Understanding Classical Conditioning and Learning Concepts
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Learning
Process of developing new information through experience.
Non-Associative Learning
Learning about a stimulus without forming associations.
Habituation
Decreased response to a non-harmful stimulus over time.
Sensitization
Increased response to a threatening or painful stimulus.
Associative Learning
Learning the relationship between two pieces of information.
Classical Conditioning
Learned response where a neutral stimulus elicits a reaction.
Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS)
Stimulus that instinctively prompts a reaction.
Unconditioned Response (UCR)
Instinctive reaction to an unconditioned stimulus.
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
Stimulus unrelated to the unconditioned response initially.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Learned stimulus that prompts a reaction after conditioning.
Conditioned Response (CR)
Learned reaction elicited by the conditioned stimulus.
Acquisition
Gradual formation of association between stimuli.
Extinction
Weakening of conditioned response without unconditioned stimulus.
Spontaneous Recovery
Reemergence of extinguished response after stimulus presentation.
Generalization
Similar stimuli produce the conditioned response.
Discrimination
Differentiation between similar stimuli based on association.
Ivan Pavlov
Russian physiologist known for classical conditioning research.

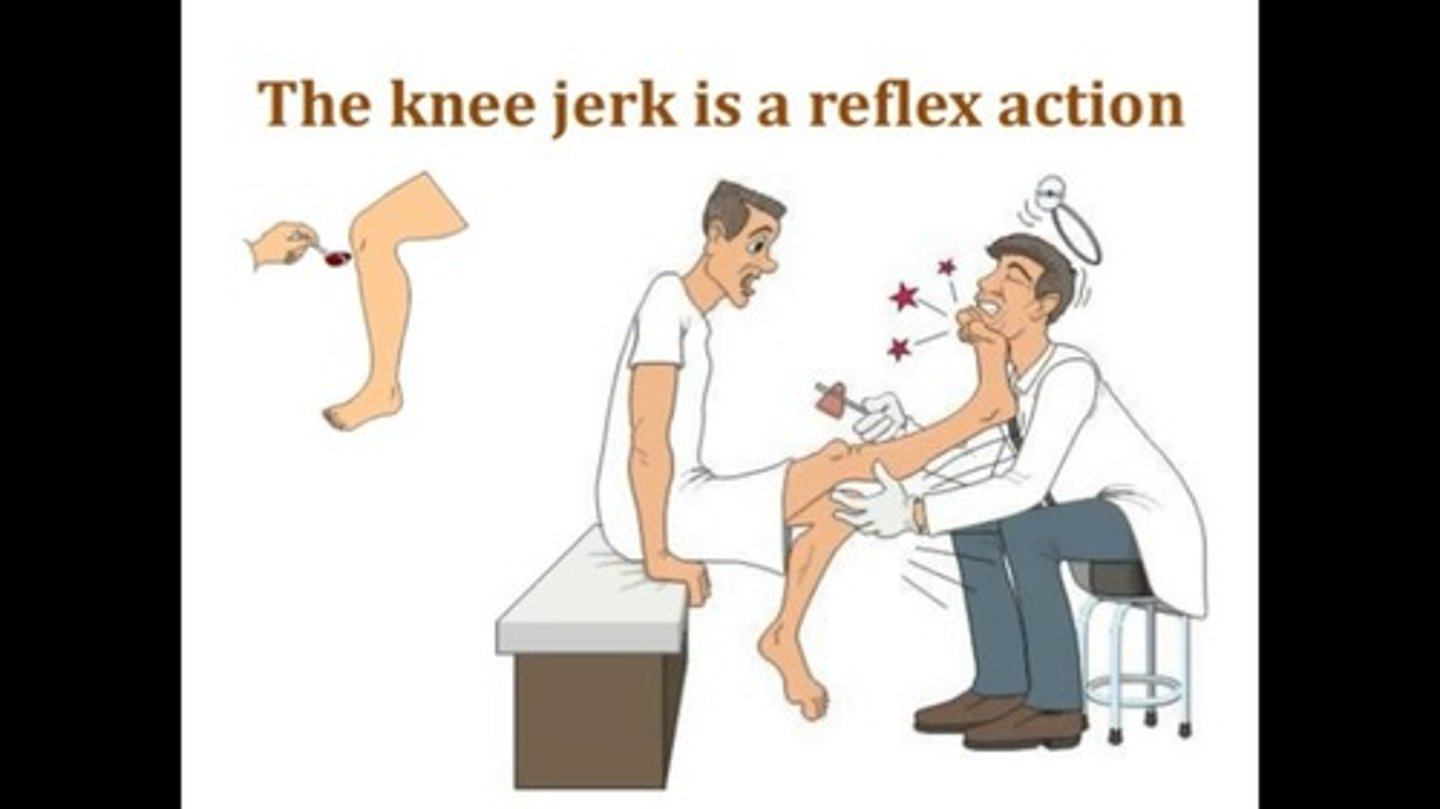
Reflexes
Motor reactions to stimuli, managed by primitive brain centers.
Instincts
Innate behaviors triggered by specific environmental events.
Sensitization
Emma's response to train noise in new apartment.
Instinct
Innate behavior occurring in response to stimuli.
Reflex
Automatic response to a stimulus, immediate and involuntary.
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Stimulus that naturally elicits an unconditioned response.
Unconditioned Response (UR)
Natural reaction to an unconditioned stimulus without learning.
Response Intensity
Strength of reaction to a stimulus over time.
Learned Response
Behavior acquired through experience rather than innate.
Nostalgia
Sentimental longing for the past, triggered by stimuli.
Frustration
Emotional response to perceived obstacles or irritations.
Concentration
Mental focus on a particular task or stimulus.
Environmental Stimulus
External factor that influences behavior or response.
Behavioral Adaptation
Change in behavior due to environmental experiences.
Emotional Conditioning
Associating emotions with specific stimuli through experience.
Contextual Learning
Learning that occurs in a specific environment or situation.
Sensory Memory
Initial brief storage of sensory information.
Cognitive Association
Linking thoughts or feelings to specific stimuli.
Reinforcement
Process that increases the likelihood of a behavior.
Stimulus Generalization
Responding similarly to similar stimuli.
Warmth and Happiness
What example is a Conditioned emotional response related to “cookies' smell”.
Sound of Can Opener
An Example of Neutral stimulus that becomes conditioned stimulus for Luna the cat.
Feeding Luna
Unconditioned stimulus causing natural excitement response.
Running to Kitchen
Unconditioned response to the smell of food.
Cans Without Feeding
Trigger for extinction of conditioned response in Luna.
Conditioning Responses
Responses that change through conditioning processes.
Realistic Scenario Creation
Developing scenarios including all conditioning components.
Eyewitness Testimony
Reliability of accounts from witnesses in legal cases.
Amnesia
Memory loss affecting past or new information.
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories after an injury.
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memories prior to a traumatic event.
Memory Errors
Inaccuracies or distortions in recollecting past events.
Forgetting
Loss of information from long-term memory.
Memory Distortion
Alteration of memories over time, leading to inaccuracies.
Memory Intrusion
Involuntary recall of distressing past memories.
Memory-enhancing Strategy
Techniques to transfer information to long-term memory.
Rehearsal
Conscious repetition of information for retention.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Connecting new information to existing knowledge.
Chunking
Grouping information into manageable units for memory.
Mnemonics
Memory aids that enhance recall through association.
Focused Study Sessions
Concentrated periods of study to improve learning.
Study Cycle
Structured approach to studying for better retention.
False Memories
Inaccurate recollections of events that did not occur.
Memory Problems
Issues affecting the accuracy and reliability of memory.
Learning Techniques
Methods to improve understanding and retention of information.
Memory Test
Assessment of recall ability using specific items.
Memory Activity
Exercises designed to evaluate and enhance memory.
Self-reference effect
Making material personally meaningful enhances memory.
Forgetting curve
Information retention decreases rapidly over time.
Retrieval cues
Clues that aid in recalling stored information.
Hippocampus
Brain region crucial for memory processing.
Memory processing
The method by which information is encoded and retrieved.
Web of retrieval cues
Network of associations that facilitate memory recall.
Memory enhancement techniques
Strategies to improve information retention and recall.
Vowel counting activity
Exercise to engage attention and memory skills.
Recall exercise
Task to retrieve previously learned information.
Original list
Set of words used for recall practice.
Memory retention
Ability to keep information in long-term memory.
Personal relevance
Connection of material to one's own life for better recall.
Memory cues
Hints or prompts that trigger memory retrieval.
Association
Linking new information with familiar concepts.
Memory drop-off
Rapid decline in information recall over time.
Learning chapter
Section covering foundational concepts of learning.