Weathering (Karst landscapes)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Surface features in karst landscapes
Limestone pavements
Swallow holes
Disappearing streams
Dolines/sinkholes
Underground features of karst landscapes
Stalactite
Stalagmite
Pillars
Curtains
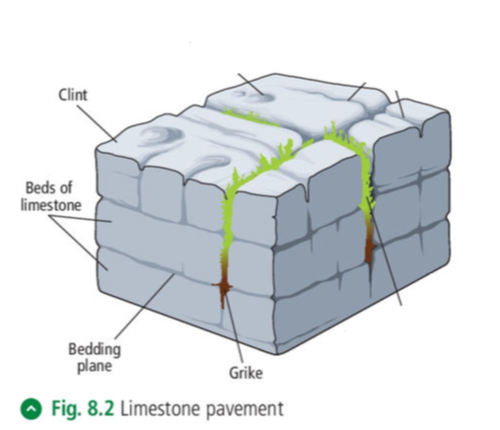
Limestone pavements
Limestone pavements are extensive areas of flat limestone rock.
The first soil cover must be removed. Then the limestone is then chemically weathered by carbonation.
Rainwater mixes with CO² and forms a weak carbonic acid. When it falls on exposed limestone, it dissolves the calcium carbonate that keeps the rock together.
Percolating through the permeable limestone, the carbonic acid attacks joints in the rock.
The joints are widened and spread, making gaps in the limestone (grikes).
Rocks of limestone called clints remain on the surface, seperated by grikes.
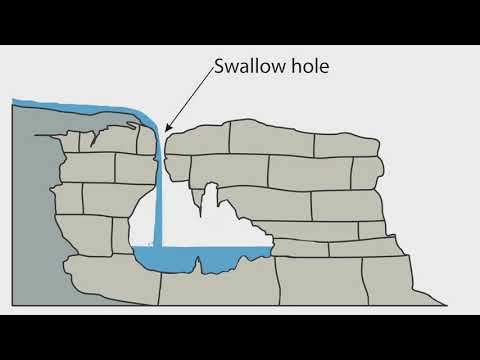
Swallow holes
Swallow holes are large openings formed in river beds in limestone areas.
Streams can erode the vertical joints/grikes in the permeable limestone via hydraulic action, abrasion and solution.
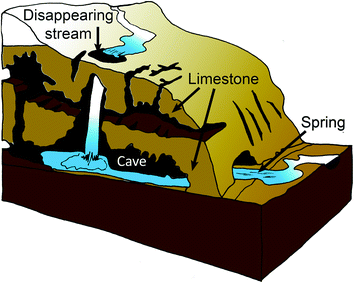
Disappearing streams
Disappearing streams are streams of water that instantly disappear underground via swallow holes.
They play a big role in the formation of caves and caverns underground.
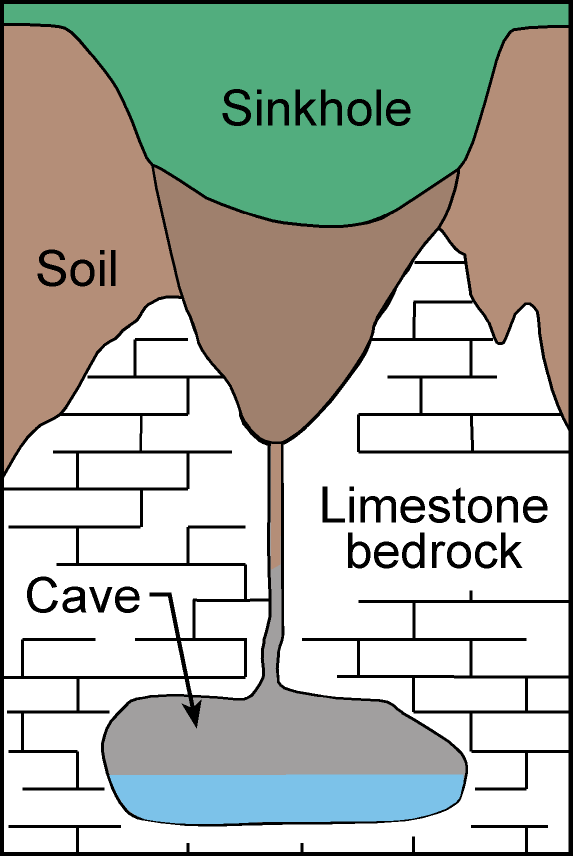
Dolines/Sinkholes
Dolines are deep hollows formed on the ground surface when a cave roof collapses.
When a limestone cave grows upwards, layers of rocks can become too weak to support itself.
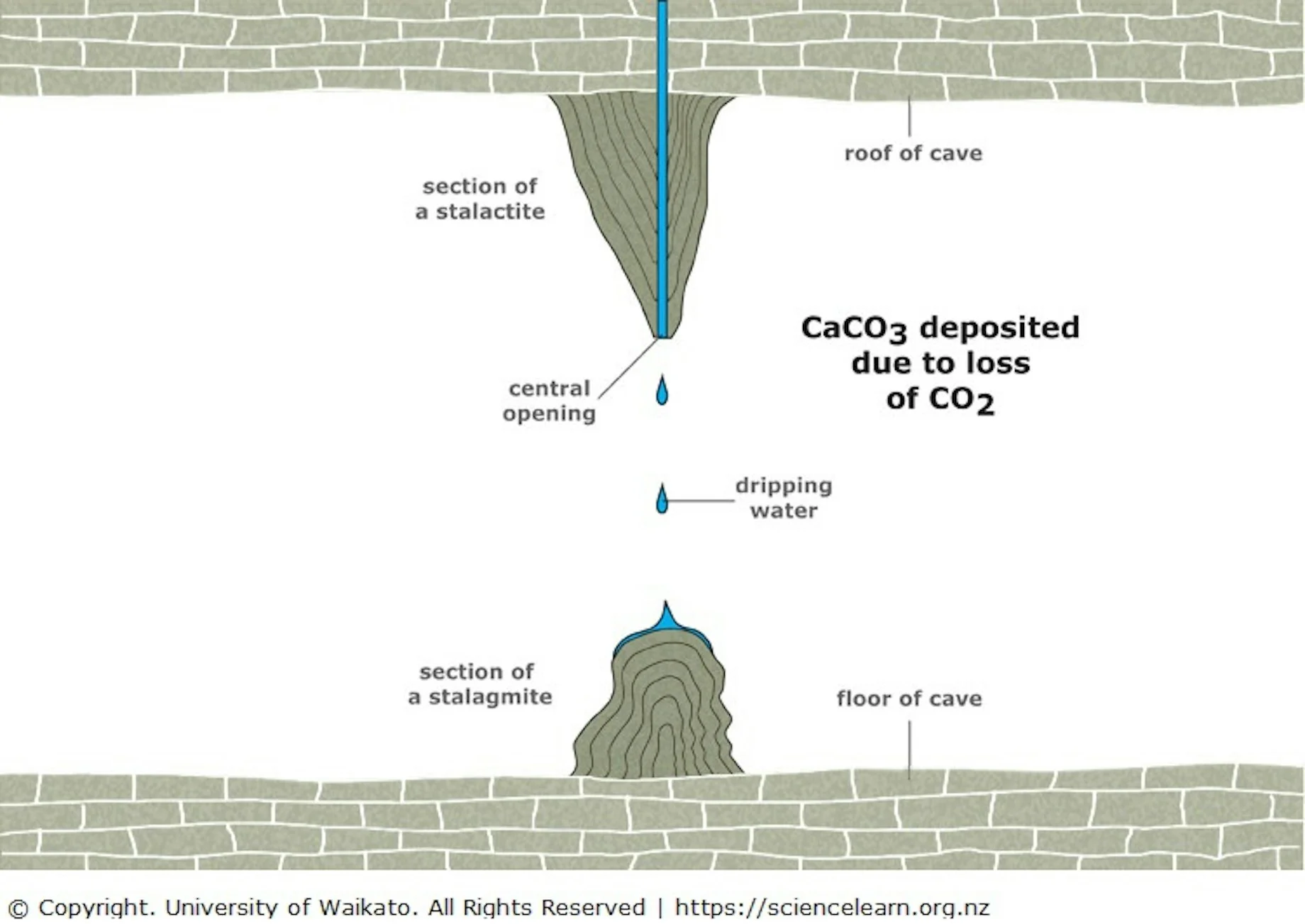
Stalactites
Stalactites are underground features of a karst landscape that form on the roof of caves. It’s a build up of calcium carbonate deposits that grow down from the cave roof.
A limestone feature formed in an underground cave is known as speleothem.
The stalactites form when water filled with dissolved calcium carbonate which is known as calcite percolates through the limestone layers until it reaches the area filled cave.
The water drips down slowly from a narrow joint opening on the cave ceiling.
Once the water comes into contact with air-filled cave it makes a chemical reaction and reverses the original chemical reaction, forming new calcium carbonate.
The water continues dripping down till it forms stalactites and stalagmites.
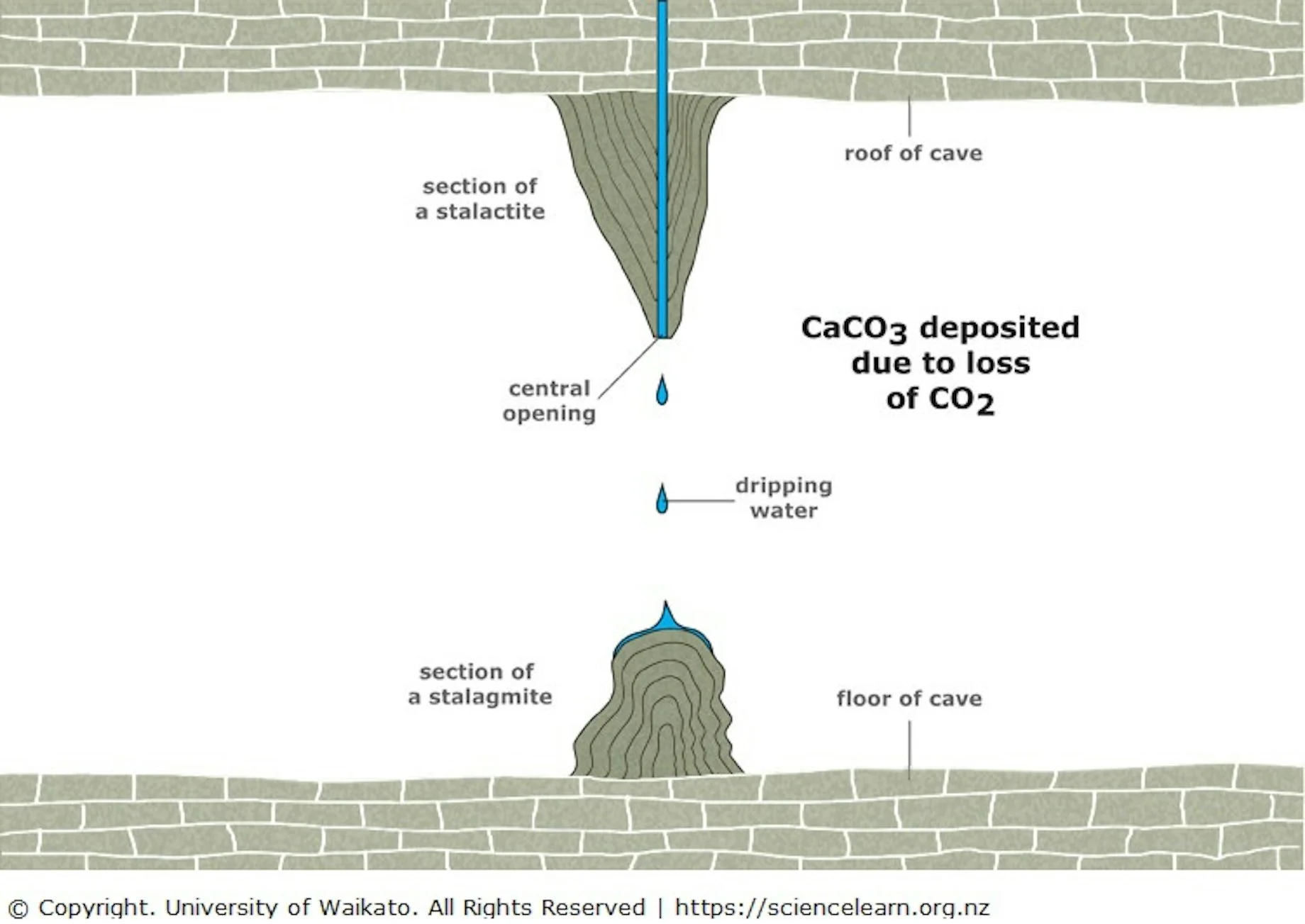
Stalagmite
As calcium bicarbonate falls from stalactites, evaporation also affects it as it falls leaving behind calcite.
The calcite accumulates overtime forming stalagmites that grow upwards and are larger and stronger.
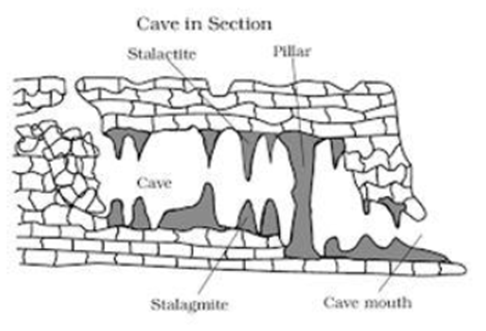
Pillars
Pillars or columns are formed when stalactites and stalagmites grow so huge they join together.
Curtains
Curtains are formed when calcite deposits form a continuous, narrow but solid structure hanging from a cave roof. They grow down with age.