VT 111 Lec. 1 Intro/Directional Terms
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Anatomy
Form and structure
Physiology
Function of the body and its parts
Microscopic Anatomy
Anatomy observed with the assistance of a microscope
Macroscopic Anatomy
Anatomy that can be seen with the unaided eye; also called gross anatomy
Pattern of Structural Hierarchy
Atoms
Molecules
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ systems
Organism
11 Body Systems of Animals
Skeletal
Integumentary
Nervous
Urinary/excretory
Endocrine
Reproductive
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Digestive
Muscular
Sensory
Lymphatic (not really a system)
Homeostasis
A state of dynamic equilibrium maintained in the body by feedback and regulatory processes in response to internal and external changes.
Components of a Homeostatic System
Sensor: (AKA control center) detects change
Variable: The parameter being controlled by the system (temperature, chemical concentration, etc.)
Effector: the structure that changes the variable
Life Functions of the Animal Body
Maintaining boundaries
Movement
Detect and respond to environmental change (stimuli)
Take in and digest food
Metabolism
Excretion
Growth
Reproduction
Maintaining Boundaries
● Plasma (cell) membrane protects the inside of the cell from the outside
● Maintain membrane integrity (hydrophobic nature as well as cholesterol stabilizes the membrane)
● Maintain and support the integument (skin) as a barrier
Movement
●All activities promoted by the muscle system: Propulsion, etc.
●Manipulating of the environment: digging, etc.
●Skeletal system provides a system of levers
●Propelling digesta through the G.I. tract
Detect & Respond to Environmental Change (Stimuli)
●Detection is the responsibility of the nervous system
●Elaborate system of sensors are present: Special senses, as well as baroreceptors, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, etc.
●Animal must be able to respond to changes to maintain homeostasis: Increase or decrease blood pressure, temperature, glucose, etc.
Take in & Digest Food
●Ingest food, prehend (grab) food
●Secretion of digestive enzymes
●Absorption of nutrients across the gut wall
Metabolism
The orderly set of chemical reactions that occur within cells
Break down of complex substances
Usage of small substances as building blocks for larger structures
Usage of nutrients and oxygen to convert energy/ATP
Metabolic processes are regulated by hormones
Metabolic products are transported in the blood
Excretion
Elimination of solid and aqueous waste from the body
Production of carbon dioxide (CO2)
Regulation of pH
Osmoregulation - maintaining salt regulation (electrolytes) in the body
Growth
Increase in the number of cells
Increase in body size
For growth to occur:
Anabolic rate > Catabolic rate
Reproduction
Can be at the cellular level:
Reproducing daughter cells for growth or repair (mitosis)
Can be at the organismal level:
Reproduction of whole new organisms (sexual reproduction via fertilization of gametes created via meiosis)
Two basic animal strategies:
Many offspring produced, few survive, little parental investment in survival
Few offspring produced, higher survival rate, considerable parental investment in survival
Importance of Anatomical Terminology
Have the same meaning regardless of the orientation of the animal or the position of the observer; eliminates confusion
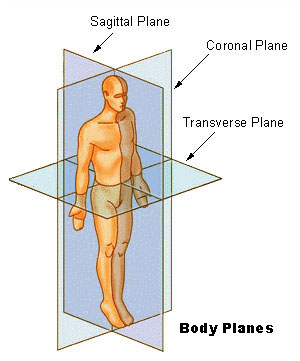
Body Planes
Sagittal Plane
plane from cranial-caudal, separates body into unequal L/R halves
Median Plane
similar to sagittal except through the exact midline of the body
Transverse Plane
plane across the body, separates into cranial and caudal halves
Dorsal Plane (aka, coronal or frontal):
Dorsal (aka, coronal or frontal): separates into dorsal and ventral halves
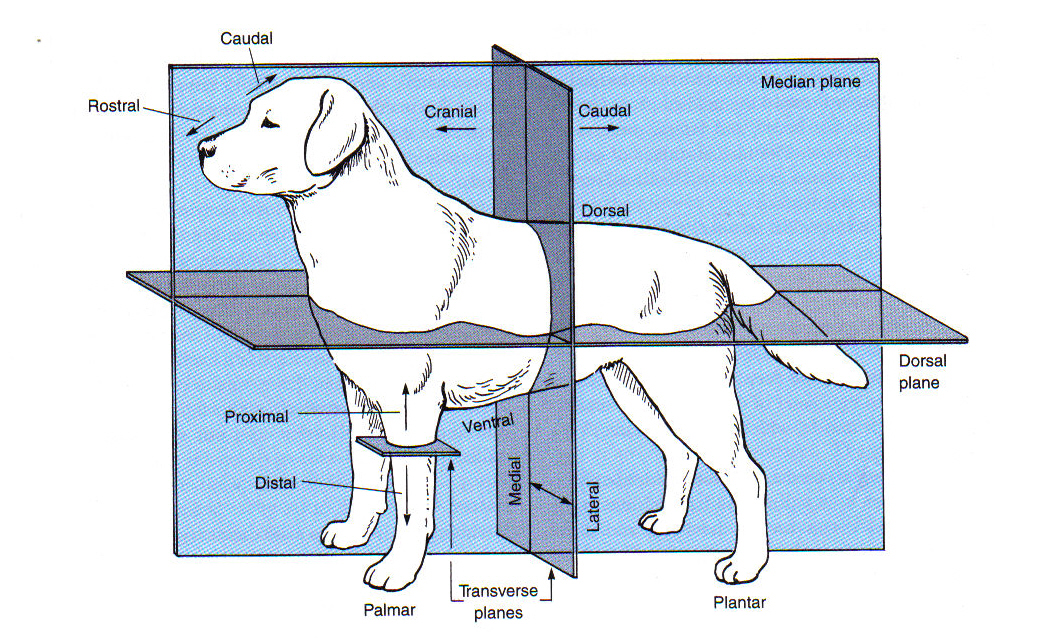
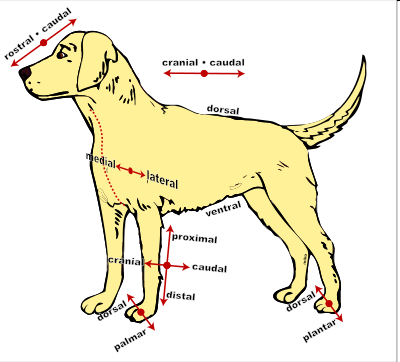
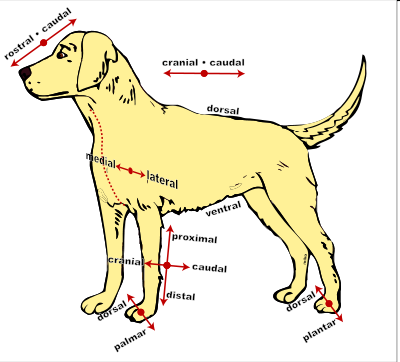
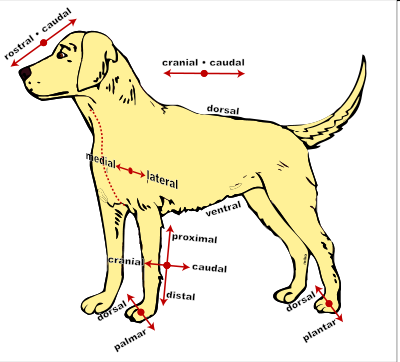
Directional Terms for Animals
Anterior
Toward the head
Posterior
Toward the tail
Cranial
Towards the head
Caudal
Toward the tail
Dorsal
Toward the back
Ventral
Toward the belly
Medial
Toward the midline
Lateral
Toward the side; away from the midline
Superficial
toward the surface of the body or a body part (external)
Deep
toward the center of the body (internal)
Rostral
Toward the nose
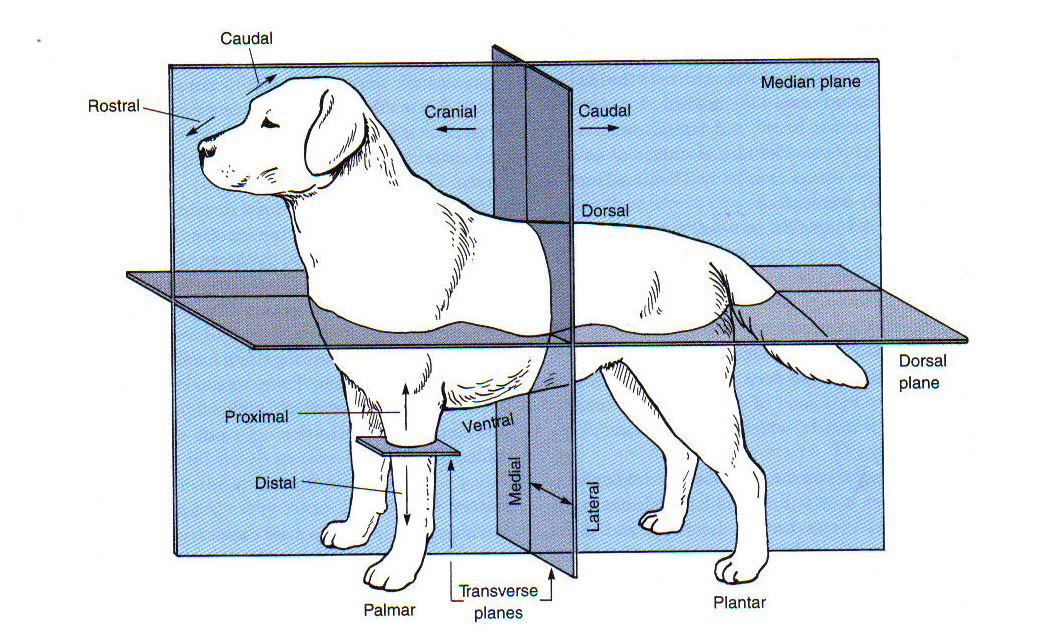
Directional Terminology Pertaining to Limbs
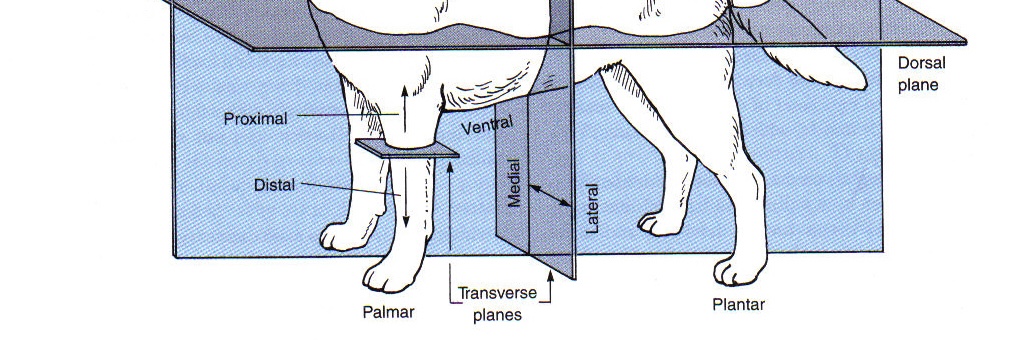
Proximal
toward the beginning attachment point on a limb
Distal
away from the beginning attachment point on a limb
Palmar
the caudal surface of the forelimb from the carpus down
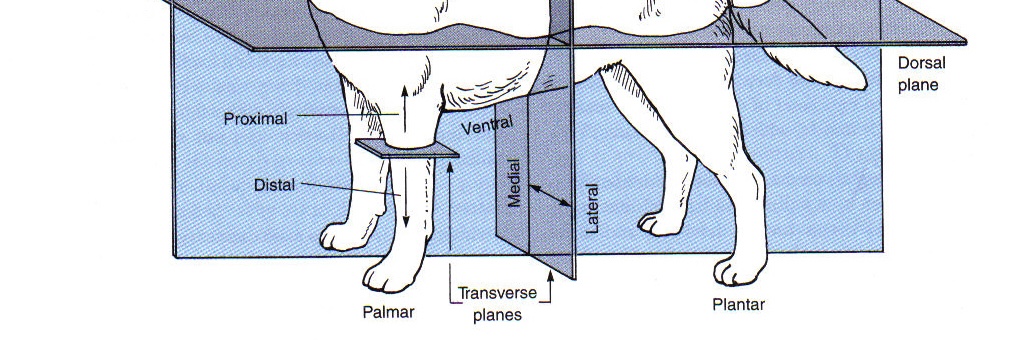
Plantar
the caudal surface of the hindlimb from the tarsus (hock) down
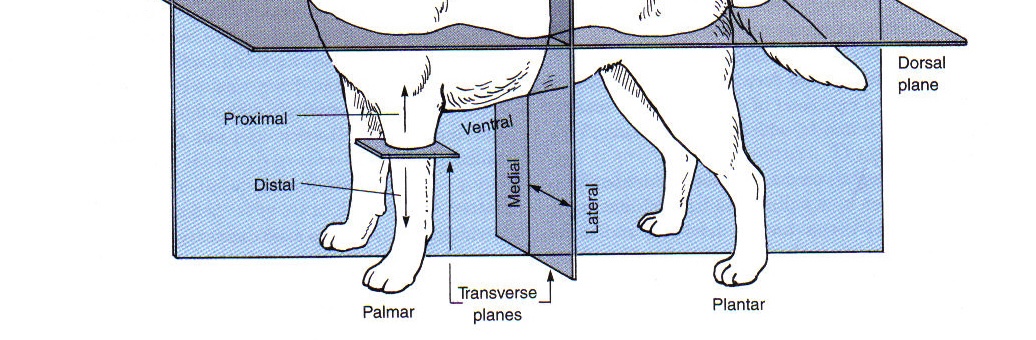
Dorsal (limbs)
toward the top of an animal
Cranial (limbs)
the “front” surface of a limb proximal to the carpus or tarsus
Caudal (limb)
toward the tail (or “back” surface of a limb
Axial
refers to the central axis of the body
Appendicular
refers to the appendages and their associated girdles (pelvic, pectoral)
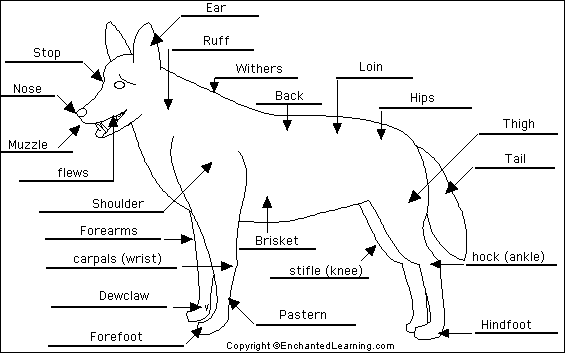
Regional Terminology
Axillary
Armpits of the animal
Brachial
Upper arm
Buccal
Cheek
Carpal
“Wrist” area of an animal
Cervical
Neck region
Cranial
Head
Digital
Toes
Femoral
Thigh
Flank
The part of the side between the ribs and the hip; the side of a quadruped
Hock
Ankle
Inguinal
Area where thigh meets the trunk
Nasal
Nose; rostrum
Oral
Mouth
Orbital
Eye area
Occipital
Back of head
Patellar
Knee
Sternal
Breast bone area; ventral thorax
Stifle
Knee
Tarsal
Ankle
Thoracic
Chest
Umbilical
Navel
Withers
Dorsal in between shoulder blades
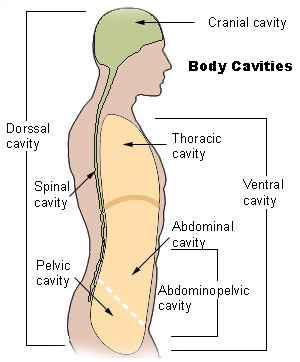
Body Cavities
Dorsal:
Cranial cavity
Spinal cavity
ONLY
Ventral:
Cranial
Thoracic: heart, lungs
Caudal
Abdominopelvic
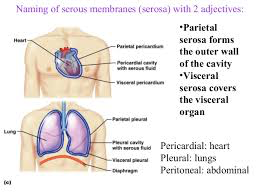
Serous Membranes
Lungs (Thoracic cavity)
Lined by pleura
Layers over organs: Visceral layer = visceral pleura
Layers lining cavity:
Parietal layer = parietal pleura
Fluid in between layers
Abdomen (Abominopelvic cavity)
Lined by peritoneum
Layer over organs: Visceral layer = visceral peritoneum
Layer lining the cavity: Parietal layer = parietal peritoneum
Heart (Thoracic cavity)
Lined by the pericardium
Layer over organs: Visceral layer = visceral pericardium
Layer lining the cavity: Parietal layer = parietal pericardium
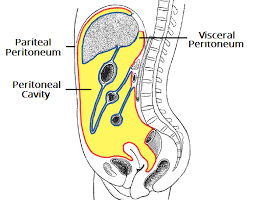
Serous Membranes
covers walls and organs in the thoracic
and abdominopelvic cavities.
Parietal Layer
line the walls of the body cavity
Visceral layer
covers the organs (the viscera).
Serous Space/Fluid
Between the parietal and visceral layers.
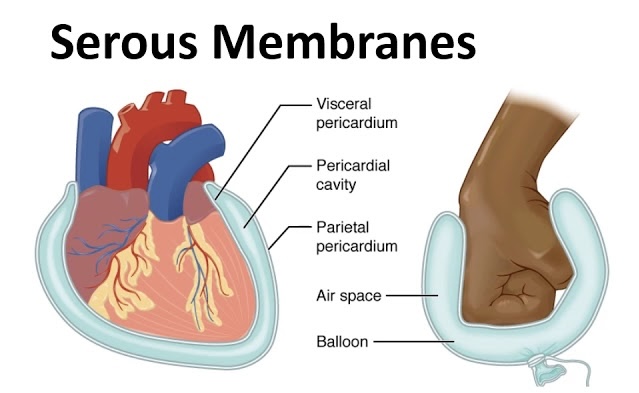
3 Serous Membranes
1. Pleura - Serous Membrane that surrounds the lungs. One for each lung.
2. Pericardium - Serous Membrane that surrounds the heart.
3. Peritoneum - Serous membrane that surrounds several organs in the abdominopelvic cavity.