Physio Chapter 1 (The Minds Machine)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
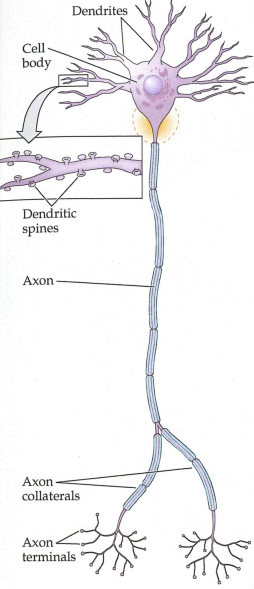
Neurons “nerve cells”
Basic units of the nervous system
Typical Neuron has FOUR main parts and what do they do?
Dendrites: receive information
Cell body (soma): integrates information
Axon: carries impulses from neuron
Axon terminal: transmit neuron signals to other cells
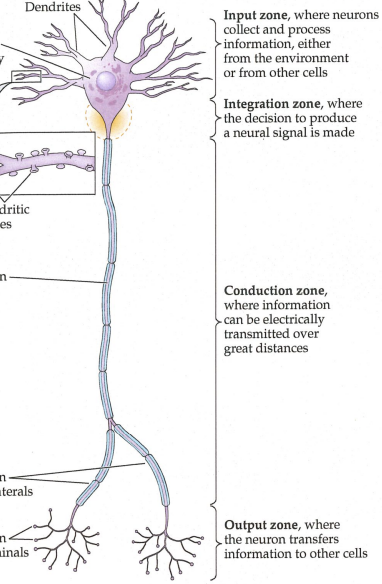
Neurons almost always contain what? (hint: 4 things)
input zone, integration zone, conduction sone, and output zone
Synapse
Cellular location where info is transmitted from a neuron to another cell
Glial Cells aka glia
nonneuronal brain cells. Provide structural, nutritional, and other support to the brain
Neuron Doctrine
neurons and other cells of the brain are structurally, metabolically, and functionally independent.
info is transmitted from neuron to neuron across small gaps called “synapses”
Input Zone
Dendrites (receive info from other neurons via synapses)
Integration Zone
Cell Body [Soma, plural Somata] (receives additional synaptic input and integrates the info that has been received)
Conduction Zone
Axon [Nerve Fiber] (a single extension, carries the neuron’s own electrical signal away from the cell body)
When an axon splits into multiple branches
axon collaterals
Output Zone
Axon Terminals [Synaptic Boutons] (specialized swellings at the ends of the axon that transmit the neuron’s signal across synapses to other cells)
Three Principal Types of Neurons
Multipolar
Bipolar
Unipolar
Multipolar
many dendrites (branches) and a single axon, most common
Bipolar Neurons
single dendrite at one end of the cell and single axon at the other end (especially common in sensory systems like vision)
Unipolar Neurons (Monopolar)
a single extension (or process) usually thought of as an axon that branches in two directions after leaving the cell body. One end is the input zone, the other an output zone with terminals. (transmit touch info from body into the spinal cord)
Synaptic Cleft
space between presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
Synapses THREE principal components
presynaptic membrane (axon terminal)
synaptic cleft
postsynaptic membrane (dendrite or cell body)