Evidence of Evolution and Natural Selection
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Theory of Natural Selection
The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
Natural Selection (NS)
Believed to be the main process that brings about evolution.
Darwin's Definition of Natural Selection
This preservation of favorable variations and the destruction of injurious variations, I call Natural Selection, or the Survival of the Fittest.
Era
A large span of time marked by character, events, changes on earth, denotes a clearly defined period of time.
Periods
One of several subdivisions of geologic time enabling cross-referencing of rocks and geologic events from place to place.
Epoch
A division of time that is a subdivision of a period and is itself subdivided into ages.
Fossils
Preserved remains or traces of animals, plants, and other organisms from the past.
Sedimentary Rock
Types of rock that are formed by the deposition and subsequent cementation of that material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water.
Radioactive Dating
A method of dating rocks and minerals using radioactive isotopes.
Radioactive Isotope
Natural or artificially created isotope of a chemical element having an unstable nucleus that decays.
Half-Life
The time required for a quantity to reduce to half its initial value.
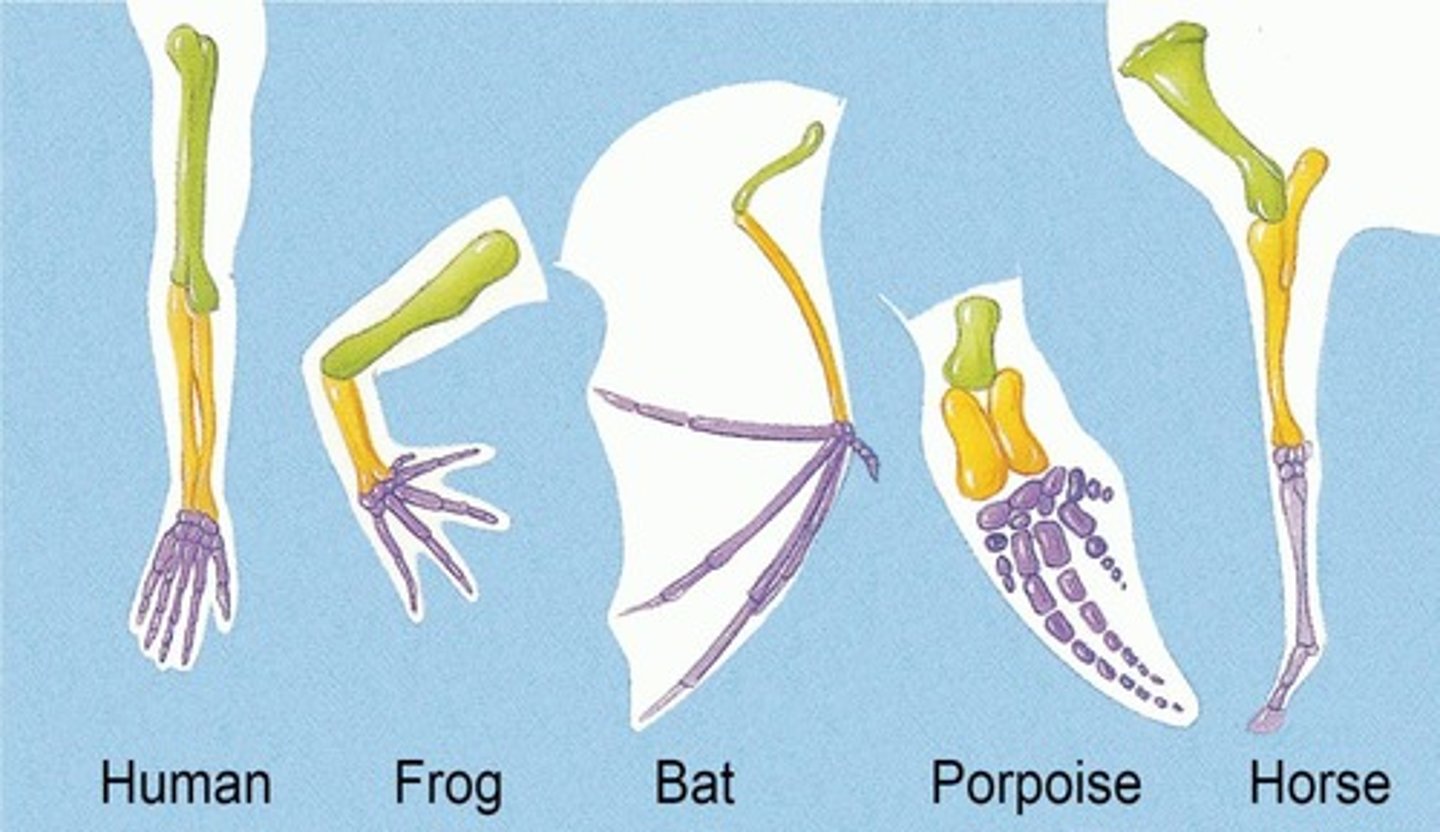
Homologous Structures
An organ or bone that appears in different animals, underlining anatomical commonalities demonstrating descent from a common ancestor.
Analogous Structures
Various structures in different species having the same function but have evolved separately, thus do not share common ancestor.

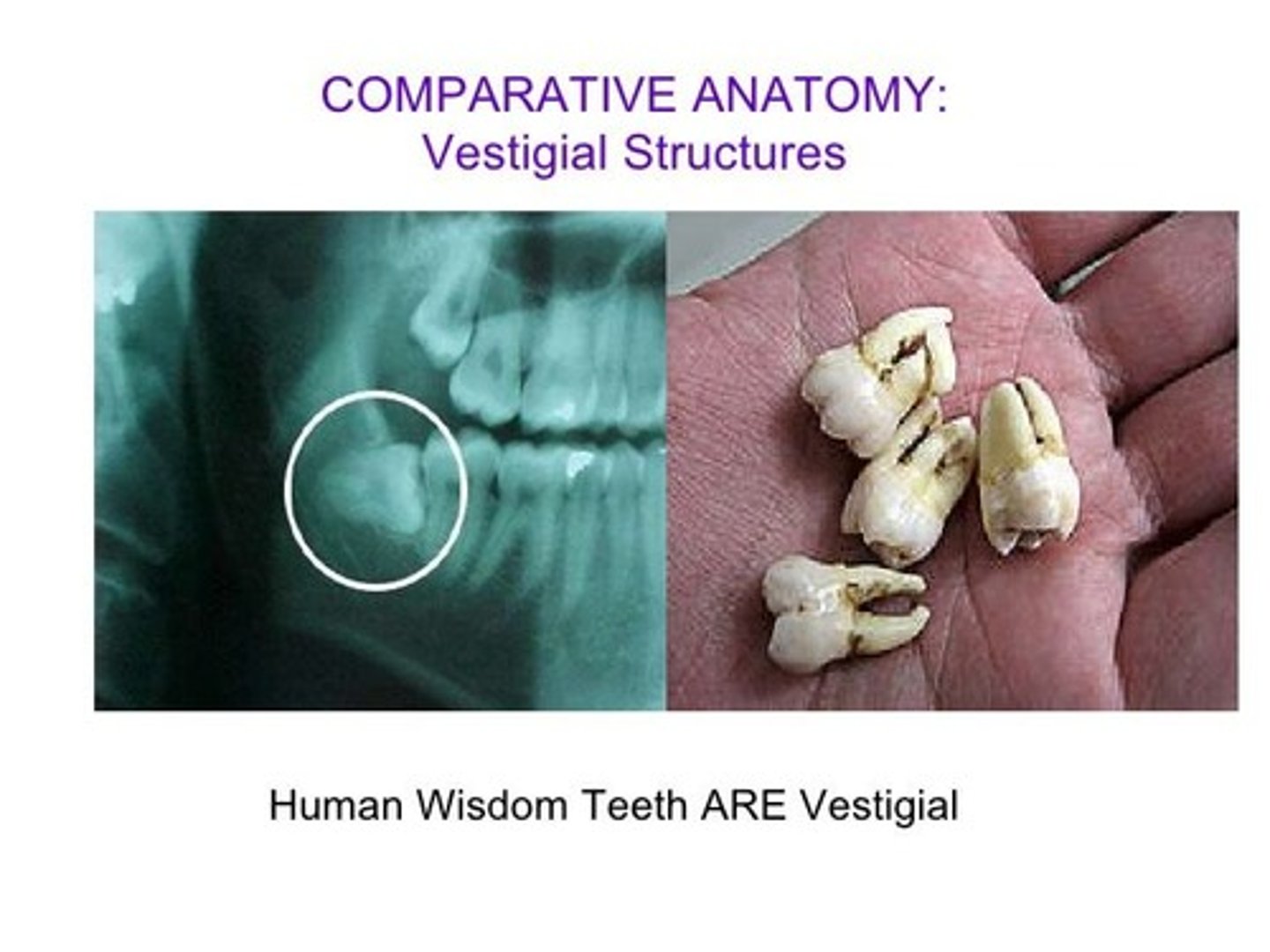
Vestigial Structures
Anatomical feature that no longer seems to have a purpose in the current form of an organism of the given species.
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
Developmental features are characteristics that are apparent during the embryonic development of an organism.