L15 The Hypothalamus and Autonomic Control (Imported from Quizlet)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
11
How many major nuclei are in the hypothalamus?
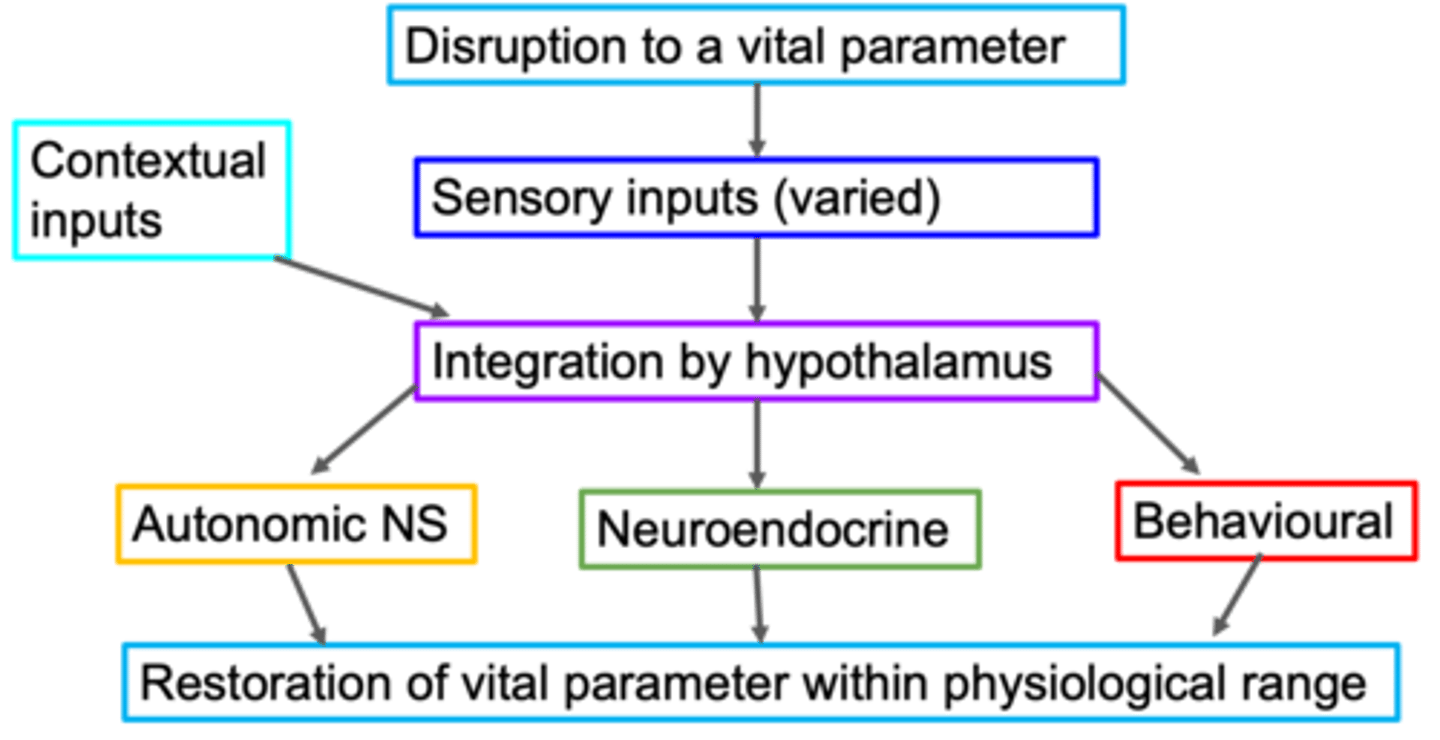
Homeostasis
What is the hypothalamus the master regulator of?
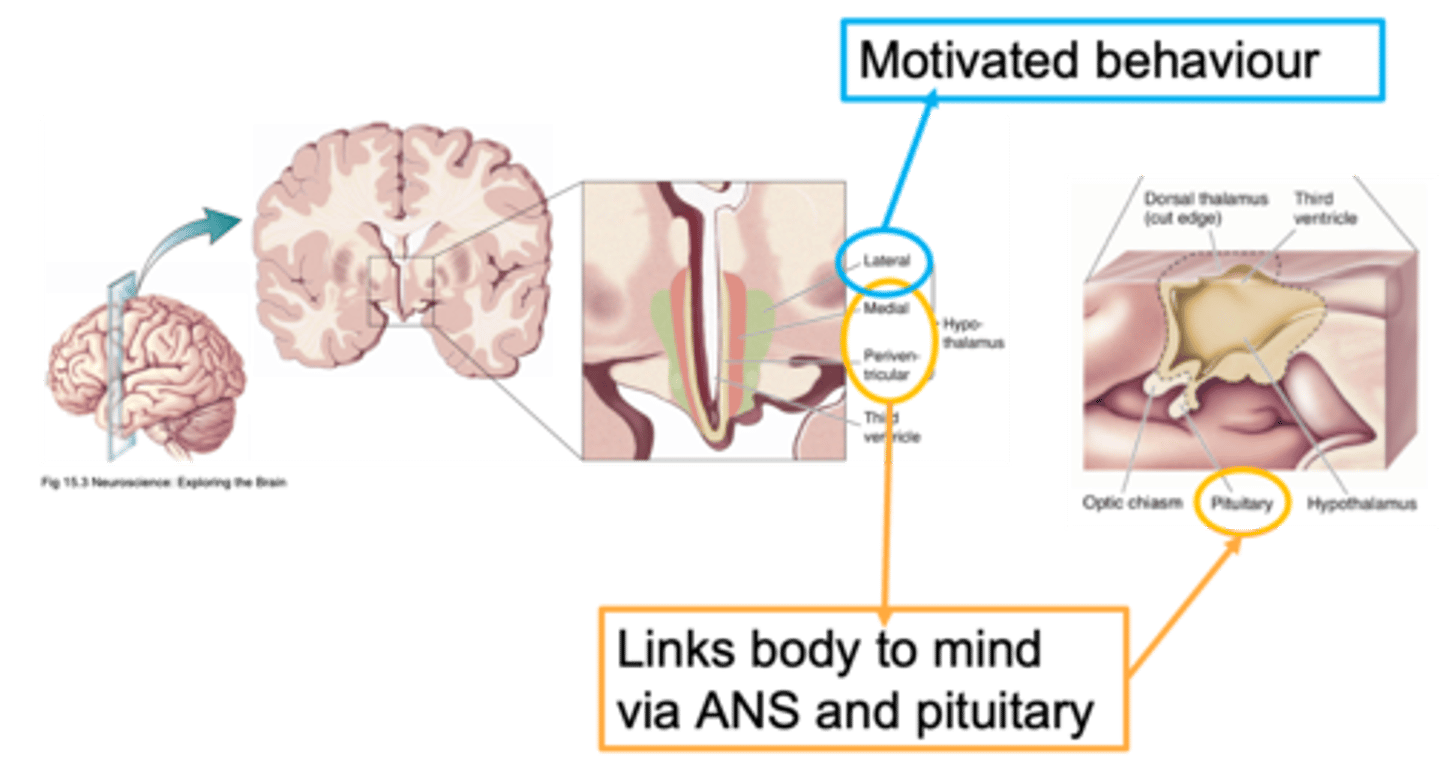
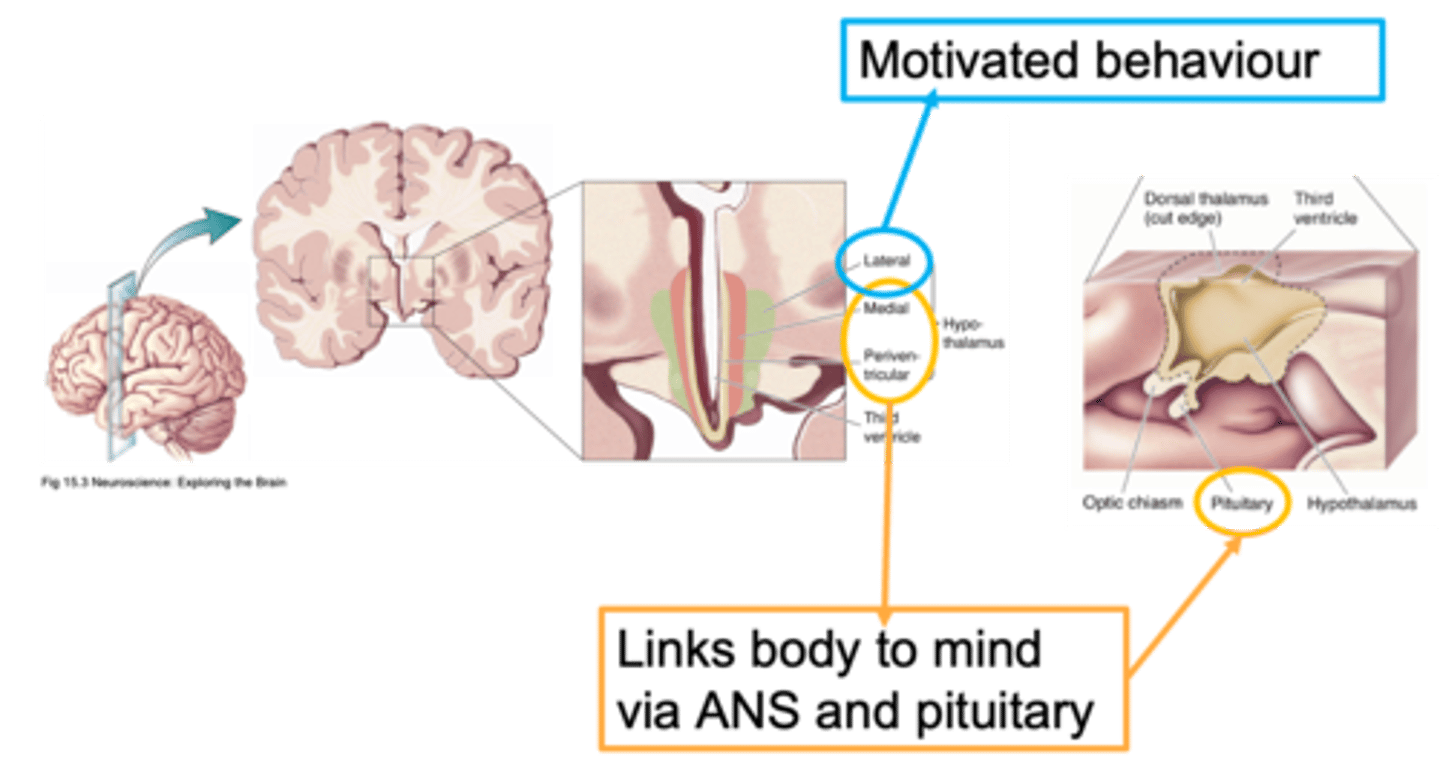
Lateral, medial, periventricular
Ways to distinguish areas of the hypothalamus is through defining it as __________, _________ or ________________
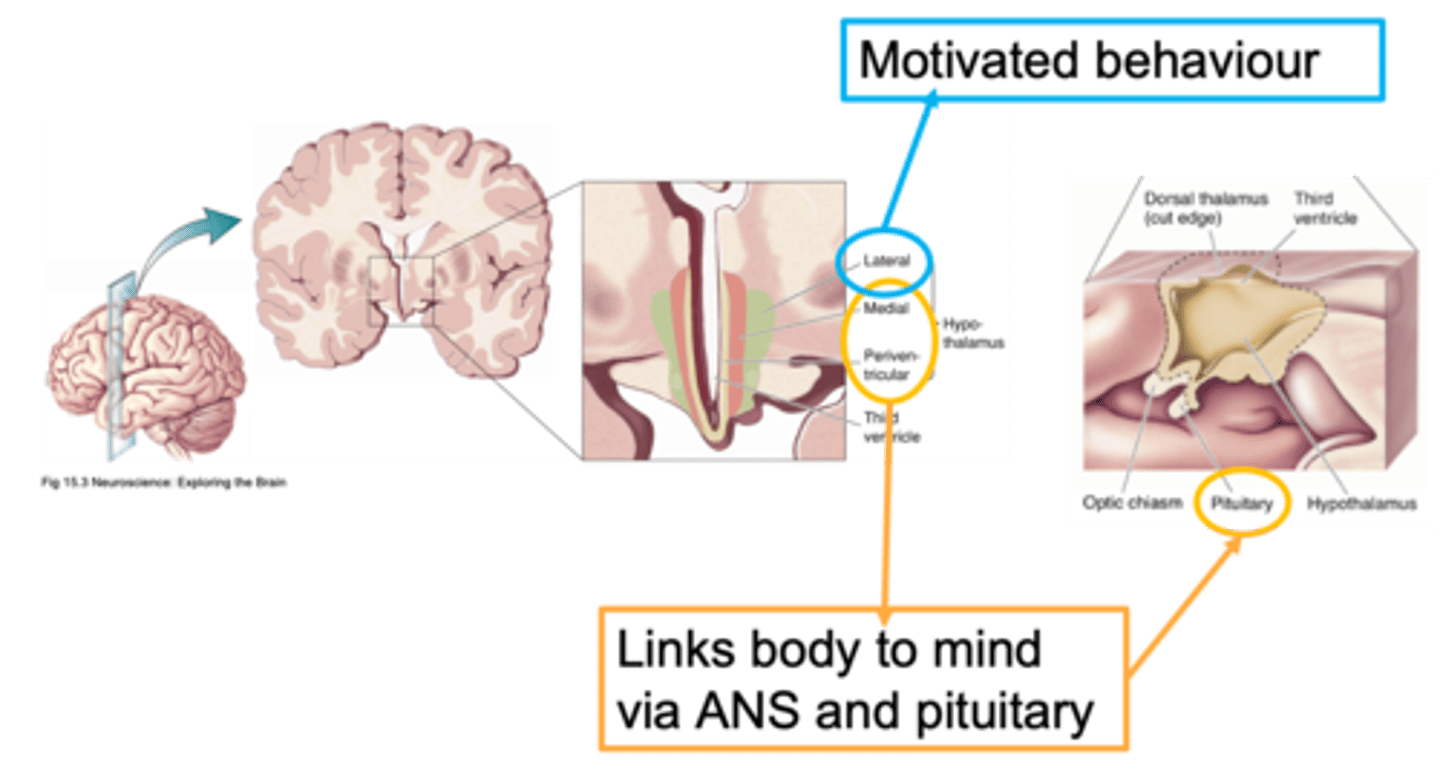
Close to the outside of the brain
What does lateral mean?
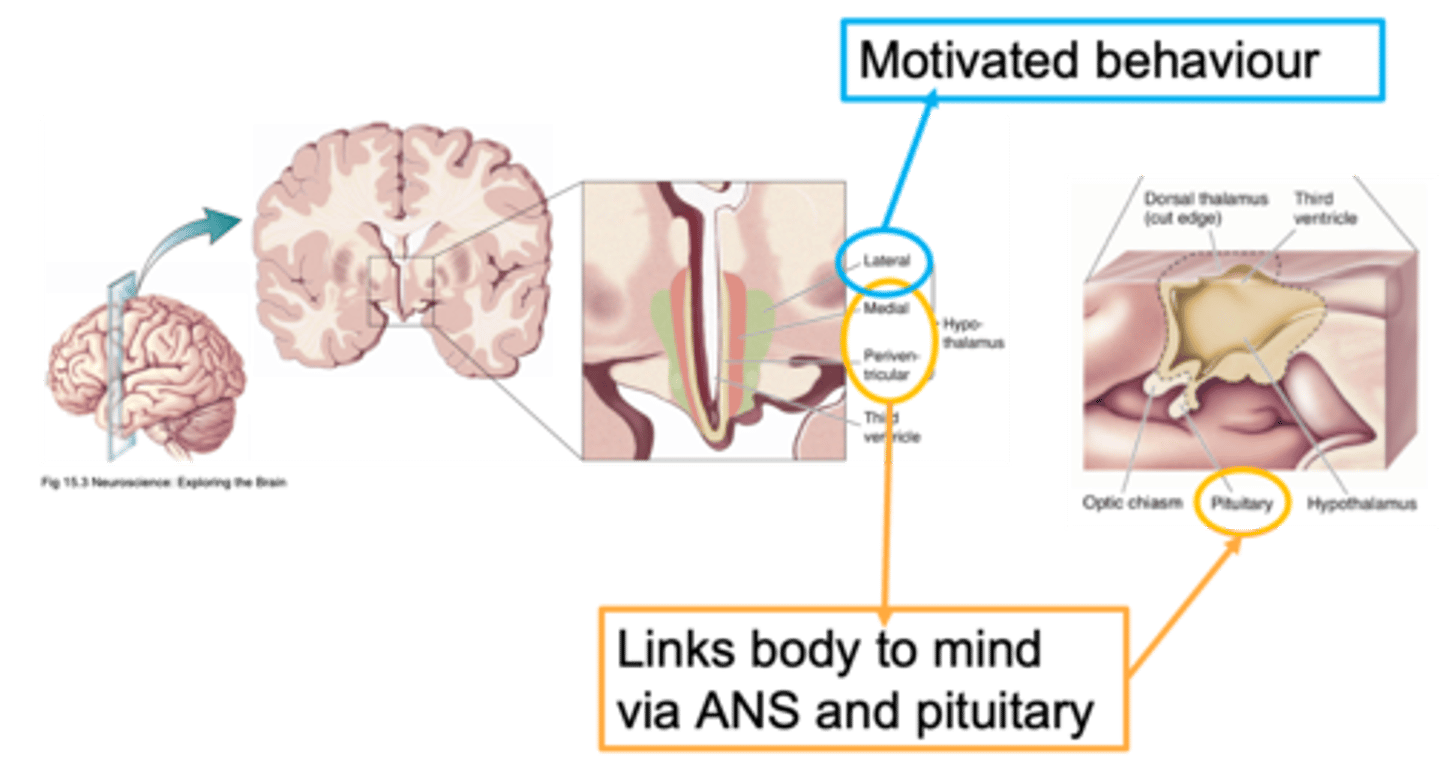
Closer to the midline
What does medial mean?
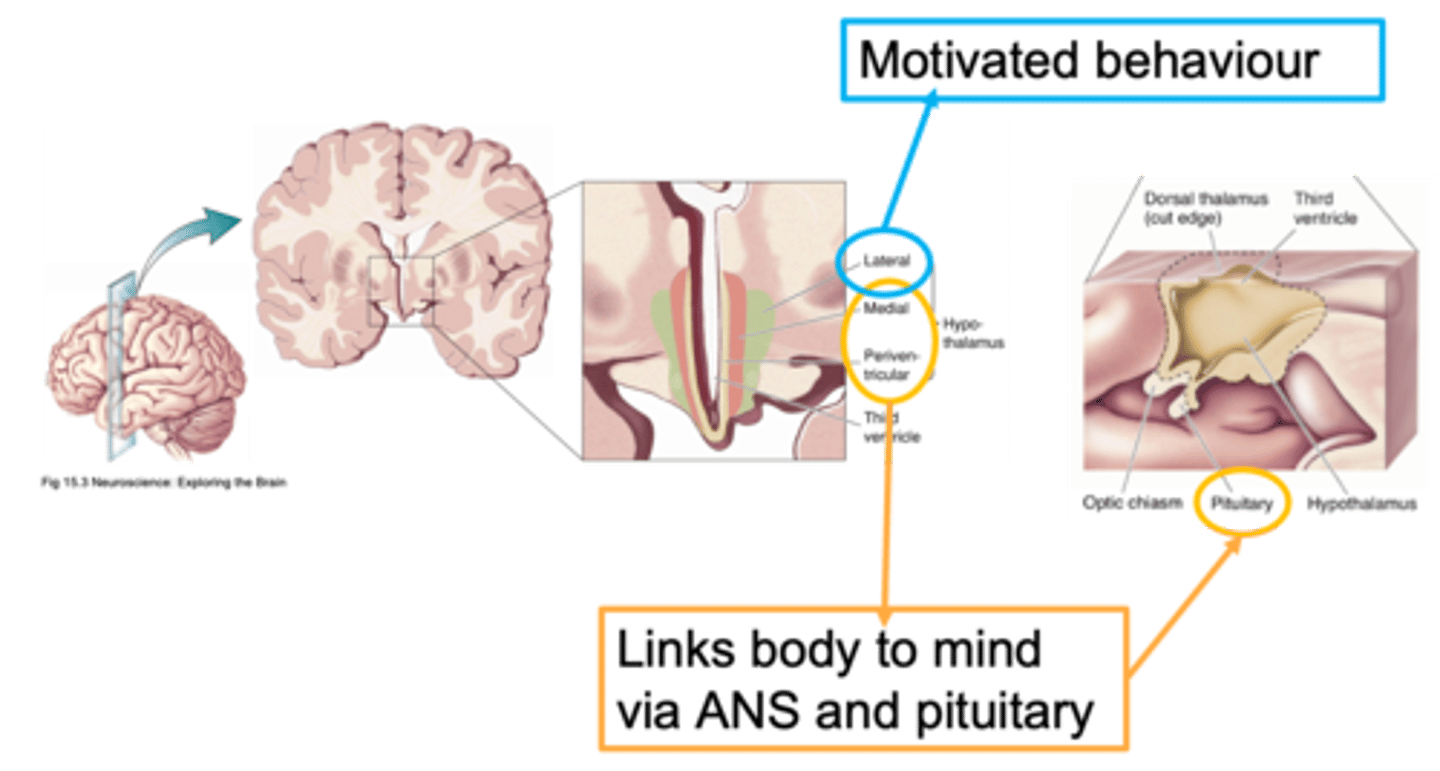
Regions that are adjacent/next to the ventricle
What does periventricular mean?
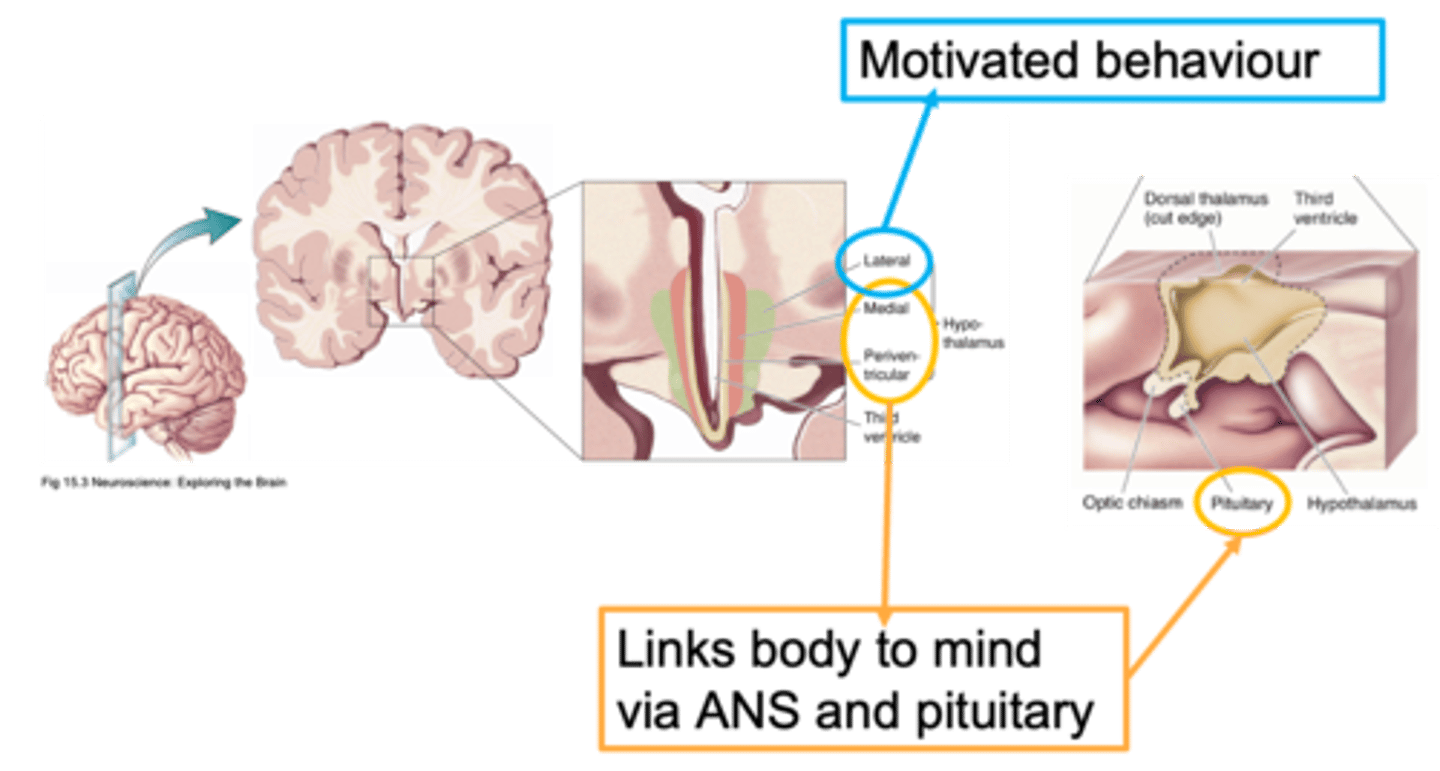
Homeostasis
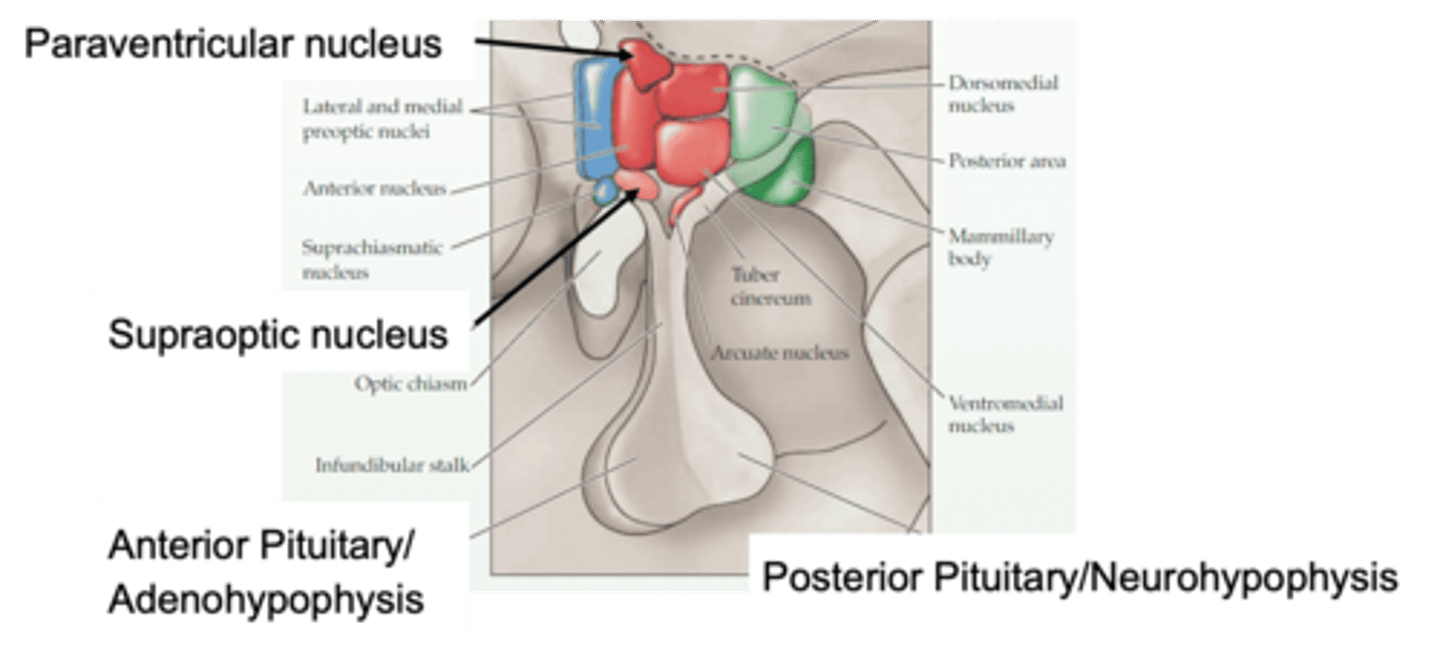
Nuclei of the hypothalamus
What does this image show?
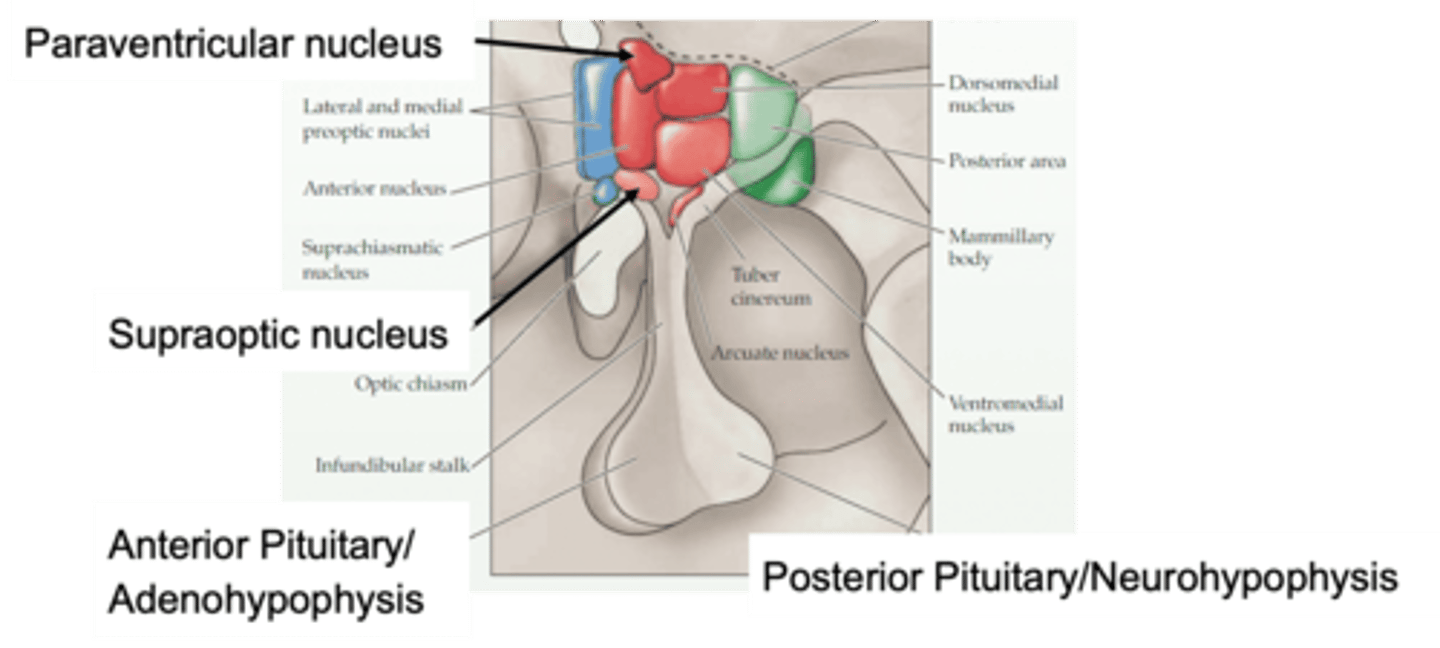
ANS, neuroendocrine
The paraventricular nucleus can be involved in both _____ and ___________________ responses
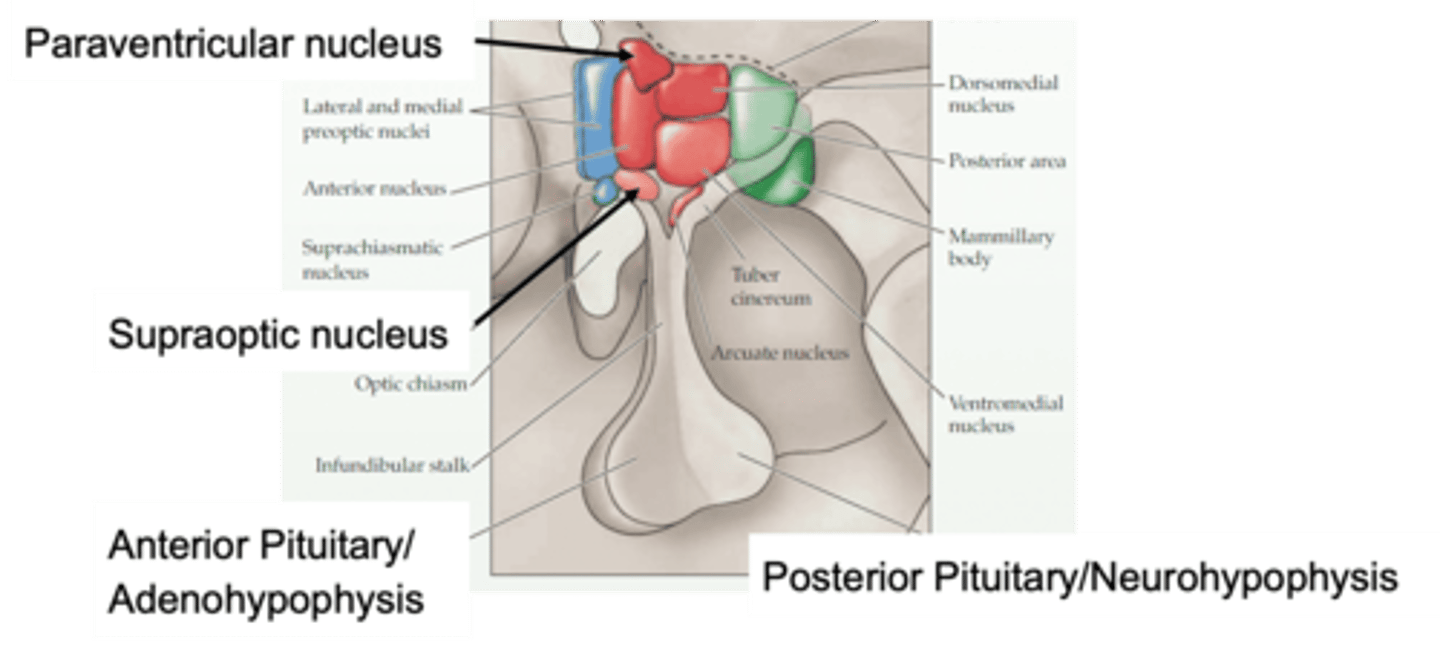
Down the middle
What is a sagittal section?
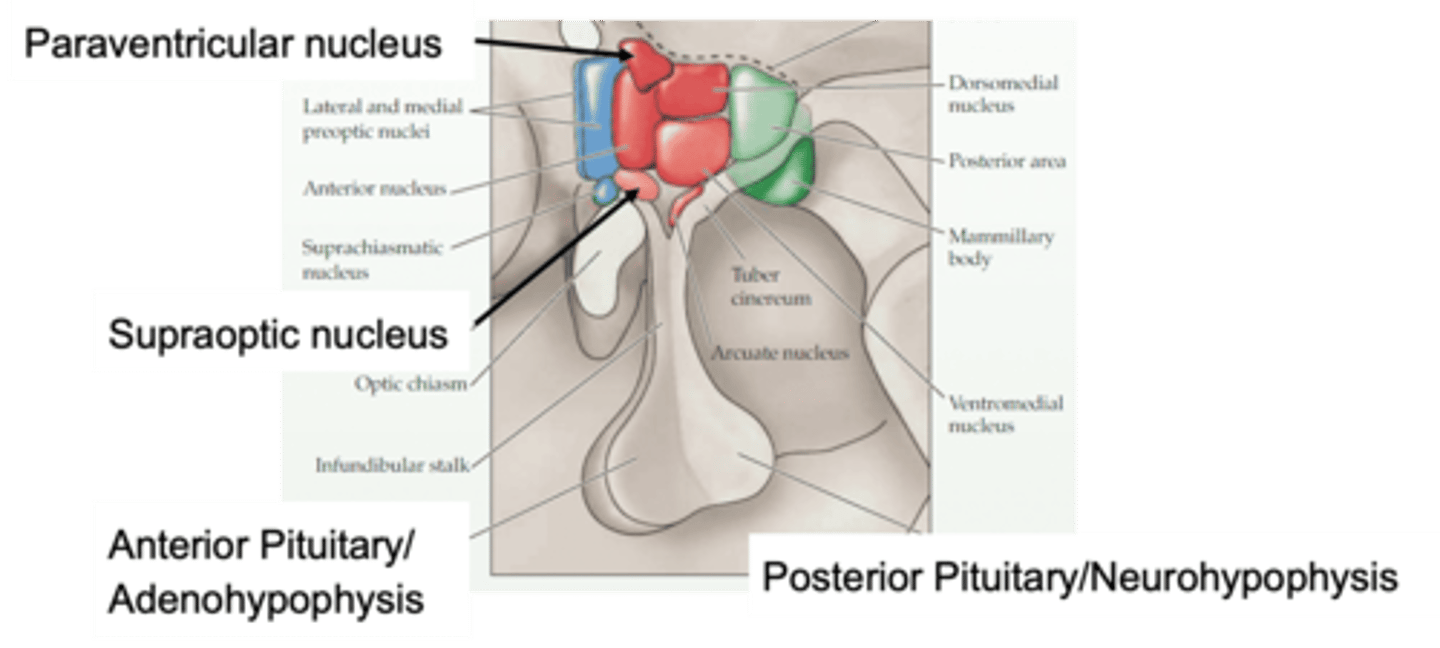
Important for the hypothalamus in terms of this function in homeostasis
Why is the paraventricular nucleus important?
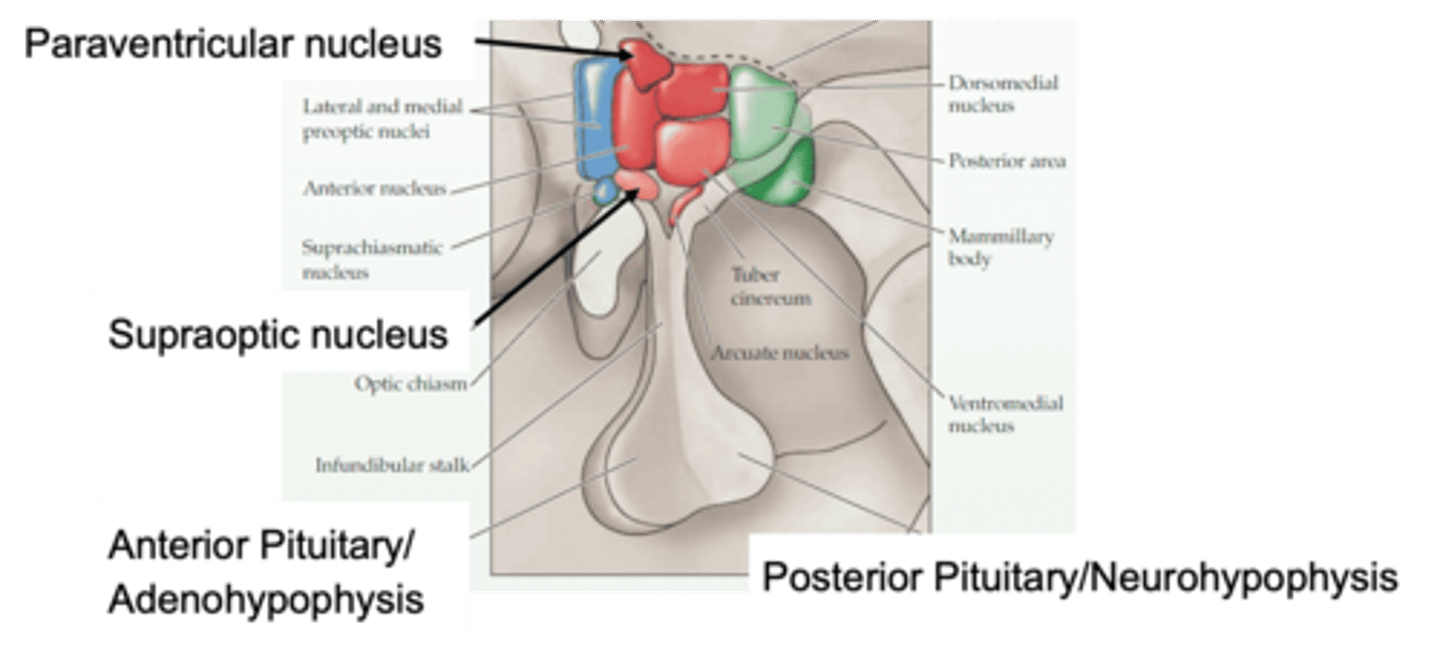
Pituitary stalk
The hypothalamus is linked to the pituitary by a _______________ ______ (infundibular stalk)
Anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) and posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis)
The pituitary stalk splits the pituitary into 2 different areas, what are they?
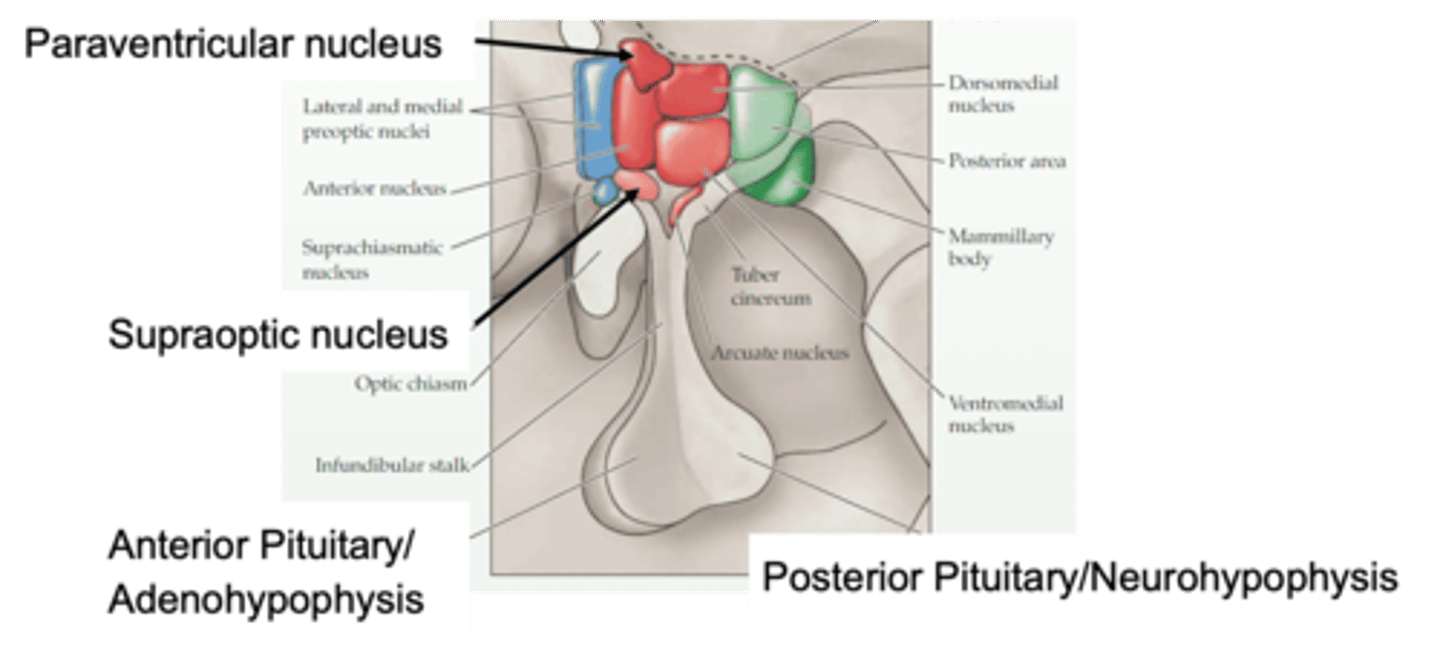
Neurohypophysis is down growth from the CNS and is actually part of the nervous system tissue developmentally
Adenohypophysis is grown upwards from a different region so its not neural tissue
Why do the neurohypophysis and adenohypophysis have different names other than being anterior and posterior?
Hormone releasing cells
What are troph cells?
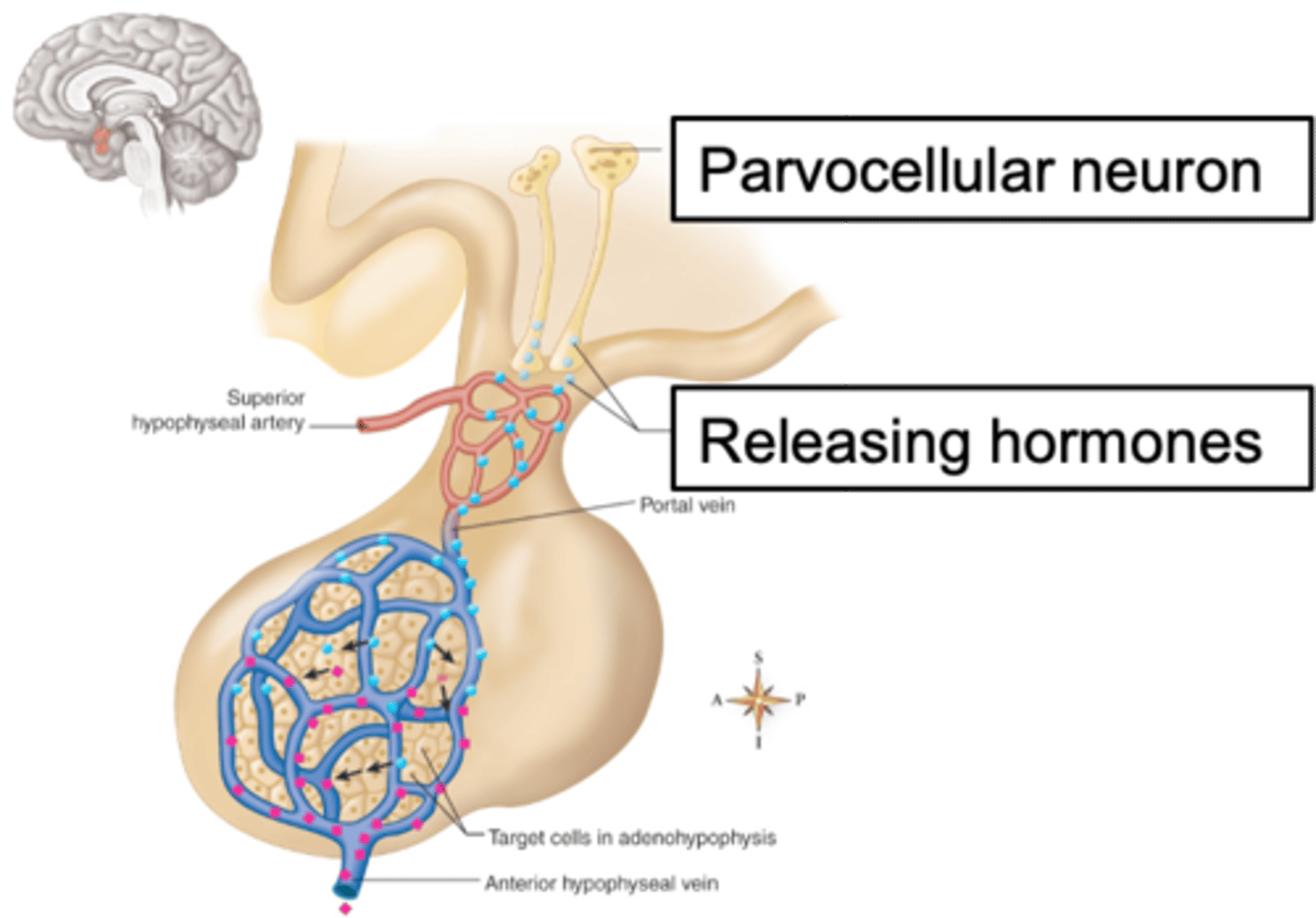
Troph cells, hormones, parvocellular
Adenohypophysis has _______ _______ stimulated by releasing ____________ from ______________ neurons of the hypothalamus
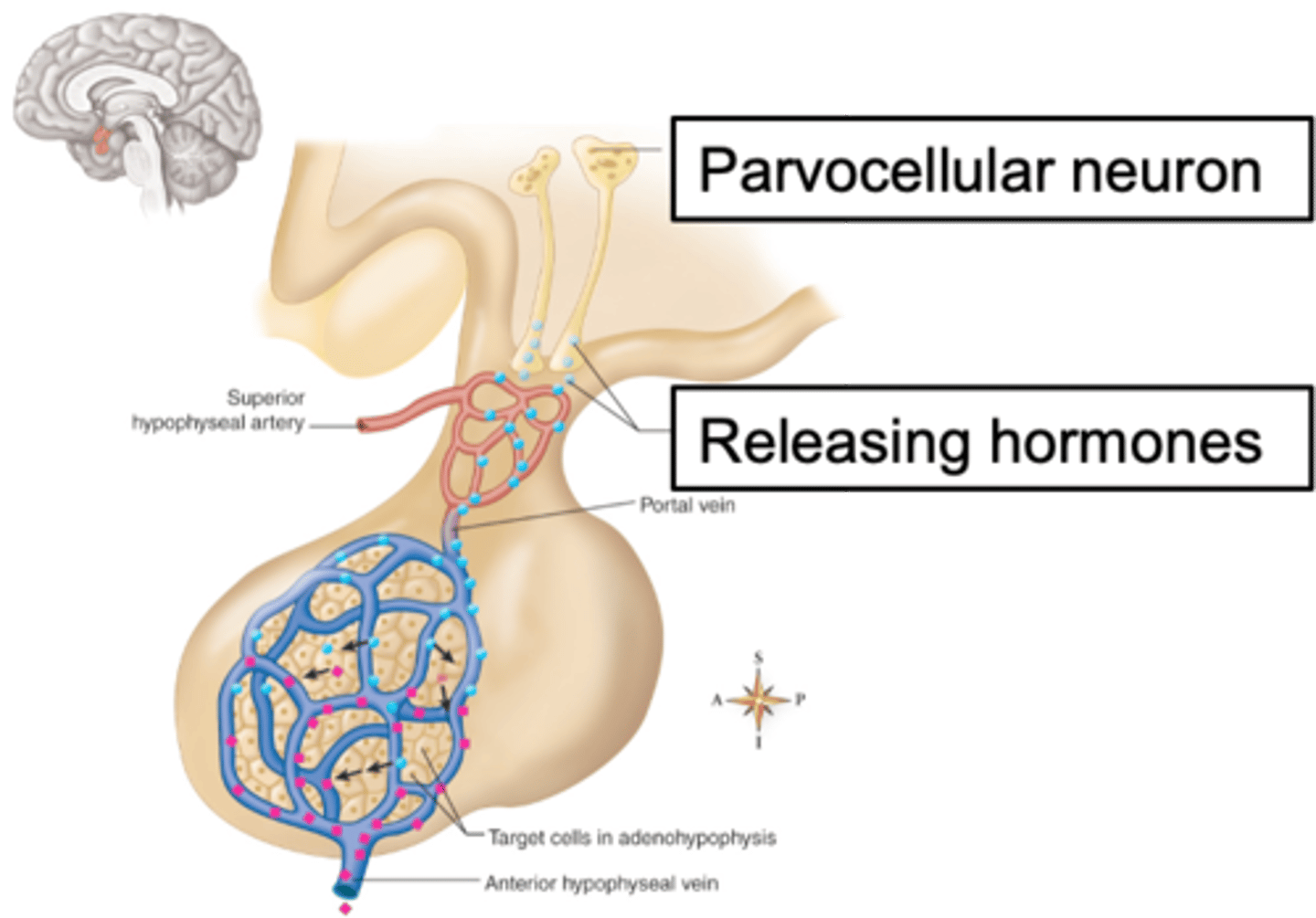
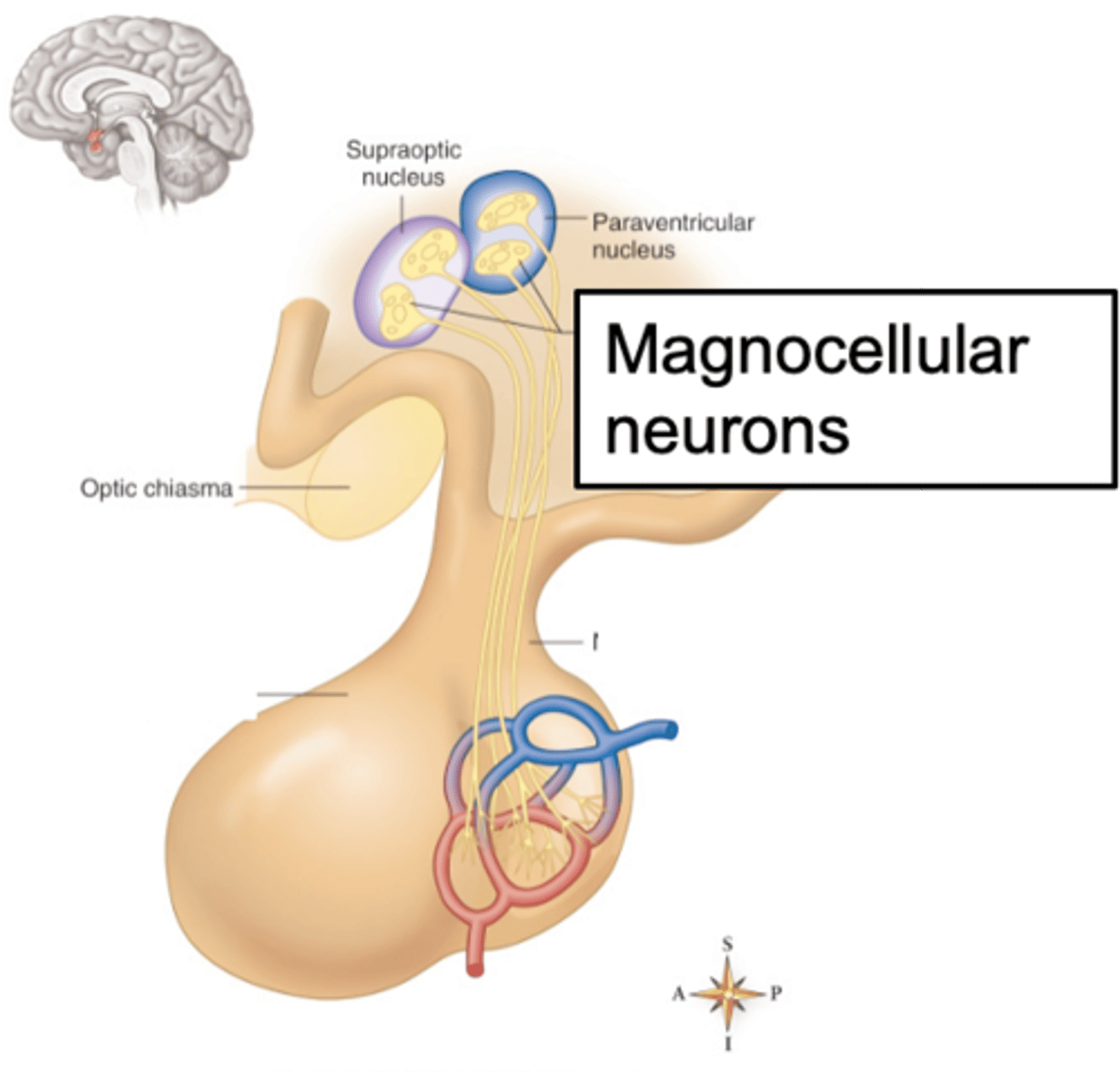
Magnocellular, systemic circulation
Neurohypophysis releases hormones from the ________________ neurons directly into ____________ ___________
Blood from one tissue to another without returning to heart or lungs
What is a portal system?
Stimulating effect on other hormones
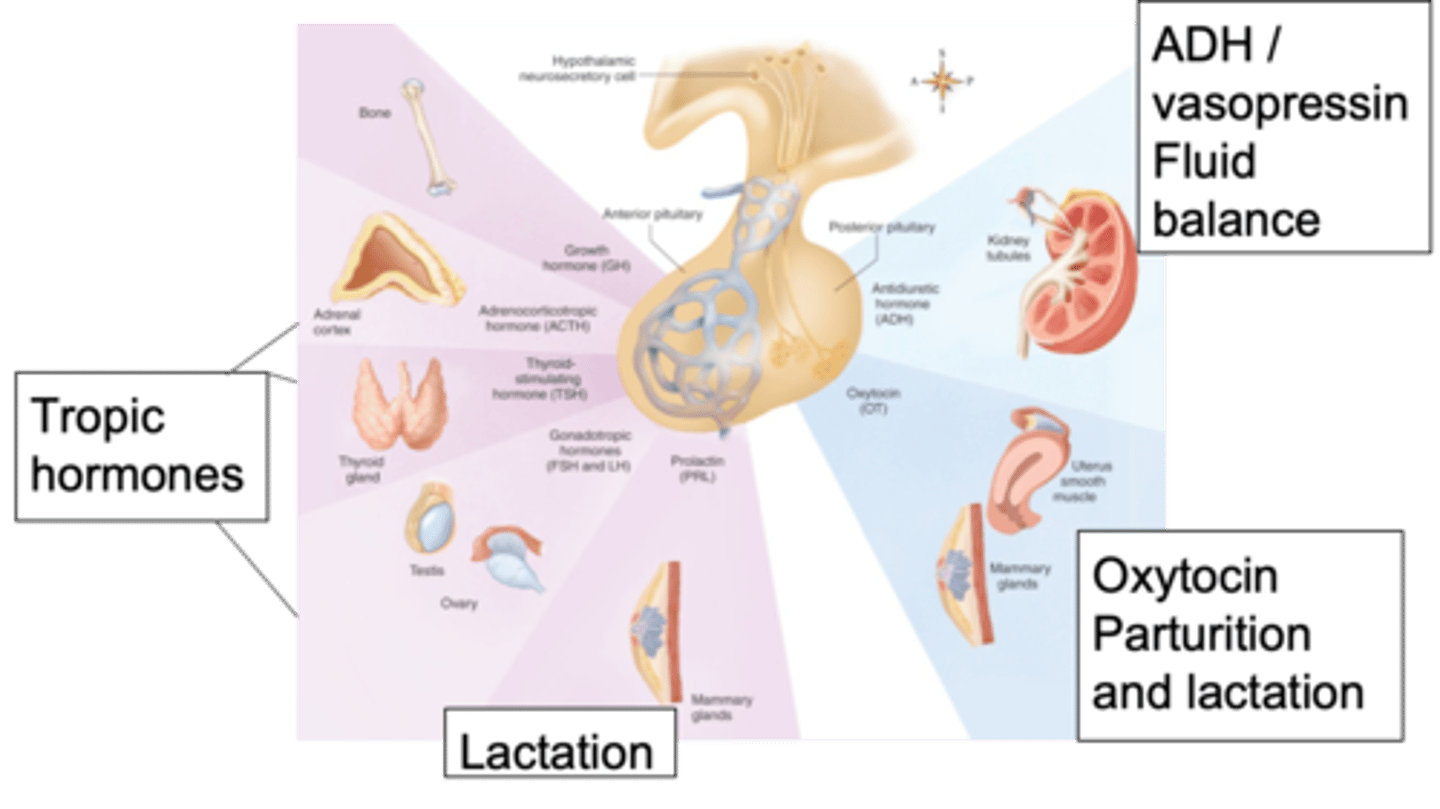
This image shows the major pituitary hormone, what are tropic hormones doing?
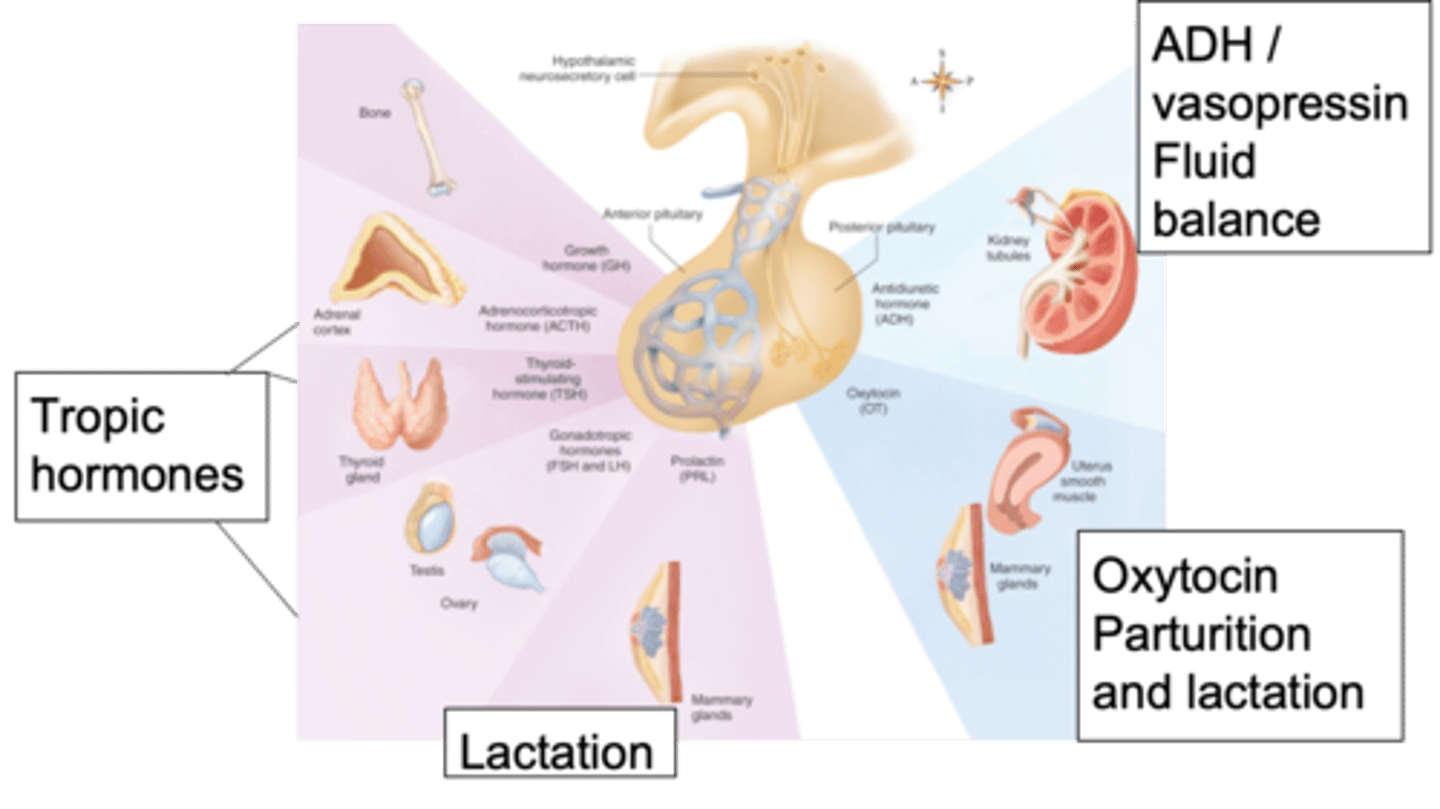
Growth hormones released through Troph cells
Adrenal corticotropic hormone which initiates the release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex
Thyroid stimulating hormones will stimulate the release of thyroid hormones
Gonadotropin hormones go on to stimulate the release of hormones from the testes
Prolactin which affects the mammary glands
Looking at the anterior pituitary, tropic hormones will affect things like growth - name some hormones and their effects
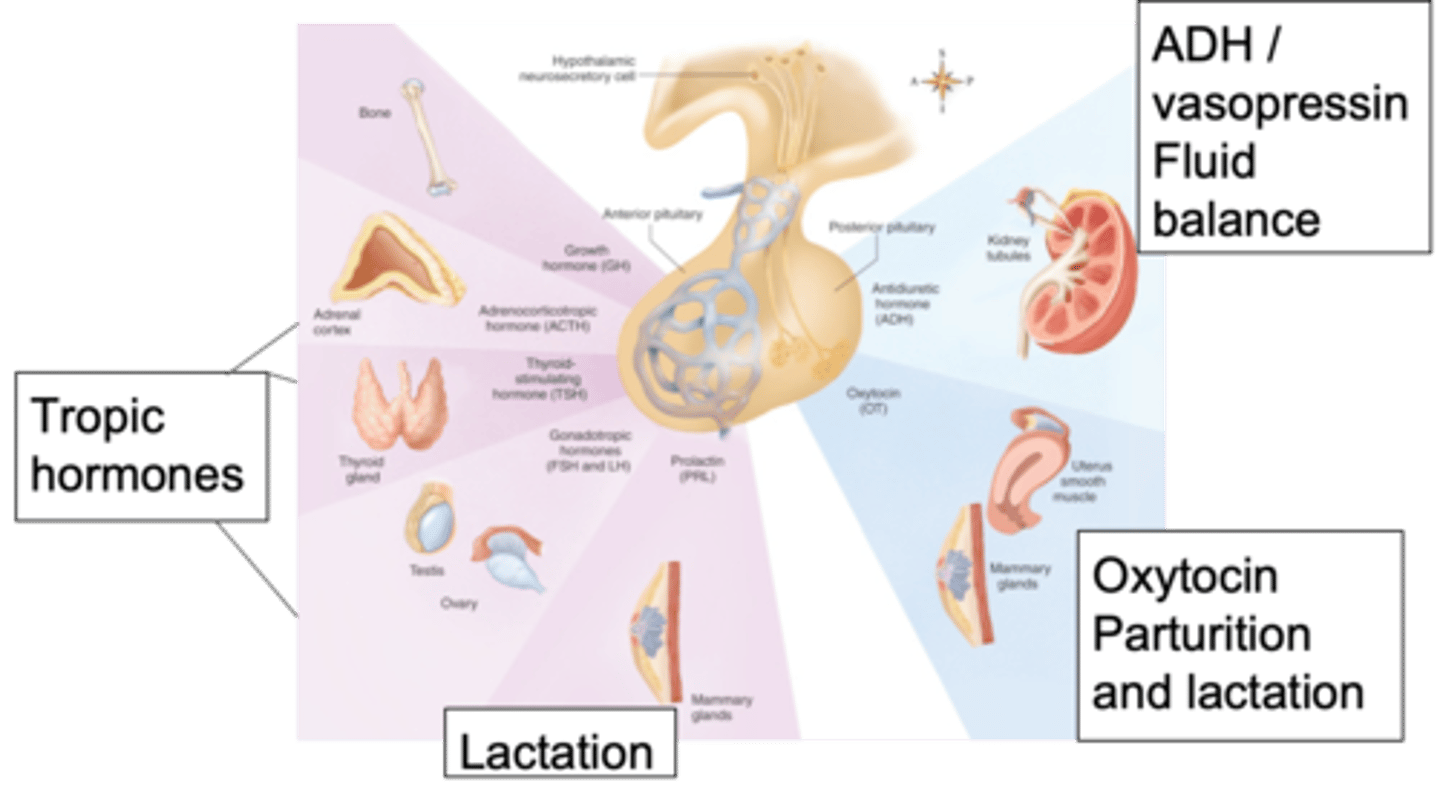
Metabolism in the thyroid, stress response through cortisol, growth or different menstrual cycles and production of things within the reproductive system
The hypothalamus through the pituitary gland is capable of influencing what?
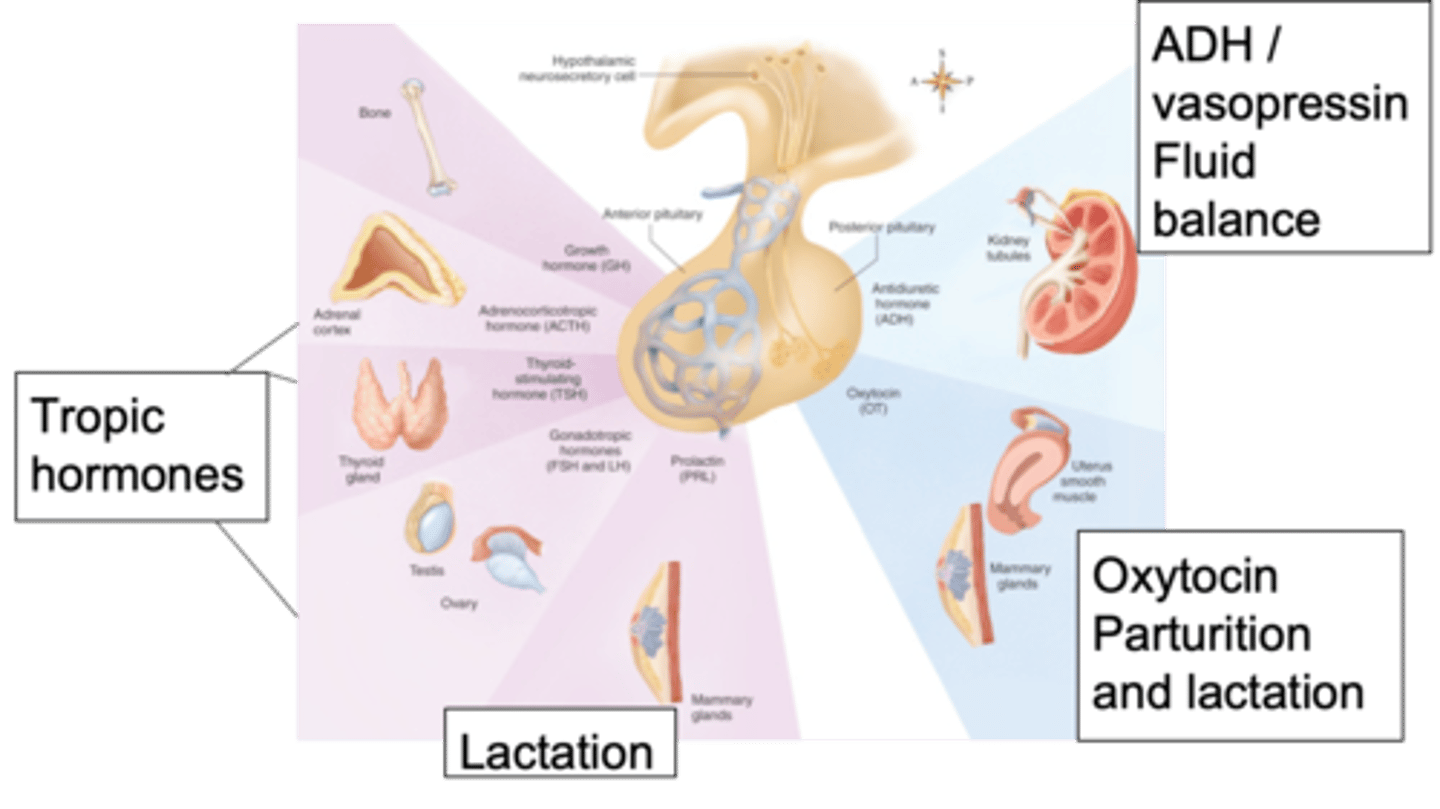
Anti-diruetic hormone (vasopressin), oxytocin
Looking at the posterior pituitary, we have 2 important hormones - what are they?
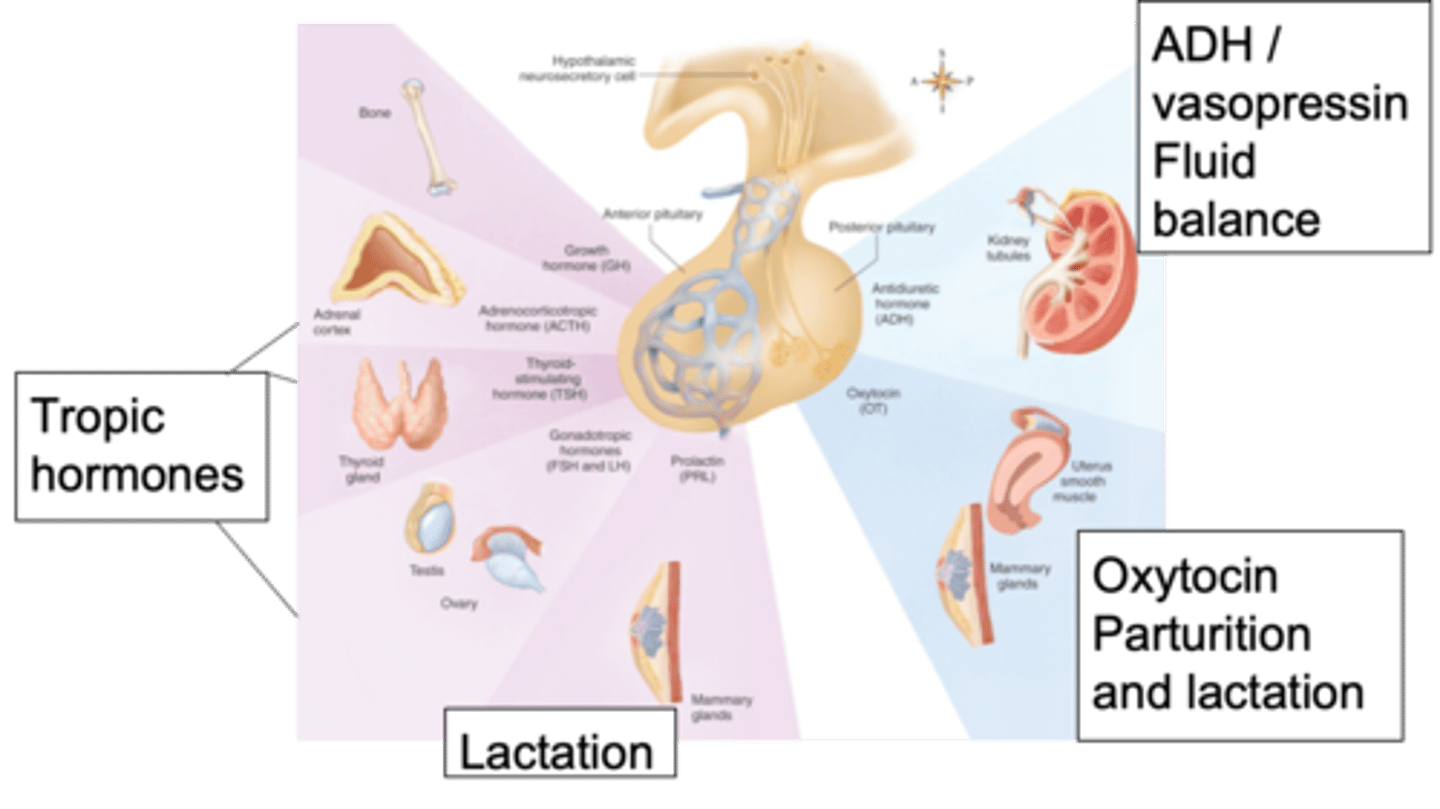
Fluid balance, maintaining the right volume in the blood and the right osmolality
What role does the anti-diuretic (vasopressin) hormone play?
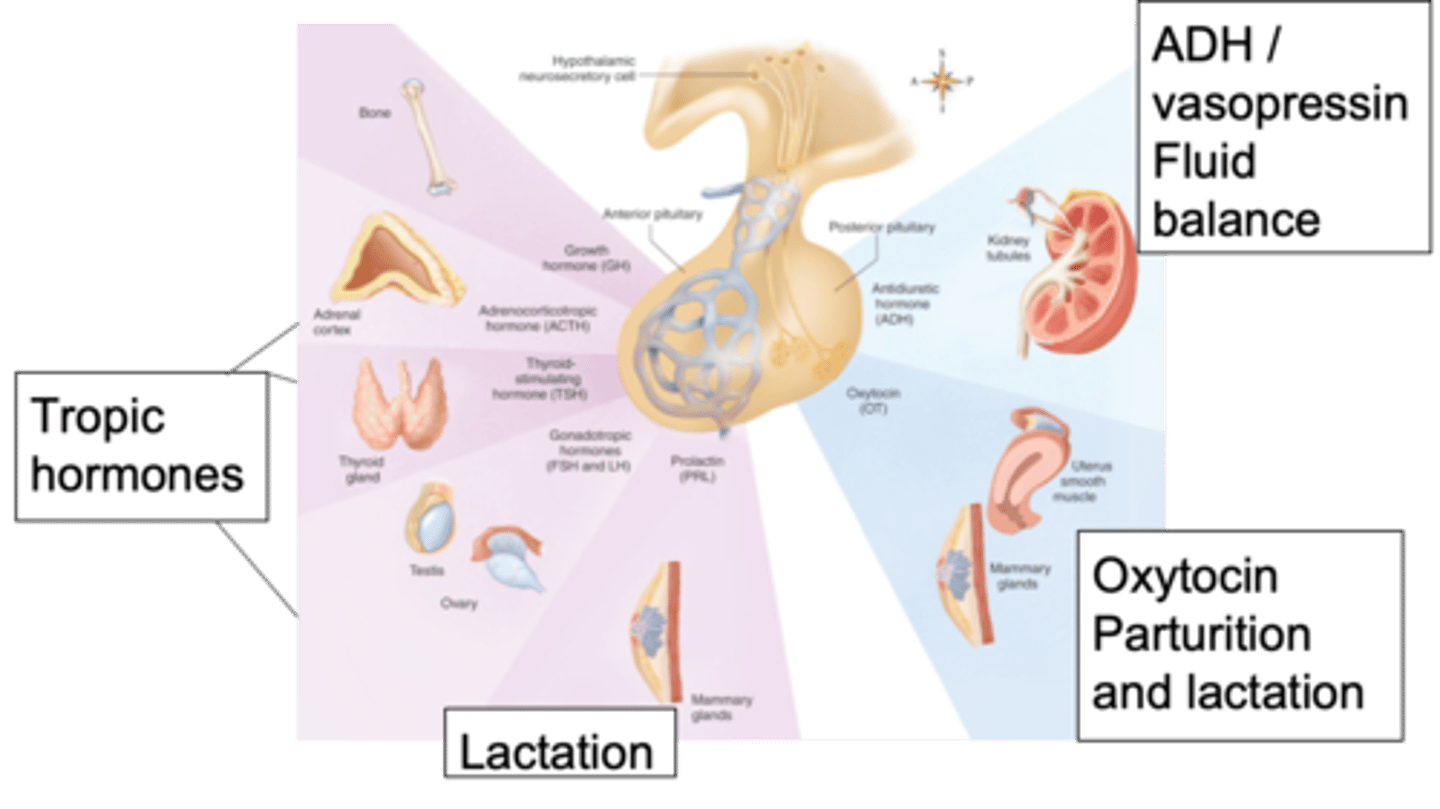
Parturitions (birth) and lactation, involvement in emotions and strength of relationships built between people
What role does oxytocin play and what is it involved in?
Involuntary
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is ____________
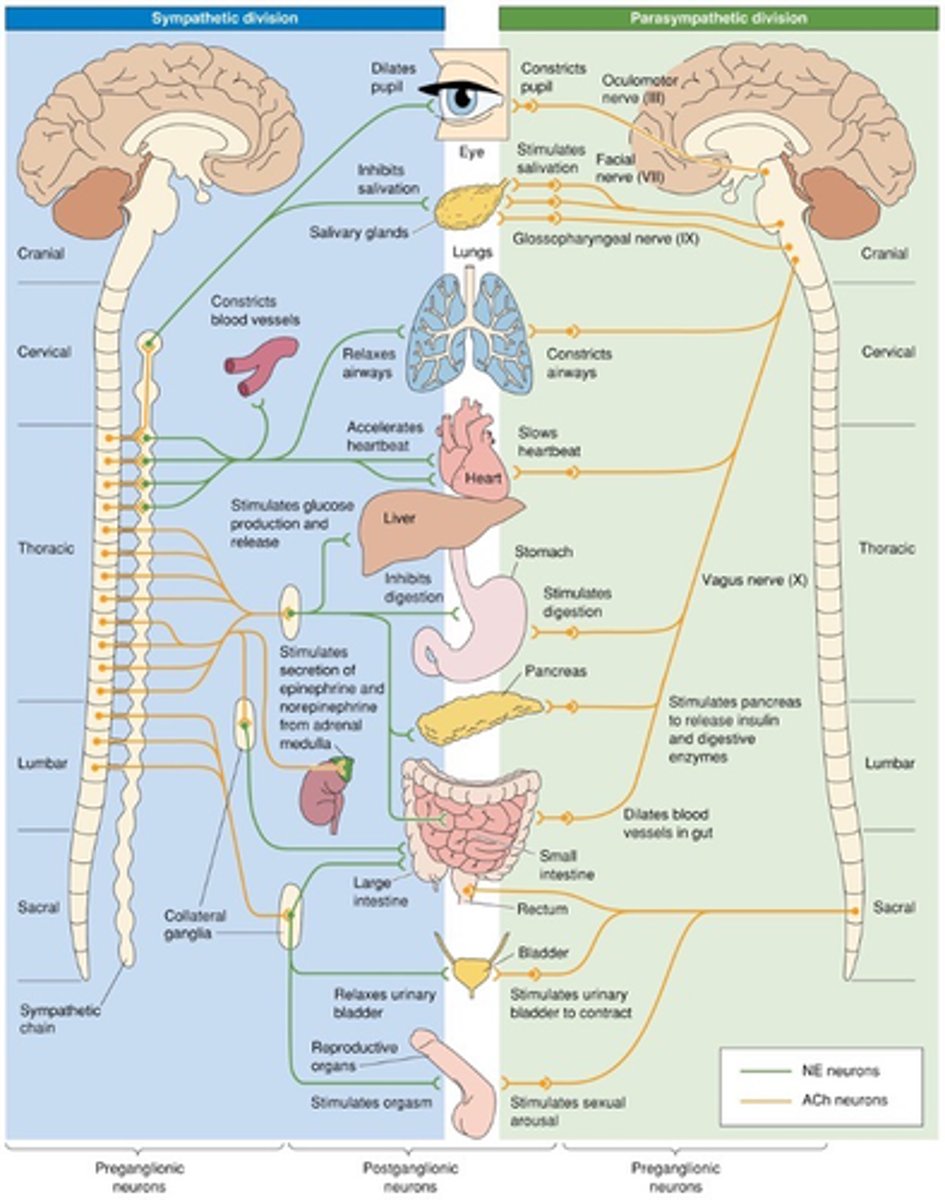
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
What are the 2 efferent pathways of the ANS?
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands (generally innervate the same tissue but normally have opposing effects)
What are the 3 innervate effectors of the ANS?
The hypothalamus
The ANS can function without what?
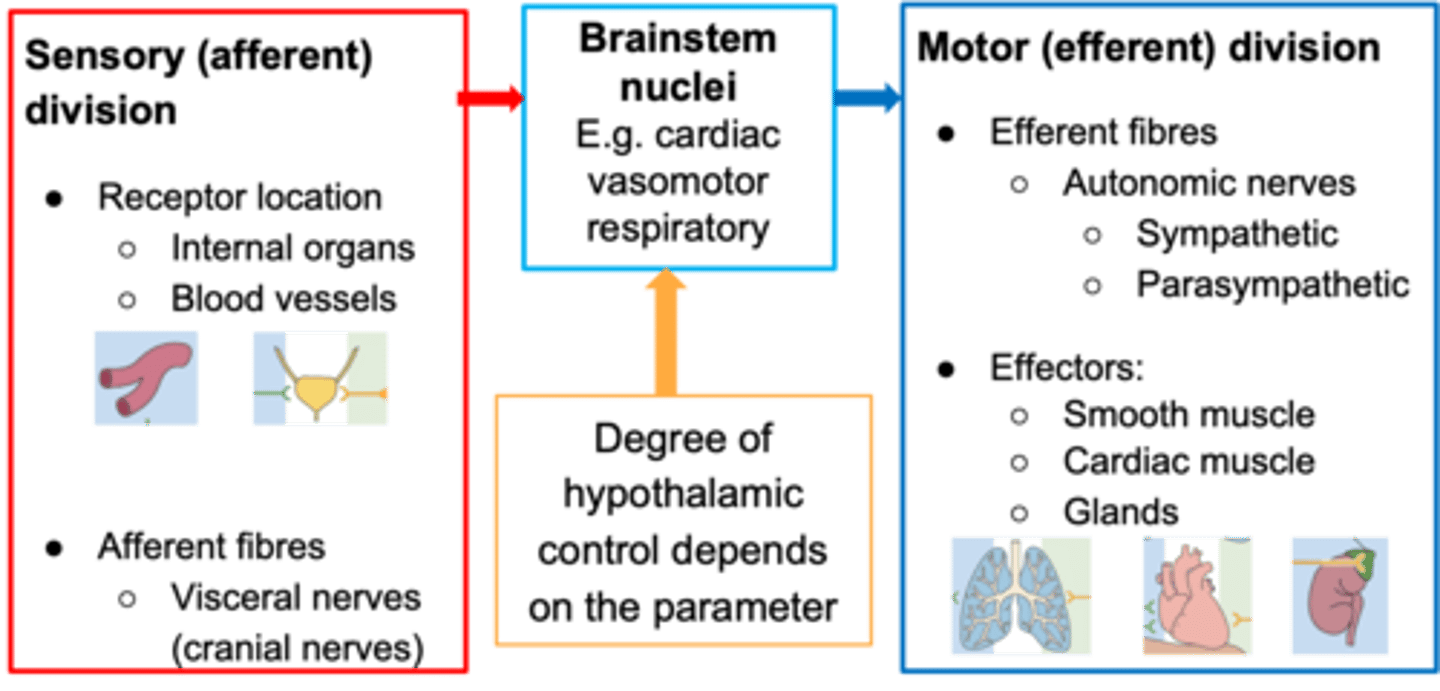
Regulation of body temperature
Which of the following requires greater input from the hypothalamus: pupillary constriction/dilation, salivation, regulation of body temperature?
Pre-ganglion and post-ganglion
There are 2 main types of neurones, what are they?
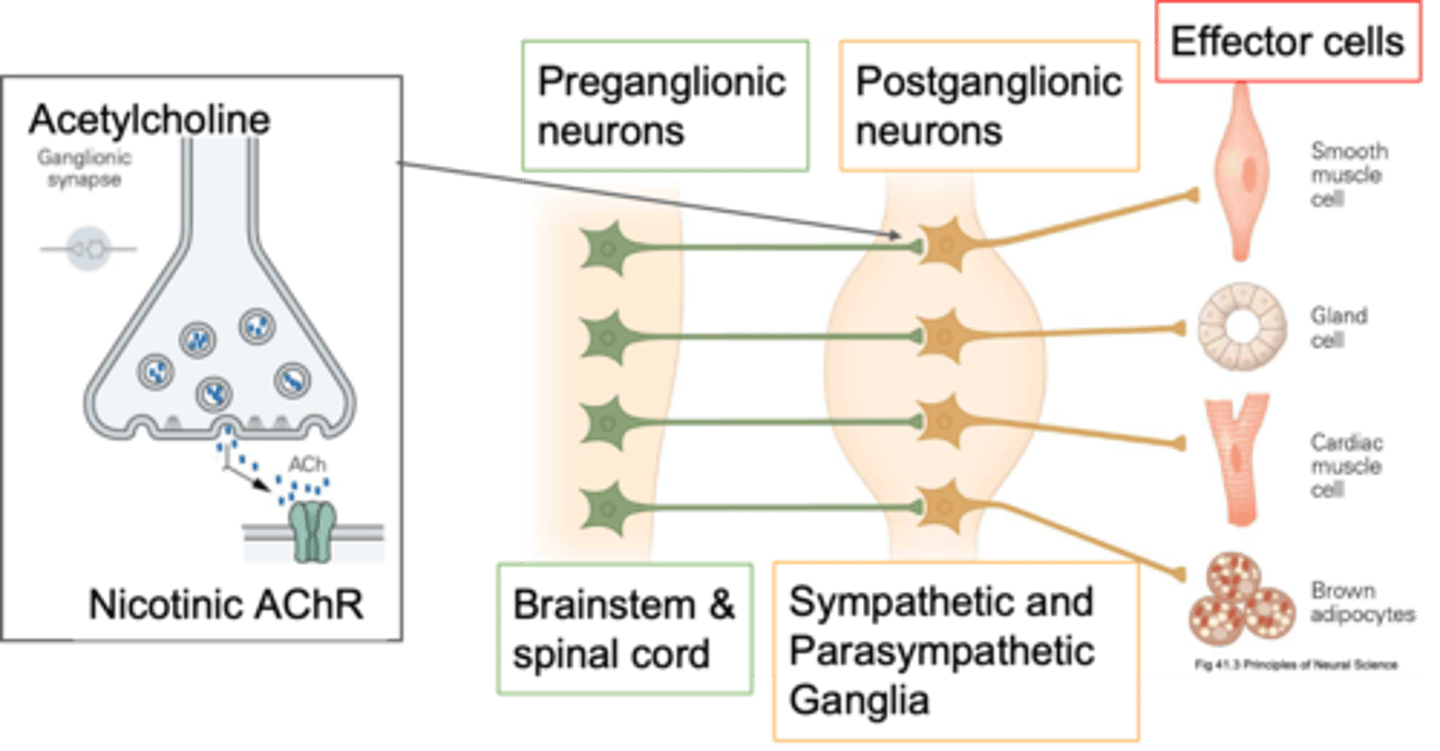
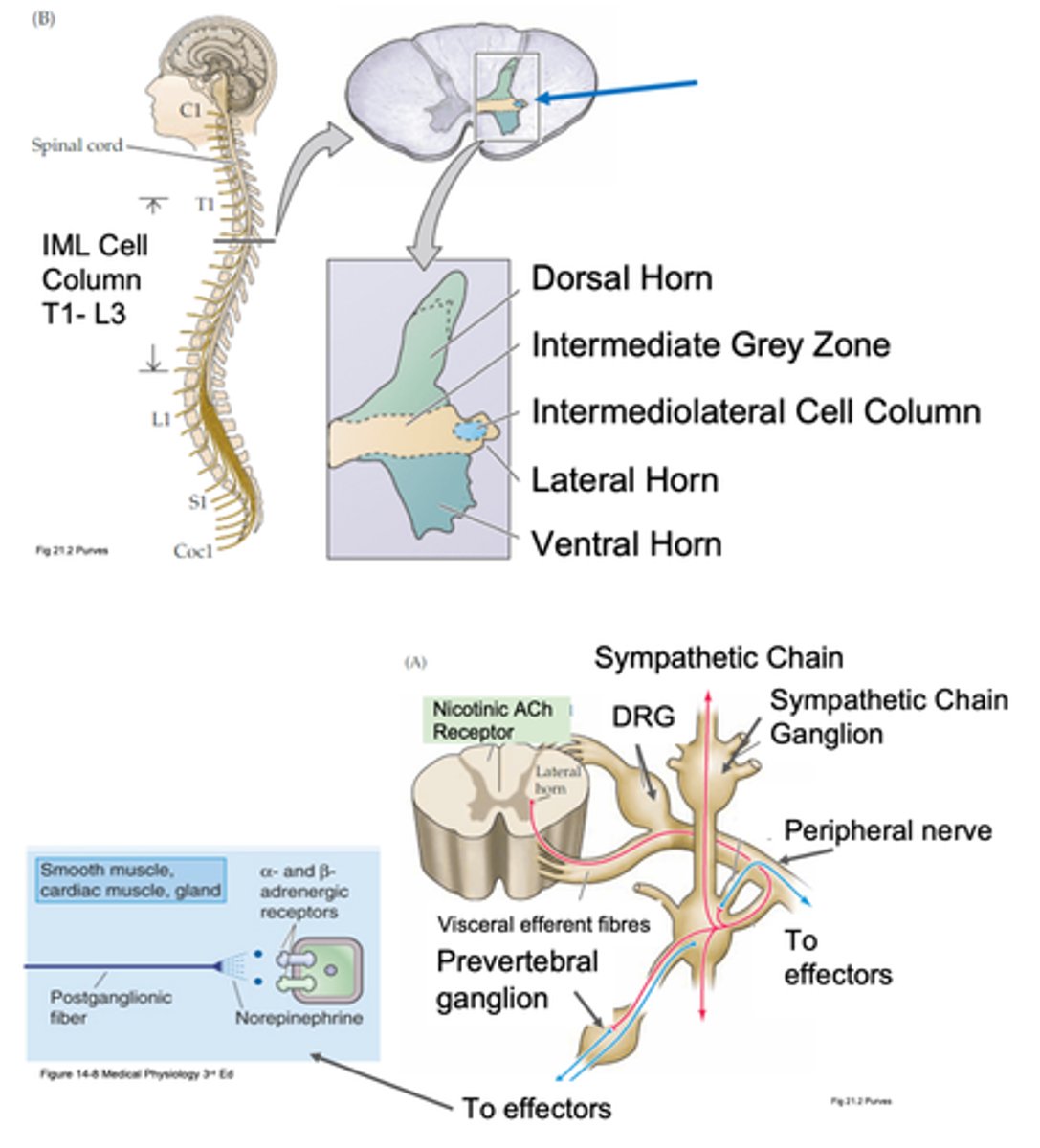
In the CNS (some of them in the brain stem, some in spinal cord)
Where are pre-ganglion neurones found?
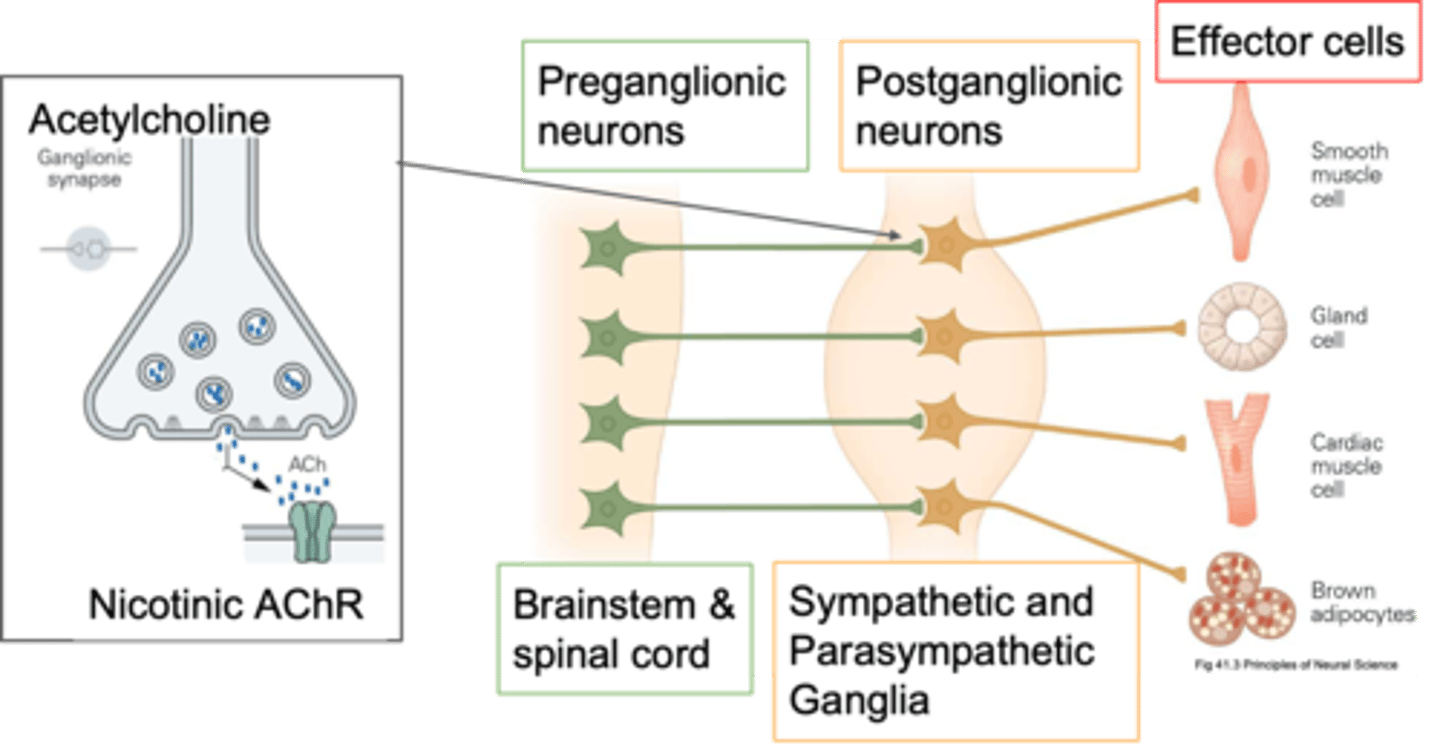
In the periphery because they're found in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia (some close to target organs, some close to spinal cord)
Where are post-ganglionic neurones (cell bodies) found?
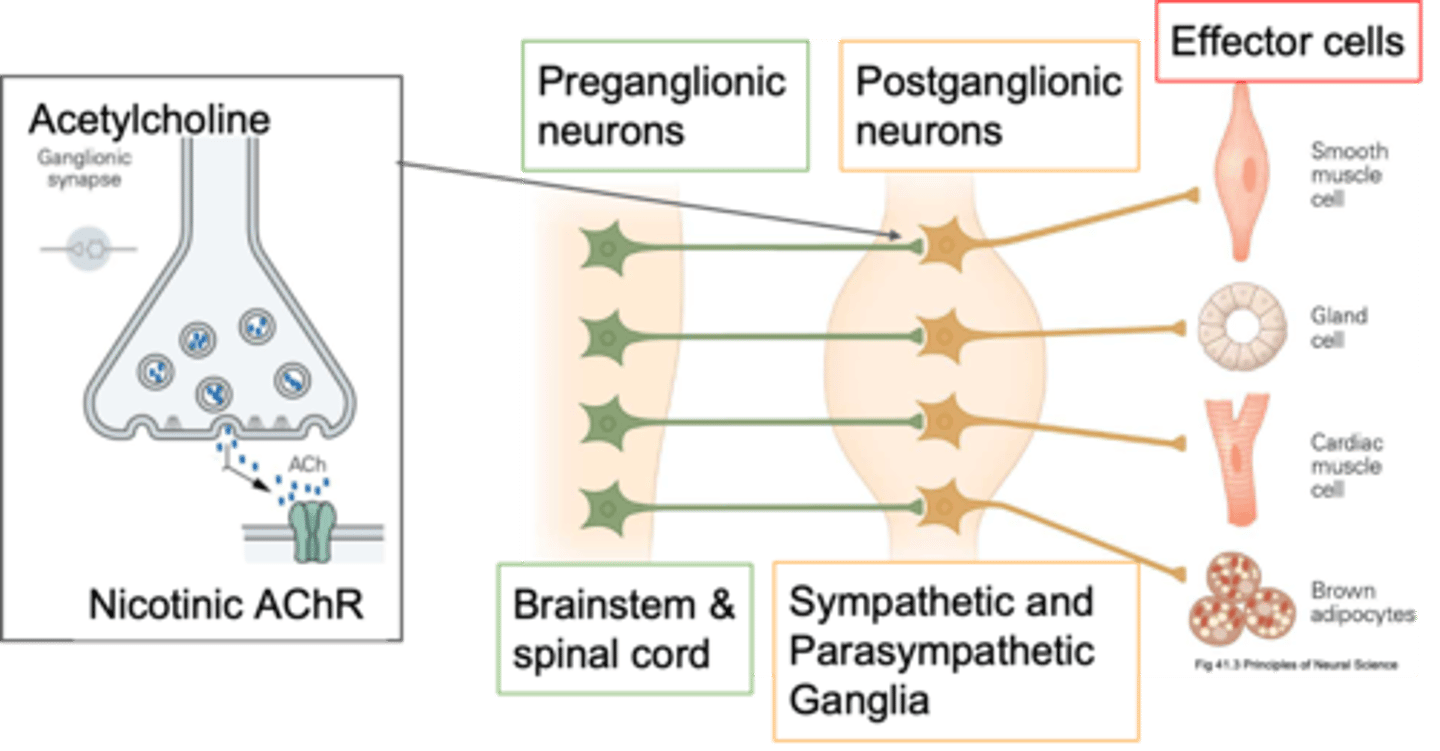
Post-ganglionic
If your cell body is in a ganglion, what kind of neurone is it?
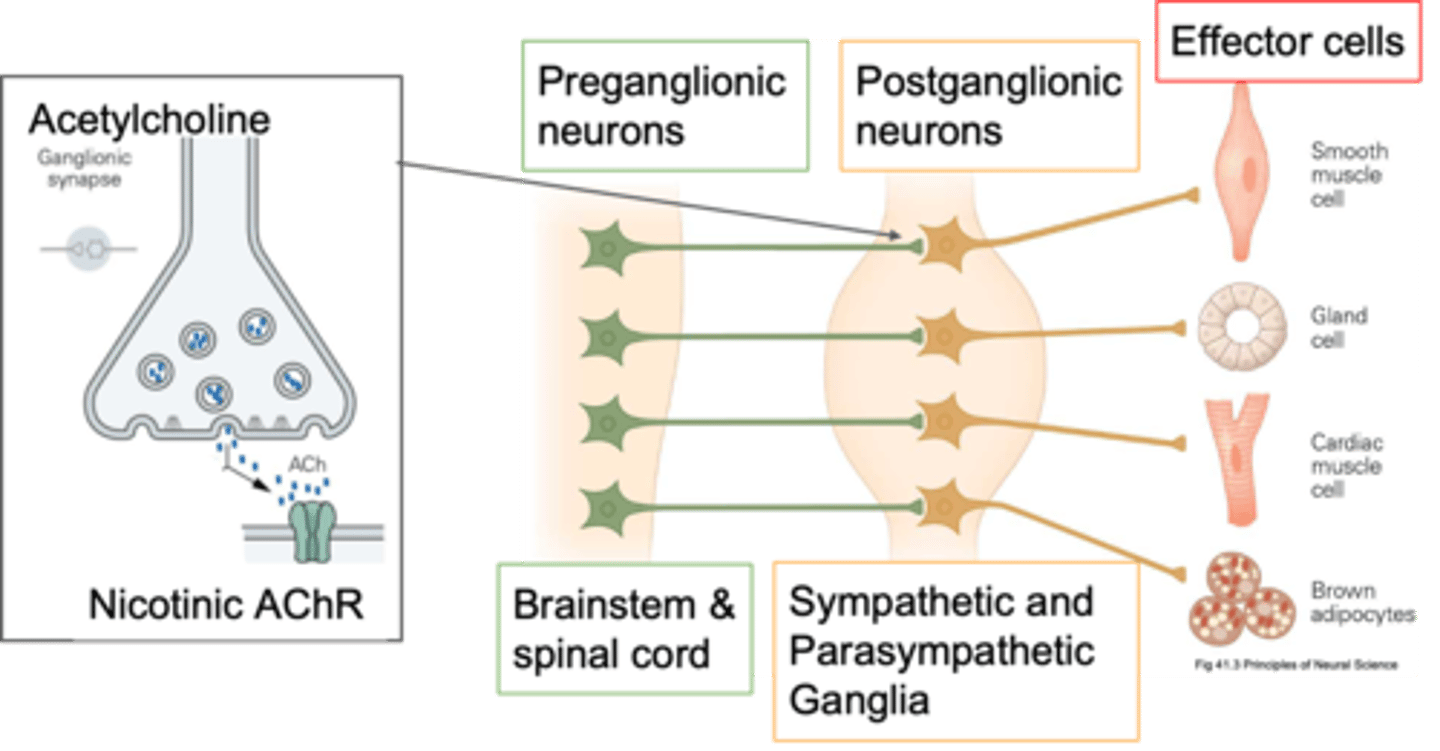
Periphery, cholinergic synapses
Pre-ganglionic neurones send their axons out into the ____________ and innervate the post-ganglionic neurones and how they innervate them is via ____________ ___________
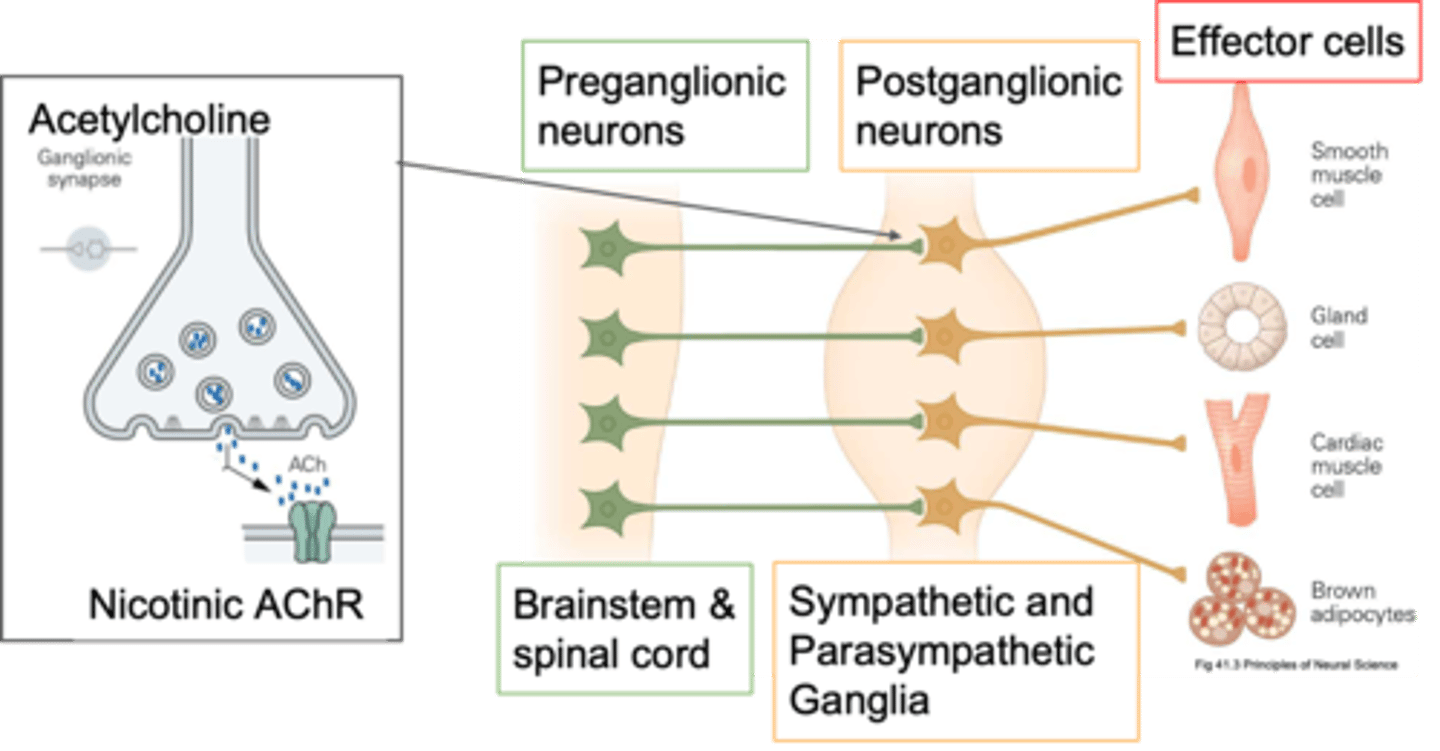
Cholinergic
Pre-ganglionic neurones are primarily what?
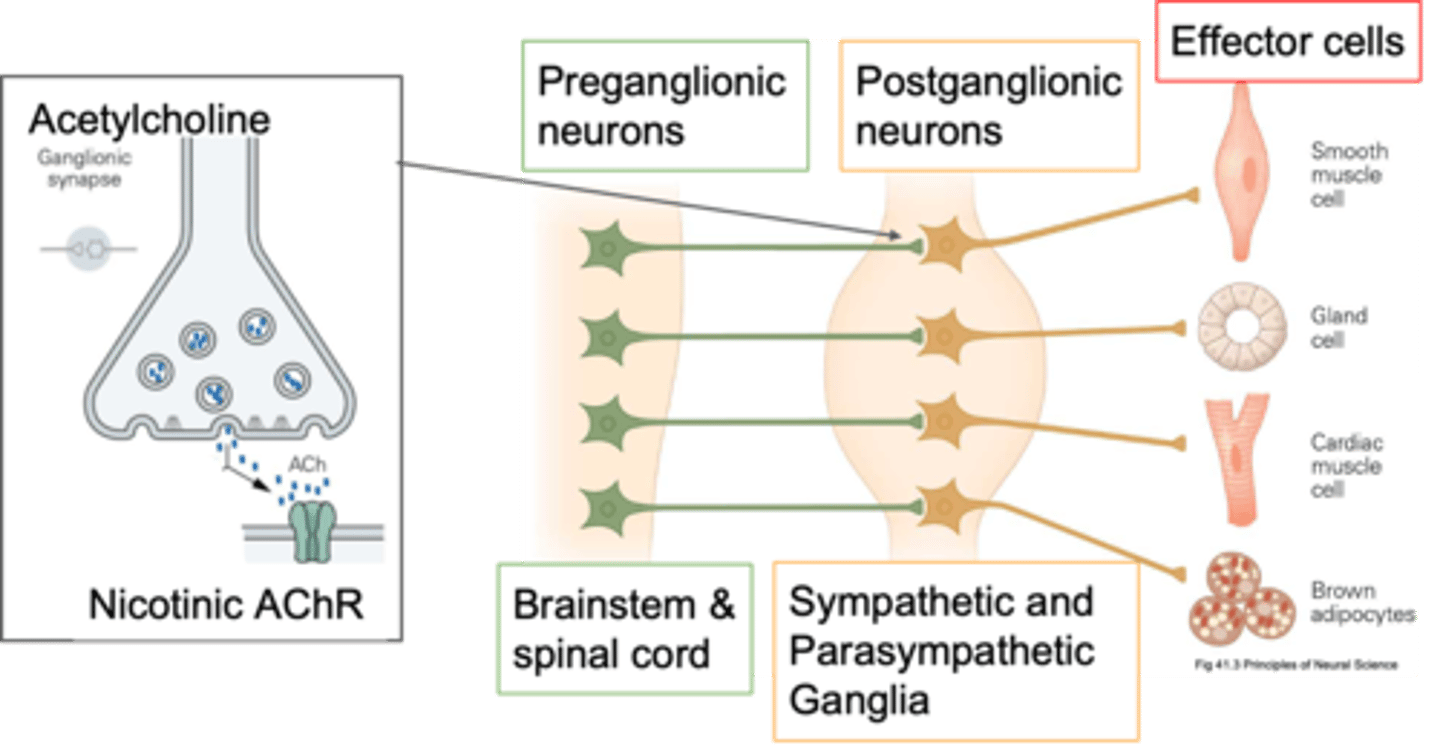
ACh, other things depending on what its trying to do, it also has co transmitters so it might release ATP
What do pre-ganglonic neurones release?
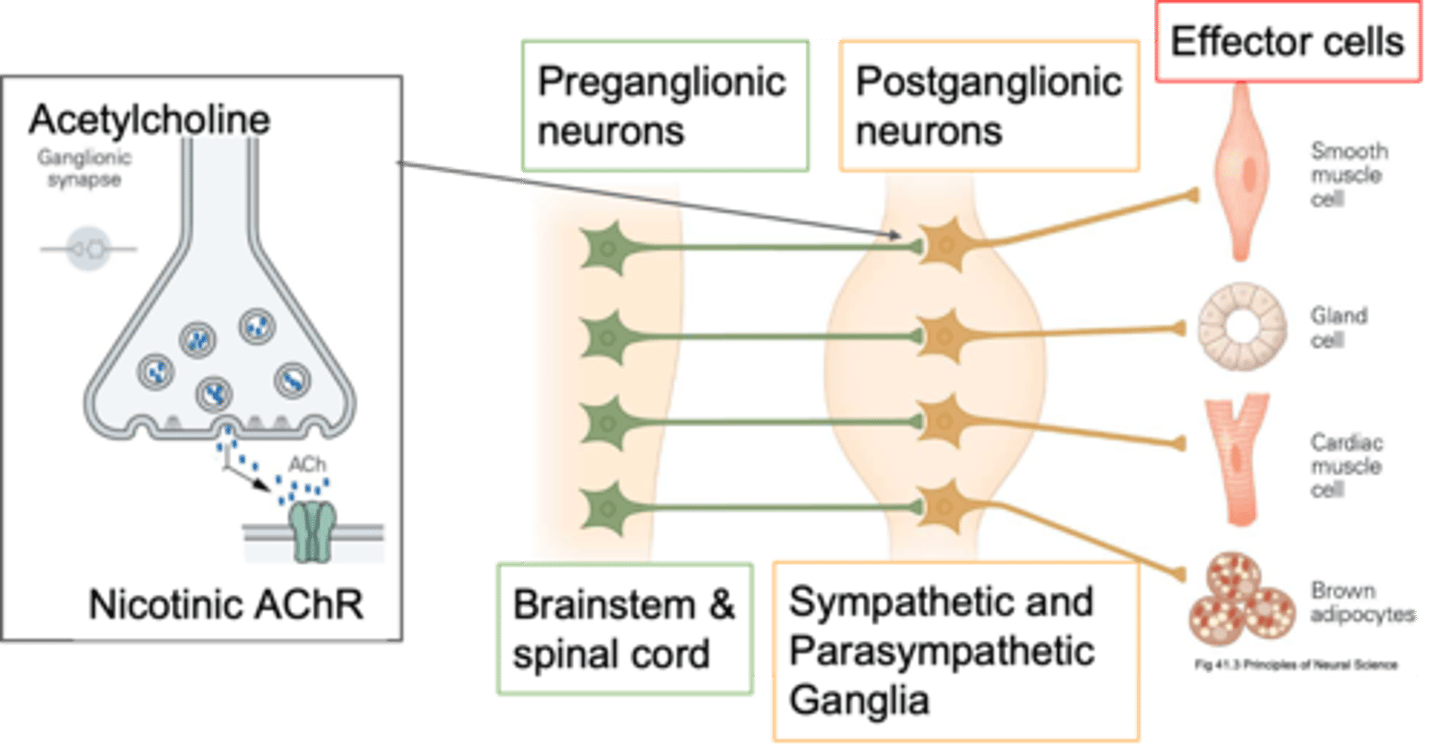
Sympathetic organisation
Activation of presynaptic GABAb heteroreceptors on glutamatergic terminals and by postsynaptic GABAb receptors
What controls sympathetic preganglionic neurons?
Sacral parasympathetic organisation
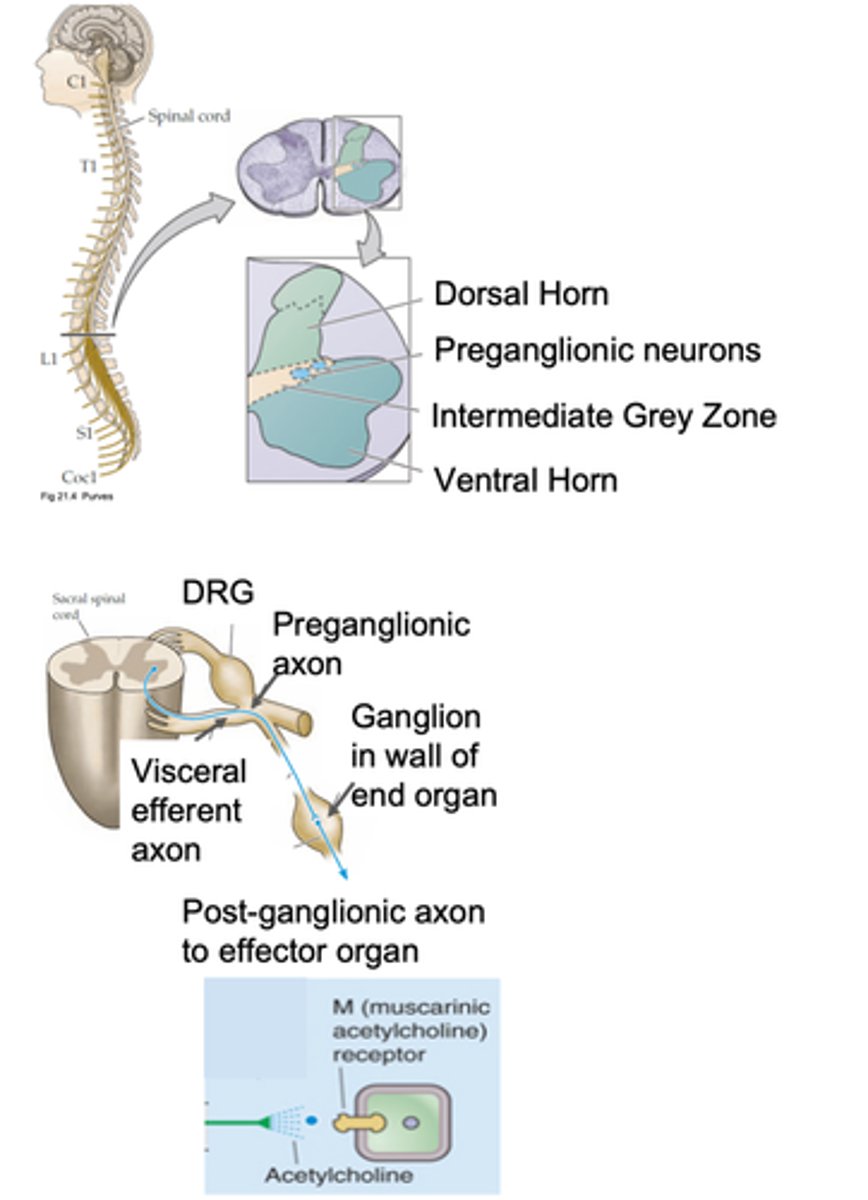
Thoracic, cranial
Genetic expression of sacral pre-ganglionic neurons is more similar to __________ pre-ganglionic neurons than __________ pre-ganglionic neurons
Controls the size of the pupil
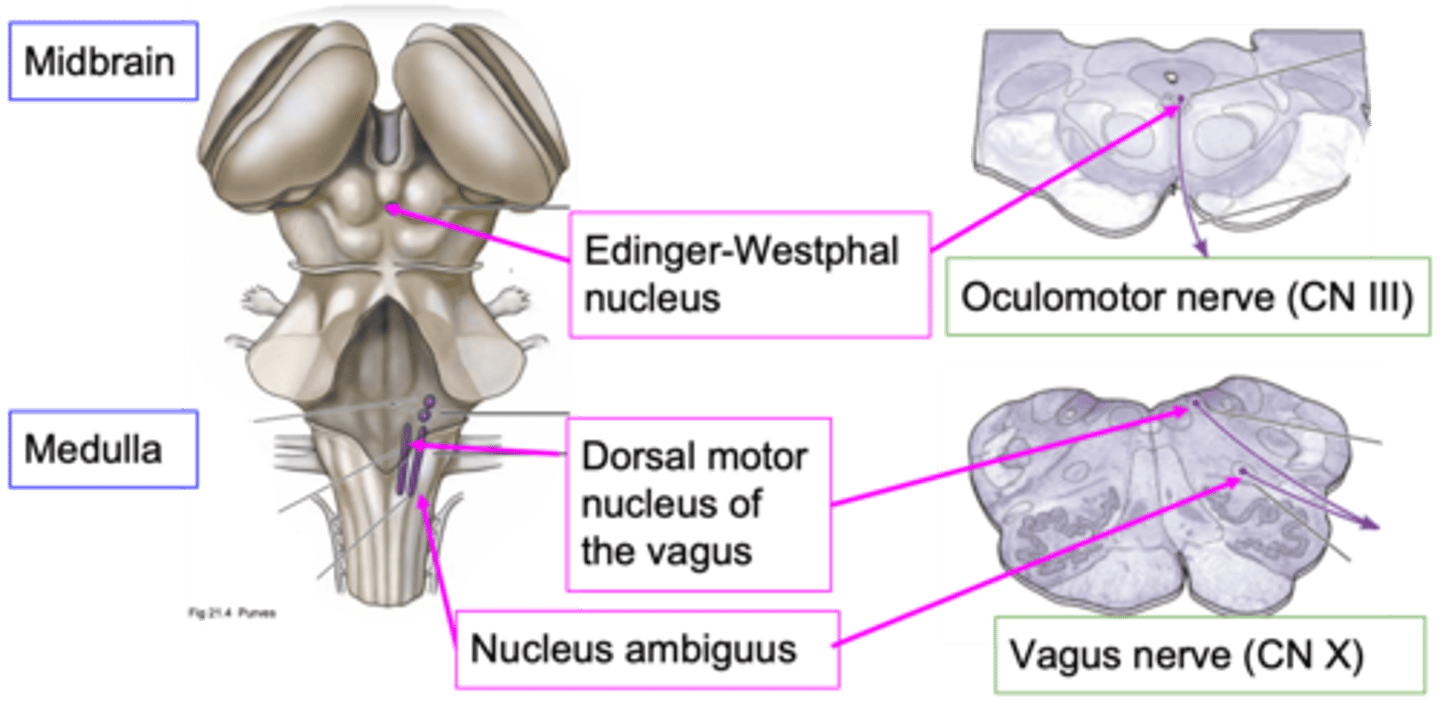
What does CN III (cranial nerve 3) do?
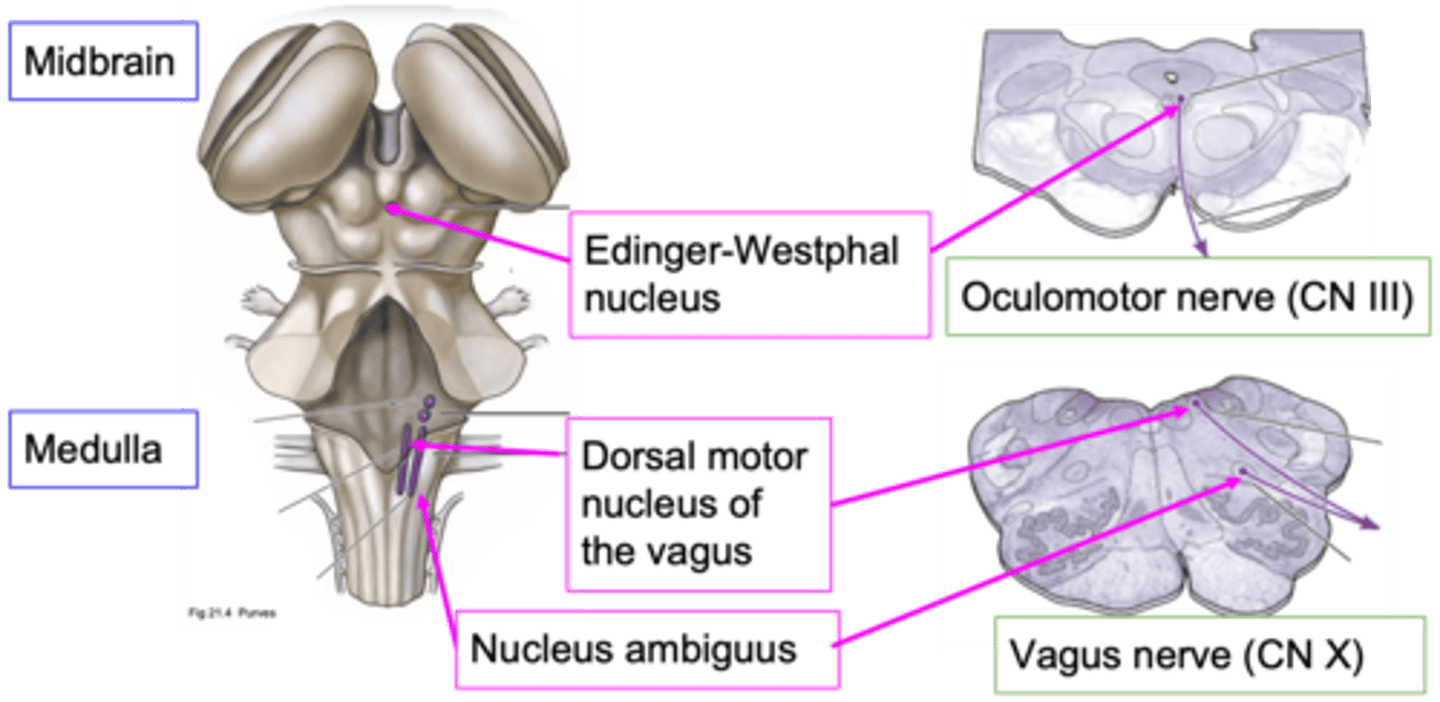
Moving the muscle of the eye, influencing the muscle within the eye that affects pupil diameter
What are the other functions of the oculomotor nerve?
Hypothalamic
Influencing pupil diameter doesn't need which control?
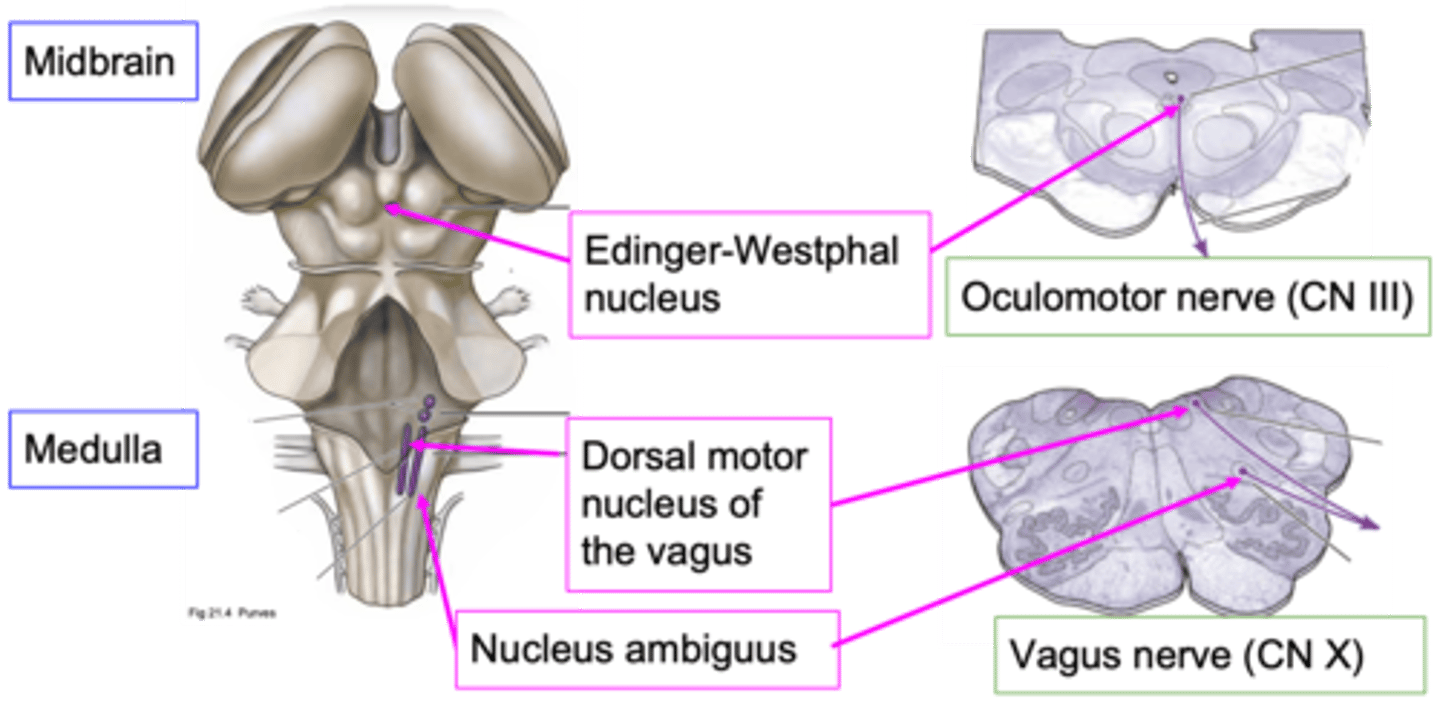
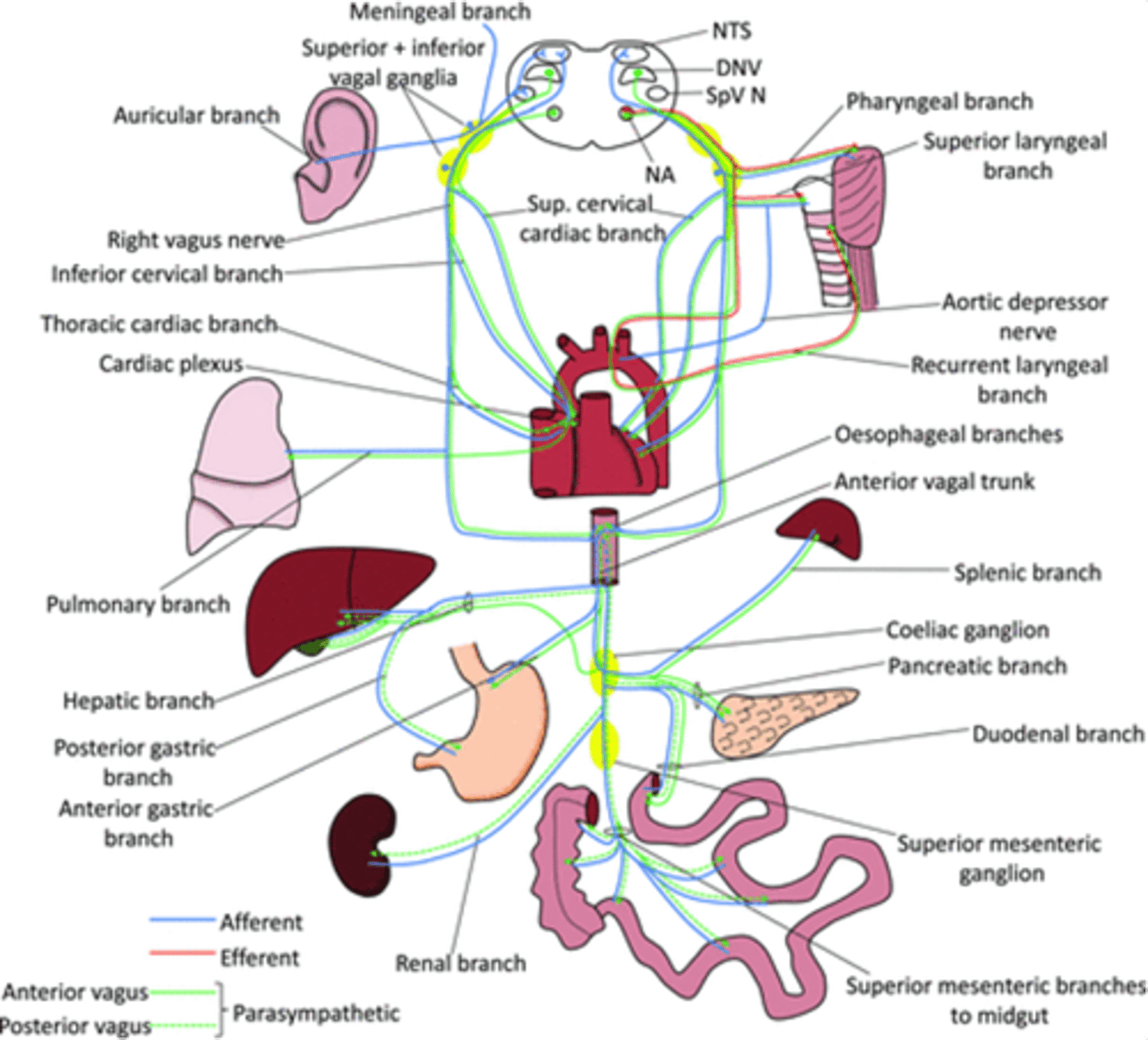
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and nucleus ambiguus
Which nuclei are important nuclei for where the vagus nerve originates?
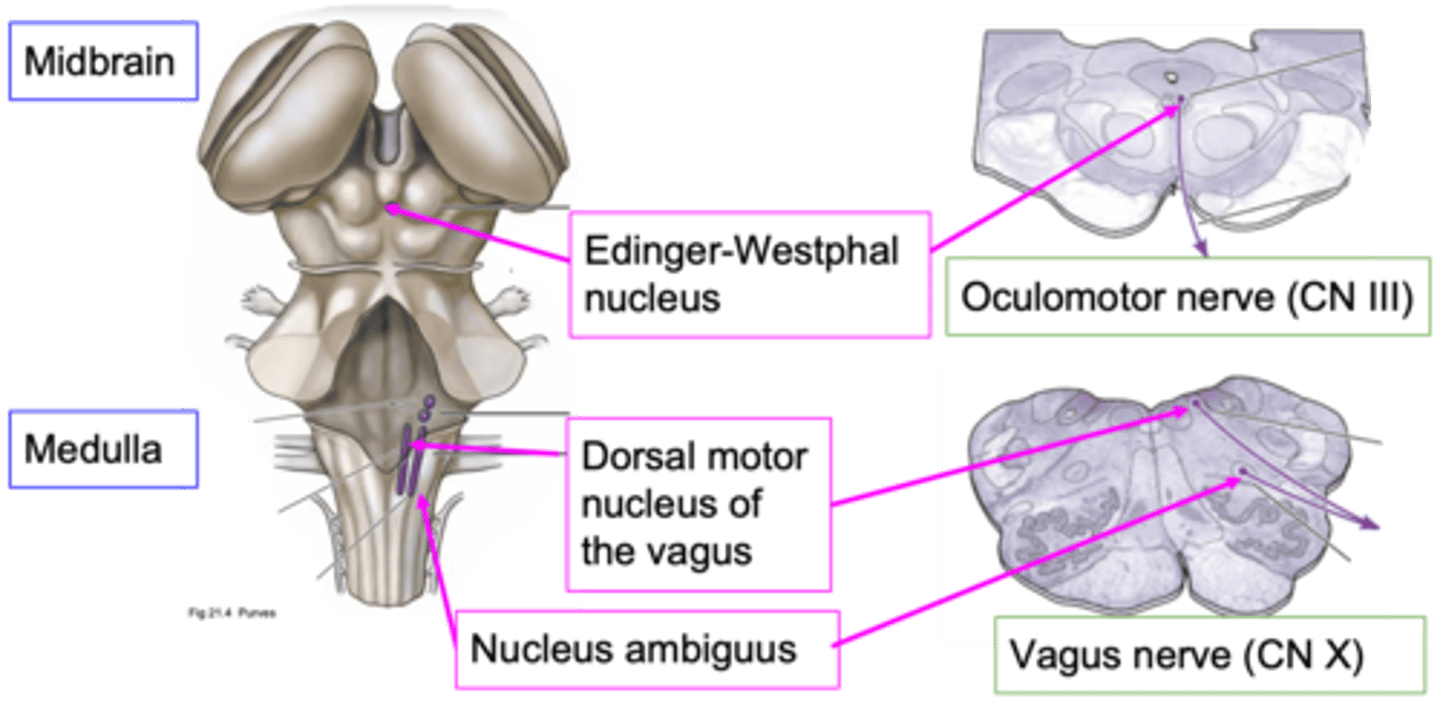
~80%
How much of the total parasympathetic outflow does the vagus nerve carry?
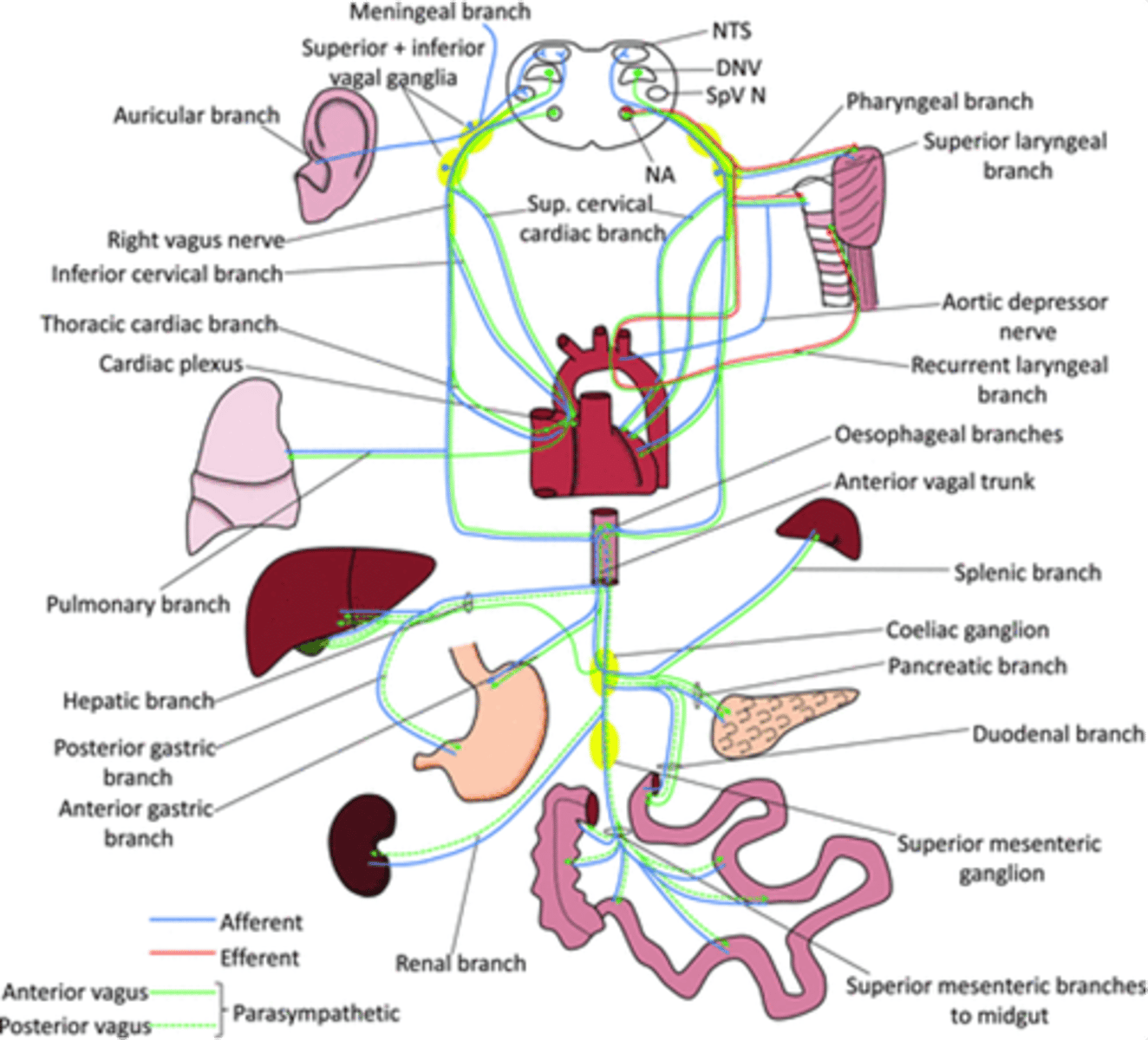
Visceral afferents
The vagus nerve also carries tonnes of ___________ __________ - vagal nerve stimulation
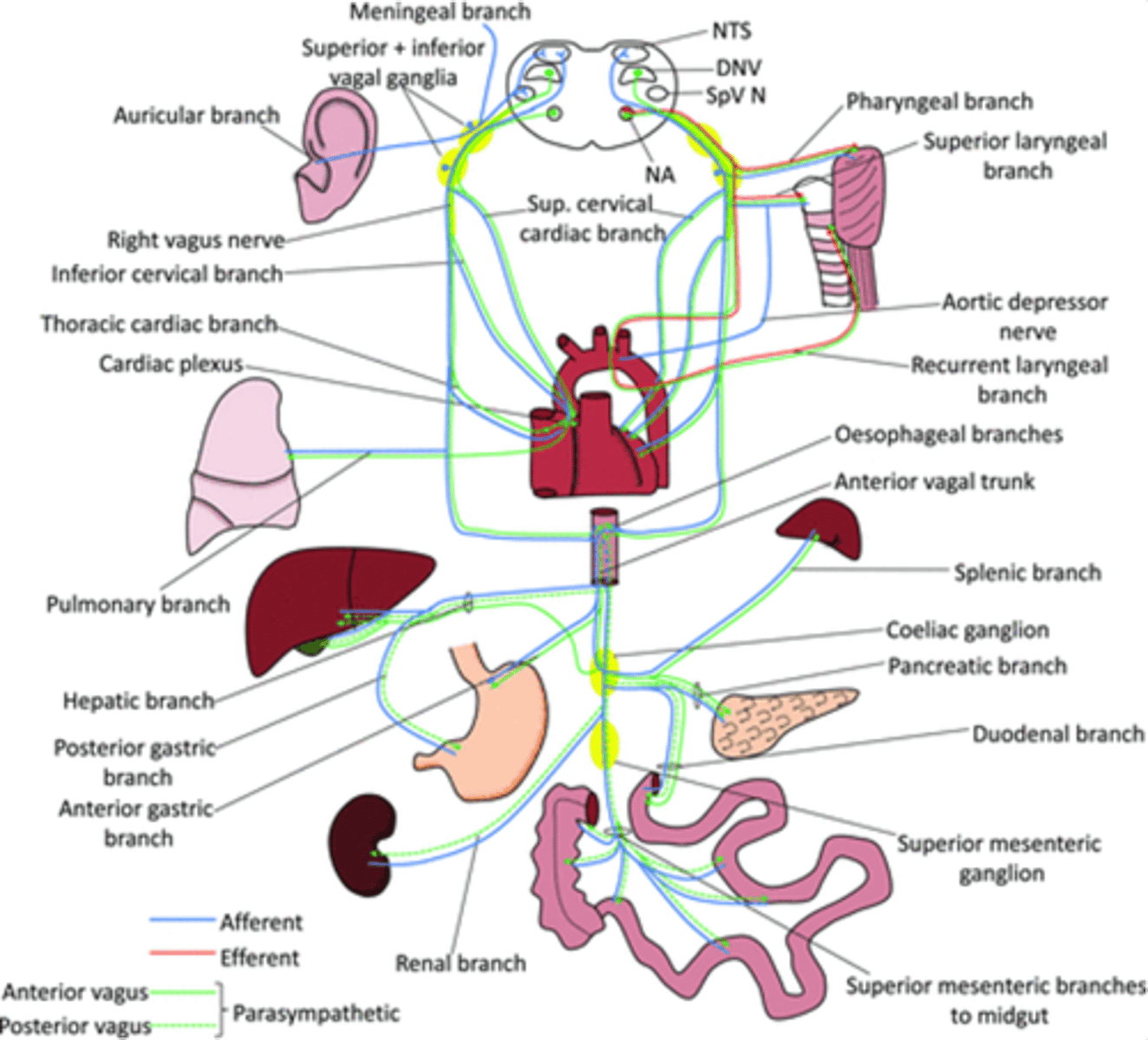
Afferent and innervation of the vagus nerve
What does the blue line show?