PAS 407 Pleural Cavity and Lungs
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
pulmonary cavity
bilateral regions of the thoracic cavity containing the lungs
pleural cavity considered the region between surface of lung and internal surface of thoracic wall
- mostly a potential space
- contains small volume of fluid to limit friction
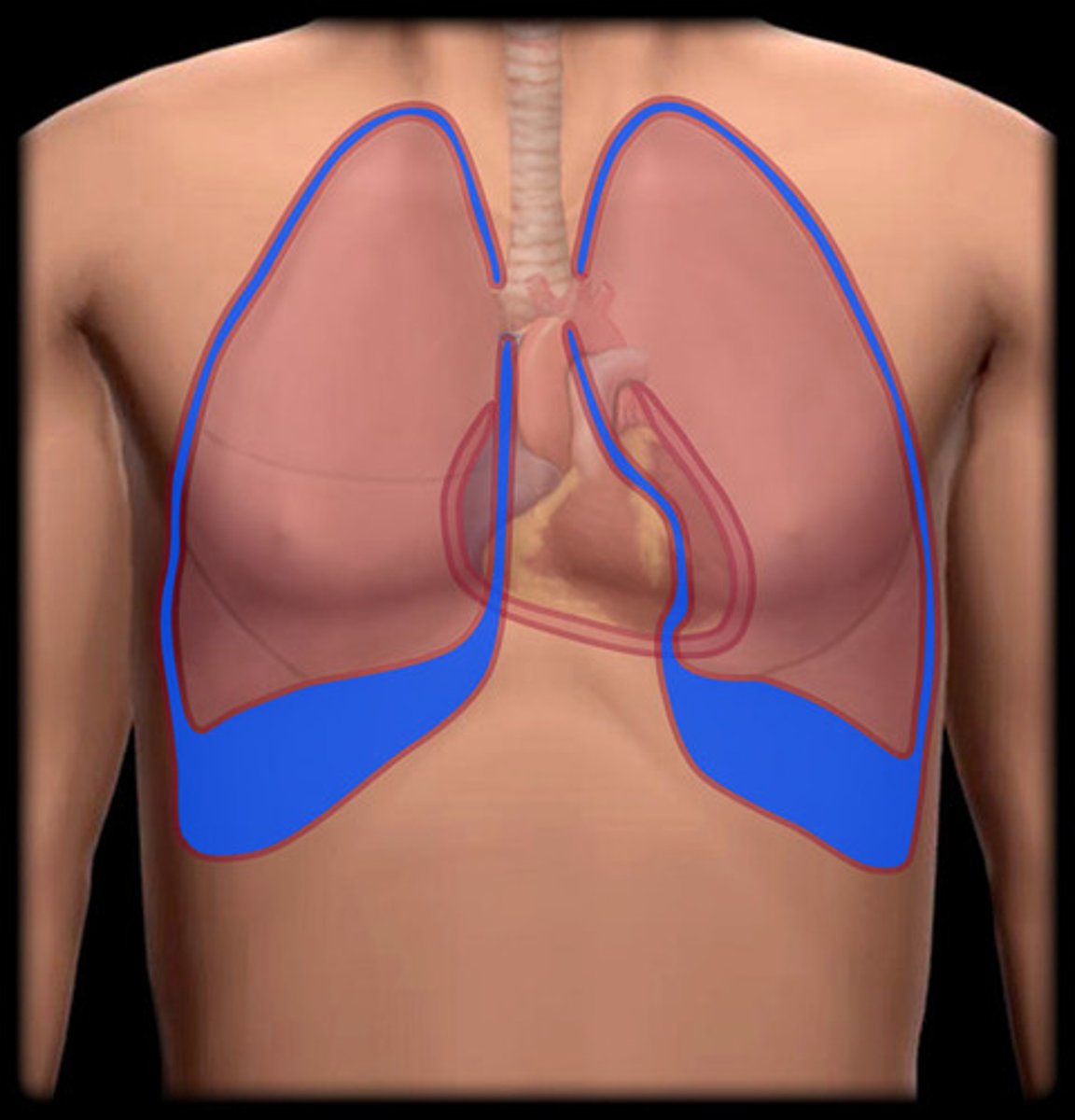
what is the pulmonary cavity boarded by?
pleural sac
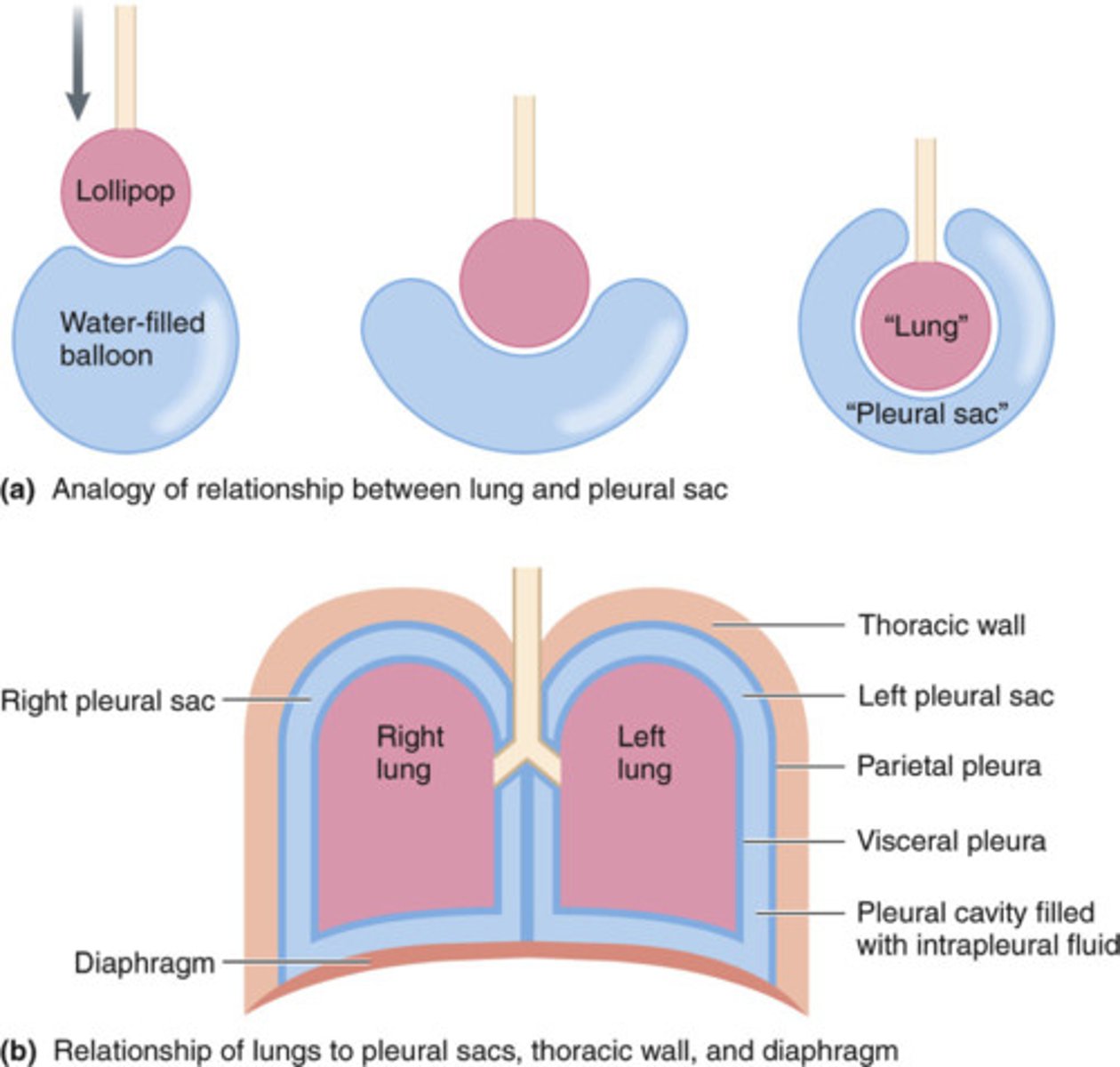
pleural sac
double layer of serous pleural membrane, continuous at hilum of lung
results in 2 layers of pleura
- visceral and parietal pleura
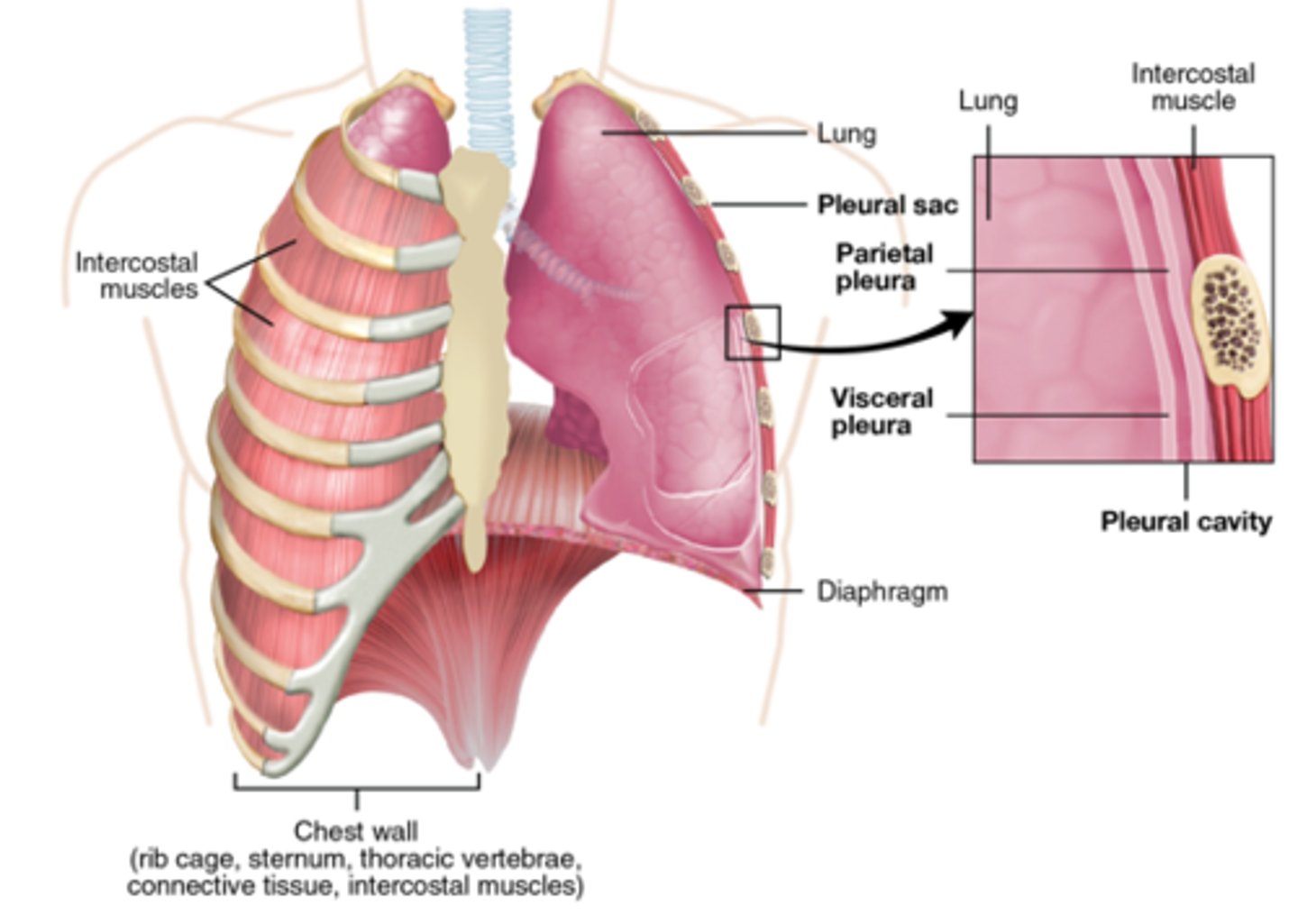
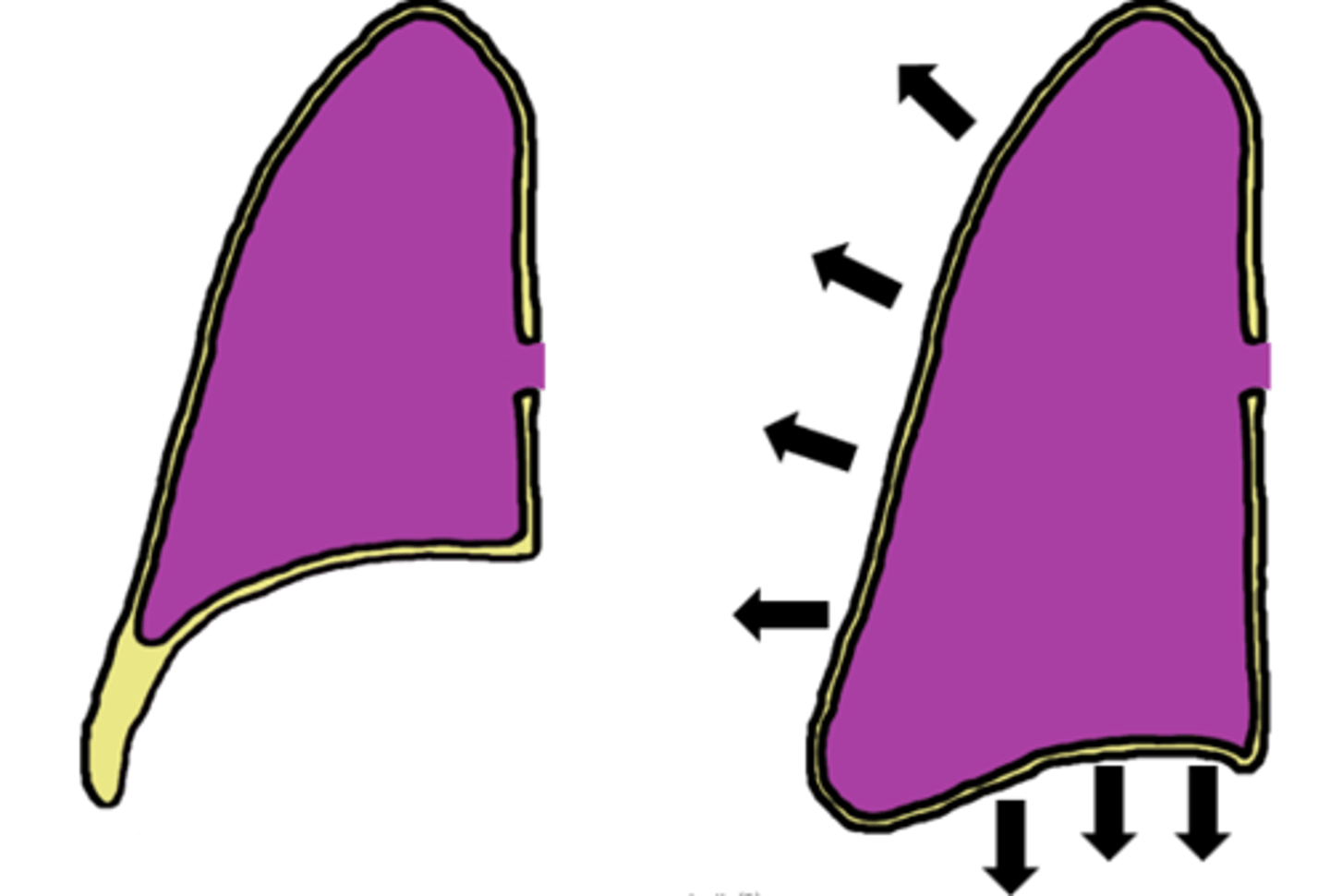
what does pleural sac generate?
- generates hydrostatic pressure necessary for expansion/compression of lungs during ventilation
- diaphragm, external intercostals contract to expand pulmonary cavity
- hydrostatic tension results in pull on visceral pleura by parietal pleura
Visceral pleura
portion of serous membrane which adheres to surface of lung
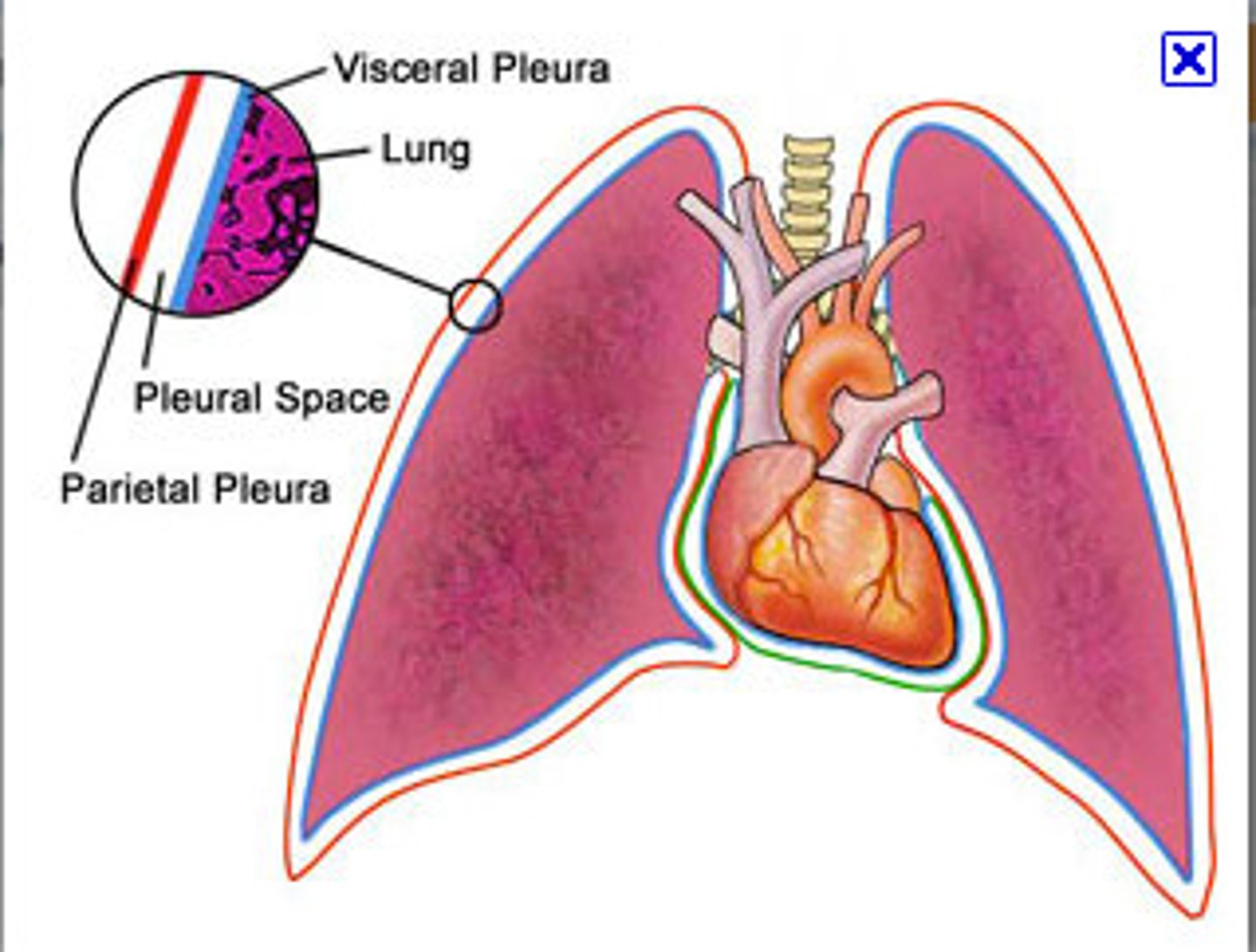
parietal pleura
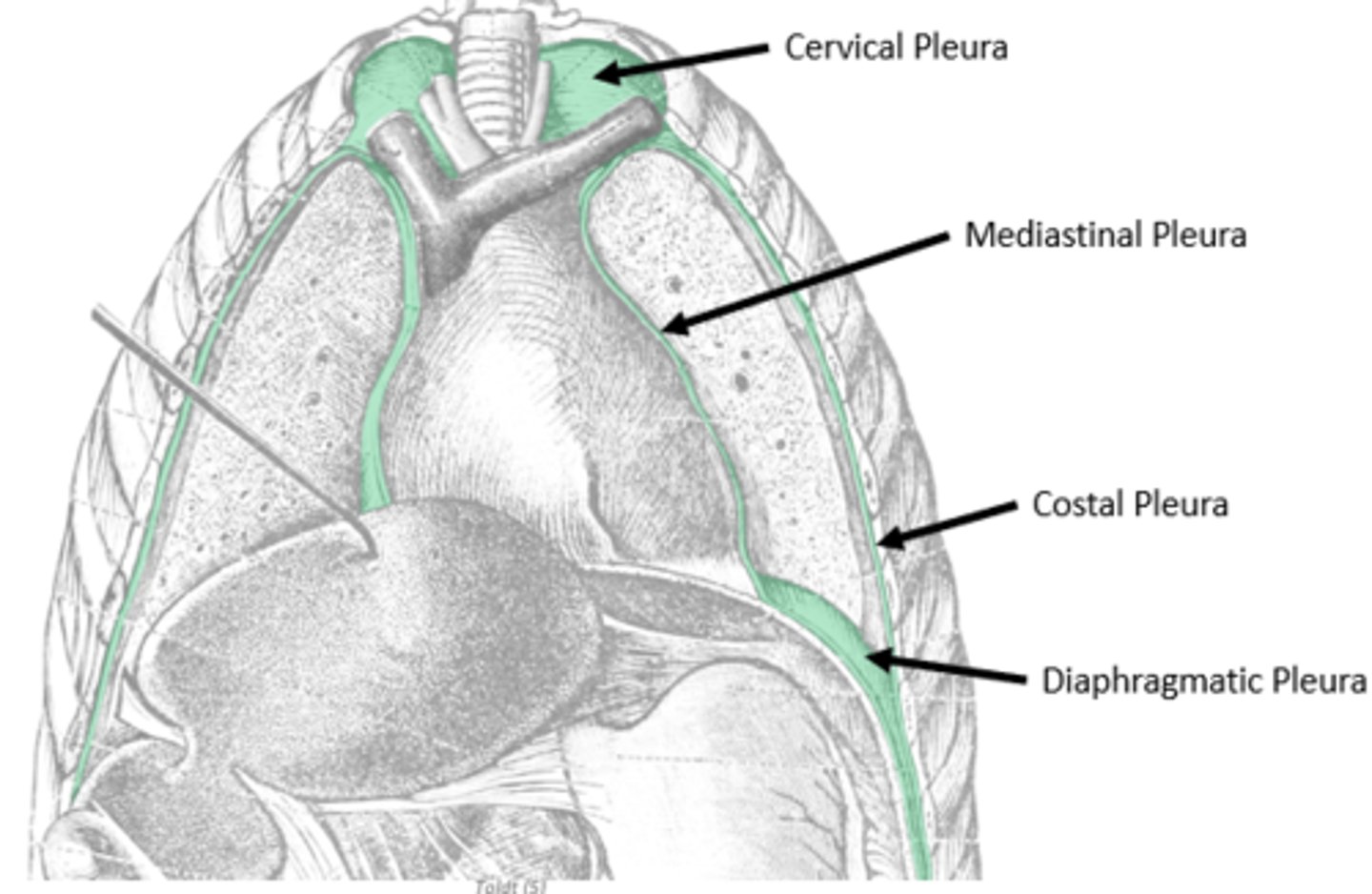
internal covering of pleural cavity
anchored to wall through endothoracic fascia
("wallpaper glue")
divided into coastal, cervical, mediastinal, diaphragmatic portions
pleural recesses
during expiration, diaphragm receeds superiorly
portions of thoracic cavity fold upon itself
- cost diaphragmatic recess and cost mediastinal recess
costomediastinal recess
· Portion of the costal pleura over lining the sternum makes contact with the mediastinal pleura
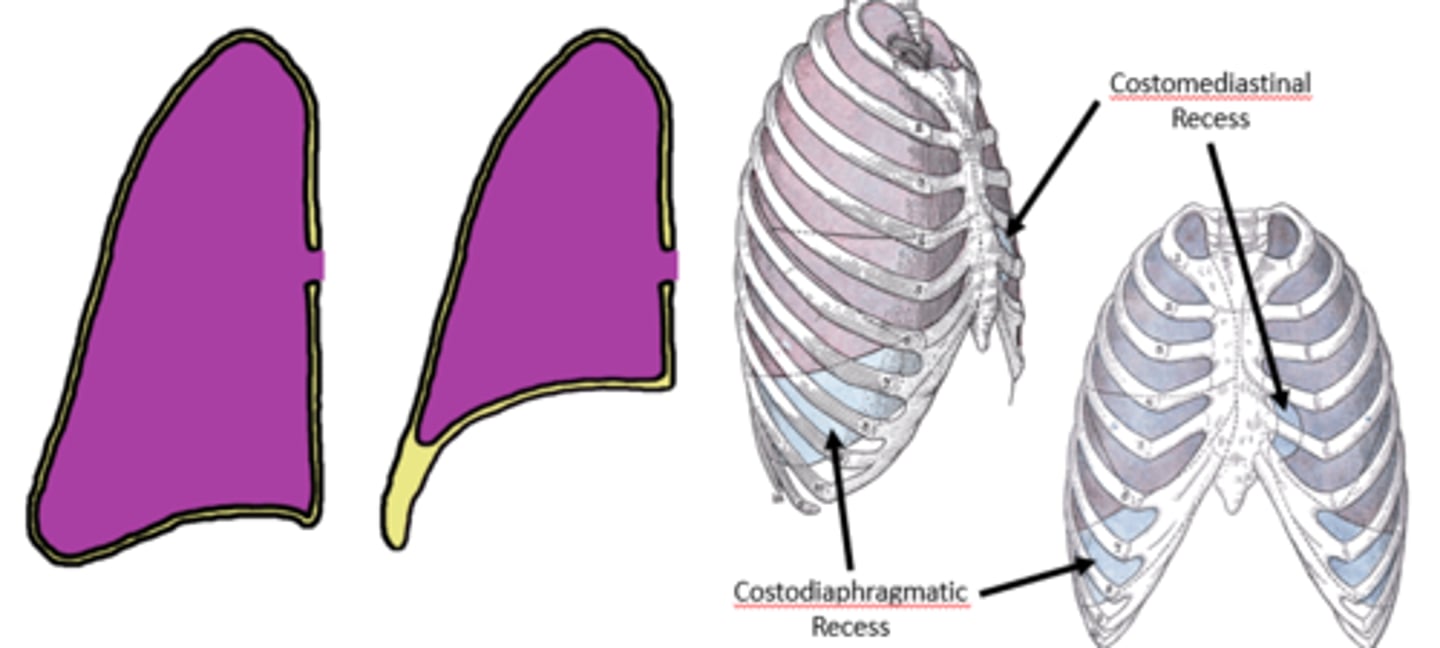
costodiaphragmatic recess
- where costal parietal pleura is in contact with diaphragmatic parietal pleura
- Is the common site for sampling pleural fluid
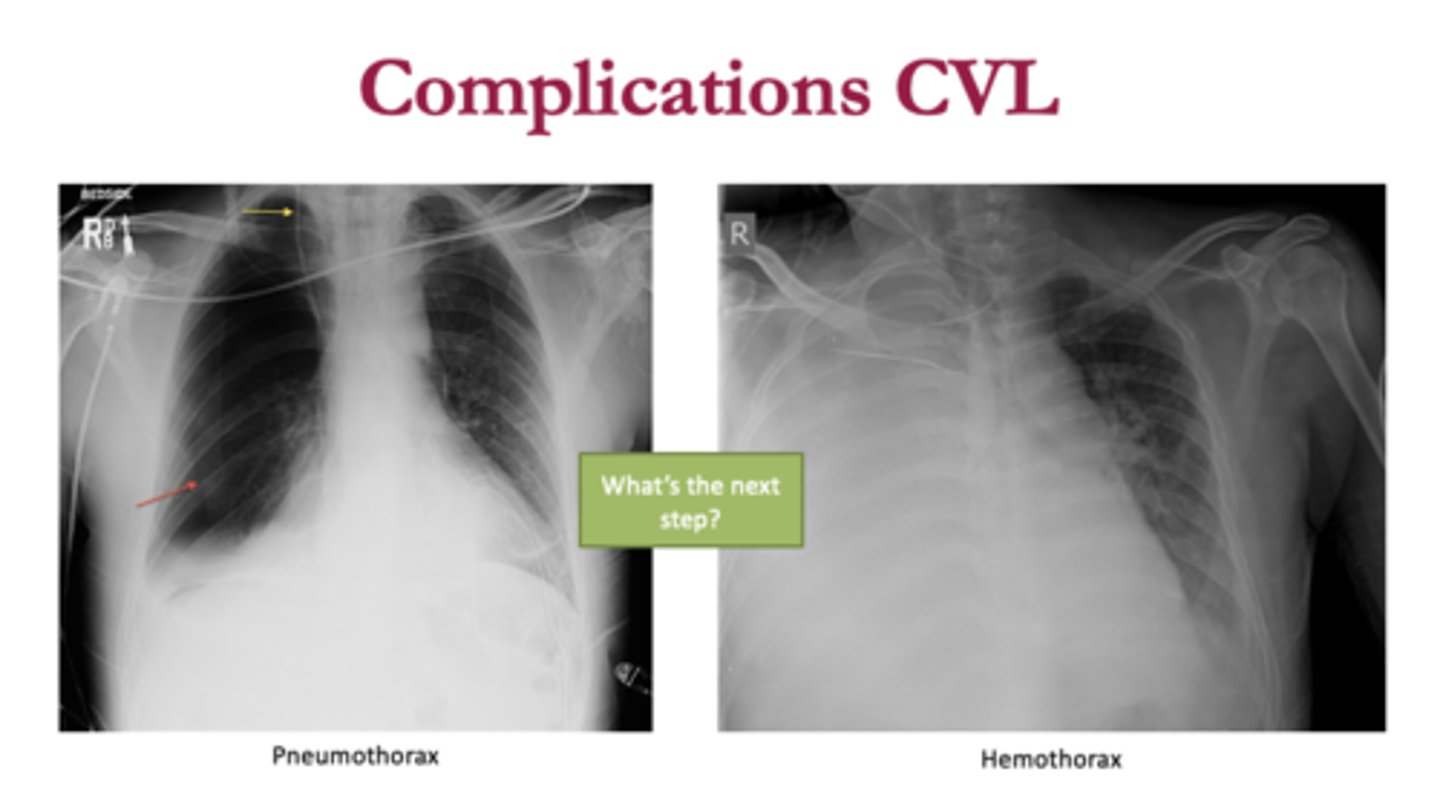
Lung Collapse
o When parietal pleura is torn, lung recoils as air is sucked into the pleural space; results in pneumothorax
o If blood accumulates in pleural space, lung collapse due to hemothorax
pleurisy (pleuritis)
- Inflammation of the visceral pleura surrounding lungs
- result in pleural friction rub
- "grating sound" or "stepping on fresh snow"
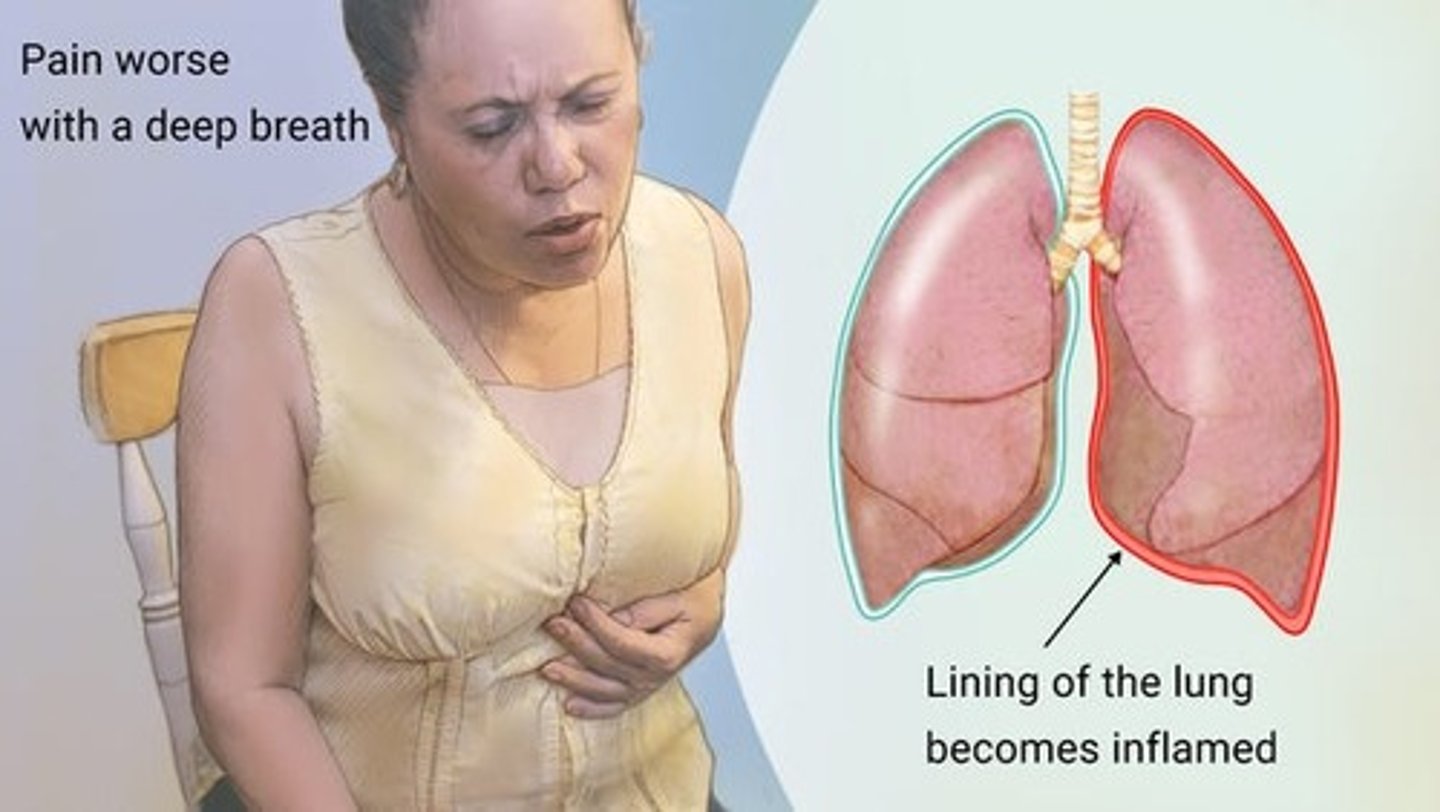
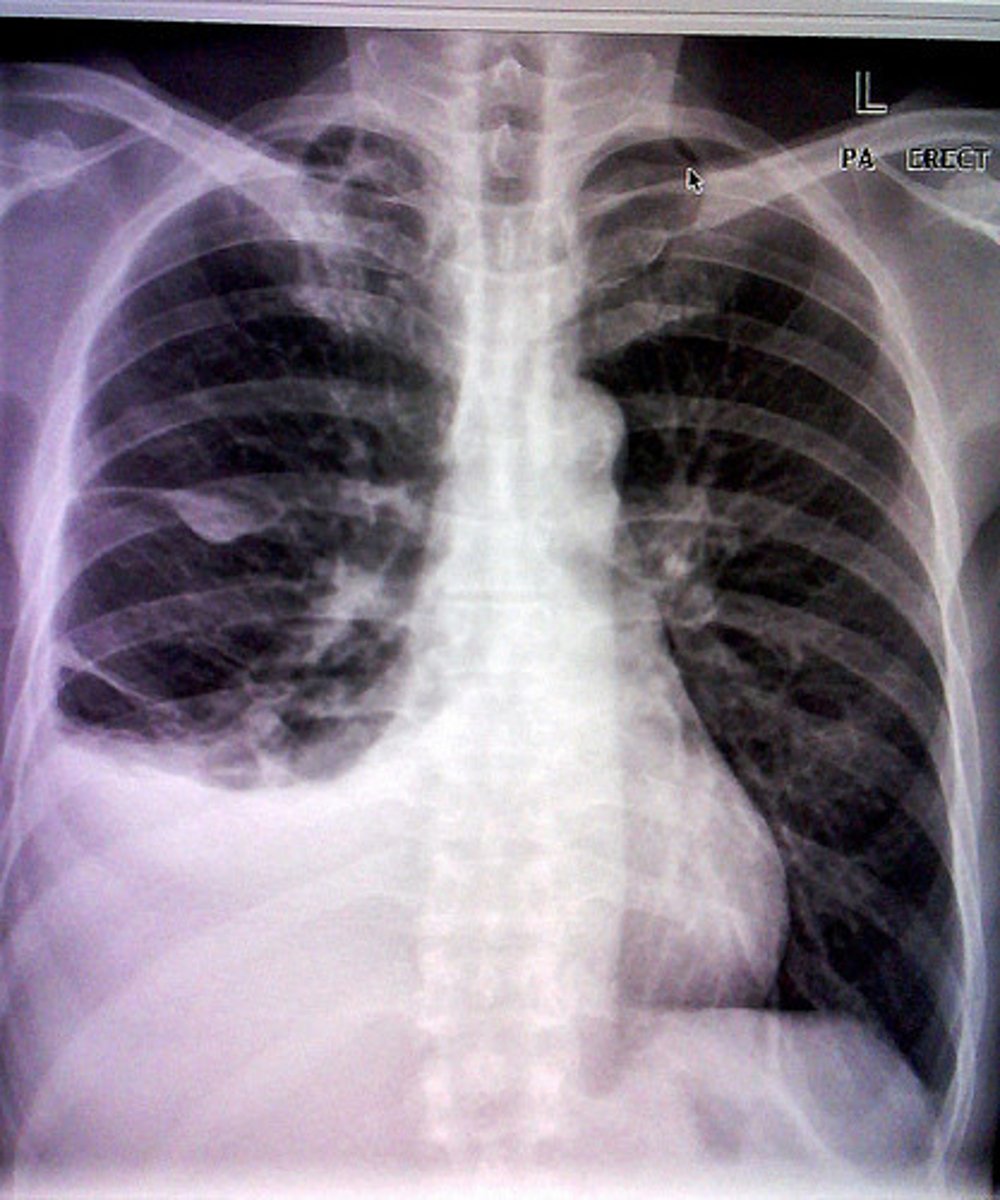
Pleural effusions
- abnormal fluid in the pleural cavity
- Common in pneumonia, COPD, heart failure, other conditions
lungs
- organs of gas exchange (air-blood interface)
- natural recoil sufficient to retract pulmonary cavity during passive ventilation
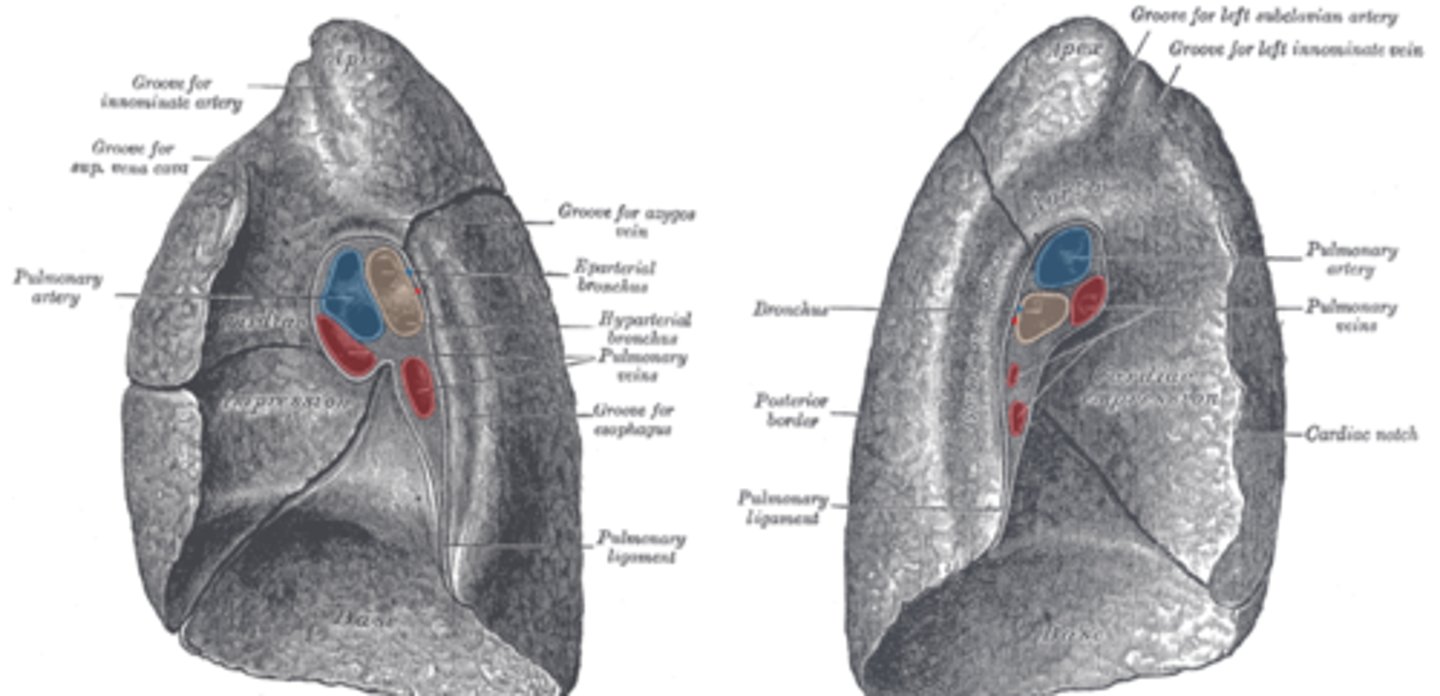
Impressions on the right lung
Right lung - grooves for vena cava, esophagus
impressions on the left lung
Left lung - cardiac notch for heart, groove for arch of aorta
pulmonary artery, what does it carry
most superior portion of root
carries deoxygenated blood to lung for gas exchange
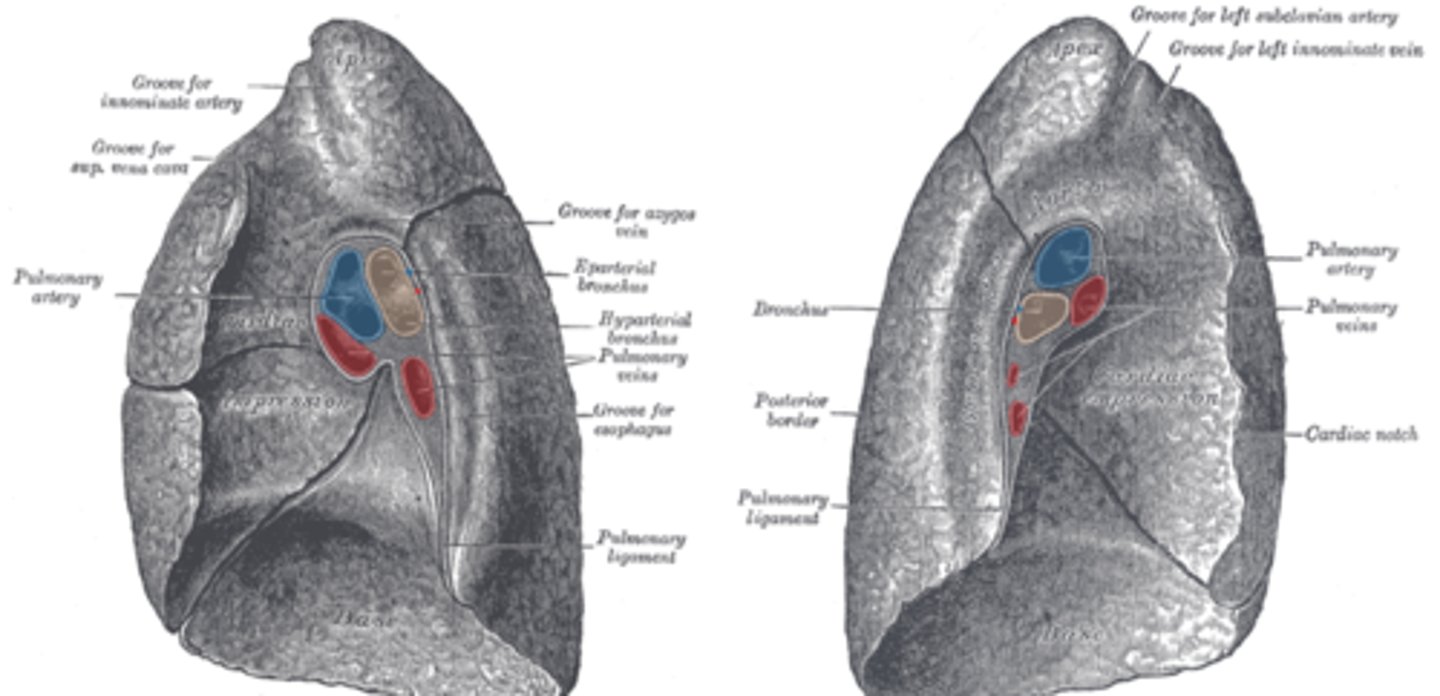
pulmonary vein, what does it carry
- carrying reoxygenated blood back to heart for circulation throughout body
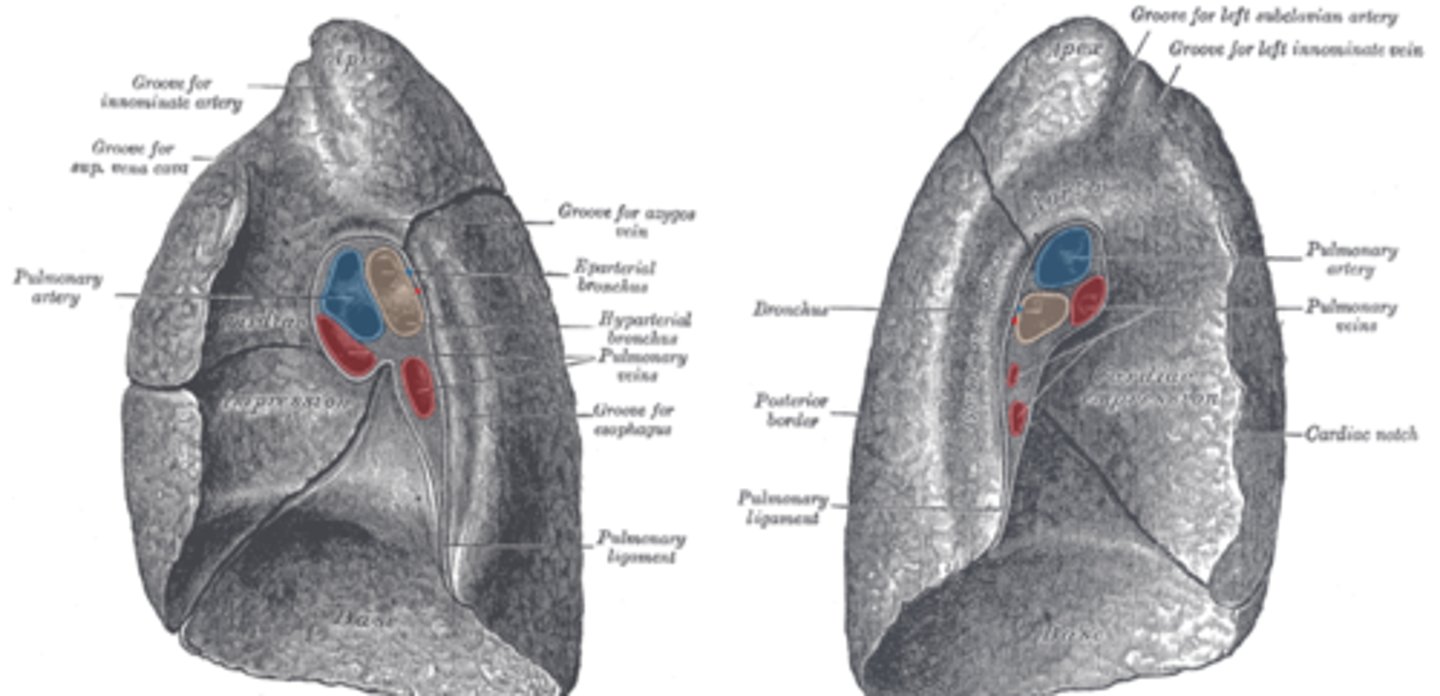
Primary bronchus, which side is wider?
- a pair of branches of the trachea that lead to the right and left lung; consist of incomplete rings
- right bronchus wider, shorter, more vertical
splits into secondary bronchi
bronchiole artery/vein
- From the thoracic aorta, delivers oxygen rich blood to regions of lung for its own gas exchange
- Veins drain into the azygous/
hemiazygous system for return to the heart
divisions of lung
- 3 lobes on right
- 2 lobes on left
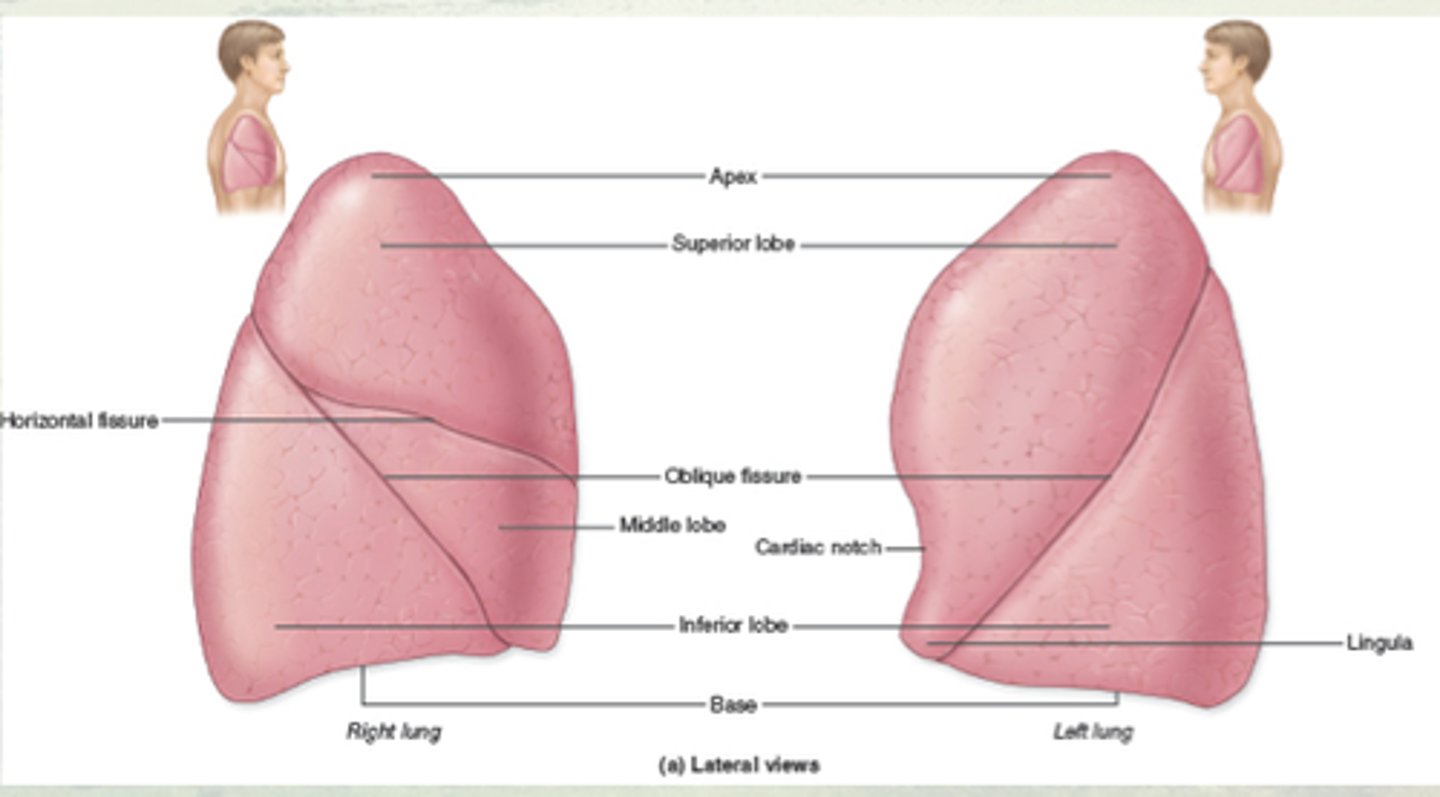
How are Lungs further divided
lungs further subdivided into
bronchio
pulmonary segments
- 10 in right lung
[3 in superior, 2 in middle, 5 in inferior lobe]
- 8 in left lung
[4 in superior and 4 in inferior lobe]
- each segment contains 20-25 terminal bronchioles, ending in alveolar sacs
![<p>lungs further subdivided into</p><p>bronchio</p><p>pulmonary segments</p><p>- 10 in right lung</p><p>[3 in superior, 2 in middle, 5 in inferior lobe]</p><p>- 8 in left lung</p><p>[4 in superior and 4 in inferior lobe]</p><p>- each segment contains 20-25 terminal bronchioles, ending in alveolar sacs</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/59b3d629-fb5b-45dd-9eee-cae17bceb350.jpg)
2 major pulmonary lymph plexuses in lung
superficial and deep plexus
lymph drains into superior/inferior tracheobronchial nodes, up into bronchomediastinal trunks and ultimately into right/left subclavian veins either directly or indirectly through right lymphatic duct/thoracic duct, respectively
Bronchitis
o Inflammation of the upper divisions of the bronchial tree
o Characterized by productive cough (mucous secretions)
o Acute bronchitis typically resolves within 3 weeks
o Chronic bronchitis the symptoms last >3 months for at least 2 years
pneumonia
o Inflammation of the alveolar sacs, most commonly from bacterial, viral infection
o Thickening of alveolar wall through inflammation and accumulation of fluid in the sacs compromises gas exchange
o Presents with coughing, fever, chills, labored breathing, and stabbing chest pain
superficial plexus
drains superficial structures in lung into bronchopulmonary lymph nodes
deep plexus
drains internal structures branching from root of lung into intrinsic lymph nodes, continue to bronchopulmonary lymph nodes
bronchopulmonary lymph nodes drain into
superior/inferior tracheobronchial nodes, up into broncho
mediastinal trunks and ultimately into right/left subclavian veins
nerves of lung
derived from pulmonary plexus
- runs mainly posterior within root of lung
- post-synaptic sympathetic fibers from sympathetic trunk
- presynaptic parasympathetic fibers from vagus nerve
- visceral afferents for pain detection
thoracentesis
- surgical puncture to remove fluid from the pleural space
- Normally aim for midscapular line between ribs 10 and 12
Chest tube placement
- Used for removal of larger quantities of fluid, air
- Normally aim for midaxillary line between rib 8 and 10