Lecture 7: N Fixation and Ammonia Assimilation
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover the essential concepts related to nitrogen fixation and ammonia assimilation, including relevant enzymes, biochemical pathways, and the significance of nitrogen metabolism in living organisms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
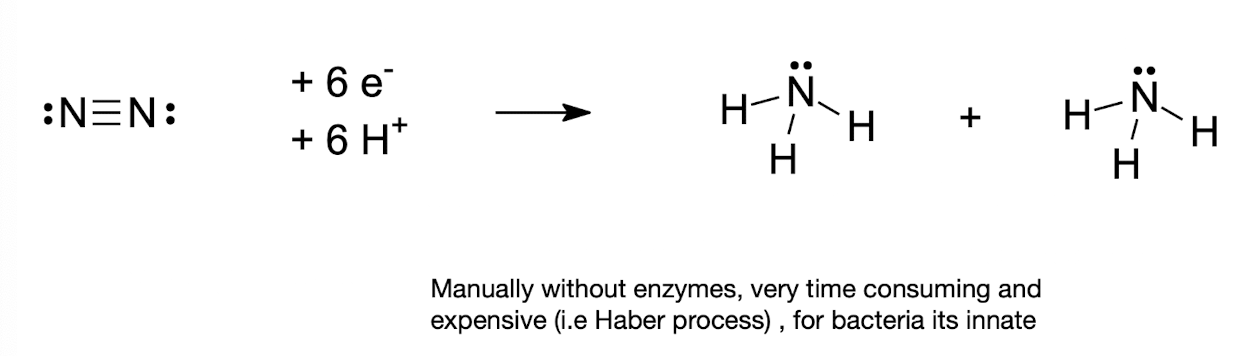
What is nitrogen fixation?
The reduction of N2 to NH3
What enzyme complex is required for nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogenase, which consists of a reductase and nitrogenase.

What metal cofactors are commonly found in nitrogenases?
Molybdenum with Iron (Fe) or vanadium, which cages the N2 molecule with ATP hydrolysis creating conformational changes that force e- onto the N2 to reduce it to NH3.
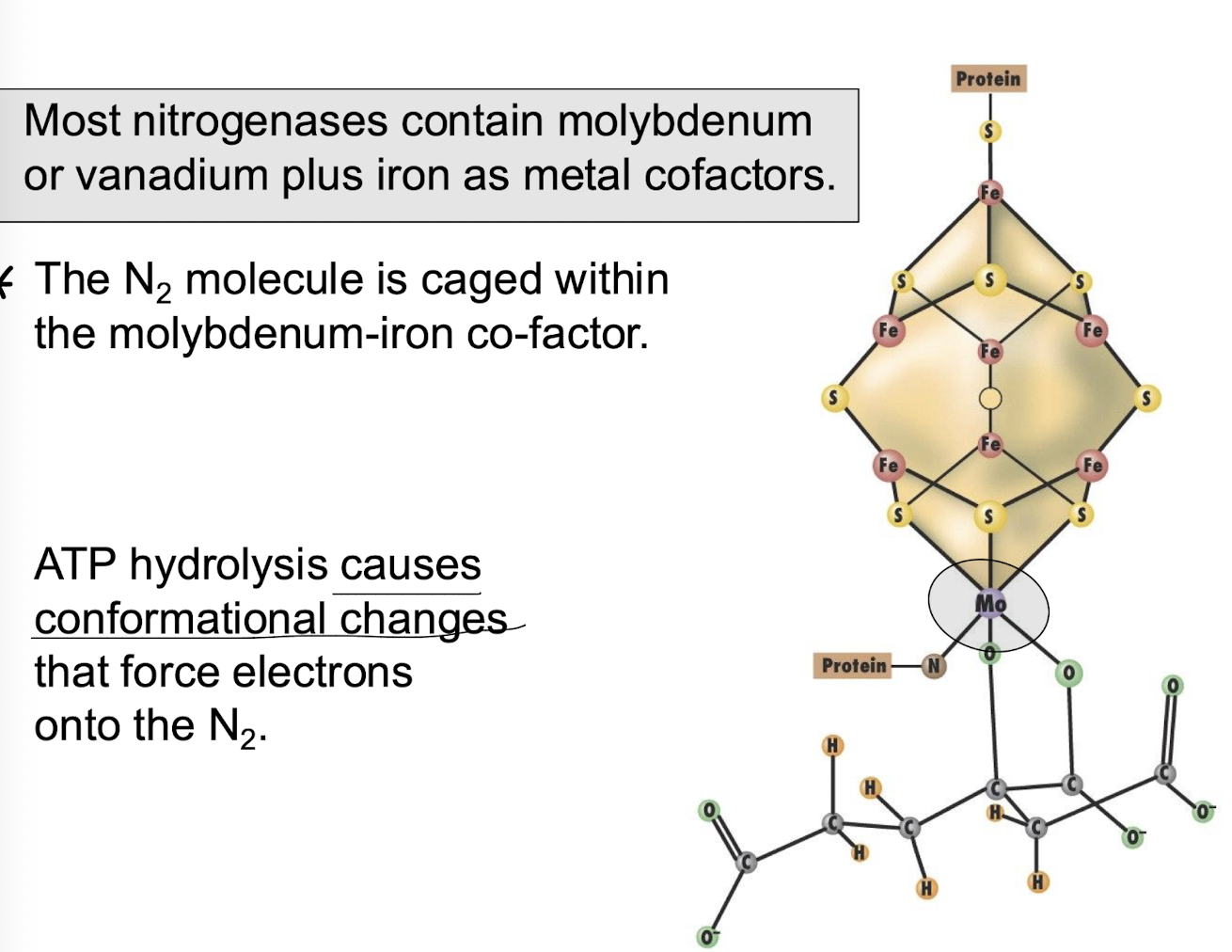
How can the reactions in the nitrogenase enzyme complex be illustrated?

What is the primary source of ammonia for cells?
Ammonia (NH3) is derived primarily from atmospheric N2 gas.
What is the role of ATP in nitrogen fixation?
ATP provides the energy required to overcome the stable N-N triple bond during fixation.
How do plants and microbes obtain ammonia from nitrate?
They can reduce nitrate to ammonia using nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase
What products are generated during nitrogen fixation?
Nitrogenases generally produce both H2 and NH3.
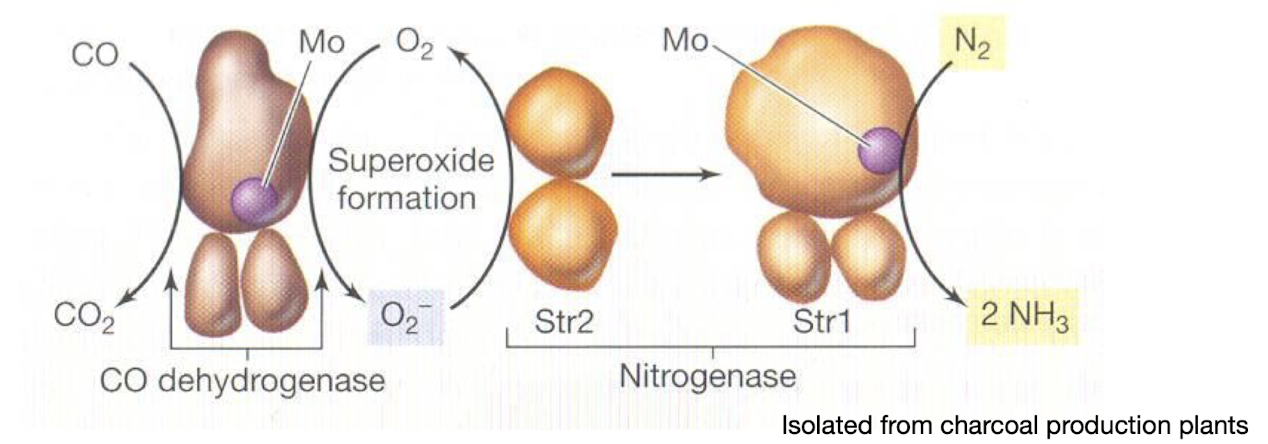
Why is the nitrogenase of Streptomyces thermoautotrophicus deemed unusal?
It uses CO as its electron source instead of the more common ferredoxin or flavodoxin.
Superoxide is an intermediate in electron transfer.
The nitrogenase is resistant to O2.
Requires less ATP for N fixation
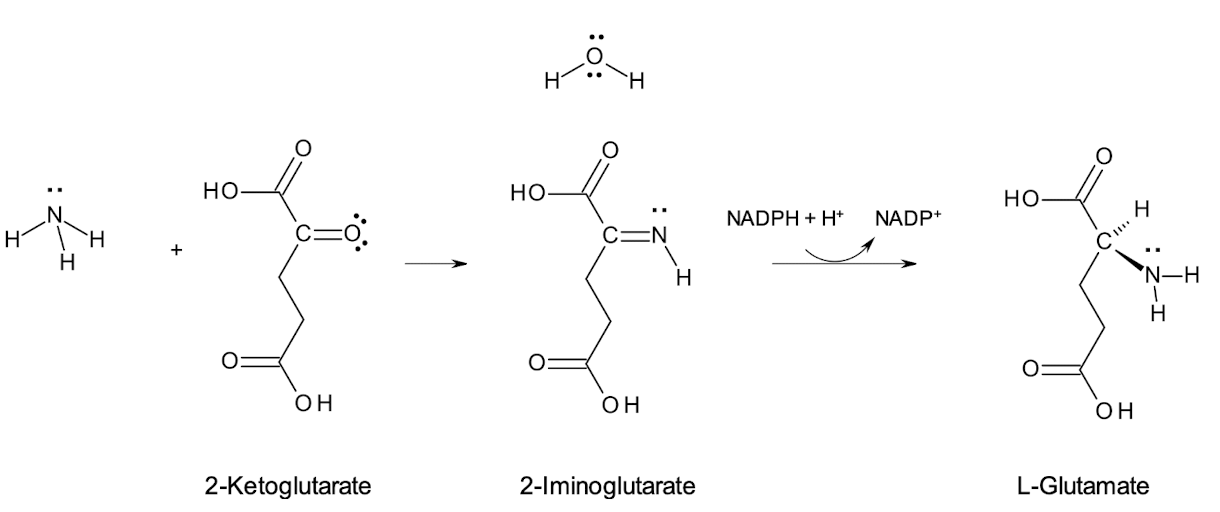
What is the first step in ammonia assimilation by bacteria?
Reductive amination of α-ketoglutarate’s imine to form glutamate (GLU).

What does glutamate dehydrogenase do in the ammonia assimilation?
This enzyme facilitates the conversion of ammonia and α-ketoglutarate (imine) into glutamate, using NAD(P)H as a reducing agent.
What is the second step in ammonia assimilation by bacteria?
Amidation of the side-chain carboxyl groups of GLU and ASP to form GLN and ASN
(the chemical reaction that forms an amide from an amine and a carboxylic acid or its derivative)
What enzyme forms glutamine (GLN) from GLU and NH3?
Glutamine synthetase
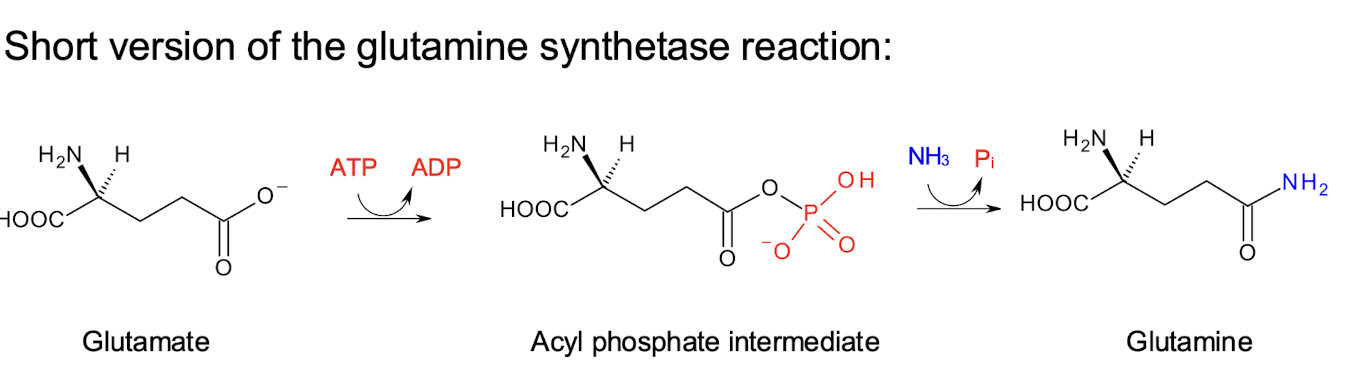
What is the reaction catalysed by Glutamine synthetase?
An ATP-requiring reaction
1st the enzyme forms glutamate 5-phosphate, a reactive intermediate.

2nd, the intermediate then reacts with ammonia (NH3), which displaces a phosphate to form the amide found on GLN and regenerate ADP and phosphate.
What is the chemical reaction catalysed by glutamate synthase to form GLU?
GLN + a-ketoglutarate + NADH + H+ → GLU + GLU + NAD+

The amide of GLN is hydrolysed, the NH3 released is used for reductive amination of a-ketoglutarate.

How can we summarise ammonia assimilation?
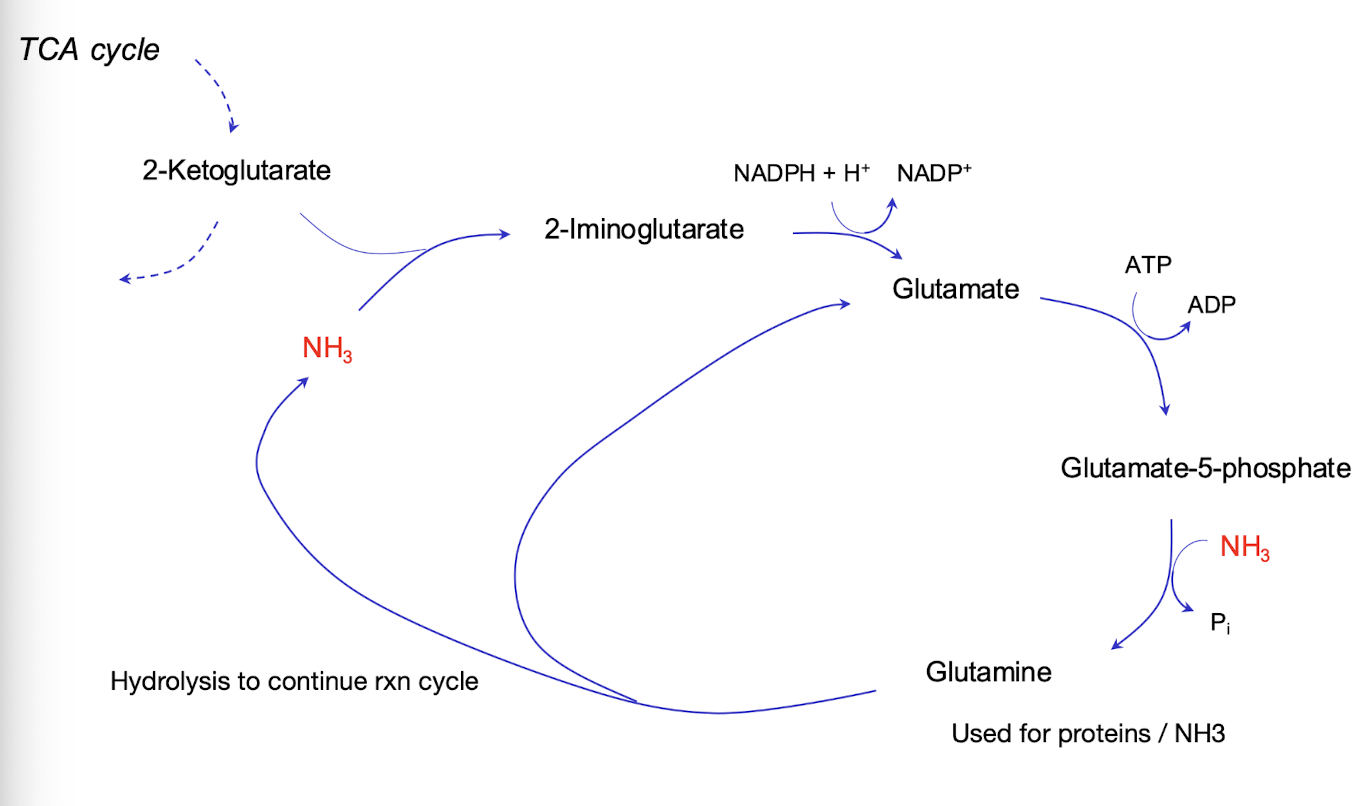
2-ketoglutarate (a-ketoglutarate) is generated by TCA cycle and forms 2-iminoglutarate when reacted with ammonia (NH3).
This intermediate is then reduced using NADPH to form glutamate (GLU) through the action of glutamate dehydrogenase
Subsequently glutamine (GLN) is synthesised from GLU by glutamine synthetase, forming GLU-5P using ATP and ammonia.
Hydrolysis of the amide on GLN releases ammonia, which is then utilized for further amino acid synthesis.
What is the main type of amino acids sourced from glutamine?
Glutamine is the source of amino groups for the biosynthesis of several other compounds: purines, TRP, HIS and carbamoyl phosphate (a precursor of pyrimidines and ARG).
What is the primary function of glutamate in amino acid metabolism?
Glutamate is the amino group donor for most transaminations

What cofactor do transaminases have?
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) where PLP-enzymes facilitating the transfer of amino groups during transamination reactions.

In a PLP-dependent enzyme, an amino acid condenses with the
co-factor to form an _______
imine intermediate which is then hydrolyzed to regenerate the amino acid and produce a corresponding keto acid.
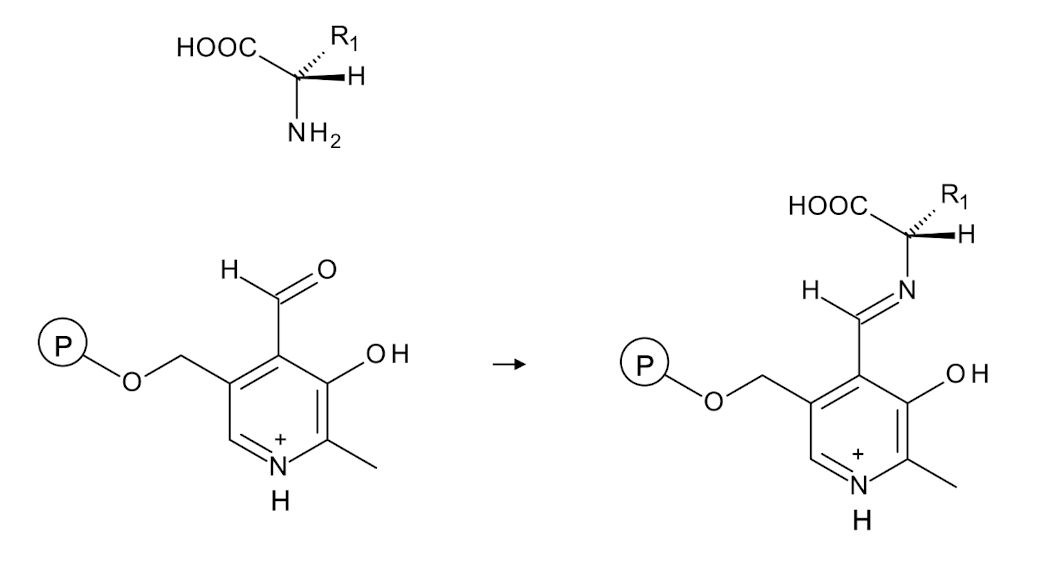
What reactions does this PLP cofactor facilitate when condensed with an amino acid?
Transamination (remove a-proton)
Decarboxylation reactions (cleave off carboxyl group)
Aldolases cut off the SC
Allowing for the transfer of amino groups and the conversion of amino acids.

What 3 AAs are synthesised from the intermediate 3PG ?
Cysteine
Serine
Glycine
What is an example of an AA synthesised from pyruvate?
Alanine

What 2 AAs are synthesised from oxaloacetate?
These are aspartate and asparagine.
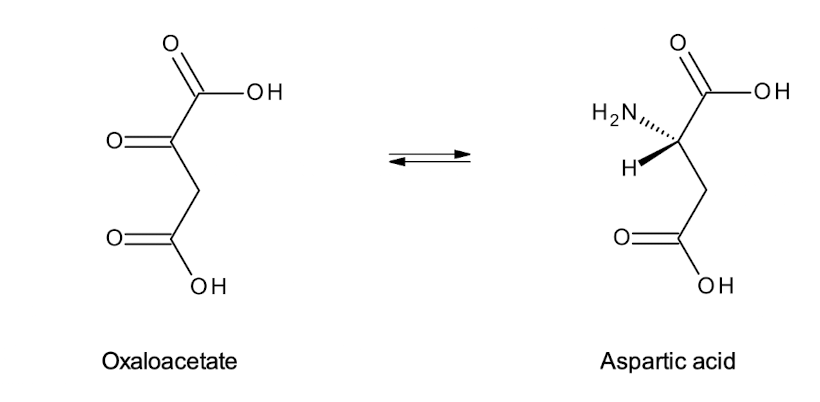
What 3 AAs are synthesised from a-ketoglutarate?
Glutamate, Glutamine, and Proline.
How is PRO synthesised from GLU?
Conversion of the 𝛾 carboxyl group of GLU to a more reactive aldehyde.
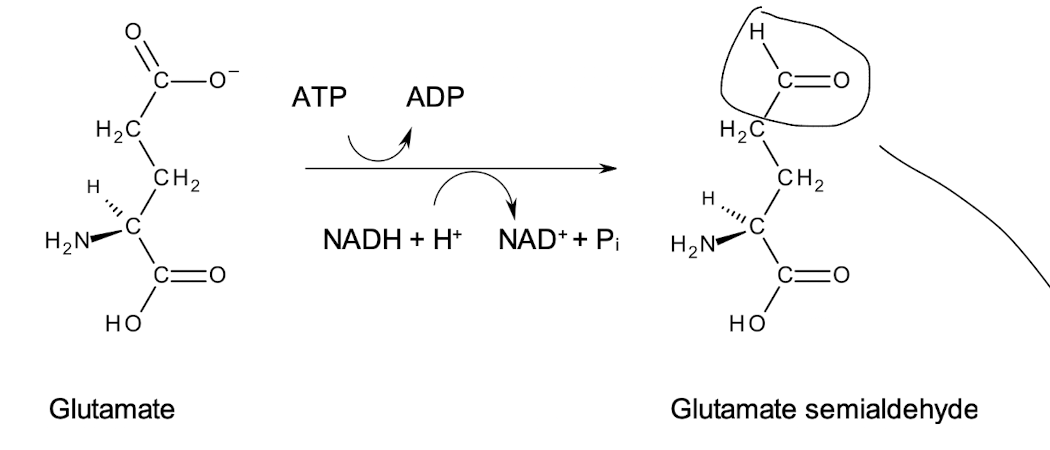
With glutamate semialdehyde, the a-amino group and the aldehyde group form an imine [No enzyme required]
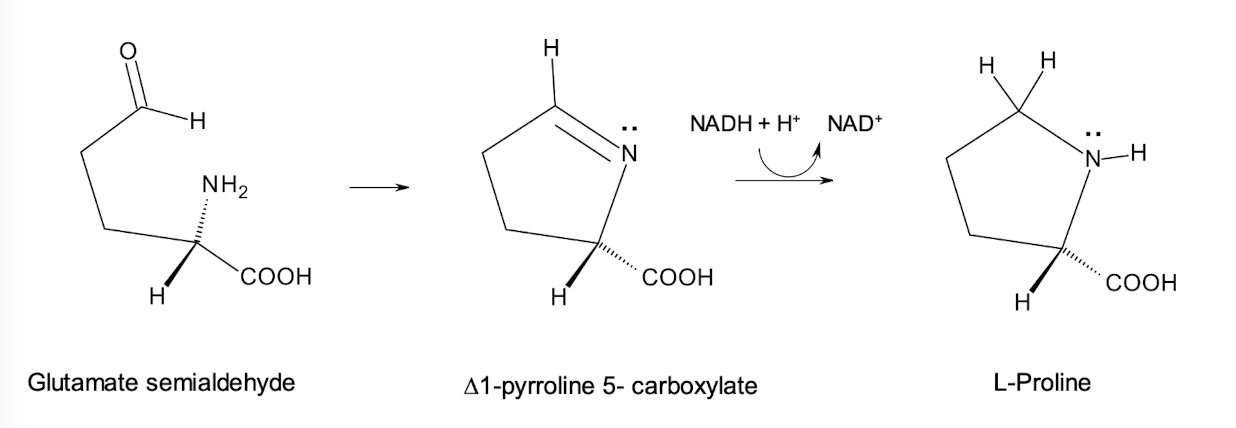
Lastly, PRO is generated through a NADH-dependent reduction reaction, converting the imine to proline.
Reduction of a carboxylic acid to a _____ requires energy in the form of ____ and ____
Aldehyde, ATP and NADH
Oxidation of an aldehyde to a _______ generates NADH and ATP
carboxylic acid
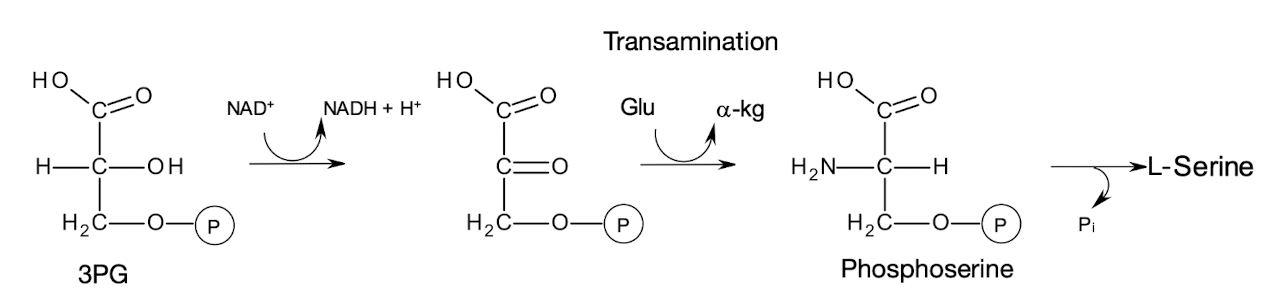
What are the 3 steps of how SER is synthesised from 3PG?
Oxidation to form 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate
Transamination from GLU to form 3-phosphoserine
Dephosphorylation to form SER
How is CYS synthesised & its importance ?
An acetyl group is transferred from CoA to the hydroxyl group of SER to form O-acetylserine.
The acetyl group is replaced by sulphide to form CYS.
It is the source of sulphur for all other sulphur-containing metabolites in cells (MET, CoA etc. etc.).
Cysteine biosynthesis is important in sulphur assimilation

What is APS and its relation in dissimilative metabolism?
Adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (APS) is a key intermediate in the sulfation pathway, allowing for the conversion of sulfate into sulfide in dissimilative metabolism.
It plays a crucial role in anaerobic respiration when SO42- is used as terminal EA

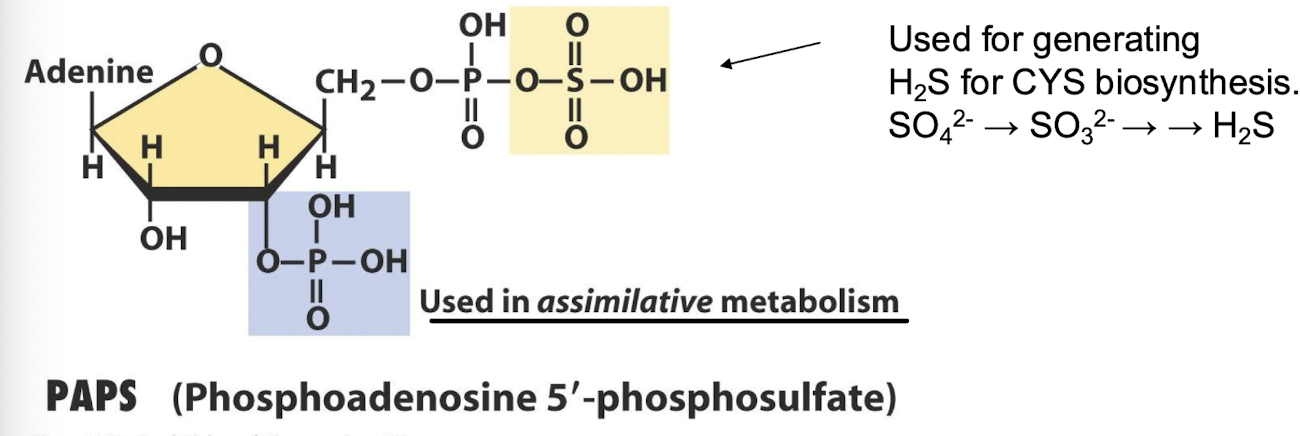
What is PAPS and what is it used for in relation to CYS biosynthesis?
PAPS (3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate) is a key sulfate donor by generating H2S for sulphide (replaces acetyl group from CoA)
It assists in the transfer of sulfate groups during the synthesis of sulfur-containing compounds.
How is GLY synthesised?
By the conversion of SER to GLY, catalysed by a PLP enzyme, serine hydroxymethyltransferase.
This cleaves off the side chain of serine and transfers it to tetrahydrofolate (THF).
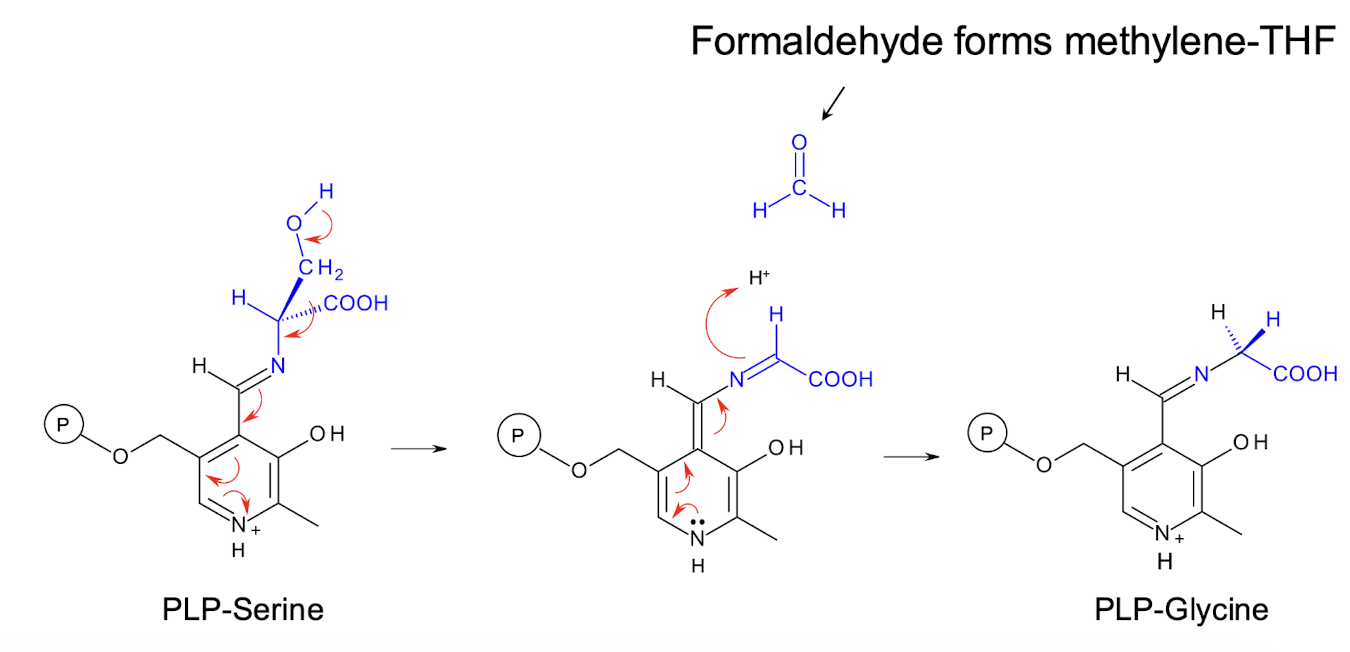
2 steps of the serine hydroxymethyltransferase reaction:
(1) catalyses synthesis of GLY from SER
(2) provides methylene-THF for synthesis of nucleotides.
THF
Reduced, biologically active form of folic acid (Vit B9)
THF is a 6-methylpterin derivative linked to p-aminobenzoic acid and GLU residues.

Why must folate be reduced twice to give the active cofactor THF?
It is the oxidised form and is reduced 2x (using NADPH) by Dihydrofolate reductase
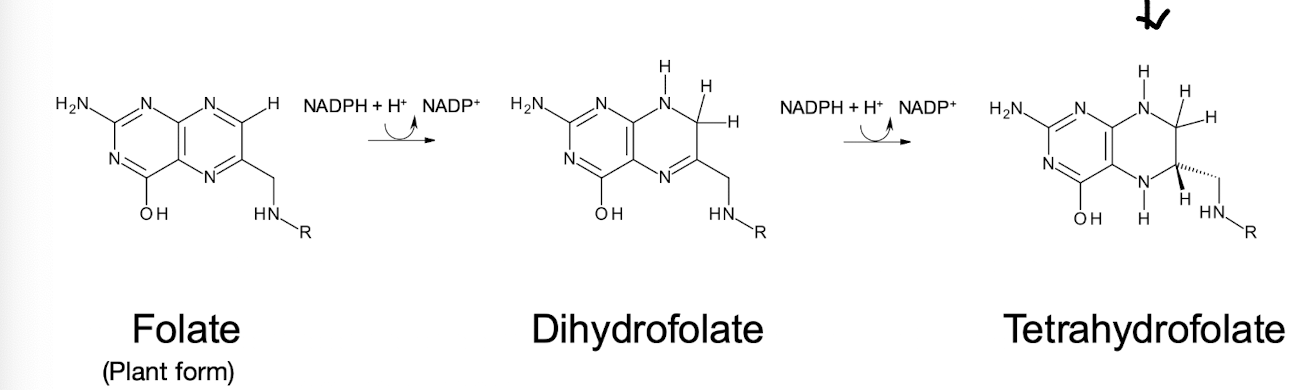
What is the significance of tetrahydrofolate (THF) in metabolism?
THF transfers one-carbon units (methyl or formyl groups) to precursors in biosynthesis.
e.g.
(1) Purine nucleotides
(2) Thymidine
(3) Methionine
(4) N-formylmethionine (prokaryotes only)
What is the role of sulfanilimide antibiotics?
They inhibit folate biosynthesis in bacteria, are analogues of p-aminobenzoic acid
Why is dihydrofolate reductase an important drug target?
Because inhibiting this enzyme reduces folate levels in bacteria, thereby obstructing DNA synthesis and cell growth.
e.g. Trimethoprim and pyrimethamine specifically inhibit bacterial and protozoal DHFRs: used as antibacterial and antimalarial drugs.
How are amino acids typically synthesized in industry?
By chemical synthesis or from overproducing bacteria e.g. Corynebacterium species
Why are Corynebacterium species overproduced to create AA?
Corynebacterium species overproduce metabolites because regulation of their biosynthetic pathways is simple and breaks down easily e.g. via operon control
e.g. Corynebacterium glutamicum naturally overproduces glutamate.
What plant protection mechanism involves glyphosate?
It inhibits aromatic amino acid biosynthesis and is used as a herbicide.

Why is the enzyme dinitrogenase reductase important?
It is part of the nitrogenase complex that facilitates nitrogen fixation.
How is the purine ring constructed?
More or less atom by atoms on a ribose-5’-phosphate with the addition of various amino acids and carbon units.
This process involves key enzymes and intermediates, leading to the formation of purines such as adenine and guanine.
What precursors contribute ring atoms?
The sequence of precursors that contribute ring atoms is:
Glutamine, Glycine, Formyl-THF, Glutamine, CO2, Aspartate, Formyl-THF
All provide one ring atom except glycine which contributes 3.
The purine ring is built up on a ribose sugar that is derived from PRPP

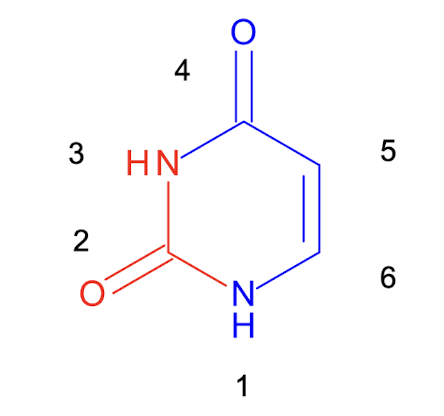
What is the precursor of all pyrimidine nucleotides?
Uracil, which has its N1, C4,5,6 derived from ASP and C2 and N3 from carbamoyl phosphate
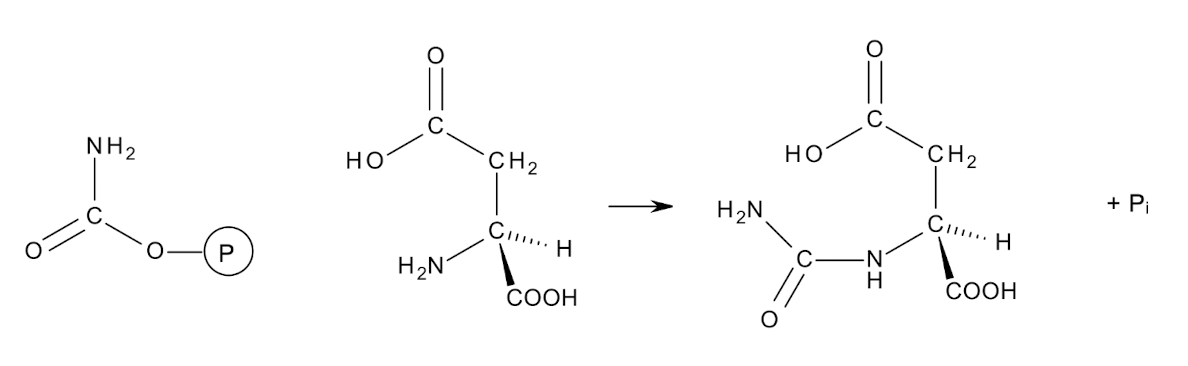
What compound is used for biosynthesis of nucleotides like pyrimidines?
Carbamoyl phosphate is an activated carbon-nitrogen
compound
Aspartate transcarbamoylase transfers it to the amino group of ASP to form N-carbamoyl aspartate
What enzyme helps form the pyrimidine ring?
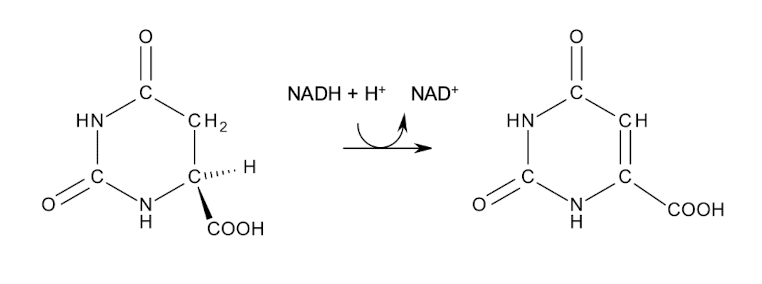
Dihydro-orotase forms the pyrimidine ring of 5,6-dihydro-orotate.
→ Oxidation then gives orotate.
The pyrimidine ring is assembled and then attached to ribose.
The purine ring is constructed on a ribose sugar.
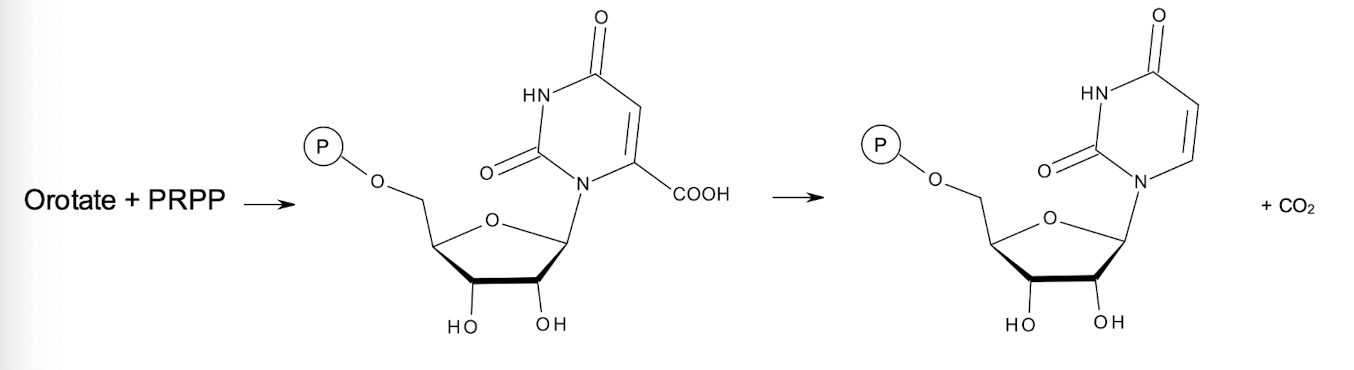
How is UMP formed?
UMP is formed from orotate condensing with PRPP (5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate) forming OMP (orotidine monophosphate), which is then subsequently decarboxylated to yield UMP.
what is the function of ribonucleotide reductase?
It catalyses the reduction of ribonucleotides (ADP, GDP, CDP etc) to deoxyribonucleotides (dNDPs), crucial for DNA synthesis.