Aphasia Test 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Disadvantages of beside screening
non-standardised, hard to be consistent, subjective
2
New cards
Advantages of beside screening
flexible, fast, gives direction for further assessment
3
New cards
What does FAST stand for?
Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test
4
New cards
What does BEST stand for?
Bedside Evaluation Screening Test
5
New cards
Examples of standardised bedside screening are…
WAB, BEST, FAST, CDS, Brisbane, IFCI-CFI
6
New cards
What does CDS stand for?
Communication Disability Screener
7
New cards
What does IFCI stand for?
Inpatient Functional Communication Interview
8
New cards
What are the 4 types of fluent aphasia?
Wernicke’s, Transcortical Sensory, Conduction, Anomia
9
New cards
What are the types of non-fluent aphasia?
Broca’s, Global, Transcortical Motor, Mixed Transcortical
10
New cards
What is neuroplasticity?
The brain's ability to repair itself and regenerate connections after TBI or stroke.
11
New cards
Wernicke’s Aphasia characteristics
fluent, poor comprehension, poor repetition
12
New cards
Anomic Aphasia characteristics
fluent, good comprehension, good repetition
13
New cards
Conduction Aphasia characteristics
fluent, good comprehension, poor repetition
14
New cards
Transcortical Sensory Aphasia characteristics
fluent, poor comprehension, good repetition
15
New cards
Transcortical Motor Aphasia characteristics
non-fluent, good comprehension, good repetition
16
New cards
Broca’s Aphasia characteristics
non-fluent, good comprehension, poor repetition
17
New cards
Mixed Transcortical Aphasia
non-fluent, poor comprehension, good repetition
18
New cards
Global Aphasia
non-fluent, poor comprehension, poor repetition
19
New cards
What does WAB stand for?
Western Aphasia Battery
20
New cards
The fibral tract that connects the Broca’s and Wernicke’s area is called the…
Arcuate fasciculus
21
New cards
The first step of the auditory comprehension pathway is…
The ear converts acoustic energy into electrochemical energy into electrochemical energy and transmits it to the brainstem via CN VIII (vestibulocochlear).
\
\
\
\
22
New cards
In the auditory comprehension pathway, the electrochemical energy transmits from the brainstem to the….
thalamus
23
New cards
In the auditory comprehension pathway, information is relayed from the thalamus to the ____ __for__ ______.
Primary auditory cortex (A1) for signal processing
24
New cards
In the auditory comprehension pathway, info goes from A1 to the ____ __area where__ ____ is attached.
Wernicke’s area, where meaning is attached
25
New cards
In the auditory comprehension pathway, info goes from the Wernicke’s area to the ___ __area for__ _______
Broca's area, higher-level syntactical processing.
26
New cards
Visual information is projected to the thalamus under BA _/_, *via the* ___ tracts.
\
\
BA 41/42 via the optic tracts.
27
New cards
In the visual pathway, the thalamus projects to the __ lobe’s visual areas (BA *- and -* __)__ for visual processing via the ____ tract.
occipital, BA 17-19, geniculocalcarine tract.
28
New cards
The visual areas project 2 different streams of vision. These are the -- and -- streams.
dorsal, ventral
29
New cards
The dorsal stream of vision is responsible for the “---” of vision.
“where”
30
New cards
The ventral stream of vision is responsible for the “---” of vision.
“what”
31
New cards
When reading, the ----, ---- and ---- temporal reading systems activate.
anterior, paneto and occipito
32
New cards
In the oral production of language pathway, desire and thoughts to communicate originate in the --- cortex and are sent to the ----’s area for --- --- and ---- planning.
\
\
prefrontal cortex, Broca’s area, language encoding and speech planning
33
New cards
In the oral production of language pathway, the Broca’s area projects information to the ---- --- --- at the top of BA 6 which activates --- ---.
supplementary motor area (SMA), speech plans.
34
New cards
In the oral production of language pathway, the SMA then relays now active plans to the ---- ---- cortex
primary motor cortex
35
New cards
In the oral production of language pathway, the primary motor cortex then sends the plans to the --- --- for execution.
speech muscles
36
New cards
In the written expresison of language pathway, language-encoded thoughts are sent to the --- ---- cortex (BA 6) for ------ motor planning.
premotor, handwriting
37
New cards
In the written expression of language pathway, motor plans are sent to the --- --- cortex.
primary motor cotex
38
New cards
In the written expression of language pathway, the primary motor cortex then sends the writing plans to the --- --- for execution.
dominant hand
39
New cards
In the written expression of language pathway, which part of which lobe coordinates the visuospatial aspects of writing?
left superior parietal lobe
40
New cards
Saliency is where…
lexical items should be topical
41
New cards
What are the elements of the ICF framework?
Impairment, Acitivty, Participation, Environment
42
New cards
Paraphasia (basic definition)
when a person with aphasia says a word but it is not the intended word
43
New cards
“chair” instead of “table” is an example of….
semantic paraphasia
44
New cards
“rat” instead of “cat” is an example of…
mixed paraphasia (semantic and phonemic)
45
New cards
“letophone” instead of “telephone” is an example of…
phonemic paraphasia
46
New cards
“aidou” instead of “eyebrow” is an example of…
neologism
47
New cards
“lamp” instead of “dog” is an example of…
random paraphasia
48
New cards
Circumlocution is…
using a description of the word instead of the target word
49
New cards
Agrammatism is…
limitations in sentence structure and functional morphology, missing grammatical elements, syntactic comprehension
50
New cards
Stereotypial utterance/automatism is…
ability to only produce one word, phrase or meaningless sound combination
51
New cards
Perseveration is…
unintentional repetition of a linguistic unit (getting stuck on something)
52
New cards
Non-fluent aphasia is generally associated with lesion in the….
anterior to central sulcus in the dominant language hemisphere
53
New cards
Fluent aphasia is generally associated with lesion in the…
posterior to central sulcus in the dominant language hemisphere
54
New cards
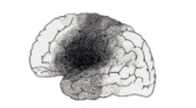
What type of aphasia?
Broca’s
55
New cards
Bedside screening tests…
auditory comprehension, spontaneous speech, word finding, automatic speech, repetition, reading comprehension, writing