Calcium Homestasis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Reportion (breaks down bone to release Calcium)
Bone resorption
Reduces calcium excretion
Kidney reabsorption
Vitamin D activation
Increases intestinal absorption
Put The High
Mnemonic for Parathyroid Hormone
affect storage, absorption and excretion of calcium ions
Parathyroid hormone, and calcitonin
in body fluids must be closely regulated
Calcium ion
Hormones and calcium ion are
balance
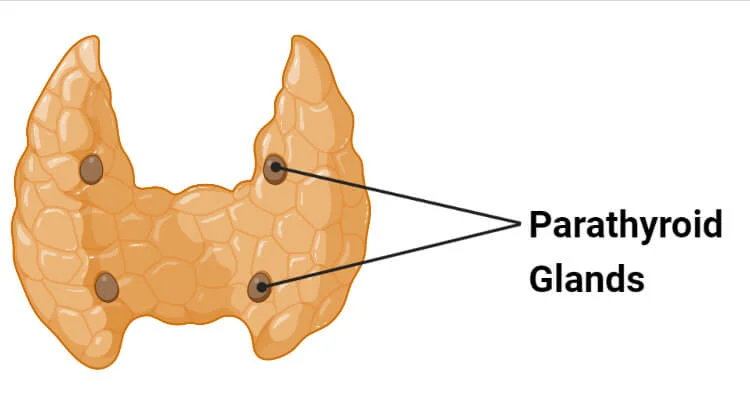
Parathyroid hormone are produced by
parathyroid glands in the neck
Increase blood calcium ion levels by
1.) Stimulating activity (indirectly)
2.) Increasing intestinal absorption of calcium by enhancing calcitriol secretion by kidneys.
3.) Decrease calcium excretion by kidneys
What is a hormone and endocrine
Calcitonin
Calcitonin secreted by C sells in
thyroid
blood calcium ion levels
Decrease
Inhibiting
osteoclast activity
Increasing calcium excretion and reducing calcitriol secretion by
kidneys
Decreasing intestinal absorption of
calcium

Low calcium level causes the parathyroid glands to secrete
(Parathyroid Gland Response)
(Increase Blood Calcium)
Parathyroid hormone
What is stimulated to release stored calcium ions from bone
(Bone Response)
(Increase Blood Calcium)
Osteoclast (Calcium released)
Intestinal absorption of Calcium (Intestinal Response)
(Increase Blood Calcium)
increases (calcium absorbed)
Kidneys absorb (Kidney’s Response)
(Increase Blood Calcium)
calcium ions (Calcium Conserved)
C cells in the thyroid gland secrete
(Decrease in blood calcium)
calcitonin (thyroid gland response)
activity decreases osteoblast activity unaffected (Bone Response)
(Decrease in Blood Calcium)
Osteoclasts (Calcium release slowed)
Intestinal absorption of calcium (Intestinal Response)
(Decrease in Blood Calcium)
decreases (Calcium absorbed slowly)
Kidney excretes (Kidneys Response)
(Decrease in Blood Calcium)
Calcium ions (Calcium excreted)
(Increased Calcium Loss in Urine)
Hyaline Cartilage makes up part of the
Embryonic Skeleton
Disintegration of Chondrocytes in the
diaphysis
Primary ossification
blood vessels penetrate the cartilage
Fibroblast migrating with
blood vessels
osteoblasts produce
spongy bone
Bone formation
spreads
Blood vessels and osteoblast migrate into
Epiphysis
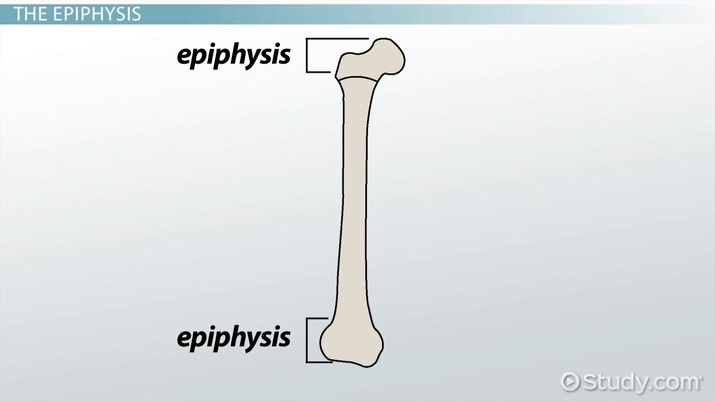
Formation of spongy bone of the
epiphysis
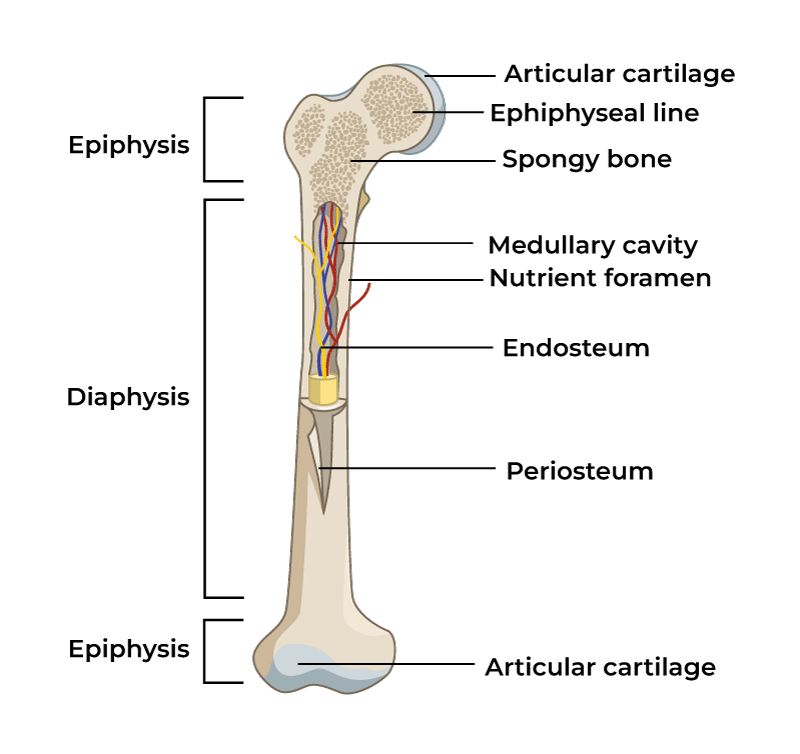
at the metaphysis new hyaline cartilage is produced causing bone elongation (epiphyseal side)
Epiphyseal plate
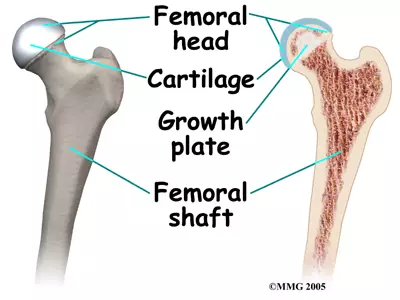
Osteoblasts migrate from diaphysis and replace
cartilage (diaphysis side)
rate of cartilage production decrease and the epiphyseal plate become narrower until it disappears (epiphysial closure)
At Puberty
Only a linen remains in the
epiphyseal line: bone elongation ends
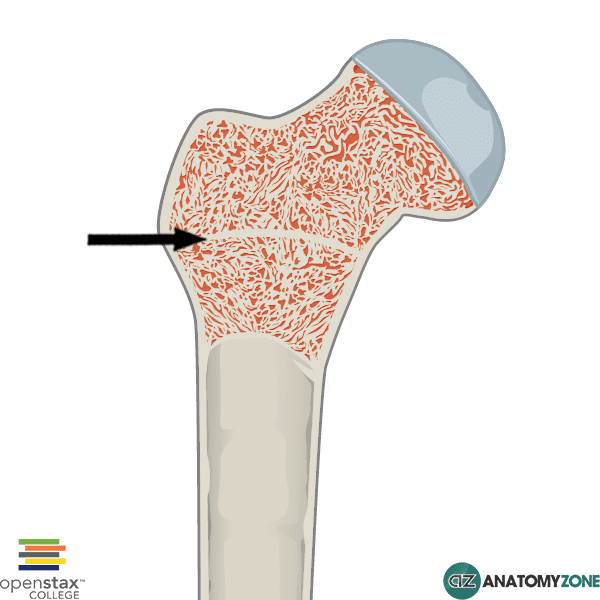
Hyaline cartilage remains at the joint
(articular cartilage)