Kidney - Ultrafiltration
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is ultrafiltration?
Filtering of the blood at a molecular level
Where does ultrafiltration occur?
Bowman's capsule
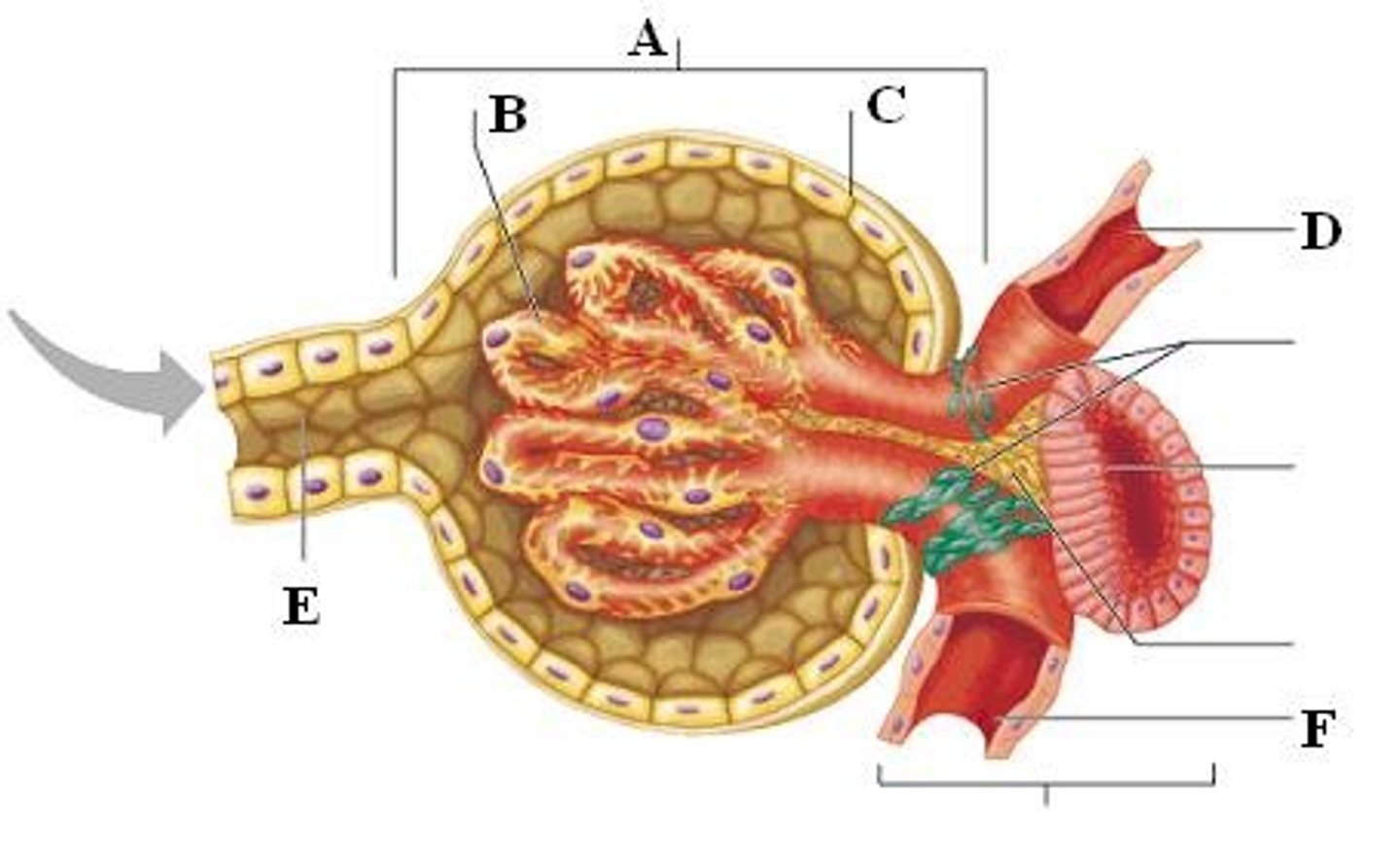
Afferent and Efferent arteriole
Afferent arteriole brings blood in at a higher pressure
Efferent arteriole has blood leave at a lower pressure
Afferent arteriole Lumen
The afferent arteriole has wider lumen. Therefore there is a higher hydrostatic pressure generated in the glomerulus.
What are the endothelium of capillaries made of?
Squamous epithelium
Does the capillary endothelium have small pores/fenestrations?
Yes
Pressure difference
Pressure is higher in the glomerulus than in the Bowman' capsule, which pushes the fluid out into the renal capsule.
What are the substances that are filtered out and into the renal capsule called?
Glomerular filtrate
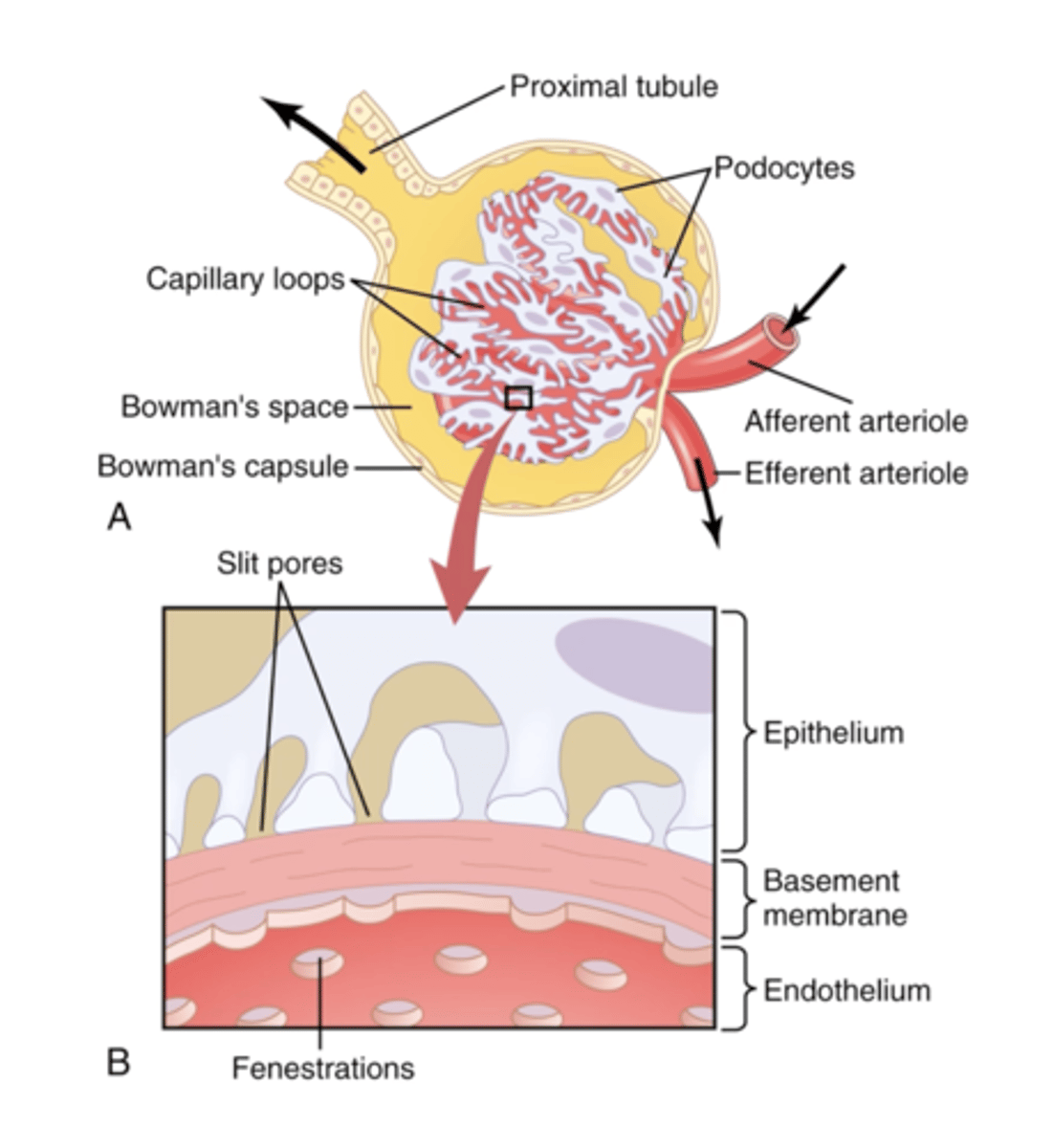
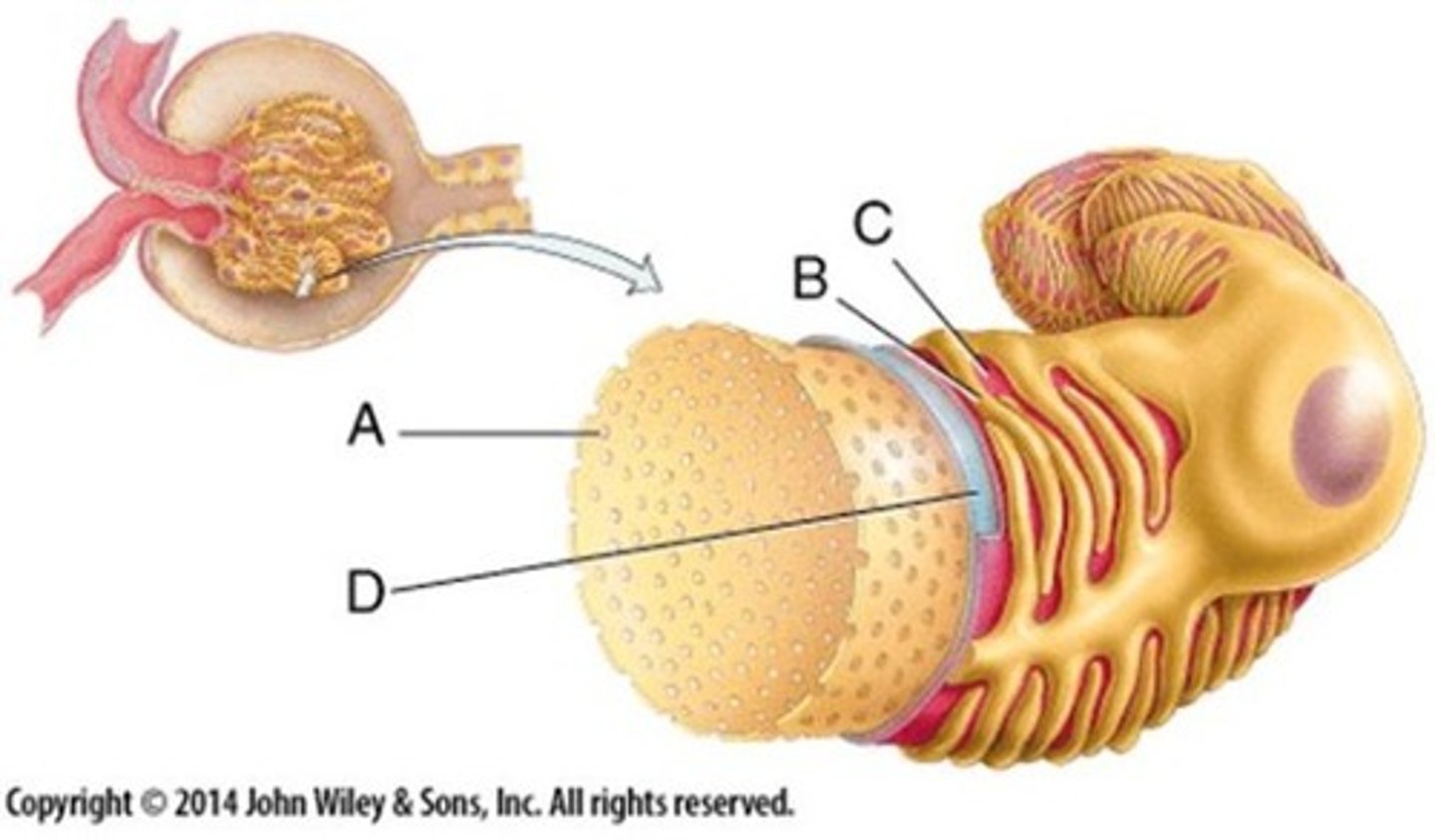
The barrier between the capillary and lumen of the Bowman's capsule consists of...
3 layers
Endothelium
Basement membrane
Podocytes
Endothelium
Contains pore called fenestrations, narrow gaps which allow blood plasma and substances to pass through
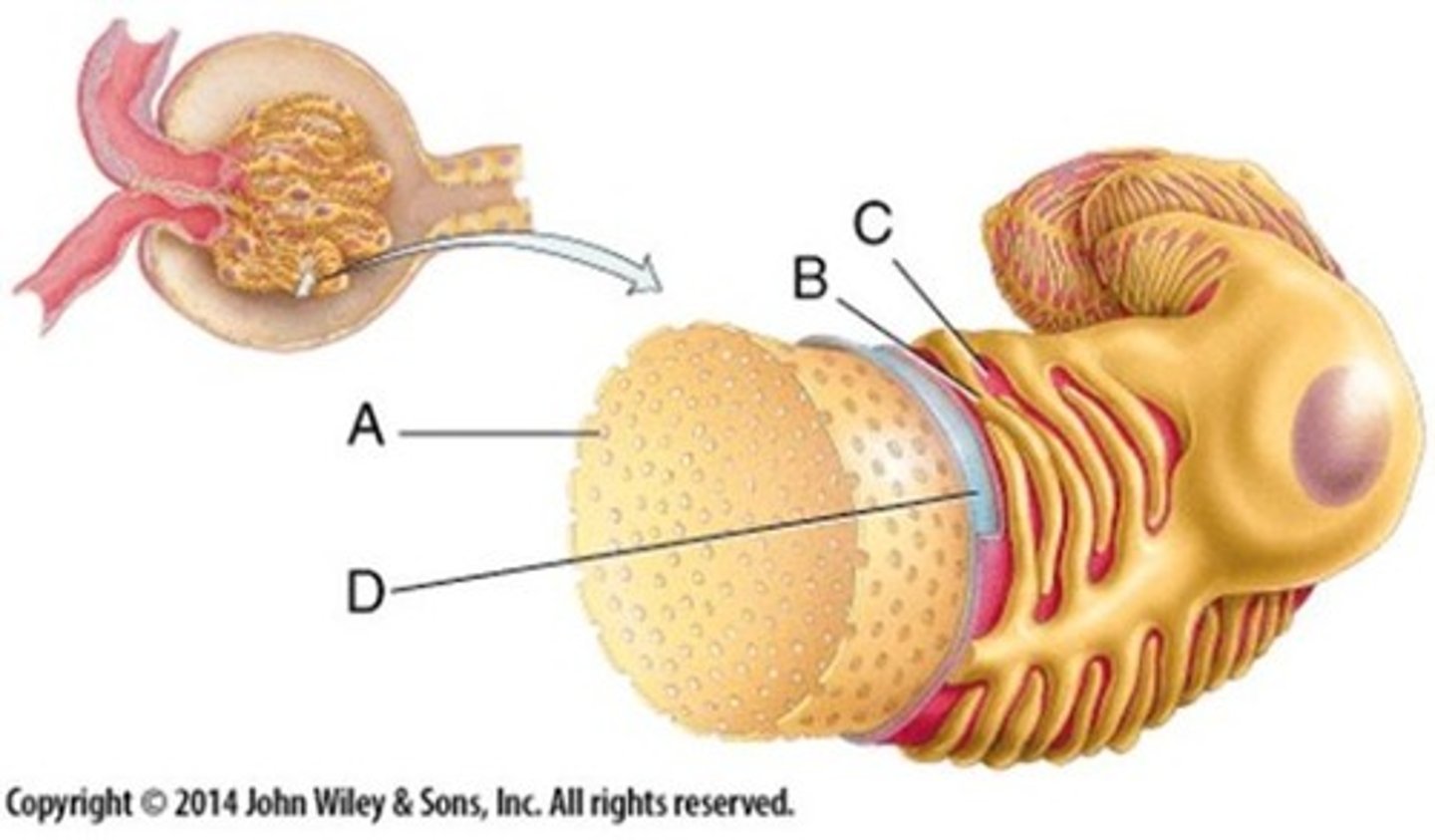
Basement membrane
Stops the removal of large substances from the blood
Podocytes
Specialised cells
Finger like projections (pedicels) that wrap around the capillaries to ensure any cells, platelets, or large plasma proteins that have managed to get through the epithelial cells and the basement membrane do not get in the tubule itself.
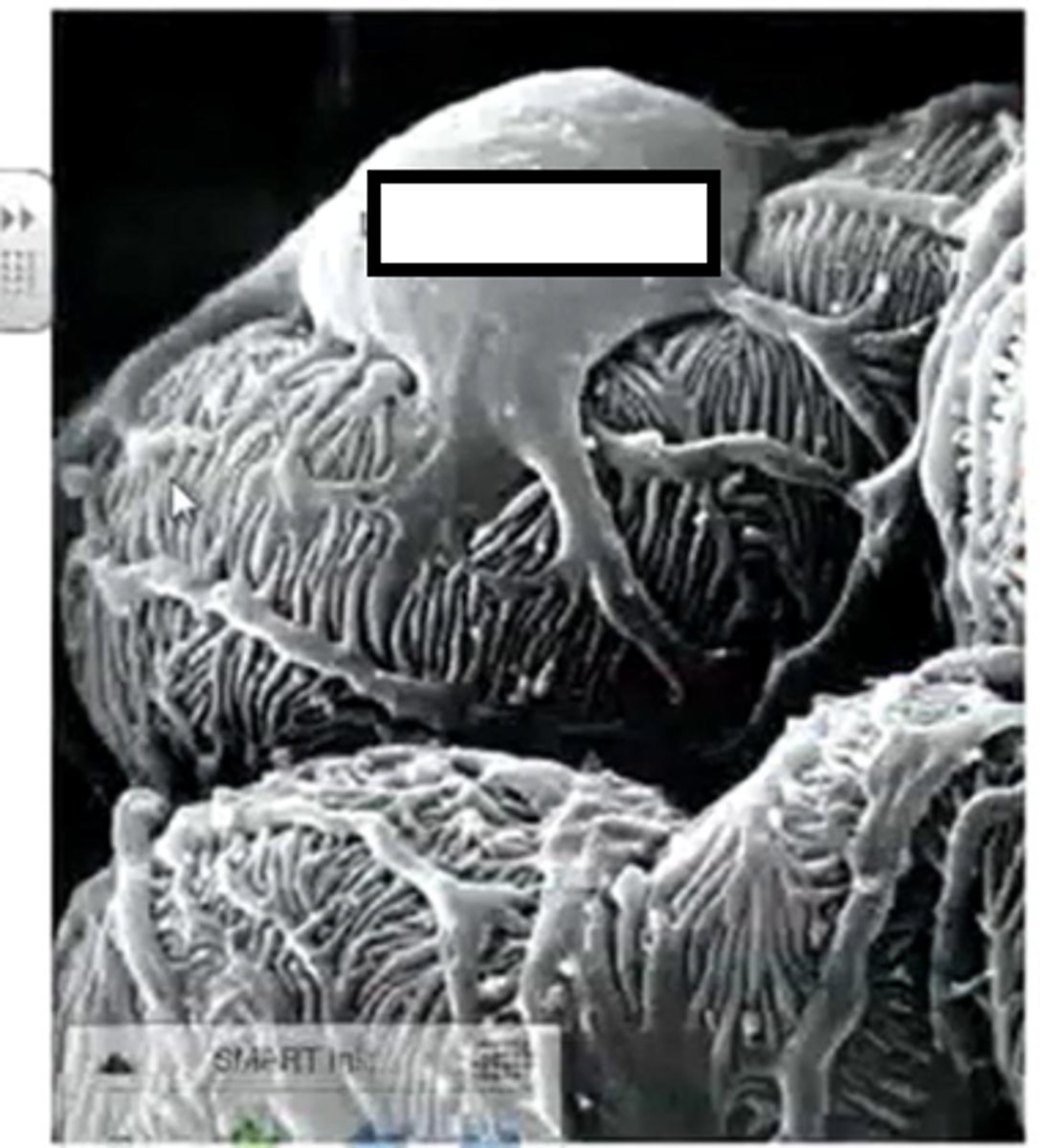
Molecules below what molecular mass can pass between the pedicels of podocytes during ultrafiltration?
69,000
Where does the filtrate go once its passed the 3 layers?
It enters the capsule
Is ultrafiltration efficient?
Yes
Up to 20% of the water and solutes are removed from the plasma as it passes through the glomerulus.
How does a given volume of blood leaving the glomerulus differ from the same volume of blood entering the glomerulus?
Fewer dissolved ions
Lower water potential
Why does the blood leaving the glomerulus have fewer dissolved ions and a lower water potential?
When blood undergoes ultrafiltration, plasma proteins and RBCs are too large to pass out of the blood, but water and dissolved ions can.
Therefore, the blood leaving the glomerulus has a lower water potential and fewer dissolved ions
Why does higher blood pressure lead to an oedema?
Because the higher blood pressure forces too much fluid out into the glomerular filtrate.
Why would there be a lot of proteins in the urine?
If the basement membrane was damaged