Derm E2- inflammatory/life threatening/misc. disorders
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is pityriasis rosea?
acute self limiting skin disorder characterized by appearance of inflammatory oval, papulosquamous lesions
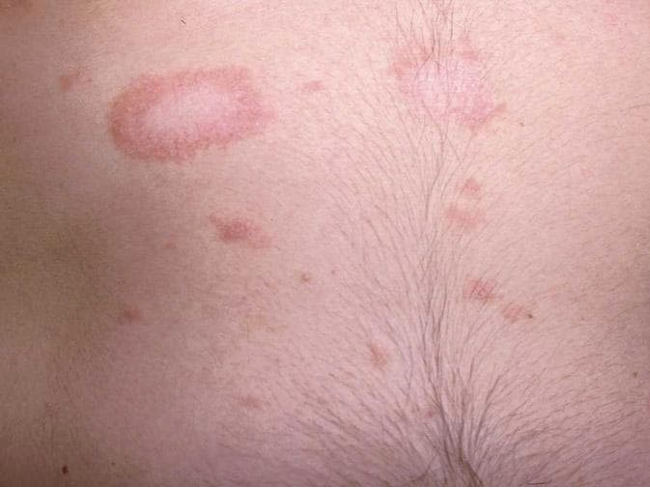
what is the cause of pityriasis rosea?
unknown but linked to some virus (HHV-7, H1N1, COVID-19)
what are the clinical features of pityriasis rosea?
- ± pruritus, typically asx
- pink/hyperpigmented, scaly, oval papulosquamous lesions
- starts w/ herald patch: single, round/oval sharply demarcated lesion on chest/neck/back; eventually becomes scaly w/ central clearing known as “collarette scale”
- 1-2 wks later: smaller ovals in crops along lines of cleavage = christmas tree pattern rash
location: trunk and proximal extremities
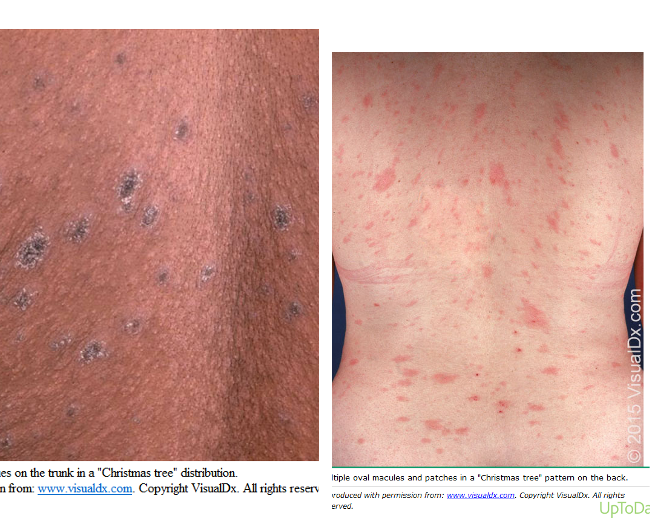
what are risk factors for pityriasis rosea?
older children, young adults, F > M
What is tx for pityriasis rosea?
resolves spontaneously in 6-8 wks; symptomatic relief;
medium potency TCS for pruritus
what are the clinical features of lichen planus?
6 Ps: pruritic, purple (violet), polygonal, planar, papules or plaques (papulosquamous rash)
wichham’s striae (fine white lines visible on papules/plaques)
positive koebner phenomenon
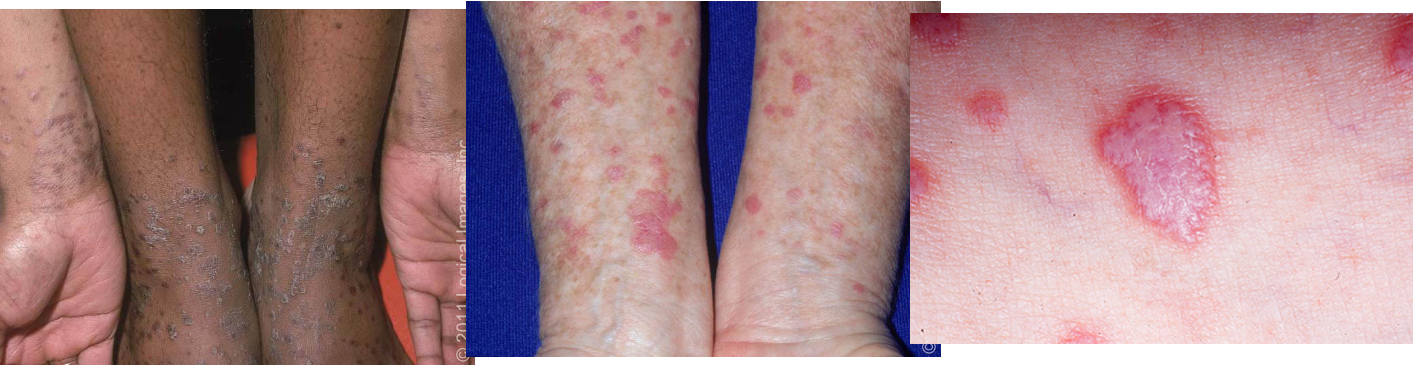
Where is lichen planus located?
skin (volar surfaces of wrists/ankles), oral cavity, genitalia, scalp, nails, esophagus
what are risk factors for lichen planus?
middle age, hep C, metal allergy, meds (ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazide diuretics, NSAIDs)
What is cutaneous lichen planus?
tiny papules that coalesce to form plaques; Wickham striae present
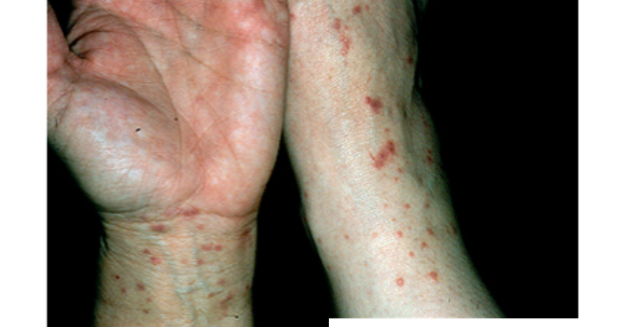
what is oral lichen planus?
can present as lace like wick hams striae on buccal mucosa or atropich/erosive lesions that are painful and burn w/ hot or spicy foods;
persistent loss of appetite due to pain w/ eating
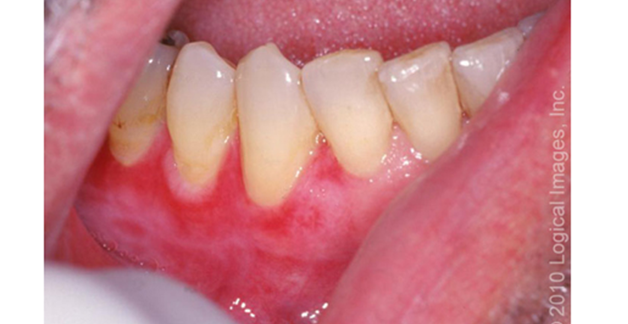
what is genital lichen planus?
violaceous papules on glans penis or vulva
vuvlo-vaginal-gingival syndrome involves epithelium of vulva, vestibule, vagina, and mouth
resistant to tx
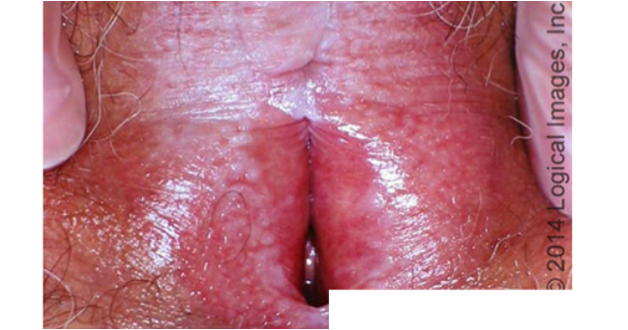
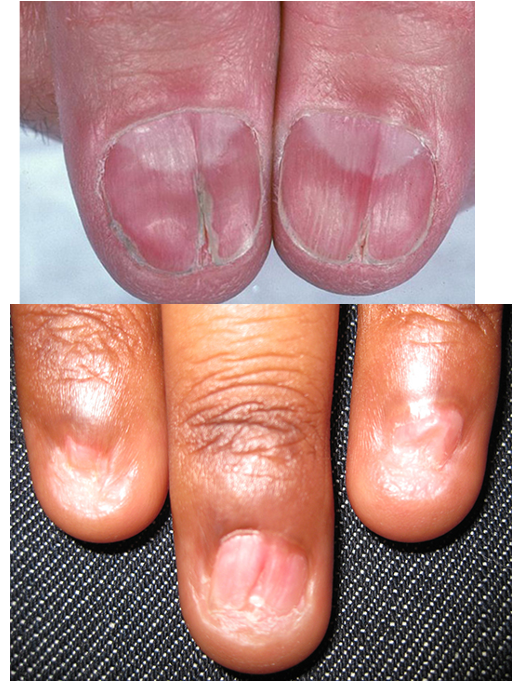
what is nail lichen planus?
varies from minor dystrophy to total nail loss; nail plate thinning and fissuring; longitudinal ridging- trachyonchyia; rapidly progressive
tx w/ intralesional or system corticosteroids
How do you dx lichen planus?
dermoscopy: visualize Wickham’s striae
punch or shave bx
what is 1st line tx for lichen planus?
high potency to super high potency TCS
reevaluate in 2-3 wks
lower potency for face/intertriginous
alt: intralesional corticosteroids
triamcinolone acetonide
systemic glucocorticoids or phototherapy if generalized
What is second line tx for lichen planus?
systemic glucocorticoids, phototherapy, oral retinoids
What can you prescribe for additional symptomatic tx for lichen planus?
oral antihistamines
What patient education would you give for lichen planus?
oral lesions: avoid spicy/acidic foods
residual hyperpigmentation is common
scalp: hair loss is permanent
if sx not responding to TCS after 6 wks → switch to 2nd line tx
What is granuloma annulare?
self limiting dermatosis characterized by erythematous or skin colored annular plaques; exact cause unknown
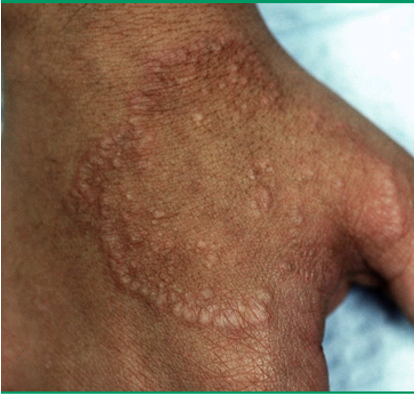
What are clinical features of granuloma annulare?
localized: asx, erythematous or skin colored, annular plaque w/ firm, rope like border and central clearing
SC: deep dermal or sc, solitary or multiple nodule; rare
generalized: widespread, erythematous or skin colored papules and plaques; lesions may be hyper or hypo pigmented
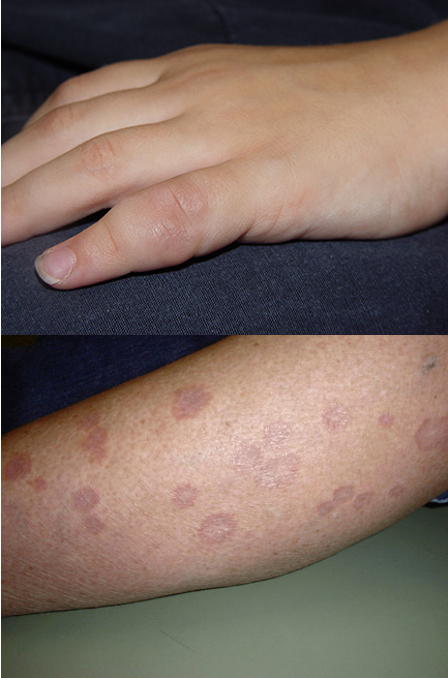
what are the locations for granuloma annulare?
distal extremities and trunk
what are risk factors for granuloma annulare?
children/young adults, DM, hyperlipidemia, malignancy, thyroid dz, infx, meds (allopurinol, amlodipine, diclofenac, topiramate)
How do you dx granuloma annulare?
KOH to r/o tinea; skin bx to confirm
histology: lymphohistiocytic infiltrate, degeneration of collagen, and mucin deposition
what is tx for granuloma annulare?
1st line: topical or intralesional corticosteroids
alt: topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus)
refractory lesions: cryotherapy, phototherapy, pulse dye laser
What is erythema multiforme (EM)?
acute, immune mediated condition characterized by distinctive target like lesions on skin
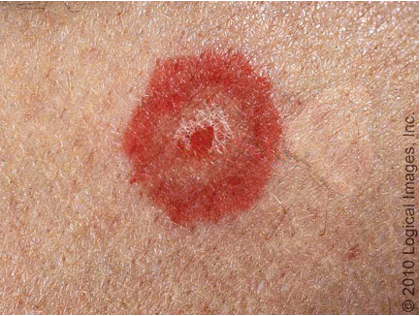
What is cause of erythema multiforme (EM)?
bacterial, fungal, viral infx (HSV MC; mycoplasma pneumoniae MC în children)
malignancy, autoimmune dz, sarcoidosis, hormonal imbalances, COVID-19, meds (sulfa drugs, anticonvulsants, abx)
what is EM minor?
little/no mucous membrane involvement; vesicles but no bullae; eruption confined to face or extremities, classic target lesions;
rash starts on extensor surfaces of extremities and spreads centripetally
assoc. w/ HSV days prior
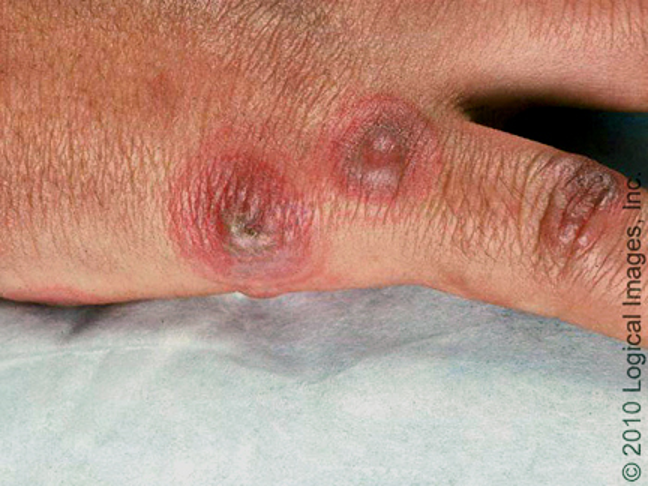
what is EM major?
mucous membrane involvement; occurs w/ drug rxn; lesions in pharynx/larynx
flu like prodrome
systemic sx: fever, chelates, stomatitis, vulvitis, balanitis, conjunctivitis
How do you dx EM?
clinical; skin bx confirmatory
vacuolar interface dermatitis w/ marked infiltration w/lymphocytes along derma-epidermal junction; CD8 and macrophages seen
How do you tx EM?
sx: antihistamines (for pruritus), analgesics, TCS medium potency
if HSV: oral valacyclovir
if mycoplasma: azithromycin
if due to drug/medication: withdraw ASAP
What causes brown pigment?
melaninw
what causes blue pigment?
hemoglobin
what causes red pigment?
oxyhemoglobin
what causes yellow pigment?
carotenoids
what is post inflammatory hyperpigmentation?
reactive melanosis that occurs as a sequela of cutaneous inflammation; hyperpigmented macule or papules
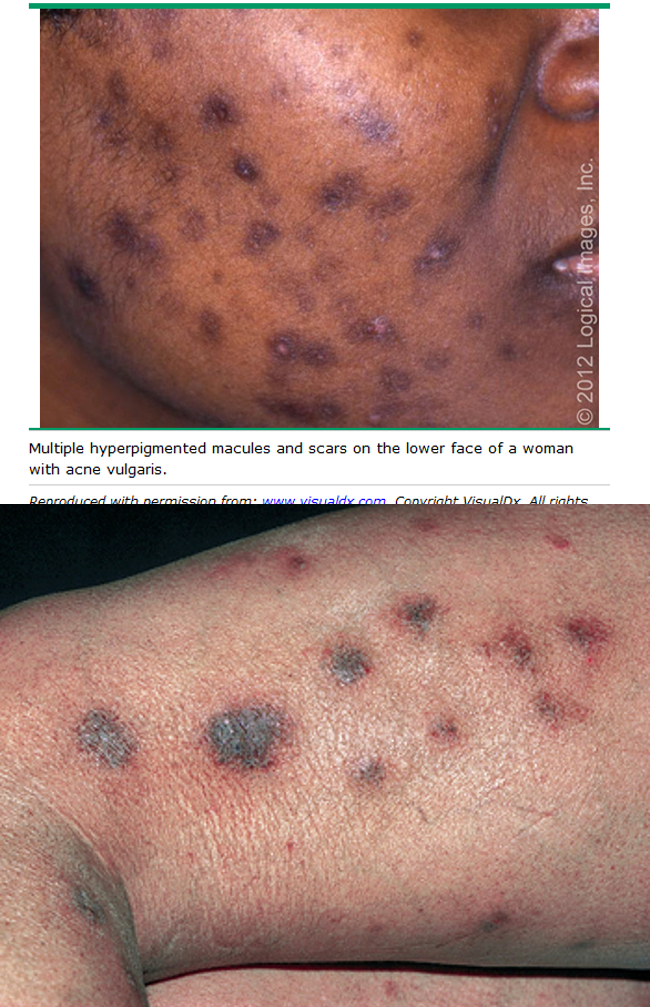
what are risk factors for post inflammatory hyperpigmentation?
phototype III-VI
what causes post inflammatory hyperpigmentation?
acne, lichen planus, atopic/contact derm, trauma, drug eruptions
what is tx for post inflammatory hyperpigmentation?
apply sunscreen SPF 30 or higher
1st line: topical hydroquinone
2nd line: topical retinoids (tretinoin), chemical peels, lasers
what is post inflammatory hypopigmentation?
acquired after partial or total loss of pigment that may occur after inflammation or infectious dermatoses; hypopigmented macules/patches
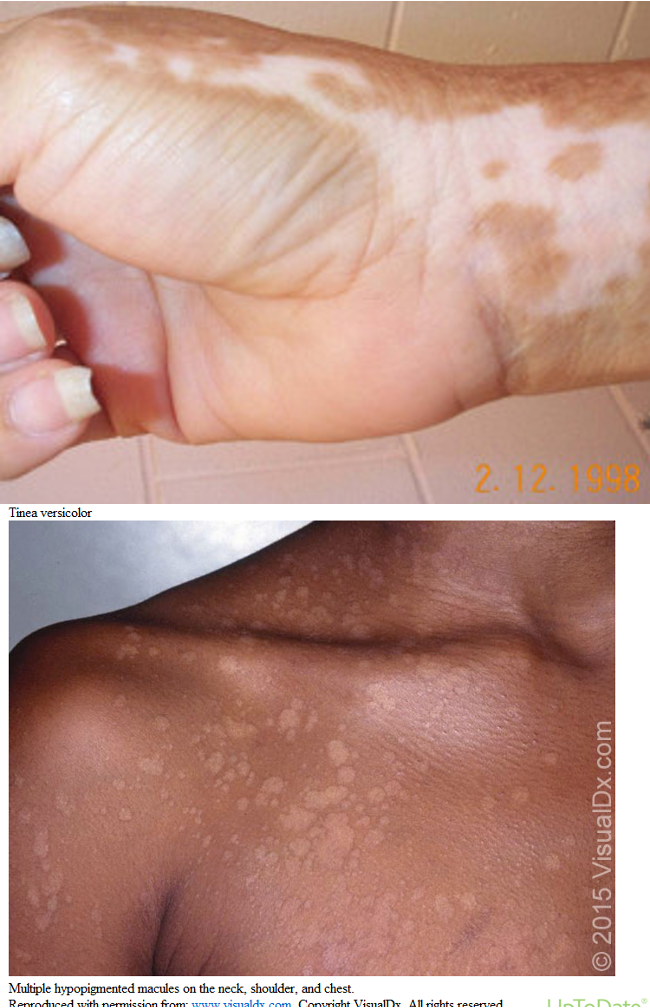
what causes post inflammatory hypopigmentation?
chemic leukoderma/contact vitiligo, drug induced leukoderma (TCS), halo nevus, psoriasis, pityriasis versicolor
What is melasma?
chronic, recurring disorder of hyperpigmentation arising from hyperfunctinal melanocytes that deposit excessive amts of melanin in epidermis and dermis; cause unknown
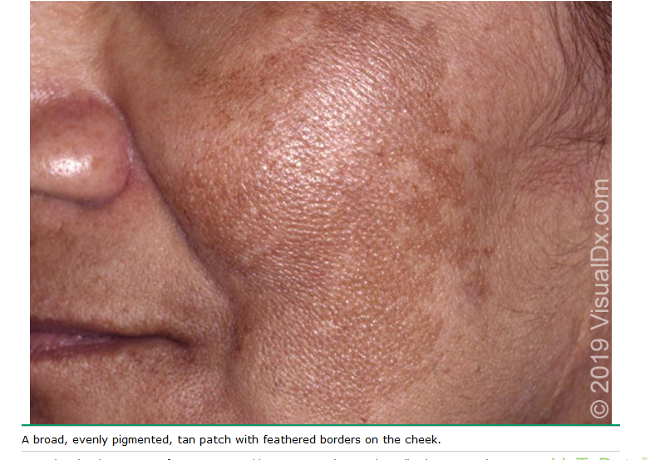
what are clinical features of melanoma?
light/dark brown hyperpigmentation that occurs in sun exposed areas; symmetric; pigmentation evolves rapidly
most commonly on the face
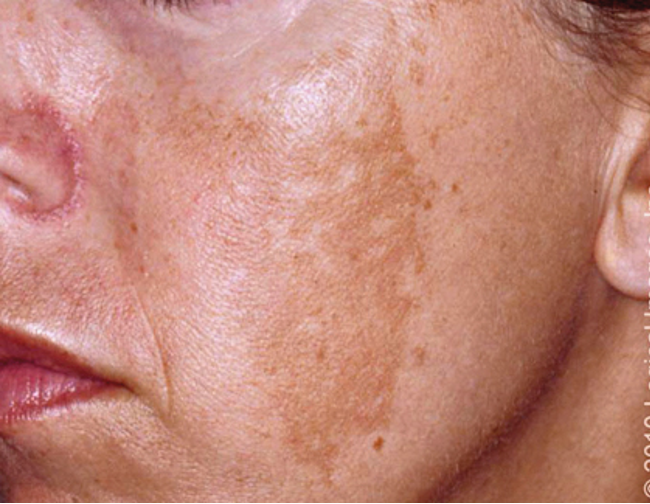
what are risk factors for melasma?
pregnancy, Fitzgerald III-VI, medications, idiopathic, F > M
What is 1st line tx for melasma?
topical hydroquinone cream or topical tretinoin (Retin A)
what is 2nd line tx for melasma?
chemical peels or oral tranexamic acid (lysteda)
what patient education would you give for a pt w/ melasma?
avoid sun exposure and wear sunscreen; no estrogen exposure
what is acanthosis nigricans?
common condition characterized by velvety, hyperpigmented plaques on skin; unknown cause
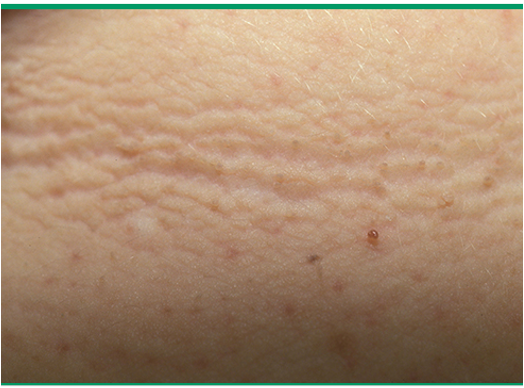
what are clinical features of of acanthosis nigricans?
sickened, velvety to verrucous, grey brown plaques; skin tags may be present
location: intertriginous areas (neck and axilla common)
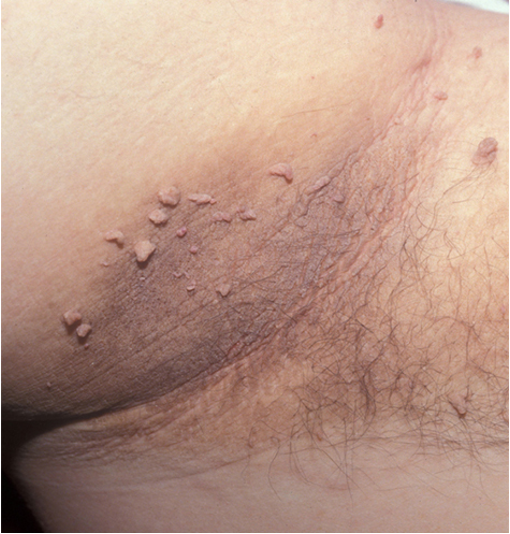
what are risk factors for acanthosis nigricans?
elevated glucose, metabolic syndrome, obesity, malignancy (gastric adenocarinomes- RARE)
what is tx for acanthosis nigricans?
tx underlying cause- wt loss, metformin
topical retinoids (retin a)
topical vit d analogs
What is vitiligo?
common disorder which results from loss of melanocytes in the epidermis; cause known
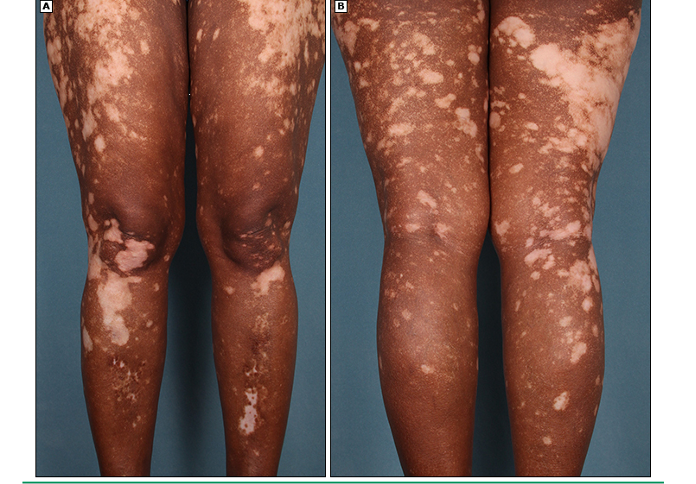
what are the clinical features of vitiligo?
sharply marginated depigmented macule and patches; can be focal or generalized; poliosis- dec or absence of melanin in hair, eyebrows, eyelashes
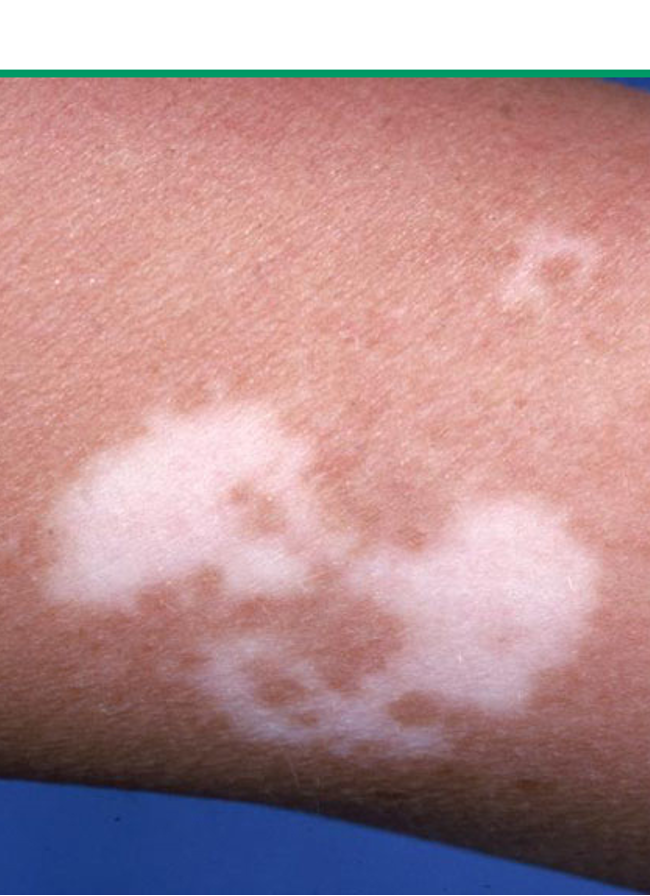
what are risk factors for vitiligo?
autoimmune/endocrine dz- thyroid dx and DM MC
2nd and 3rd decase
genetics
how do you dx vitiligo?
clinical, skin bx (complete loss of melanin pigment in epidermis and absence of melanocytes); labs to evaluate for other disorders (TSH, free T4, CBC, HgbA1c)
what is the tx for vitiligo?
sunscreen spf 30+
localized (<10%TBSA)
TCS- mometasone or clobetasol
topical calcineurin inhibitors- tacrolimus or pimecrolimus for face/neck
disseminated: UVB phototherapy
refractory
targeted phototherapy
combo photo + topical calcineurin or steroids
depigmentation→ beaching w/ monobenzone 20% cream
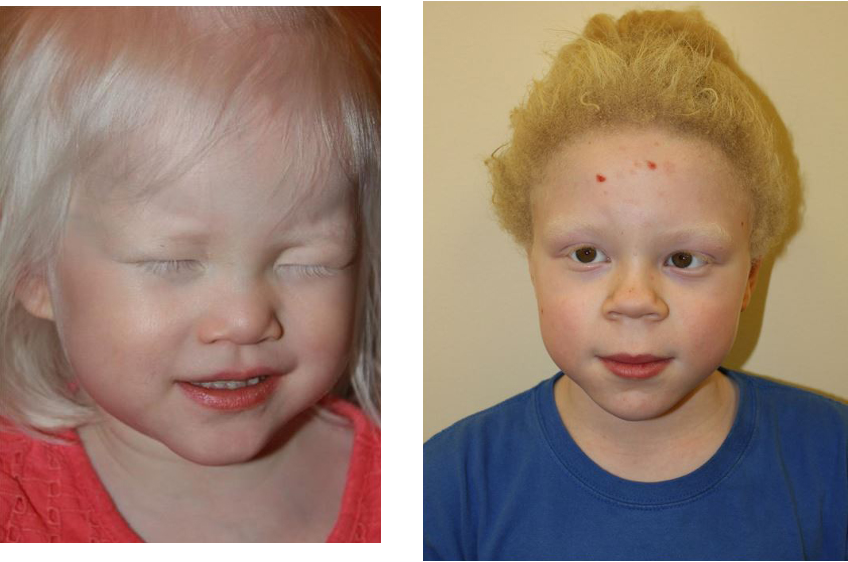
What is albinism?
group of inherited abnormalities characterized by congenital reduction or absence of melanin pigment; caused by autosomal recessive genetic alteration
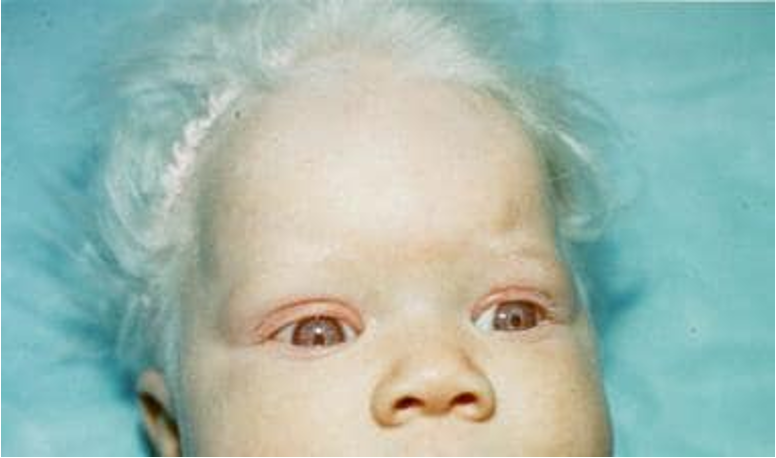
What are clinical findings of albinism?
ocular: reduced iris pigment, photophobia, nystagmus, iris transillumination, yellow/orange retina, reduced VA
skin: hypo pigmented macules/patches; white or reddish blond hair
What is the pathophysiology of albinism?
melanin pathway consists of series of rxns that converts tyrosine into 2 types of melanin: eumalin → black brown and pheomelanin → yellow
genetic mutations affecting tyrosinase along this pathway result in reduced melanin production
what does histology show in albinism?
molecular testing → classify gene alteration; NOT necessary for dx
how do you tx/prevent albinism?
sunscreen, eye protection, ophtho and derm referrals
What are two severe mucocutaneous rxns characterized by extensive necrosis and detachment of epidermis involving the face, trunk, and extremities?
SJS and TEN
Which mucocutaneous rxn is less severe and has skin detachment < 10% of BSA?
SJS
which mucocutaneous rxn has skin detachment 10-30% of BSA?
SJS/TEN overlap
which mucocutaneous rxn has skin detachment of >30% BSA?
TEN
what are risk factors for SJS and TEN?
HIV, malignancy, genetics, SLE
what causes SJS and TEN?
drug induced: MC agents (allopurinol, anti seizure, sulfa, NSAIDs, TNF antagonists, tramadol, sertraline)
infx: m. pneumoniae, EBV, GAS, HSV, influenza, hepatitis, mumps
idopathic
what are prodromal findings of SJS and TEN?
fever, flu like sx precede cutaneous findings by 1-3 days
what are cutaneous findings of SJS and TEN?
diffuse erythema, ill defined coalescing erythematous macules w/ purpuric centers, skin tenderness, flaccid blisters and epidermal detachment
what are mucosal findings of SJS and TEN?
painful, hemorrhagic erosions of oral mucosa and vermillion border; stomatitis, severe conjunctivitis w/ purulence (85% pts), urethritis, ulcerative and erosive vaginitis, genital ulcers and bulla
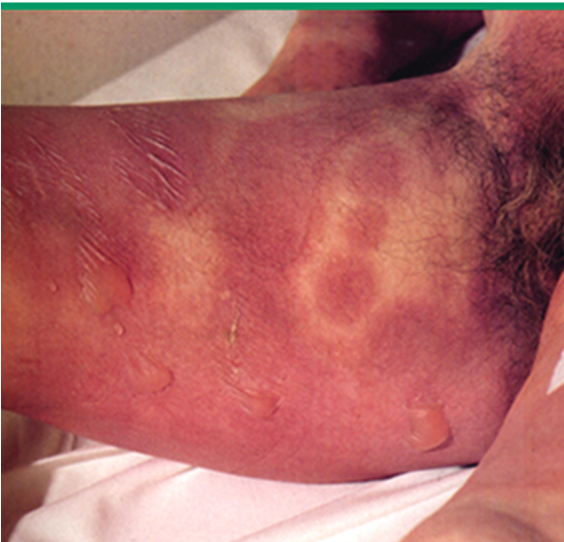
what is this
SJS
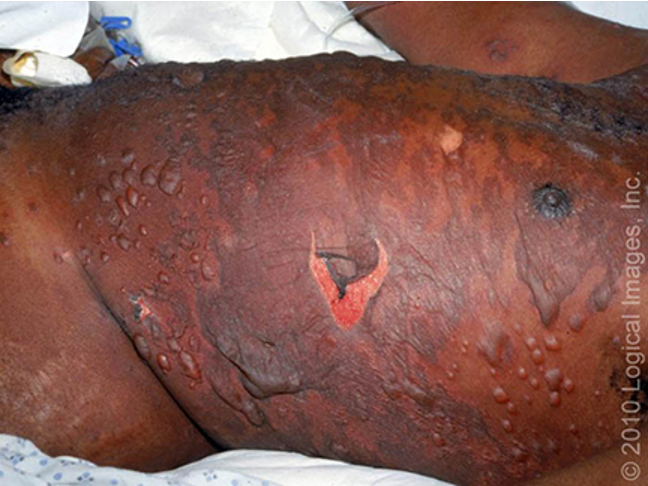
what is this?
TEN
What are PE findings for SJS and TEN?
tachycardia
positive nikolsky sign
erythematous macules, targeted lesions, or diffuse erythema progressing to vesicles and bulla
painful mucosal erosions
necrosis and sloughing of epidermis
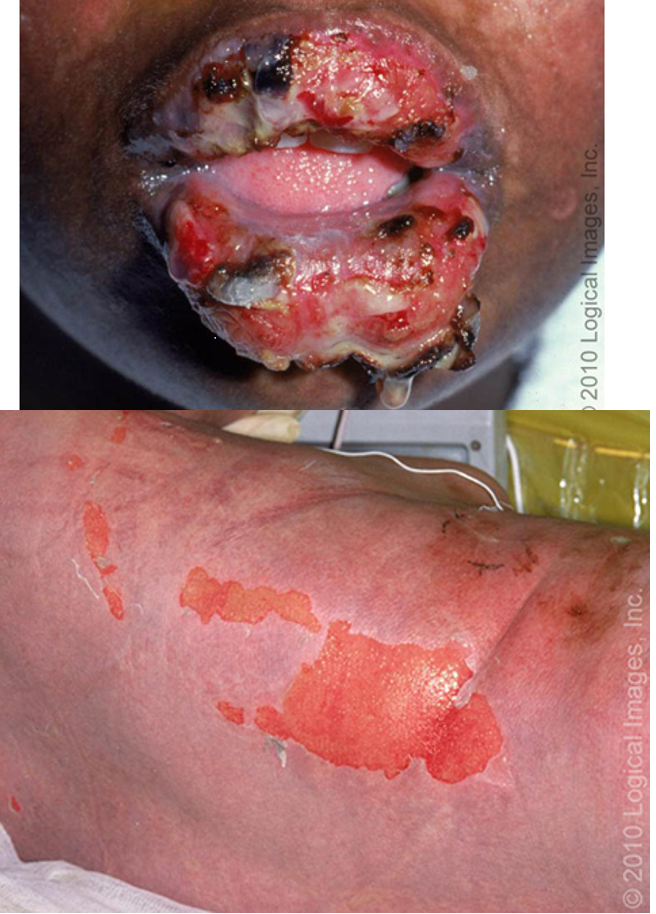
how do you dx SJS and TENs?
H&P
CBC- anemia, lymphopenia, neutropenia
CMP- electrolyte abnormalities, elevated BUN/Cr, elevated glucose, hypoalbuminemia
elevates ESR and CRP
skin bx: full thickness necrosis and separation of epidermis at the DEJ
What is the tx for SJS and TENs?
early dx → stop offending agent
admit to ICU
supportive: wound care, fluid/electrolyte, temp management, nutritional support, infx prevention, pain control, airway management
medication: systemic glucocorticoids, IVIG, cyclosporine (sandimmune)
What is androgenetic alopecia?
pattern baldness
what is scarring alopecia?
permanent, irreversible;
chemical/physical trauma
bacterial/fungal infx
lichen planopilaris
herpes zoster
what is non scarring alopecia?
reversible;
SLE, secondary syphilis, thyroid dz
alopecia areata: immune mediated disorder that targets anagen hair follicles
pathognomic finding: exclamation point hairs- recurrent, non scarring type of hair loss
what is tx for androgenetic alopecia?
topical minoxidil 5% for onset < 5 yrs
oral finasteride (propecia) 1 mg daily
what is tx for alopecia areata?
preferred: intralesional corticosteroids
alt: TCS high potency
what are clinical features of venous stasis ulcers?
red, pruritic patches of stasis dermatitis precede ulceration; pain w/ ambulation; non healing ulcers; leg edema
usually on medial aspect of lower legs above malleolus
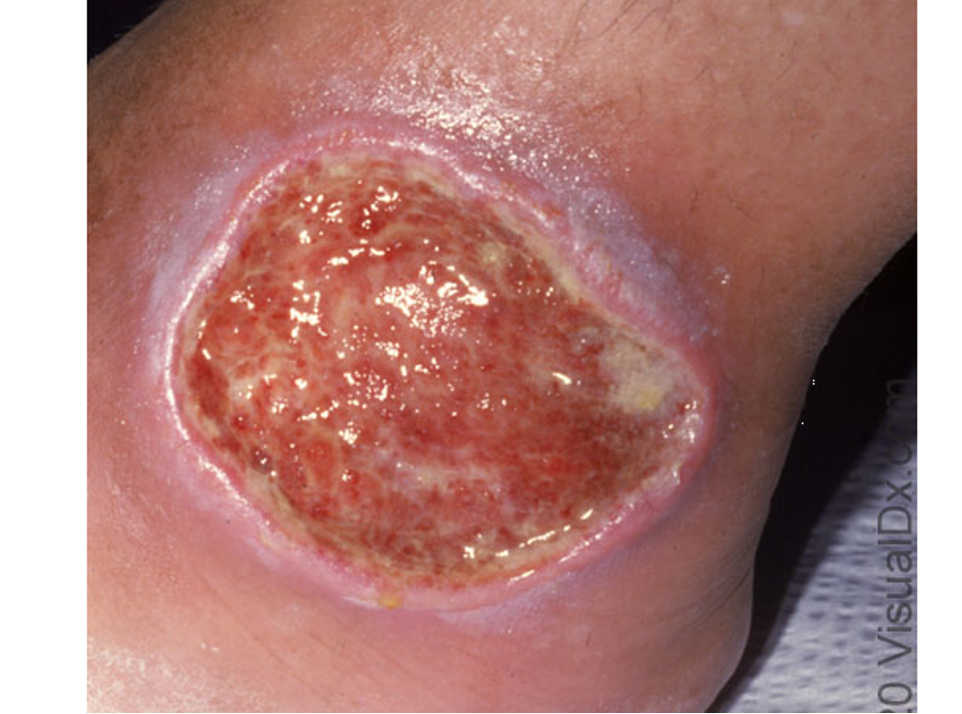
what are risk factors for venous stasis ulcers?
varicosities, thrombophlebitis, immobility, venous insufficiency
what is tx for venous stasis ulcers?
abx if infected or signs of cellulitis
wound debridement
wound dressings- aquacel ag, mepilex ag
what is stage I pressure ulcer?
intact skin w/ impending ulceration; non blanchable erythema
what is stage II pressure ulcer?
partial thickness loss of skin involving epidermis and dermis that appears as open shallow ulcer w/ pink wound bed
what is stage III pressure ulcer?
full thickness loss of skin w/ extension into SC tissue not through the underlying fascia;
may include undermining and tunneling to adjacent tissue
what is stage IV pressure ulcer?
full thickness tissue loss w/ extension into muscle, bone, tendon, or joint capsule;
slough or eschar present in the wound;
osteomyelitis w/ bone destruction and dislocation/pathologic fractures found
what is an unstageable pressure ulcer?
full thickness tissue loss in which base of ulcer is covered by slough or eschar → full depth cannot be appreciated
How do you dx pressure ulcer?
staging wound depth
ulcer location, size, maceration and induration to be recorded
labs: CBC, ESR
tissue bx: if no improvement, suspect bacteria invasion
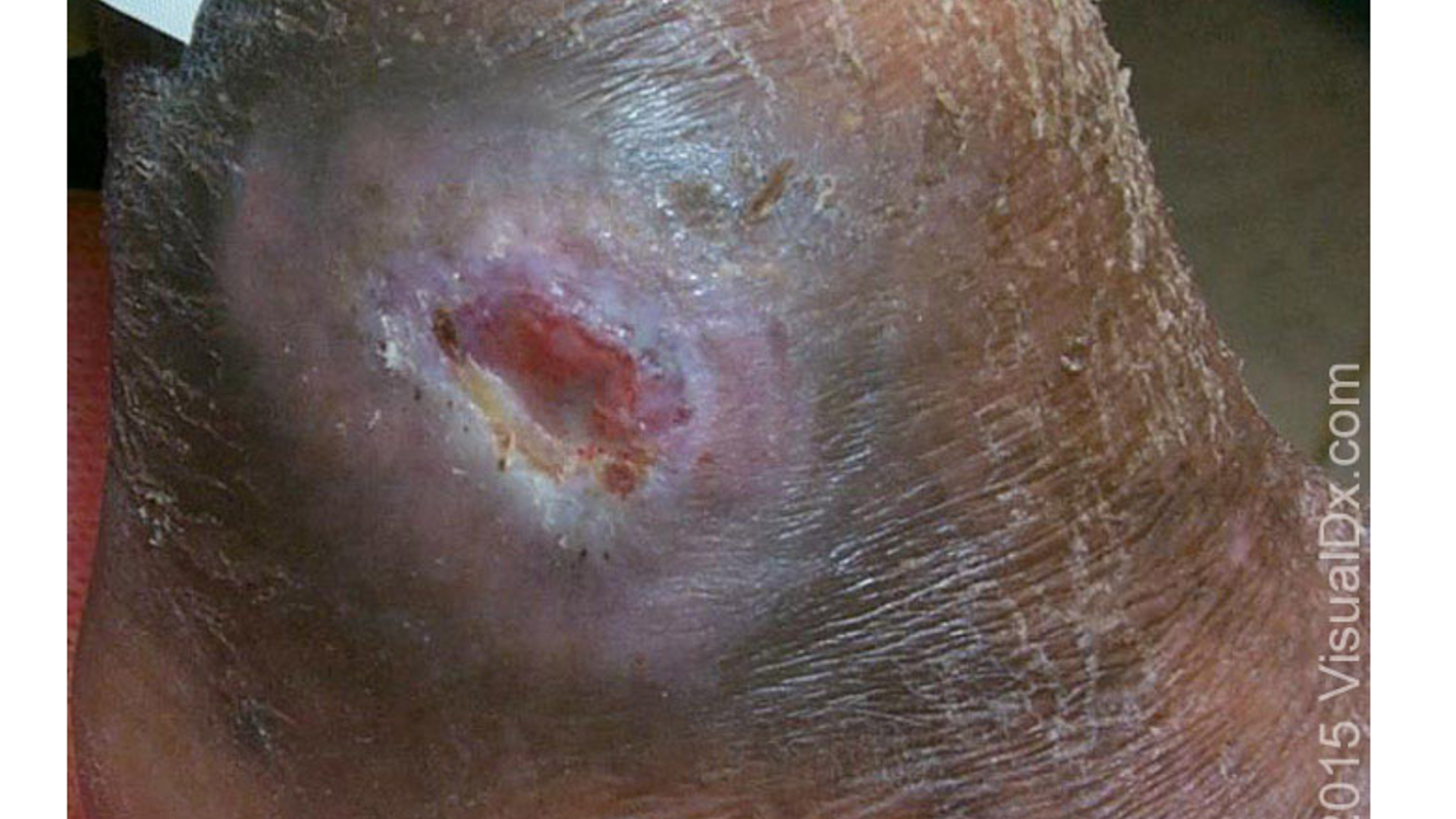
What is tx for pressure ulcers?
remove pressure→ frequent repositioning
wound debridement if necrotic
prevent infx
wound care: hyperbaric oxygen, electrotherapy, wound dressings