ERE Week 1 - Market failure
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
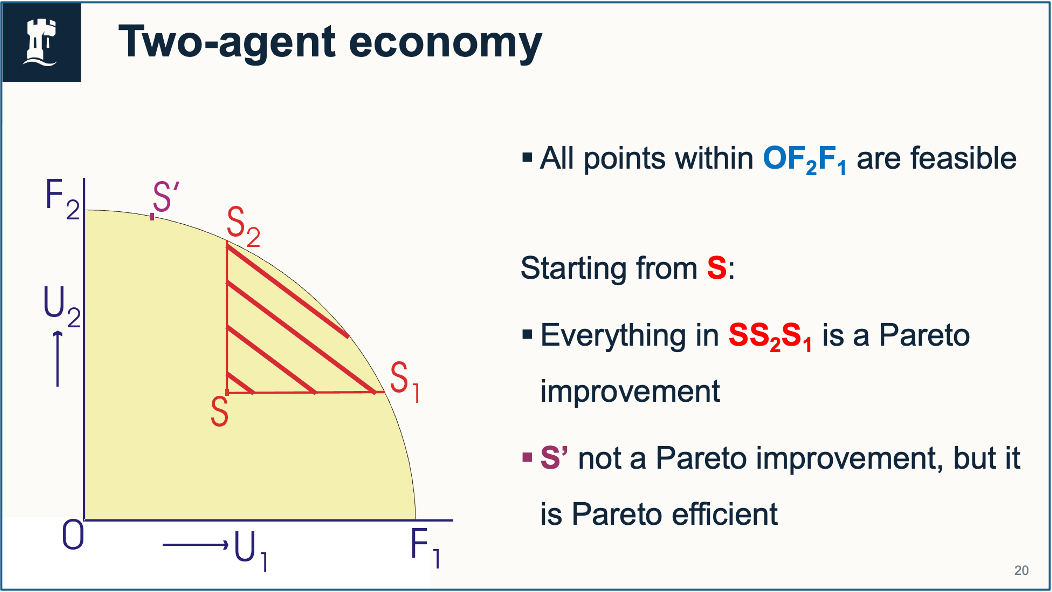
Pareto improvement
At least 1 person benefits & no one is worse off
Pareto efficiency vs Pareto improvement
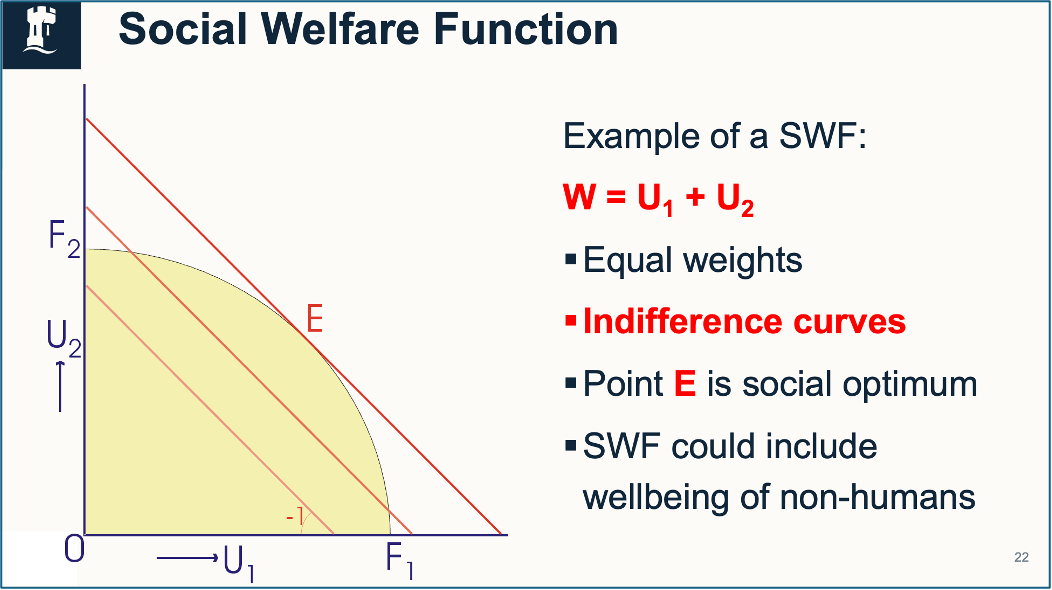
Social welfare function
W(U1,U2)
Helps us choose which project to undertake
Efficient policy
Where winners from the project compensate the losers
only works if the transfers are feasible
If compensation then pareto improvement
If no compensation then on aggregate everyone should benefit
When is a project worth undertaking
if it is a Pareto improvement
Pareto efficiency
Pareto improvements are no longer possible
No one can be made better off without making
anyone worse off
Conditions for efficient markets
Markets exist for all goods and services
Perfectly competitive markets
Perfect information
Property rights are fully assigned
No externalities
All goods and services are private goods
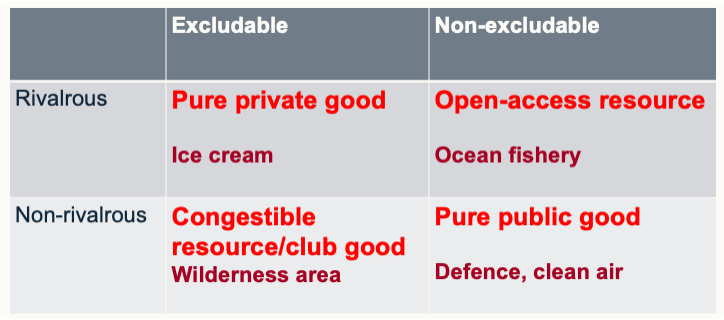
Public goods
Non-rival
Non excludable
Voluntary provision of public goods almost always leads to under provision due to free riding
Non rivalrous goods
My consumption does not diminish your consumption
Non-excludable
No one can be excluded from consumption
Types of good table
Externality
Production or consumption decisions of one agent affect the utility or production possibilities of another agent in an unintended way
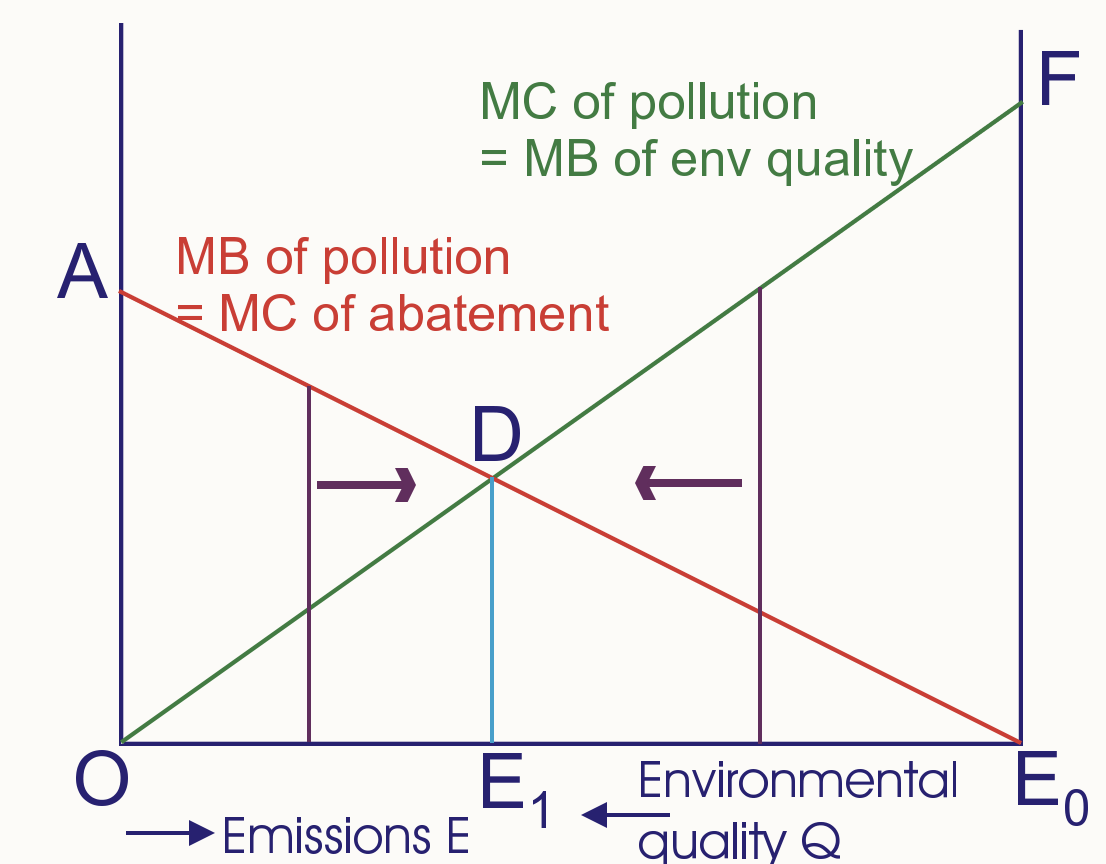
Basic Pollution diagram
Without policy polluters emit E0 → MC abatement = 0
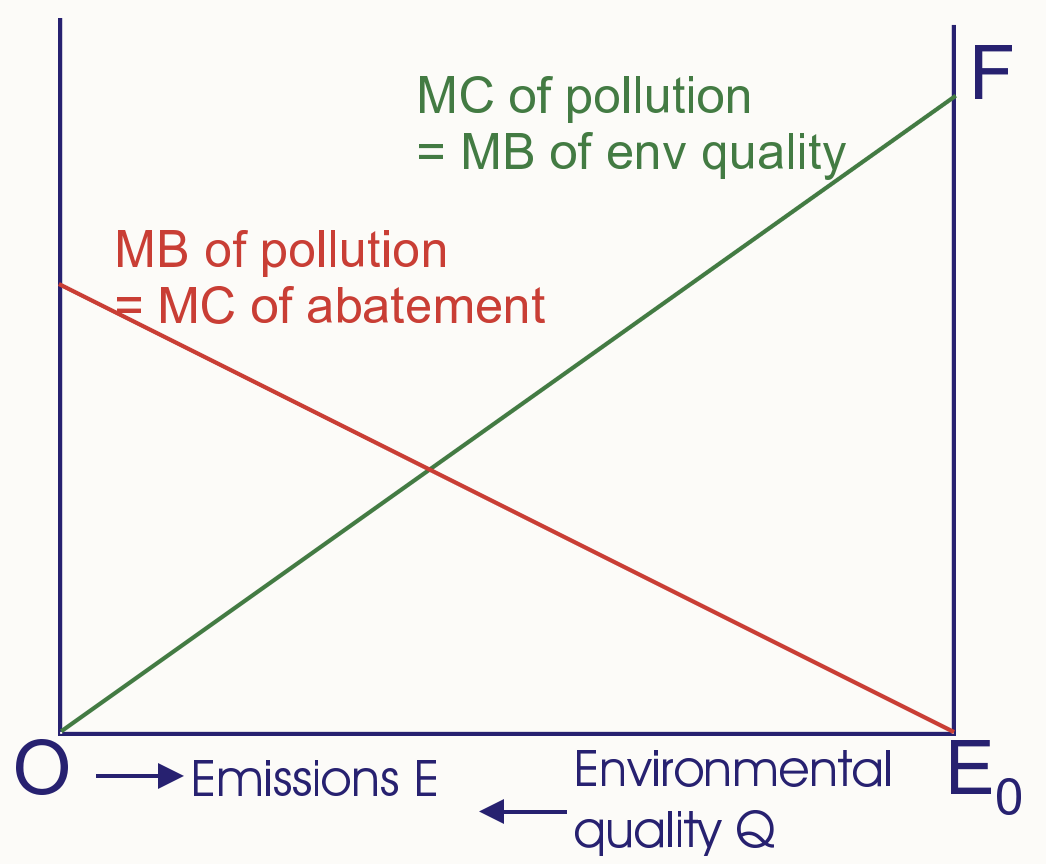
Optimal Pollution diagram
Optimal pollution = E1 → MC abate = MC pollute
Total cost minimised + Total benefit maximised
Polluter + victim want to maximise joint benefit → Victim pays polluter to reduce E to E1 OR Polluter pays victim to allow E1
Government role in environment
Assign and enforce property rights
Doesn’t matter for efficiency to whom property rights are assigned
Coase theorem
When property rights are assigned, bargaining between affected parties will result in the efficient level of pollution irrespective of the distribution of property rights
Victim pays polluter
Victim pays polluter to reduce E to E1
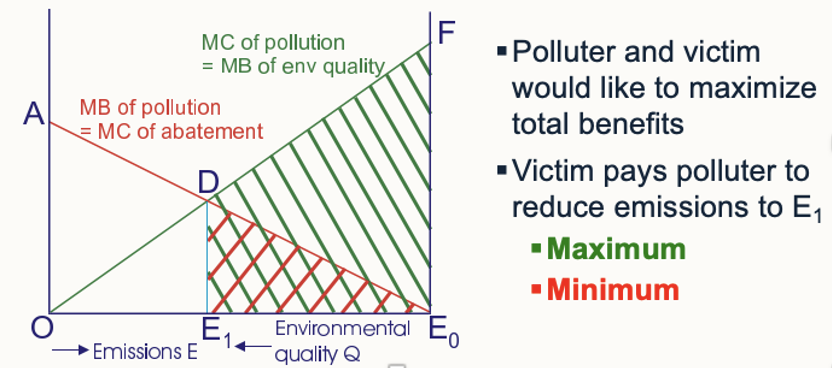
Victim holds property rights
Polluter pays victim to allow E1
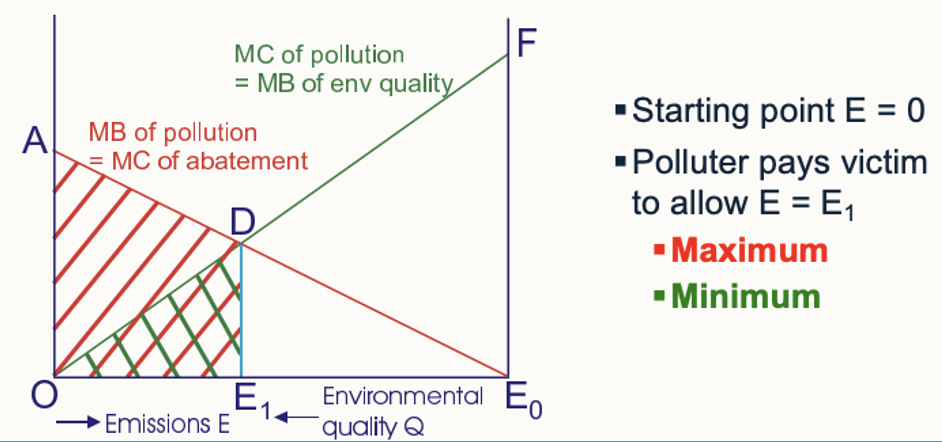
Problems with Coase theorem
Transaction costs
Strategic behaviour
Instability of the grand coalition
Problems with Coase theorem - transaction costs
Identifying all polluters and victims
Identifying Costs + Benefits
Getting all agents together (Free riding)
Cost of bargaining
Problems with Coase theorem - Strategic behaviour
Bargaining may break down
Problems with Coase theorem - Instability of the grand coalition
At least 3 parties + 2 externalities → Ideal is a grand deal that solves all externalities at once
Some parties could break away from that and come up with own deal that solves their own problems → At expense of those left out
Coase theory example - Vittel overview
Mineral water source in NE France was being polluted from nearby farmers
Late 1980s: Vittel notes increase in nitrate concentration in spring water from nearby intensive farming (corn)
However under EU law, farmers weren’t going over the legal level
Coase theory example - Vittel options

Coase theory example - Vittel TC

Coase theory example - Vittel overcoming TC

Coase theory example - Vittel Results
Contracts with 34 out of 37 farmers in 10 years
96% of targeted lands
Contracts for 18 – 30 years
Decrease in nitrate concentration
Coase theory example - Vittel Costs to get results
