Evo Devo
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
blastomeres retain all genetic info and totipotency until when?
16 cell stage
are ICM cells pluripotent or totipotent?
pluripotent - does not form extraembryonic
important factors for ICM pluripotency
Oct4, Sox2, and Nanog
iPS cells are:
pluripotent: makes most but not all somatic cell types
housekeeping genes
expressed by all/most somatic cell types and provides proteins for basic cell structure and metabolism
tissue-specific genes
determines cell’s phenotype
miRNA
small non-coding RNAs that attach to specific mRNA for translation inhibition or degradation
where is Pax6 found and what is it?
a transcription factor found only in eyes, pancreas, and neural tube - crucial for eye formation
knowing Pax 6 must work with other TFs to activate, which TFs are required?
lens cells: Sox2, Maf, and delta-EF3
pancreas cells: Pbx1, Pdx1, and CREB
how long is chromatin in total?
2 meters
histone ______ increases gene accessibility
which tails?
acetylation of H3 and H4 - neutralizes charge
pioneer transcription factors (+example)
accesses tightly coiled chromatin to initiate local relaxation - pioneers the opening of the region
ex: Pbx1
histone methylation ________ gene accessibility
alters - may either increase or decrease
trimethylation of H3 at lysine 4 - promotes transcription
dimethylation or trimethylation at lysines K9 and K27 - promotes silencing
where does DNA methylation occur?
CpG sequences - catalyzed by Dnmt
DNA methylation in a gene’s promoter ________ transcription
represses
genomic imprinting
refers to the concept that some genes will only be active when located on the maternally or paternally derived chromosome
Igf2 is ______ derived and _______ fetal growth
paternally
promotes
Igf2r is _________ derived and ________ fetal growth
maternally
inhibits
steps of DNA methylation during development
DNA methylation is maintained from parental copies
DNA methylation is removed
DNA methylation initiates
DNA methylation is modified
X chromosome inactivation is initiated at the _______ locus and is mediated by ________ (non-coding RNA)
XIC
Xist
X chromosome inactivation involves extensive methylation of H3, H4, and cytosines of the DNA?
True
primordial germ cells are diploid or haploid?
diploid
germ plasm
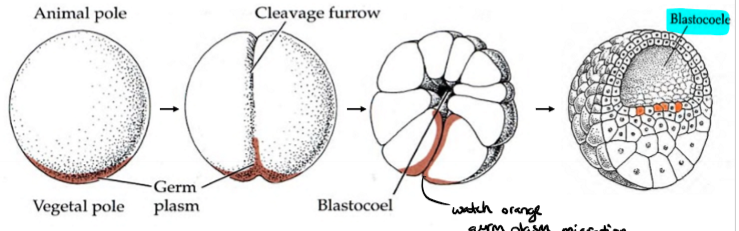
nuclei in the _______ pole plasm develop into pole cells after 9 divisions
posterior
pole cells become
gametes
produced by gut and repels pole cells
Wunen
secreted by developing gonads as chemotactic factor
Hedgehog
a gcl mutation will result in ______ flies
sterile
pole plasm constituents
nanos - binds 3’ UTR to inhibit certain translation
polar granule component - inhibits RNA poly II
Piwi - acts with microRNAs
Vasa - translation initiation factor
Oskar - anchors other constituents in posterior
PGCs in humans develop in ______ region where TFs _______ and _______ are expressed
posterior
Blimp1
Prdm14
SDF-1
from gonads, attracts PGCs in some vertebrates
pluripotency genes expressed by:
ICM
hESCs
iPS
diapedesis
cells squeeze through walls of other cells - between cells
what does the female gonadal ridge produce to drive oogenesis pathway?
Wnt4 - allows activation of Beta-catenin in nucleus
CYP26B1
degrades retinoic acid
Prophase stages
leptotene
zygotene
pachytene
diplotene
diakinesis
Type A spermatogonium
founder population, perpetually replicating
Sertoli cells release
retinoic acid and GDNF
sperm development stages
spermatogonia - primary spermatocytes - secondary spermatocytes - spermatids - spermatozoa
stage of arrest in oogenesis
diplotene - caused by phosphorylation
amphibians synthesize proteins rapidly following fertilization thanks to rRNA amplification in the ________ stage
pachytene
cortical granules are derived from
Golgi vesicles
ovulation is triggered by
LH surge
Graafian follice
mature primary oocyte
until fertilization, oocytes are arrested in
metaphase II as secondary oocytes
resact and speract
chemotactics of sea urchin eggs
progesterone and CRISP1
cumulus layer chemotactics
Izumo to
Juno (and CD9)
fast block to polyspermy
rapid depolarization (in aquatics)
Slow block to polyspermy
cortical granules release their contents coating the egg - gives swelling and elevation, hardens membrane, and removes bindin receptors
catalyzes slow block hardening:
Udx1 - catalyzes peroxidase activity
zygotic cleavage lacks these two phases of the cell cycle
G1 and G2
blastocoel develops
32 cell stage
blastocoel development gives rise to layer:
ICM and trophoblast (extraembryonic chorion)
Cdx2
blocks pluripotency genes, inactivated by hippo at ICM layer
potency of trophoblast cells
unipotent - placental tissue only
are translation or transcription required for early blastomere cleavage?
translation only - maternal deposits yay
maskin can block translation through binding proteins at which end of mRNA?
both - loopy gal
translation requires 5’ cap
true
main function of gastrulation
form the three primary germ layers
sites of gastrulation:
mouth first
anus first
protostome
deuterostome
where does dorsal lip form?
grey crescent region - just below marginal zone
lines roof of blastocoel during gastrulation
fibronectin fibrils
chordamesoderm
early population of deep marginal zone cells from dorsal lip involution
differences in gastrulation of birds compared to amphibian
starts with delamination instead of involution
ingression at primitive streak
_______ portion of the notochord develops earlier
anterior
ISP2
trypsin-like enzyme secreted by uterine endometrial glands to digest the zona pellucida and hatch the balstocyte
adhesion molecules on blastocyst to attach to endometrium
L-selectin, integrins, and HB-EGF
decidualization
prep for implantation
syncytiotrophoblast
connects to endometrium and secretes proteases
cytotrophoblast
standard outer lining
______ _______ encourage cell specification
growth factors
placenta
chorion and uterine endometrium
early pregnancy factor
produced by trophoblast cells of implanting blastocyst to suppress maternal immune response
human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
produced by trophoblast cells of implanting blastocyst - signals corpus luteum to maintain progesterone production
2 male pronuclei
bad embryo, good placental chorion
2 female pronuclei
good embryo, bad placental chorion
specification vs determination
cell fates - reversible vs irreversible
autonomous specification
cytoplasmic determinants
conditional specification relies on
induction between cells
yellow crescent CYTOPLASM in tunicates specifies:
muscle cells - via Macho1 (activates Tbx6 TF)
necessity experiment
removes function
sufficiency experiment
adds function
skn1 in c. elegans
specifies muscle and endoderm - double mutation lacks these
P granules
cytoplasmic determinants - settle in c. elegans posterior via microfilament assistance - specify germ cells
PIE1
transcriptional repressor of somatic differentiation
blastomere potency
multipotent
2 components of induction systems
inducer
“competent” responding tissue - tissues typically lose this over time as they become more specialized
instructive induction
specifies a multipotent responding tissue to a specific fate
permissive induction
induction providing conditions for an already specified tissue to complete its predetermined fate
specification of E fate requires _______ induction
P2
mom-2 mutation
more mesoderm - no intestine as E blastomeres adopt MS fate
mom-2 usually is a Wnt protein in P2 used to induce E fate from EMS
in charge of instructive induction in sea urchins
micromeres
woah wait dorsal lip has inductive properties?
yeah bro for neural ectoderm
genes to set up D/V and A/P axes in drosophila
maternal-effect
A/P axis
gurken/torpedo at posterior - sets up microtubule network
anterior - bicoid - blocks caudal
posterior - nanos - inhibition of hunchback
*in unfertilized egg
torso
promotes development of acron and telson - both extremities
tailless + huckebein + bicoid = acron
tailless + huckebein = telson
D/V axis
gurken/torpedo around dorsal edge of oocyte - inhibits pipe
pipe cascade
pipe - snake - Easter - spatzle - receptor Toll (ventral) - pelle - cactus - dorsal (TF) —— dorsal active in ventral region fantastic
dorsal mutants
do not form ventral tissues