O2 transport snd regulation 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Total Blood Oxygen =
O2 dissolved in plasma (PaO2)~2%
+
O2 bound to hemoglobin (HbO2)~ 98%
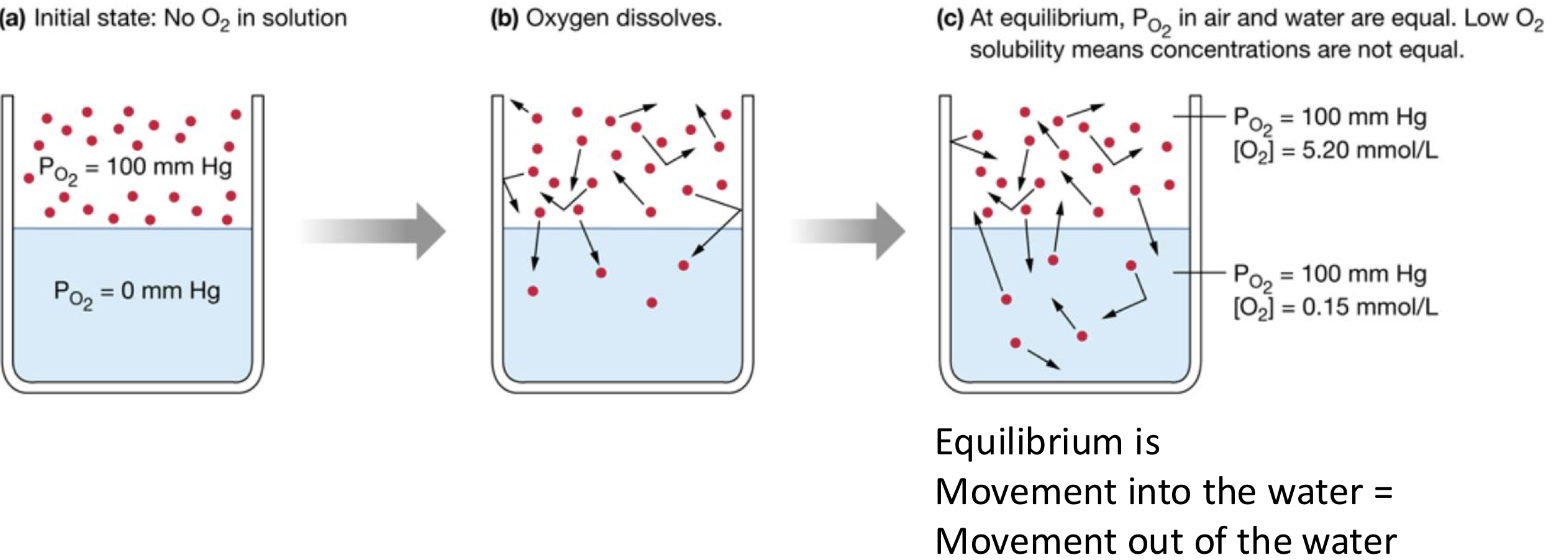
Why does our body use O2 bound to hemoglobin and not dissolved O2?
Oxygen is not very soluble in liquid
How does hemoglobin transport oxygen?
one hemoglobin can bind up to four oxygen molecules To transport them

Cooperative Binding
More O2 binds to Hb, increases affinity of Hb to O2
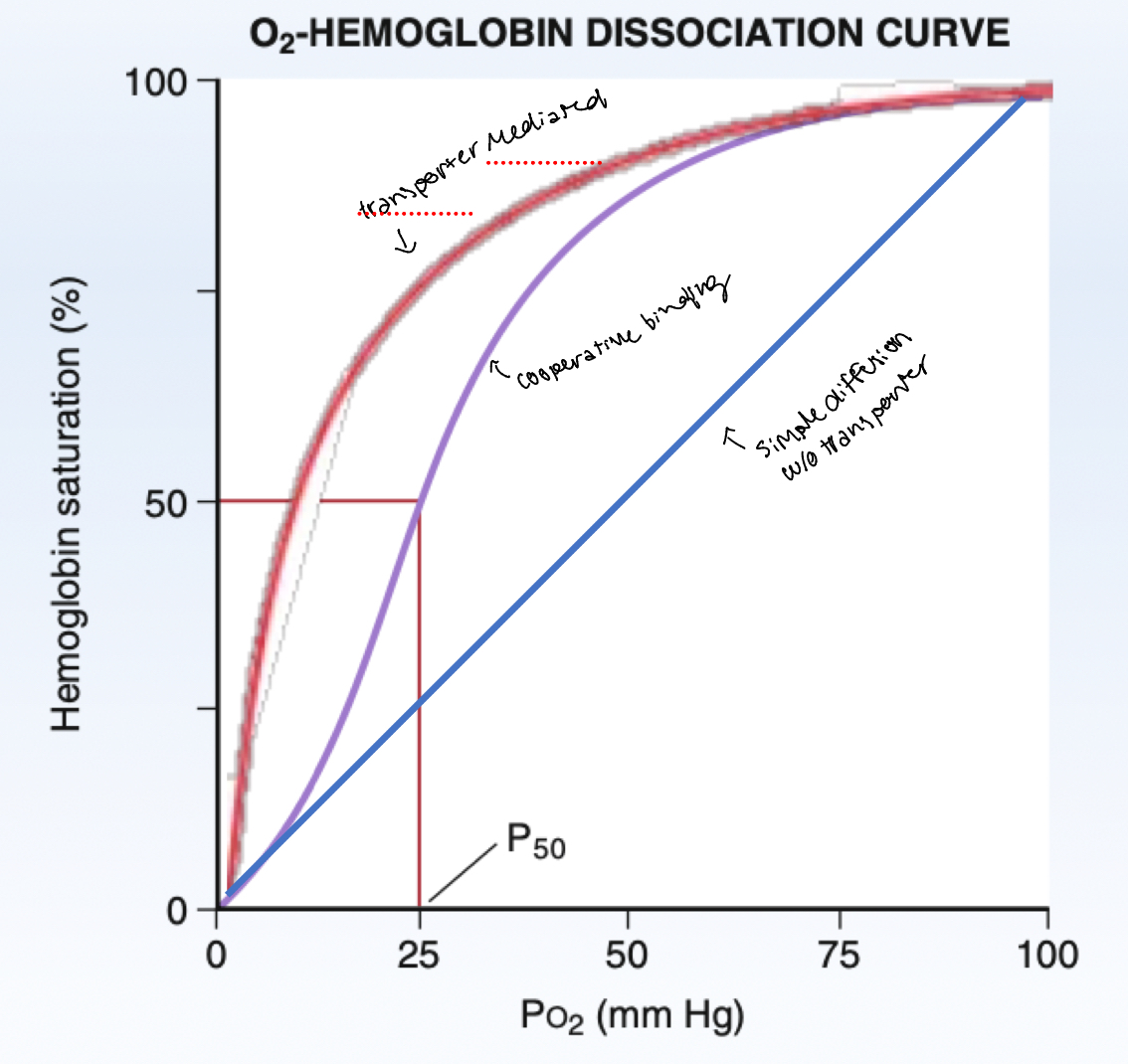
Cooperative binding is biologically
advantageous
1. Hemoglobin is at 75% saturation when it returns to the lungs, possessing the
highest affinity to O2 – perfect for O2 binding to Hgb at the lungs
2. When there is less O2 bound, Hgb’s affinity to O2 decreases, so more O2 will unbind. This is perfect for when you need to offload O2 quickly (think running away from tigers)
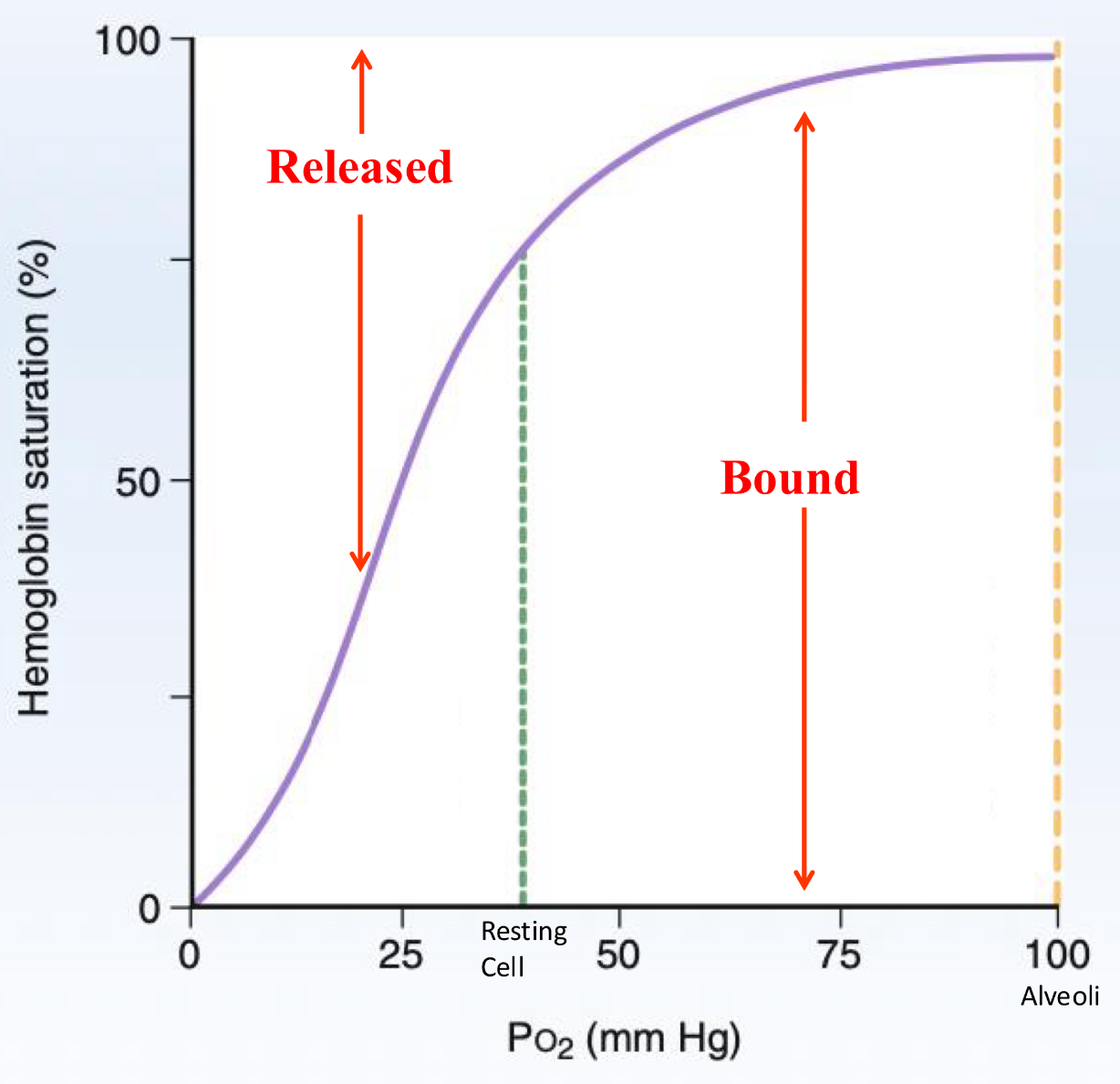
How do you unload O2?
Decrease Hb affinity to O2
Ex. When running
When do you need to change the affinity to O2 aka unload more O2?
Running away from tigers aka increased metabolic state in which you are using up lots of O2
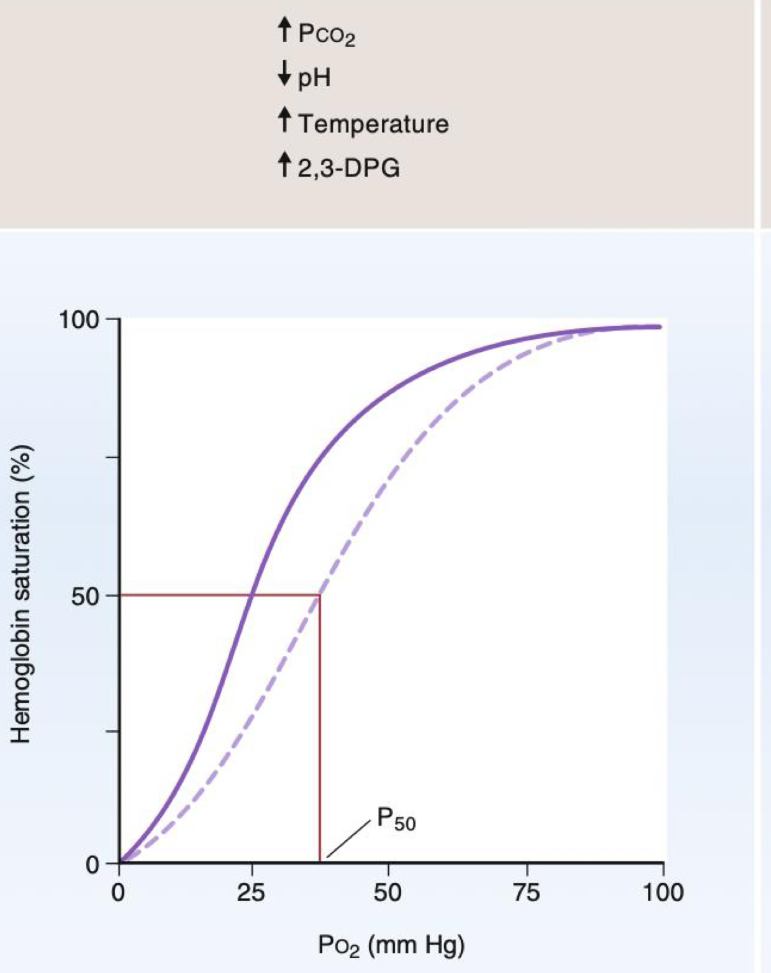
Metabolic byproducts
- CO2 (a byproduct of cellular respiration) when high low o2 affinity
- pH (H+ is a byproduct of CO2 breakdown)
- Temperature (a byproduct of muscle movement) when high low o2 affinity
- 2,3 BPG (a byproduct of metabolism)
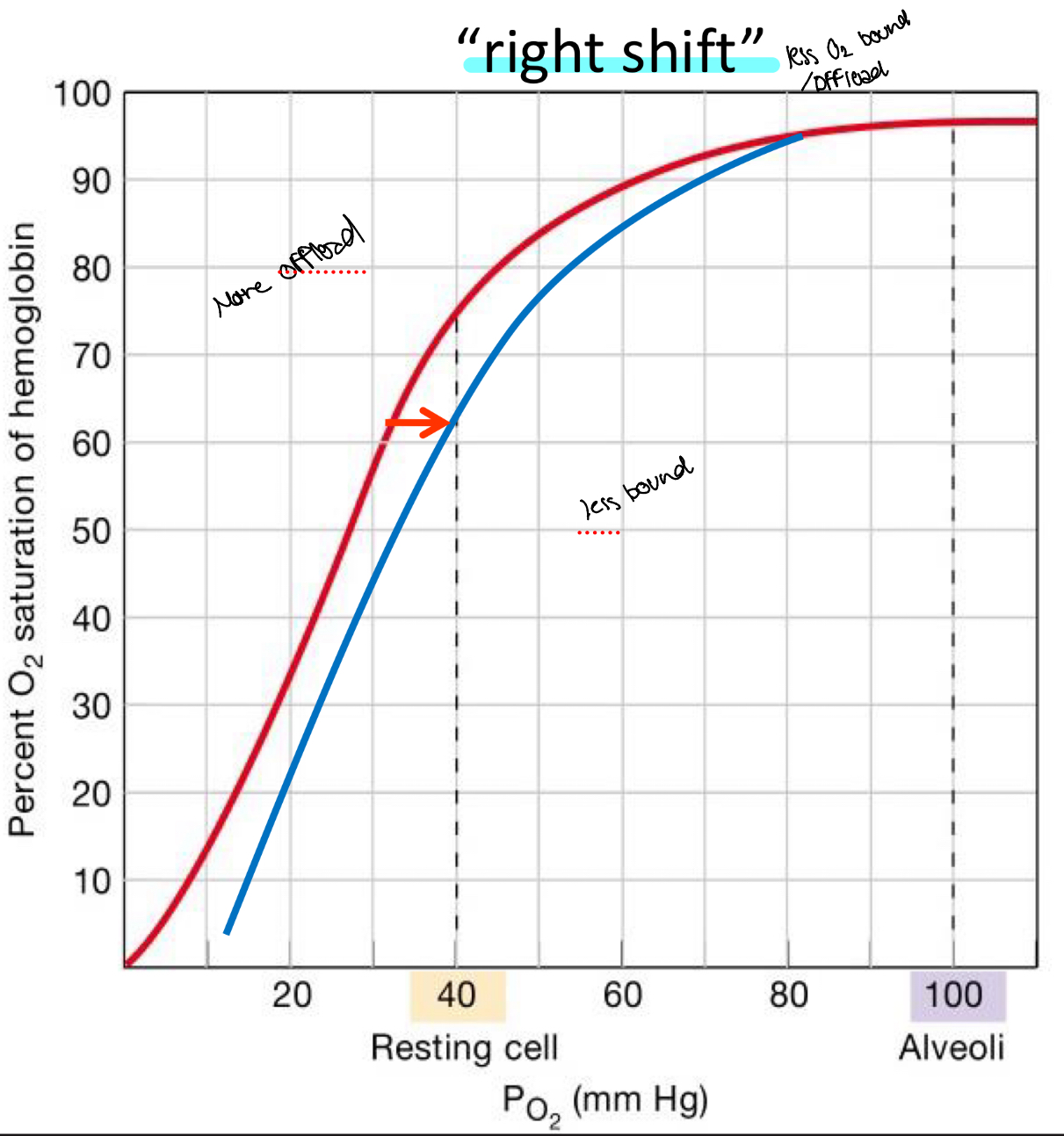
Factors that decrease affinity of Hb for O2 cause
Offload o2
You want less affinity to O2 when in a metabolically demanding state so you can unload more O2
↑ Metabolic byproducts
- ↑ CO2 (a byproduct of cellular respiration)
- ↓ pH (H+ is byproduct of CO2 breakdown)
- ↑ Temperature (a byproduct of muscle movement)
- ↑ 2,3 BPG (a byproduct of metabolism)
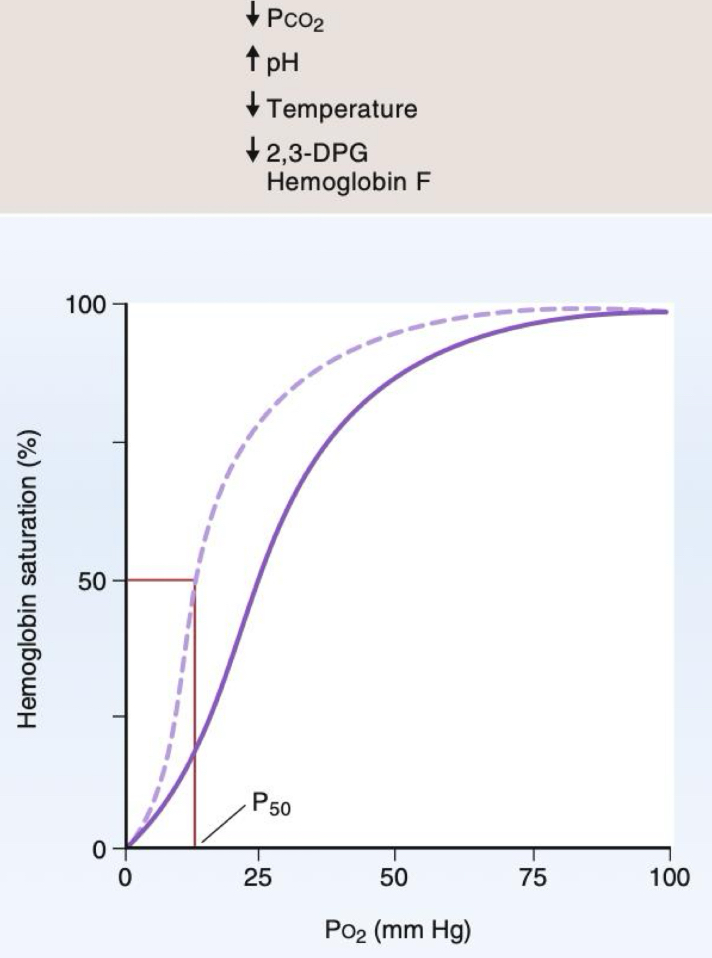
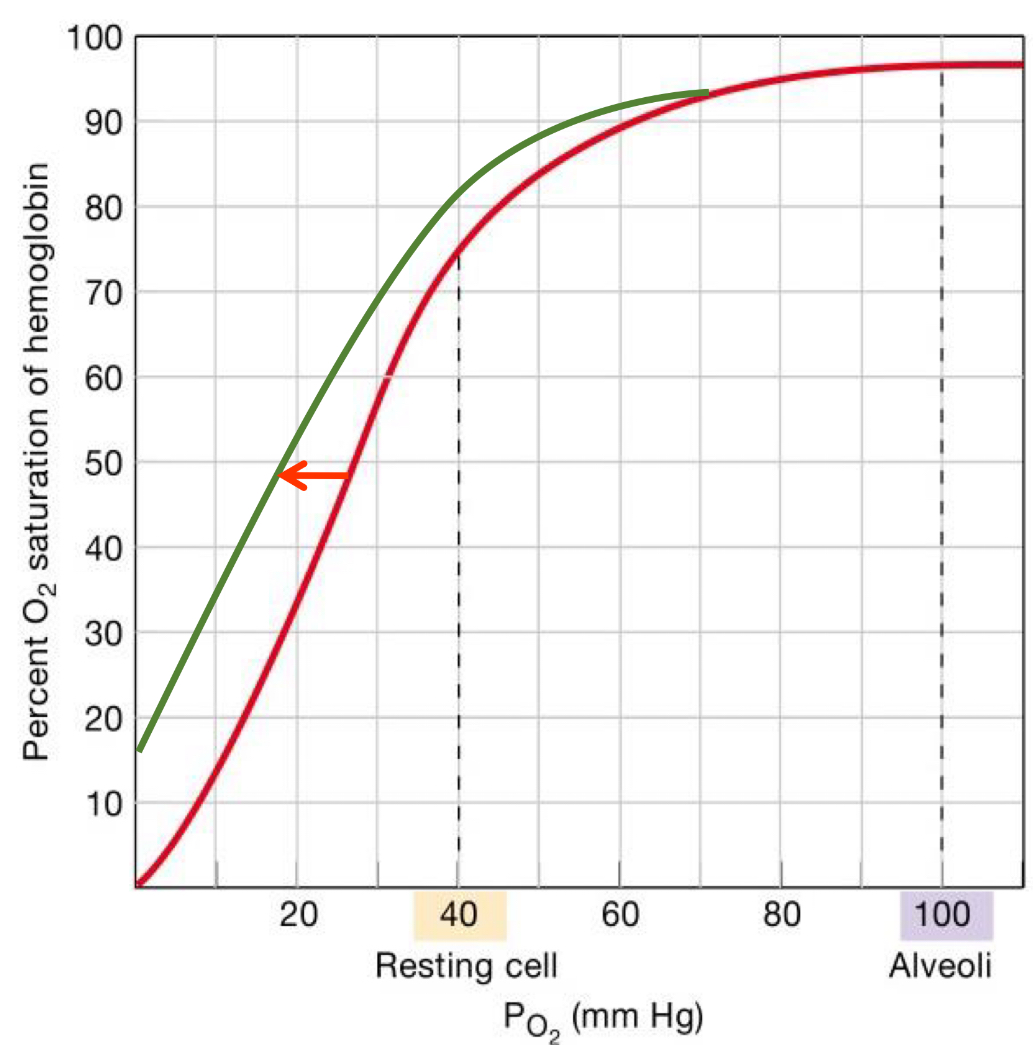
A left shift means more bound, increased affinity
Hypothermia low t
Alkalosis low hydrogen
Hypocapnia low co2
Anaerobic metabolism no o2
Shift to right
Shift to left