Chapter 7 (NS) & 8 (synapses)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Nervous system are composed of what two cells? What can glial cells specifically NOT do? What percentage makes up glial cells?
neurons and glial cells (do NOT send synapses) 75-90%
What part of the neuron does protien systhesis occur?
Soma (body)
What part of the neuron are MOST of the Na+ channels?
Axon Hillock
What is the name of the protein that carries NT from soma to Axon terminal (makes transport faster) ?
Kinesins
What is retrograde transport
Neurotransmitter from soma to axon terminal
WHat is anterograde transport?
Neurotransmitter from Axon terminal to soma
What do ligand gated channels cause?
graded potentials
What are graded potentials? (which charges can the neruon be?)
Neuron depolarizes but does NOT reach aboslute threshold. Can go postitve or MORE negative
When a neuron transitions from a negative to a positive charge inside, what is this process called? (or mem. the potential is more positive)
Depolarization
When a neuron transitions from a negative to MORE negative insdie the cell what is this called?
hyperpolarization
When a neuron goes BACK to negative at resting membrane potential, what is this called?
Repolarization
To have an action potentil WHAT do you need to cross?
Absolute threshold
To activate a neruon means to make it more what?
Positive
To inhibit neuron means to make it more what?
Negative
What is a refractory period?
The time AFTER an action potential where Neruon can’t fire again.
Most pseudounipolar neurons are (sensory or motor)
Sensory
Most mulipolar neurons are (sensory or motor)
Motor
What is a ganglion in the nervous system?
A group of somas together
What is the difference between oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells?
Oligodendrocytes wrap around MANY axons, schwann only wrap around one axon.
When there are spaces between each mylien what are these spaces called?
Nodes of raniver
What are the two types of synaptic transmissions?
Electrical and Chemcial
What is the fast electrical synaptic transmission called? And what are they for/in?
Gap junctions are for synchronous, fast, and bidirectional synapses. Cardiac/smooth muscle
What are chemical synaptic transmission? (what type of neutron do they use & most common type of junction)
Indirect communication, chem. messengers, pre/post synapses. axodendritic
What is something that electrical synapses can do but NOT chemical?
Excite or inhibit AT THE SAME TIME
What is the first step to a synapse?
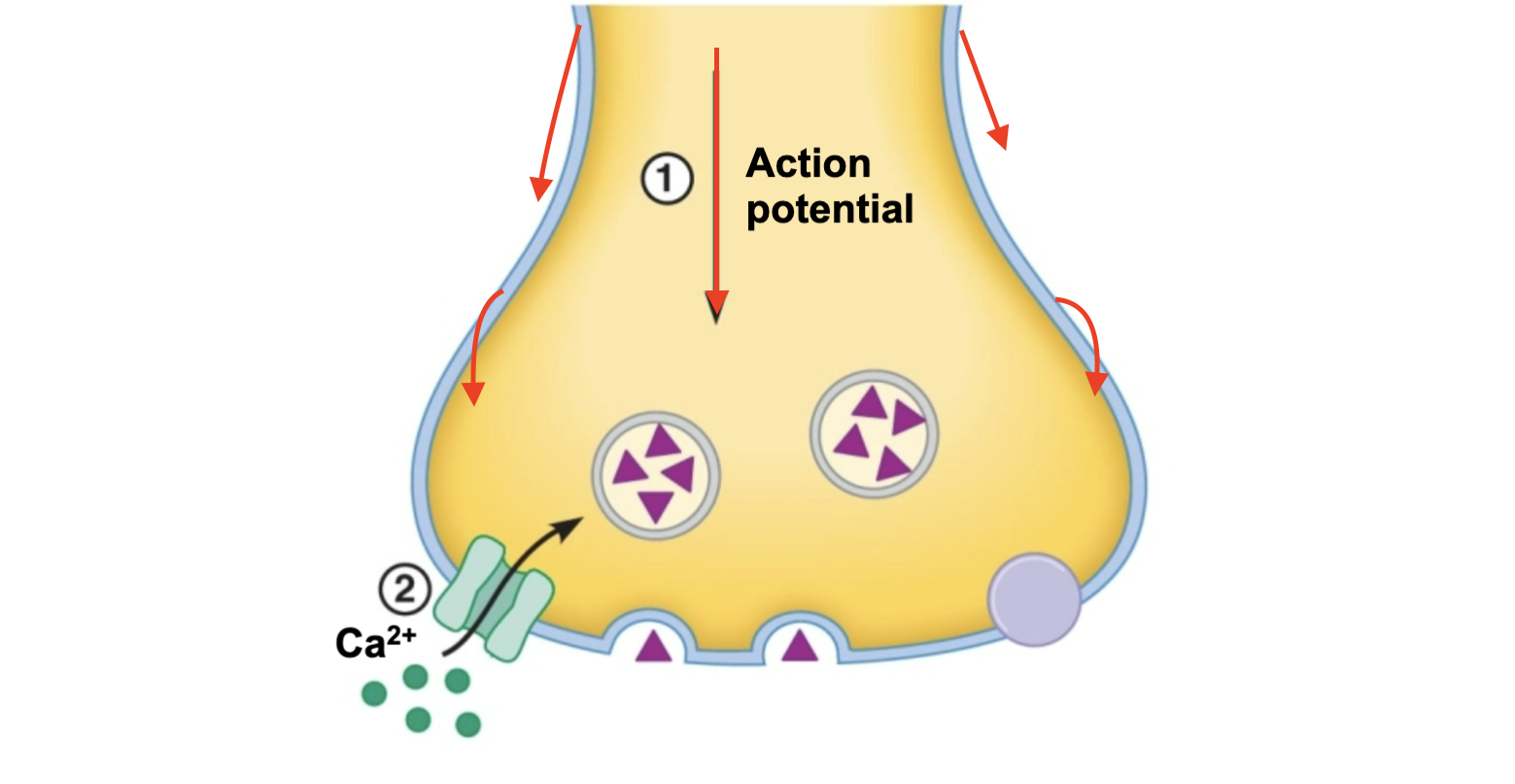
Action potential reaches Axon term & Ca+ channels open
What is the second step to synapses?
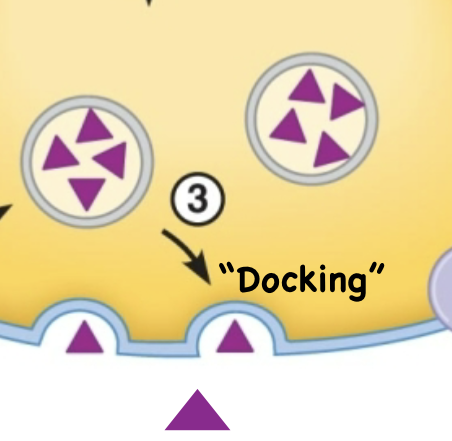
Release of Ca+ causes NT to dock at axon term and exocytosis out the cell
What is the third step to synapses?
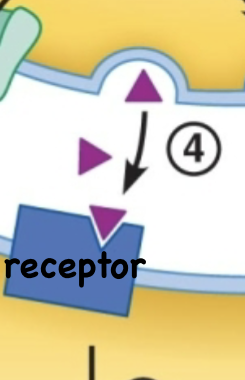
Neurotransmitter binds to receptor of post-synaptic cell which causes cell repsonse
What is the fourth step to synapses?
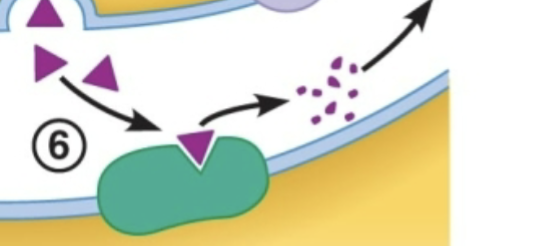

leftover NT either are degraded by enzyme, reuptake back into cell, or diffused out
What happens in the post-synaptic neuron AFTER a synaptic transmission? What are the two main types?
Singal transduction occurs. ionotropic/channel-linked or metabotropic (G-protien)
In the post-synaptic cell what are the two potentials occur from signal transduction?
Excitatory potential and inhibitory potential
Which of the two EPSP are fast or slow & ionotropic or metabotropic
Fast (ionotropic) & slow (metabotropic)
In EPSP What two fast channels cause this & Which direction are they going? (2)
Na+ channels open (sodium comes in because HIGHER electrical and chemical gradient) and K+ channels (potassium goes out)
In EPSP, describe the steps to how the metabotropic transport works & the end result of this?
NT binds to G-protein. protein is activated which activates enzyme, which activates 2nd messenger, that activates ANOTHER enzyme, which closes the K+ channel
In IPSP list all channels used…(4)
K+ channles, Cl ATPase pump, Cl- leak channel, and Cl- leak channel and cation channel
How can leaky K+ Channel cause Inhibitory post-synaptic potential?
WHen K+ STAY open the cell becomes less postive
How do Cl- ATPase pump cause IPSP?
ATP pushes Cl out the cell so there is a high gradient of Cl. THEN channel opens and Cl is diffused in cell
How can Cl- leak channel cause IPSP?
Cl- is comes in and out of the cell which causes membrane stablization
How can leaky Cl- AND cation channel (like Na+) cause IPSP?
Cl- comes in/out AND Na+ comes in and out, which makes membrane stabilization
Divergent means?
One neuron synapes to MANY
Convergent means?
MANY neurons synapses to ONE