FAR - Chapter 4 - Financial Instruments
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is the IAS 32 definition of a financial instrument?
any contract that gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity
What is the IAS 32 definition of a financial asset? (4 things)
Cash
A contractual right to receive cash
A contractual right to exchange financial assets/financial liabilities on favourable terms
An equity instrument in another entity.
What is the IAS 32 definition of a financial liability?
A contractual obligation to deliver cash
A contractual obligation to exchange financial assets/liabilities on unfavourable terms.
What is the IAS 32 definition of a equity?
Residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting all of its liabilities.
According to IAS32, what must an issuer of a financial instrument classify it as?
the issuer of a financial instrument must classify it as a financial liability, financial asset or equity instrument on initial recognition according to its substance.
What should a financial instrument be presented as, if it meets the criteria of a financial liability?
If a financial instrument meets the definition of a financial liability, then it should be presented as such (a financial liability), regardless of its legal form.
What do we classify redeemable preference shares as?
A financial liability
What do we classify irredeemable preference shares with dividends that are not cumulative or mandatory?
As equity
What do we classify irredeemable preference shares with dividends that are cumulative or mandatory?
As a financial liability
Should classification of financial instruments change after the date of issue according to IAS 32?
NO
What value are all financial assets initially recognised at?
Their fair value
What value are financial assets initially recognised at?
For financial assets this is usually then adjusted for the transaction costs by adding them on
FV (cash paid) + transaction costs
What value are financial liabilities initially recognised at?
For financial liabilities an adjustment will be made for transaction costs by deducting them
FV - transaction costs)
What is the IFRS 13 definition of fair value?
'the price that would be received tosell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transactionbetween market participants at the measurement date
What are all financial assets and liabilities measured at?
amortised cost using the effective interest rate
What is the coupon rate?
The coupon rate (aka nominal rate) is the amount of interest paid – always given as a percentage of the nominal value.
What is the effective rate of interest?
The effective rate of interest spreads all of the costs of the liability (such as transaction fees, issue discounts, annual interest payments and redemption premiums) to the SPL over the term of the instrument.
If required in the exam, this will be given to you.
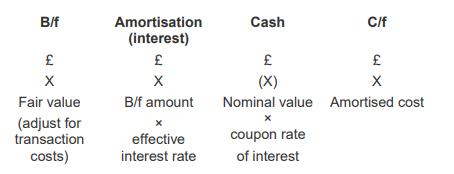
What is the calculation matrix for financial assets and financial liabilities?
b/f (fair value ± transaction costs) X
Amortisation (interest) - b/f amount x effective interest rate X
Cash - nominal value x coupon rate of interest - (X)
c/f - amortised cost
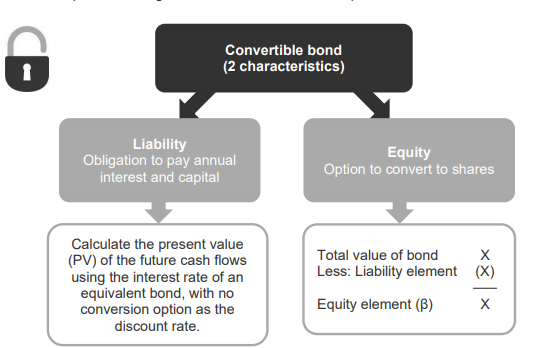
What is a compound instrument?
A compound instrument is a financial instrument that has characteristics of both equity and a liability, for example a convertible bond.
What type of accounting is required for convertible bonds? & how?
Split accounting
Liability (Obligation to pay annual interest and capital)
Calculate the present value (PV) of the future cash flows using the interest rate of an equivalent bond, with no conversion option as the discount rate
Equity (Option to convert shares)
Equity element = Total value of bond - liability element
What will the liability element be held under by IFRS 9>
Amortised cost
What are treasury shares?
Where a company acquires its own shares as an alternative to making dividend distributions and/or as a way to return excess capital to shareholders
What is the treatment for treasury shares and where can they be disclosed?
they should be debited to equity (i.e. they are shown as negative equity)
no gain or loss should be recognised on their purchase
Treasury shares can either be disclosed on the face of the SFP or in the notes.
What’s the double entry for treasury shares?
DR Treasury shares
CR cash
Do the issue of treasury shares affect share capital and share premium?
NO
What 2 categories of disclosures are required?
(1) information about the significance of financial instruments
(2) information about the nature and extent of risks arising from financial instruments, and how the entity manages those risks.
What quantitative disclosures are required for financial instruments?
An entity must disclose the carrying value of each class of financial instrument.
The fair value of each class of financial instrument should also be disclosed.
What qualititative disclosures are required for financial instruments?
The entity must disclose information to enable users to understand management’s attitude to risk.
Disclosures may focus on the entity’s credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk.
What is credit risk?
The risk that one of the entities to whom it has advanced a loan will be unable to repay the money
What is market risk?
the potential for losses in investments due to overall market movements.
Do zero-coupon bonds have cash payments (in the cost table)?
NO
No repayments of principal sum
For zero-coupon bonds, will there be finance costs or finance income?
Finance income is the amortisation (interest)
For convertible bonds, will there be finance costs or finance income?
There are finance costs that are (amortisation interest - cash payments)
What is the cash payment for irredeemable preference shares?
Preference share capital * fixed dividend rate in share name
What is the cash payment for convertible bonds?
Total amount of convertible bond * & in its title