Ap micro 4 and 5
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Market Failure
Inability of a market to bring about the allocation of resources that best satisfies the wants of society; involving under or over allocation due to externalities.
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer and producer surplus, also known as social surplus.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for an additional unit and its market price.
Producer Surplus
The difference between the actual price a producer receives and the minimum acceptable price.
Efficient Markets
Markets where resources are allocated in a way that maximizes total surplus, reflecting product and allocative efficiency.
Productive Efficiency
Production of a good in the least costly way, occurring at the output level where per-unit costs are minimized.
Allocative Efficiency
Apportionment of resources among firms to maximize the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
Efficiency Losses (Deadweight Losses)
Reductions in combined consumer and producer surplus due to underallocation or overallocation of resources.
Externalities
Costs or benefits from production or consumption that affect third parties outside the transaction.
Negative Externalities
Costs imposed on third parties by the production or consumption of goods, without compensation.
Positive Externalities
Benefits obtained by third parties from the production or consumption of goods, without compensation.
Government Intervention
Actions taken by the government to correct market failures, particularly related to externalities.
Pigovian Tax
A tax levied on the production of a product that generates negative externalities, aimed at reducing overproduction.
Public Goods
Goods characterized by nonrivalry and nonexcludability, typically provided by the government due to their inefficiency in production by private sectors.
Free-Rider Problem
The inability of potential providers to obtain payment from users of a good because it is nonexcludable.
Quasi-Public Goods
Goods that have large positive externalities but could have excludability applied, often supported by government.
Government Failure
Inefficiencies in resource allocation due to problems in the public sector operations.
Principal-Agent Problem
Conflict of interest where agents pursue their own objectives at the expense of principals' goals.
Special-Interest Effect
When a small group benefits substantially at the expense of a larger group, often leading to inefficient political outcomes.
Rent-Seeking Behavior
Attempts by individuals or groups to gain benefits through political influence rather than productive economic activity.
Regulatory Capture
When a regulatory agency becomes dominated by the industry it is meant to regulate, leading to ineffective regulation.
Moral Hazard Problem
The risk that individuals will behave recklessly once they are insured against certain risks.
Adverse Selection Problem
When one party in a contract has more information than the other, leading to high risks for the less informed party.
Inadequate Buyer Information
Lack of information that results in underallocation of resources, such as unqualified individuals posing as professionals. (buyers not knowing enough information about the buyers)
Inadequate Seller Information
Situations where sellers lack necessary data about buyers, leading to reduced market activity.
Subsidies to Buyers
Government financial support to lower the cost of products/services to consumers.
Subsidies to Producers
Government financial support intended to decrease production costs and increase supply.
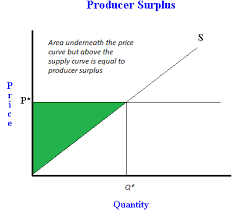
producer surplus
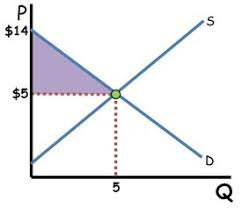
consumer surplus
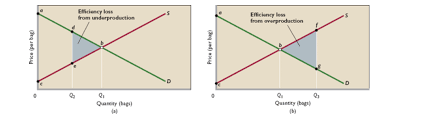
efficiency loss from underproduction and from overproduction
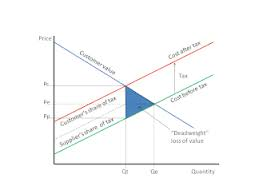
dead weight loss