Ex 27: Functional Anatomy of the Endocrine Glands
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BMS508L w/ Brett Gunn
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
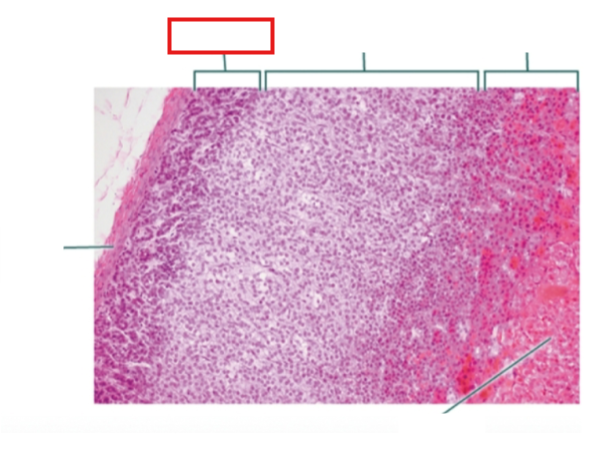
What structure is highlighted?
zona glomerulosa
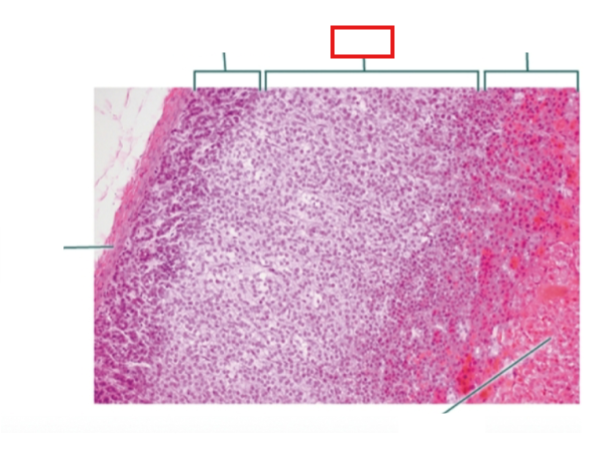
What structure is highlighted?
zona fasciculata
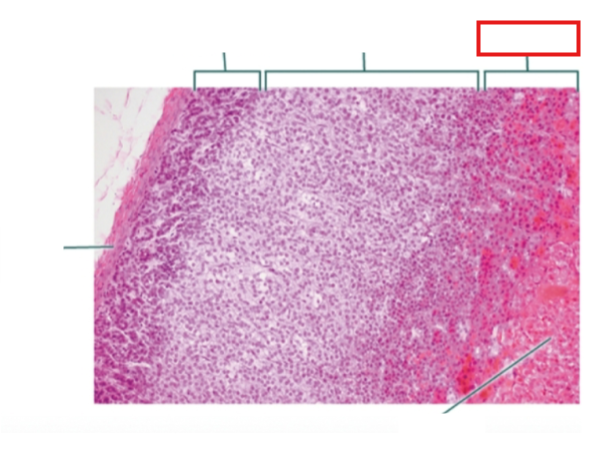
What structure is highlighted?
zona reticularis
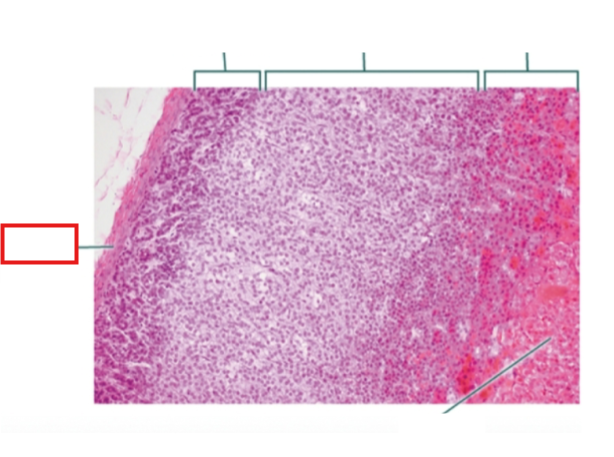
What structure is highlighted?
Capsule
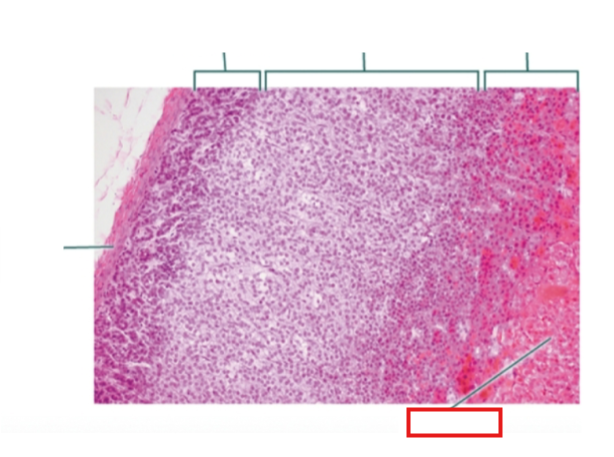
What structure is highlighted?
medulla
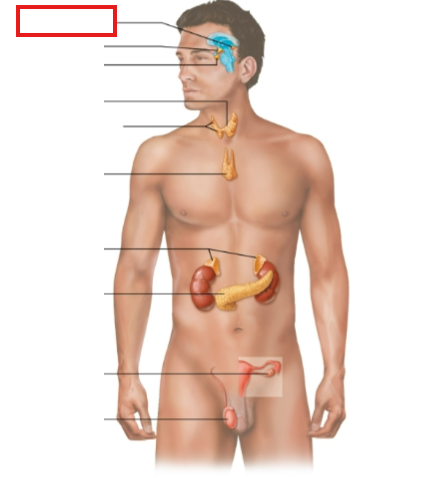
What structure is highlighted?
pineal gland
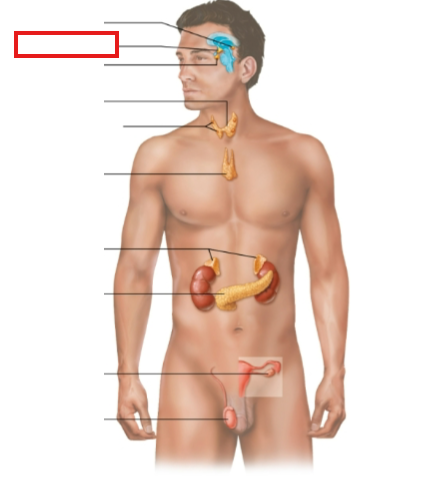
What structure is highlighted?
hypothalamus
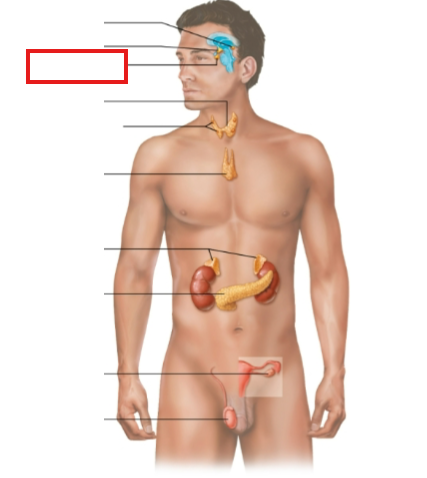
What structure is highlighted?
pituitary gland
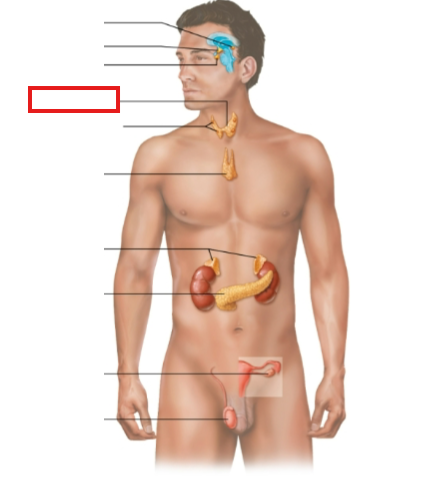
What structure is highlighted?
thyroid gland
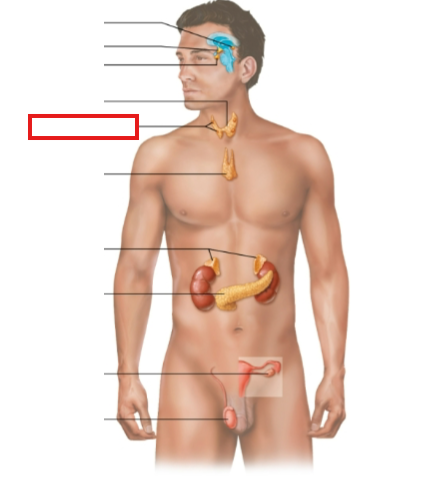
What structure is highlighted?
parathyroid glands
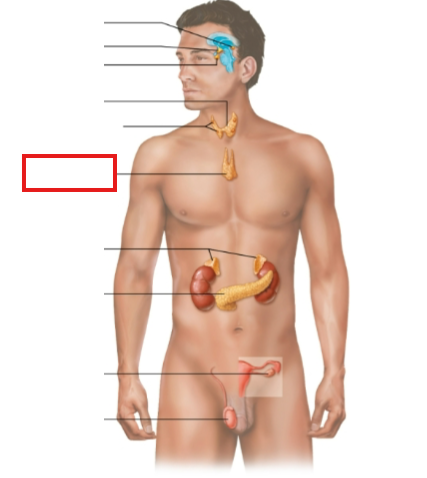
What structure is highlighted?
thymus
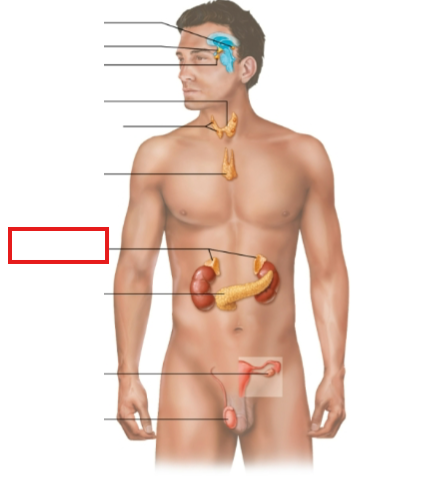
What structure is highlighted?
adrenal glands
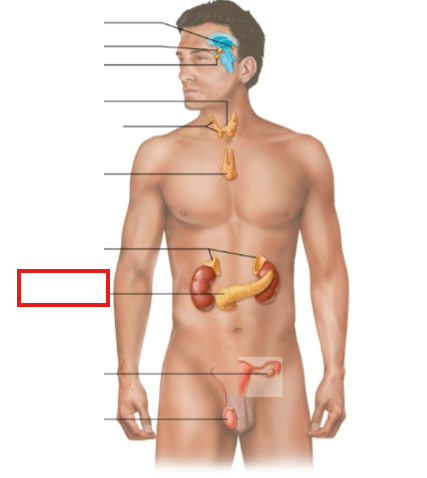
What structure is highlighted?
pancreas
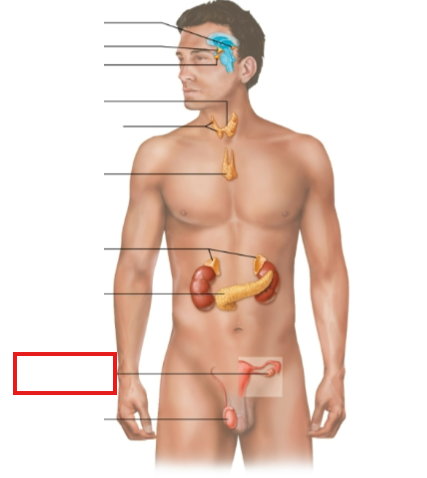
What structure is highlighted?
ovary (female)

What structure is highlighted?
testes (male)
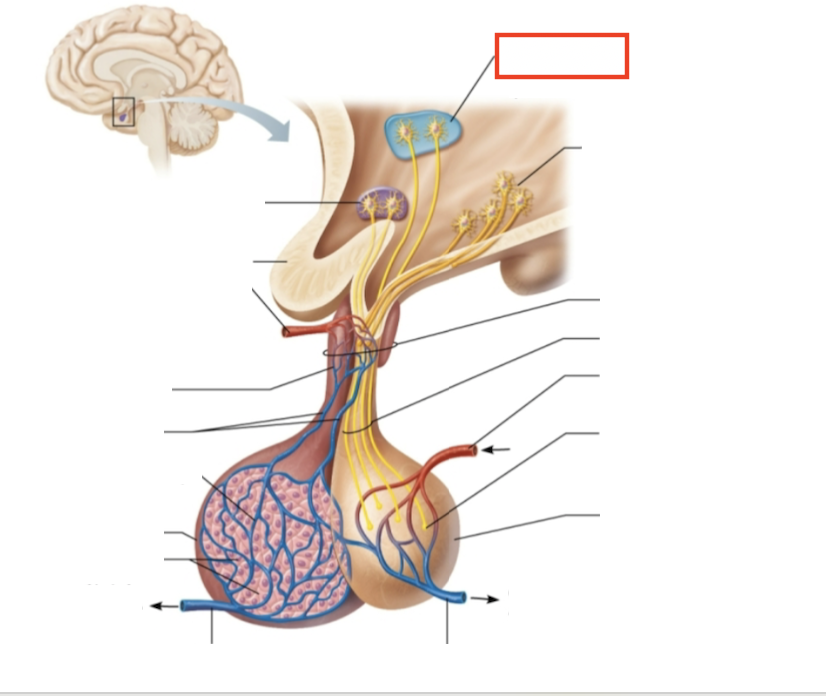
What structure is highlighted?
hypothalamic neurons in the paraventricular nuclei
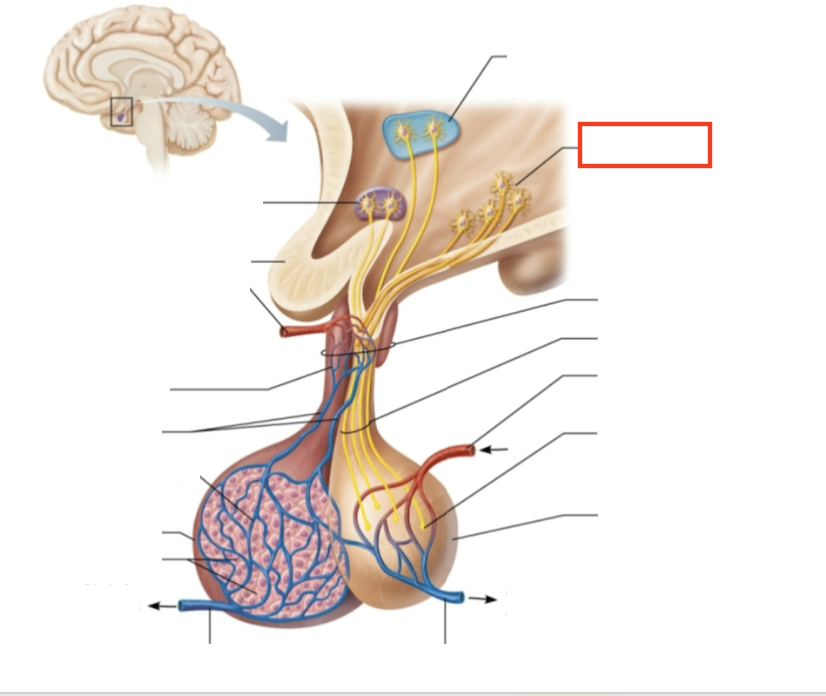
What structure is highlighted?
neurons in the ventral hypothalamus
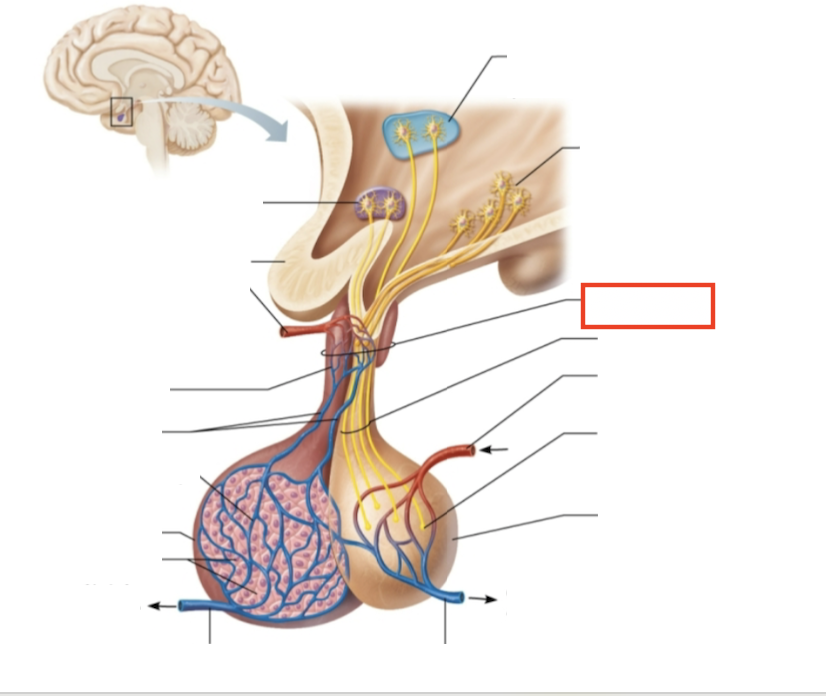
What structure is highlighted?
infundibulum (connecting stalk)
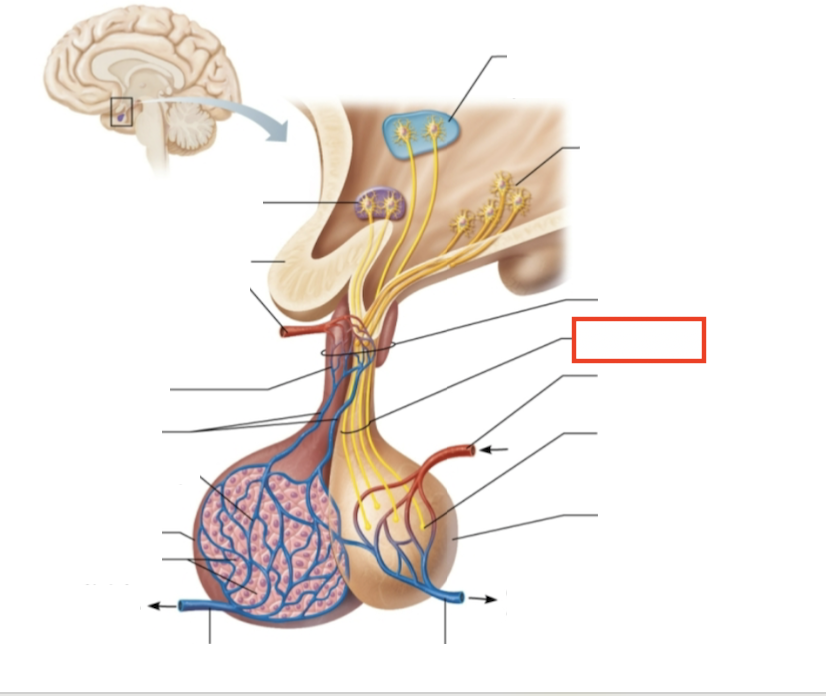
What structure is highlighted?
hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract
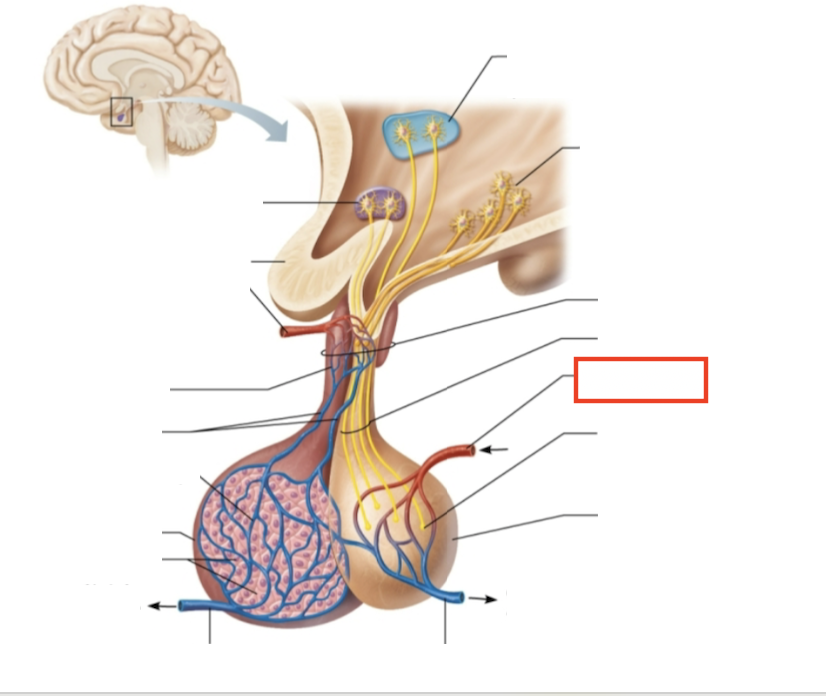
What structure is highlighted?
inferior hypophyseal artery
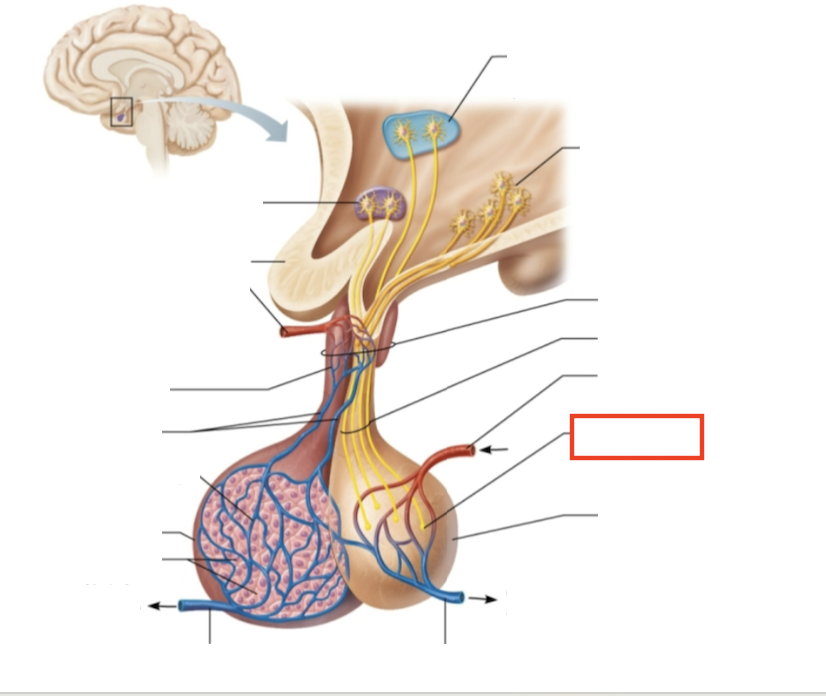
What structure is highlighted?
neurohypophysis (storage area for hypothalamic hormones)
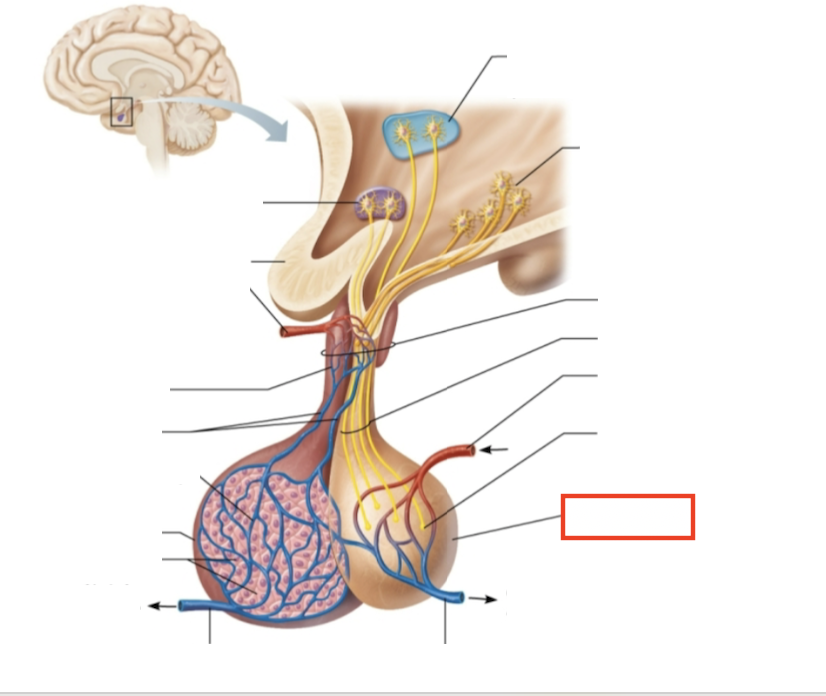
What structure is highlighted?
posterior pituitary
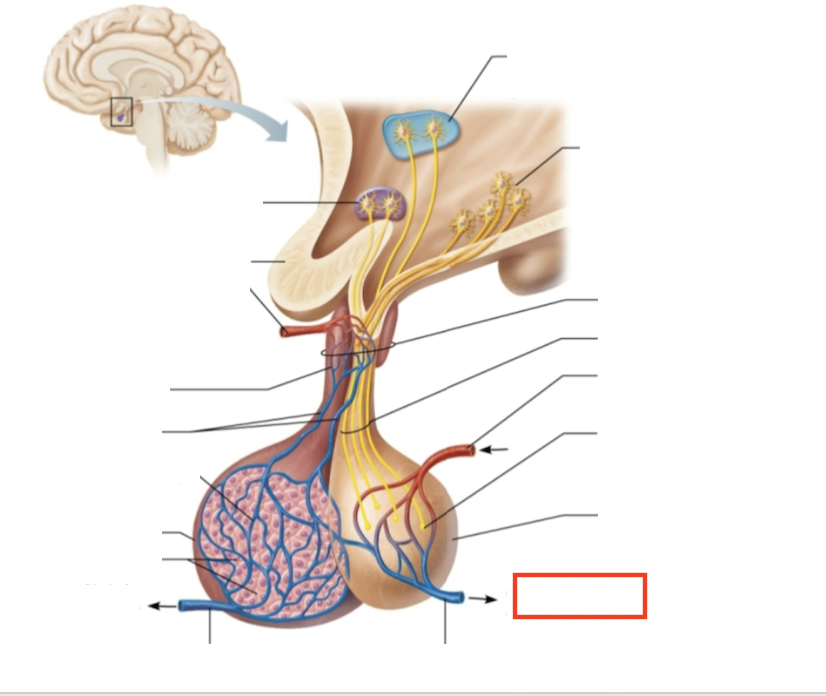
What molecules are produced here?
oxytocin, ADH
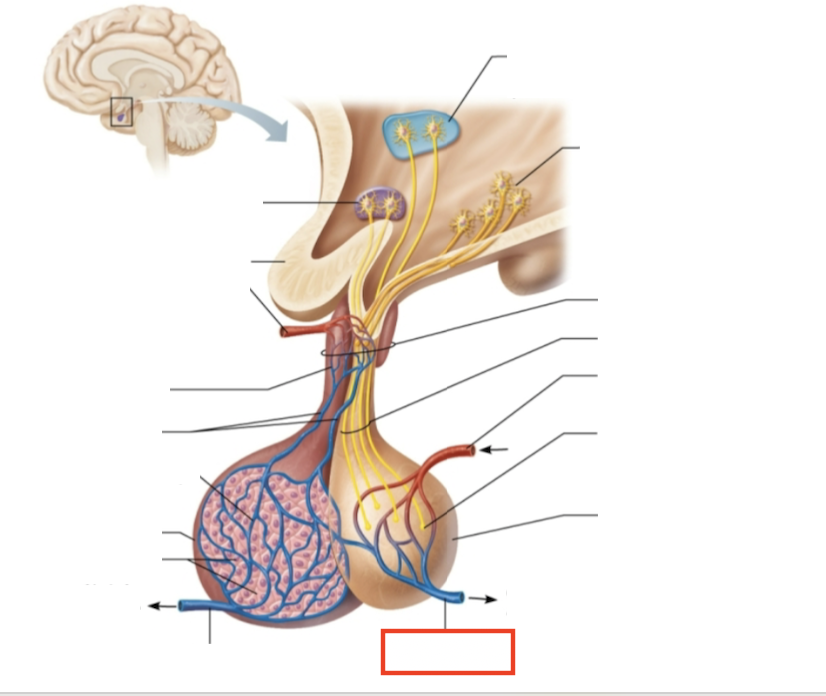
What structure is highlighted?
venule
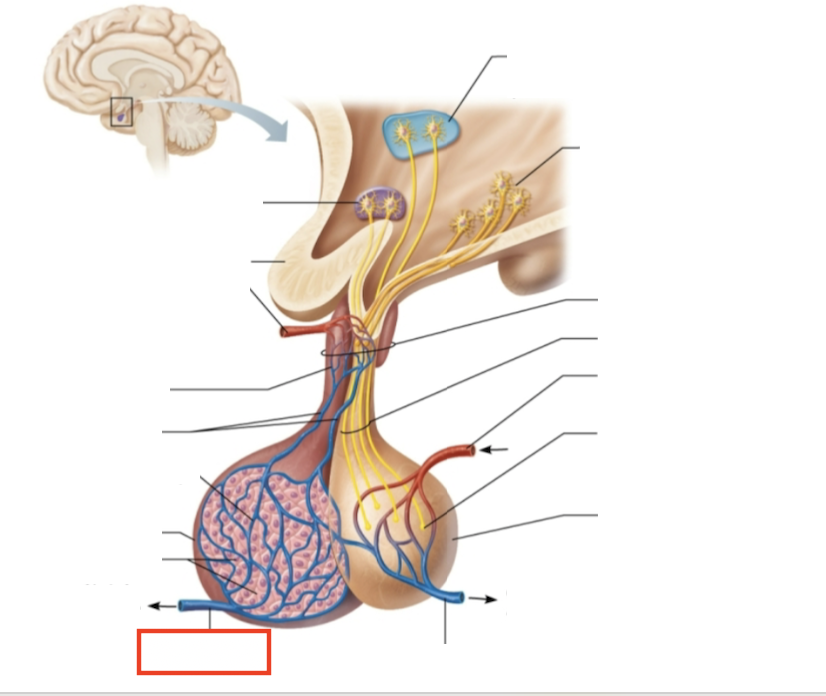
What structure is highlighted?
venule
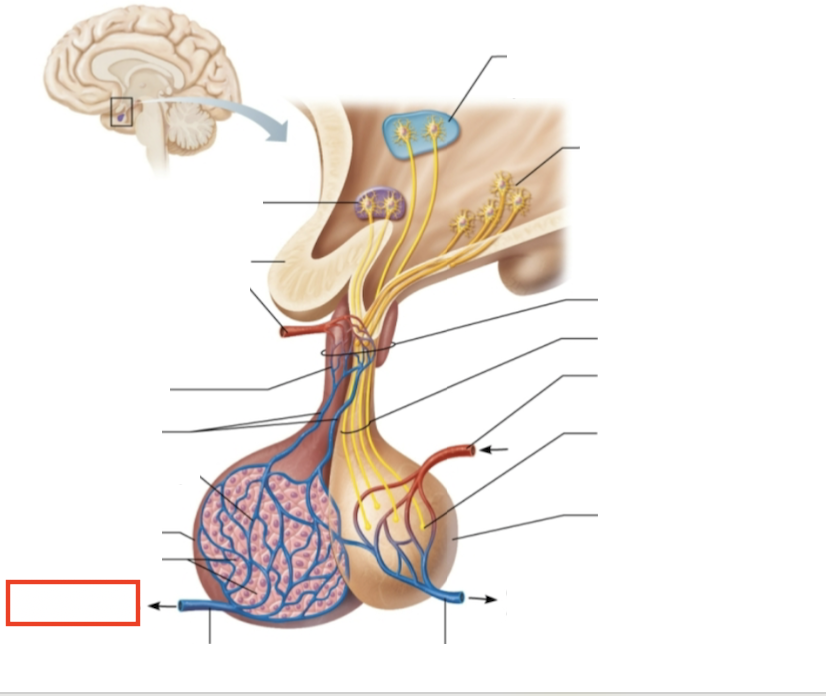
What molecules are produced here?
TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, PRL
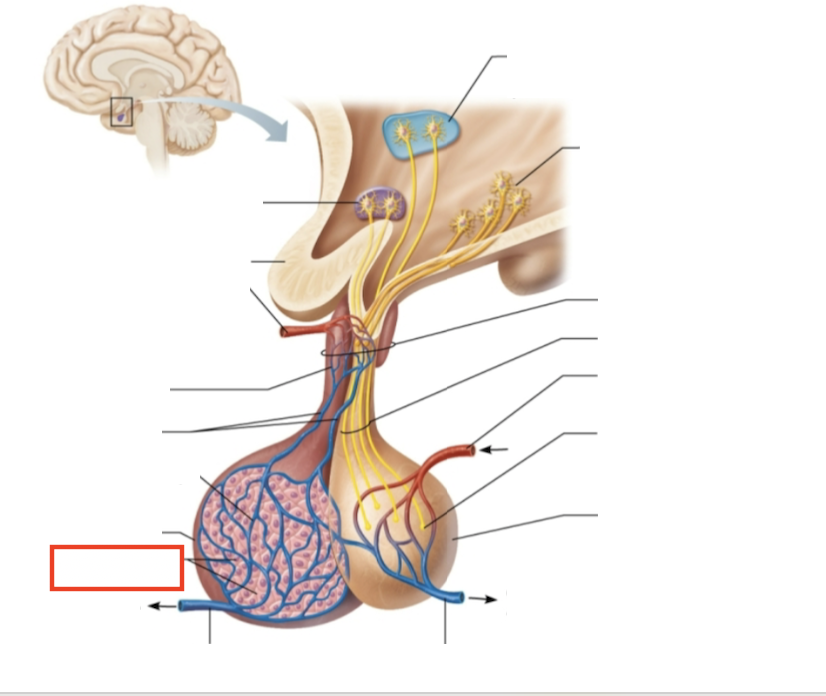
What structure is highlighted?
secretory cells of adenohypophysis
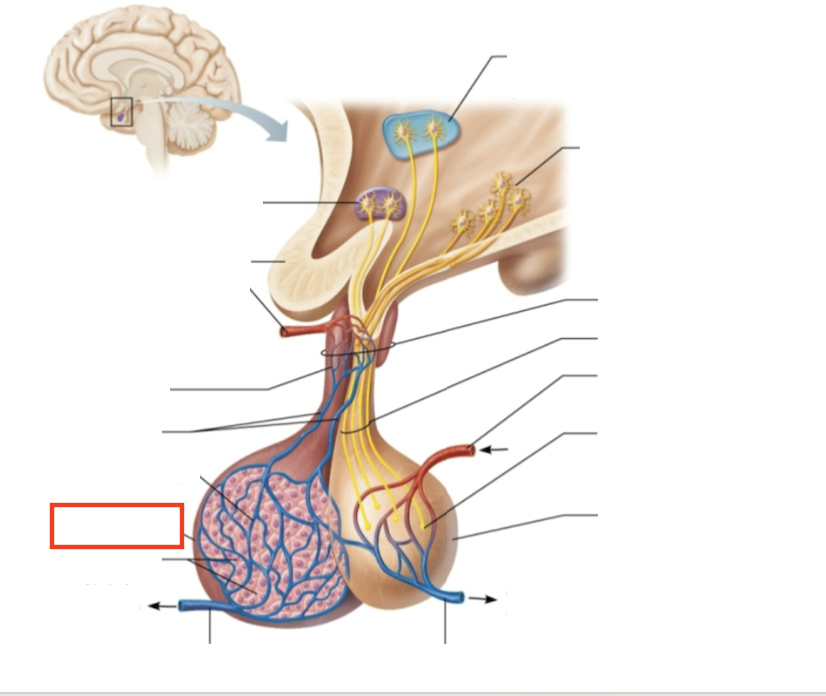
What structure is highlighted?
anterior pituitary
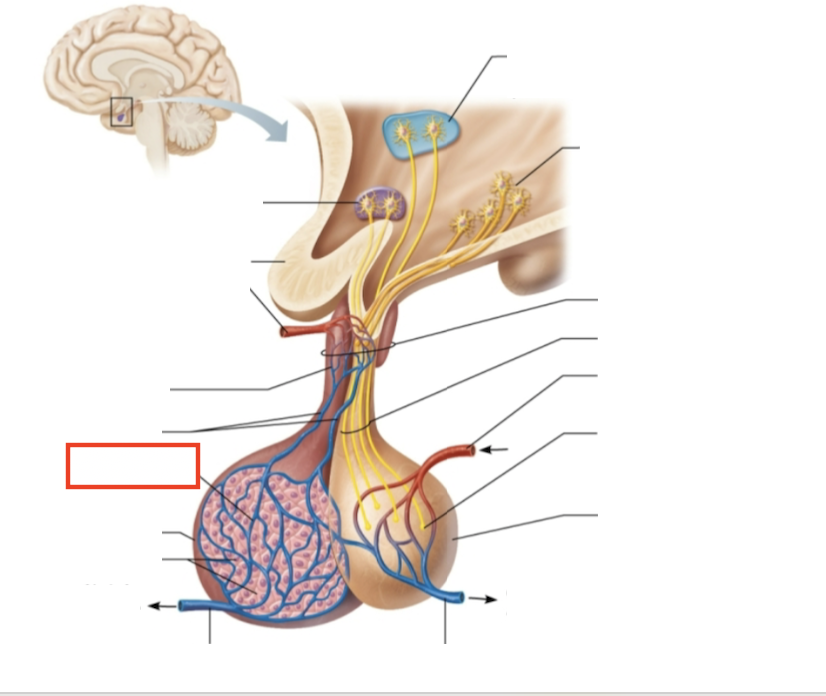
What structure is highlighted?
secondary capillary plexus
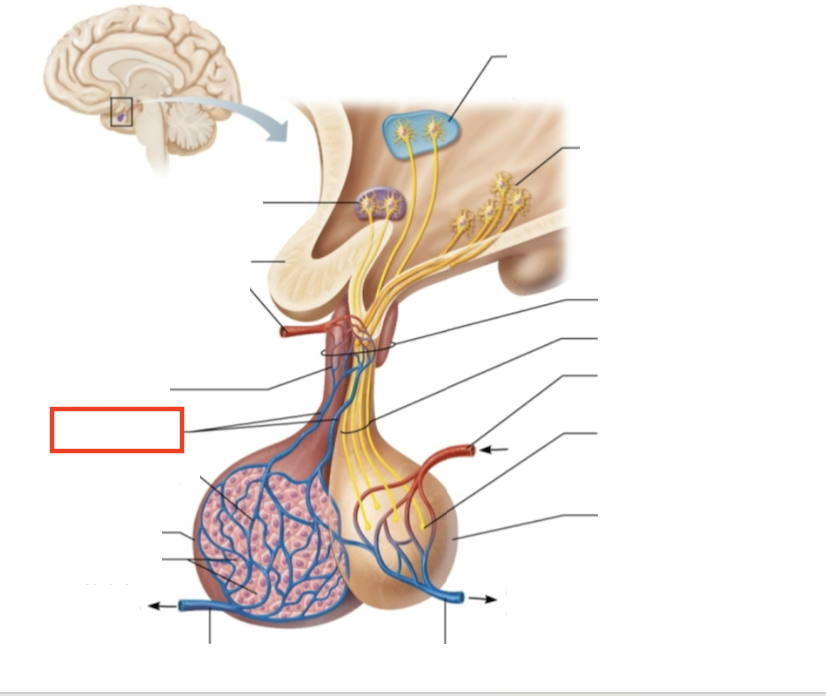
What structure is highlighted?
hypophyseal portal veins
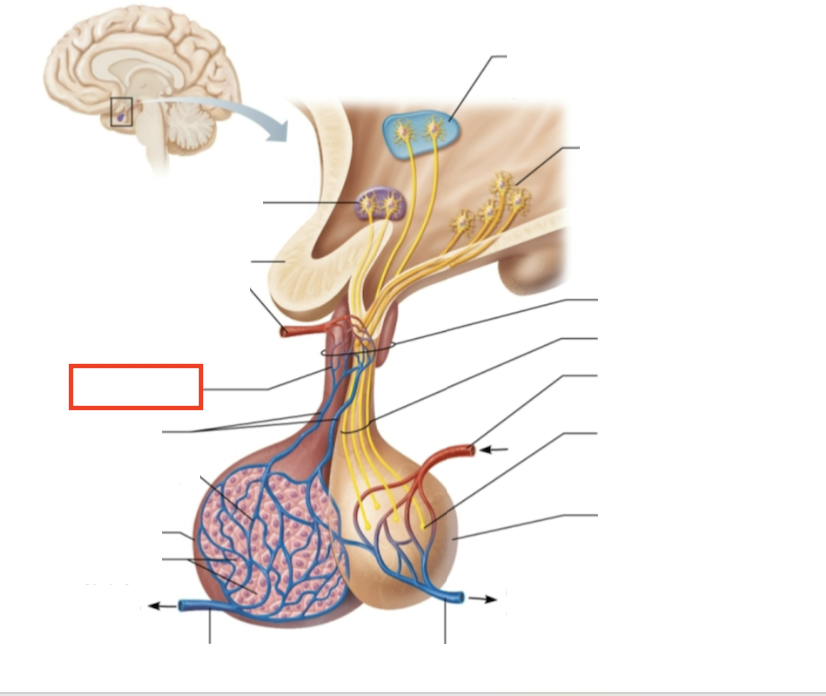
What structure is highlighted?
primary capillary plexus
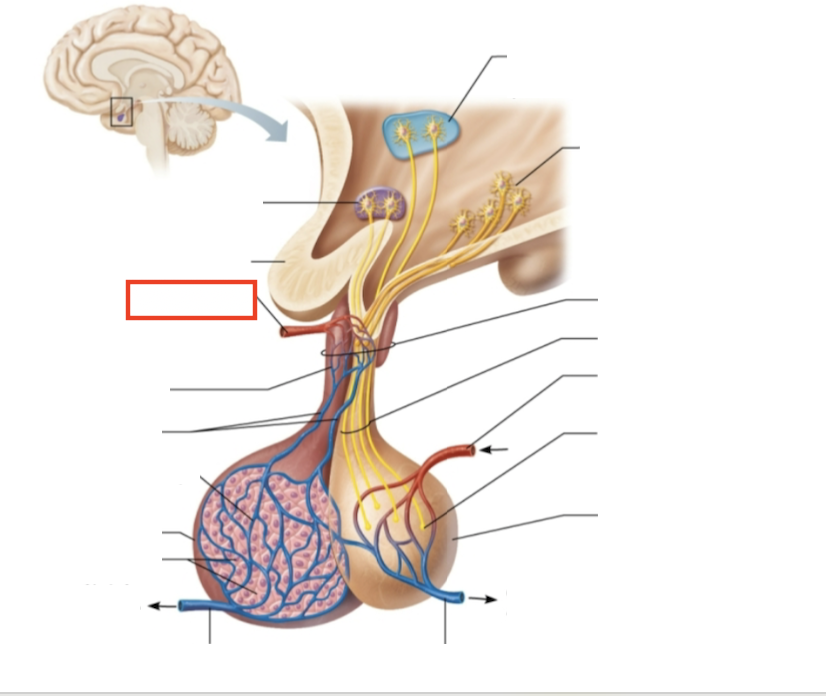
What structure is highlighted?
superior hypophyseal artery
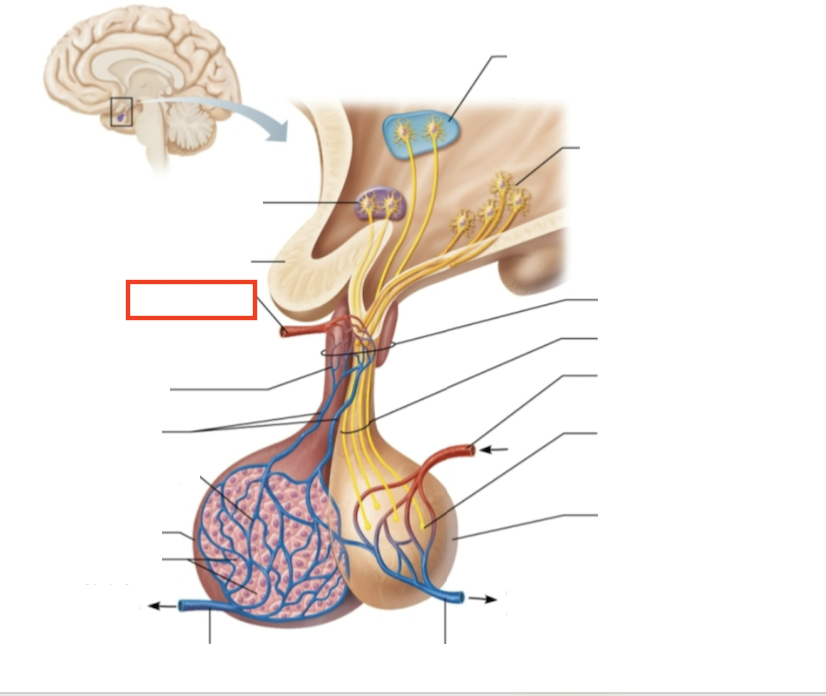
What structure is highlighted?
superior hypophyseal artery
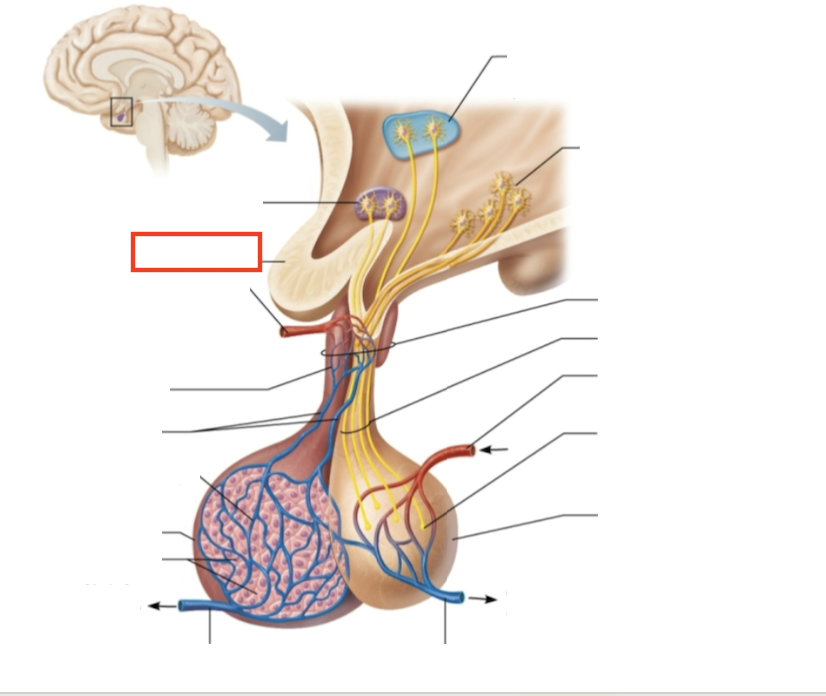
What structure is highlighted?
optic chiasma
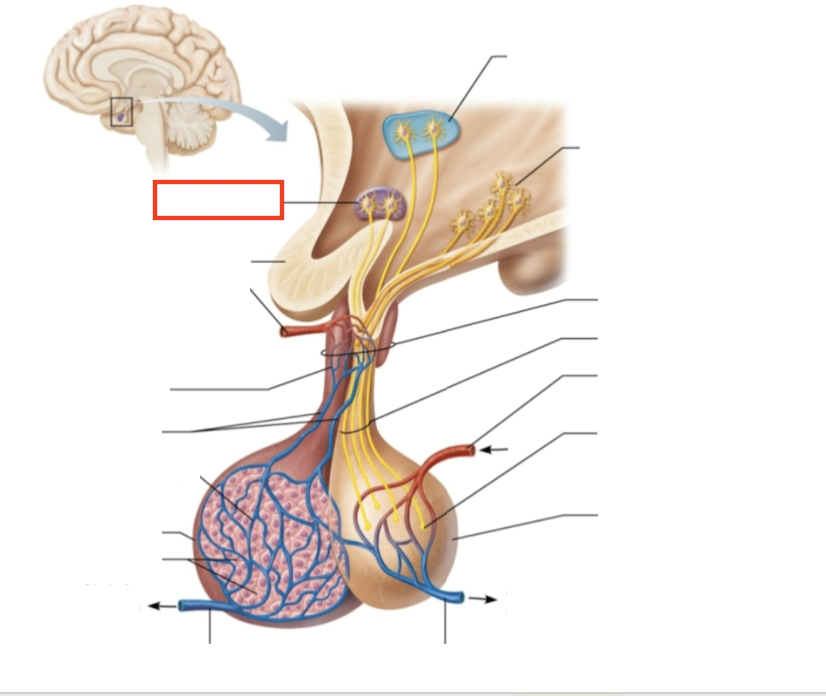
What structure is highlighted?
hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic nuclei
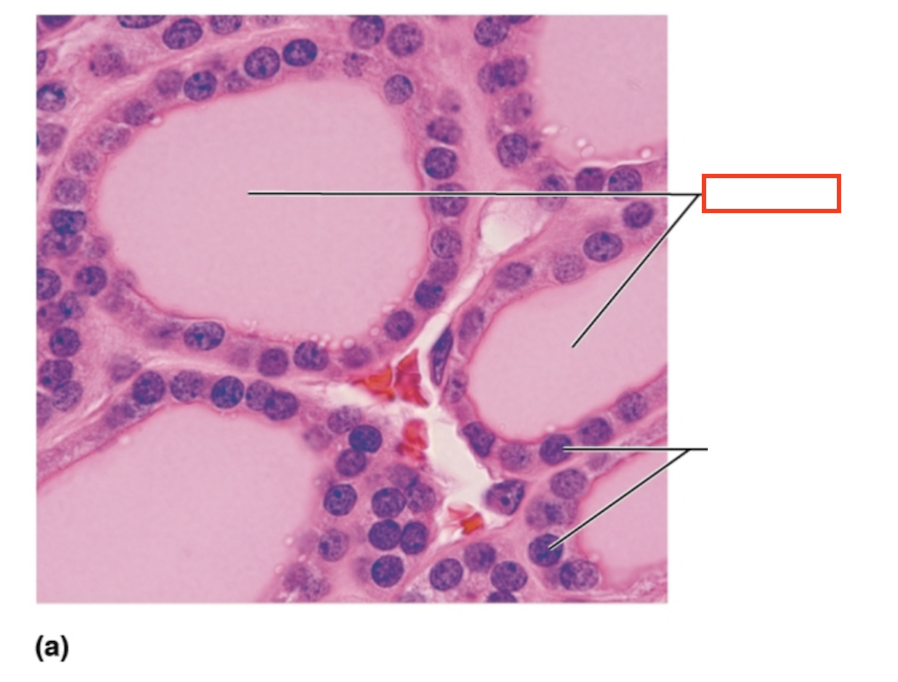
What structure is highlighted?
colloid filled follicles
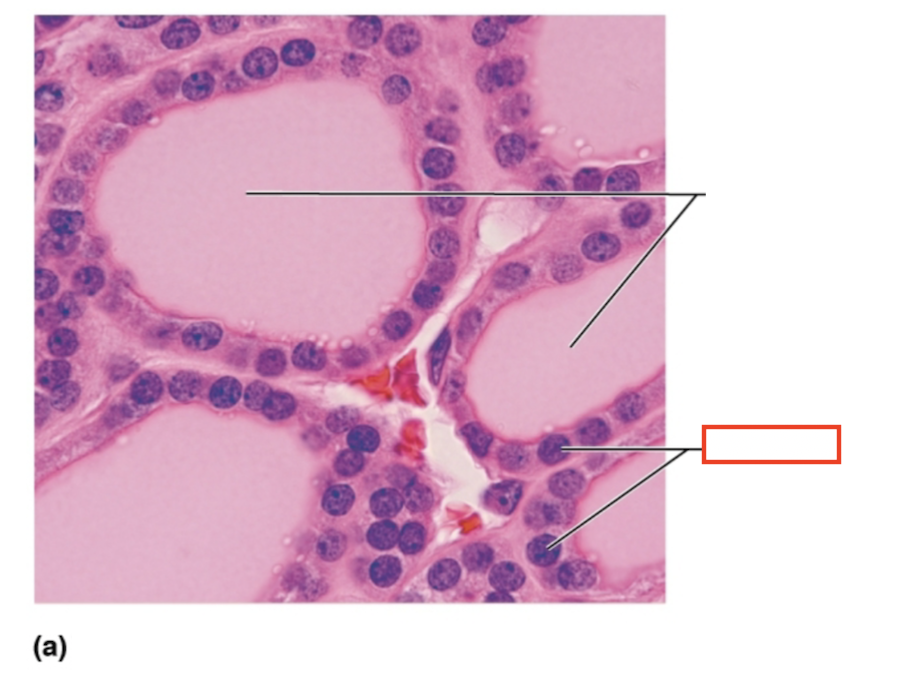
What structure is highlighted?
follicular cells
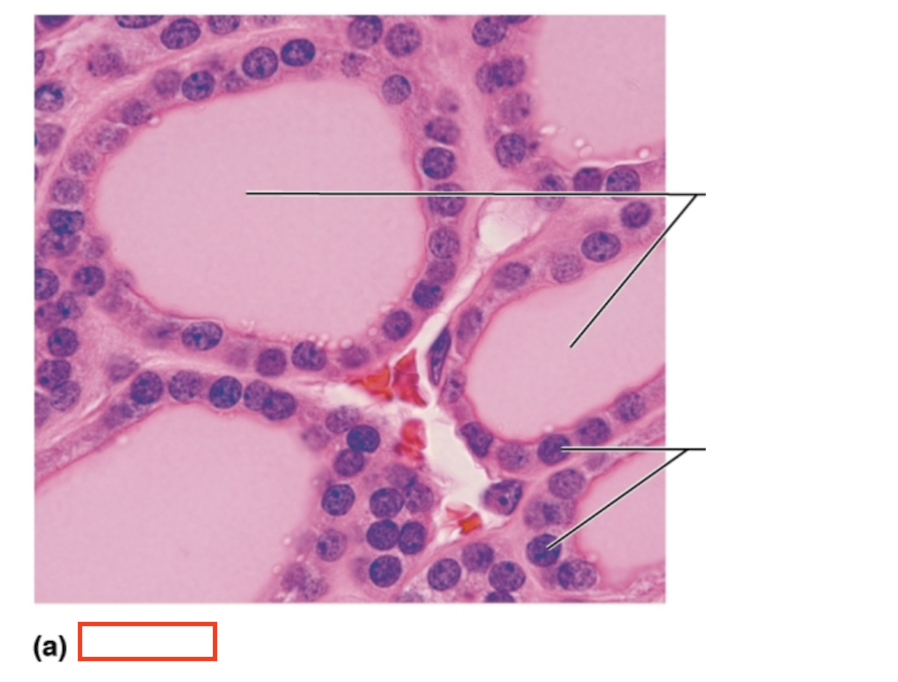
What tissue is shown?
thyroid gland
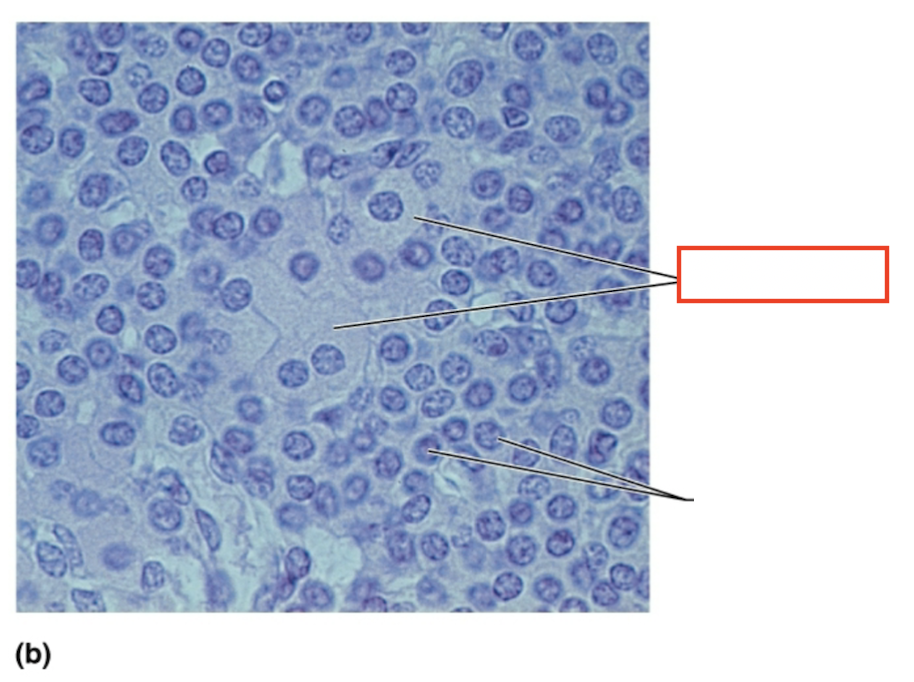
What structure is highlighted?
oxyphil cells
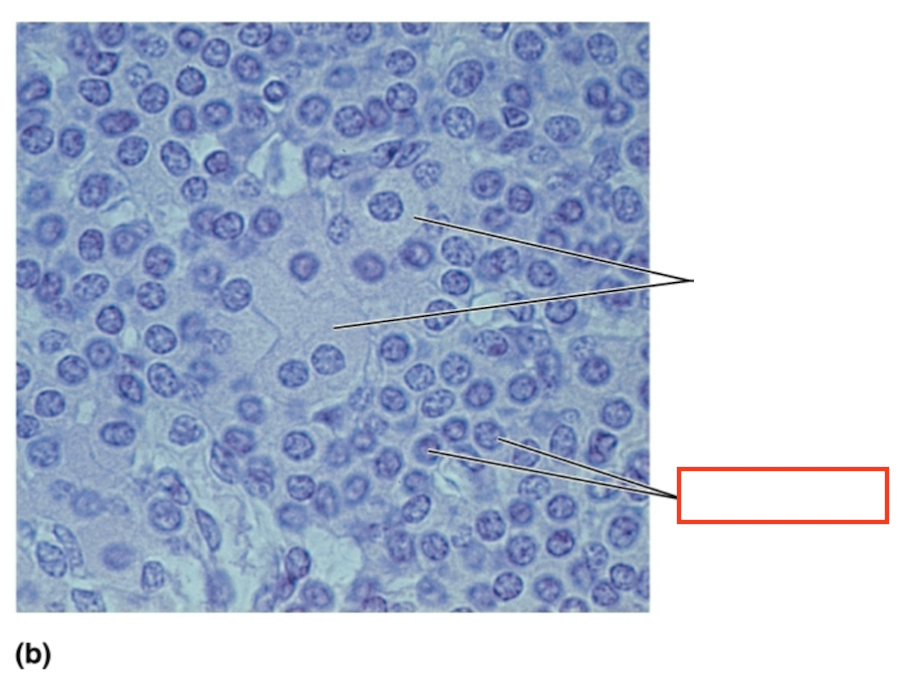
What structure is highlighted?
parathyroid cells
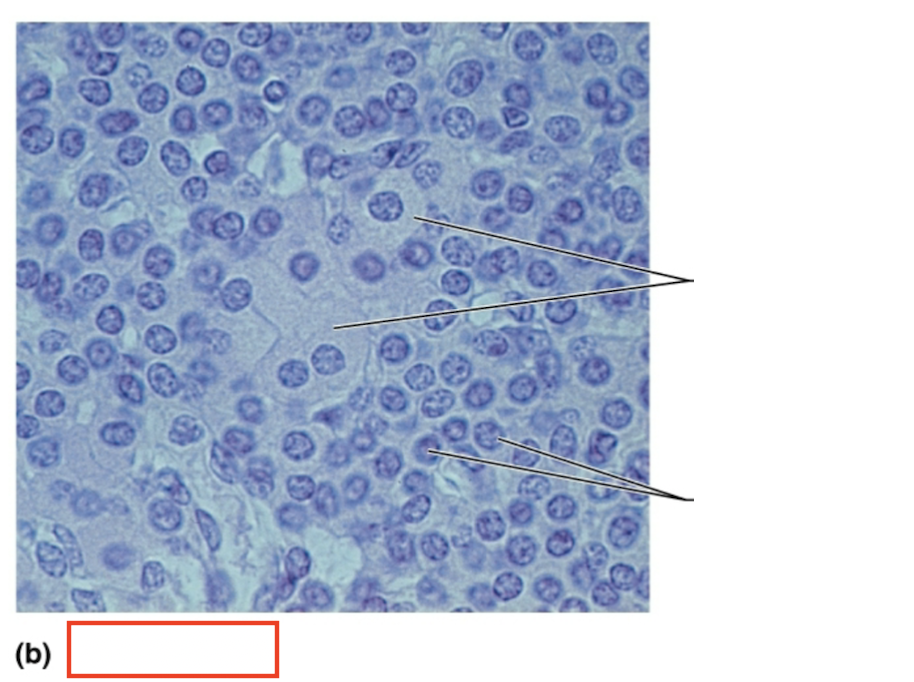
What tissue is shown?
parathyroid gland
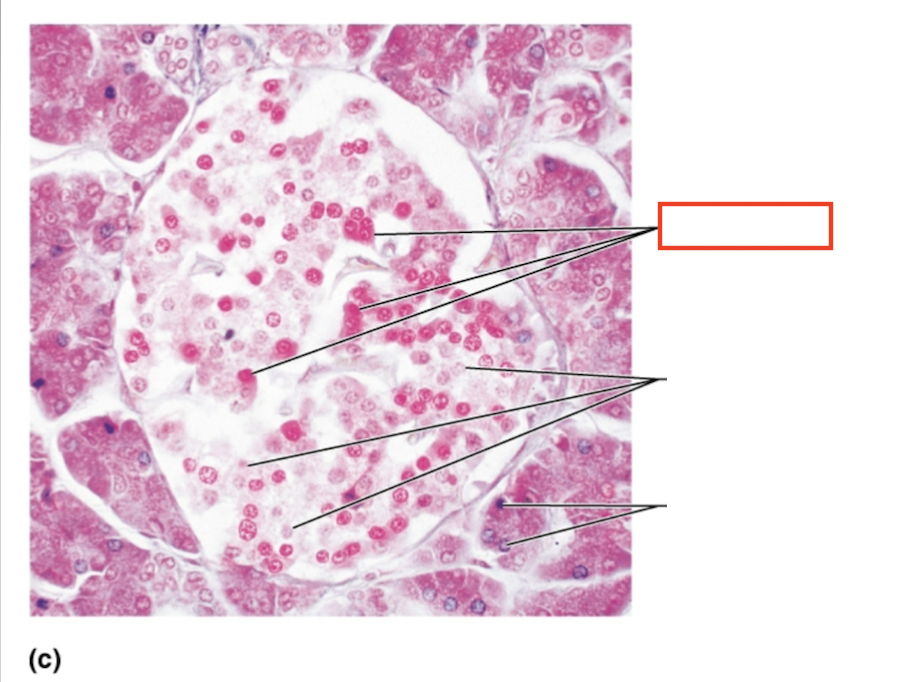
What structure is highlighted?
alpha cells (glucagon producing)
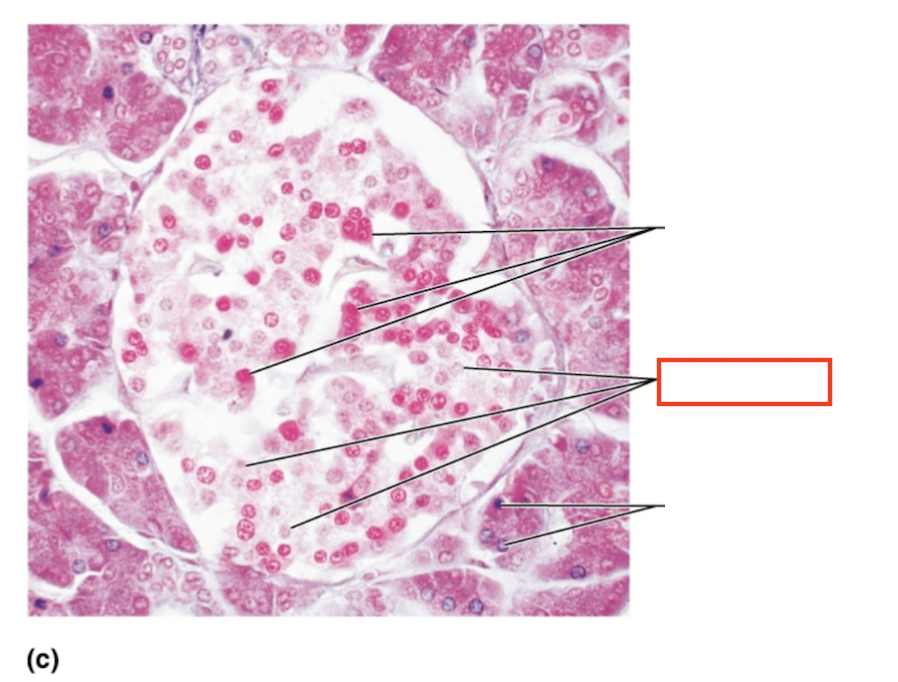
What structure is highlighted?
beta cells (insulin producing)
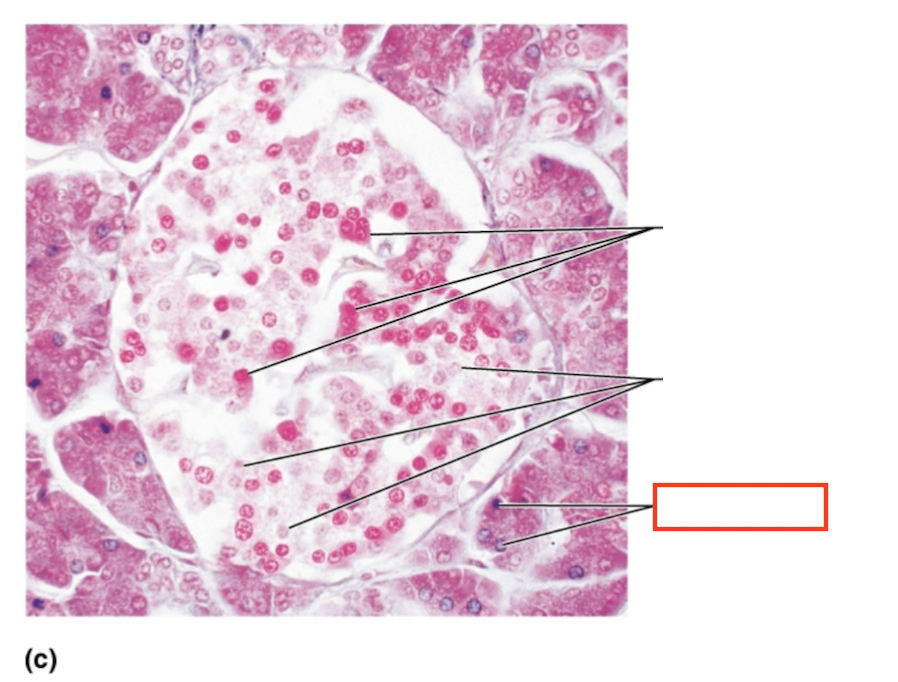
What structure is highlighted?
pancreatic acinar cells (exocrine)
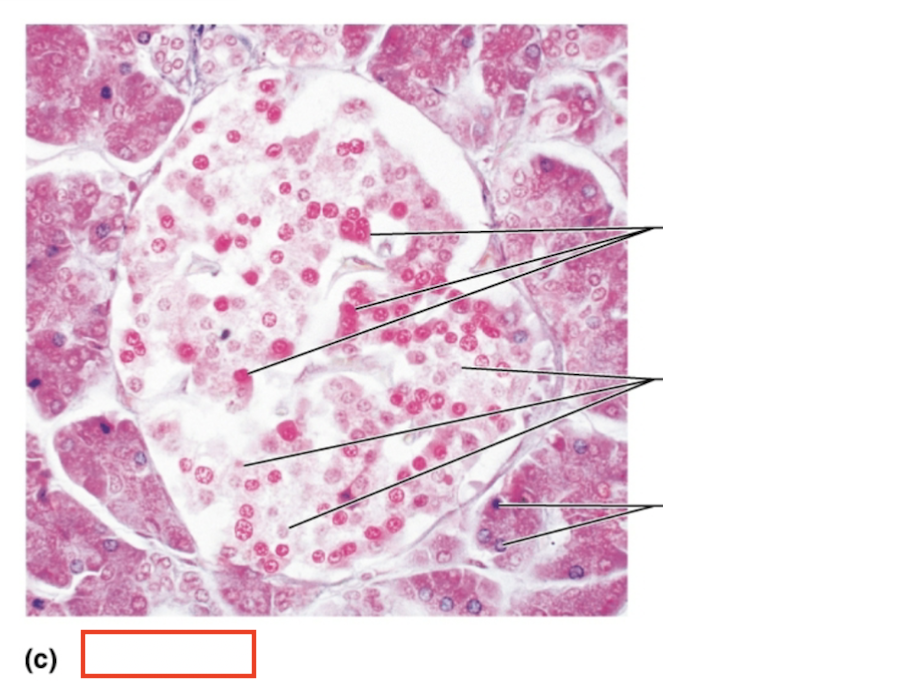
What tissue is shown?
pancreatic islet
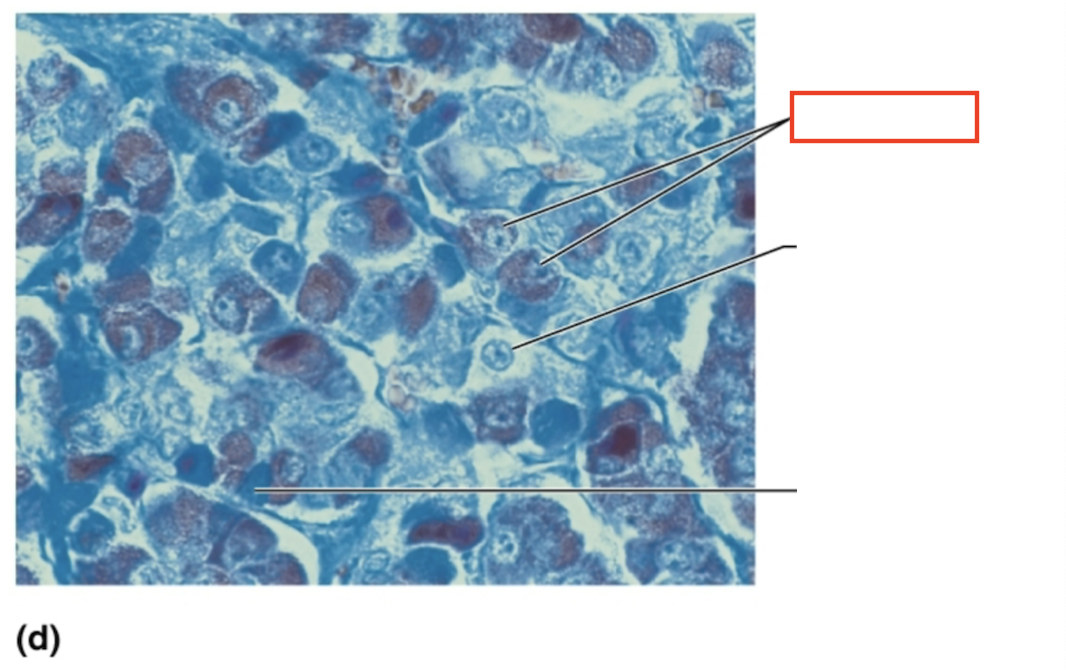
What structure is highlighted?
acidophils
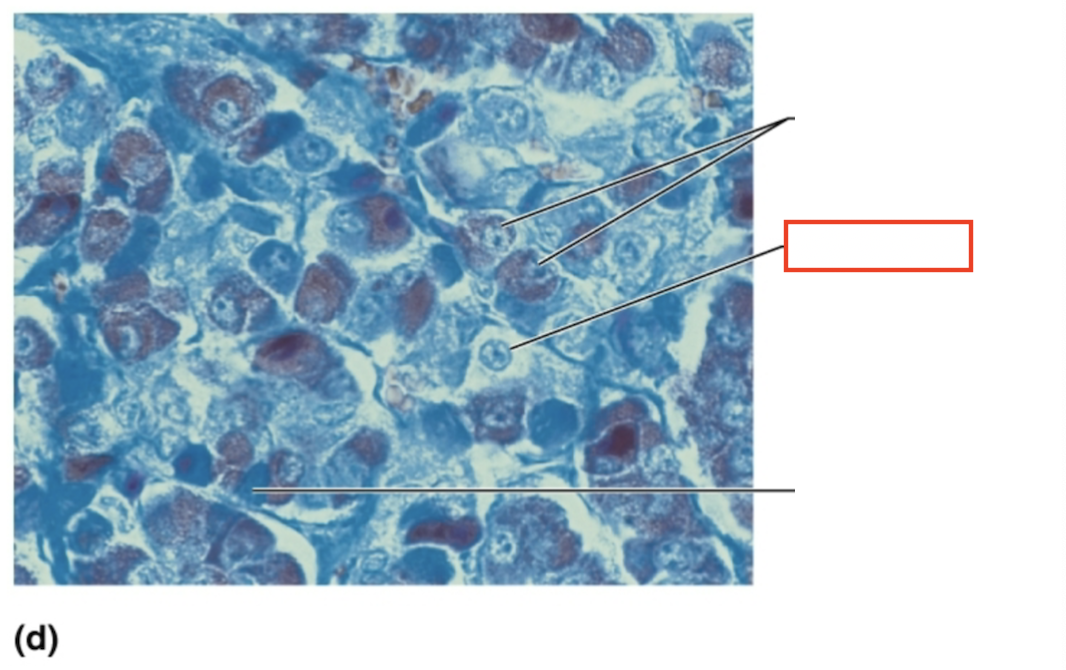
What structure is highlighted?
chromophobe
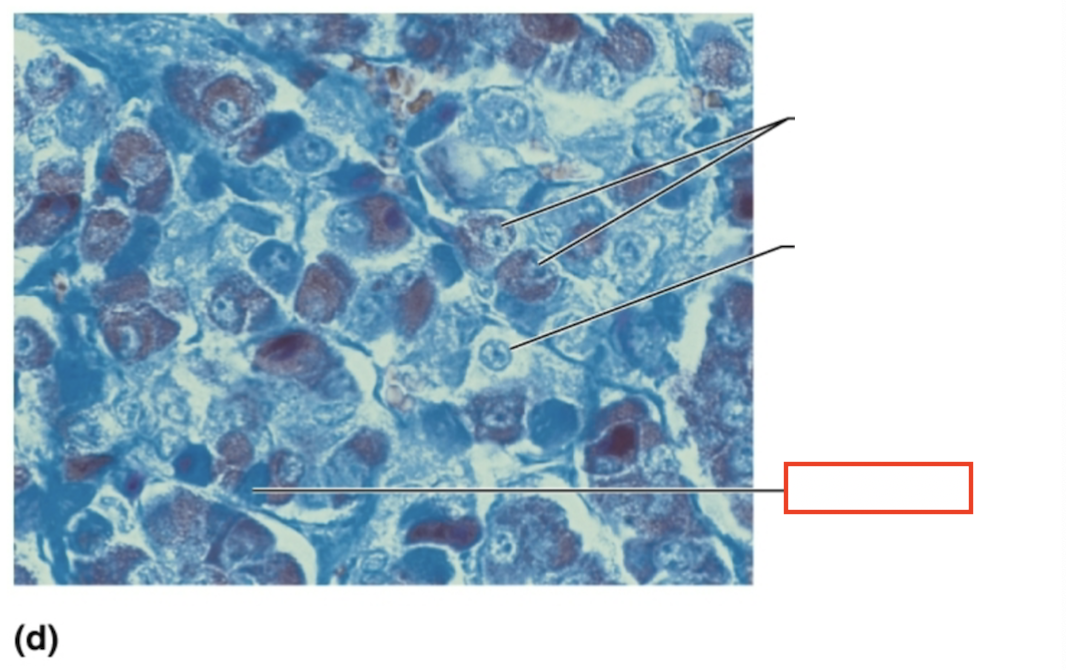
What structure is highlighted?
basophil
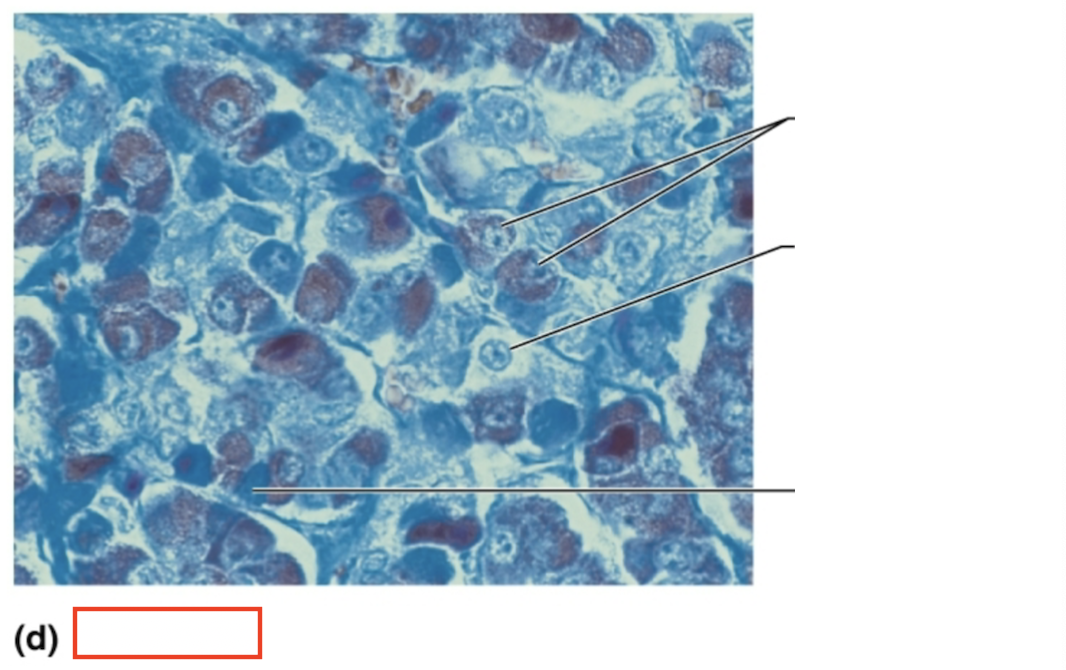
What tissue is shown?
anterior pituitary
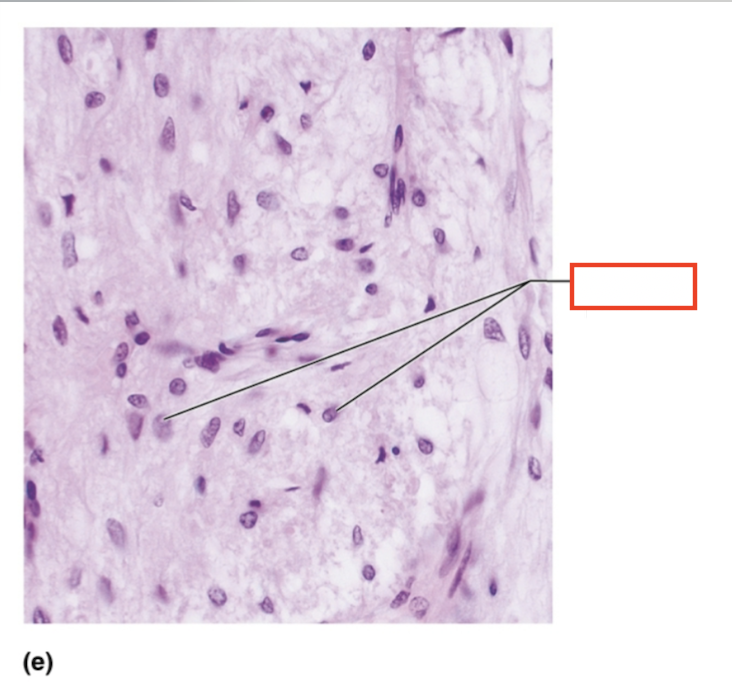
What structure is highlighted?
pituicyte nuclei
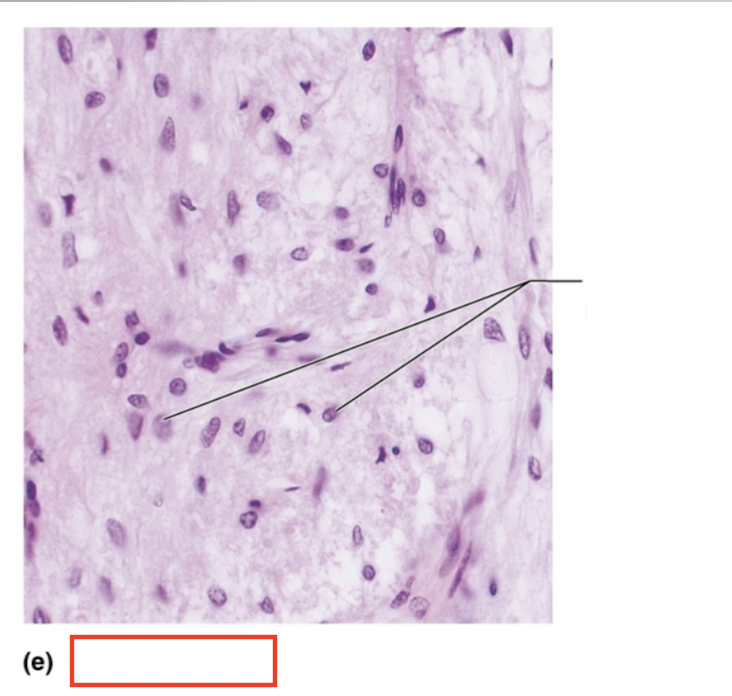
What tissue is shown?
posterior pituitary
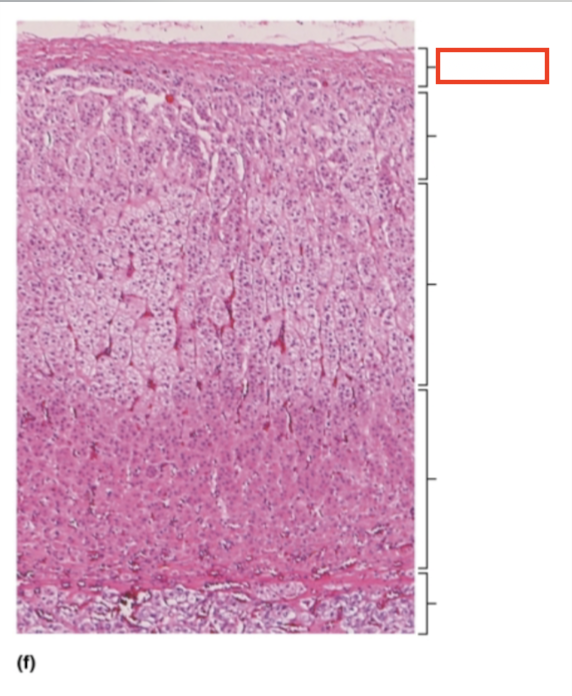
What structure is highlighted?
capsule
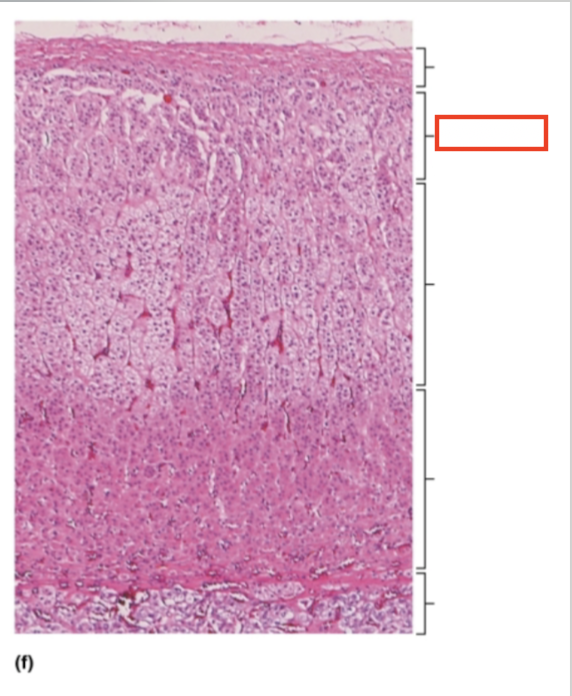
What structure is highlighted?
zona glomerulosa
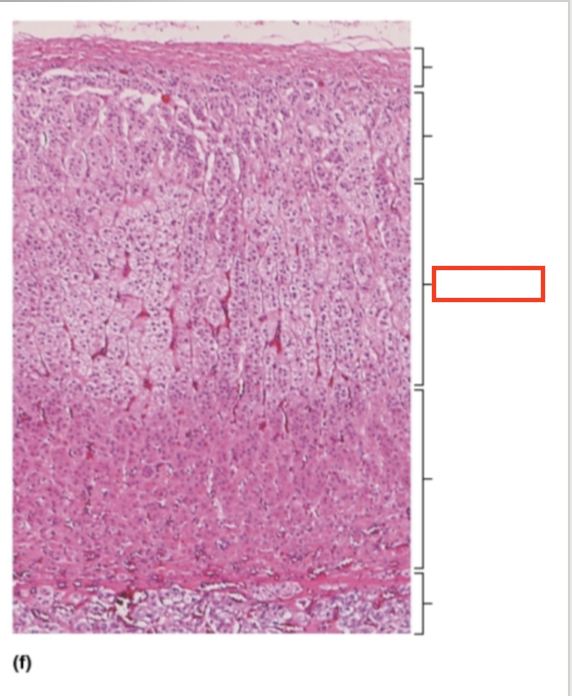
What structure is highlighted?
zona fasciculata
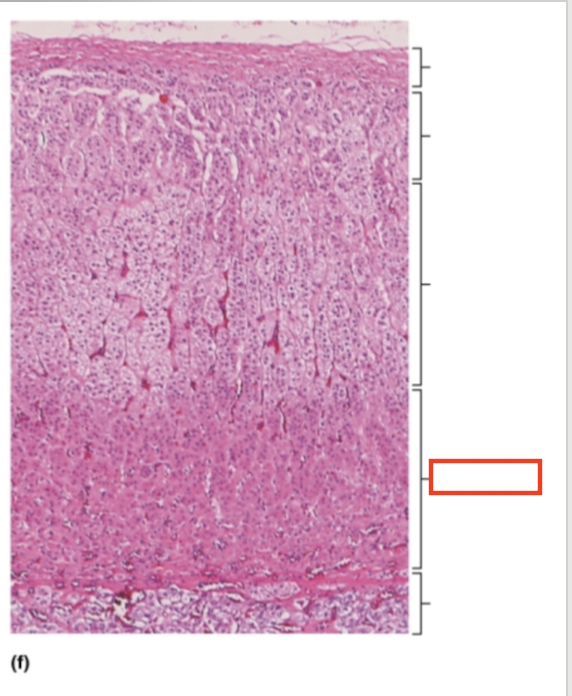
What structure is highlighted?
zona reticularis
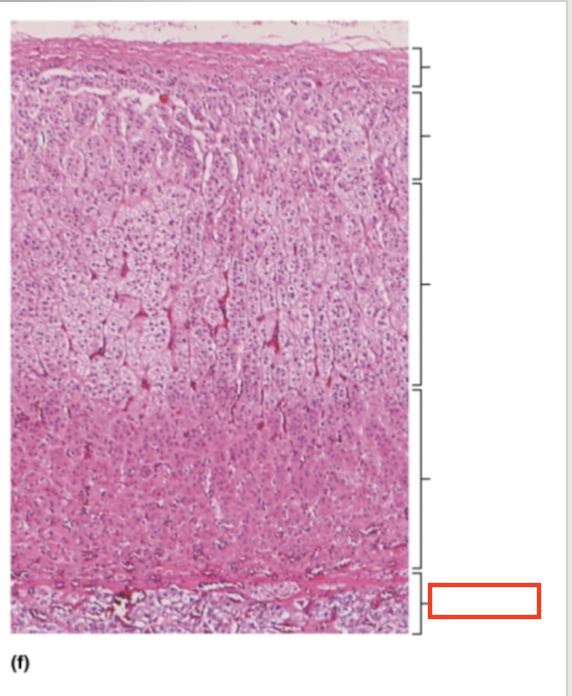
What structure is highlighted?
adrenal medulla
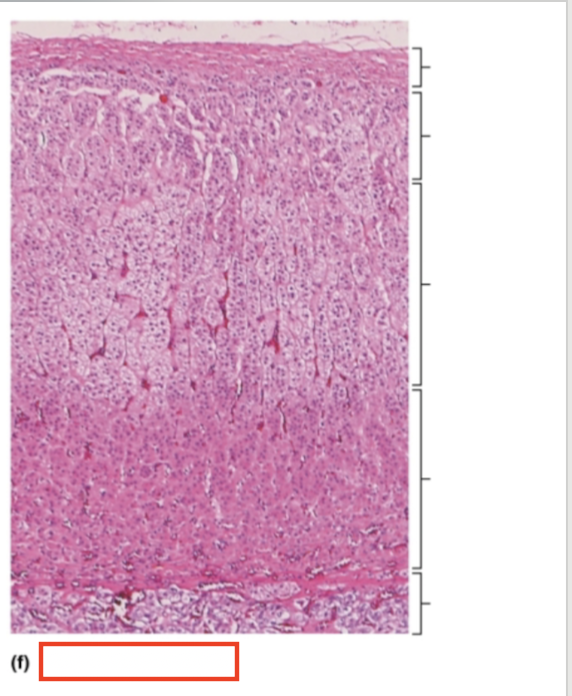
What tissue is shown?
adrenal gland
What hormones are released by the anterior pituitary gland?
TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, GH, PRL
What are the tropic hormones?
TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH
What is the target organ and effects of TSH?
thyroid gland; stimulates the secretion of thyroid hormones T3 and T4
What is the target organ and effects of FSH?
ovaries and testes (gonads); females - stimulates ovarian follicle maturation and estrogen production; males - stimulates sperm production
What is the target organ and effects of LH?
ovaries and testes (gonads); females - triggers ovulation and stimulates ovarian production of estrogen and progesterone; males - stimulates testosterone production
What is the target organ and effects of ACTH?
adrenal cortex; stimulates the release of glucocorticoids and androgens (mineralocorticoids to a lesser extent)
What are the target organs and effects of GH?
liver, muscle, bone, and cartilage, mostly; stimulates body growth and protein synthesis, mobilizes fat and conserves glucose
What is the target organ and effects of PRL?
mammary glands in the breasts; stimulates milk production (lactation)
What hormones are synthesized by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary?
oxytocin and ADH
What is the target organ and effects of oxytocin?
uterus and mammary glands; stimulates powerful uterine contractions during birth and stimulates milk ejection (let down) in lactating mothers
What is the target organ and effects of ADH?
kidneys; stimulates the kidneys to reabsorb more water, reducing urine output and conserving body water
What hormones are produced by the thyroid gland?
thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) collectively referred to as thyroid hormone (TH), calcitonin
What is the target organ and effects of T4 & T3 (TH)?
Most cells of the body; increases basal metabolic rate (BMR); regulates tissue growth and development
What is the target organ and effects of calcitonin?
Bones; no known physiological role in humans. When the hormone is supplemented at doses higher than normally found in humans, it does have some pharmaceutical applications
What is the target organ and effects of PTH?
Bones and kidneys; increases blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts and by stimulating the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium. Also stimulates the kidneys to convert vitamin D to calcitriol, which is required for the absorption of calcium in the intestines
What hormones are produced by the parathyroid gland?
parathyroid hormone
What are the target organs and effects of PTH?
bones and kidneys; increases blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts and by stimulating the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium. PTH also stimulates the kidneys to convert vitamin D to calcitriol, which is required for the absorption of calcium in the intestines
What hormones are produced in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex?
mineralocorticoids; mostly aldosterone
What hormones are produced in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex?
glucocorticoids; mostly cortisol
What hormones are produced in the zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex?
gonadocorticoids; androgens (most are converted to testosterone and some to estrogen)
What are the target organs and effects of aldosterone?
kidneys; increases the reabsorption of sodium and water by the kidney tubules. increases the secretion of potassium in the urine
What are the target organs and effects of cortisol?
most body cells; promotes the breakdown of fat and protein, promotes stress resistance, inhibits the immune response
What are the target organs and effects of androgens?
bone, muscle, integument, and other tissues. in females, androgens contribute to body growth, contribute to development of pubic and axillary hair, and enhance sex drive. they have insignificant effects in males.
What hormones are produced by the adrenal medulla?
catecholamines; epinephrine and norepinephrine
What are the target organs and effects of catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)?
most body cells; mimics sympathetic nervous system activation, fight-or-flight response.
What hormones are released by the pancreas?
insulin, glucagon
What are the target organs and effects of insulin
most cells of the body, accelerates the transport of glucose into body cells; promotes glycogen, fat, and protein synthesis
What are the target organs and effects of glucagon?
primarily the liver and adipose; accelerates the breakdown of glycogen to glucose, stimulates the conversion of lactic acid into glucose, releases glucose into the blood from the liver
What hormones are produced by the ovaries?
estrogens and progesterone
What are the target organs and effects of estrogens?
most cells of the body; promote the maturation of the female reproductive organs and the development of secondary sex characteristics
What are the target organs and effects of estrogens and progesterone (together)?
uterus and mammary glands; regulate the menstrual cycle and promote breast development
What are the target organs and effects of testosterone?
most cells of the body; promotes the maturation of the male reproductive organs, the development of secondary sex characteristics, sperm production, and sex drive
What hormone is produced by the testes?
testosterone
What stimulates testosterone production?
LH and FSH
What stimulates estrogen and progesterone (together) production?
LH and FSH
What stimulates estrogen production?
LH and FSH
What stimulates glucagon production?
decreased blood glucose levels, sympathetic nervous system stimulation
What stimulates insulin production?
increased blood glucose levels, parasympathetic nervous system stimulation
What stimulates catecholamine (epinephrine & norepinephrine) production?
nerve impulses from preganglionic sympathetic fibers
What stimulates gonadocorticoid (androgen) production?
ACTH
What stimulates glucocorticoids (cortisol) production?
ACTH
What stimulates mineralocorticoid (mainly aldosterone) production?
Angiotensin II release and increased potassium in the blood. ACTH in times of severe stress
What stimulates parathyroid hormone production?
low levels of blood calcium