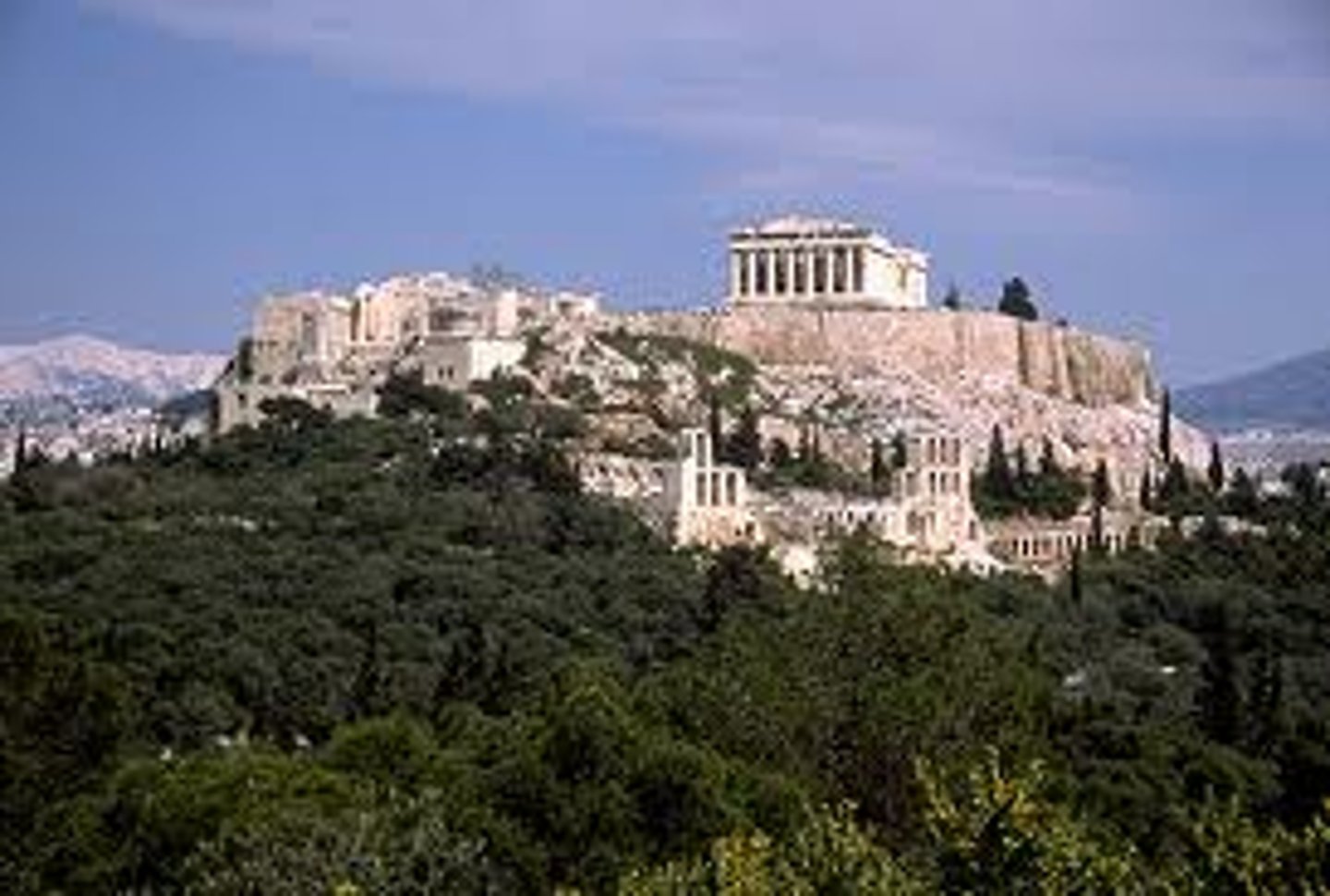
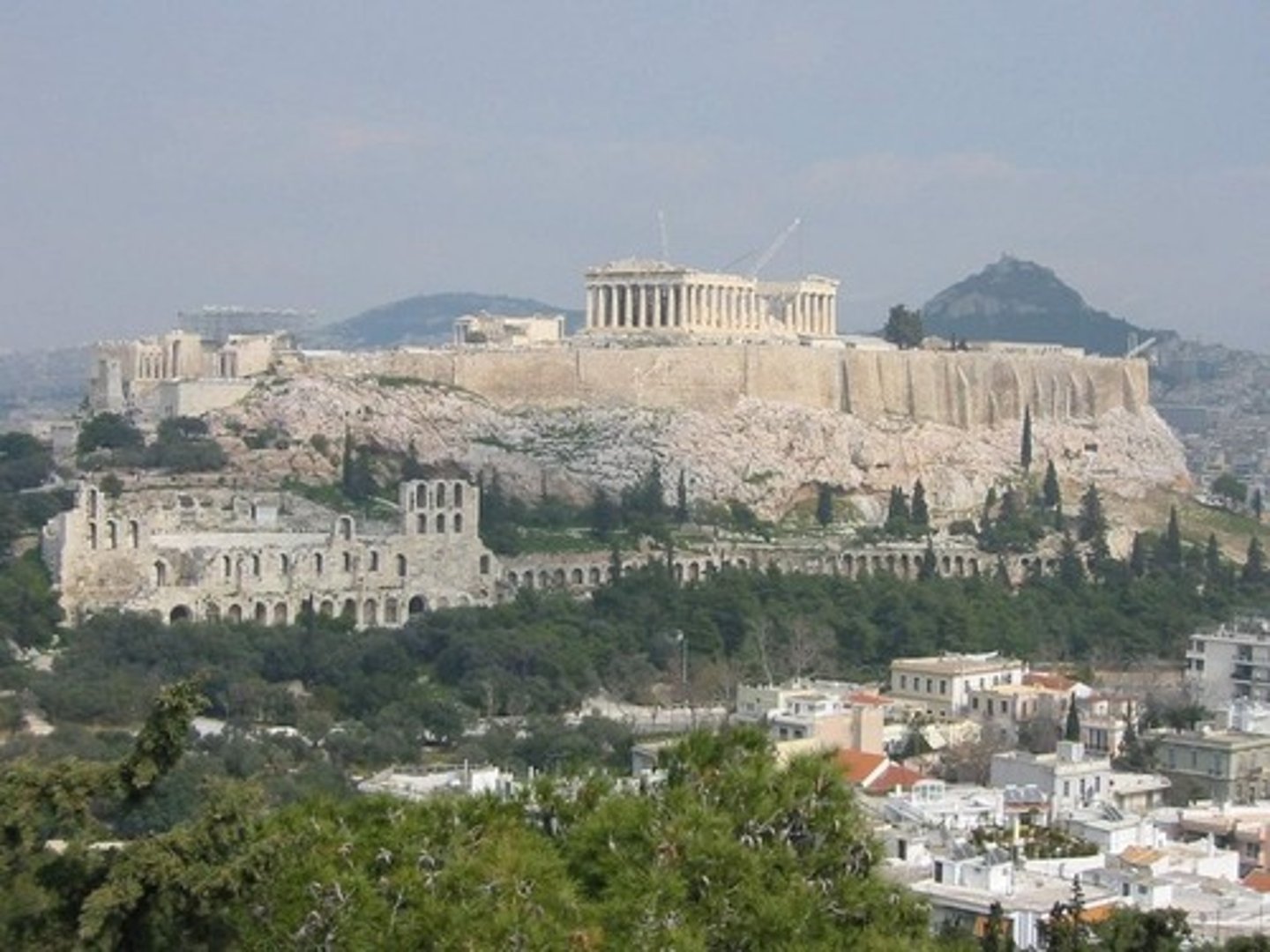
Acropolis, Athens, Greece
An ancient citadel located on an extremely rocky outcrop above the city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historic significance, the most famous being the Parthenon.

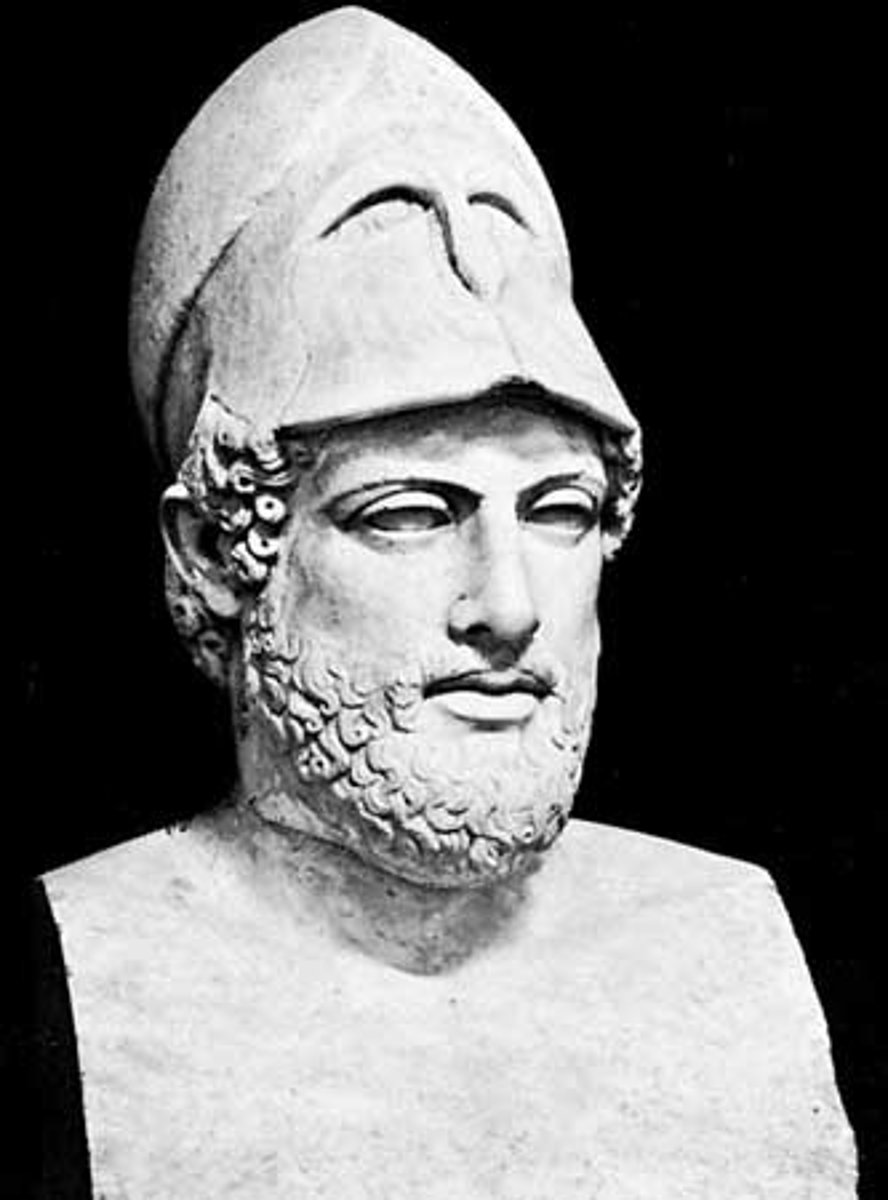
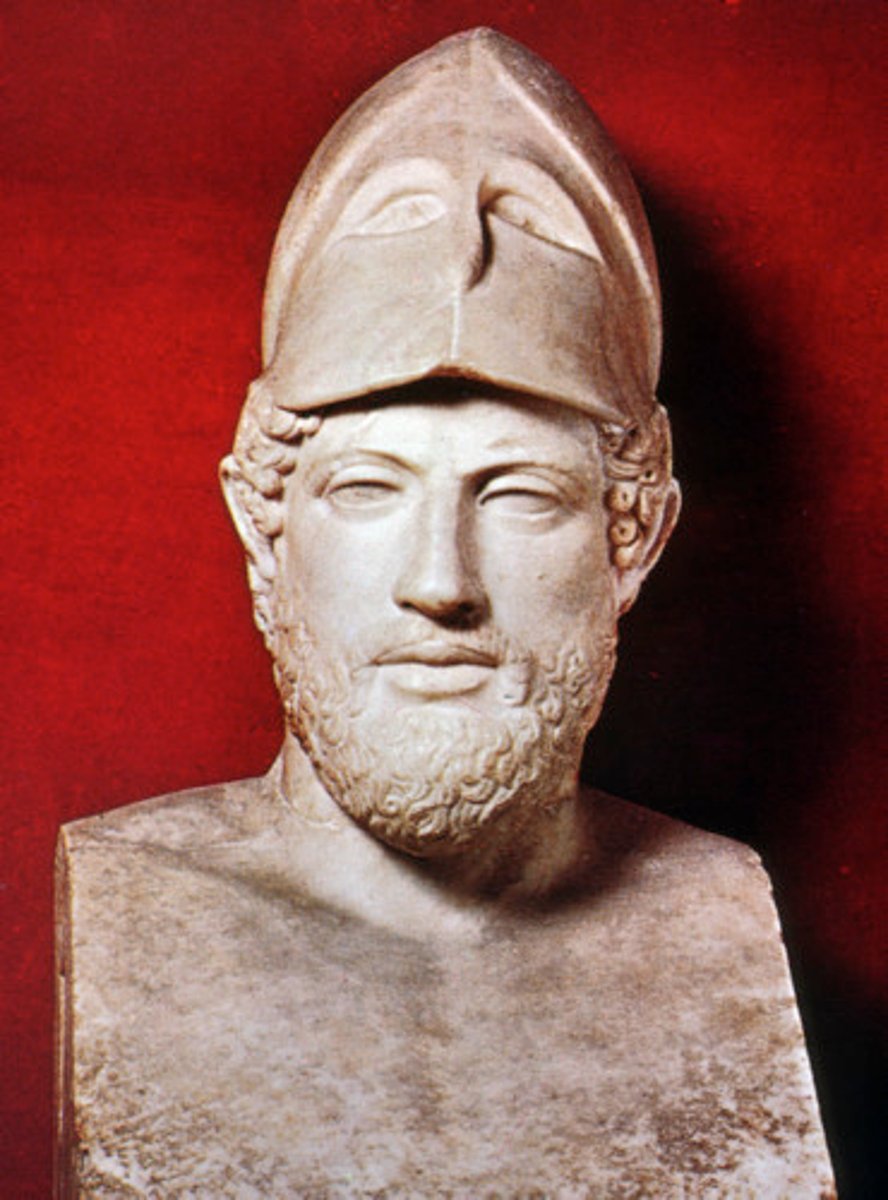
ca. 429 B.C. - KRESILAS, Pericles.
Roman marble copy after a bronze original of
approx. 6' high.
A bust of the Athenian statesman and general Pericles which survives in the form of four marble copies from the Roman Imperial period.

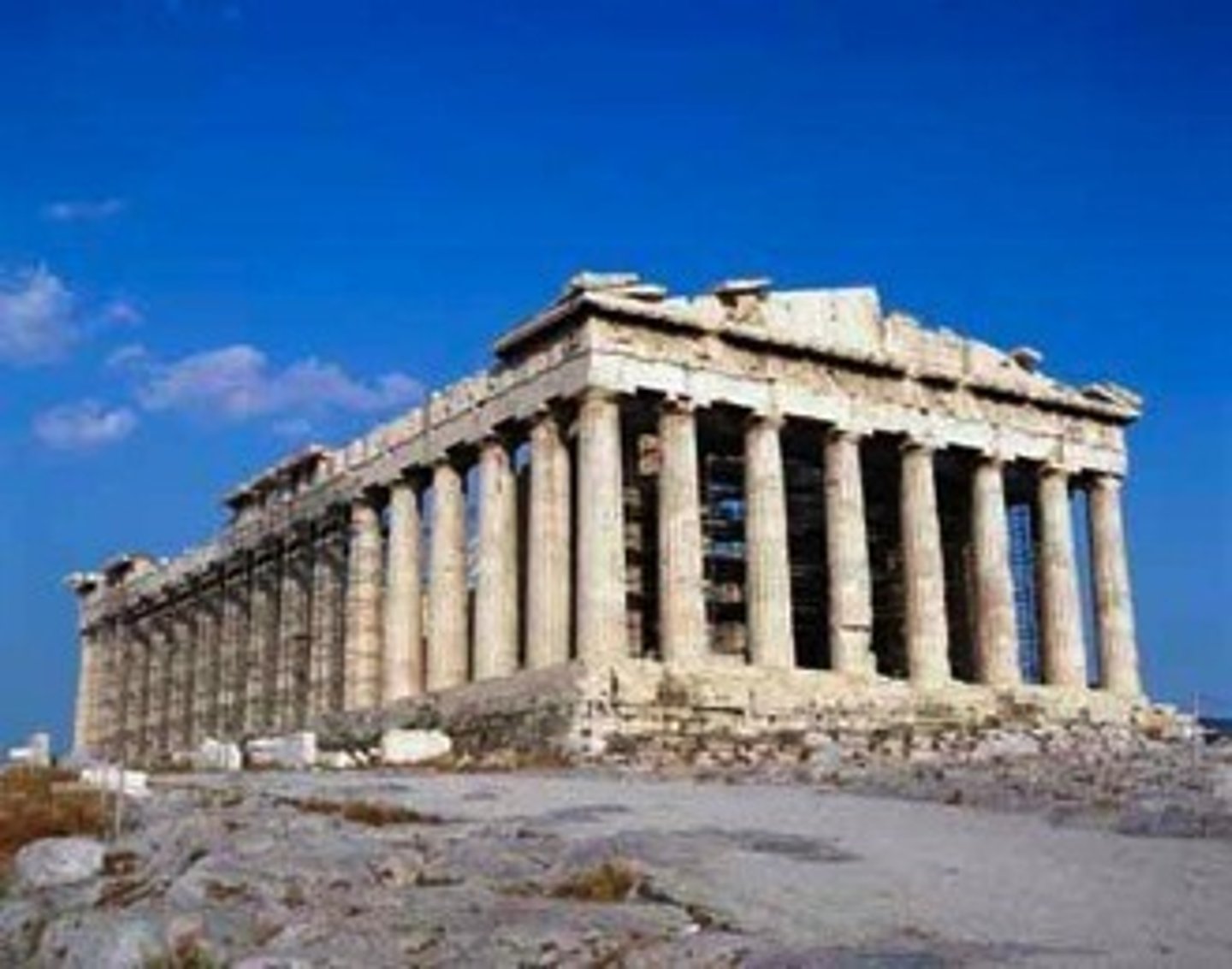
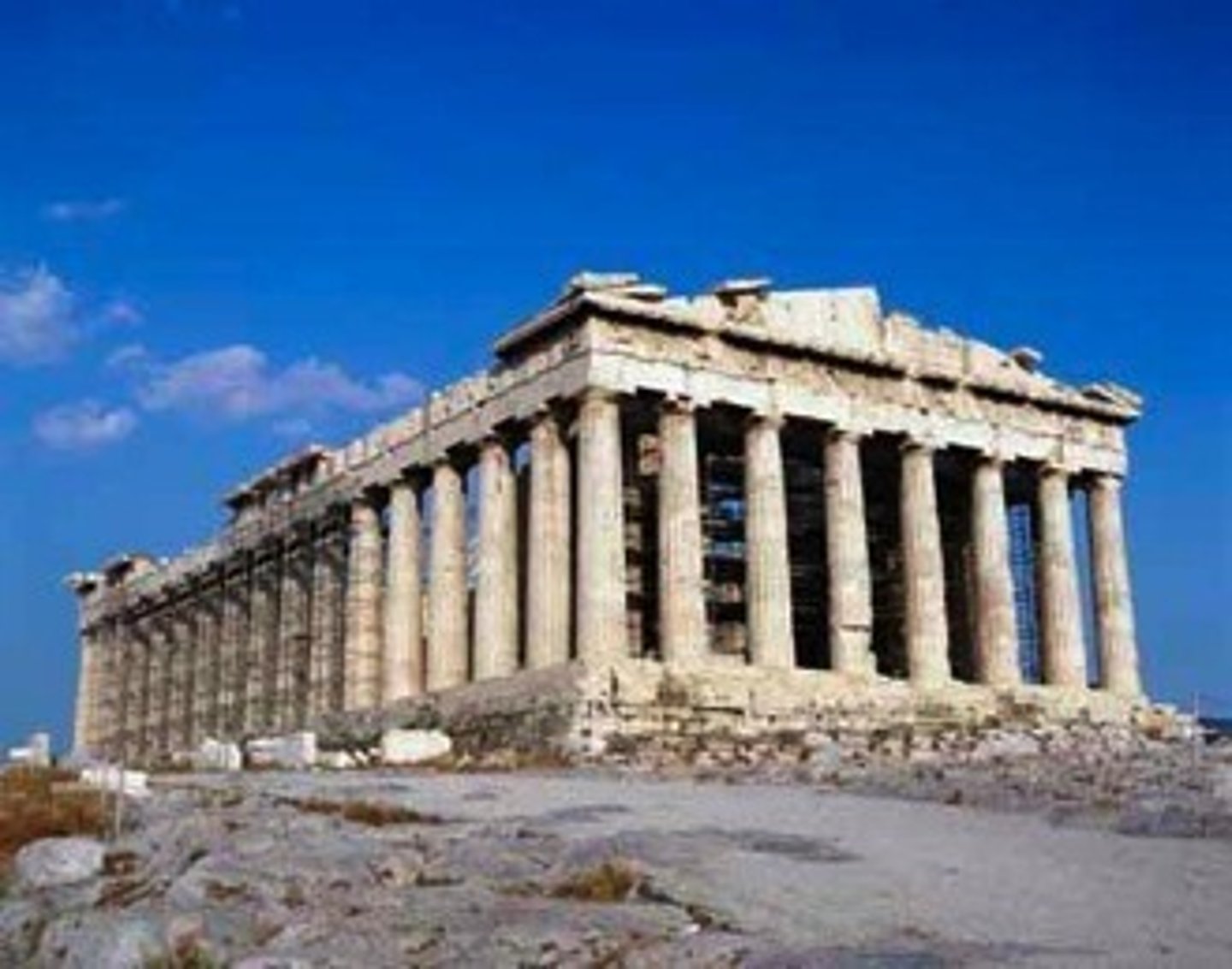
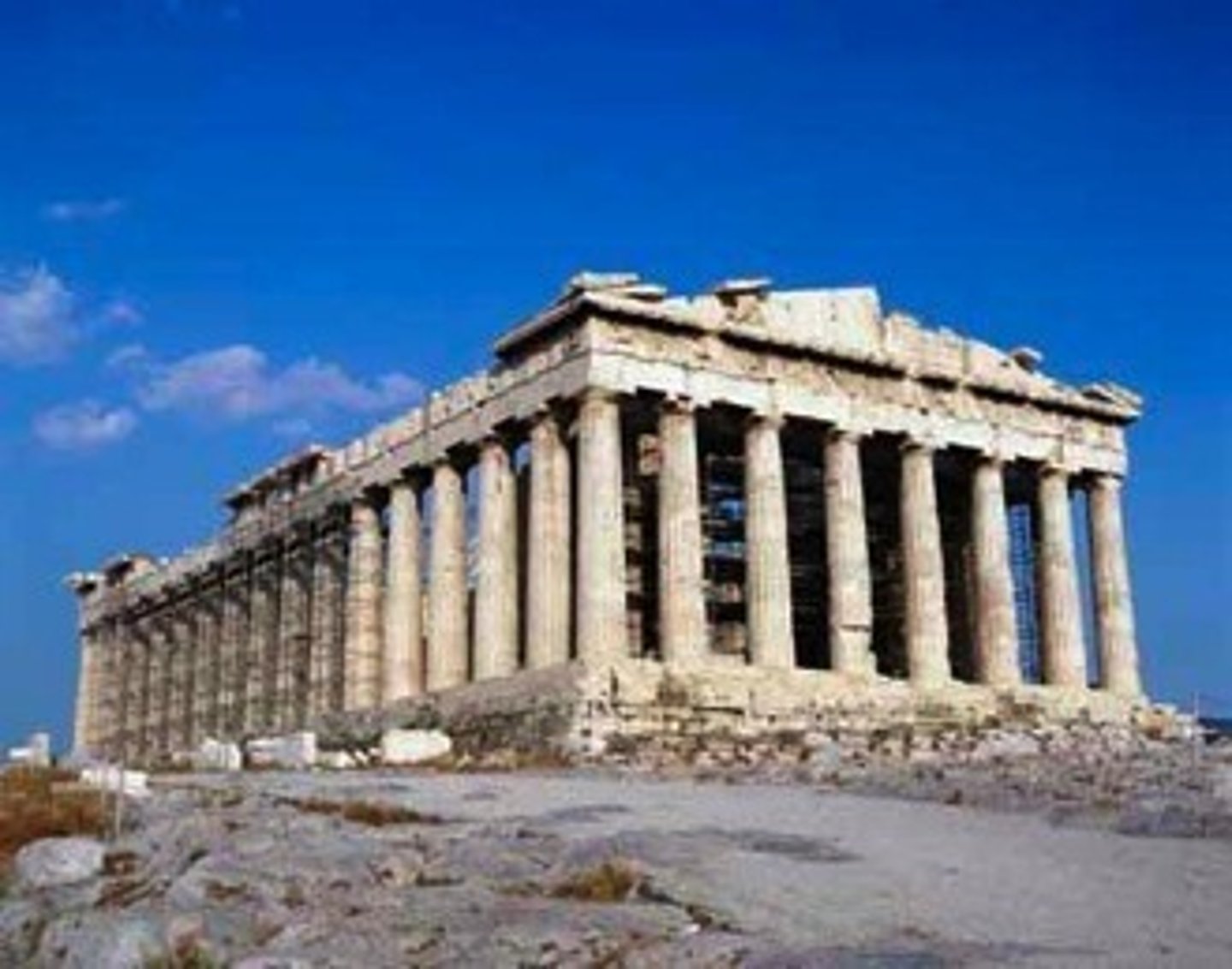
Parthenon - 447 BC
A former temple, on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the goddess Athena

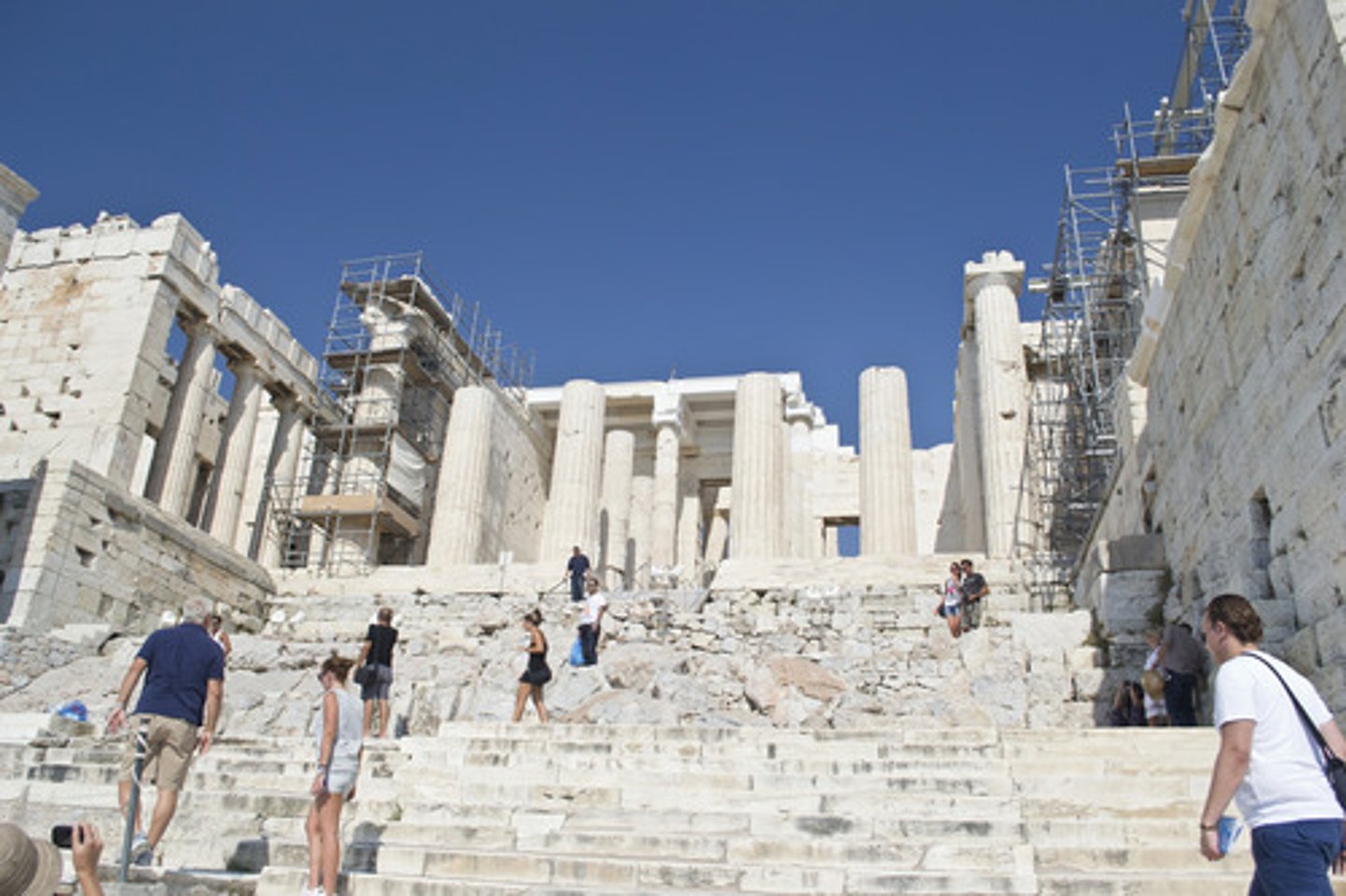
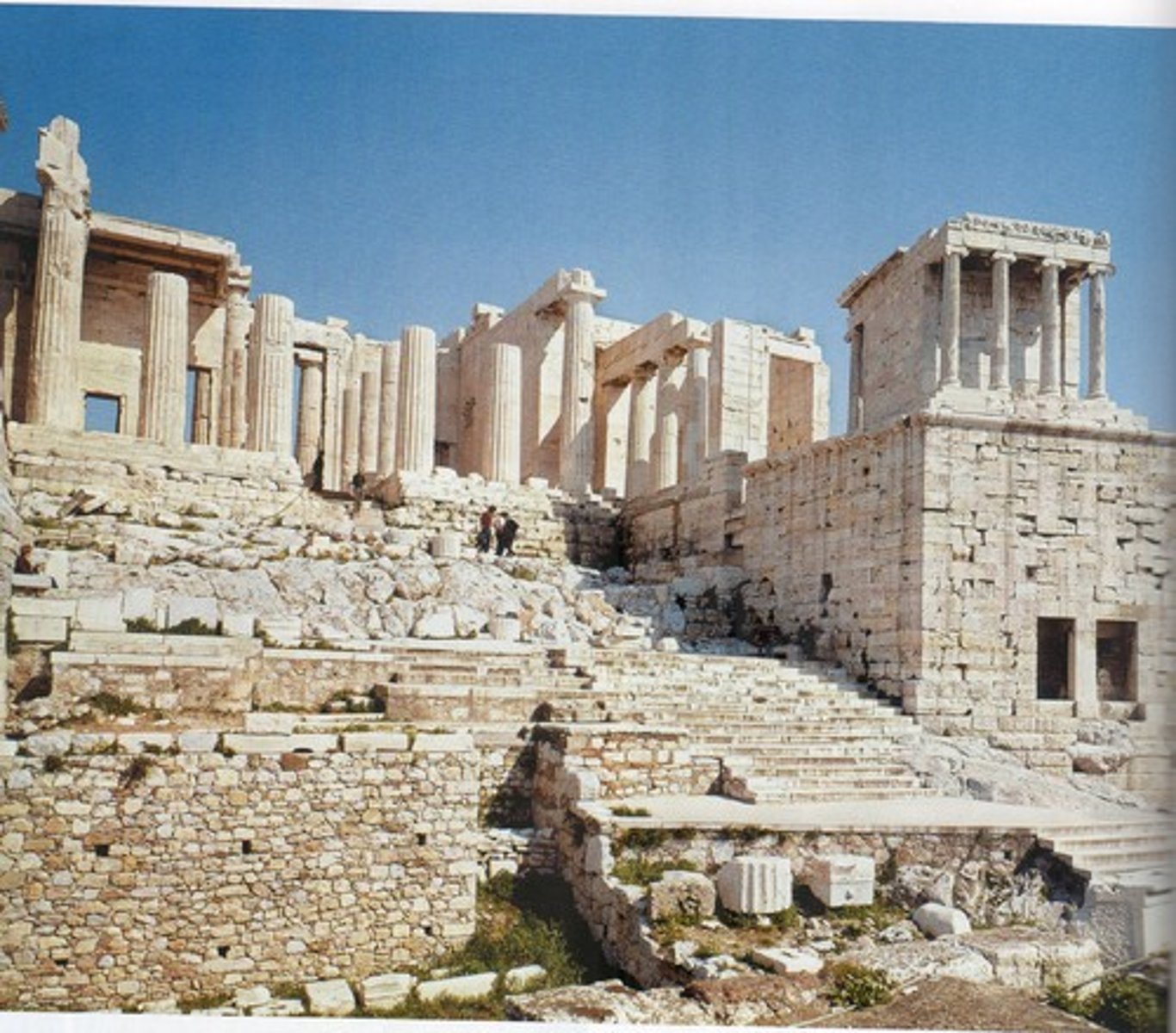
Propylaia
Serves as the entrance to the Acropolis in Athens

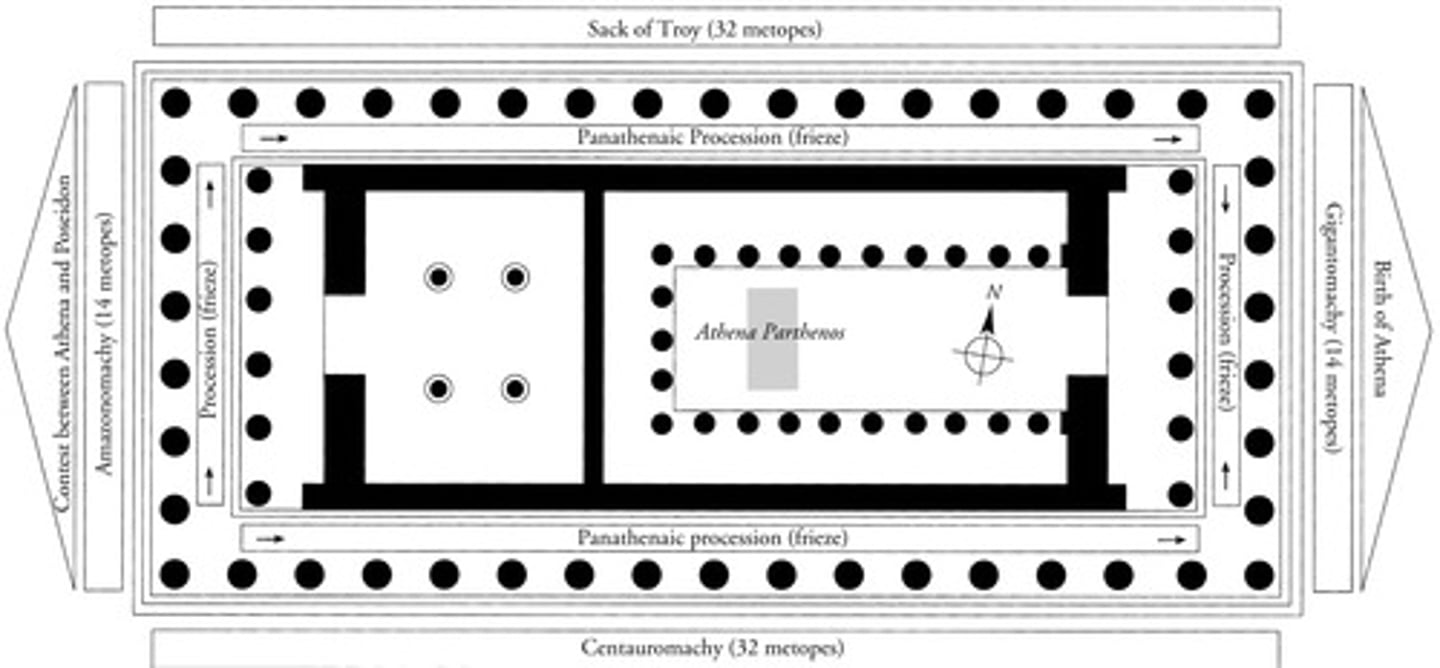
Schematic showing the inner cella of the Parthenon
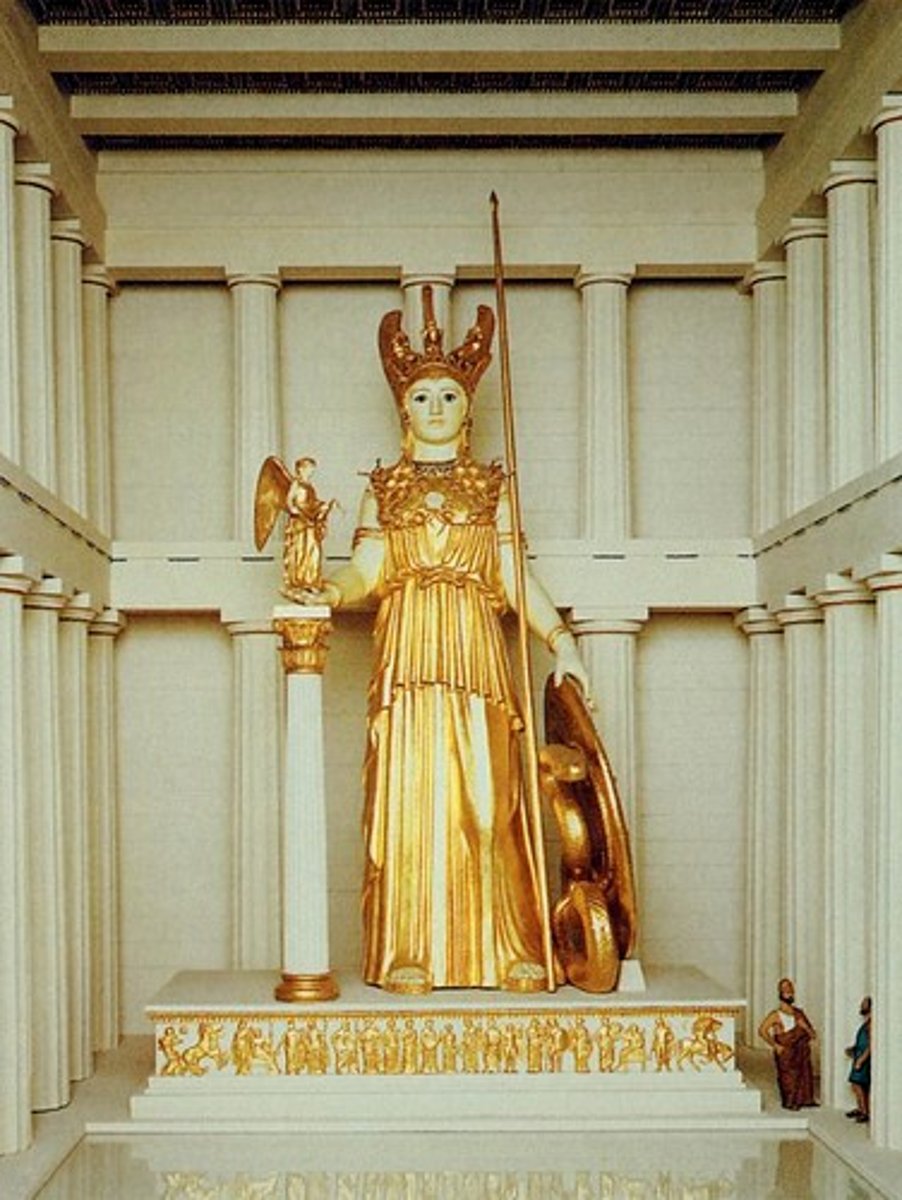
ca. 438 BC: PHIDIAS, Athena Parthenos, in the cella of the Parthenon, Acropolis, Athens, Greece

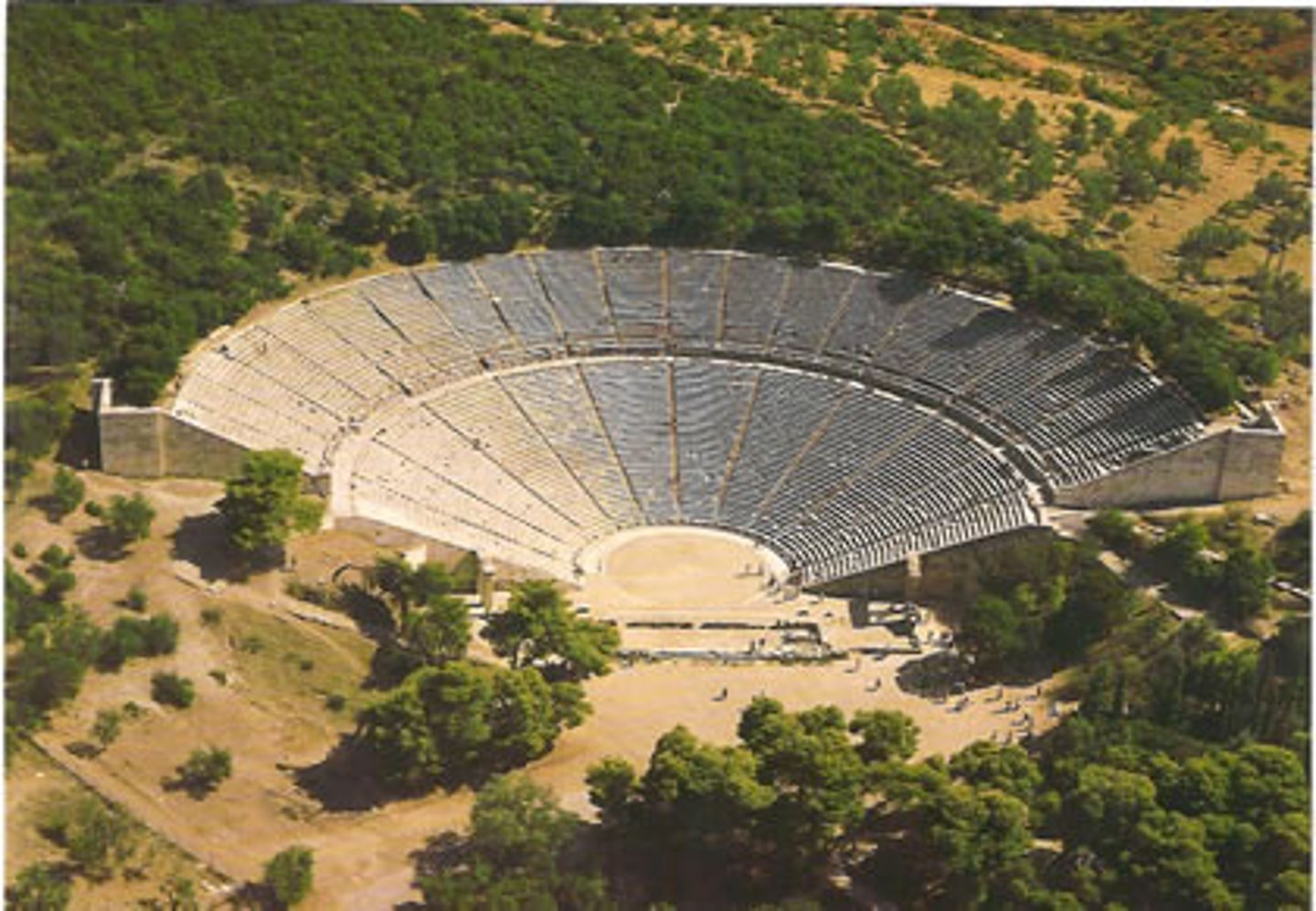
ca. 350 B.C. - POLYKLEITOS THE YOUNGER, Theater, Epidauros, Greece

4
How many metopes are there at the Parthenon
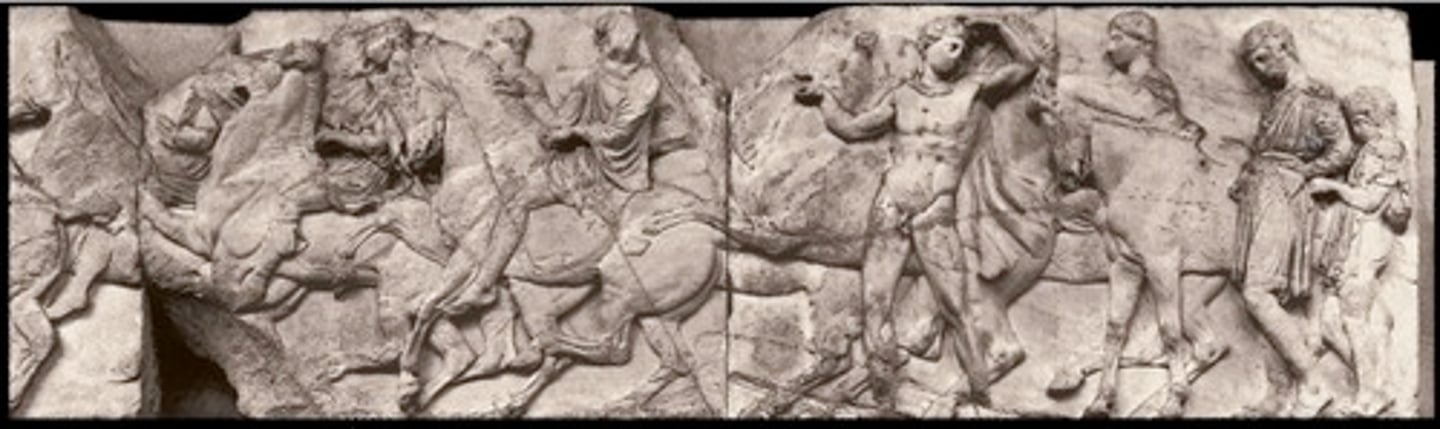
fall of troy, centaurs vs Lapiths, Athenians vs Amazons and greek gods fighting giants
What are the metopes at the parthenon
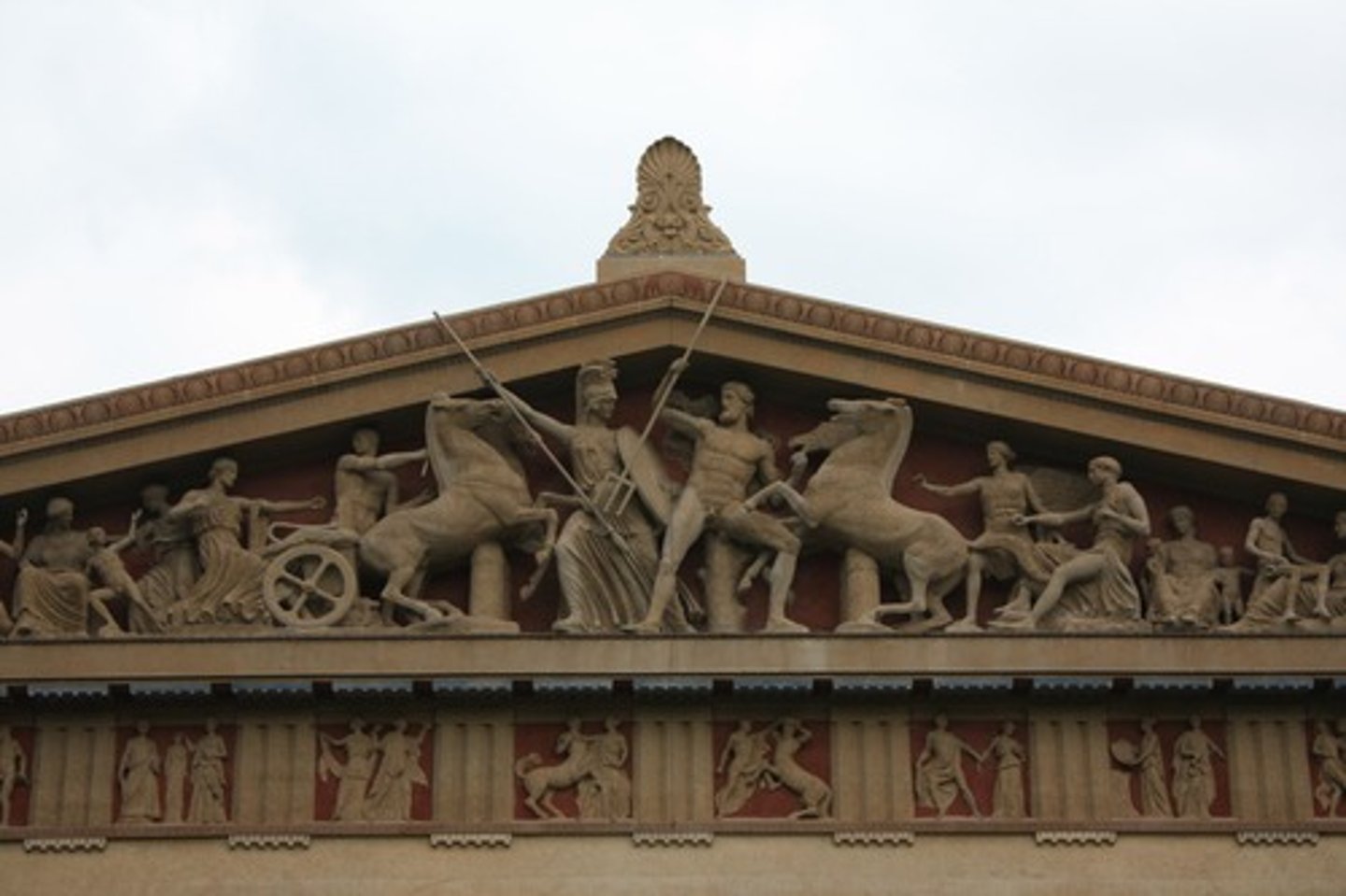
East pediment at the Parthenon
What is this
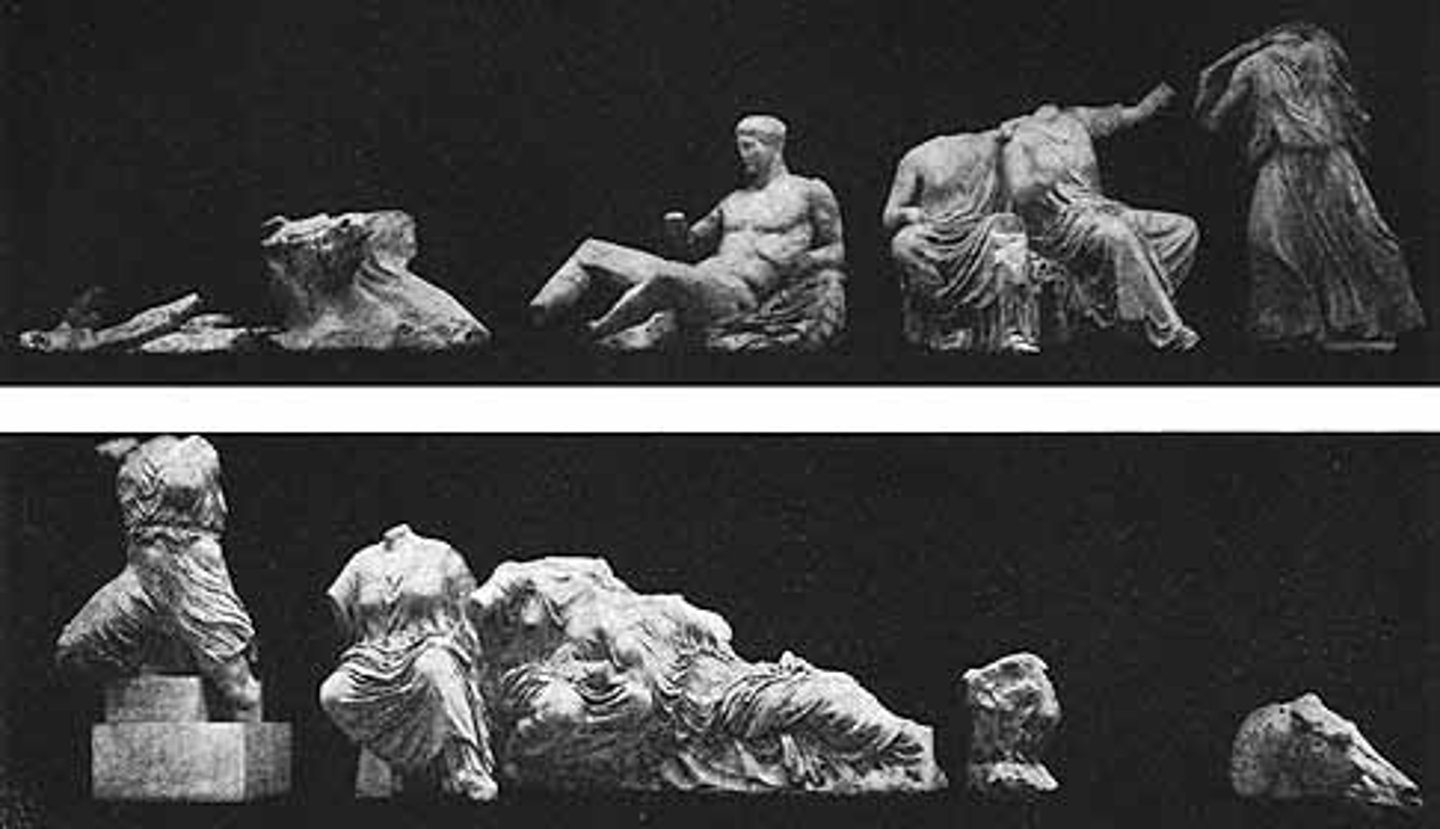

Birth of Athena
what is the east pediment at the parthenon
West pediment at the parthenon
what is this

Athena vs Poseidon
what is the west pediment at the Parthenon
East pediment at the temple of Zeus at Olympia
what is this
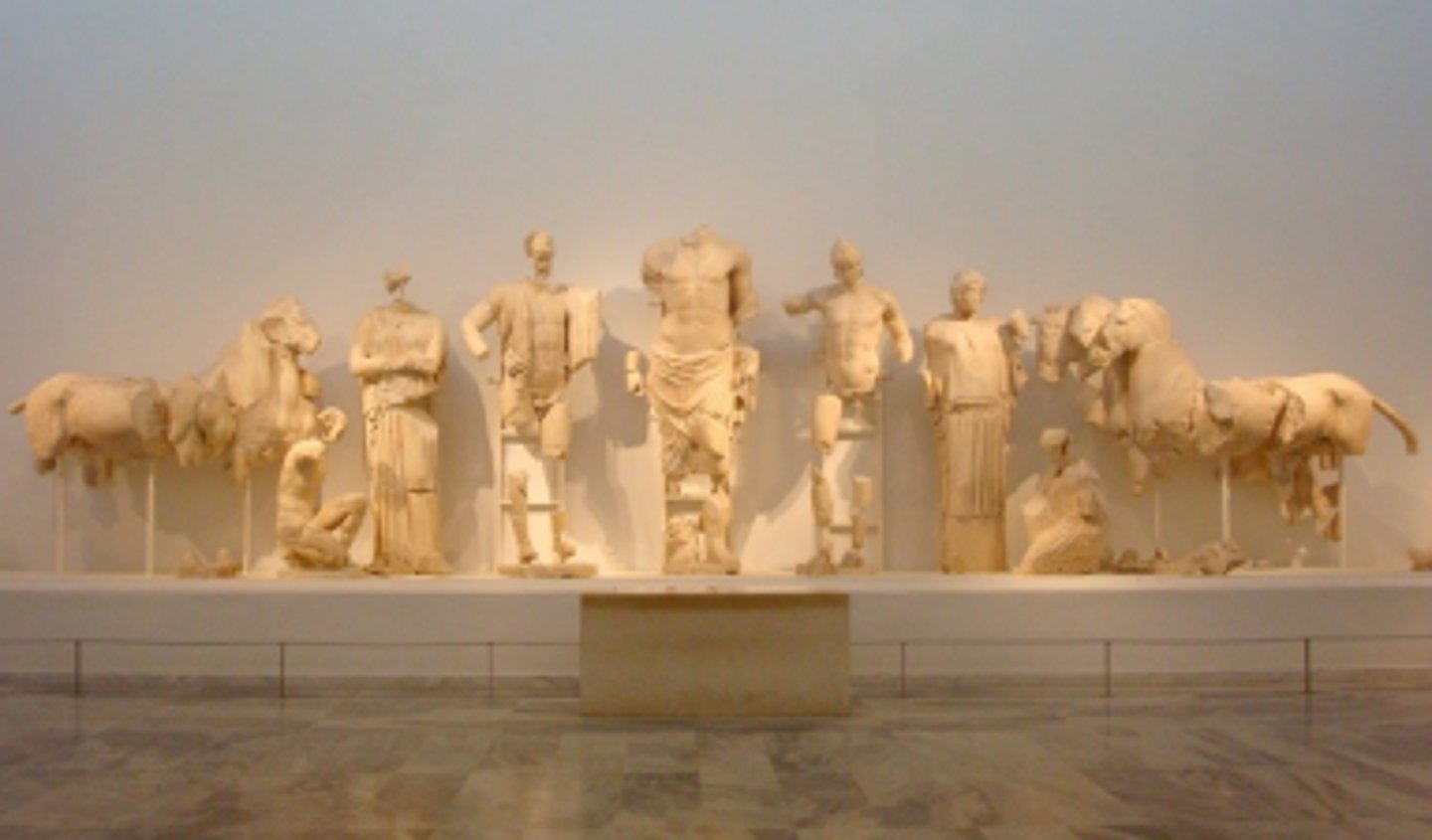

chariot race between pelops and oinomaos
what is the east pediment at the temple of zeus at Olympia
West pediment at the temple of Zeus at Olympia
what is this

Centauromachy
what is the west pediment at the temple of Zeus at Olympia
Herakles 12 labours
what are the metopes at the temple of Zeus at Olympia
Apples of hisperadies, cleaning the Augean stables, cretan bull and nemean lion
what are the depictions on the metopes at the temple of Zeus at Olympia
East pediment at the temple of Aphaia
what is this

Early destruction of Troy
what is the East pediment at the temple of Aphaia
West pediment at the temple of Aphaia
what is this

later destruction of Tory
what is the west pediment at the temple of Aphaia
metope at Temple C
what is this
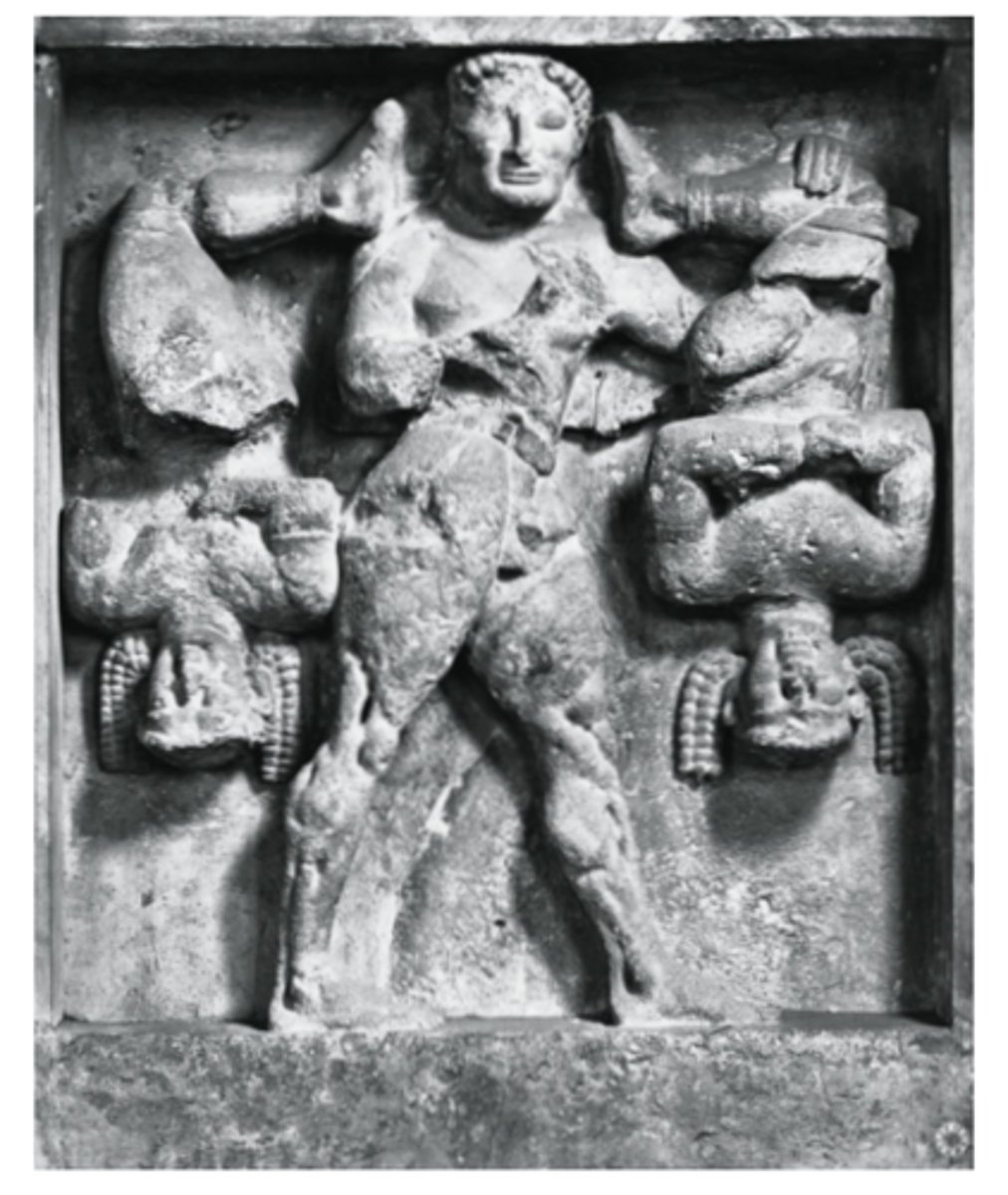

Herakles and the kerkopes
what does this depict
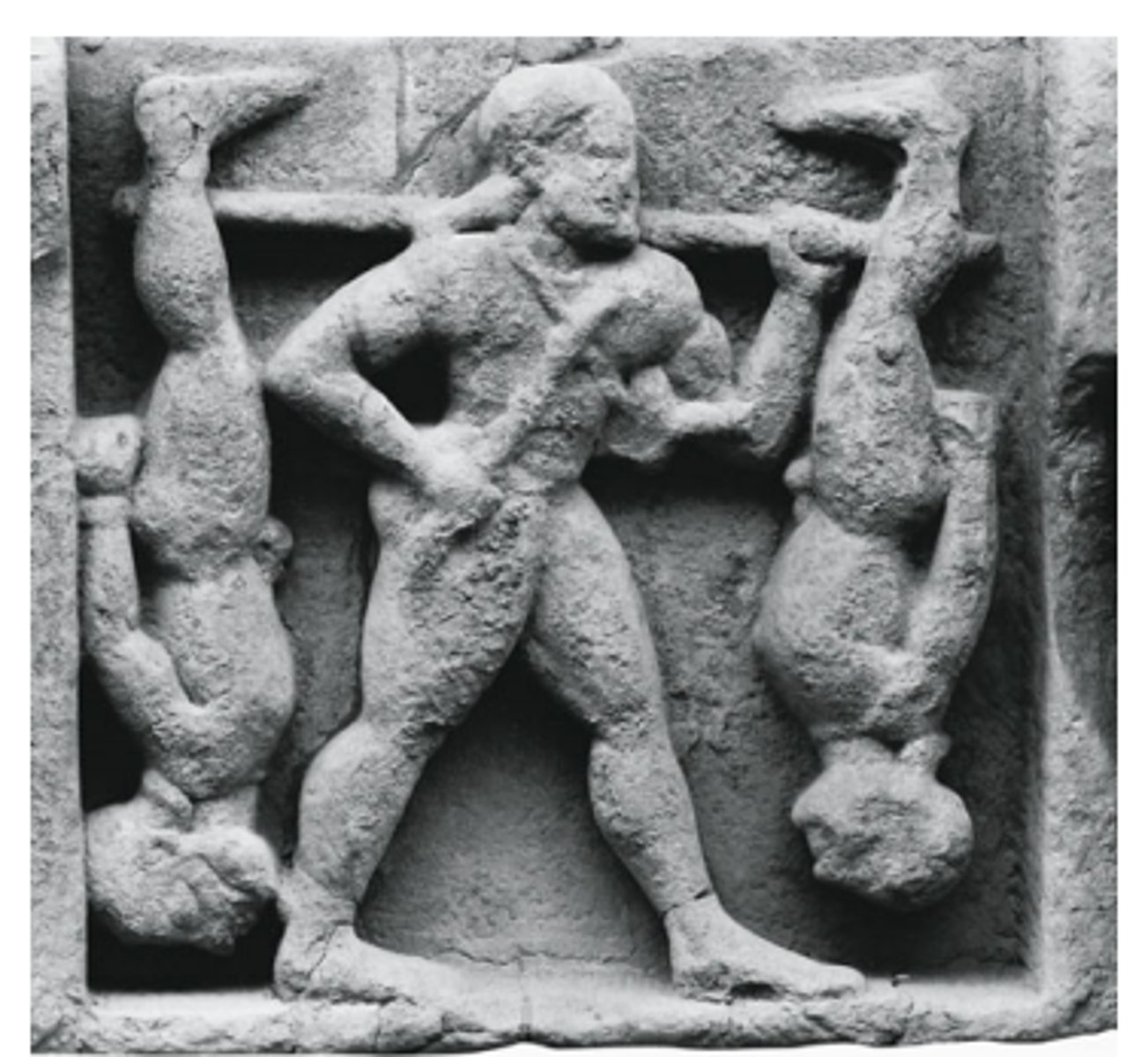

Metope at Temple C
what is this

Heroic cattle raid
what does this depict
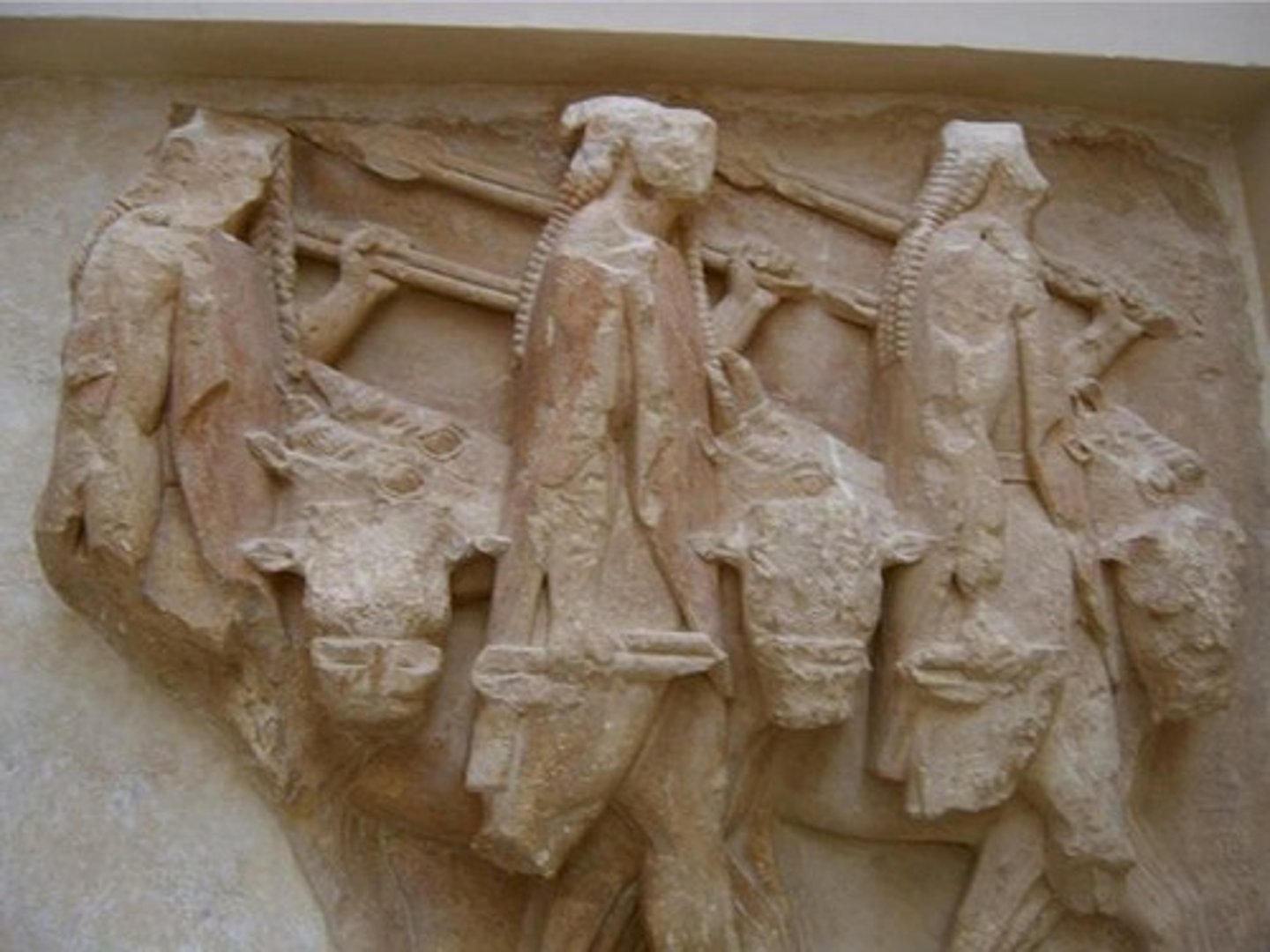

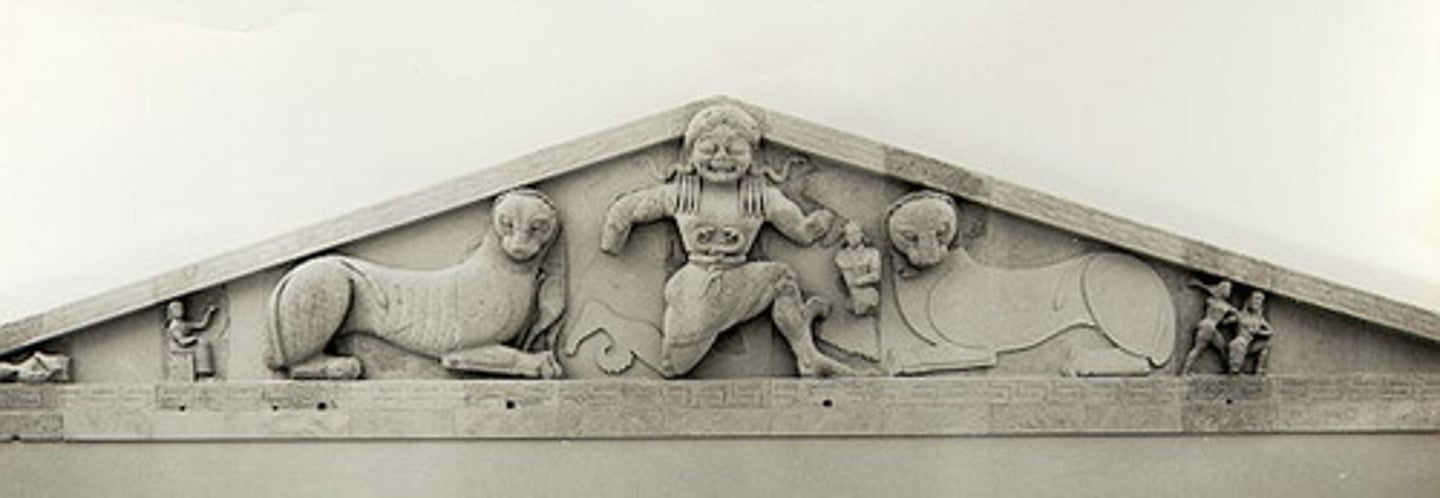
pediment at the temple of Artemis
what is this
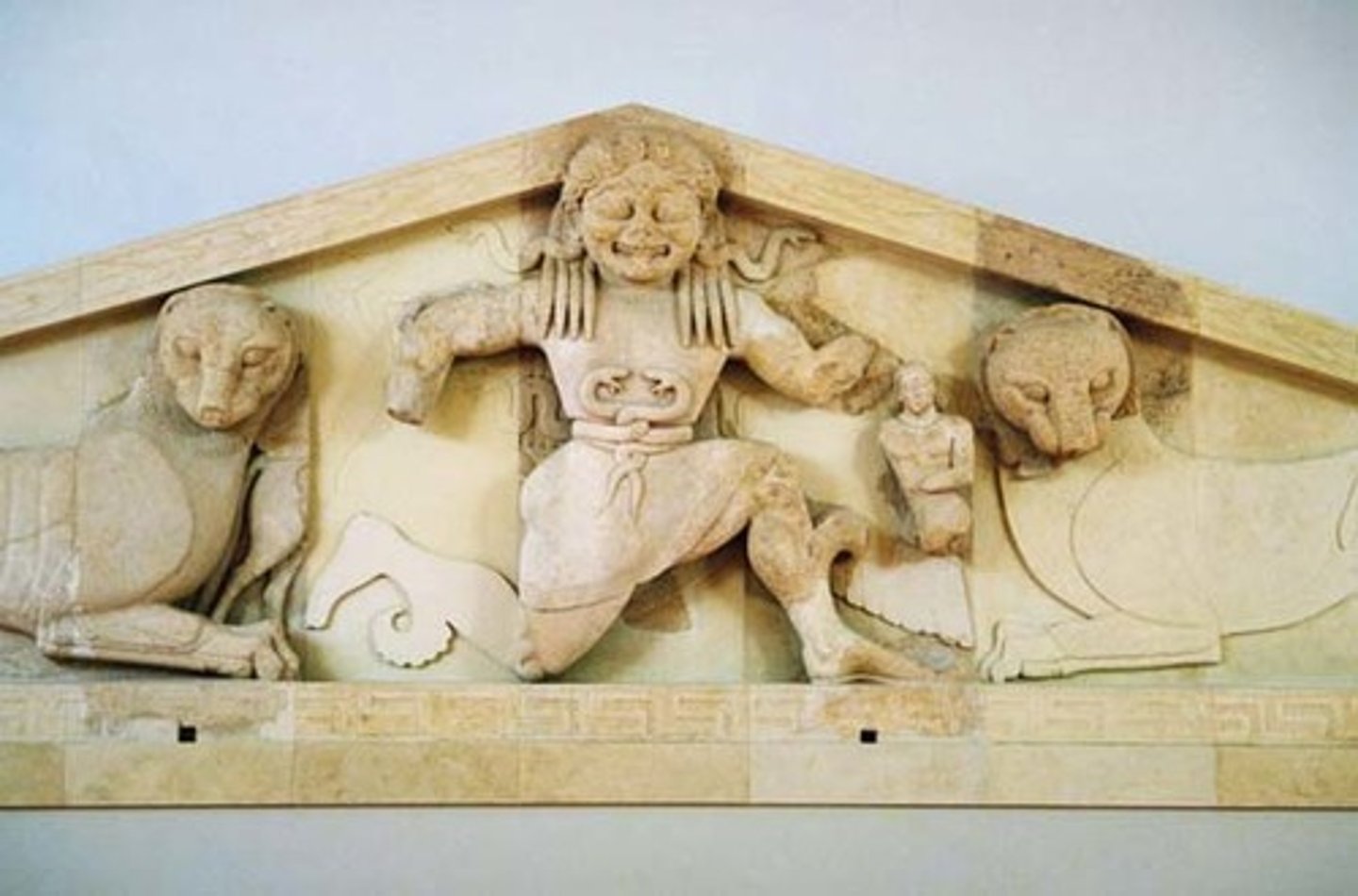

Medusa in between two felines
what is the pediment at the temple of Artemis
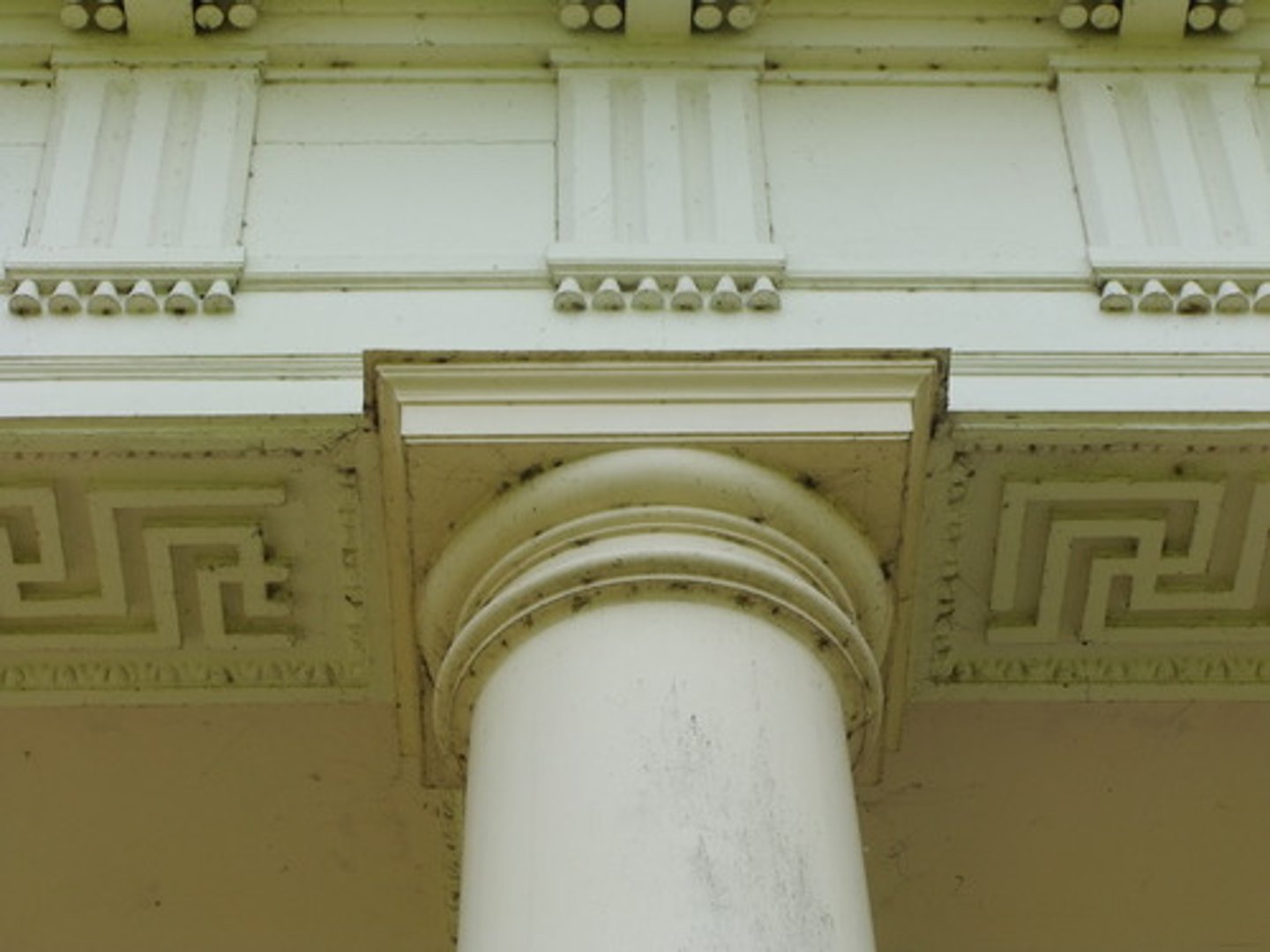
Doric order

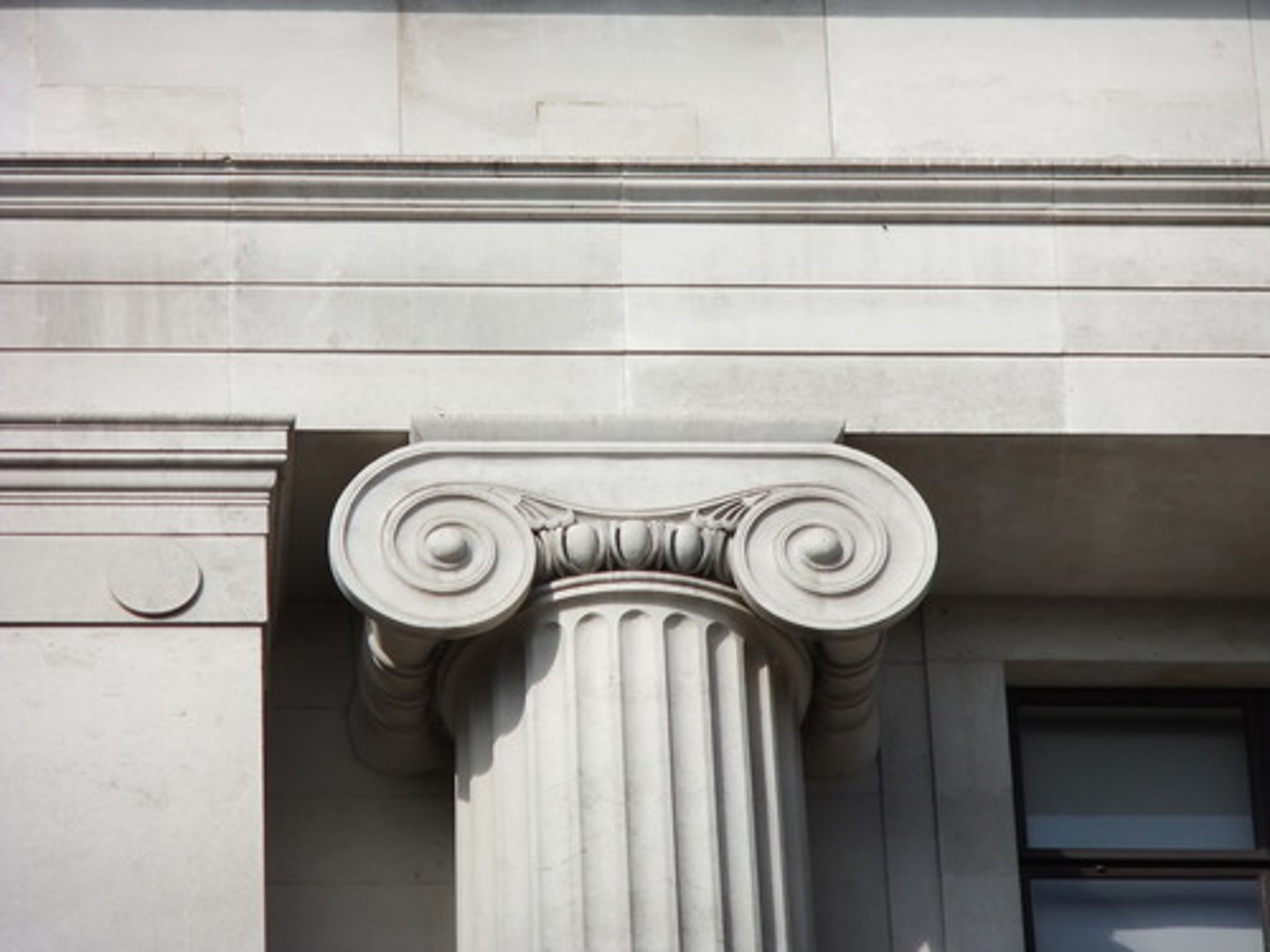
Ionic order

Corinthian order

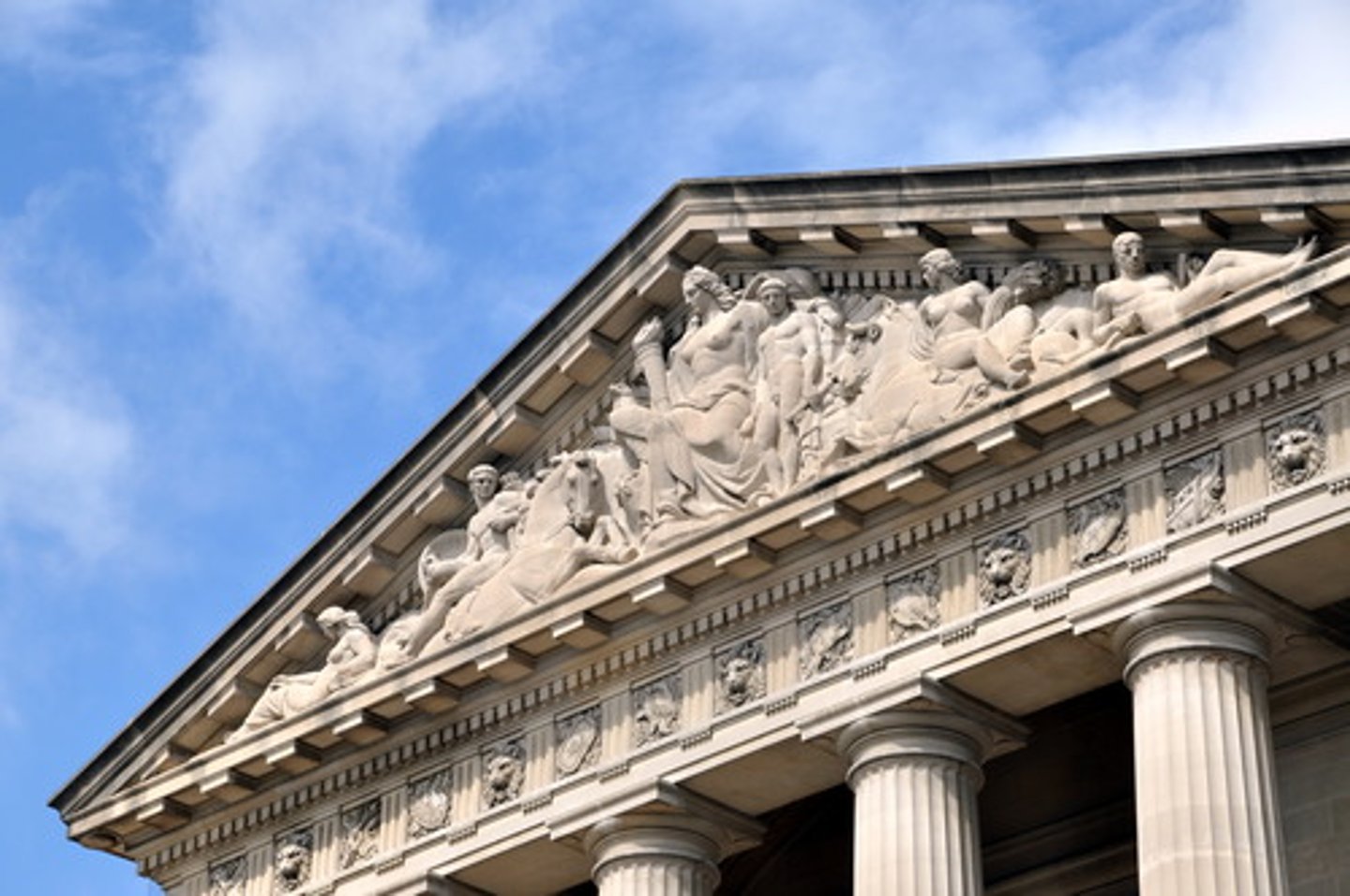
Pediment

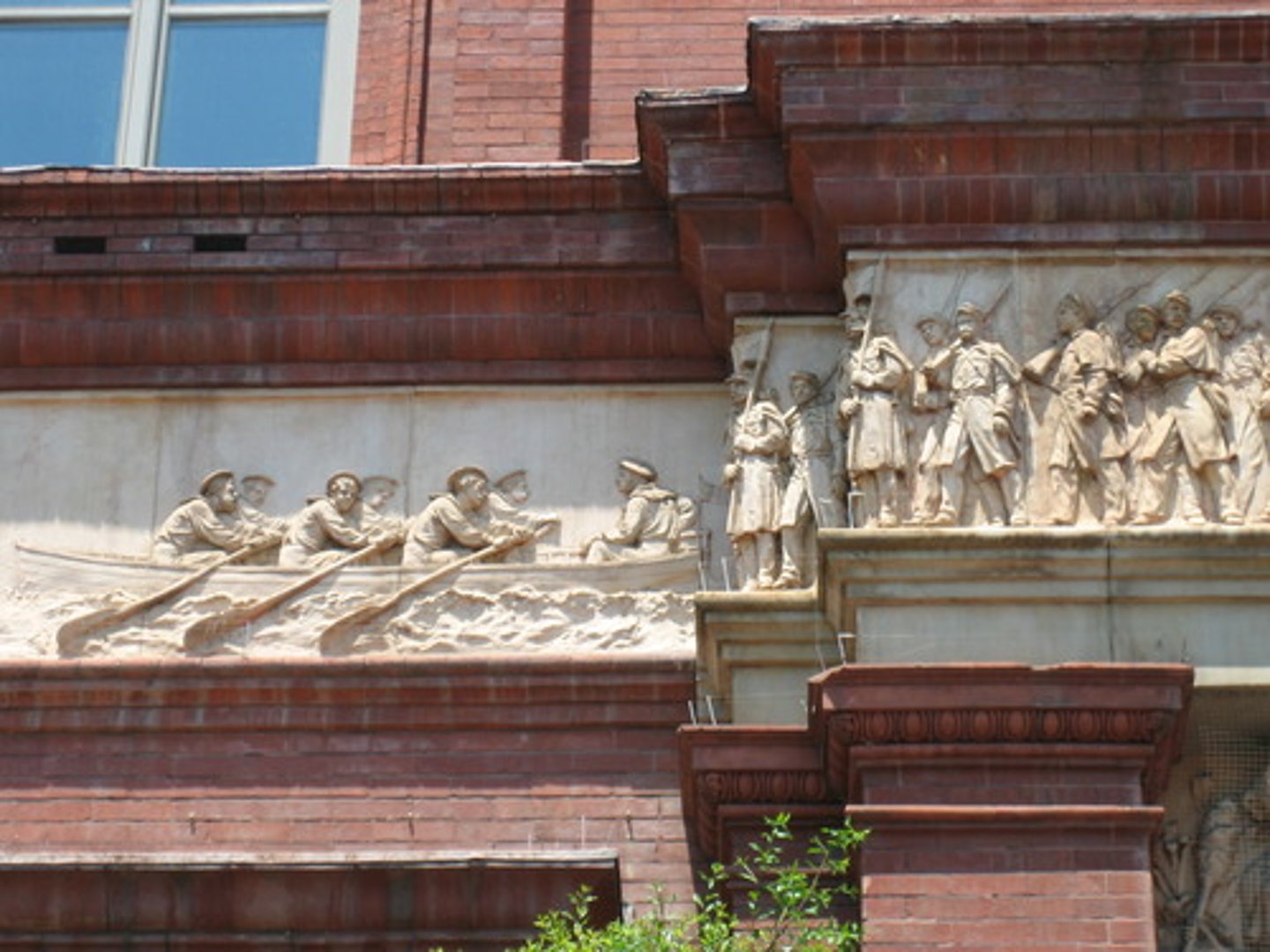
frieze

beauty
very pleasing to the senses
symmetry
having the same shape, size, and position on both sides of a dividing line
clarity
clearness, accuracy
balance
equal distribution of weight
proportion
proper relation between parts
function
to serve a purpose
Nike
The Greek goddess of victory
Acropolis
is an ancient citadel located on a high rocky outcrop above the city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historic significance, the most famous being the Parthenon.

Propylaea
is any monumental gateway entrance to the Acropolis in Athens.
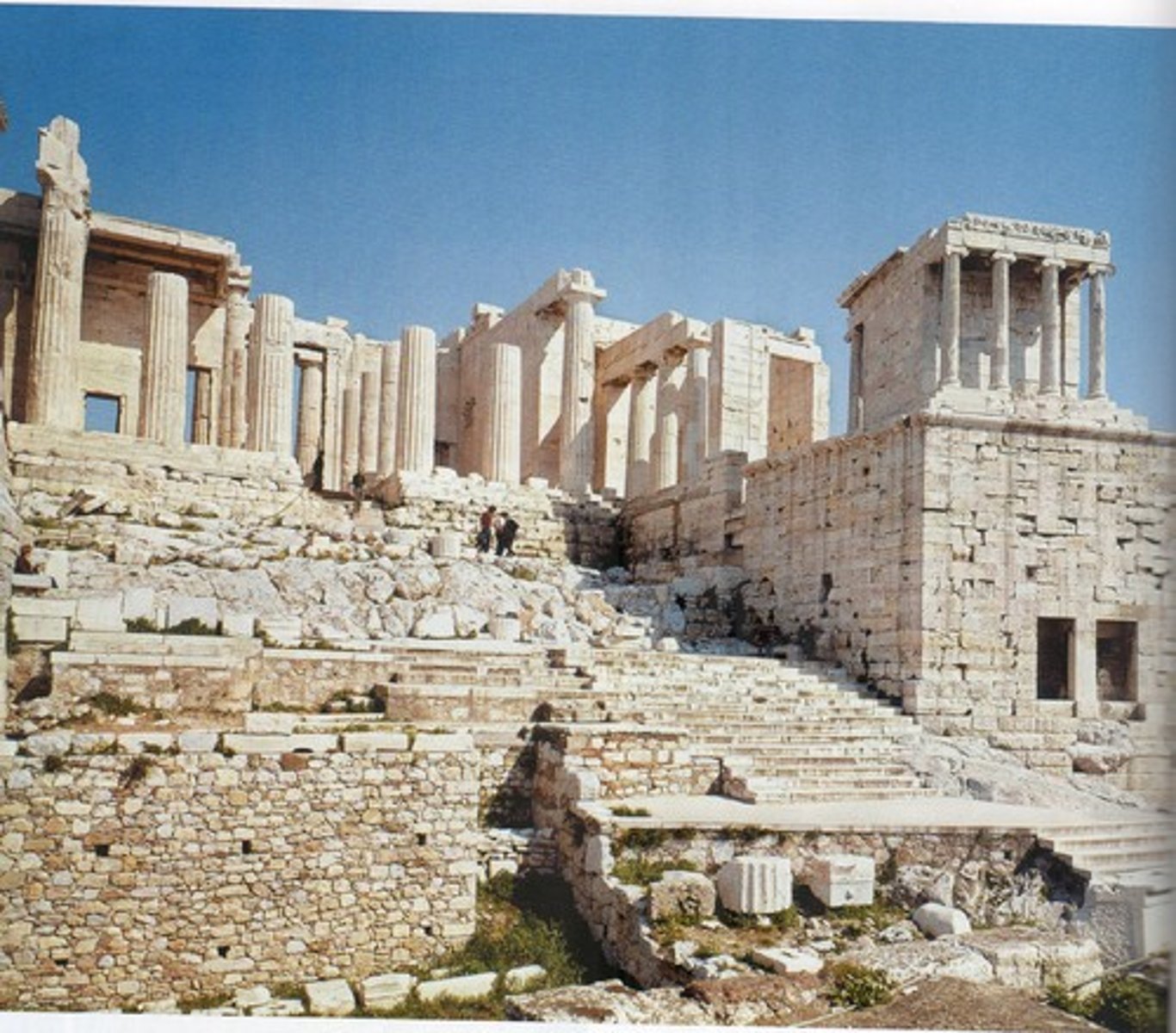

Mnesicles
was an ancient Athenian architect active in the mid 5th century BCE, the age of Pericles. Plutarch identifies him as architect of the Propylaea, the Periclean gateway to the Athenian Acropolis

Temple of Athena Nike
Acropolis - Athens, Greece
420 BCE
Kallikrates
Classical Greek - Ionic
is a temple on the Acropolis of Athens. Built around 420BC, the temple is the earliest fully Ionic temple on the Acropolis
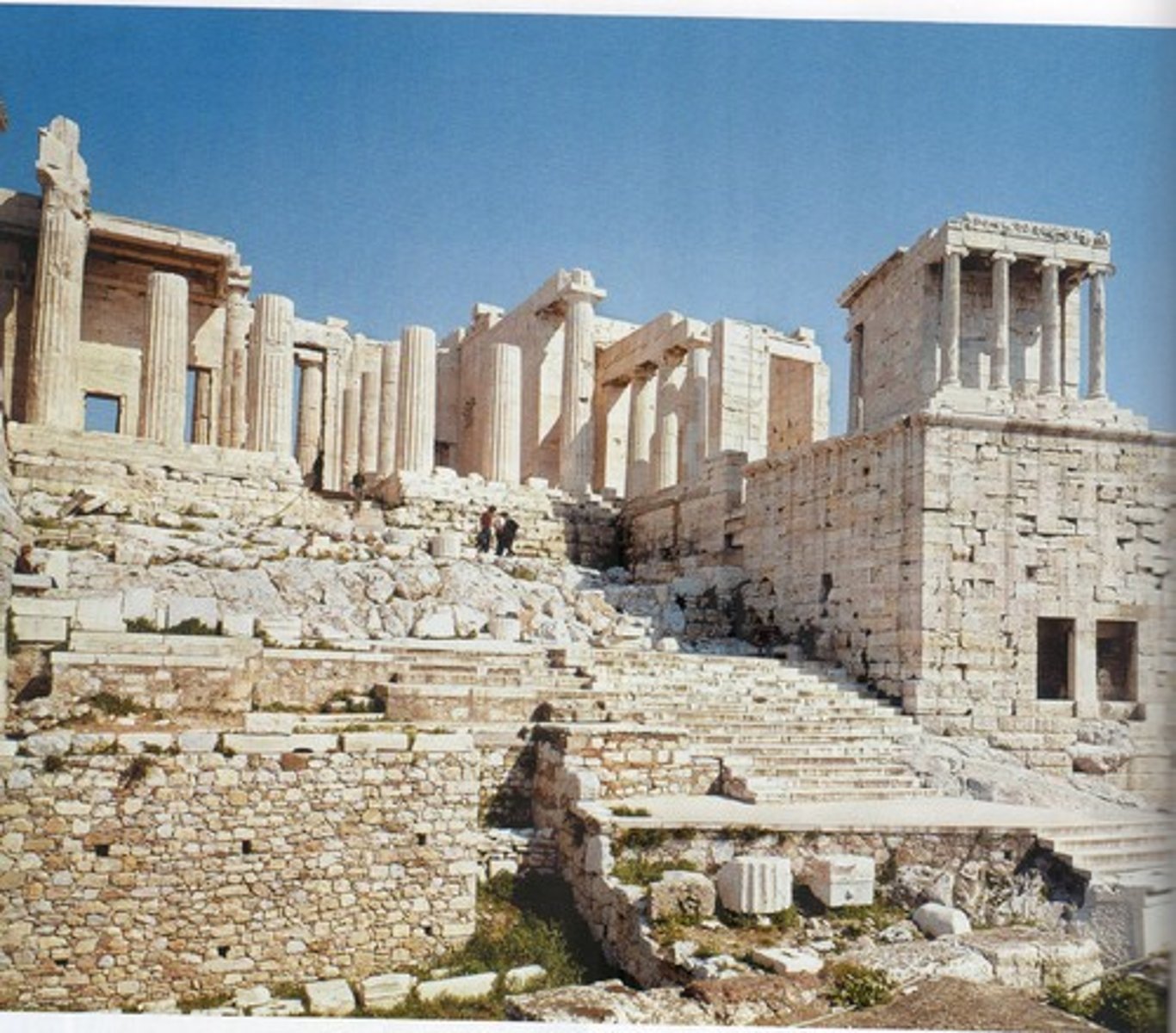
Erechtheum
is an ancient Greek temple on the north side of the Acropolis of Athens in Greece which was dedicated to both Athena and Poseidon
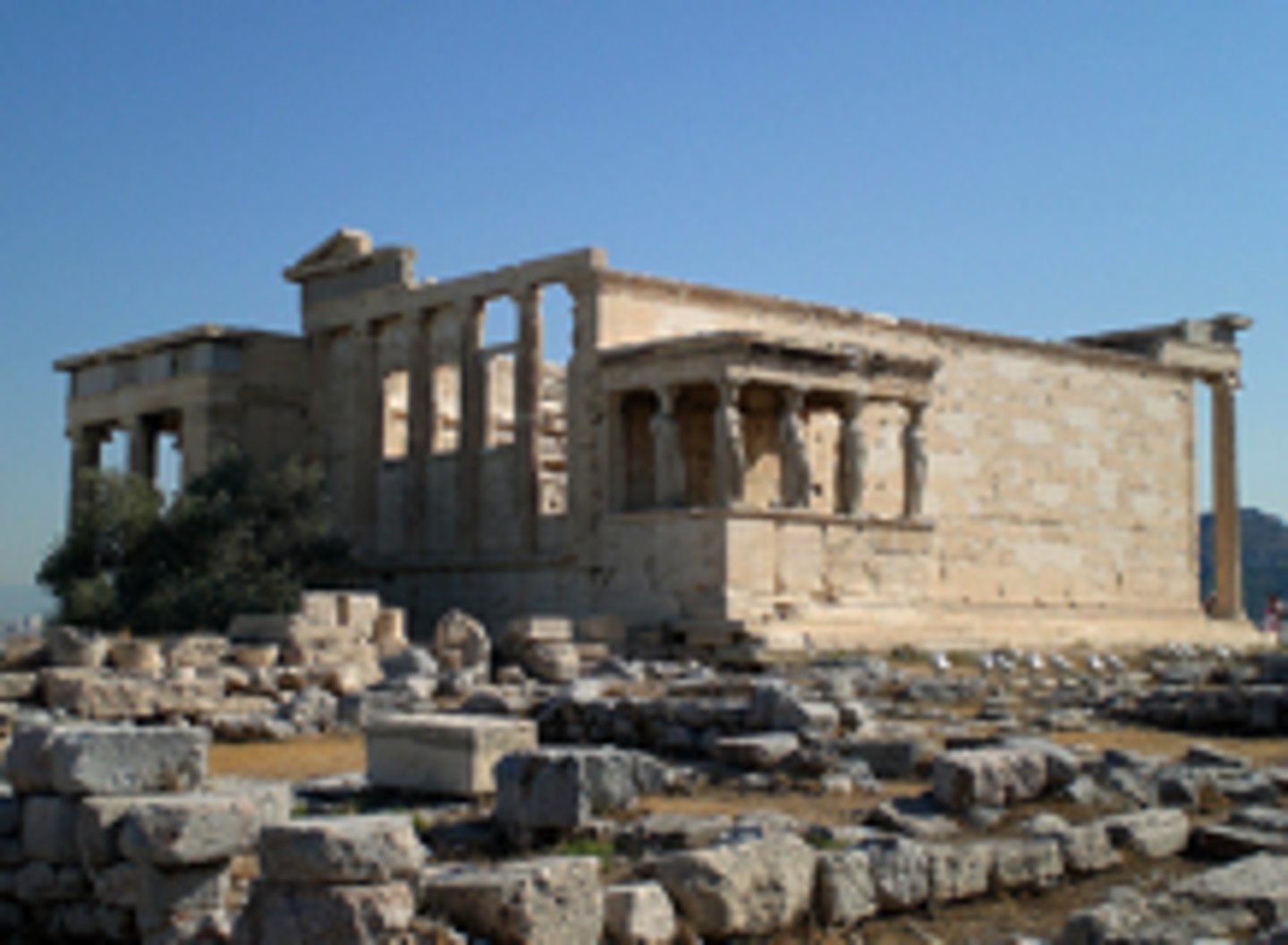

Parthenon
is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their patron.
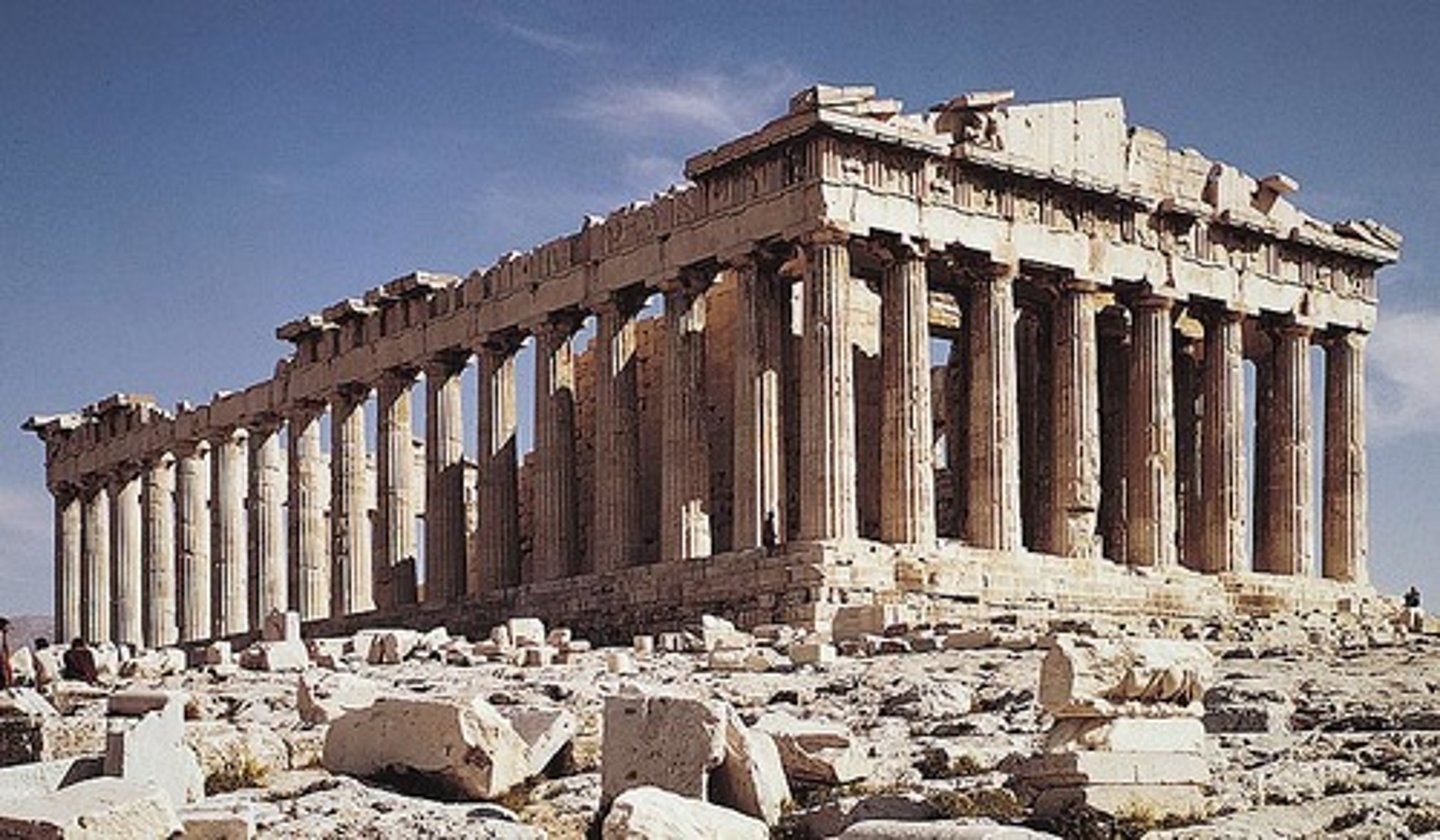

Ictinus, Callicrates and Carpion
architects of the Parthenon.
Pheidias
Sculptor of the Parthenon.
Perikles
was arguably the most prominent and influential Greek statesman, orator and general of Athens during the Golden Age— specifically the time between the Persian and Peloponnesian wars.

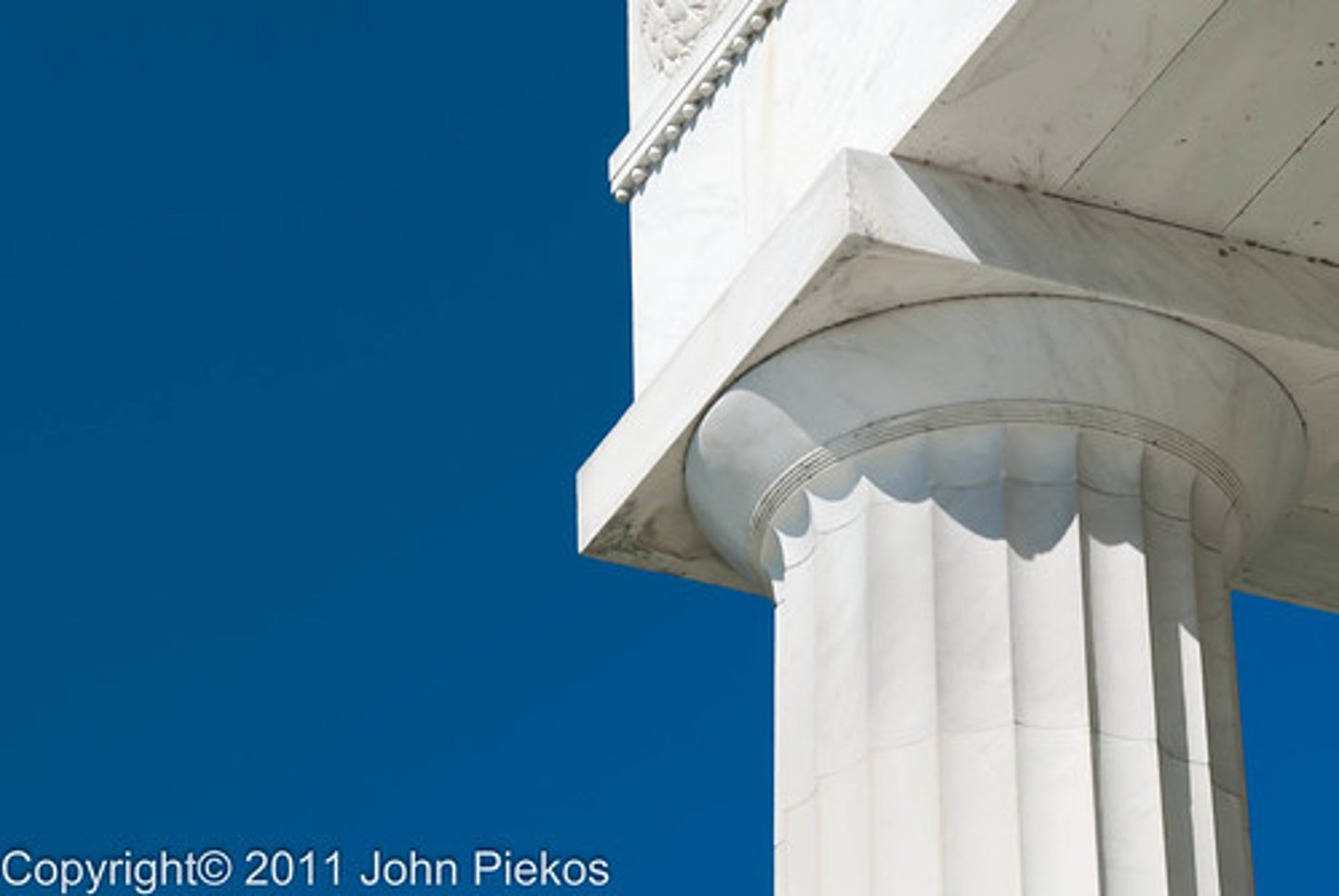
Doric
columns were stouter than those of the other orders. Their smooth, round capitals are simple and plain compared to the other two Greek orders. A square abacus connects the capital to the entablature.

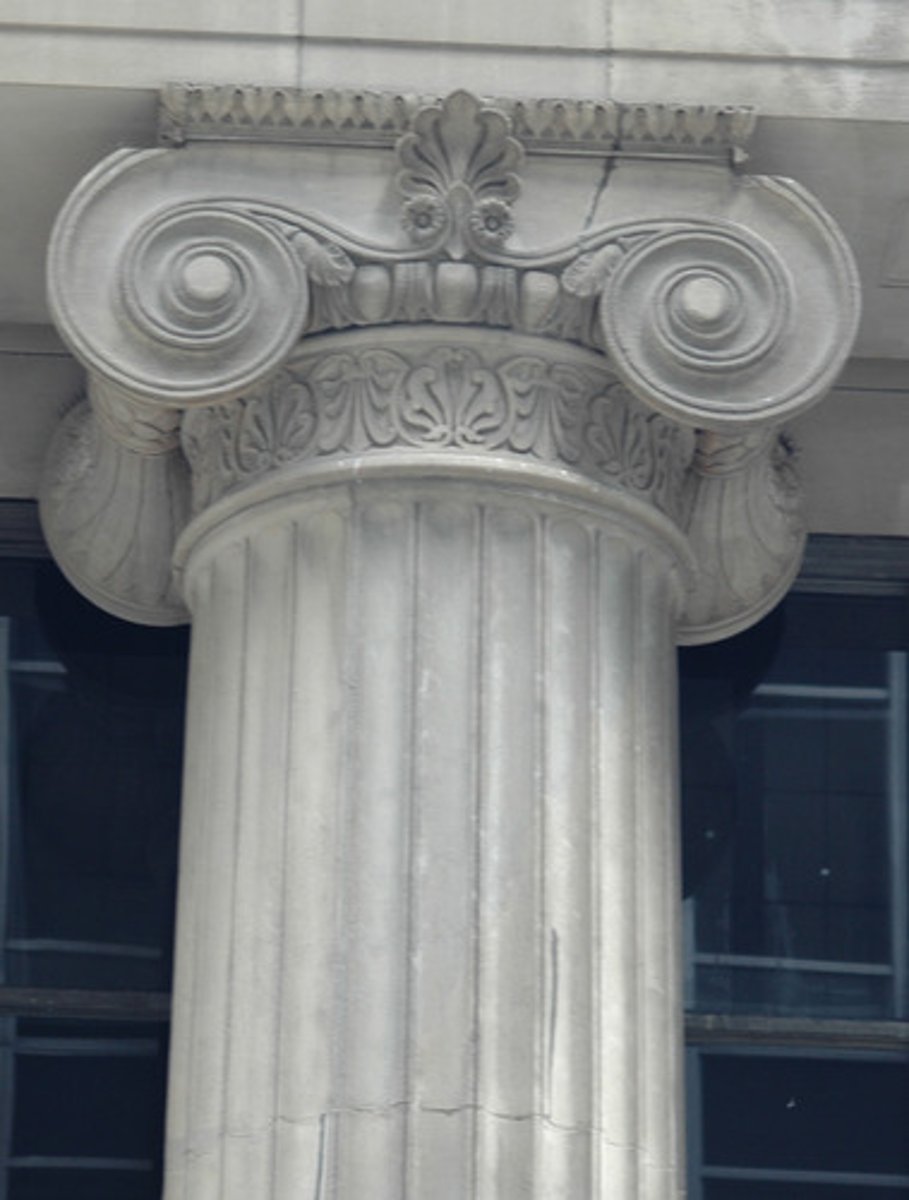
Ionic
are the thinnest and smallest columns out of the three canonic orders. It's capital is characterized by the use of volutes. They normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform; the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart.

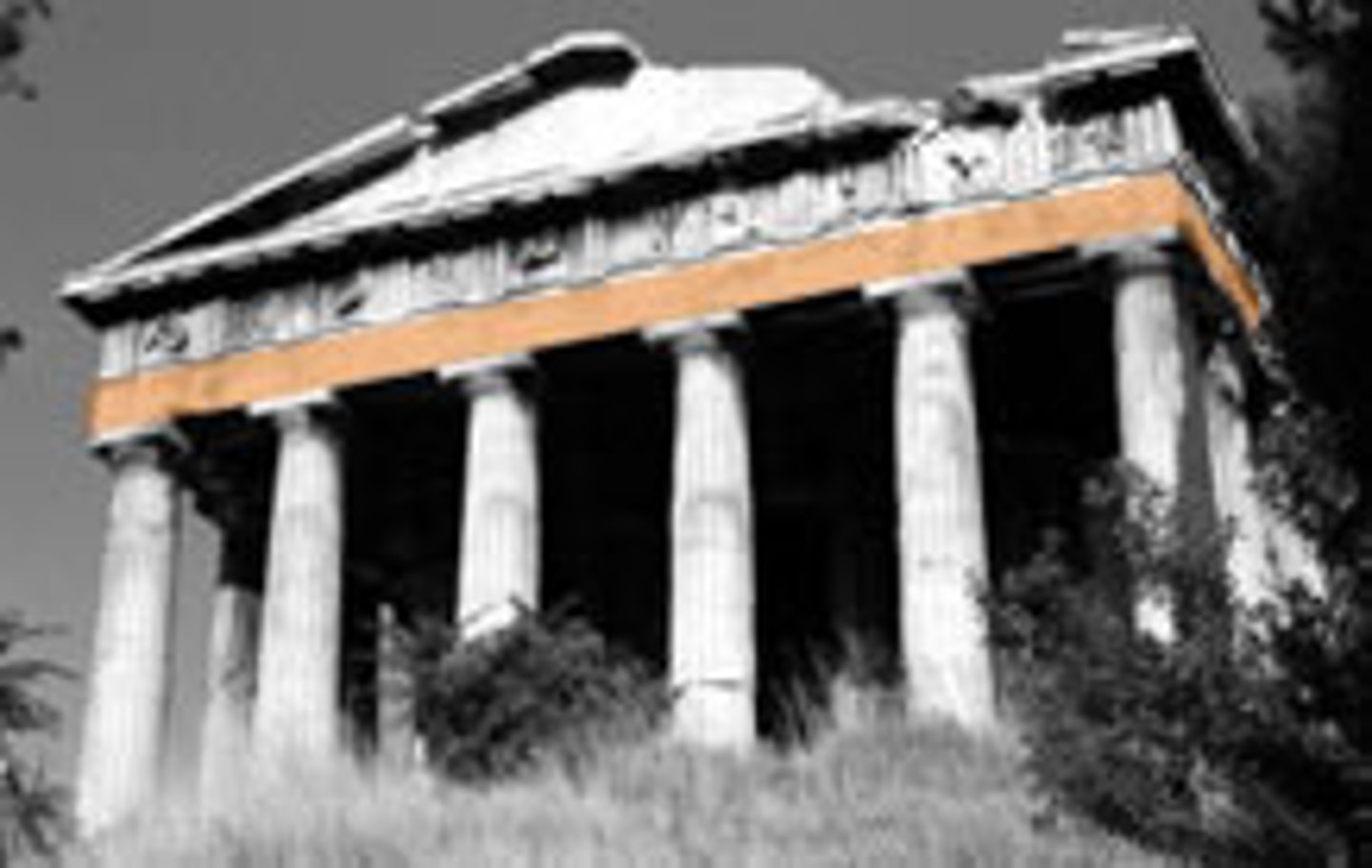
Architrave
is the lintel or beam that rests on the capitals of the columns. It is an architectural element in Classical architecture.

doric
what order?
ionic
what order?
Corinthian
what order?
capital
top part of column.

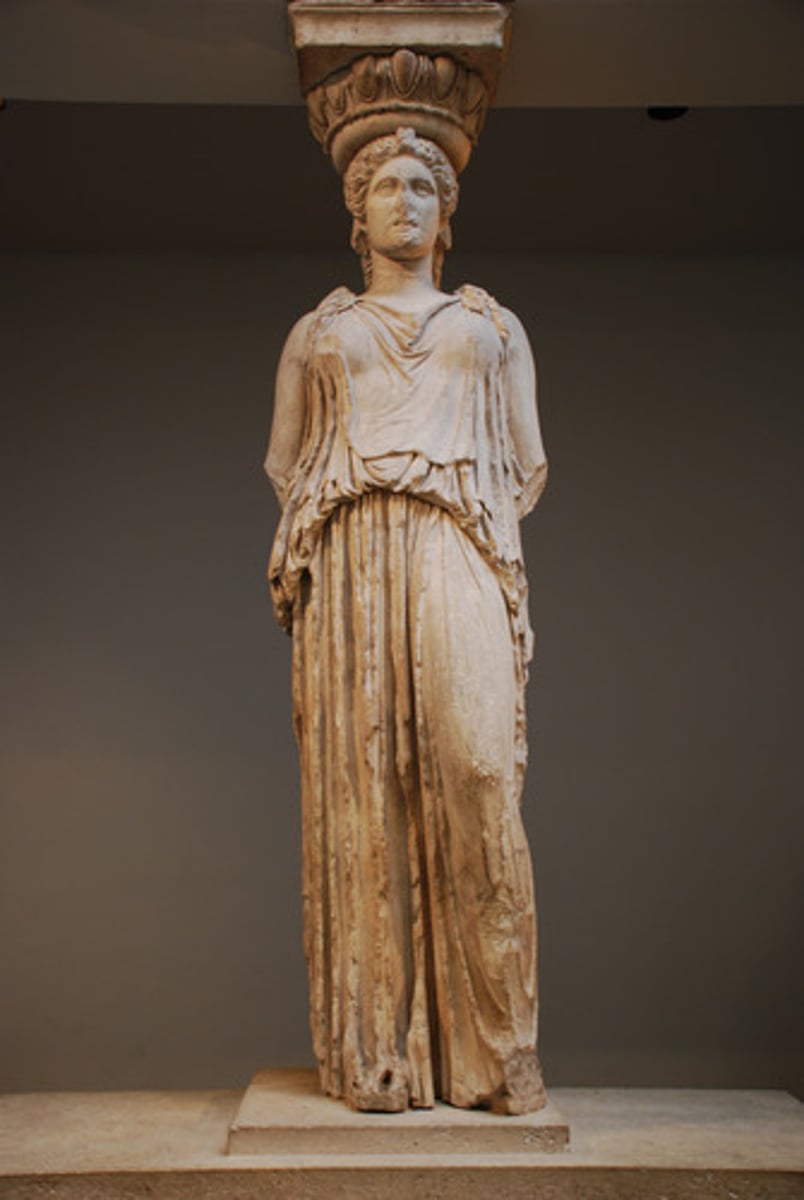
caryatid
is a sculpted female figure serving as an architectural support taking the place of a column or a pillar supporting an entablature on her head.

Colonnade
a row of columns supporting a roof, an entablature, or arcade.

Cornice
is the topmost element of the entablature.
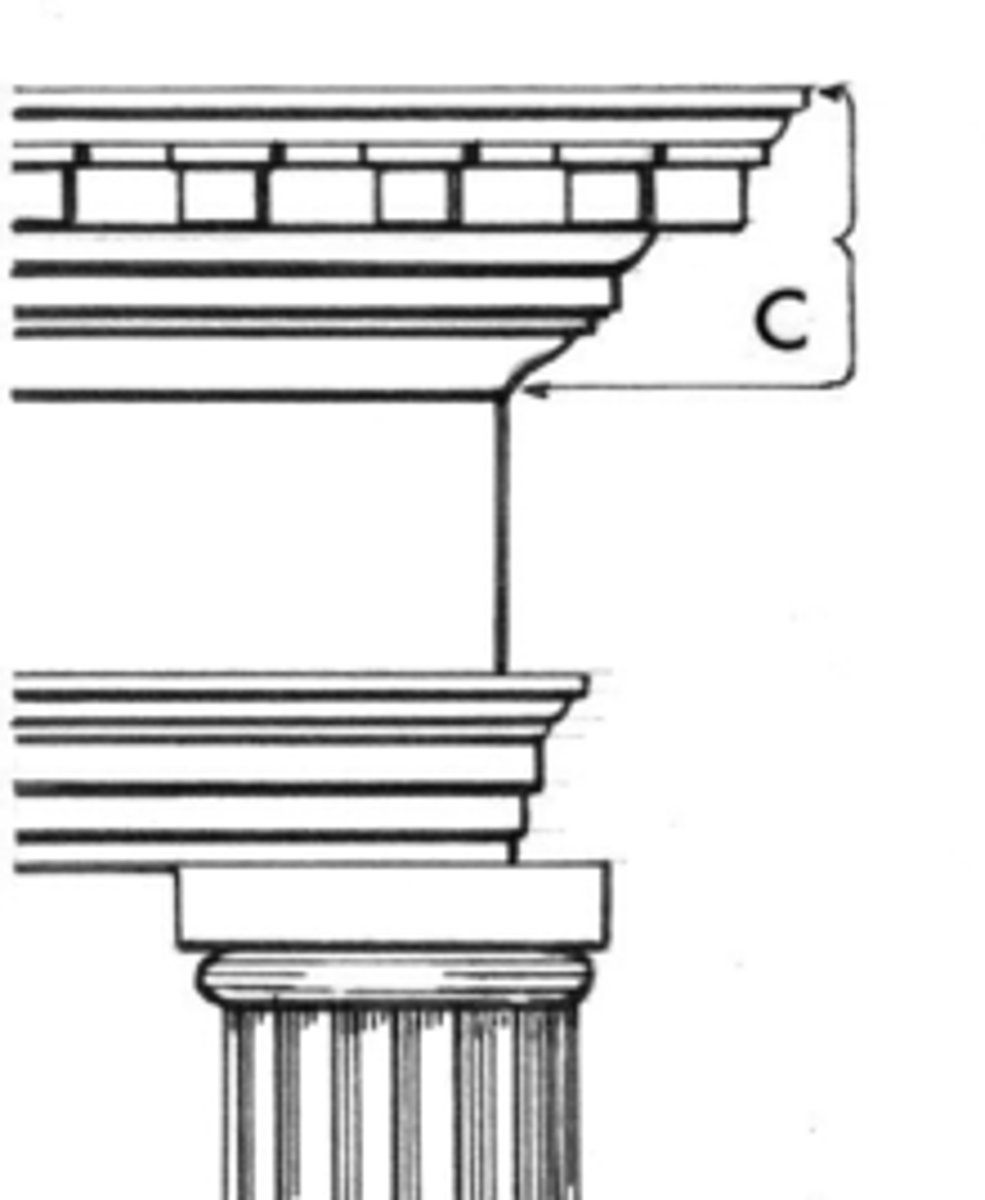
Entablature
a horizontal, continuous lintel on a classical building supported by columns or a wall, comprising the architrave, frieze, and cornice.

Entasis
a slight convex curve in the shaft of a column, introduced to correct the visual illusion of concavity produced by a straight shaft.
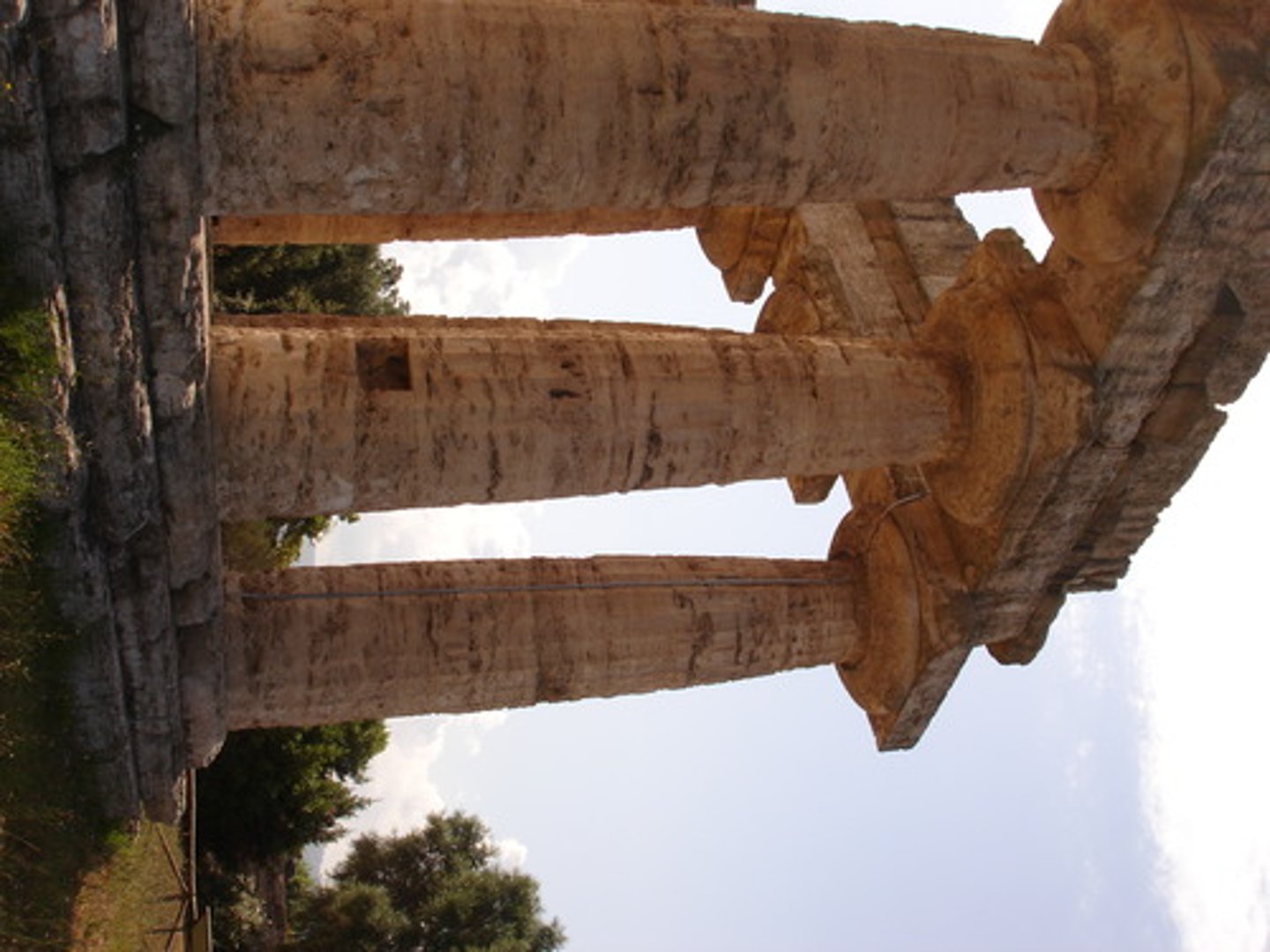

greek Frieze
is a long narrow band of sculpture that runs along the architrave of a Greek temple or another building. One of the most famous of theses is the one on the Parthenon in Athens, Greece.

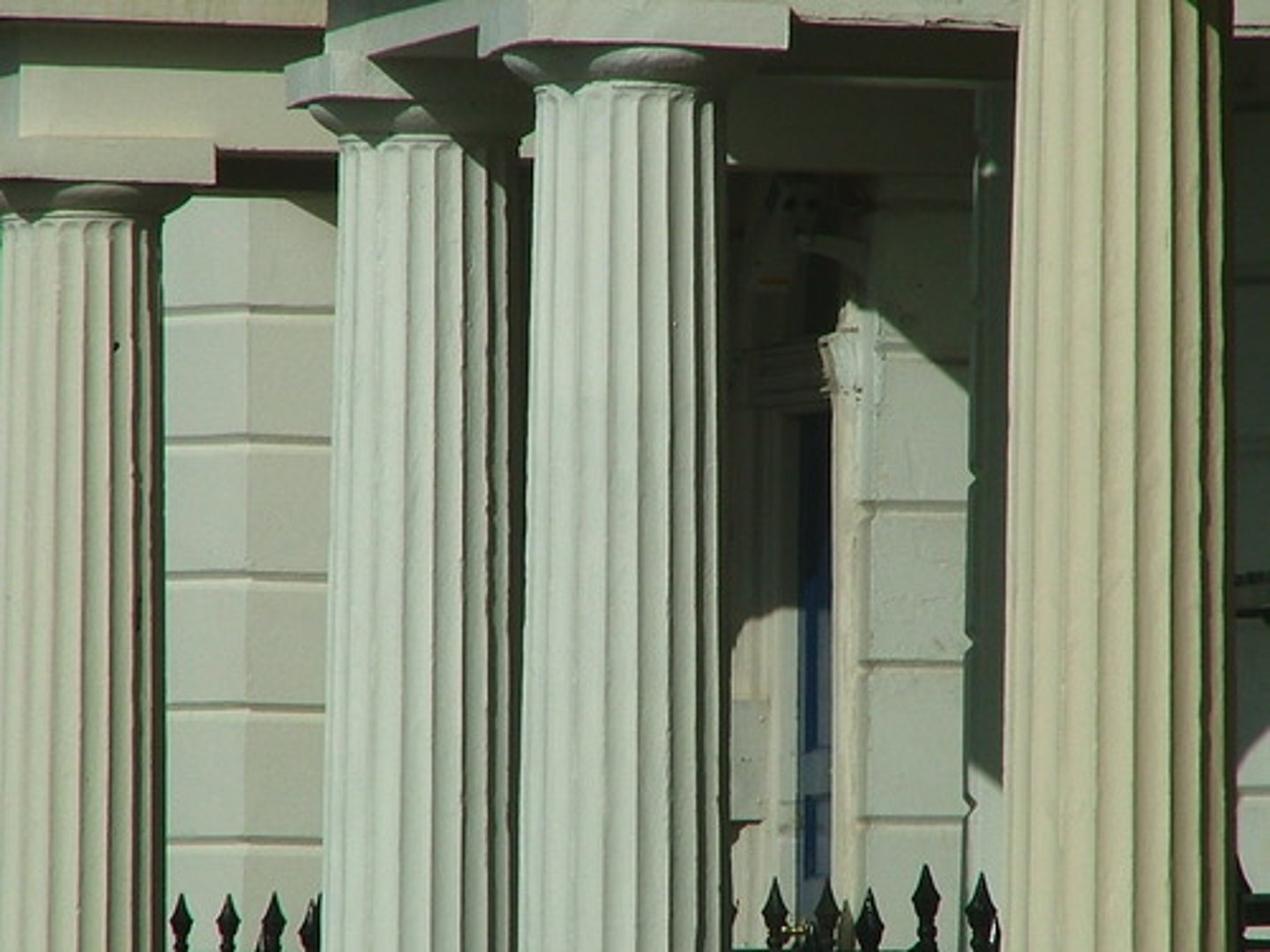
Flute
is the shallow grooves running vertically along a surface.

mausoleum
a building, especially a large and stately one, housing a tomb or tombs.
Metope
is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze.
Naos
Temple, holy place.
Pediment
the triangular upper part of the front of a building in classical style, typically surmounting a portico of columns.

Triglyph
is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze, so called because of the angular channels in them, two perfect and one divided, the two chamfered angles or hemiglyphs being reckoned as one.
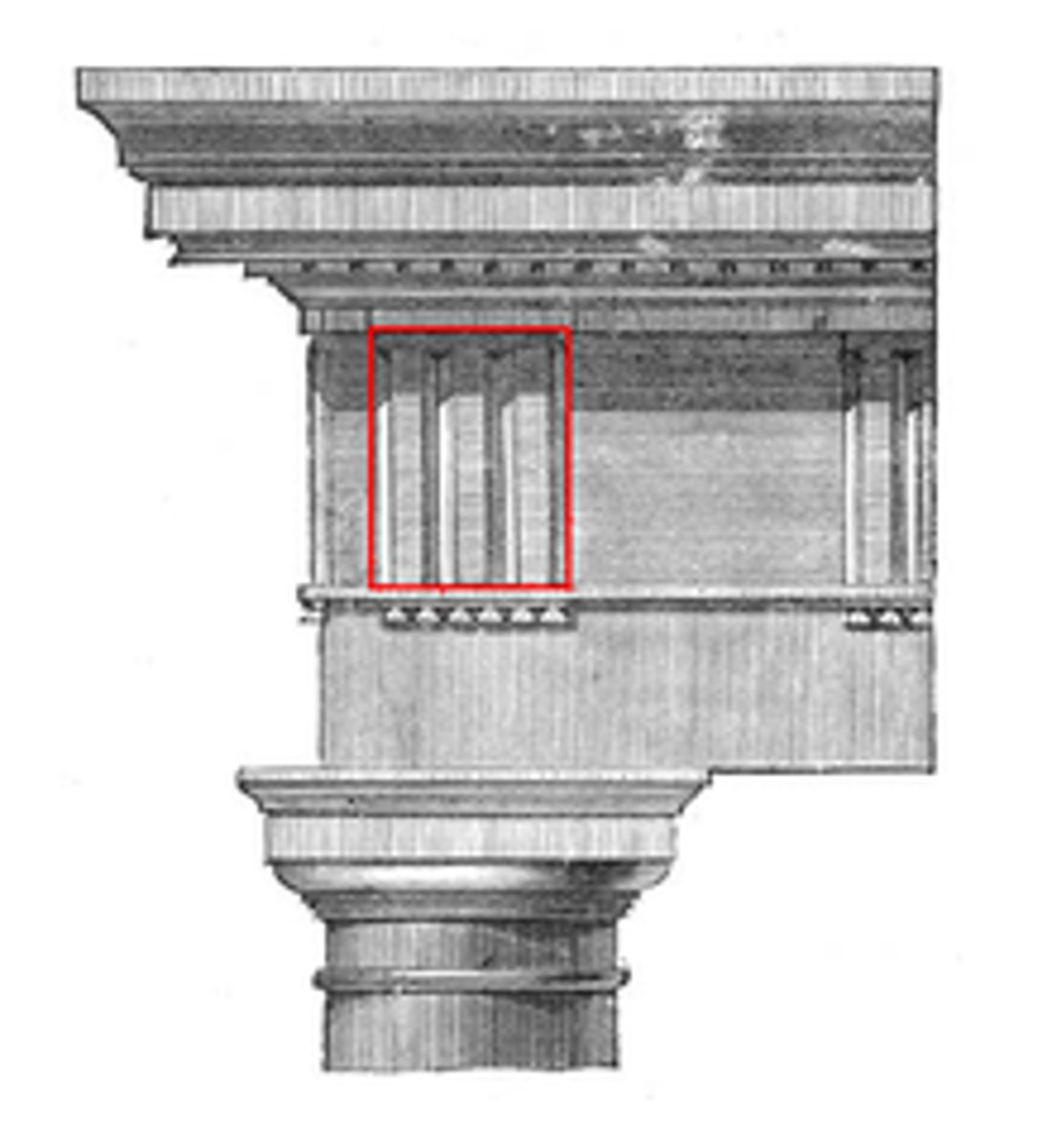
Volute
a spiral scroll characteristic of Ionic capitals and also used in Corinthian and composite capitals.
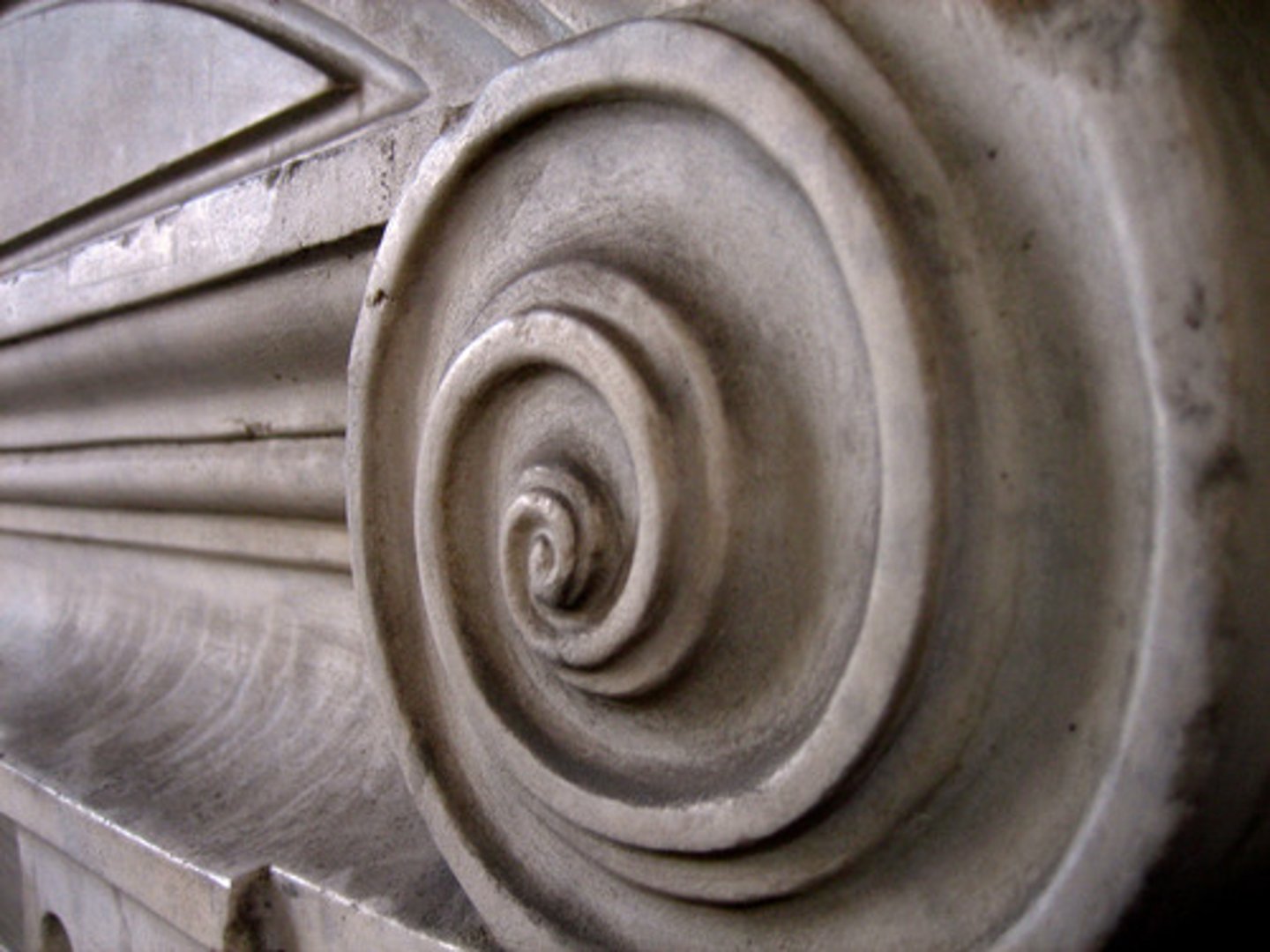

Stylobate
the foundation or base upon which a building or the like is erected
Tholos
a circular structure, often a temple, of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, and in classical or neoclassical architecture.
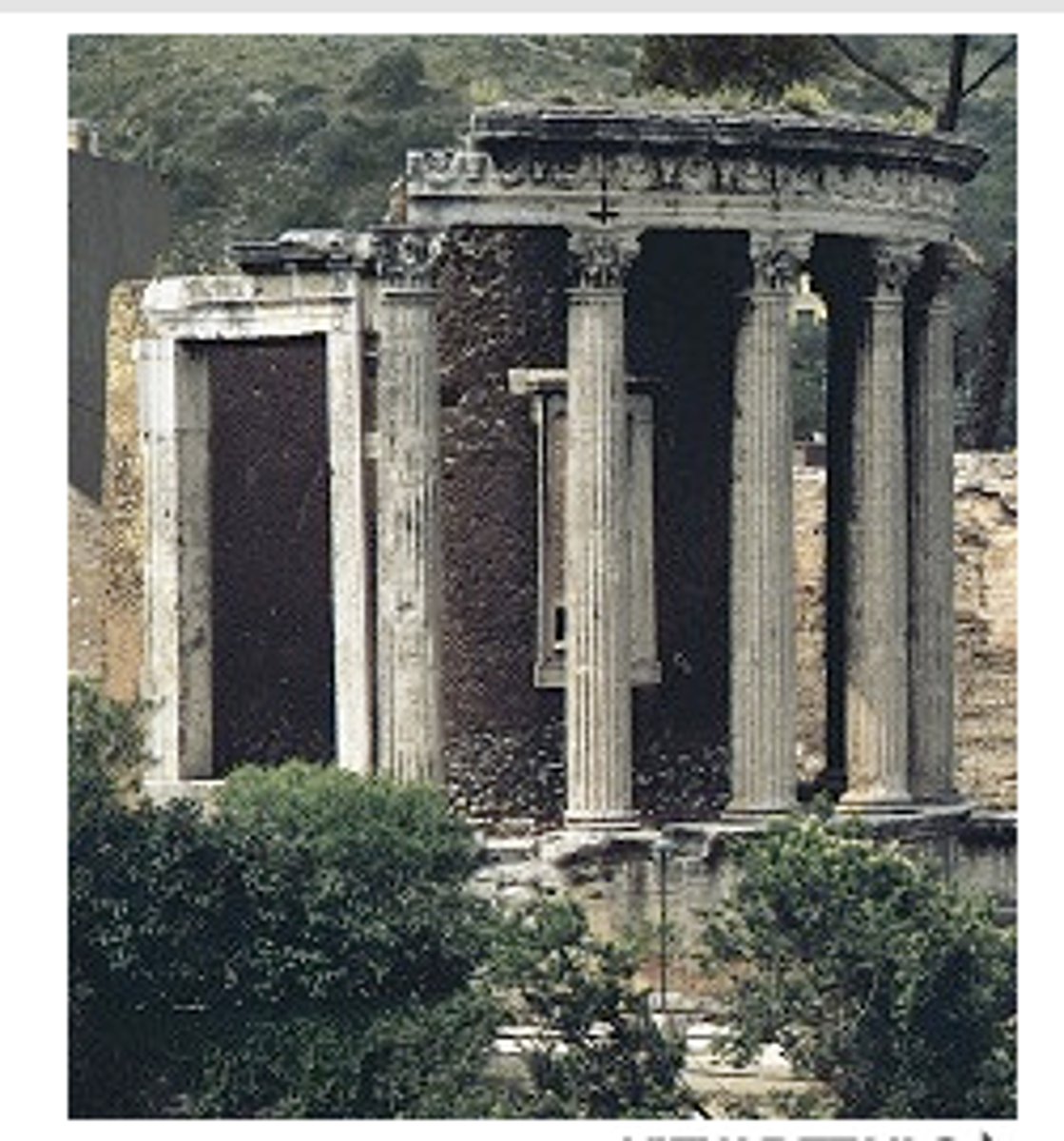

stoa
is a covered walkway or portico, commonly for public use. Early versions were open at the entrance with columns.
Peripteral
having a single row of pillars on all sides in the style of the temples of ancient Greece.

Shaft
this rests upon the base, is a long, narrow, vertical cylinder that in some orders is articulated with fluting.

Corinthian (1)
is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
Callicrates
architect of the Temple of Athena Nike.
Corinthian: Fanciest
Ionic: Spirals (Volutes)
Doric: Least Fancy
Fancyness
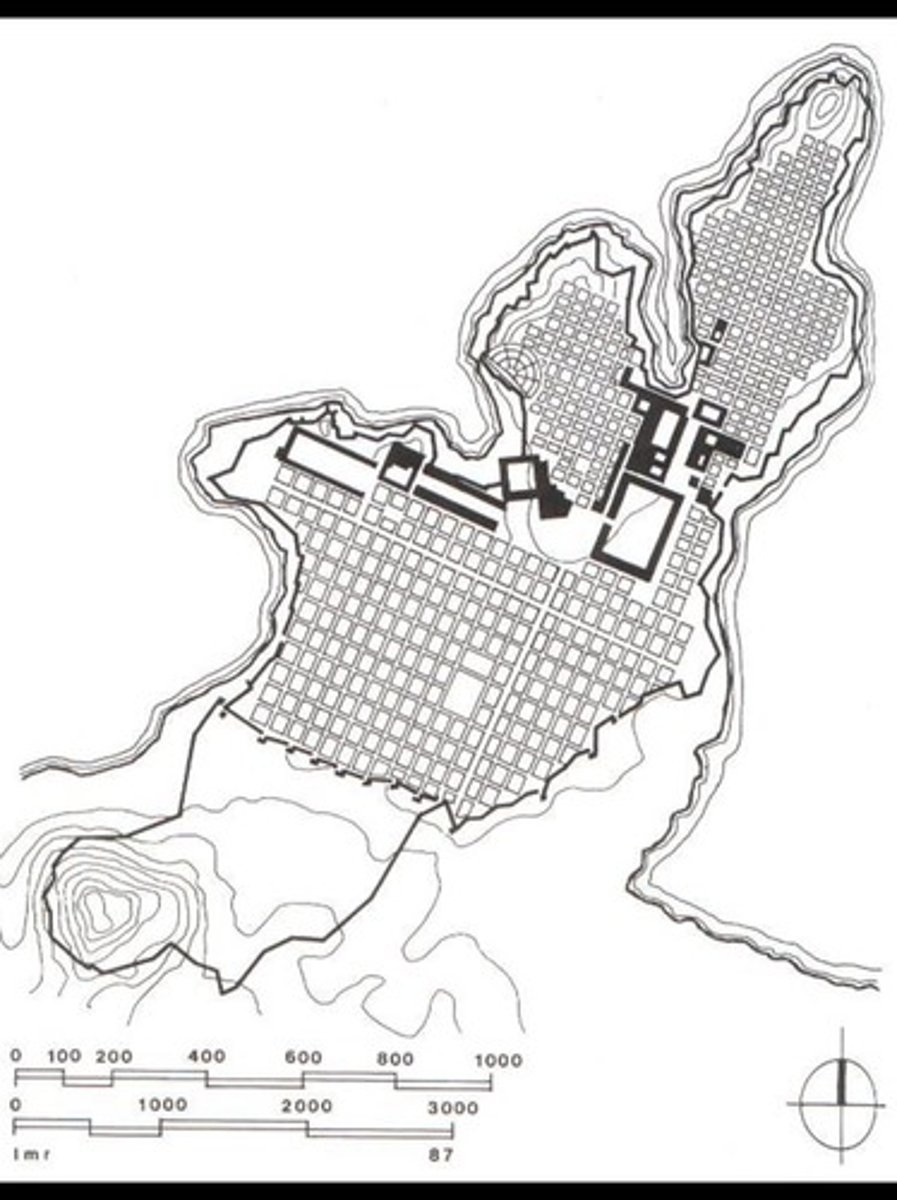
Town Plan of Miletus
Miletus, Greece
479 BCE
Hippodamus
Grid Plan
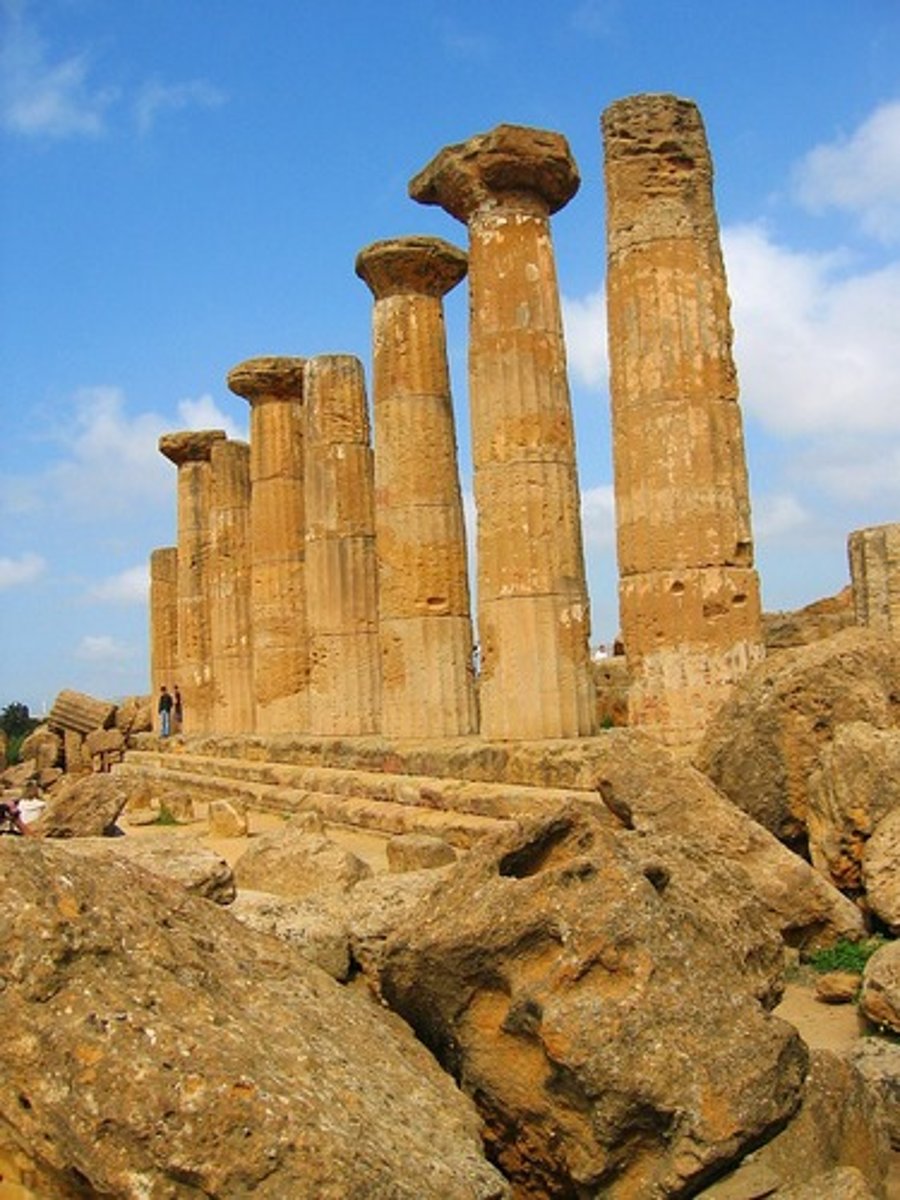
Temple of Hera II
Paestum, Italy
470 - 460 BCE (470 BCE)
Architect Unknown
Greek - Doric

Acropolis
Athens, Greece
479 BCE
Pericles
Greek

Parthenon
Acropolis - Athens, Greece
448 - 432 BCE (436 BCE)
Iktinos and Kallikrates
Classical Greek - Doric

Propylaea
Acropolis - Athens, Greece
437 BCE
Mnesicles
Classical Greek - Doric

Erechtheion
Acropolis - Athens, Greece
421 - 407 BCE (413 BCE)
Architect Unknown
Classical Greek - Ionic
