1.1 Global Warming and Climate Change
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does Earths atmosphere mainly consist of, and its composition?
78% Nitrogen (N2) + 21% Oxygen (O2) + 1% Other gases
What sphere is majority of the gas contained in?
Troposphere
What is the Oxygen, Nitrogen, and other 1% gases in the atmosphere considered as?
Greenhouse gases
Explain the greenhouse effect in 3 steps
Infrared, Visible, or UV Raditation from the sun reaches earths atmosphere.
~30% of the radiation is then reflected back from the earths surface, and the rest is absorbed.
around ~48% of the radiation is then absorbed into greenhouse gases within the atmosphere and the earths surface.
What stable average surface temperature does the greenhouse effect maintain, and what would it be if the greenhouse effect didn’t exist?
Exist: 15oC
Didn’t Exist: -18oC
What are some examples that contribute to the natural greenhouse effect?
Carbon, Nitrogen, and Water cycle
What are some examples that contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect?
Combustion of Fossil Fuels, Deforestation, and Agriculture
How do greenhouse gases cause climate change?
Due to anthropogenic activities causing more greenhouse gases to enter the atmosphere —> Less thermal energy is emitted back by earth and the atmosphere —> A new equilibrium temperature is established that exceeds the current equilibrium value = CLIMATE CHANGE
What is a greenhouse gas
Molecules that trap heat int he form of radiation in the earths atmosphere preventing it from escaping to space.
What has significant research around climate change proven?
Temperatures have risen 0.8oC over the past 100 years. (Australia is closer to 1.0oC)
What are the 5 potential impacts of climate change
Increase in temperature - Caused by evaporation of water vapour and is accelerated by increased of temperature therefore is a cycle effect
Melting of land and sea ice - caused by increase temperature, and as a consequence threatening the existence of species. (Less ice = more radiation absorption, as ice helps reflect radiation)
Heating of oceans - As oceans absorb more heat, this contributes to melting of land and sea ice, coral bleaching, and ocean acidification.
Extreme Weather events becoming more common (bushfires, tsunamis, floods, rainfall, etc) - Potentially has big effects on biodiversity on ecosystems such as vegetation and crop production and animal and plant species abilities to adapt in environments.
Rising Sea Levels - Due to water expanding in heat and ice melting into the ocean, which puts low-level communities at risk.
What is accelerating ocean acidification and how is it occuring?
Ocean absorbs 30% of the atmospheric CO2 being released into the atmosphere which reacts with water to form H3O+ causing a decrease in pH (82 → 8.1 since 1750), therefore increasing CO2 emissions due to anthropogenic sources are accelerating this.
What are the 2 consequence of ocean acidification
Decreased carbonate ions = More difficult for shells to be built making them more fragile and weak
Increased hydronium ions = can react with and dissolve carbonate shells
Why is increased ocean acidification detrimental?
As calcifying organisms play a large part in the ocean ecosystem expecially at the bottom of the food web, which is essential for higher organisms. This can also affect the habitats of other organisms.
How do you calculate pH or hydronium ions?
pH: substitute hydronium ion concentration and multiply with -log
Hydronium ion conentration: make the pH a negative and raise to 10.
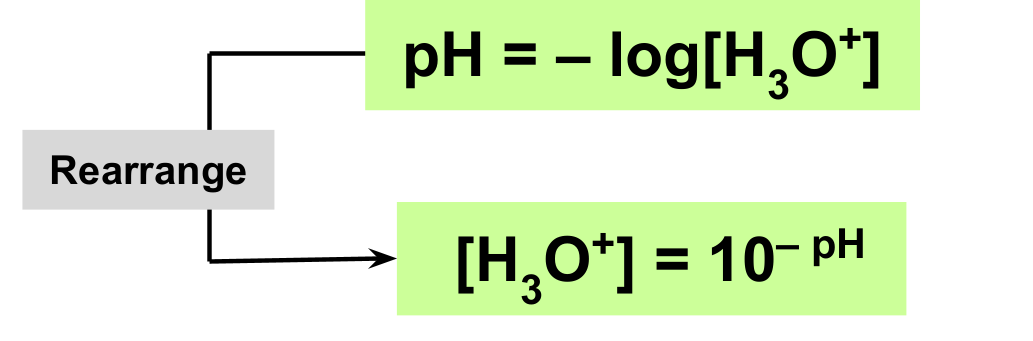
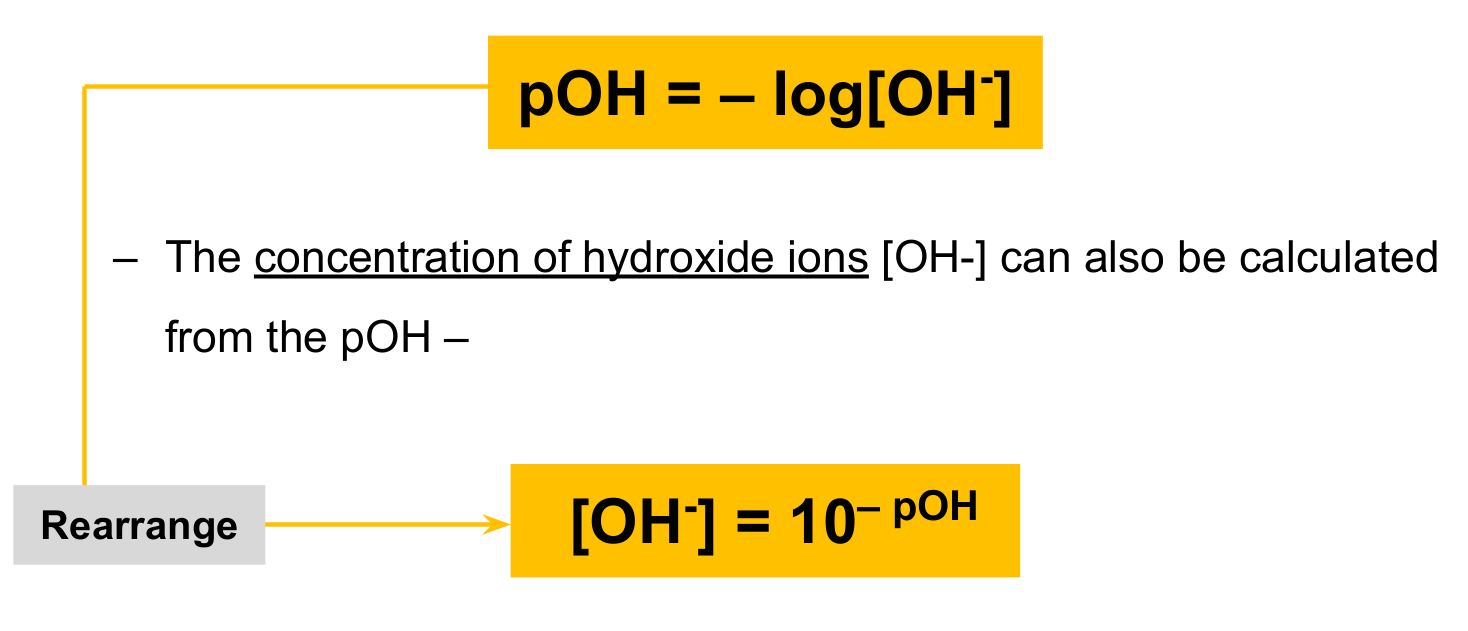
How do you calculate pOH or hydroxide ions?
pOH: substitute hydroxide ion concentration and multiply with -log
Hydroxide ion conentration: make the pOH a negative and raise to 10.
Whats the first step of ocean acidification starting with CO2
CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid
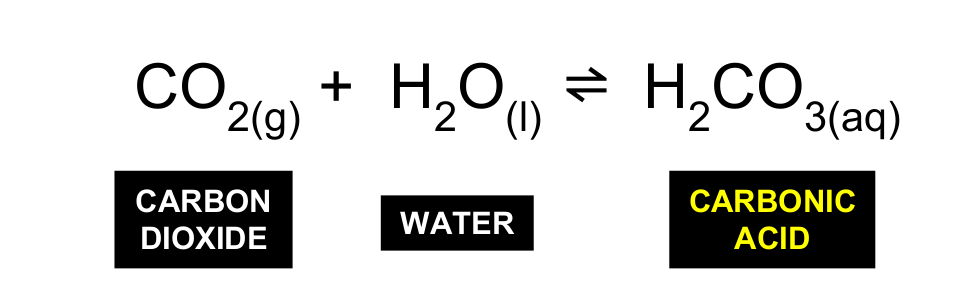
What occurs in the second step of ocean acidification
Carbonic acid is a weak acid therefore partially ionises into hydronium ions and hydrogencarbonate ions
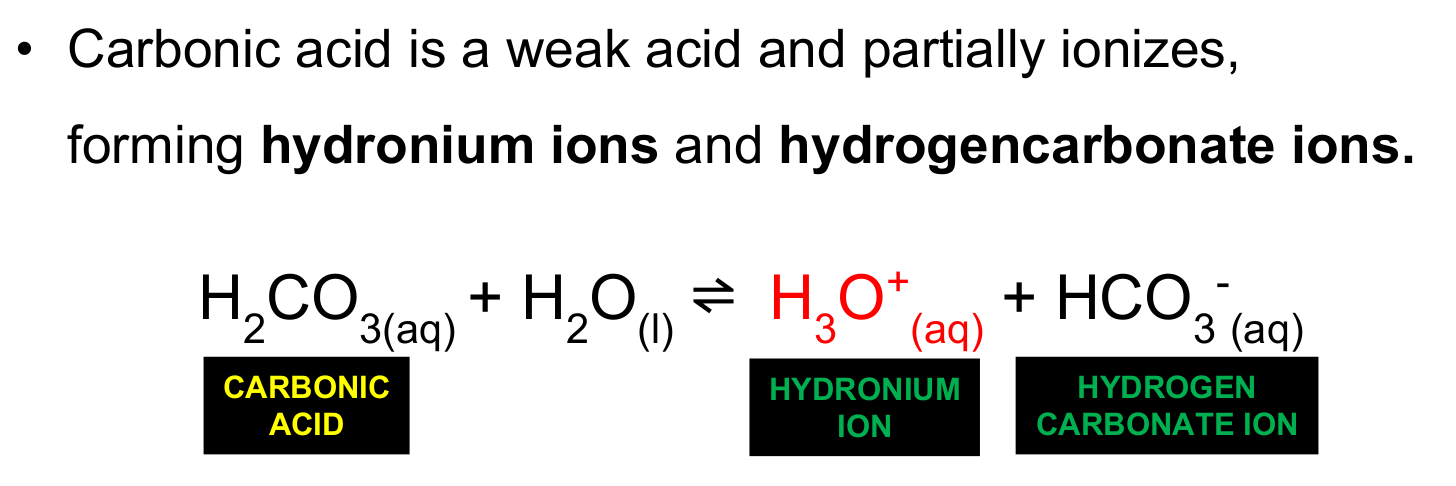
What occurs in the third step of ocean acidification
Hydrogencarbonate ion ionise into more hydronium ions and carbonate (important for the development of shells.)
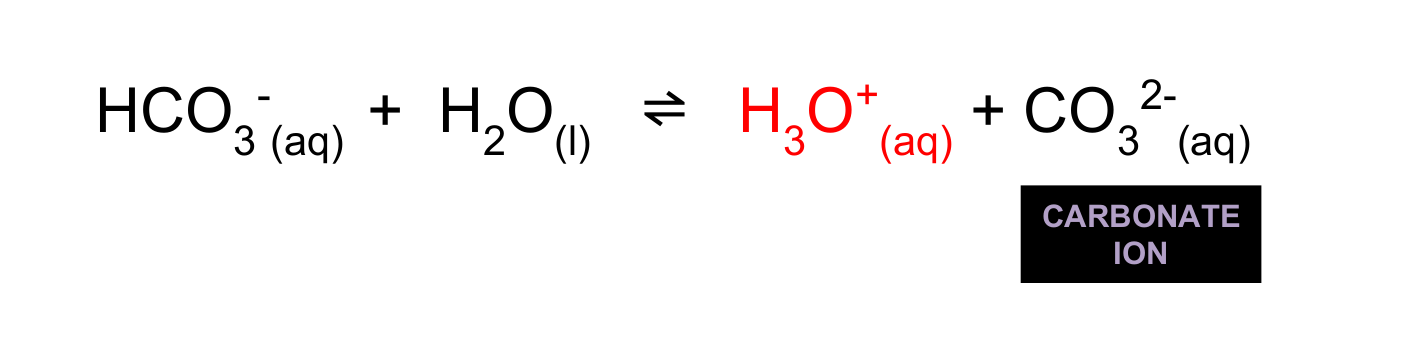
How and why can pOH be calculated from pH
As water is an amphiprotic substance and can “self-ionise” acting as a base or acid in small amounts.
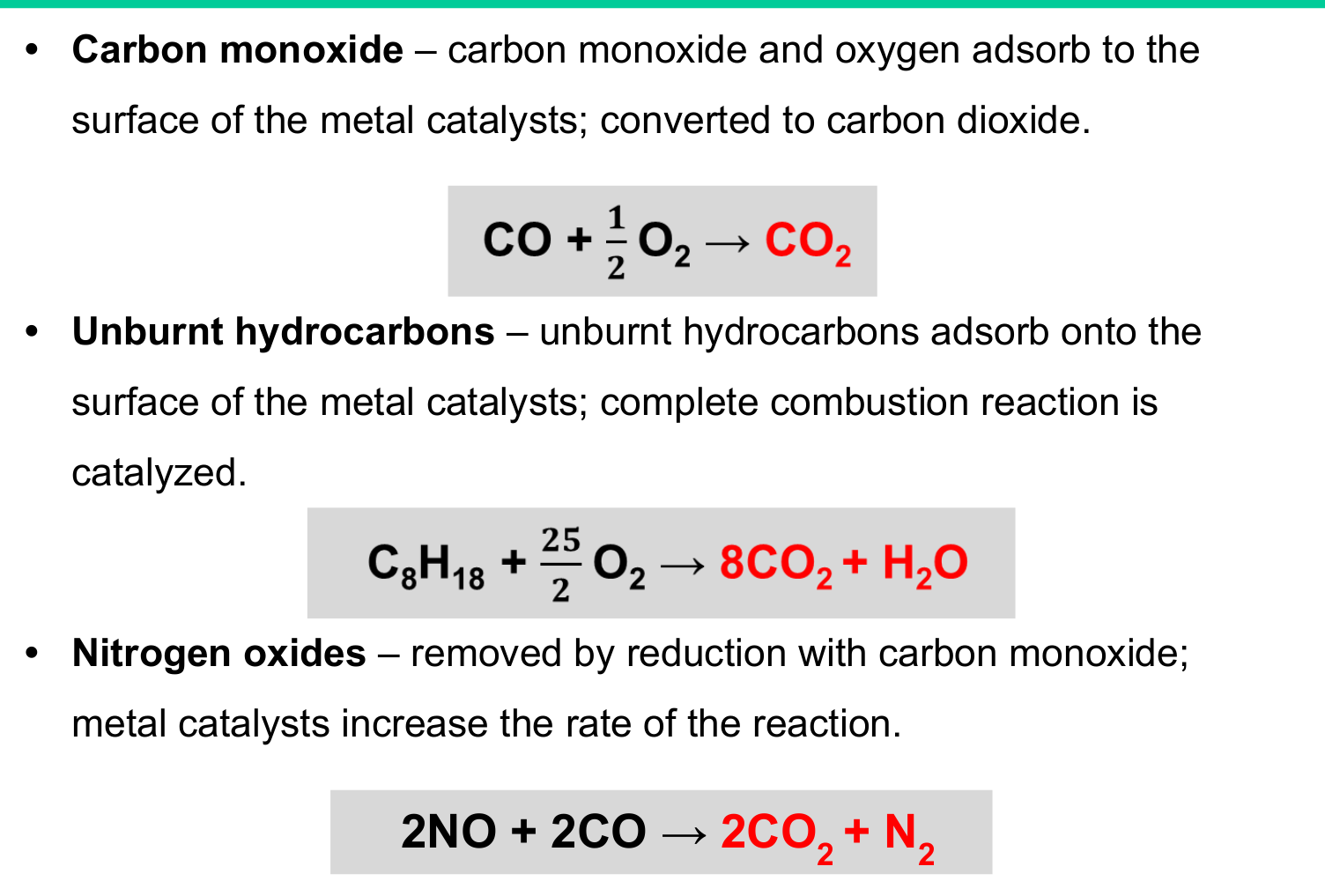
Remember the 3-way reactions for catalytic converters
What are the conditions required for photochemical smog