2. Fundamentals
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
Electrochemistry
processes that influence the charge transfer across interfaces between chemical phases
2
New cards
One phase
is an electrolyte where charge is transported by ions
3
New cards
What form is one phase
solution, melt or an ionically conductive solid material)
4
New cards
The other phase
is often an electrode, but can be also another electrolyte, where charge is transported by electrons
5
New cards
What form is the other phase
metallic conductor, carbon, semiconductor).
6
New cards
How are electrochemical experiments conducted?
By applying :
- A constant electrical voltage/potential (E) ⇒ measure the resulting current (I)
- A constant current (I) ⇒ measure the resulting voltage/potential (E)
- A constant electrical voltage/potential (E) ⇒ measure the resulting current (I)
- A constant current (I) ⇒ measure the resulting voltage/potential (E)
7
New cards
Potentiometry
the use of electrodes to measure voltages that provide chemical information
8
New cards
the working electrode is called
indicator electrode IE
9
New cards
An induced voltage is measured with a(n) ___.
high-input impedance voltmeter
10
New cards
Electric voltage... (E)
is the energy per unit charge gained or lost when a charge is moved from some reference point at which the potential is defined to be zero
11
New cards
Voltage
is the difference in potential between two (arbitrary) points at which the potential is not necessarily zero (vs. the reference point).
12
New cards
Electrical variables
Potetnial E
Currnt I
Charge Q
Currnt I
Charge Q
13
New cards
External Variables
Temperature (T)
Pressure (p)
Time (t)
Pressure (p)
Time (t)
14
New cards
Electrode variables
Material, surface area (A)
Geometry, surface condition
Geometry, surface condition
15
New cards
Solution variables
Bulk concentration of electroactive species (CO , CR)
Concentration of other species (electrolyte, pH)
Solvent
Concentration of other species (electrolyte, pH)
Solvent
16
New cards
Mass transfer variables
Diffusion
Convection
Migration
Convection
Migration
17
New cards
Galvanic cell is without..
applied external voltage
18
New cards
Electrolytic cell is with...
applied external voltage
19
New cards
What is measured with a voltmeter with a high input impedance? the potential cannot be measured so what is done instead
Only the potential differences ∆E
20
New cards
Which cell has a Red Cat
The Galvanic Cell
21
New cards
Cell potential is calculated by...
the cathode and anodes reduction potentials
E^0
E^0
22
New cards
The redox couple with the higher standard potential X the redox couple with the lower standard potential.
oxidizes
23
New cards
The redox couple with the higher standard potential
will be the reduction reaction and the cathode
24
New cards
The redox couple with the lower standard potential
will be the oxidation reaction and the anode
25
New cards
The reaction is X if ΔG0 < 0
spontaneous
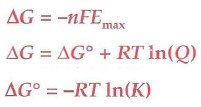
26
New cards
The charge Q is proportional to the....
moles of Zn that has been oxidized to Zn2+
27
New cards
The current I is proportional to the...
reaction rate
28
New cards
Faraday's Law equation
Q=nFN
29
New cards
Reaction rate equation
dN/dt =ν = I/nF
30
New cards
dN/dt in the reaction law
is the number of moles that reacts per time unit.
31
New cards
Power equation
P = E * I = U*I
32
New cards
Energy equation
P *t = E*I*t
33
New cards
Electrolysis involves
forcing a current through a cell to produce chemical reactions at the electrodes and decomposition of the materials.
34
New cards
Electrolysis of water
Water decomposes to hydrogen and oxygen gases