Lesson 4.5. CNS Stimulants
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Methylxanthines
xanthine derivatives found in plants that acts as CNS Stimulants
phosphodiesterase
Mechanism of Action of Methylxanthines:
a. competitive inhibition of ______________________
b. antagonism of ______________________
a = ?
adenosine receptors
Mechanism of Action of Methylxanthines:
a. competitive inhibition of ______________________
b. antagonism of ______________________
b = ?
Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine
Potency of Methylxanthine in CNS Stimulation
Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine
Potency of Methylxanthine in Respiratory Stimulation
Theophylline, Theobromine, Caffeine
Potency of Methylxanthine in Skeletal Muscle Stimulation
Theophylline, Theobromine, Caffeine
Potency of Methylxanthine in Diuresis
Theophylline, Theobromine, Caffeine
Potency of Methylxanthine in Coronary Dilation
Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine
Potency of Methylxanthine in Cardiac Stimulation
CYP
METABOLISM OF METHYLXANTHINES:
a. liver _________
b. _____________ (into uric acid)
a = ?
xanthine oxidase
METABOLISM OF METHYLXANTHINES:
a. liver _________
b. _____________ (into uric acid)
b = ?
Structure of Methylxanthines
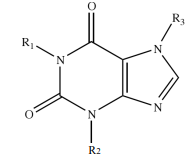
1,3,7-Trimethylxanthine
IUPAC name of Caffeine
1,3-Dimethylxanthine
IUPAC Name of Theophylline
3,7-Dimethylxanthine
IUPAC Name of Theobromine
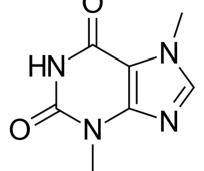
Structure of Caffeine
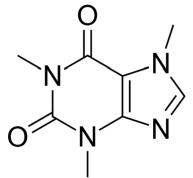
Structure of Theophylline

Structure of Theobromine
Depression
condition has been hypothesized to bebasedonthebalanced relationship between 5-HT, NE and DA neurotransmitters
TCAs (SNRI/NSRI), SSRIs, MAOIs, 5HT2 Antagonist/SRM
Antidepressant Drugs
Tricyclic Antidepressants (SNRIs/NSRIs), SSRIs, NDRI, and SARI
agents target a transporter protein: SERT (Serotonin Transporter), NET (Norepinephrine Transporter), and DAT (Dopamine Transporter)
SNRIs
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
SSRI
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
NDRI
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibotors
SARI
Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors
transporter proteins
Mechanism of Action of TCAs (SNRIs/NSRIs), SSRIs, NDRI, and SARI:
a. blocks _______________________ preventing inactivation of NTs, allowing NTs to function.
b. increased levels of ________________________________________________ relieves the signs of NT deficiency — antidepressant activity
a = ?
5-HT (serotonin), NE (norepinephrine), and DA (dopamine)
Mechanism of Action of TCAs (SNRIs/NSRIs), SSRIs, NDRI, and SARI:
a. blocks _______________________ preventing inactivation of NTs, allowing NTs to function.
b. increased levels of ________________________________________________ relieves the signs of NT deficiency — antidepressant activity
b = ?
Serotonin Reuptake Transporter (SERT)
Mechanism of Action of Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRIs):
selectively blocks _______________________________________
Norepinephrine reuptake transporter (NET) and Serotonin Reuptake Transporter (SERT)
Mechanism of Action of Norepinephrine/Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (NSRIs):
blocks ________________________________________________________ (binding is dependent on NE:5HT potency ratio)
anti-HAM (Histaminic-Adrenergic and Muscarinic)
TCAs (SNRI/NSRI) are known to produce “_________” effects like phenothiazines
anti-H1
Mechanism of Action of Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRIs) and Norepinephrine/Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (NSRIs):
a. sedation
b. orthostatic hypotension
c. dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention
a = ?
anti-α1
Mechanism of Action of Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRIs) and Norepinephrine/Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (NSRIs):
a. sedation
b. orthostatic hypotension
c. dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention
b = ?
anti-M1
Mechanism of Action of Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor (SNRIs) and Norepinephrine/Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (NSRIs):
a. sedation
b. orthostatic hypotension
c. dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention
c = ?
TCA Structure
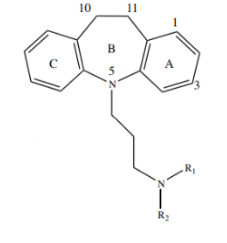
2° N
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
essential for SNRI selectivity
C3-X
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
increases activity and affinity for NET & SERT
3C long ending with an amine
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
B-ring side chain:
a. must be ___________________________
b. ____________________________ decreases affinity for NET & SERT
a = ?
branching side chain
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
B-ring side chain:
a. must be ___________________________
b. ____________________________ decreases affinity for NET & SERT
b = ?
propylene
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
Replacement of Ring N with ________________ = max potency
C10-C11
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
_______________ double bond = increase activity
preferential NET/SERT binding
Structure Activity Relationship of TCA:
O-replacement in C10-C11 leads to an E/Z mixture resulting to ___________________________________.
inactivation
Metabolism of TCA:
N-demethylation
a. SNRI = ____________
b. NSRI = __________________
a = ?
leads to NET inhibitors
Metabolism of TCA:
N-demethylation
a. SNRI = ____________
b. NSRI = __________________
b = ?
Atomoxetine, Duloxetine
Metabolism of TCA:
Aromatic hydroxylation
C10
Metabolism of TCA:
CYP 2D6 hydroxylation
a. SNRI at ________
b. Clomipramine at __________
a = ?
C8
Metabolism of TCA:
CYP 2D6 hydroxylation
a. SNRI at ________
b. Clomipramine at __________
b = ?
CYP 2D6 demethylation
Metabolism of TCA
Clomipramine, Venlfaxine, Doxepin
Glucuronidation
Metabolism of TCA:
other metabolism
Desipramine
DIBENZAZEPINES TCAs - “ -PRAMINE”
SNRI agent
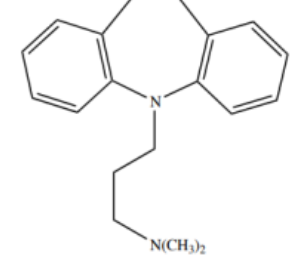
Imipramine
DIBENZAZEPINES TCAs - “ -PRAMINE”
NSRI prototype drug
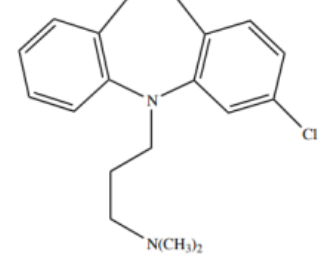
Closmipramine
DIBENZAZEPINES TCAs - “ -PRAMINE”
NSRI agent
Structure of Desipramine
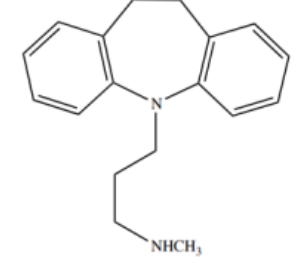
Structure of Imipramine
Structure of Clomipramine
Nortriptyline
DIBENZOCYCLOHEPTADIENE TCAs - “ -TRIPTYLINE”
SNRI Agent
has N5-C12 double bond
Protriptyline
DIBENZOCYCLOHEPTADIENE TCAs - “ -TRIPTYLINE”
SNRI Agent
C10-11 double bond
Amitriptyline
DIBENZOCYCLOHEPTADIENE TCAs - “ -TRIPTYLINE”
NSRI Agent
has a propylene moiety in the B-ring
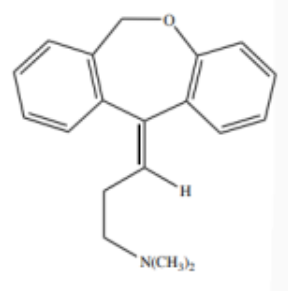
Doxepine
DIBENZOCYCLOHEPTADIENE TCAs - “ -TRIPTYLINE”
NSRI Agent (E/Z isomers)
E selectively inhibits NET
S selectively inhibits SERT
Nortriptyline Structure
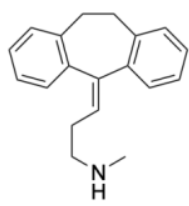
Protriptyline Structure

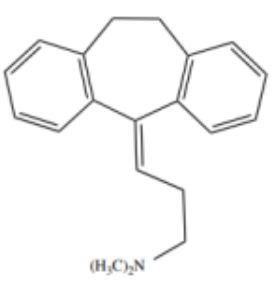
Structure of Amitriptyline
Structure of Doxepine
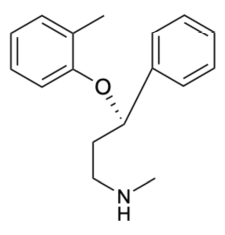
Atomoxetine
NON-TCA SNRIs / NSRIs
SNRI Agent R-enantiomer is more active
Duloxetine, Milnacipran, and Venlafaxine
NON-TCA SNRIs / NSRIs
NSRI Agent
Structure of Atomoxetine
Structure of Duloxetine
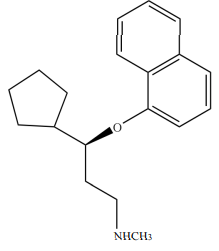
Structure of Milnacipran
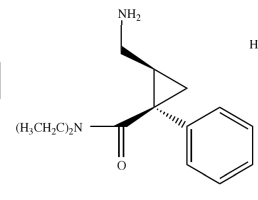
Structure of Venflaxine
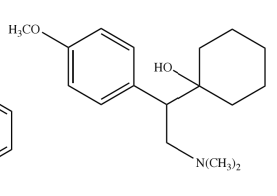
Electronegative (-X) 4-substitution
Structure Activity Relationship of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
a. ____________________________ = essential for selectivity and affinity for SERT
b. SSRI ______________ significantly affects SERT selectivity
a = ?
stereochemistry
Structure Activity Relationship of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
a. ____________________________ = essential for selectivity and affinity for SERT
b. SSRI ______________ significantly affects SERT selectivity
b = ?
SERT
Mechanism of Action of SSRIs:
inhibits __________ with high affinity and selectivity
CYP isozymes
Metabolism of SSRIs:
a. highly metabolized in the liver by ________________ (especially CYP 2D6)
b. __________________________ for N-methyl SSRIs
c. ______________________ (Sertraline)
a = ?
N-demethylation
Metabolism of SSRIs:
a. highly metabolized in the liver by ________________ (especially CYP 2D6)
b. __________________________ for N-methyl SSRIs
c. ______________________ (Sertraline)
b = ?
MAO and Glucuronidation
Metabolism of SSRIs:
a. highly metabolized in the liver by ________________ (especially CYP 2D6)
b. __________________________ for N-methyl SSRIs
c. ______________________ (Sertraline)
c = ?
E isomer
In Escitalopram, ______________ is more selective than S isomer
R isomer
In Fluoxetine,
a. _____________________ is more potent
b. _____________________ has a higher affinity for SERT
a = ?
S isomer
In Fluoxetine,
a. _____________________ is more potent
b. _____________________ has a higher affinity for SERT
b = ?
Structure of Escitalopram (S-isomer) and Citalopram (R-isomer)
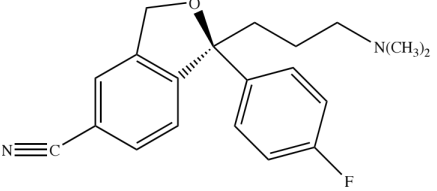
Structure of Fluvoxamine
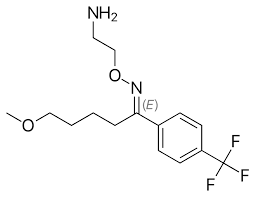
Structure of Fluoxetine
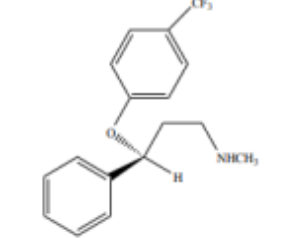
Structure of Paroxetine
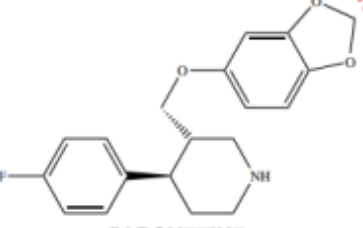
Structure of Sertraline
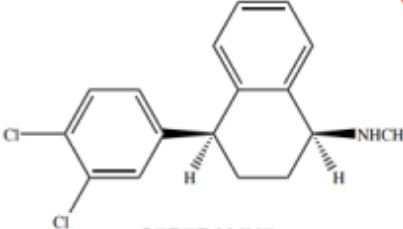
Fluvoxamine
E-isomer is essential for SERT inhibition
Paroxetine
(-)-3S,4R-isomer is more active for SERT inhibition
Sertraline
1S,4S-isomer is moreactivefor SERT inhibition
hypertensive crisis
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) may result to _________________ (severe headache, tachycardia, diaphoresis, hyperprexia) when combined with sympathomimetics or tyramine containing food.
Monoamine Oxidase
enzyme responsible for the deamination of amines
5-HT
substrate for MAO-A
Epinephrine, NE, and DA
substrates for MAO-A and MAO-B
amphetamine
Structure Activity Relationship of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors:
a. some has similar structure with ___________________
b. presence of _______________________________ = increase potency
a = ?
electron-withdrawing groups
Structure Activity Relationship of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors:
a. some has similar structure with ___________________
b. presence of _______________________________ = increase potency
b = ?
metabolism of NE, 5-HT and DA
Mechanism of Action of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
inhibits ________________________________ = increasing conc. in the brain
Oxidation and N-acetylation
Metabolism of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Moclobemide
MAOIs:
reversible inhibitor of MAO-A antidepressant w/o hypertensive crisis
Tranylcypromine
MAOIs:
resembles amphetamine with “-methyl condensing with β-carbon
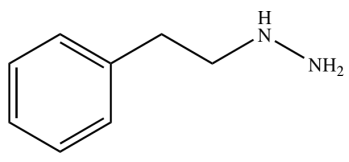
Phenelzine
MAOIs:
irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme
Selegiline
MAOIs:
selective irreversible inhibitor of MAO-B
Moclobemide Structure
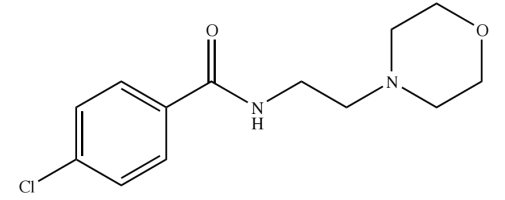
Structure of Tranylcypromine
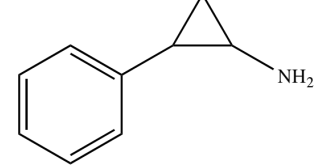
Structure of Phenelzine