Second Great Awakening and Reform Movements
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
utopian communities
Over one hundred of these experimental communities were started in the 1820s to 1860s period.

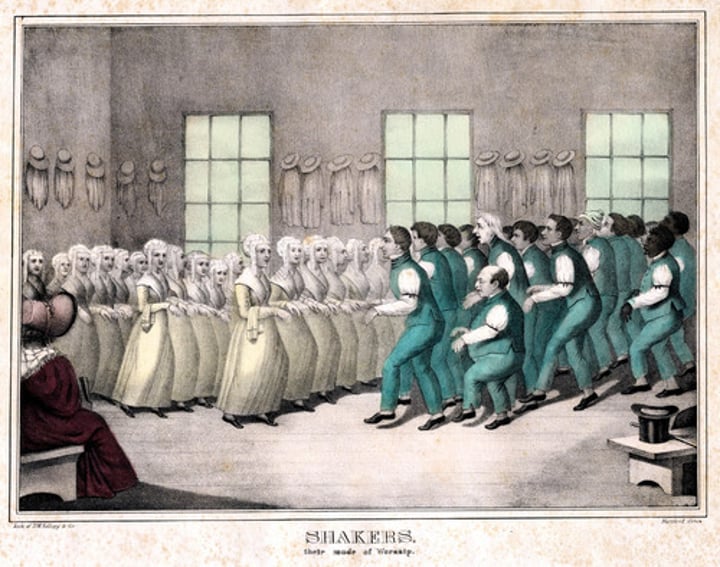
Shakers
This early religious communal movement held property in common and separated men and women.

New Harmony
Nonreligious experimental socialist community founded to solve problems of inequity and alienation caused by the Industrial Revolution

Oneida community
This community, started in 1848, was dedicated to social and economic equality. They shared property and spouses, and prospered by manufacturing silverware..

Horace Mann
He was the leading advocate of the public school movement.
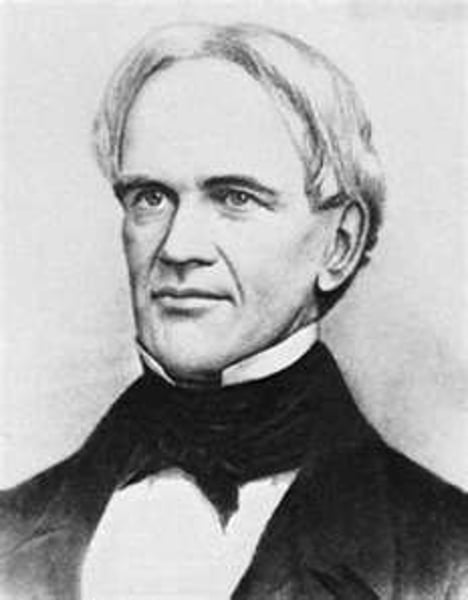

temperance
Reformers targeted alcohol as the cause of social ills. The movement started by using moral exhortation, then shifted to political action. Business leaders and politicians supported it because it improved productivity of industrial workers.

American Temperance Society
Founded in 1826, by Protestant ministers and others, they encouraged total alcohol abstinence.

asylum movement
In the 1820s and 1830s, this movement sought to improve the conditions for criminals, emotionally disturbed people, and paupers. They proposed setting up state-supported prisons, mental hospitals, and poorhouses.

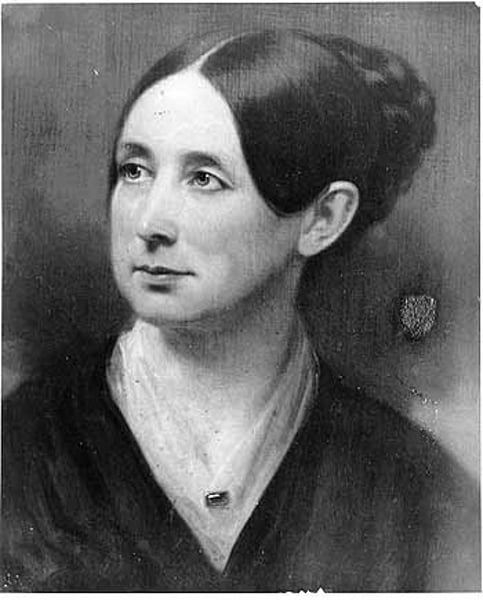
Dorothea Dix
A reformer who was responsible for improving conditions in jails, poorhouses and insane asylums throughout the U.S. and Canada. She succeeded in persuading many states to assume responsibility for the care of the mentally ill.

penitentiaries
These institutions took the place of crude jails. They believed that structure and discipline would bring about moral reform.
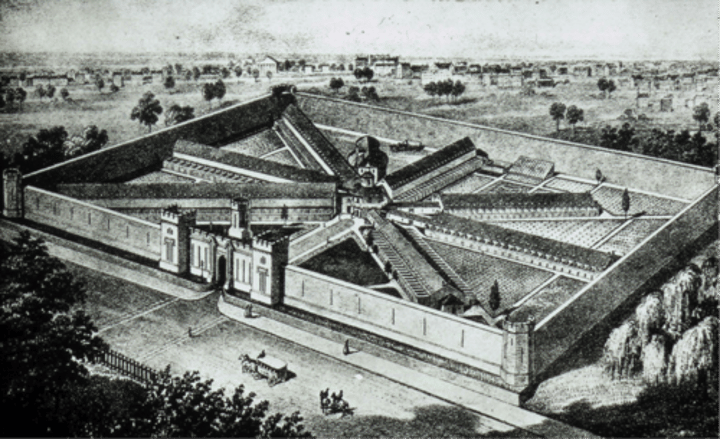
public school movement
In the 1840s, this movement to provide free education for all children spread rapidly throughout the nation.

American Colonization Society
Founded in 1817, this organization transported free black people to an African colony. This appealed to moderates, racists, and politicians. However, only 12,000 people were actually settled in Africa.

abolitionism William Lloyd Garrison; The Liberator
In 1831, he started the radical abolitionist movement with the "The Liberator" newspaper. He advocated the immediate abolition of all slavery in every state.

Liberty party
In 1840, this political party was formed in reaction to the radical abolitionists. They pledged to bring an end to slavery by political and legal means.

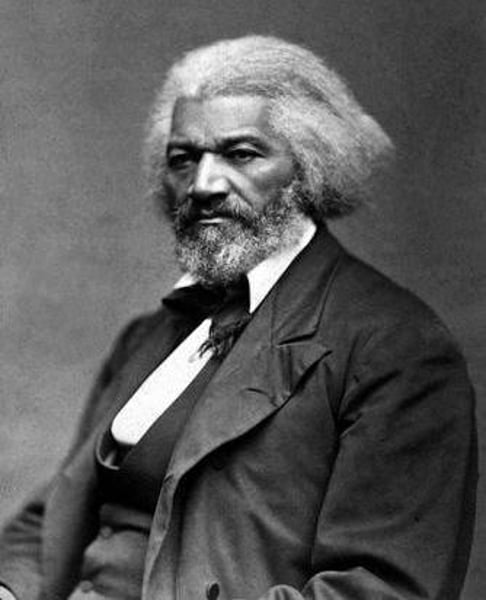
Frederick Douglass; The North Star
In 1847, this former slave started the antislavery journal, "The North Star".

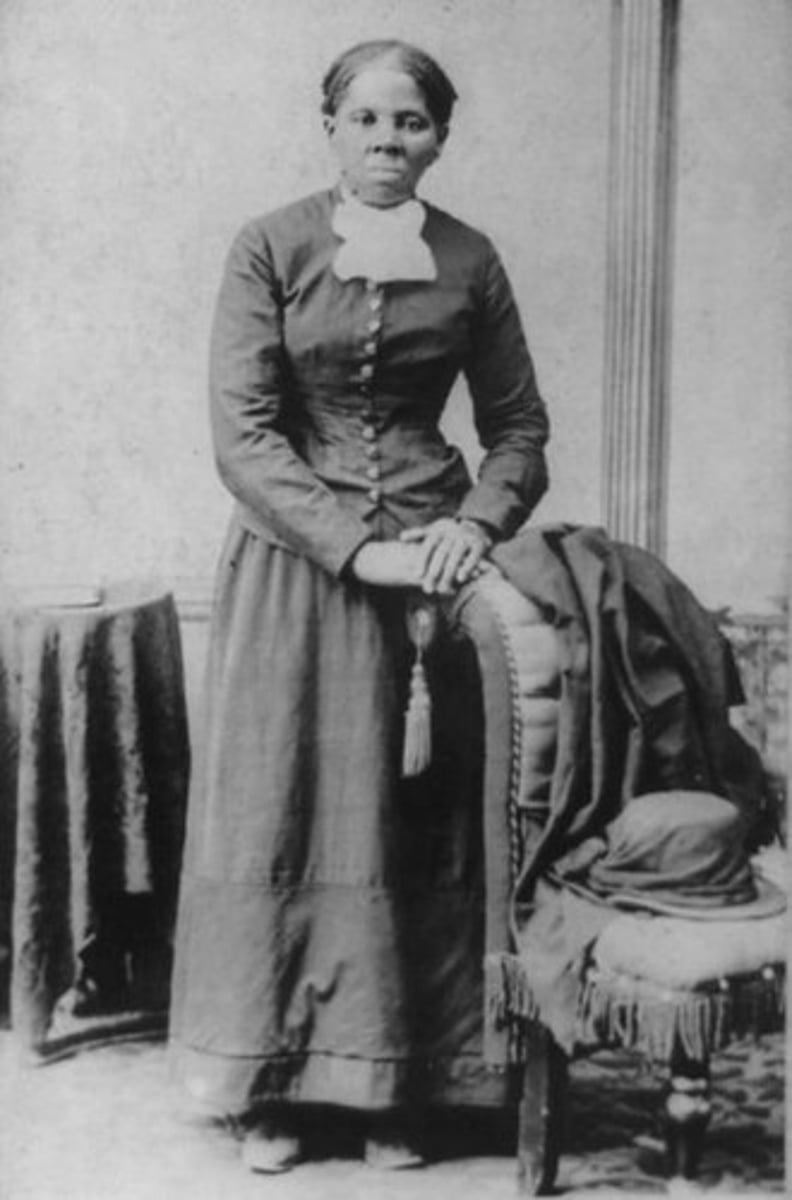
Harriet Tubman
Famous abolitionist, born a slave, she assisted fugitive slaves to escape to free territory.

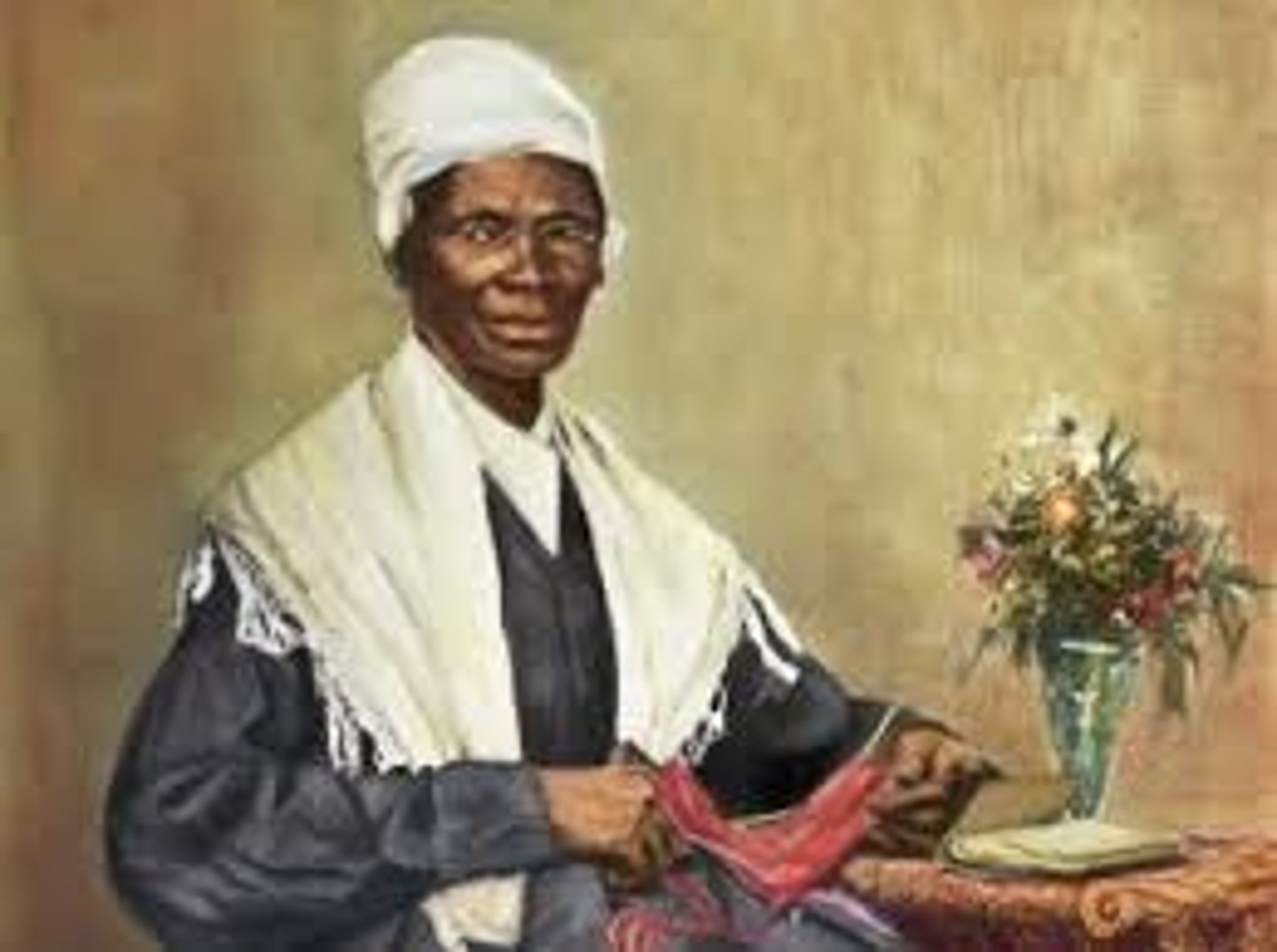
Sojourner Truth
A United States abolitionist and feminist who was freed from slavery and became a leading advocate for the abolition of slavery and the rights of women.

David Walker
An African American who advocated the most radical solution to the slavery question. He argued, that slaves should take action themselves by rising up in revolt against their owners.

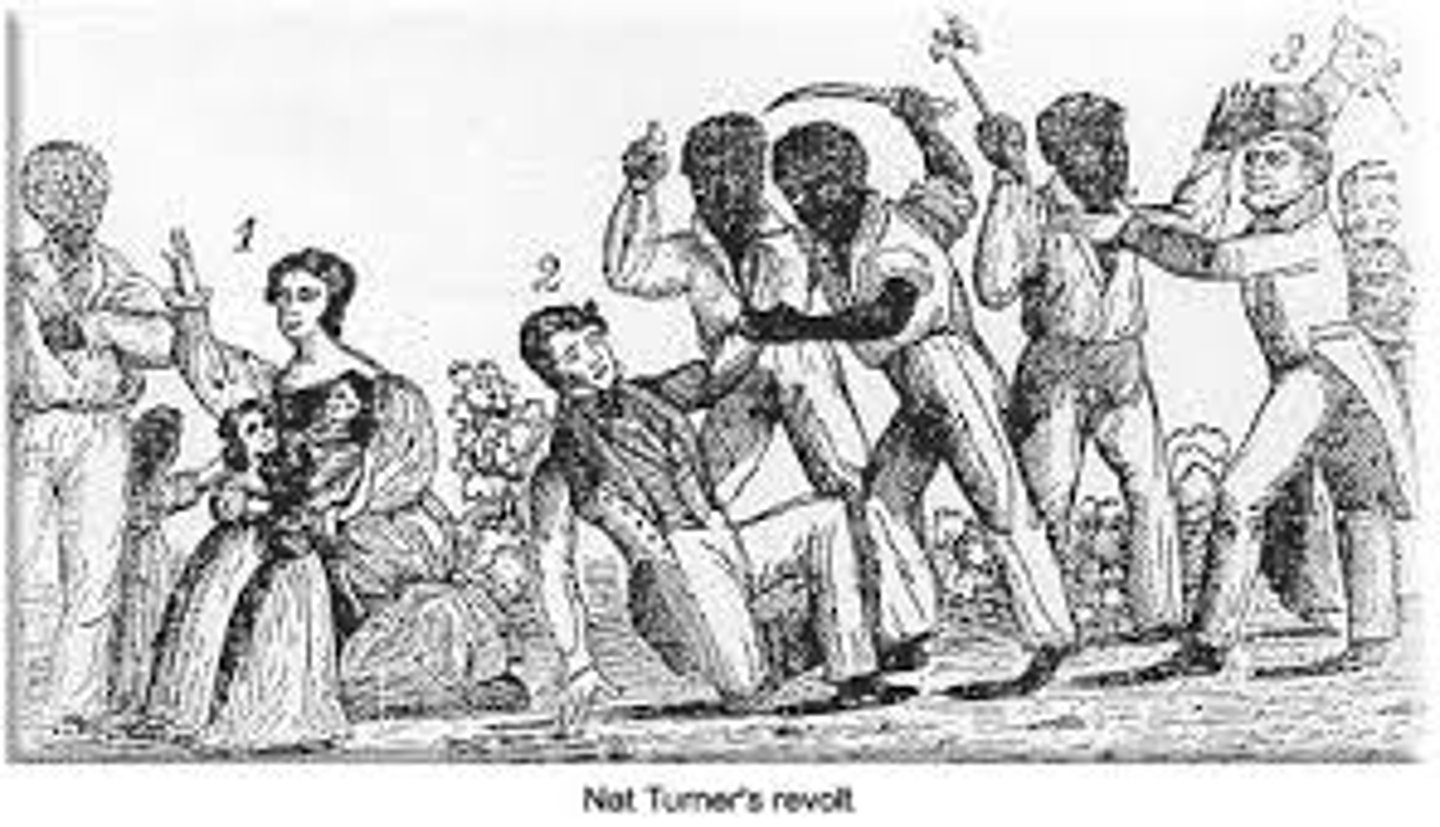
Nat Turner
In 1831, he led the largest slave rebellion in which 55 whites were killed.

antebellum period
The period before the Civil War started in 1861.

transcendentalists
They questioned the doctrines of established churches and business practices of the merchant class. They encouraged a mystical and intuitive way of thinking to discover the inner self and look for essence of God in nature. Artistic expression was more important than pursuit of wealth. They valued individualism and supported the antislavery movement.

Ralph Waldo Emerson, "The American Scholar"
The best known transcendentalist, his essays and lectures expressed the individualistic and nationalistic spirit of Americans. He urged self-reliance, and independent thinking.

Henry David Thoreau, "Walden", "On Civil Disobedience"
A pioneer ecologist and conservationist. He was an advocate of nonviolent protest against unjust laws.

Brook Farm
An attempted communal experiment in Massachusetts to achieve a more natural union between intellectual and manual labor.

Hudson River school
In the 1830s, this genre of painting founded in the Hudson River area, portrayed everyday life of ordinary people in the natural world

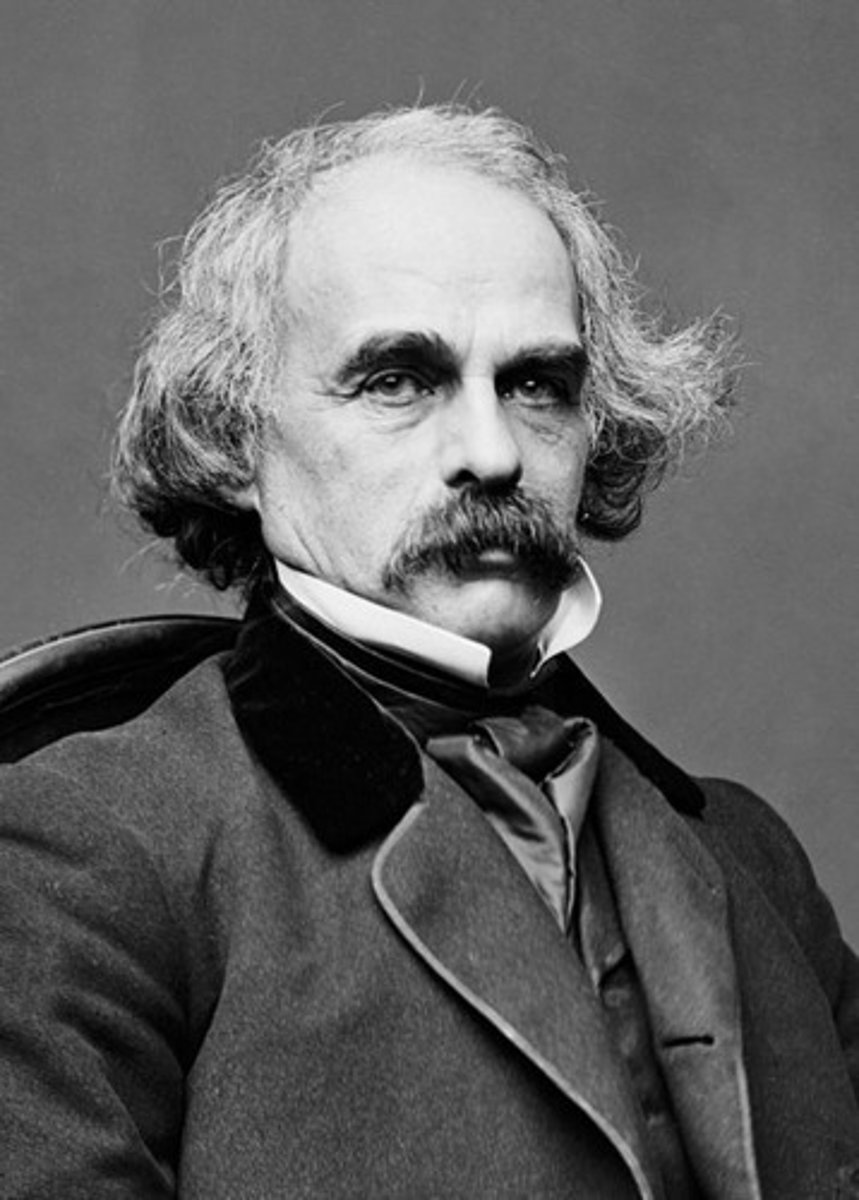
Nathaniel Hawthorne
Author of "The Scarlet Letter", which questioned the intolerance and conformity in American life. (p. 211)

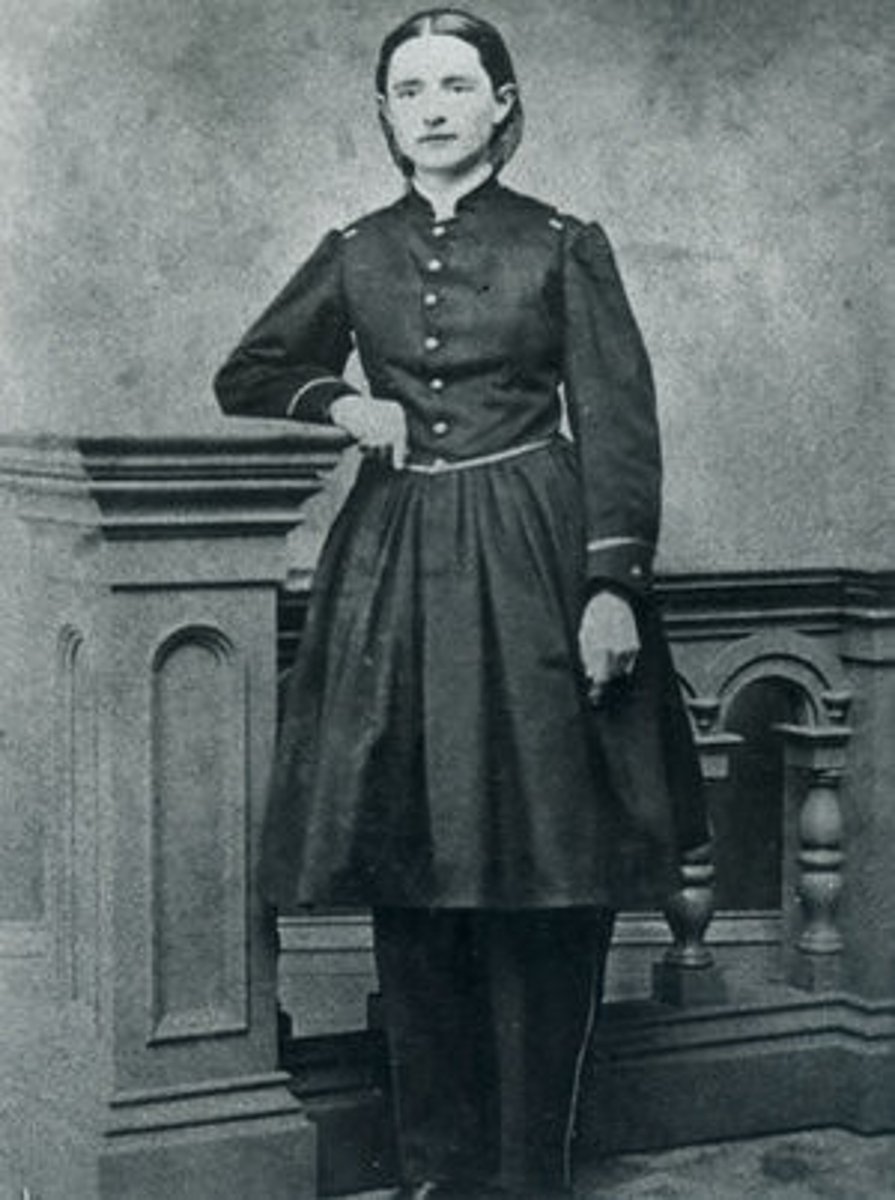
Amelia Bloomer
She urged women to wear pantalettes instead of long skirts.

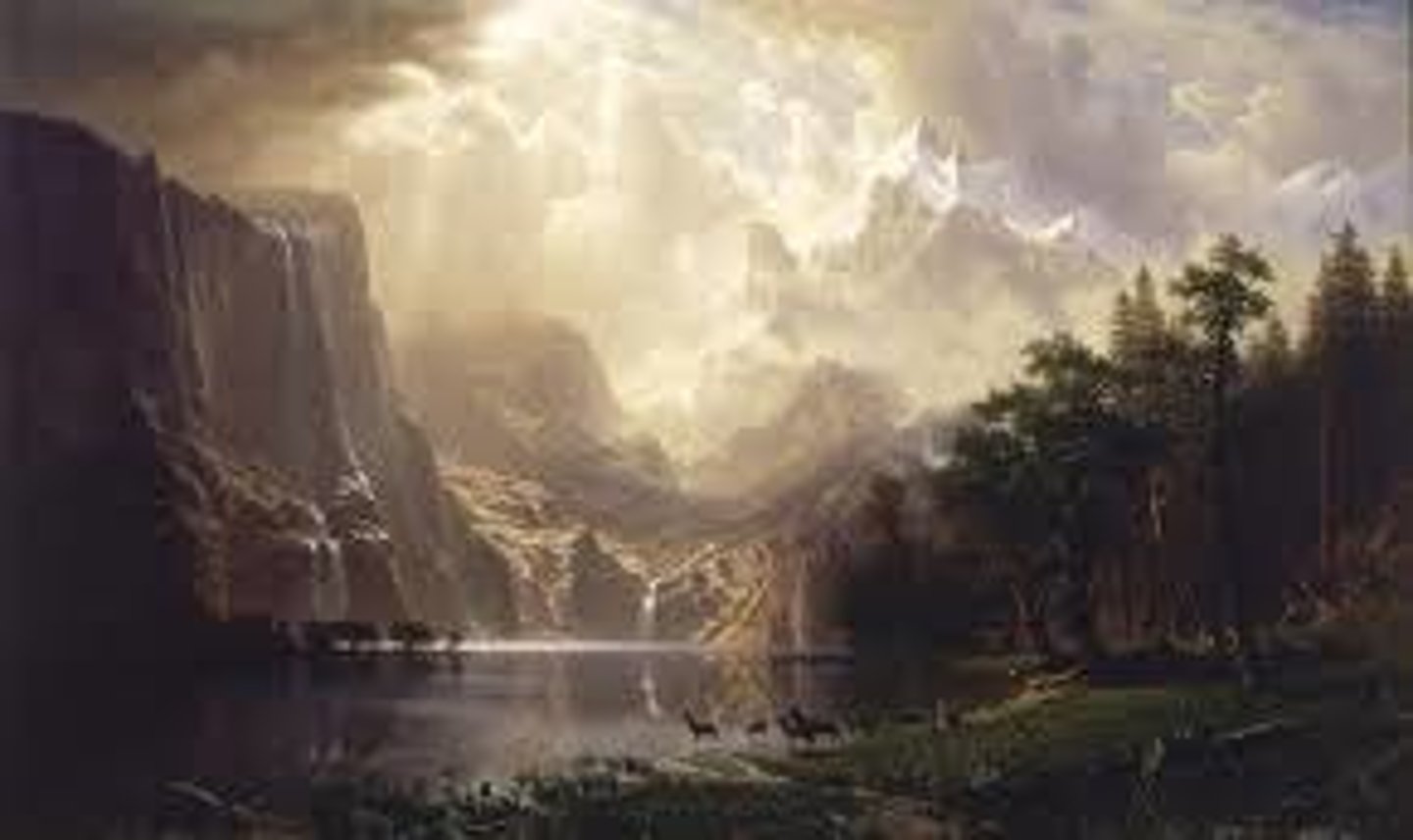
Second Great Awakening
A religious movement that occurred during the antebellum period. It was a reaction against rationalism (belief in human reason). It offered the opportunity of salvation to all
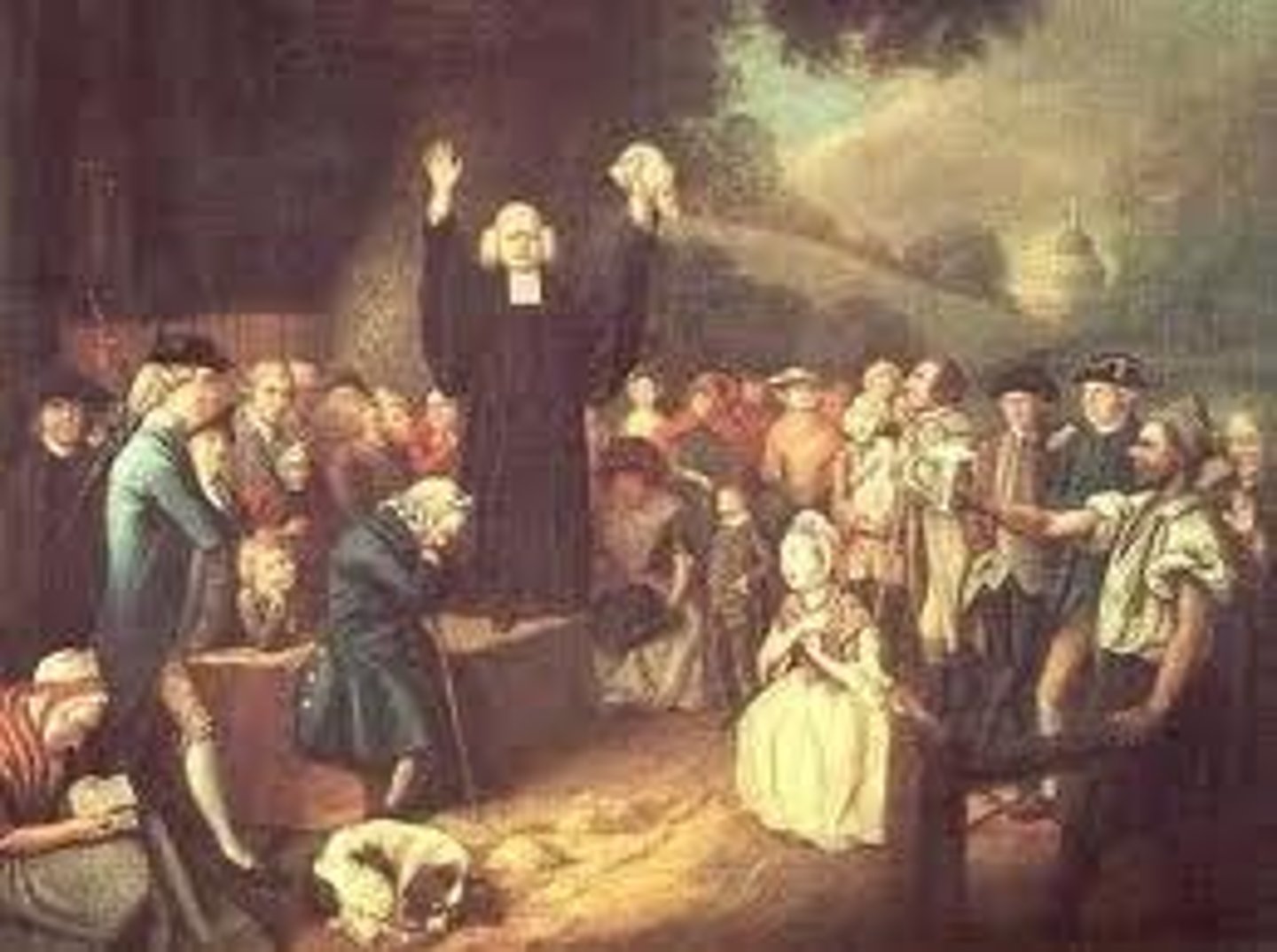

revivalism; revival camp meetings
In the early 1800s, this movement was a reaction against the rationalism of the Enlightenment. Successful preachers were audience-centered and easily understood by the uneducated
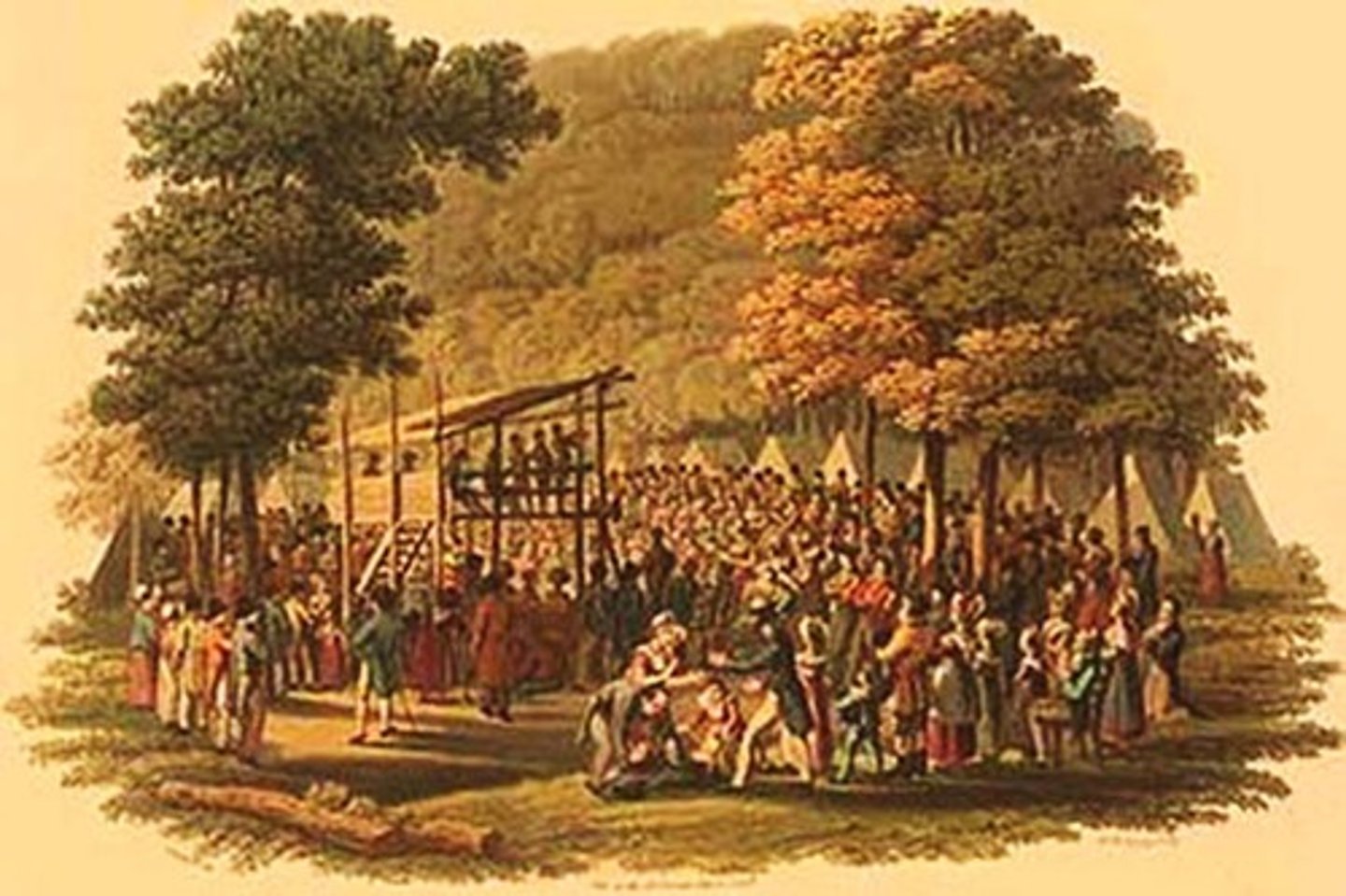

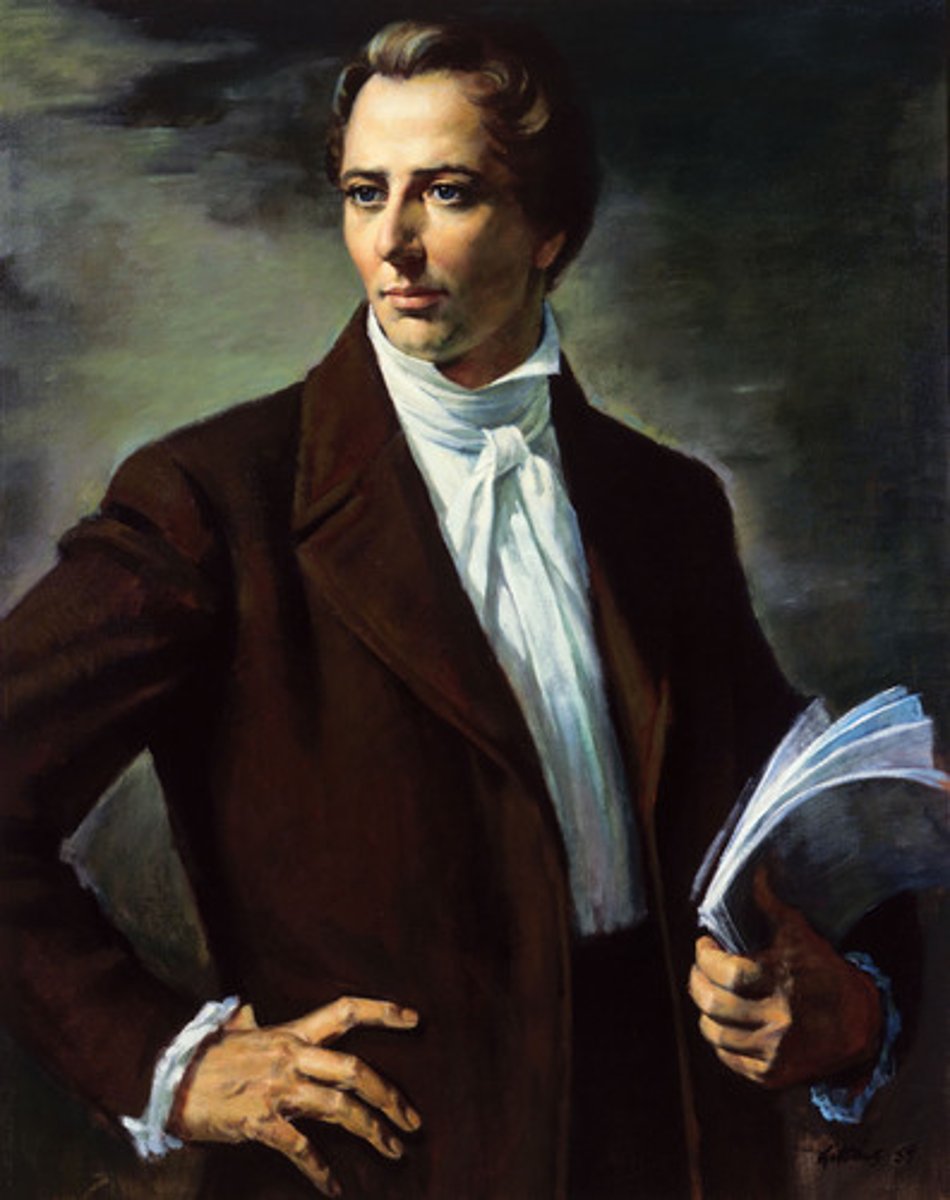
Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints; Mormons
Founded by Joseph Smith in 1830. It was based on the Book of Mormon which traced a connection between the American Indians and the lost tribes of Israel. After Joseph Smith was murdered, Brigham Young led the religious group to the Great Salt Lake in Utah.

Joseph Smith
Founded the Church of Jesus Christ of the Latter-Day Saints in New York in 1830. The church moved to Ohio, Missouri, Illinois, then finally to Utah.

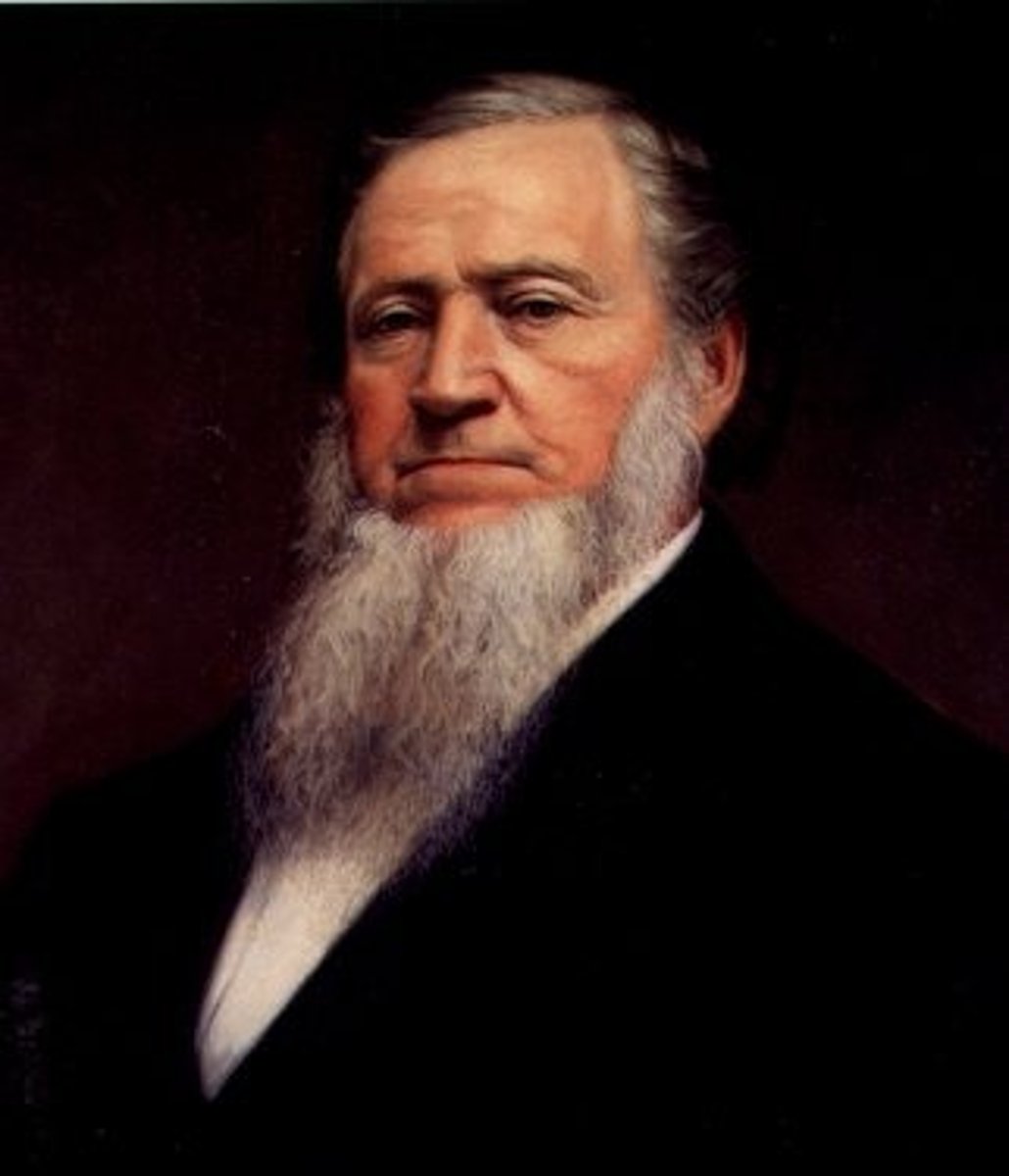
Brigham Young
After Joseph Smith was killed, he led the Mormon followers to Utah.

women's rights movement
Women started this movement because they resented the way men relegated them to secondary roles in the reform movements. (p. 214)

cult of domesticity
After industrialization occurred women became the moral leaders in the home and educators of children. Men were responsible for economic and political affairs.

Sarah Grimke, Angelina Grimke
Two sisters, born in South Carolina, they objected to male opposition to their antislavery activities.
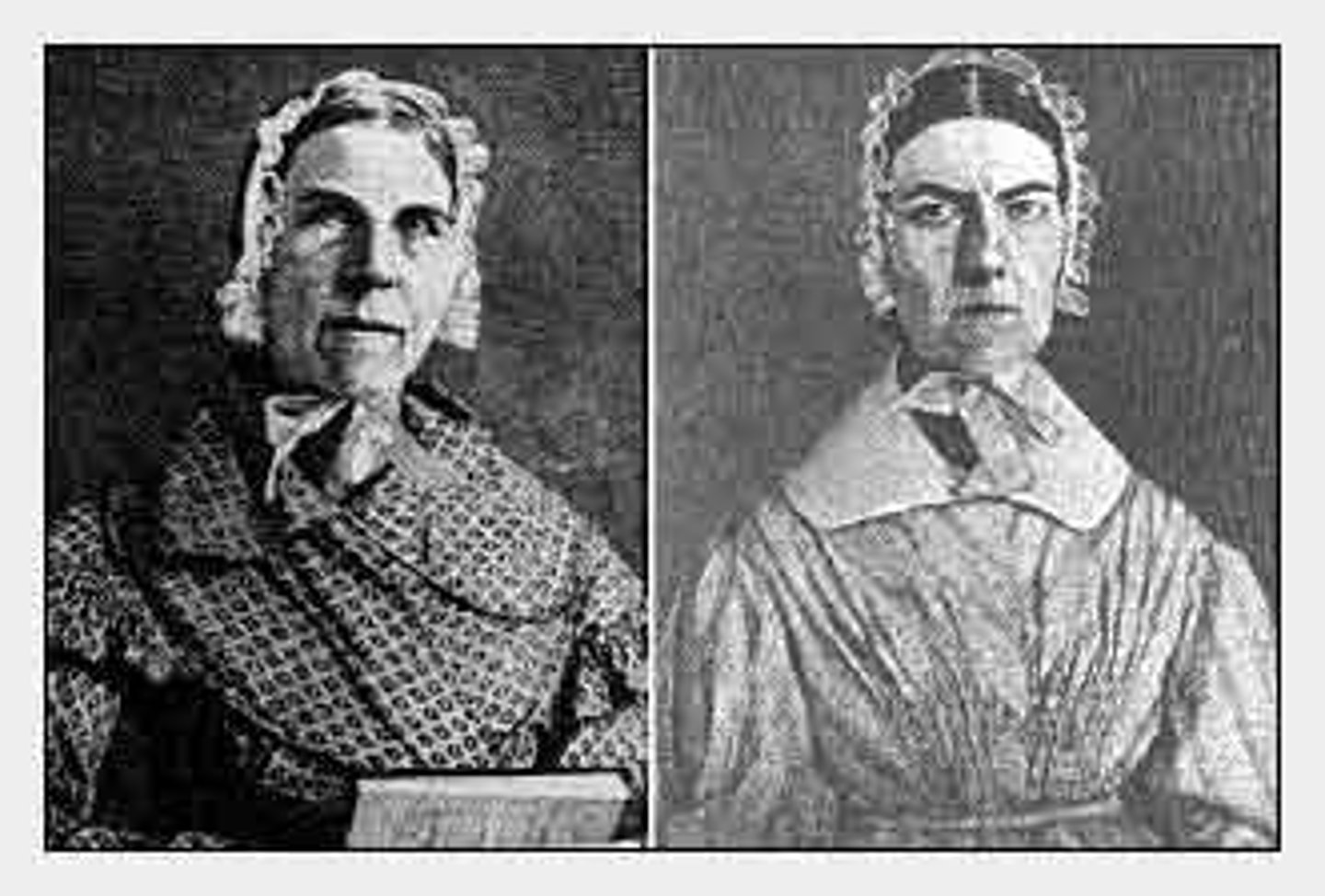

Letter of the Condition of Women and the Equality of the Sexes
Written by Angelina and Sarah Grimke, it protested males opposition to their abolitionist work.

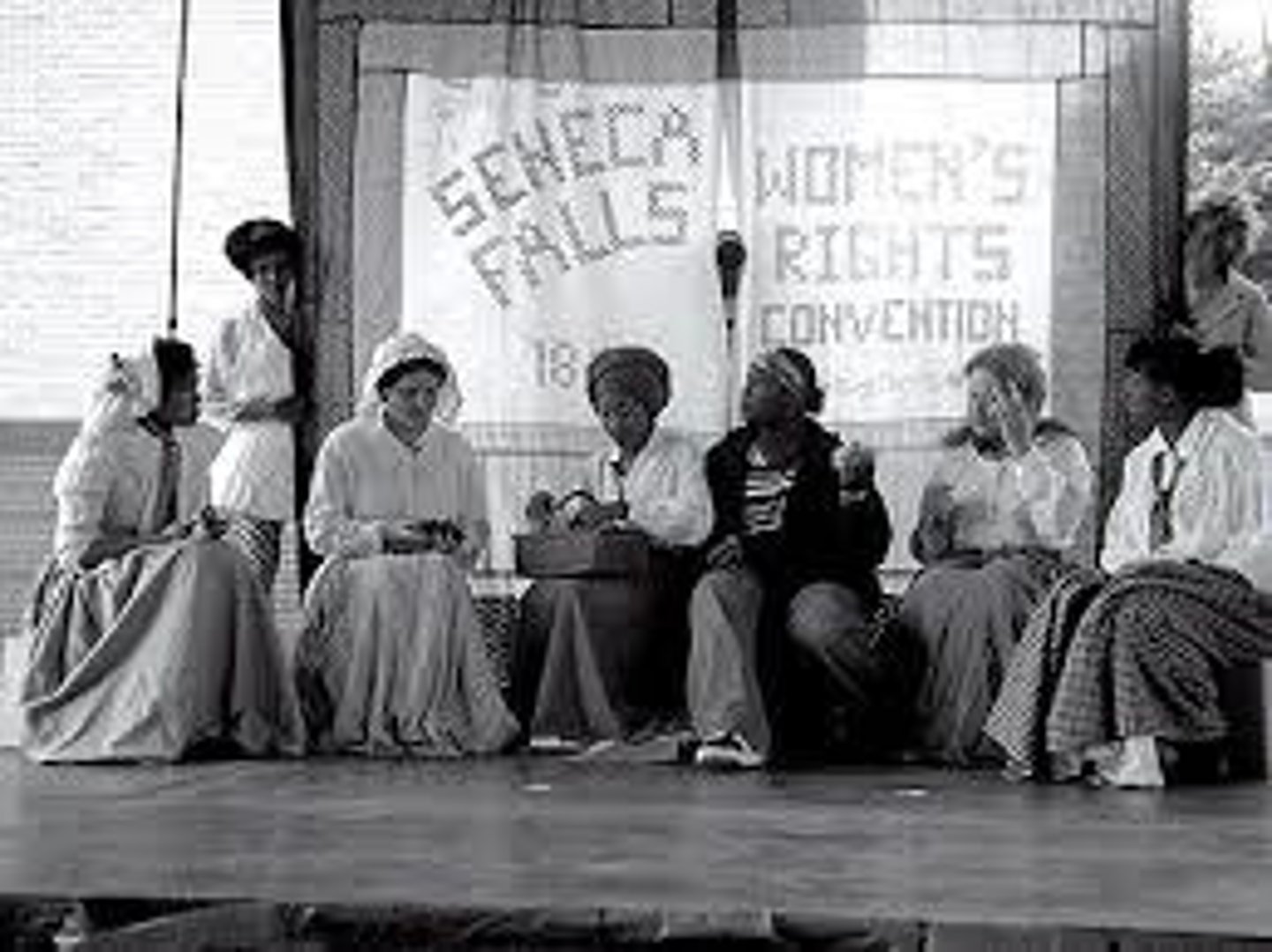
Seneca Falls Convention
In 1848, this was the first women's rights convention in U.S. history. They wrote a "Declaration of Sentiments", modeled after the Declaration of Independence, which declared all men and women equal and listed grievances

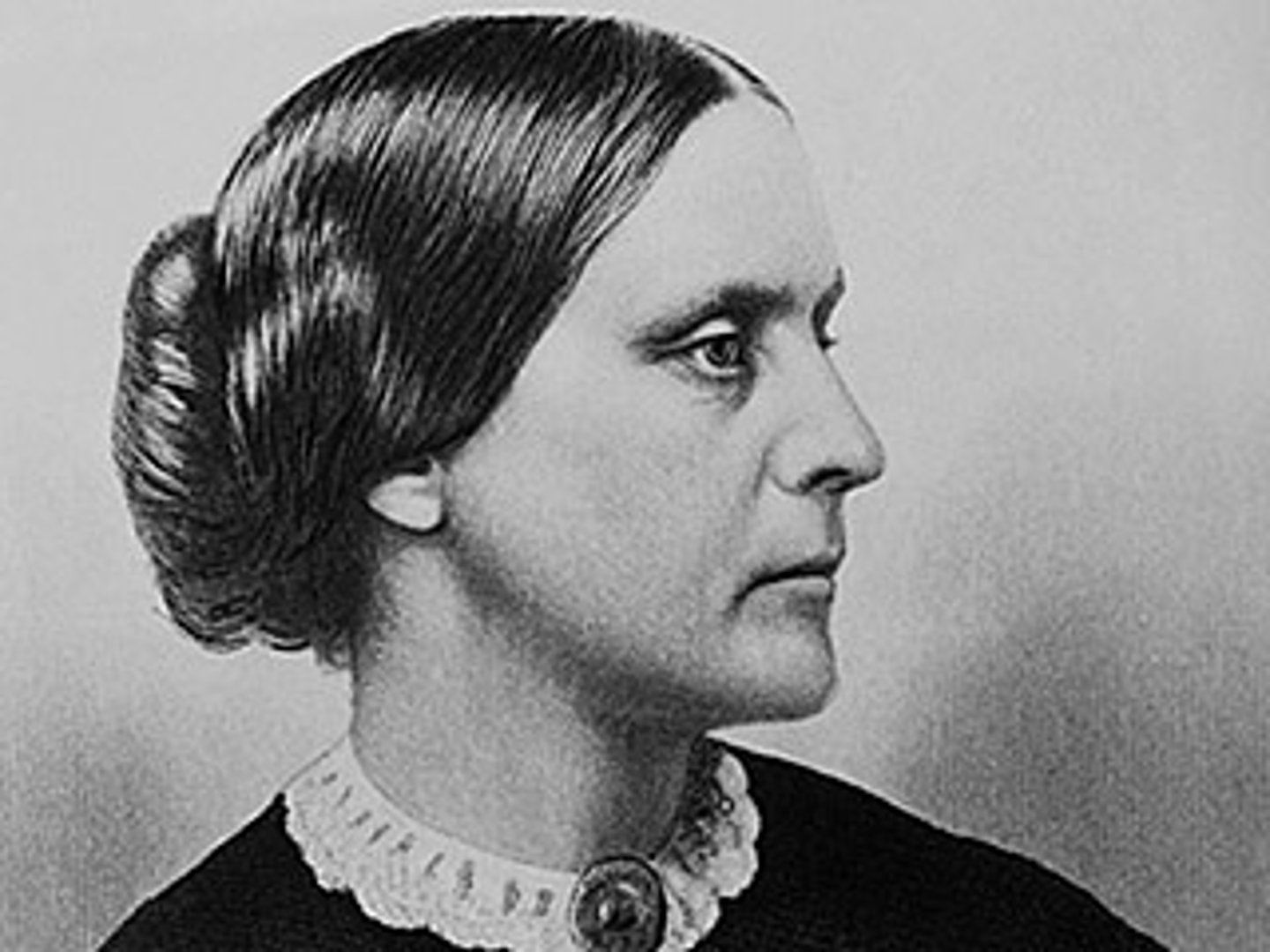
Susan B. Anthony
Social reformer who campaigned for womens rights, the temperance, and was an abolitionist. She helped form the National Woman Suffrage Association.
