TV4101 - Bovine - Nervous 4 - Exotic Dz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Important Exotic Dz with nervous signs?
- bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
- rabies
- Aujeszky’s disease
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
Part of the family of?
Overview?
Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs or prion diseases)
Transmissible, neuro-degenerative, fatal brain disease of cattle
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
Behaviour of Dz?
Central nervous signs, although variable, generally fall into
three categories (all of which may be present) which are?
CX onset insidious
- behavioural changes
- hyperaesthesia
- abnormalities in posture & gait
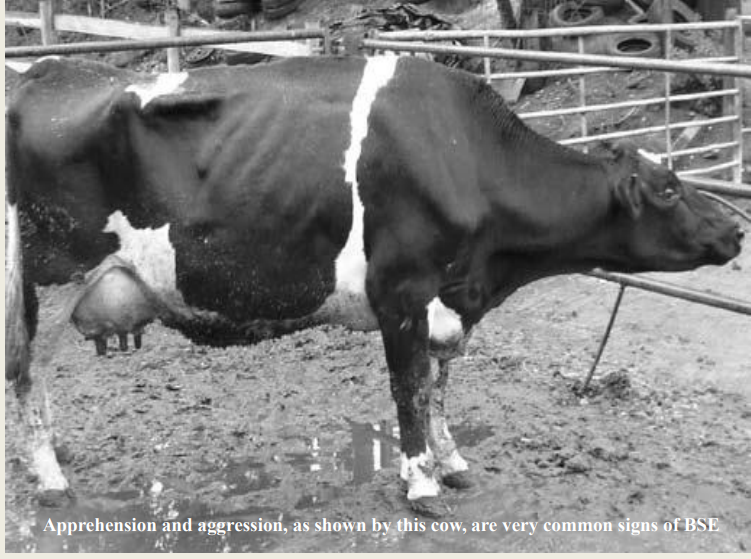
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)
Behavioural changes?
Initially
Placid → agitated or agro (e.g. kicking out at milking shed)
Later signs
- apprehension
- nervousness
- charging and pawing
- frenzy when confronted by obstacles

Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) - Hyperaesthesia
Describe it
Extreme sensitivity to sound and touch
• Cows may kick vigorously when trying to put on the milking
cups
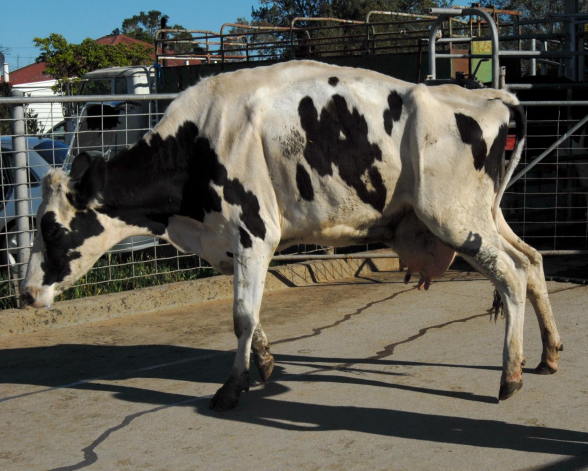
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) - Abnormal gait and posture
• Present as wide-based stance and low head carriage
• Kyphosis of the thoracic spine and lordosis of the lumbar
region (→ overall ‘S’ curvature of the vertebral column)
• Tremors, hindlimb ataxia, swaying & hypermetria when
walking
• Sharp turning may uncover problems such as knuckling of
the fetlocks, stumbling or falling

Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) - DX
Early clinical signs may be similar to?
Can also be sim to?
BSE also needs to be differentiated from?
Metabolic diseases, such as nervous ketosis and hypomagnesaemia
Ryegrass staggers
Polioencephalomalacia, hepatic encephalopathy, and other
causes of encephalitis and poisonings (e.g. lead, urea)
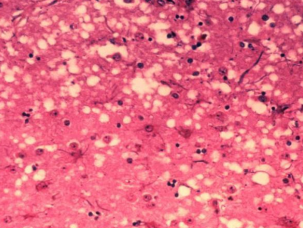
What is this?
Describe it
BSE
Histopathology of the brain with characteristic spongy
degen
BSE - Brain submission
What part of brain is submitted fresh to confirm BSE DX?
Obex region
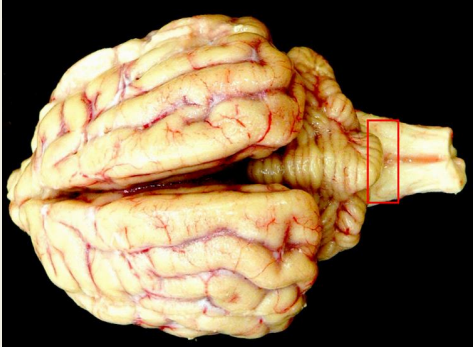
Rabies
Typically transmitted by?
Contamination of a fresh wound with infected saliva, usually associated with the bite of a rabid animal (e.g. dog, bat)
Rabies
The forms?
The form in cattle usually?
Signs vary from excitatory (‘furious’ form) to paralytic
(‘dumb’ form)
In cattle, signs are usually of the paralytic form – the furious
form is relatively rare
Rabies
Prev in cattle?
Cattle are highly susceptible to rabies; however, only one or
two animals of the herd will be infected
Rabies - CX
Furious (rare) version signs?
Persistent bellowing with a hoarse, lowered-pitch voice, pawing at the ground, or aggression. There may also be aggression, increased sexual excitement & libido
Rabies - CX
Early signs?
Behaviour change, muzzle tremors,
abnormal posture, tenesmus, yawning, photophobia and pica
Partial paralysis of the pharyngeal muscles, teeth grinding
(odontoprisis or bruxism), and excess salivation

Rabies - CX
Late clinical signs can include?
As paralysis develops we see?
Opisthotonus, seizures, and widespread paralysis
Cattle knuckle over at the fetlocks, stumble, and fall frequently until they are unable to rise → then lapse into a coma and die

Rabies - Paralytic Form needs to be DDX from?
- botulism
- thrombo-embolic meningo-encephalitis (TEME)
- polioencephalomalacia
- intoxications such as lead, urea, and organophosphates
- cerebral babesiosis and theileriosis
Aujesky’s Dz (pseudorabies aka mad itch)
Overview?
Prevalence in cattle?
Viral disease causing encephalomyelitis and respiratory
infections
Sporadic (cattle are dead end hosts as primarily dz in pig)
Aujesky’s Dz (pseudorabies aka mad itch)
Most striking clinical sign is?
It manifests as?
Other signs?
Intense pruritus of a localised area of skin (‘mad itch’) – neck, trunk, and hindlimbs are most commonly affected (at least initially)
Licking, rubbing or gnawing → self-mutilate
High fever and sweating
Aujesky’s Dz (pseudorabies aka mad itch)
Within 24hrs we see?
Other signs?
Animal is recumbent, but is still able to rise and walk unsteadily
Clonic convulsions,
bellowing,
teeth grinding,
depression or aggression,
pharyngeal paralysis,
rapid shallow breathing, and cardiac irregularities
Aujesky’s Dz (pseudorabies aka mad itch)
Disease should be differentiated from:?
- nervous ketosis
- intoxications or other infections that produce severe neurological signs; e.g. rabies