molecular genetics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
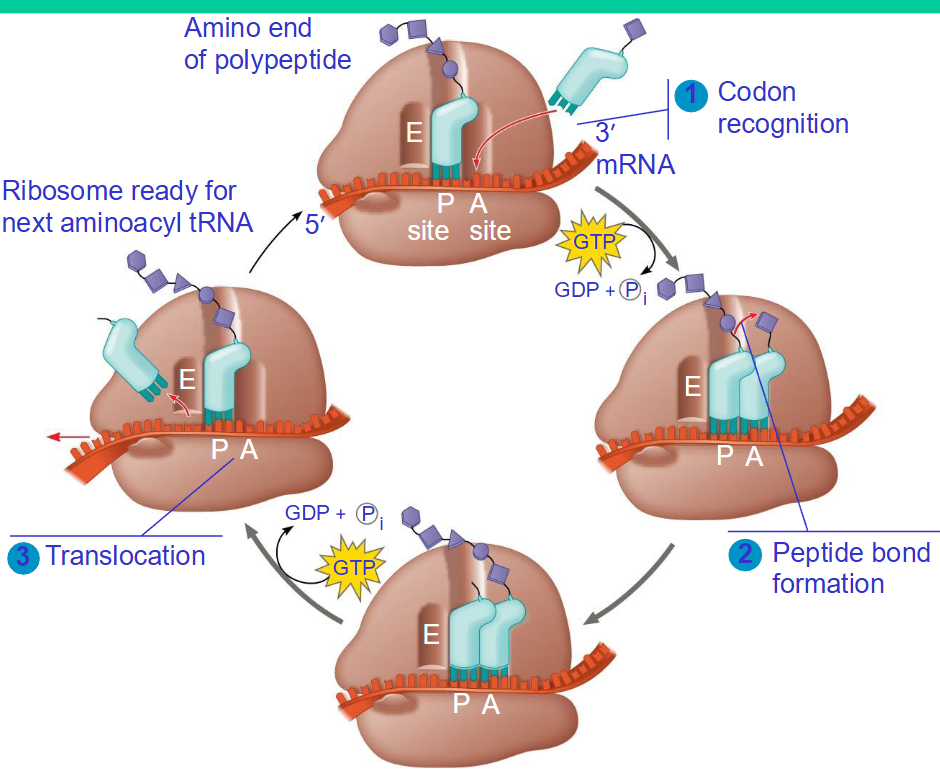
what are the sites on ribosomes
P - site (peptidyl site) - binds to the tRNA holding the growing polypeptide chain of amino acids
A - site (acceptor) - binds to tRNA holding the new amino acid to be added to the polypeptide chain
E -site (exit) - binds a tRNA that already unloaded its amino acid and it is going to be released
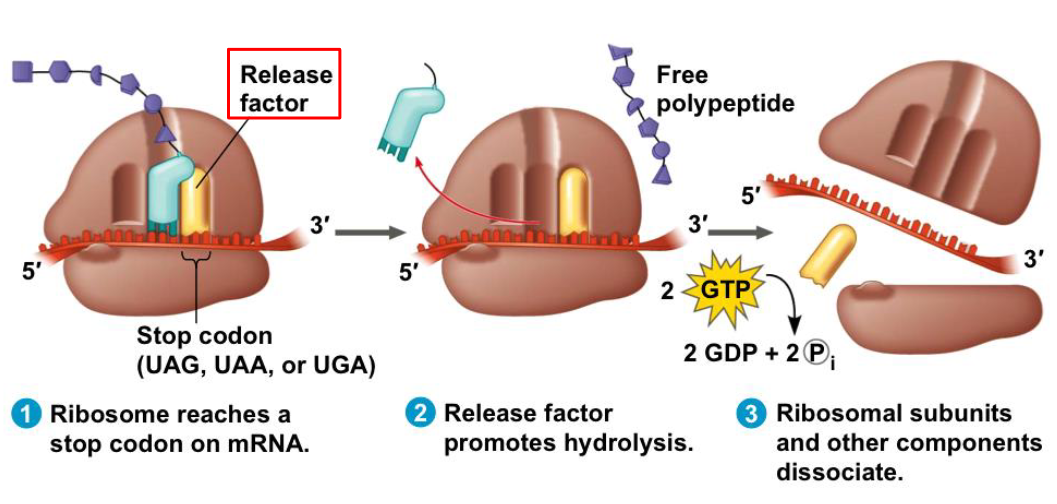
how does termination take place?
a release factor binds directly to the stop codon in the A site
addition of H20 molecule instead of an amino acid
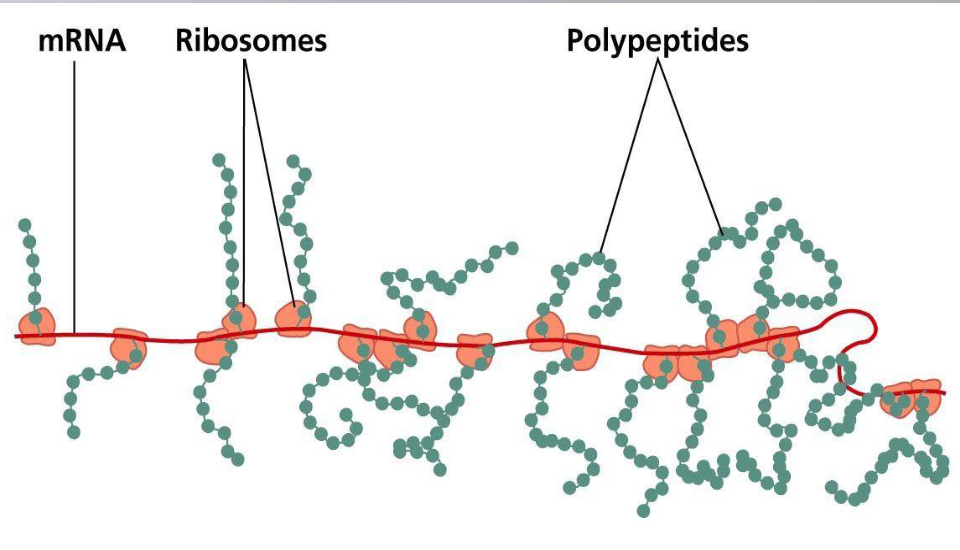
what are polyribosomes?
in prokaryotes mRNA is translated to protein as soon as its made
in eukaryotes mRNA has to be transported out of the nucleus before it can be translated
in both cases several ribosomes can simultaneously translate one mRNA molecule
what are open reading frames?
contigous sequence of DNA or RNA that starts with a start codon and ends with stop codon indicating a region with potential of being translated into a protein
does not include introns
dna sequences read in 5’ to 3’ direction
operons in bacteria
gene expression in eukaryotes
control expression of individual genes
scales of regulation:
epigenetic
transcriptional
post - transcriptional
translationl
post - translational
what is gene expression?
the overall process of producing a protein from the gene that encodes the protein
Promoter activation
• Initiation of transcription and translation
• Alternative splicing
• Translation
• Protein folding and targeting
how can mRNA be measured using the nothern blot
transcriptome = entire set of RNA molecules (all mRNA)
the northern blot:
rna gel electrophoresis - smaller mRNA molecules travel furtherst
rna with gel is blotted onto a membrane that binds to RNA
short piece of single stranded DNA complementary to RNA is incubated with the membrane
the dna probe only anneals to the mRNA of interest on the membrane - the dna probe is fluorescent or radioactive
the more abundant the mRNA the more probe sticks to it
the amount of probe is measured imaging equipment
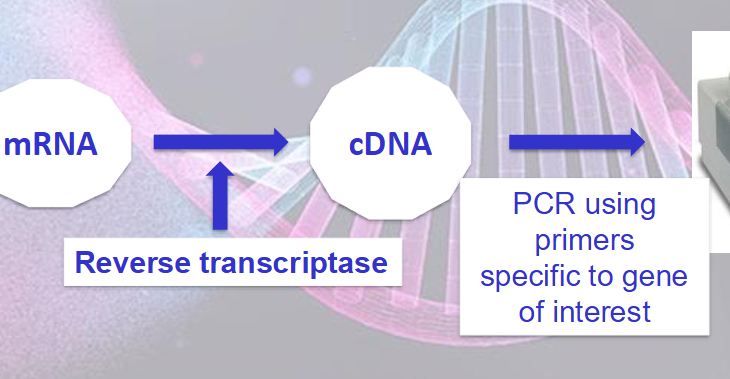
How can mRNA be measured using RT - PCR
RT - retrotranscription
retrotranscriptase - viral enzyme that synthesises ssDNA from mRNA
polyTprimer binds to the mRNA poliA tail
RT synthesises cDNA of all the genes in the tube
we select gene of interest with primers and PCR
what are microarrays?
microarrays - allows the study of whole transcriptomes
each well/cell in the grid contains unique short RNA or DNA probes complementary to genes of interest
array is incubated with mRNA or cDNA of a sample
Fluorescent labelling allows detection of the amount of nucleic acid bound to each short DNA sequence on the array
spot intensity provides mRNA quantity for each single mRNA
how else can you study whole transcriptomes
RNA sequencing
next generation sequencing allows whole genomes to be sequenced relatively cheaply
applied to sequence all mRNA’s from an organism
the number of times a sequence is obtained for the mRNA from each gene reflects the mRNA expression level
rna sequencing is inexpensive and large number of sample can be processed together
can be used with organisms having no known genome sequence
How to measure proteins
measuring DNA/RNA is easy due to complementary base pairing
protein detection requires production of an antibody that recognises the protein
relies on ability of mammals to produce an antibody to foreign protein
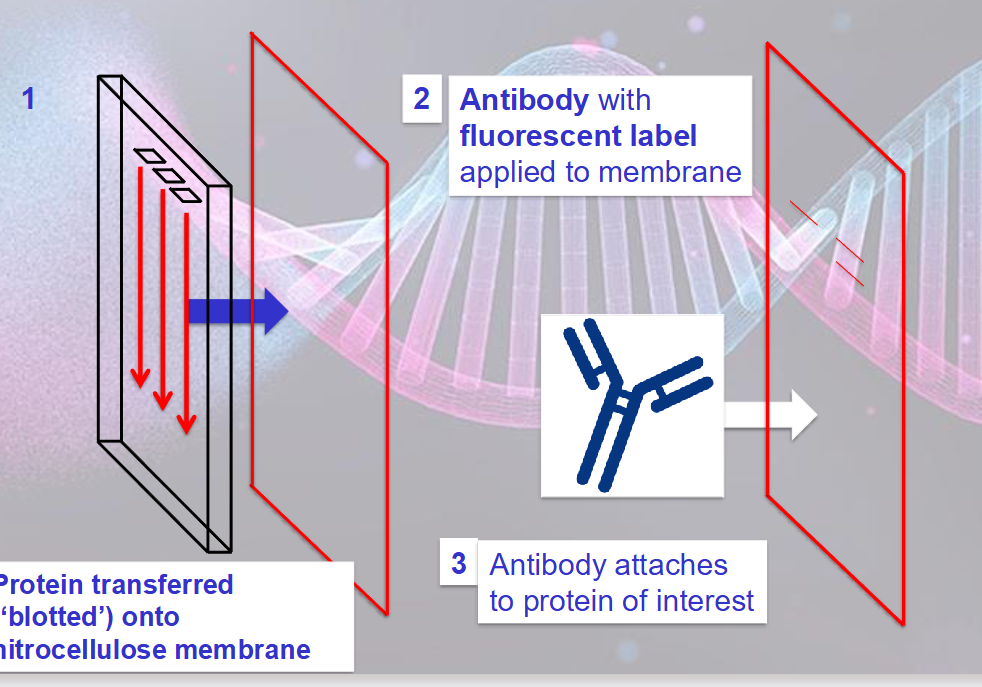
western blotting:
mix of proteins extracted from an organisms is separated using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)
PAGE gels are thin and normally arranged vertically
the protein extract is treated with detergent that gives it negative charge
darker bands indicate more antibody has attached so more of the protein of interest is present
what are small scale mutations
substitutions:
silent
missense
nonsense
all point mutations
insertions or deletions:
frameshift missense
frameshift nonsense
gain/loss of amino acids
what are large scale mutations?
alterations of chromosome numbers
alteration of chromosome structure:
deletion
duplication
inversion
translocation
what is thalassaemias
mutation which affects production of the a and b chains of haemoglobin leading to abnormal ratios
α-thalassaemia: synthesis of the α chain absent or reduced –
usually as a result of deletion of one or more α-globin genesβ-thalassaemia: synthesis of β chain absent or reduced –
usually as a result of defective processing of β-globin mRNA