(Energetics) A-Level Inorganic Chemistry
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
In an endothermic reaction, the overall standard enthalpy change is
positive, as energy is absorbed from the surroundings to break bonds
In an exothermic reaction, the overall standard enthalpy change is
negative, as energy is released to the surroundings to make bonds
The standard enthalpy change of reaction and its overall standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change when molar quantities of reactants, as stated in the balanced equation, react under standard conditions
can be endo or exo
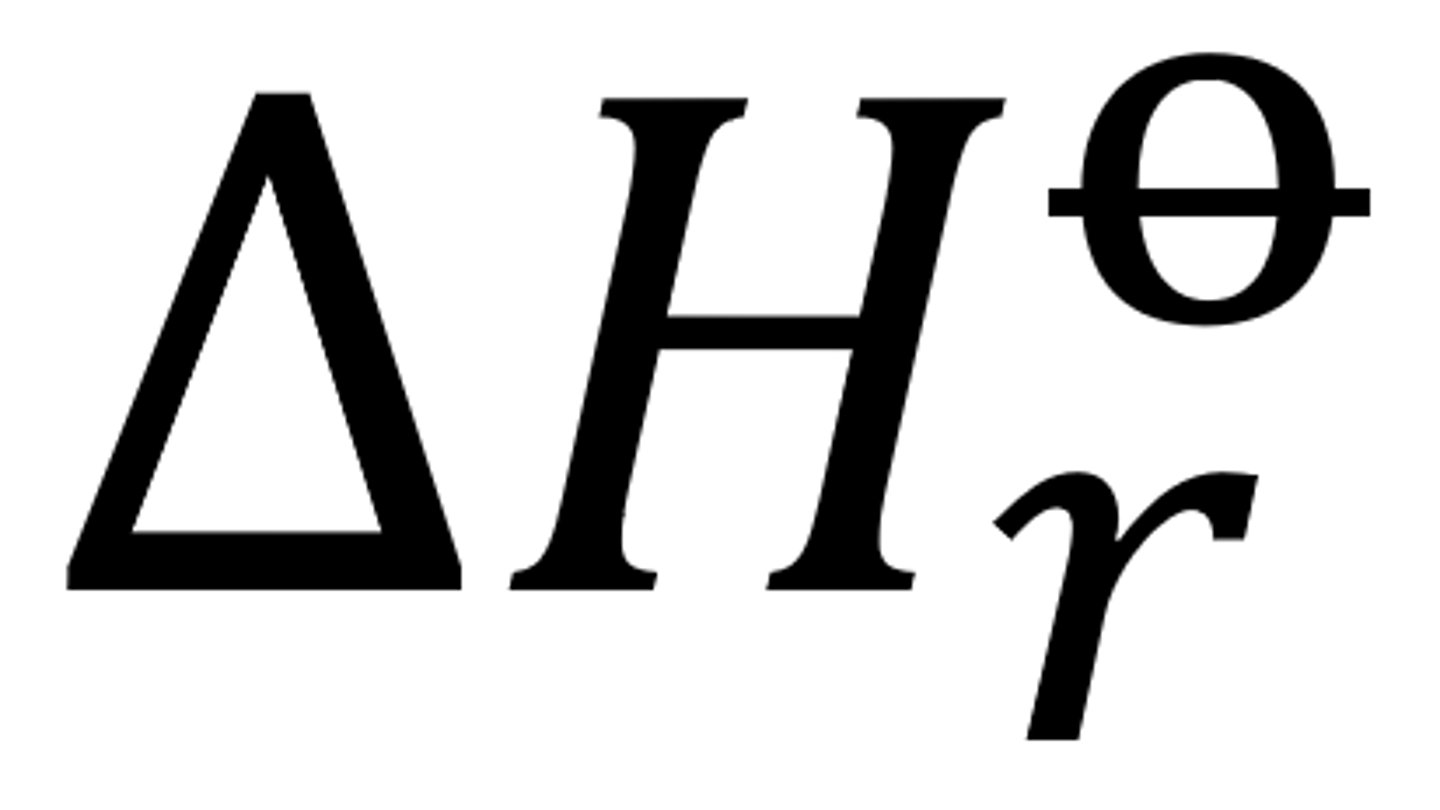
The standard enthalpy change of formation and its overall standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements with all reactants and products in their standard states under standard conditions
can be endo or exo
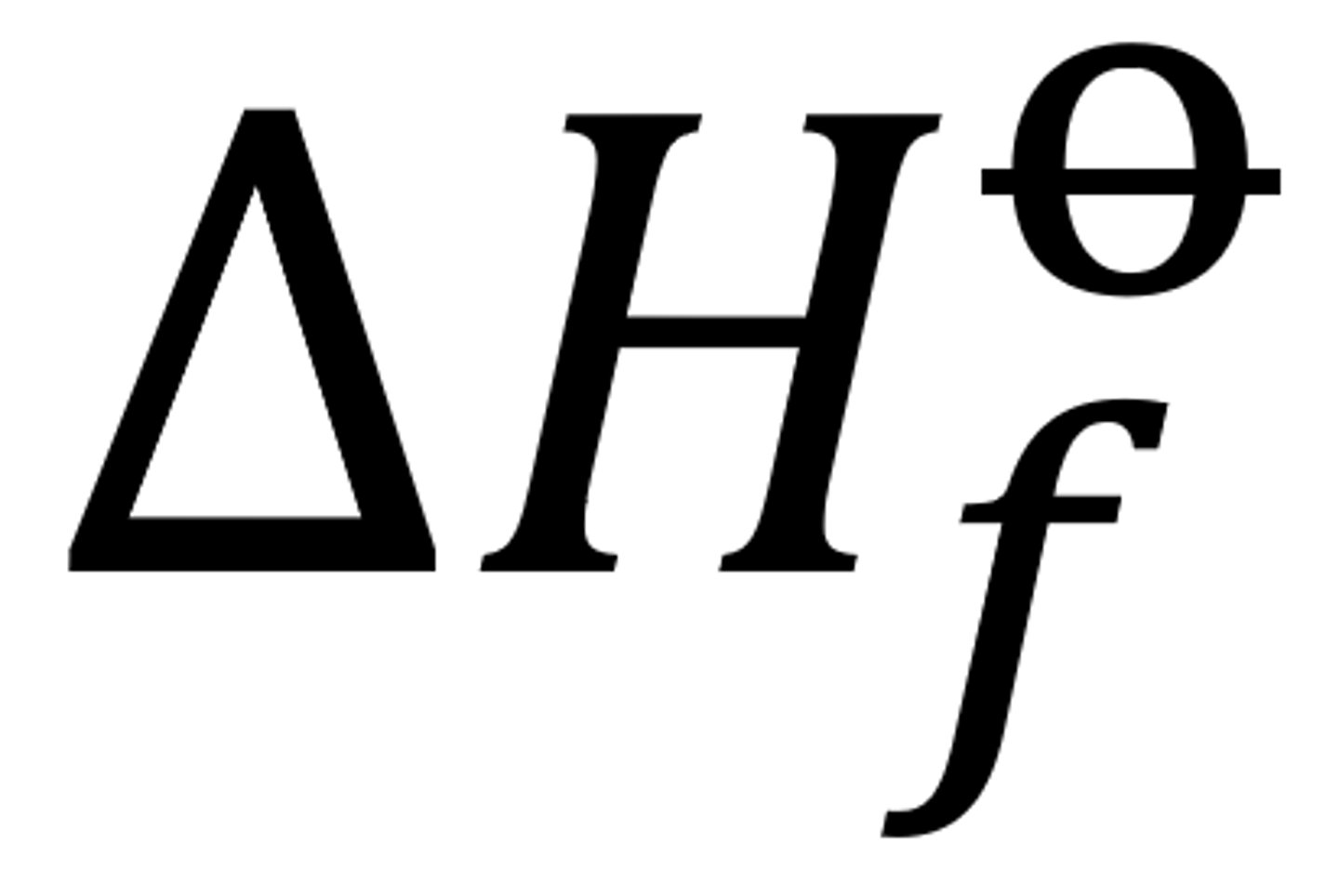
The standard enthalpy change of combustion and its overall standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is combusted completely in excess oxygen with all reactants and products in their standard states under standard conditions
this is exo
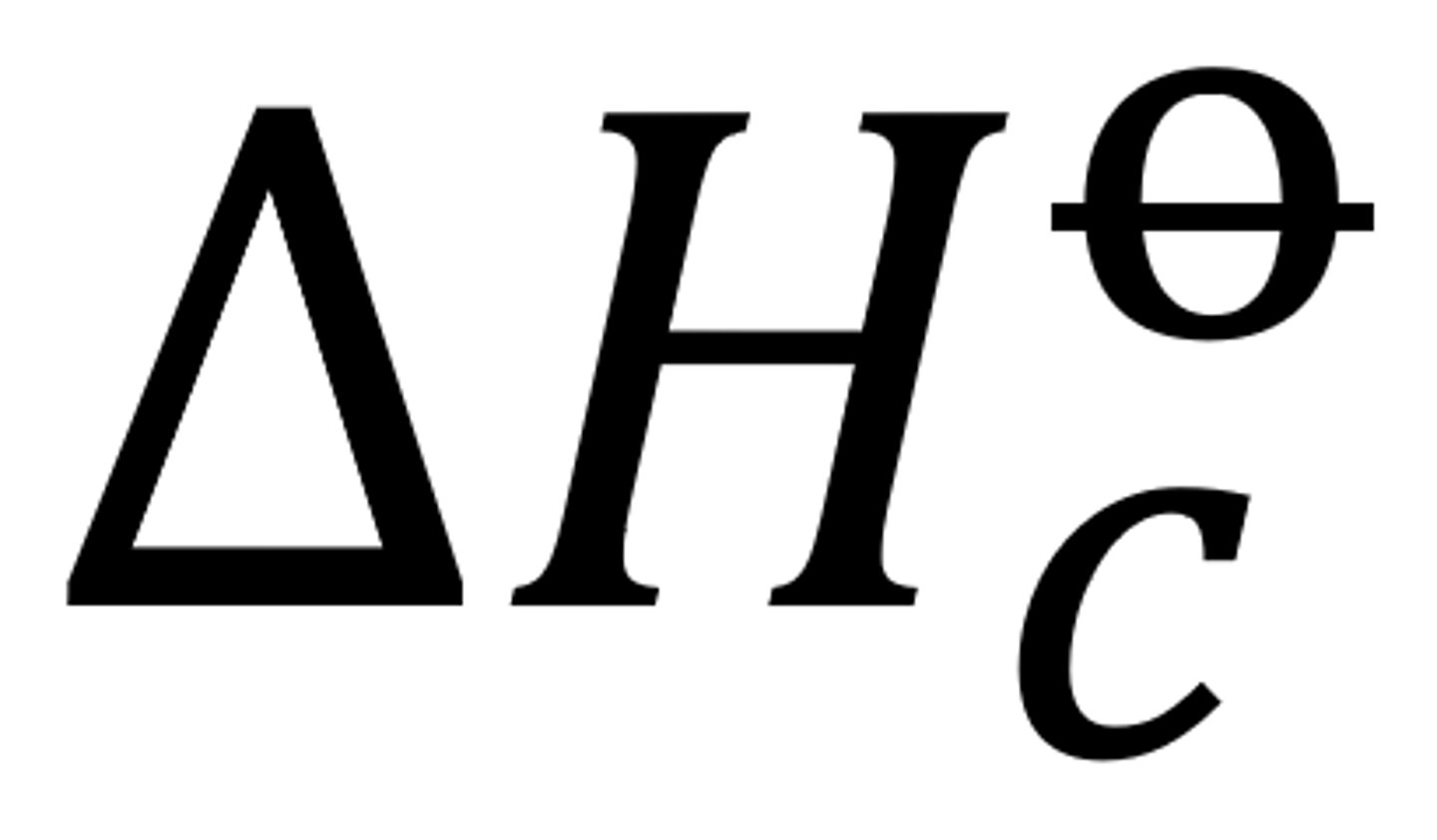
The standard enthalpy change of neutralisation and its overall standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change when an acid and an alkali react to form 1 mole of water with all reagents under standard conditions in their standard states.
this is exo

Why is the standard enthalpy change of neutralisation always exothermic
Neutralisation reactions are strongly driven by the formation of water which has strong covalent bonds between its molecules. This means more energy is released when forming these bonds than is needed to break the bonds in the reagents, resulting in a net energy release (negative change in overall enthalpy)
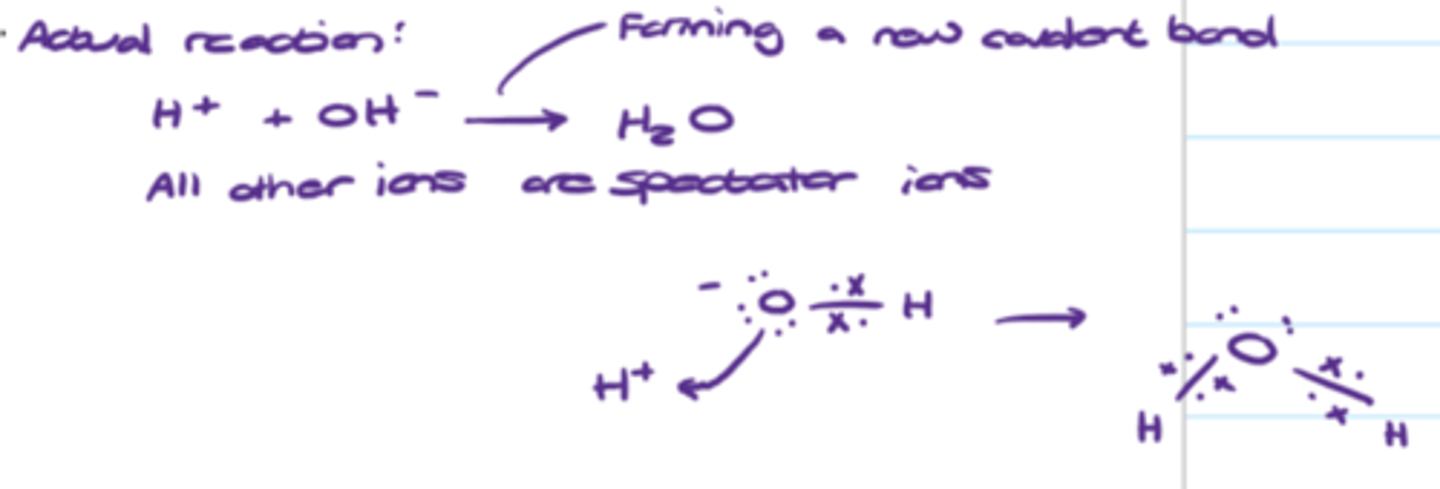
Why the standard enthalpy changes of neutralisation of strong acids and alkalis are similar
The overall reaction is between H+ and OH- ions to form water via covalent bonding. All other aqueous ions in solution are spectator ions
Why the standard enthalpy of combustion is exothermic
Burning fuels releases energy and heat and light
When a process is exothermic there is a net release in energy
More energy is released forming new bonds in the product than is required to break the original bonds
When a process is endothermic there is a net gain in energy
More energy is absorbed breaking existing bonds than required to form new bond sin the products
The standard enthalpy of formation needs to
form 1 mol of product
The standard enthalpy of neutralisation needs to
form 1 mol of water
The standard enthalpy of combustion needs to
react with 1 mol
The standard enthalpy of reaction needs to
have a balanced equation
The enthalpy change of atomisation
The enthalpy change when 1 mol of gaseous atoms is formed from the element in its standard state
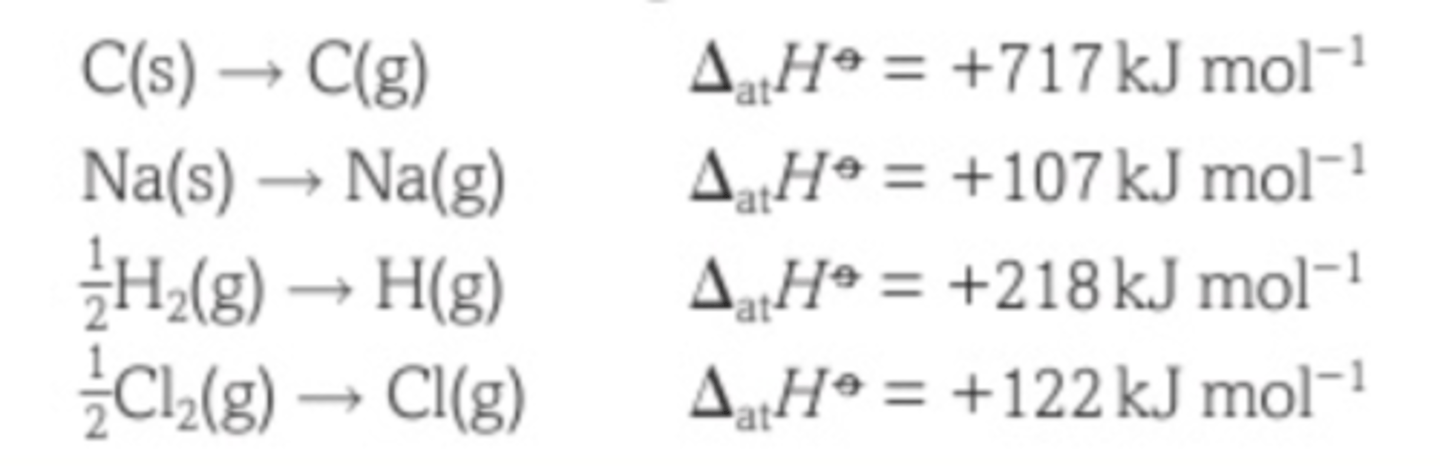
The enthalpy change of atomisation for a diatomic molecule is the same as
the bond dissociation enthalpy /2
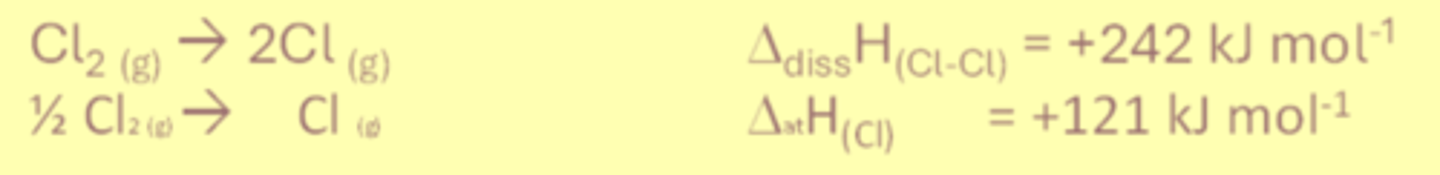
Bond dissociation enthalpy
The bond dissociation enthalpy is the standard molar enthalpy change when 1 mole of a covalent bond is broken into 2 gaseous atoms/free radicals
First ionisation enthalpy and its overall standard enthalpy change
The enthalpy change required to remove 1 mole of electrons from 1 mole of gaseous atoms to form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a 1+ charge
endothermic as is requires energy

Second ionisation energy
The enthalpy change to remove 1 mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous 1+ ions to produce one mole of gaseous 2+ ions
endo as it requires energy

First electron affinity
The enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mole of gaseous atoms gains 1 mole of electrons to form 1 mole of gaseous ions with a 1- charge
exo as it releases energy (new attraction is formed)
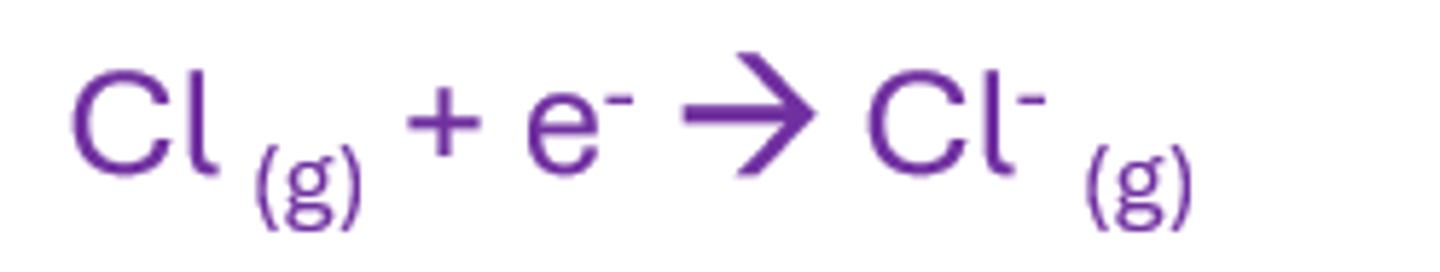
Second electron affinity
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions gains one electron per ion to produce 2- ions
endo as it requires energy (due to the repulsive forces between the anion and the e-)
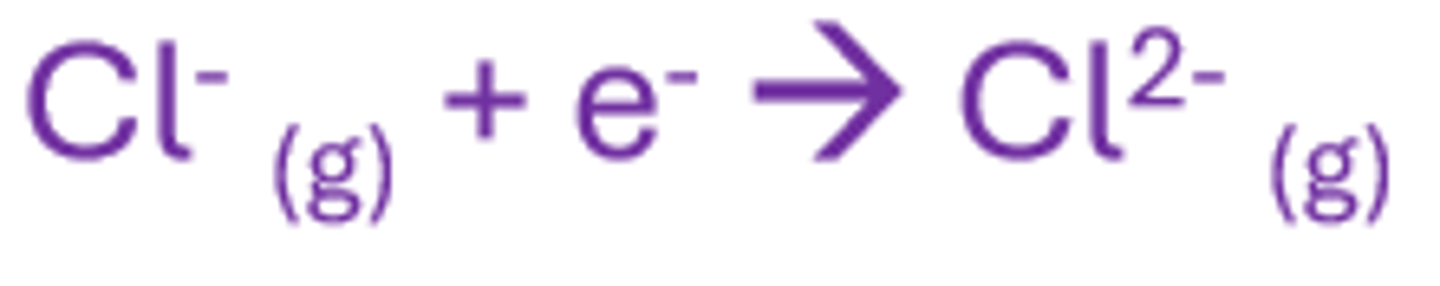
Why the 1EA is exothermic for atoms that form anions
Ions are more stable than atoms as they have a full outer shell, and there is an attraction between the nucleus and the incoming outer shell e-
The 1EA down G7
This decreases does the group since the atoms get bigger, so shielding increases, and it becomes harder to attract an electron to form a negative ion
Enthalpy of lattice formation
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal lattice is formed from its constituent ions in the gaseous phase
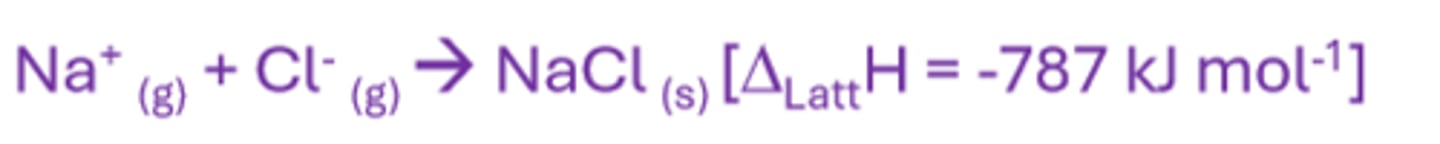
Enthalpy of hydration
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions to become hydrated such that further dilution causes no further heat change
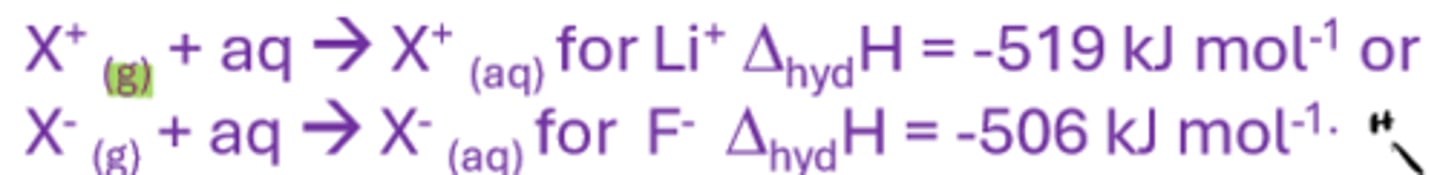
Enthalpy of solution
The enthalpy change when one more of an ionic solid dissolves in a large amount of water to ensure that the dissolved ion are well separated and do not interact with one another
Enthalpy of lattice dissociation
The standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic crystal form is separated into its constituent ions in gaseous form
Factors affecting the strength of an enthalpy of lattice formation
size of ion, charge of ion
Hess' Law (The Law of thermodynamics) and how it is used
The enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is independent of the route taken
We can use this to calculate enthalpy changes that cannot be measured directly.
Mean bond enthalpy
The energy required to break 1 mole of a bond in its gaseous state, averaged over different molecules.
This value is always positive as energy is required to break a bond.
Why mean bond enthalpies aren't accurate (or as accurate as an enthalpy change of formation)
These are values obtained from an average of different molecules.
The enthalpy change of formation is specific to the relevant molecule formed