Exam 1
4.0(4)Studied by 24 people
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 1, 2, 4 and 5 : 35 multiple choice/true or false/ 10 fill in the blank
Last updated 6:40 PM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
Communication
The process where humans collectively create and regulate social reality
* what we do!
* we are not in a communication^^S^^ course.. this is a communicatio^^N^^ course
* what we do!
* we are not in a communication^^S^^ course.. this is a communicatio^^N^^ course
2
New cards
Interpersonal communication
two individuals communicating
\
a process which occurs in a specific context and involved an exchange of verbal or nonverbal messages between two connected individuals with the intent to achieve shared meaning
\
\
a process which occurs in a specific context and involved an exchange of verbal or nonverbal messages between two connected individuals with the intent to achieve shared meaning
\
3
New cards
Reasons to study communication
1. It gives us new perspective on things we take for granted
2. learning how to communicate because we spend a large amount of time doing it
3. to increase our effectiveness so relationships can work
4
New cards
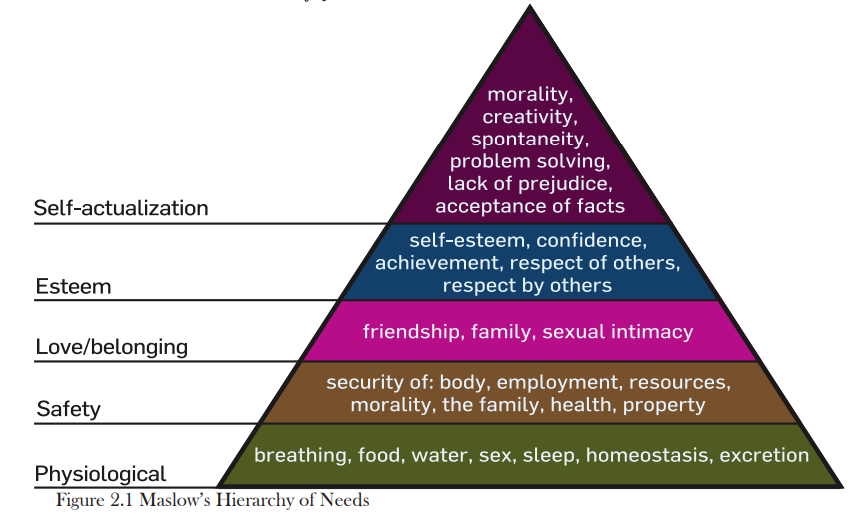
different things for meeting personal needs
1. self-actualization
2. esteem
3. love/belonging
4. safety
5. physiological
5
New cards
approaches to interpersonal communication
1. situational approach (most common)
2. developmental approach
6
New cards
communication competence
being both appropriate and effective
7
New cards
principles of interpersonal communication
1. mediated communication
2. public
3. group
4. interpersonal
5. intrapersonal
8
New cards
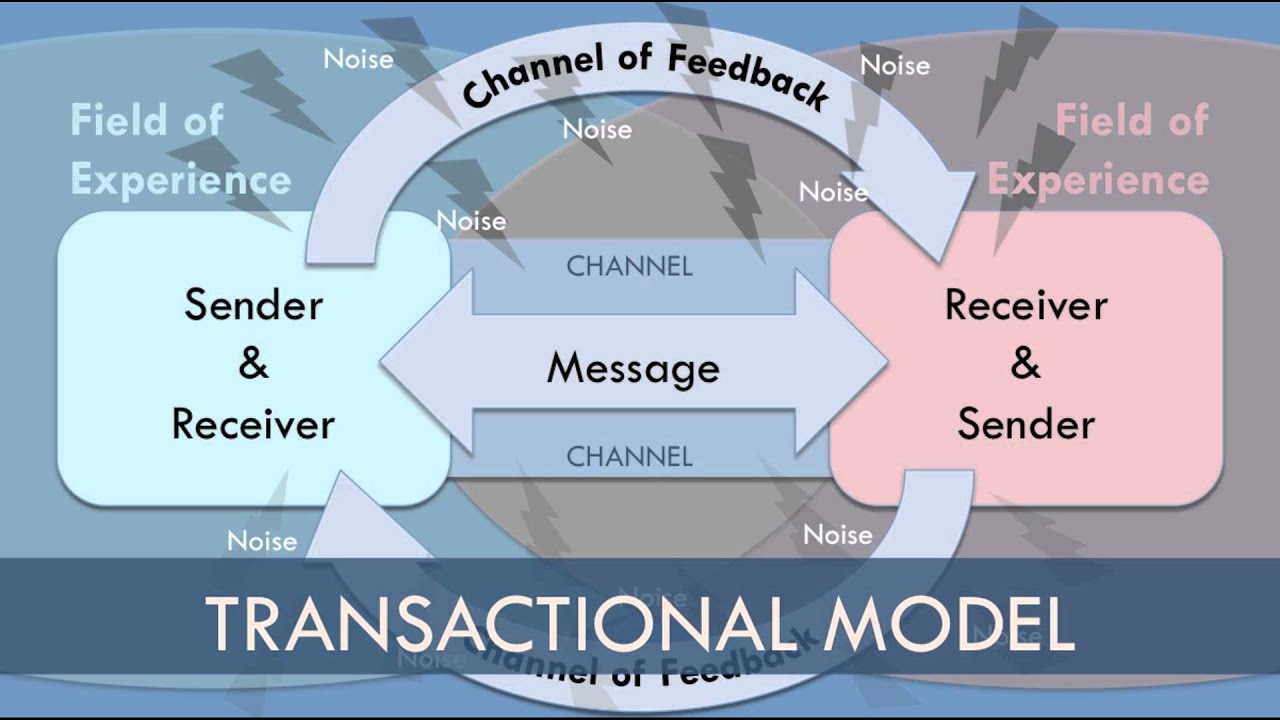
transactional model of communication
* it is two way (sender and receiver)
* it is simultaneous
* it is simultaneous
9
New cards
encoding
the sender
* speaker
* speaker
10
New cards
decoding
the receiver
* listener
* listener
11
New cards
communicationS
The channel we use to communicate generally to the masses
* telephone
* radio
* TV
* telephone
* radio
* TV
12
New cards
3 components to the perception process
1. selection/attention
2. organization of stimuli
3. interpretation
13
New cards
Language
A system of human communication using a particular form of spoken or written words or other symbols
* system of arbitrary signs and symbols used to communicate thoughts and feelings
* system of arbitrary signs and symbols used to communicate thoughts and feelings
14
New cards
relationship between symbol and referent
Symbol is something that represents something else vs
referent is the actual thing that is represented
referent is the actual thing that is represented
15
New cards
different between denotation and connotation
Denotation is the public, more conventional meaning
* dictionary definition
Connotation is the personal, emotionally charged meaning
* based on emotions and feelings
* dictionary definition
Connotation is the personal, emotionally charged meaning
* based on emotions and feelings
16
New cards
3 levels of meaning (rules)
1. semantic meaning
2. syntactic meaning
3. pragmatic meaning
17
New cards
metacommunication
communication about communication
18
New cards
metamessages
relationship messages that are sent among people who they communicate
* verbal and nonverbal
* direct and indirect
* can show disgust, appreciation, upset, annoyed, etc
* verbal and nonverbal
* direct and indirect
* can show disgust, appreciation, upset, annoyed, etc
19
New cards
functions of verbal communication
1. instrumental and regulatory functions
2. interactional and imaginative functions
3. personal functions
4. heuristic and representational function
5. cultural functions
20
New cards
different types of language
1. formal language
2. informal language
3. ambiguous language
4. relative language
21
New cards
verbal pitfalls
ways of talking that does not allow you to advance the conversation, but often makes it go worse
\
(having difficult conversations)
\
(having difficult conversations)
22
New cards
how to improve verbal communication
* be clear (KISS - keep it short and simple)
* appropriate (understand what is expected)
* concrete (pick words wisely to be specific)
* repetition, group words together, build vocabulary and read
* appropriate (understand what is expected)
* concrete (pick words wisely to be specific)
* repetition, group words together, build vocabulary and read
23
New cards
nonverbal communication
communication that is given without words
* eye contact
* body language
* eye contact
* body language
24
New cards
characteristics of nonverbal communication (omnipresent)
1. continuous
2. multi-channeled
3. intentional or unintentional
4. ambiguous
5. primary conveyor of emotions
6. we cannot not communicate
25
New cards
why is nonverbal communication important in interactions
it would be harder to stimulate accurate meaning to others
26
New cards
functions of nonverbal communication
1. complementing
2. contradicting
3. accenting
4. repeating
5. regulating
6. substituting
27
New cards
expectancy violations theory
understanding of what happens when an individual within a interpersonal interaction violates the norms for that interaction
\
* your expectation on nonverbal behavior affects how you interact with others and how you interpret the meaning of nonverbal messages
* we have expectation
\
* your expectation on nonverbal behavior affects how you interact with others and how you interpret the meaning of nonverbal messages
* we have expectation
28
New cards
two factors of expectancy violations theory
1. violation valence
2. reward value of other
3. under promise and over deliver
29
New cards
types of territoriality
1. primary
2. secondary
3. public
30
New cards
Markers
1. intimate
1. 0-18’’
2. personal
1. 18’’-4’
3. social
1. 4’-12’
4. public
1. 12’-25’+
31
New cards
different types of channels (-ics words)
1. proxemics
2. kinesics
3. vocalics
4. artifacts and physical appearance
5. Olfactics
6. Haptics
7. Oculesics
8. Chronemics
32
New cards
kinesics
How we move our body
33
New cards
5 types of gestures in kinesics
1. emblems
2. illustrator
3. adaptors
4. affect displays
5. regulators
34
New cards
Nonverbal immediacy
physical and psychological closeness that increased sensory stimulation between individuals
35
New cards
how to increase nonverbal immediacy
1. be open and approachable
2. use direct eye contact
3. use natural body movements
4. change your tone and have vocal variety
5. maintain closer physical distance
6. be purposeful and strategic
36
New cards
Appropriate communication
acceptable behaviors
37
New cards
effective
getting your desired personal outcome
38
New cards
Physical communication needs
share feelings instead of bottling them up to be more mentally clear and less stressed
\
communication is vital for our physical health because it offers a way to relieve tension.
\
(therapy-to relieve stress)
(When we are hungry we tell someone)
\
communication is vital for our physical health because it offers a way to relieve tension.
\
(therapy-to relieve stress)
(When we are hungry we tell someone)
39
New cards
Identity communication needs
communication helps us discover who we are and comments influence how we think
\
(if someone says you need makeup you will always put makeup on)
(hurtful and helpful comments + how they shape you)
\
(if someone says you need makeup you will always put makeup on)
(hurtful and helpful comments + how they shape you)
40
New cards
Social communication needs
\-communication establishes relationships
\-We share a part of ourselves with others
\-we need to communicate to maintain, create and terminate friendships
\-We share a part of ourselves with others
\-we need to communicate to maintain, create and terminate friendships
41
New cards
Practical communication needs
communication allows us to operate and do our daily tasks
* to function
(telling a doctor what hurts)
* to function
(telling a doctor what hurts)
42
New cards
Group communication
group = at least 3 people interacting with a common goal
\
\
(family, group projects)
\
\
(family, group projects)
43
New cards
Public communication
when an individual sends a specific message to an audience
\
(public speaking)
\
(public speaking)
44
New cards
Mediated communication
using a form of technology to facilitate information between two or more people
* using technology to link the one sending info to the one receiving info
\
(phone calls, emails, texts, streaming services, websites)
* using technology to link the one sending info to the one receiving info
\
(phone calls, emails, texts, streaming services, websites)
45
New cards
Self-actualization
esteem, confidence, achievement, respect of/by others
* leads to creativity and problem solving
* leads to creativity and problem solving
46
New cards
Different needs for communication
1. physical
2. identity
3. social
4. practical
47
New cards
Context of the transactional model
the setting in which the communication encounter occurs
* the situation
* what precedes and follows what you say
* the situation
* what precedes and follows what you say
48
New cards
Physical context
physical environment
* the space you are in
* the room
* location/where
* the space you are in
* the room
* location/where
49
New cards
Social context
Expectation for how you should behave and the societal norms
* appropriate
* appropriate
50
New cards
historical context
the events going on around you, including the experiences we have had
* personal events
* historical events
* personal events
* historical events
51
New cards
psychological context
Emotions you are feeling in your head
* distractions
* whats going on in your head
* distractions
* whats going on in your head
52
New cards
Cultural context
What are the cultural similarities and differences between you and the person you are interacting with
53
New cards
Relationational context
The connection between you and the person you are interacting with
* significant other
* family
* friend
* professor
* significant other
* family
* friend
* professor
54
New cards
Participants of transaction model
the individuals involved in the interaction
* we are senders and receivers at the same time
\
(encoder and decoder)
* we are senders and receivers at the same time
\
(encoder and decoder)
55
New cards
Messages of transaction model
the verbal utterances and nonverbal behaviors to which meaning is attributed during communication
* What factor
* What factor
56
New cards
Channels in transaction model
the route traveled by the message and the means of transportation
* whether its in person or online
\
(verbal and nonverbal)
* whether its in person or online
\
(verbal and nonverbal)
57
New cards
Noise in transaction model
any stimulus that interferes with the process of sharing
58
New cards
Physical noise
Things that you can hear that block what is being said
* beeping, other people talking
* auditory
* beeping, other people talking
* auditory
59
New cards
psychological noise
things in your head that are distracting you from the message, you usually aren’t actually listening because you are thinking about other things
* prevents the communication process
* sometimes you will say things you dont mean to say because your mind is somewhere else
* prevents the communication process
* sometimes you will say things you dont mean to say because your mind is somewhere else
60
New cards
semantic noise
not being able to understand what is being said because of limitations
* thick accents
* complicated words
* misunderstanding/misinterpreting
* thick accents
* complicated words
* misunderstanding/misinterpreting
61
New cards
physiological noise
things that are inside you that aren’t mental but are more physical
* things you can feel
* being hungry/stomach growl
* being hot or cold
* being tired
* things you can feel
* being hungry/stomach growl
* being hot or cold
* being tired
62
New cards
Situational approach to IPC
__external characteristics__ define whether interaction is interpersonal
63
New cards
Developmental approach to ICP
__content/quality of information exchanged__ defines whether interaction is interpersonal
64
New cards
Selection/attention of perception
using your senses to notice and choose from many stimuli
* choosing what to focus on
* based on needs
* interests and expectations
* choosing what to focus on
* based on needs
* interests and expectations
65
New cards
organization of perception
focusing in on something and sorting through it
1. proximity
2. similarity
3. closure
4. simplicity
1. proximity
2. similarity
3. closure
4. simplicity
66
New cards
interpretation of perception
interpreting the meaning of the messages and stimuli
* assigning meaning to information
* 1234 1234 1234 1234 (we know this is a credit card)
* assigning meaning to information
* 1234 1234 1234 1234 (we know this is a credit card)
67
New cards
symbol
something that represents something else
* sounds that stand for concepts
* alphabet
* words are symbols because they are a collection of sounds
* sounds that stand for concepts
* alphabet
* words are symbols because they are a collection of sounds
68
New cards
referent
the actual thing that is represented
* the connection to what a collection of sounds represents
* thing we are referring too
* the connection to what a collection of sounds represents
* thing we are referring too
69
New cards
denotation
Dictionary definition, the meaning that is agreed upon and the conventional meaning
70
New cards
connotation
the personal meaning we apply to things based on emotions and feelings
71
New cards
semantic meaning
\
denotative and connotative meanings
denotative and connotative meanings
72
New cards
syntactic meaning
the meaning based on word order and grammatical sequence
* produce (the farm was used to produce the produce)
* produce (the farm was used to produce the produce)
73
New cards
pragmatic meaning
how language is used in interactions
* purpose of what your saying
* is it a threat? question? warning? etc.
* purpose of what your saying
* is it a threat? question? warning? etc.
74
New cards
sender
The speaker or encoder
75
New cards
receiver
the listener or decoder
76
New cards
instrumental and regulatory functions
Instrumental function use language to fulfill need vs regulatory functions influence the behaviors of others through requests, rules or persuasion
77
New cards
interaction and imaginative functions
interaction → maintain or develop the relationship '
* thank you, please
imaginative → help create imaginary constructs and tell stories
* roleplay in activities
\
* thank you, please
imaginative → help create imaginary constructs and tell stories
* roleplay in activities
\
78
New cards
person function
use of language to help form your identity or self of self
* “how do you describe yourself”
* “how do you describe yourself”
79
New cards
heuristic and representation functions
Heuristic function is used to learn, discover and explore
* ex: asking questions to learn
Representation function is used to request or relay information
* ex: the light isn’t working
* ex: asking questions to learn
Representation function is used to request or relay information
* ex: the light isn’t working
80
New cards
Cultural function
using language to figure out what culture you are speaking to. Language helps describe and understand our world.
This helps us understand how culture and language coexist
This helps us understand how culture and language coexist
81
New cards
Jargon
specialized or technical language of a specific group that may not be understood by outsiders
82
New cards
Proximity
noticing the things around you and near eachother
83
New cards
similarity
Noticing things that are similar and have things in common
* the same t-shirt
* the same t-shirt
84
New cards
closure
filling in gaps with information that might not be there
* a messed up fortune cookie but we can still read what it says
* a messed up fortune cookie but we can still read what it says
85
New cards
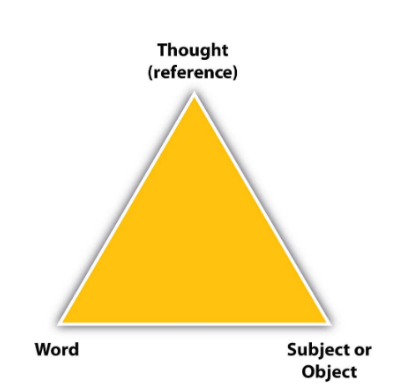
triangle of meaning
1. symbol (the word)
2. referent (the thing the word presents)
3. thought (the mental process of connecting the symbol and the referent
86
New cards
abstract words
ideas or concepts that cannot be observed or touched such as fairness, freedom and work
* vague, emotion
* vague, emotion
87
New cards
concrete words
specific things that can be perceived by the senses and it minimizes misunderstanding
* actions, touch
* actions, touch
88
New cards
formal language
official and academic language that is intelligent sounding
* can be in writing too
* can be in writing too
89
New cards
informal language
common, everyday knowledge, continuous and casual
* includes slang
* includes slang
90
New cards
ambiguous language
language that has various meaning, this often causes unclear conversations
91
New cards
relative language
based on people’s backgrounds and depends on who is communicating
92
New cards
continuous
Conversations have a clear start and end but nonverbal is always happening
93
New cards
multichanneled
two nonverbal ways at once
* waving while wearing perfume
* waving while wearing perfume
94
New cards
intentional vs unintentional
nonverbal communication is both intentional and unintentional
95
New cards
ambiguous (nonverbal)
the nonverbal movements can be difficult to interpret because everyone comes from different backgrounds. It can be contracting and movements can have different meanings depending on the situation
96
New cards
primary conveyor
nonverbal communication is the primary conveyor of emotions and we tend to believe/trust the nonverbal behavior more than the verbal
* it is easier to lie with verbal communication and harder to control nonverbal things
\
* it is easier to lie with verbal communication and harder to control nonverbal things
\
97
New cards
complementing
nonverbal behavior that is used in combination with the verbal portion of the message to emphasize the meaning
* being excited and jumping up and down
* being excited and jumping up and down
98
New cards
contradicting
when nonverbal communication contradicts verbal communication
* saying something positive but with a monotone tone
* saying something positive but with a monotone tone
99
New cards
accenting
emphasizing a word or a part of a message
100
New cards
repeating
nonverbal communication that repeats the meaning of verbal communicating assists the receiver by reinforcing the words of the sender
* the word yes and a head nod
* the word yes and a head nod