AP BIO UNIT 2: Cell Structure and Function
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
cell
basic unit of life
plasma membrane
The membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of the cell, separating the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell; selective permeable
cytoplasm
semi-fluid jelly like substance; thee region of the cell outside of the nucleus.
genetic material
carry the genes in the form of DNA
ribosomes
A complex structure of RNA and protein that synthesizes proteins from mRNA; make proteins
Eukaroytes
Describes a cell that has a nucleus; used to refer collectively to animals, plants, fungi, and protists; membrane bound organelles; bound in the nucleus (linear)
Prokaryotes
Describes a cell that does not have a nucleus; used to refer collectively to archaeans and bacteria; circular, smaller, basic
cytoskeleton
network of proteins that are rigid and help the cell keep its shape; also includes flagella and cilia
endosymbiont theory
eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between different prokaryotic cells, where one cell engulfed another and both benefited; A larger host cell engulfed smaller prokaryotic cells. The host cell provided a safe environment and food, while the engulfed cells provided energy through processes like aerobic respiration or photosynthesis. Over time, this mutually beneficial relationship became permanent, with the smaller cells evolving into organelles within the host cell. Proposes that the mitochondria and chloroplasts in eukaryotic cells originated from free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by ancestral host cells.
Mitochondria
Specialized organelles that are the site of cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells, oxidizing chemical compounds such as sugars to carbon dioxide and transferring their chemical energy to ATP. transforms glucose into ATP
Cristae
folds in mitochondria
chloroplasts
contain green pigment called chlorophyll; double membrane with thylakoids inside
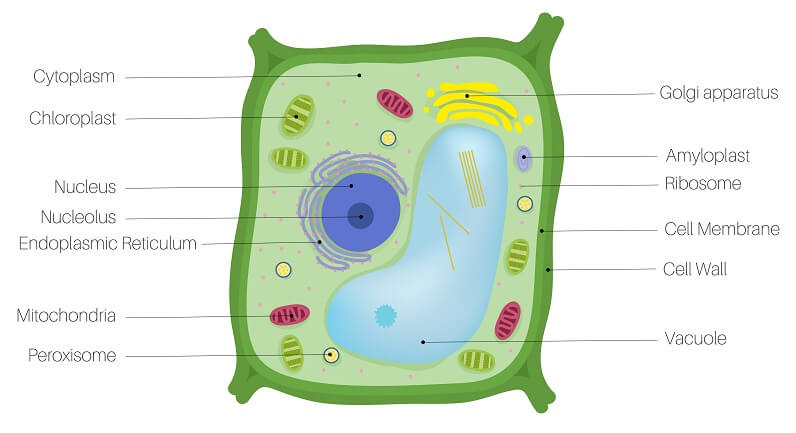
plant cells
-have cell walls
-have mitochondria and chloroplasts
-have large central vacuoles
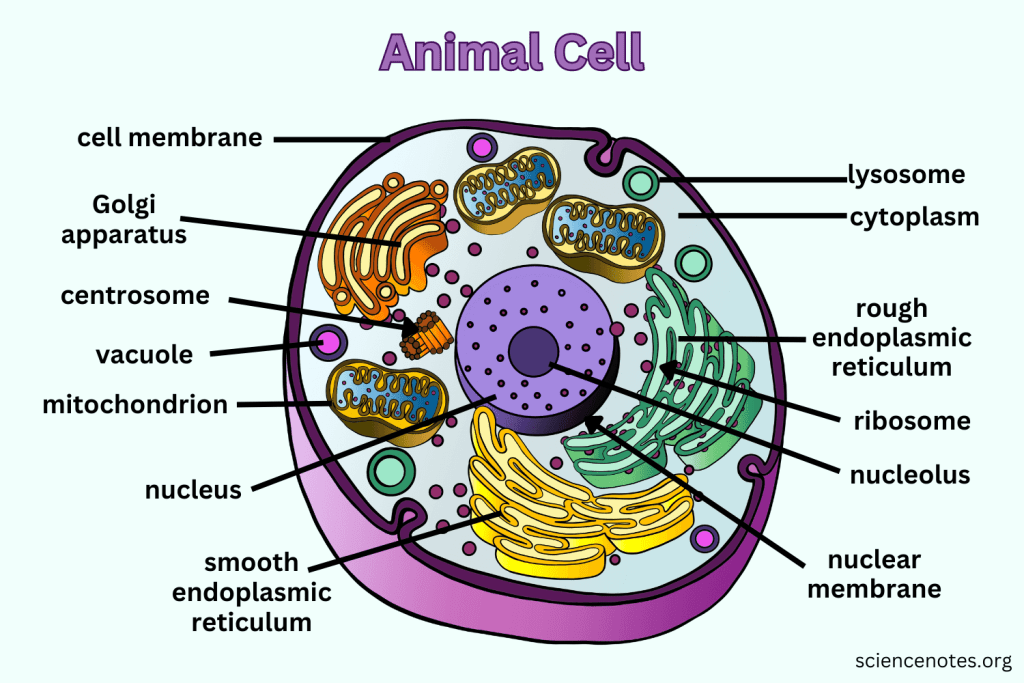
animal cells
-have no cell walls
-do not have chloroplasts
-have centrioles which helps with cell division
nucleus
stores genetic material (DNA)
nucleolus
makes RNA and ribosomes
rough endoplasmic reticulum
makes proteins for export; to synthesize and modify proteins that are destined for secretion from the cell, insertion into cell membranes, or delivery to other organelles like the Golgi apparatus and lysosomes
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
makes lipids and other things; creating lipids for membranes, synthesizing steroid hormones (like testosterone), and detoxifying harmful substances like drugs and poisons
golgi apparatus
processes (folds up) and ships proteins out of cell; a cell organelle that processes, packages, and sorts proteins and lipids for transport within or outside the cel
ribosome
make proteins for the cell
vacuole
A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac within a cell that stores water, nutrients, ions, and waste products; storage center for cell (plants—water)
peroxisome/ lysosome
to act as the cell's "digestive system," breaking down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign invaders; recycles parts of cell/digests toxins (lots of digestive enzymes)
cell wall
in plants only; rigidity of plant; made of cellulose (carb)
centriole/centrosome
animal only; helps in cell division
vesicle
small, membrane-bound sacs that transport and store substances within a cell, playing roles in metabolism, digestion, and waste removal. They are used to move materials between organelles, secrete substances like hormones out of the cell, and break down waste products and foreign invaders; part of membrane that can pinch off to transport substances
selective permeability
allows some substances in easier than others; the property of a membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by means of active or passive transport, while blocking others.
fluid mosaic model
A model proposing that the phospholipid bilayer is a dynamic structure that allows molecules to move laterally within the membrane and is a mixture, of several components, including lipids, proteins, and carbohydrate; membranes are composed of lipids and proteins (phospholipids being the most prominent)
cholesterol
fluidity buffer to keep the membrane fluid at high and low temperatures
intergral proteins
proteins that are permanently embedded within the cell membrane. They play crucial roles in various cellular functions, such as transport, signal transduction, and maintaining cell structure; transmembrane proteins; penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
peripheral proteins
A protein that is temporarily associated with the lipid bilayer or with integral membrane proteins through weak non-covalent interactions; not embedded; loosely bound
glycolipids
carbohydrates and lipids
glycoproteins
carbohydrates and proteins
diffusion
movement of molecules so they spread out evenly in the available spaces
osmosis
diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane
tonicity
ability of surrounding solution to gain or lose water
hypertonic solution
more solutes in a solution
hypotonic solution
less solutes in a solution
isotonic solution
equal amount of solutes in a solution and cell
osmotic pressure
pressure applied to a solution to prevent inward flow of water
osmotic potential
the potential of water to move from hypotonic to a hypertonic environment
osmoregulation
cells ability to control solute concentration
flaccid
a plant in an isotonic solution that will not take in water
plasmolyze
when a plant is in a hypertonic solution it will____
channel proteins
located in the membrane, help polar molecules and ions move through the membrane
aquaporins
help move water through cells
ion channels
function as gated channels which open and close depending on the ions
active transport
uses energy to move solutes against their gradient
co-transport
a single ATP molecule can drive the active transport of other solutes
exocytosis
cell secretes a biological molecule
endocytosis
cell takes in a biological molecule
phagocytosis
cell eating
pinocytosis
cell drinking
ligand
any molecule that binds to a receptor on another molecule