Why states & other actors resort to force
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what does resort to force mean?
the use of armed force or military by a state or non-state actor to pursuing objectives
what are the tools that are used when resorting to force?
military power is often used as a foreign policy tool. However, UN Charter Article 51 permits states to use force in self-defense only.
what are the utilities that were used when resorting to force?
The use of force may retain some utility (benefit)to achieve the goals of states, but doesn’t necessarily legitimise their actions.
define interstate conflicts?
a war that involves numerous states including great powers is called global war.
why do states fight? And explain each reasoning:
1) Territorial disputes- (most common since 1648.) Creation of new states, or secession or decolonization especially after World War II
2) Economic issues- involves access to resources. Economic issues have been a factor in one-fifth of the wars fought since 1945.
3) Ideology- conflicts over ideas about proper forms of governance. Types of this conflict include democracy vs. authoritarianism, capitalism vs. communism, religious and ethnic conflicts.
4) Predation- the desire to eliminate another state as a sovereign entity. Predation was at its height in the period between WWI & WWII.
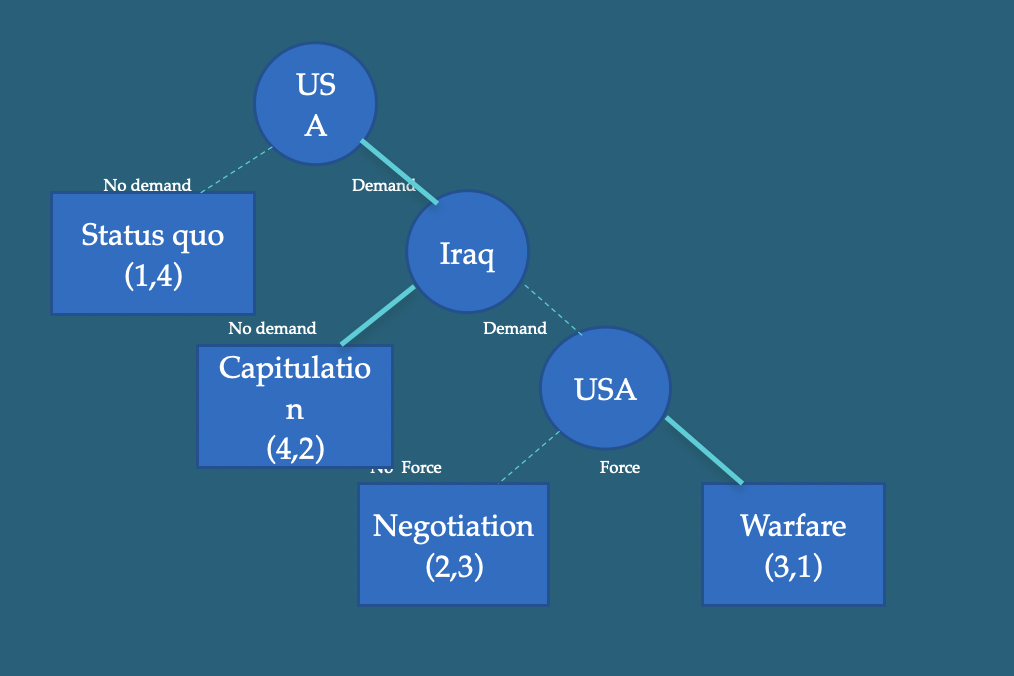
Case-game US vs Iraq 1998 over UN weapons inspection: what was the out come
Negotiation: (2,3)
Kenneth Waltz identifies 3 different levels of war analysis called (image) what are they:
First image-Human Nature
Second Image- State Organisation
Third Image- International System
define the First image-Human Nature
War can be explained by studying the human nature. Four perspectives:
what are the subtopics of Kenneth Waltz first level of war analysis
1) Ethology – argues that biological influences ( innate genetics) cause violent behavior.
2) Sociobiological- argues that natural selection(survival of the fittest) cause violent behavior.
3) Situational perspective- argues that violence is the result of types of situations that would affect individual’s perceptions.
4)Relative deprivation theory- argues that aggressive behavior stems from frustration arising out of feeling of relative deprivation to others (expectations for what they should have)
what is an example of Relative deprivation theory (first image)
Germany & Japan prior to WWI, felt they were not receiving recognition as great powers.
what are the subtopics of Kenneth Waltz second level of war analysis
1) Realists- argue that war is a tool for politicians and military personnel driven by power to achieve state’s goals, regardless to their differences in political & economic structures.
2) Liberals- stress democracy and capitalist economic structures. They argue that democracy and economic interest (capitalists’ interests)in free trade would promote world peace, which in turn encourage poor countries to develop along democratic lines.
3) Marxists/Radicals- argue that exporting surplus capital (products) became a competition among countries, ultimately leading to war among the capitalist powers. Thus, imperialism is the highest stage of capitalism.
define the Second Image- State Organization
War can be explained by studying the state political and economic structures.
define the Third Image- International System
War can be explained by the distribution of power in the international system:
what are the subtopics of Kenneth Waltz third level of war analysis
1) Bipolar system- of all types of polarity (refer to model), some theories assert that bipolarity will be most successful in avoiding a global war. Neither pole has a chance at victory because of nuclear weapons.
2) Differential growth of power- the threat to the international system stability stems directly from both the differential growth of power (economic, military, political), and a rising power that challenges the dominant power.
3) Power Transition- occurs when a rising challenger equals the power of the dominant power (hegemonic power).
what is an example of Bipolar system (third image -international system)
Bipolarity ( US & USSR)is one possible explanation for decades without a global war following World War II.
what is an example of Differential growth of power- (third image -international system)
Rise of China as a challenging power to the US power.
what is an example of Power Transition- (third image -international system)
China v. US.
define internal conflict
A war that involves numerous internal factions including intervention by great powers is called internal or civil war.
What are the impacts of an internal conflict
1) Enormously destructive and long-lasting.
2) Provoke conflicts between states.
What are the zones of an internal conflict
1) The absolute majority of conflicts are internal conflicts
example: Middle East and North Africa: More than 45 Armed Conflicts, Africa: More than 35 Armed Conflicts
2) Many wars involve external forces such as the wars in Afghanistan, Iraq Syria, Yemen, Libya, Sudan & Lebanon.
What are the reasons of an internal conflict
1) Religious & ethnic conflicts
2)Disagreement over the nature of the political system
3) Lack of political & civil rights
4) Poverty
5) Relative deprivation
6) Secession (territorial autonomy)
define ethnic conflicts
ethno-political conflicts because of cleavages along racial, tribal, linguistic, or religious lines in one nation-state.
what is an example of an ethnic conflict
Former Yugoslavia, Iraq under ISIS; Armenians in Turkey, Kurds in Turkey, Syria and Iraq; Arabs in Iran; Nigeria.
define unconventional conflicts
war or violence that do not follow traditional rules
what are the types of unconventional conflicts
1) Guerrilla warfare
2) Global Terrorism-
3) State-sponsored terrorism-
4) Information Warfare-
what does Guerrilla warfare mean under unconventional conflicts and give an example
the principal objective is to fight occupation or overthrow local regimes. Warfare acts are mainly directed against the military and governments’ officials
Example: Hamas, Islamic Jihad, Hezbollah, IRA.
what does Global Terrorisme mean under unconventional conflicts and give an example
the principal purpose is to control through use of terror and violence. The terrorists’ acts are mainly directed against civilians, governments’ workers, or noncombatant military personnel
example: ISIS, al-Qaeda, IRGC (refer to model).
what does State-sponsored terrorism mean under unconventional conflicts and give an example
terrorism conduct by a state or, by proxy support of terrorist groups through the provision of arms, training, safe-haven, and financial backing
example: Iran-Ansar Allah (Yemen), Iran-Kataeb Hezbollah (Iraq); Israel
What does Information Warfare mean under unconventional conflicts, and give an example?
range from disruption of an opponent’s ability to command and control of its military forces to psychological tactics to cyber terrorism or hacker war.
Give examples of unconventional conflicts over all:
hijacking
hostage taking
bombing
internet/cyber attacks
armed assaults, car ramming, knife stabbing
suicide attacks